Submitted:
19 June 2024
Posted:
19 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
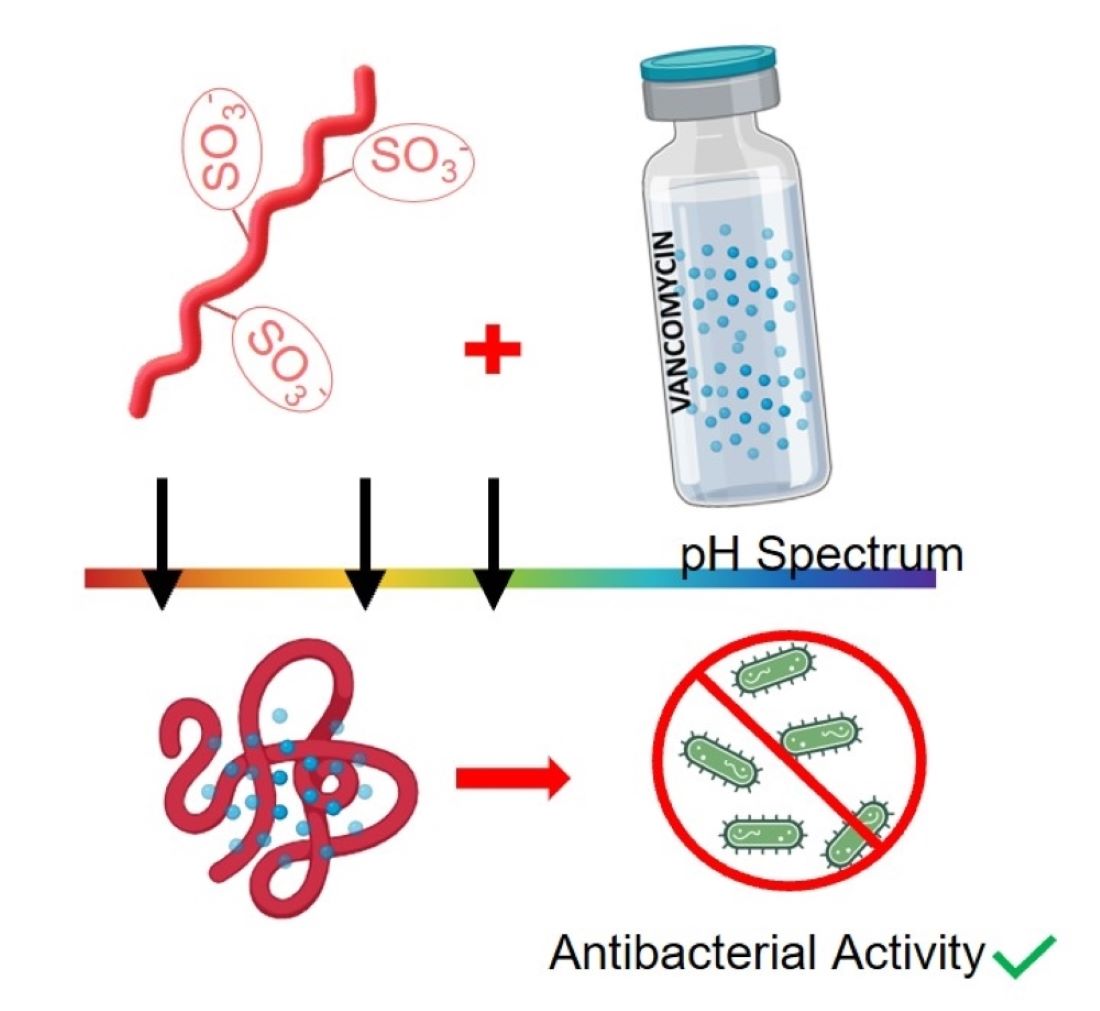
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
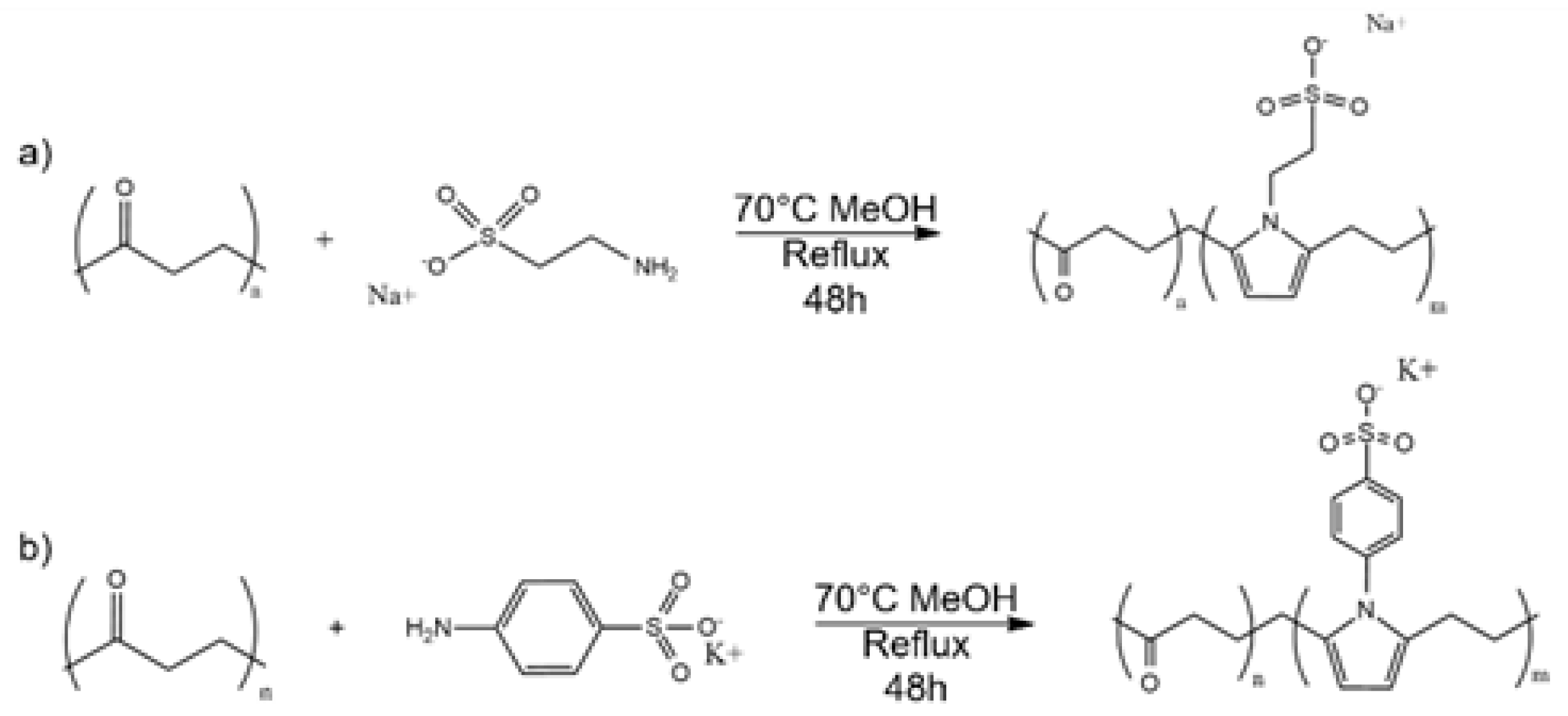
2.2. Synthesis of Aliphatic Polyketones (PK)
2.3. Synthesis of PKSK and PKT by Paal-Knorr Modification of PK with Potassium Sulfanilate Or Sodium Taurinate
2.4. Loading of Vancomycin on PKSK or PKT
2.5. Vancomycin Release
2.6. Antibacterial Activity
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis of Post Functionalized PKs
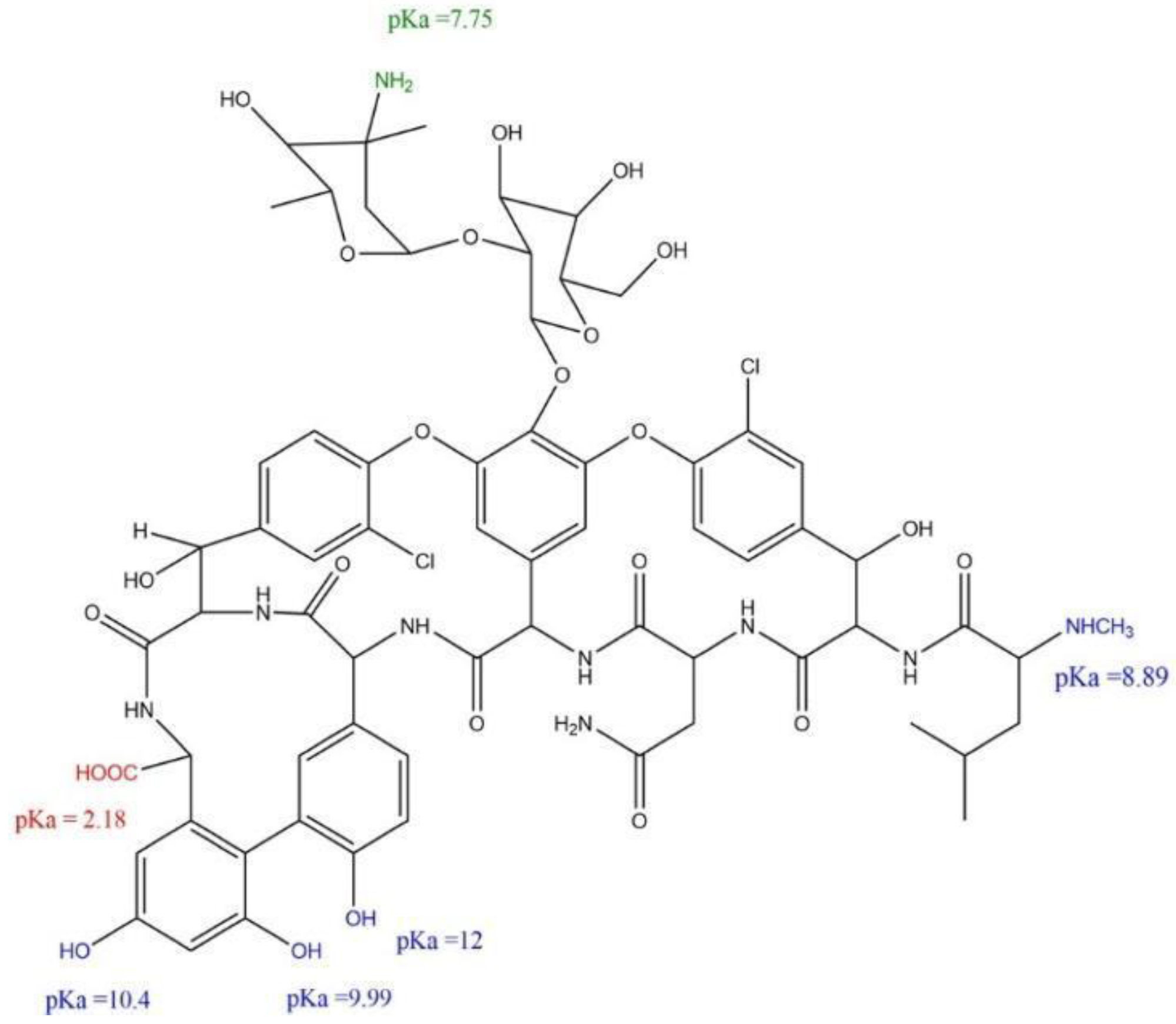
3.2. Influence of pH on Vancomycin Loading
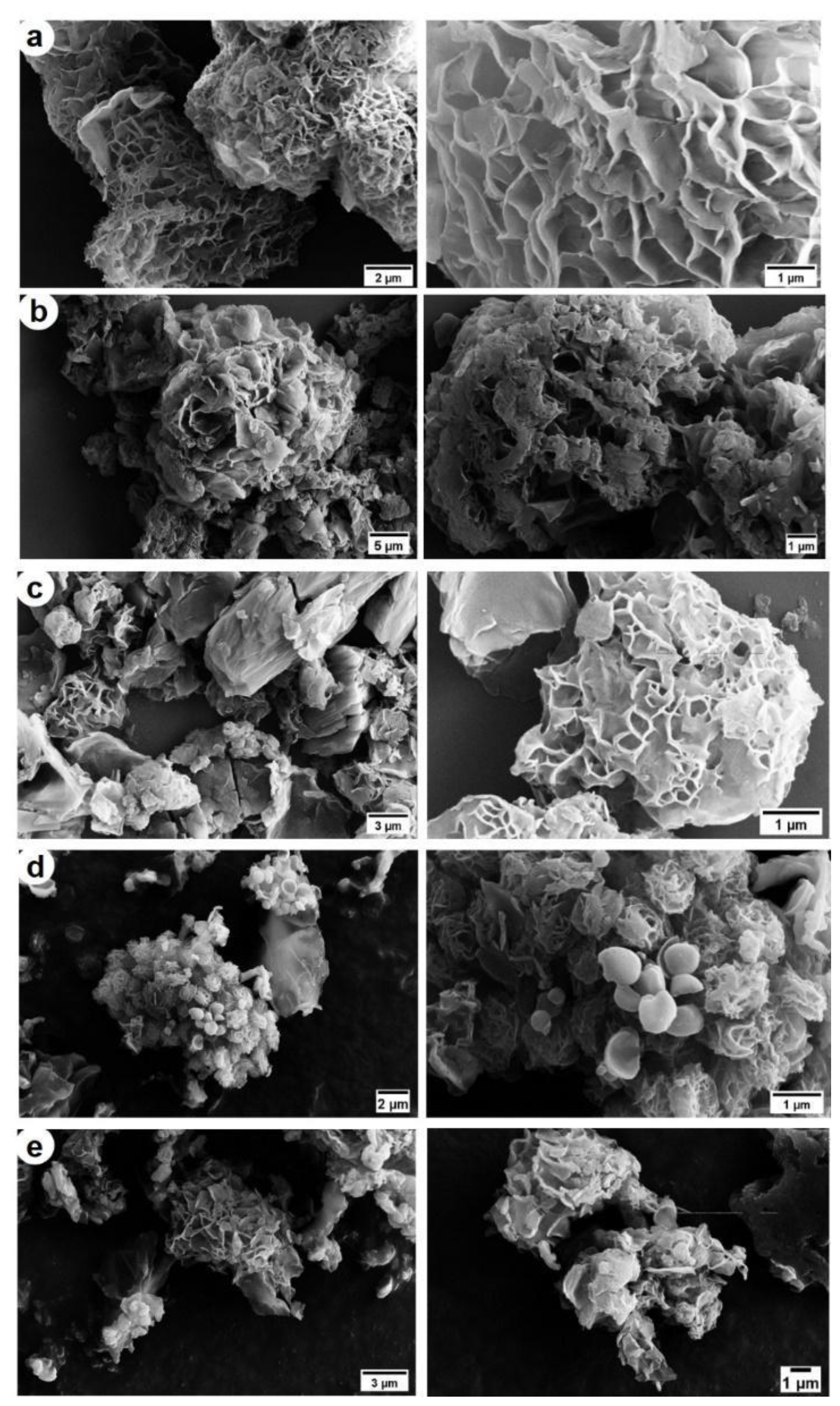
3.3. PKT-VCM and PKSK-VCM Characterisation
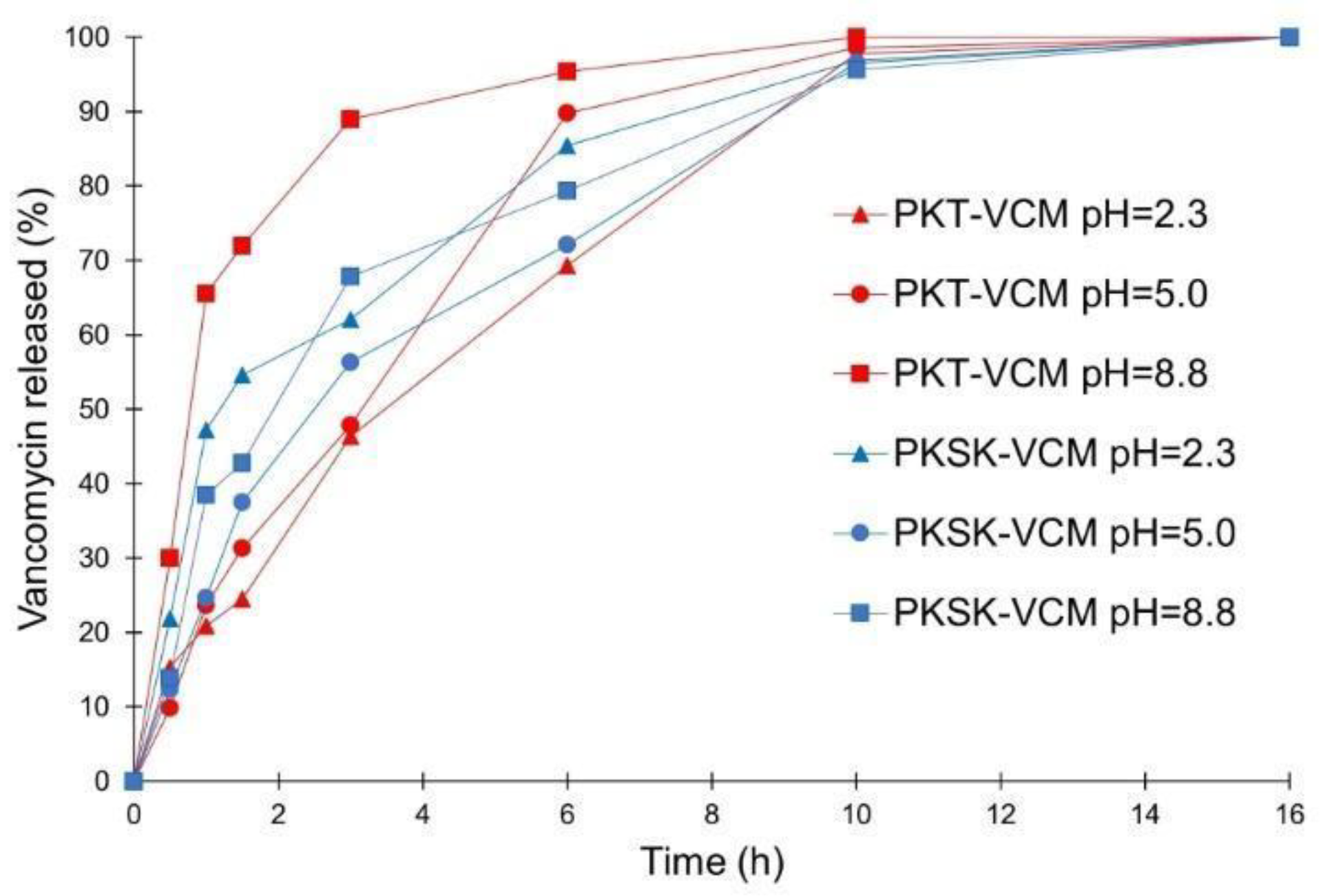
3.4. Release of Vancomycin from PK Polymers
3.5. Antimicrobial Tests
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morandini, A.; Spadati, E.; Leonetti, B.; Sole, R.; Gatto, V.; Rizzolio, F.; Beghetto, V. Sustainable triazine-derived quaternary ammonium salts as antimicrobial agents. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 28092-28096. [CrossRef]
- Reece, R.; Beckwith, C. G. The Infectious Diseases Specialist, At Risk of Extinction. J. Infect. Dis. 2023, 228, 1649–1651. [CrossRef]
- Momoh, A. O.; Asowata-Ayodele, A. M.; Olayemi, O.; David-Momoh, T. The comparative antimicrobial effects of castor, garlic, beniseed and bitter cola extracts on microorganisms isolated from hospitals’ wards. Microbes Infect. 2023, in Press.
- Shree, P.; Singh, C. K.; Sodhi, K. K.; Surya, J. N.; Singh, D. K. Bactericidal and biofilm eradication efficacy of a fluorinated benzimidazole derivative, TFBZ, against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Med. Microecol. 2023, 16, 100084. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Deshazer, H.; Rice, A. J.; Chen, K.; Zhou, C.; Kallenbach, N. R.; Multivalent Antimicrobial Peptides as Therapeutics: Design Principles and Structural Diversities. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 3436–3439. [CrossRef]
- Bruni, G.; Maggi, L.; Tammaro, L.; Lorenzo, R. D.; Friuli, V.; D’Aniello, S.;. Maietta, M ; Berbenni, V.; Milanese, C.; Girella, A.; Marini, A.; Electrospun fibers as potential carrier systems for enhanced drug release of perphenazine. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 511, 190–197. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Makabenta, J. M. V.; Schlüter, F.; Landis, R. F.; Das, R.; Cuppels, M.; Rotello, V. M. Functionalized Polymers Enhance Permeability of Antibiotics in Gram-negative MDR Bacteria and Biofilms for Synergistic Antimicrobial Therapy. Adv. Ther. 2020, 3, 2000005. [CrossRef]
- Soto, S. M. Role of Efflux Pumps in the Antibiotic Resistance of Bacteria Embedded in a Biofilm. Virulence 2013, 4, 223–229. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A., Gupta, V. K., Pathania, R. Efflux pump inhibitors for bacterial pathogens: From bench to bedside Indian J Med Res. 2019,149,129-145. [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Rong, F.; Tang, Y.; Li, M.; Feng, T.; Zhou, Q.; Li, P.; Huang, W. Targeted polymer-based antibiotic delivery system: A promising option for treating bacterial infections via macromolecular approaches. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2021, 16, 101389. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, R.; Xiao, X.; Wang, Z. Molecules that Inhibit Bacterial Resistance Enzymes. Molecules 2019, 24, 43. [CrossRef]
- De Pascale, G.; Wright, G. D. Antibiotic resistance by enzyme inactivation: From mechanisms to solutions. Chembiochem 2010, 11, 1325–1334. [CrossRef]
- Zgurskaya, H. I.; Rybenkov, V. V. Permeability barriers of Gram-negative pathogens. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 2020, 1459, 5-18. [CrossRef]
- Montanaro, L.; Campoccia, D.; Arciola, C. R. Advancements in molecular epidemiology of implant infections and future perspectives. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 5155-5168. [CrossRef]
- Abebe, G. M. Detection of Biofilm Formation and Antibiotic Resistance in Klebsiella Oxytoca and Klebsiella Pneumoniae from Animal Origin Foods . Int. J. Microbiol. 2020, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Patro, S.; Simnani, F. Z.; Singh, D.; Sinha, A.; Kumari, K.; Rao, P. V.; Singh, S.; Kaushik, N. K.; Panda, P. K.; Suar, M.; Verma, S. K. Biofilm modifiers: The disparity in paradigm of oral biofilm ecosystem. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 164, 114966. [CrossRef]
- Venter, H.; Henningsen, M. L.; Begg, S. L. Antimicrobial resistance in healthcare, agriculture and the environment: The biochemistry behind the headlines. Essays Biochem. 2017, 61, 1–10. [CrossRef]
- Rehman, S. A parallel and silent emerging pandemic: Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) amid COVID-19 pandemic. J. Infect. Public Health. 2023, 16, 611-617. [CrossRef]
- Larsson, D. G. J.; Flach, C. F. Antibiotic resistance in the environment. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 257–269. [CrossRef]
- Urban-Chmiel, R.; Marek, A.; Stępień-Pyśniak, D.; Wieczorek, K.; Dec, M.; Nowaczek, A.; Osek, Antibiotic Resistance in Bacteria-A Review. J. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1079. [CrossRef]
- Chin, K. W.; Michelle Tiong, H. L.; Luang-In, V.; Ma, N. L. The Role of Five-Membered Heterocycles in the Molecular Structure of Antibacterial Drugs Used in Therapy. Environ.Adv. 2023, 11, 100331. [CrossRef]
- Morandini, A.; Leonetti, B.; Riello, P.; Sole, R.; Gatto, V.; Caligiuri, I.; Rizzolio, F.; Beghetto, V. Synthesis and Antimicrobial Evaluation of Bis-morpholine Triazine Quaternary Ammonium Salts. ChemMedChem 2021, 16, 3172–3176. [CrossRef]
- Malaekeh-Nikouei, B.; Fazly Bazzaz, B. S.; Mirhadi, E.; Tajani, A. S.; Khameneh, B. The role of nanotechnology in combating biofilm-based antibiotic resistance. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. 2020, 60, 101880. [CrossRef]
- Birk, S. E.; Boisen, A.; Nielsen, L. H. Polymeric nano- and microparticulate drug delivery systems for treatment of biofilms. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 174, 30–52. [CrossRef]
- Sousa, A.; Phung, A. N.; Škalko-Basnet, N.; Obuobi, S. Smart delivery systems for microbial biofilm therapy: Dissecting design, drug release and toxicological features. J Control Release 2023, 354, 394–416. [CrossRef]
- Makhlouf, Z.; Ali, A. A.; Al-Sayah, M. H. Liposomes-Based Drug Delivery Systems of Anti-Biofilm Agents to Combat Bacterial Biofilm Formation. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 875. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Mohler, J.; Mahajan, S. D.; Schwartz, S. A.; Bruggemann, L.; Aalinkeel, R. Microbial Biofilm: A Review on Formation, Infection, Antibiotic Resistance, Control Measures, and Innovative Treatment. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1614. [CrossRef]
- Elumalai, K.; Srinivasan, S.; Shanmugam, A. Review of the efficacy of nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems for cancer treatment. J. Biomed. Technol. 2024, 5, 109-122. [CrossRef]
- Amidon, G. L.; Lennernäs, H.; Shah, V. P.; Crison, J. R. A theoretical basis for a biopharmaceutic drug classification: The correlation of in vitro drug product dissolution and in vivo bioavailability. Pharm. Res. 1995, 12, 413–420. [CrossRef]
- Patra, J. K.; Das, G.; Fraceto, L. F.; Campos, E. V. R.; Rodriguez-Torres, M. D. P.; Acosta-Torres, L. S.; Diaz-Torres, L. A.; Grillo, R.; Swamy, M. K.; Sharma, S.; Habtemariam, S.; Shin, H. S. Nano based drug delivery systems: Recent developments and future prospects. J. Nanobiotechnology 2018, 16, 71. [CrossRef]
- Al-Hussaniy, H. A.; Аlmajidi, Y. Q.; Oraibi, A. I.; Alkarawi, A. H. Nanoemulsions as medicinal components in insoluble medicines. Pharmacia 2023, 70, 537–547. [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, A.; Almotairy, A. R. Z.; Henidi, H.; Alshehri, O. Y.; Aldughaim, M. S. Nanoparticles as Drug Delivery Systems: A Review of the Implication of Nanoparticles' Physicochemical Properties on Responses in Biological Systems. Polymers 2023, 15, 1596. [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhuang, Y.; Shen, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, B.; Xiao, Z.; Dai, J. Aligned Scaffolds with Biomolecular Gradients for Regenerative Medicine. Polymers 2019, 11, 341. [CrossRef]
- Adepu, S.; Ramakrishna, S. Controlled Drug Delivery Systems: Current Status and Future Directions Molecules 2021, 26, 5905. [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Tan, P.; Fu, S.; Tian, X.; Zhang, H.; Ma, X.; Gu, Z.; Luo, K. Preparation and application of pH-responsive drug delivery systems. J. Control Release 2022, 348, 206–238. [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S. K.; Yadav, B.; Kumar Gupta, M.; Harish, S. A Comprehensive Review on Solid Dispersion Technique to Enhance the Solubility and Bioavailability of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs. Int. J. Pharm. Res. 2023, 14, 106-117. https://www.ijppronline.com/index.php/IJPPR/article/view/313.
- Sole, R.; Buranello, C.; Di Michele, A.; Beghetto, V. Boosting physical-mechanical properties of adipic acid/chitosan films by DMTMM cross-linking. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 209, 2009–2019. [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Alrobaian, M. M.; Molugulu, N.; Agrawal, N.; Numan, A.; Kesharwani, P. Pyramid-Shaped PEG-PCL-PEG Polymeric-Based Model Systems for Site-Specific Drug Delivery of Vancomycin with Enhance Antibacterial Efficacy. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 11935–11945. [CrossRef]
- Park, M. R.; Seo, B. B.; Song, S. C. Dual ionic interaction system based on polyelectrolyte complex and ionic, injectable, and thermosensitive hydrogel for sustained release of human growth hormone. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 1327–1336. [CrossRef]
- Palleria, C.; Di Paolo, A.; Giofrè, C.; Caglioti, C.; Leuzzi, G.; Siniscalchi, A.; De Sarro, G.; Gallelli, L. Pharmacokinetic drug-drug interaction and their implication in clinical management. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2013, 18, 601-10.
- Stipa, P.; Marano, S.; Galeazzi, R.; Minnelli, C.; Mobbili, G.; Laudadio, E. Prediction of drug-carrier interactions of PLA and PLGA drug-loaded nanoparticles by molecular dynamics simulations. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 147, 110292. [CrossRef]
- Al Ragib, A.; Chakma, R.; Dewan, K.; Islam, T.; Kormoker, T.; Idris, A. M. Current advanced drug delivery systems: Challenges and potentialities. Int. J. Drug Deliv. Technol. 2022, 76, 103727. [CrossRef]
- Beghetto, V.; Gatto, V.; Conca, S.; Bardella, N.; Scrivanti, A. Polyamidoamide dendrimers and cross-linking agents for stabilized bioenzymatic resistant metal-free bovine collagen. Molecules 2019, 24, 3611–3622. [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.- Q.; Zou, H.; Liu, W.-B.; Liu, N.; Wu, Z.-Q. Bottlebrush Polymers Based on RAFT and the "C1" Polymerization Method: Controlled Synthesis and Application in Anticancer Drug Delivery. ACS Macro Lett. 2022, 11, 179-185. [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zou, H.; Liu, N.; Wu, Z.- Q. Recent Advances in Polyallenes: Preparation, Self-Assembly, and Stimuli-Responsiveness. Chem. Asian J. 2021, 16, 3864. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.- Q.; Hu, G.; Xu, X. – H.; Kang, S. – M.; Liu, N.; Wu, Z. – Q. Synthesis of Redox-Responsive Core Cross-Linked Micelles Carrying Optically Active Helical Poly(phenyl isocyanide) Arms and Their Applications in Drug Delivery. ACS Macro Lett. 2018, 7, 1073-1079. [CrossRef]
- Larson, N.; Ghandehari, H. Polymeric Conjugates for Drug Delivery. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 840–853. [CrossRef]
- Irby, D.; Du, C.; Li, F. Lipid–Drug Conjugate for Enhancing Drug Delivery. Mol. Pharmaceutics. 2017, 14, 1325–1338. [CrossRef]
- Dalela, M.; Shrivastav, T. G.; Kharbanda, S.; Singh, H. pH-Sensitive Biocompatible Nanoparticles of Paclitaxel-Conjugated Poly(styrene-co-maleic acid) for Anticancer Drug Delivery in Solid Tumors of Syngeneic Mice. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2015, 7, 26530–26548. [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Jin, T. Polymer-Based Sustained-Release Dosage Forms for Protein Drugs, Challenges, and Recent Advances. AAPS PharmSciTech 2008, 9, 1218–1229. [CrossRef]
- Mansour, A.; Romani, M.; Acharya, A. B.; Rahman, B.; Verron, E.; Badran, Z. Drug Delivery Systems in Regenerative Medicine: An Updated Review. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 695. [CrossRef]
- Asadi, N.; Del Bakhshayesh, A. R.; Davaran, S.; Akbarzadeh, A. Common biocompatible polymeric materials for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 242, 122528. [CrossRef]
- Pei, X.; Wang, J.; Cong, Y.; Fu, J.; Recent progress in polymer hydrogel bioadhesives. J. Polym. Sci. 2021, 59, 1312–1337. [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, Y.; Yan, Y.; Gan, L.; Xu, J.; Zhou, G. Recent Advances in Biodegradable and Biocompatible Synthetic Polymers Used in Skin Wound Healing. Mater. 2023, 16, 5459. [CrossRef]
- Zehetmaier, P. C.; Vagin, S. I.; Rieger, B. Functionalization of aliphatic polyketones. MRS Bull. 2013, 38, 239–244. [CrossRef]
- Bartsch, G. C.; Malinova, V.; Volkmer, B. E.; Hautmann, R. E.; Rieger, B. Biokompatibilität von CO-Alkene-Polymeren mit aus urologischen Geweben isolierten primären Zellen und undifferenzierten Zellen. BJU Int. 2007, 99, 447–453. [CrossRef]
- Knorr, L. Synthese von pyrrolderivaten. Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges. 1884, 17, 1635-1642. [CrossRef]
- Brubaker, M. M.; Coffman, D. D.; Hoehn, H. H. Synthesis and Characterization of Ethylene/Carbon Monoxide Copolymers, A New Class of Polyketones. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1952, 74, 1509-1515. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q. – Y.; Wu, S. – W. Methyl Fluorosulphonyldifluoroacetate; a New Trifluoromethylating Agent. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun., 1989, 11, 705-706. [CrossRef]
- Green, M. J.; Lucy, A. R.; Lu, S.; Paton, R. Functionalisation of alkene–carbon monoxide alternating copolymers via transketalisation reactions. J.Chem.Soc.Chem.Commun. 1994, 2063. [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Paton, R. M.; Green, M. J.; Lucy, A. R. Synthesis and characterization of polyketoximes derived from alkene-carbon monoxide copolymers. Eur. Pol. J. 1996, 32, 1285. [CrossRef]
- Khansawai P., Paton, R. M.; Reed, D. Polyketones as alternating copolymers of carbon monoxide. Chem.Commun. 1999, 1297. [CrossRef]
- Nozaki, K.; Kosaka, N.;. Graubner, V. M; Hiyama, T. Methylenation of an Optically Active γ-Polyketone: Synthesis of a New Class of Hydrocarbon Polymers with Main-Chain Chirality. Macromol. 2001, 34, 6167–6168. [CrossRef]
- Reuter, P.; Fuhrmann, R.; Mucke, A.; Voegele, J.; Rieger, B.; Franke, R. P. Functionalization of aliphatic polyketones. Macromol. Biosci. 2003, 3, 123. [CrossRef]
- Matteoli, U.; Beghetto, V.; Scrivanti, A.; Aversa, M.; Bertoldini, M.; Bovo, S. An alternative stereoselective synthesis of (R)- and (S)-Rosaphen® via asymmetric catalytic hydrogenation. Chirality 2011, 23, 779-783. [CrossRef]
- Araya-Hermosilla, R;. G. M. R.; Lima, Raffa, P.; Fortunato, G.; Pucci, A.; Flores, M. E.; Moreno-Villoslada I.; Broekhuis, A.A.; Picchioni, F. Intrinsic self-healing thermoset through covalent and hydrogen bonding interactions. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 81, 186-197. [CrossRef]
- Ratna, D. Handbook of Thermoset Resins; Smithers Rapra: Shawbury, UK, 2009.
- Vavasori, A.; Ronchin, L. Polyketones: Synthesis and Applications. In Encyclopedia of Polymer Science and Technology, 2017, pp 1–41.
- Araya-Hermosilla, E.; Moreno-Villoslada, I.; Araya-Hermosilla, R.; Flores, M. E.; Raffa, P.; Biver, T.; Pucci, A.; Picchioni, F.; Mattoli, V. pH-Responsive Polyketone/5,10,15,20-Tetrakis-(Sulfonatophenyl)Porphyrin Supramolecular Submicron Colloidal Structures. Polymers 2020, 12, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Zhou, L.; Wu, Z.- Q. Alkyne-Palladium(II)-Catalyzed Living Polymerization of Isocyanides: An Exploration of Diverse Structures and Functions. Acc.Chem.Res. 2021, 54, 3953−3967. [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Zhou, L.; Wu, Z. -Q. Helix-Induced Asymmetric Self-Assembly of π-Conjugated Block Copolymers: From Controlled Syntheses to Distinct Properties. Acc.Chem.Res. 2023, 56, 2954-2967. [CrossRef]
- Agostinelli, E.; Belli, F.; Tempera, G.; Mura, A.; Floris, G.; Toniolo, L.; Vavasori, A.; Fabris, S.; Momo, F.; Stevanato, R. Polyketone polymer: A new support for direct enzyme immobilization. J. Biotechnol. 2007, 127, 670–678. [CrossRef]
- Araya-Hermosilla, E.; Parlanti, P.; Gemmi, M.; Mattoli, V.; Di Pietro, S.; Iacopini, D.; Granchi, C.; Turchi, B.; Fratini, F.; Di Bussolo, V.; Minutolo, F.; Picchioni, F.; Pucci, A. Functionalized aliphatic polyketones with germicide activity. RSC Advances. 2022, 12, 35358-35366. [CrossRef]
- Cetinkaya, Y.; Falk, P.; Mayhall, C. G. Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococci Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2000, 13, 686–707. [CrossRef]
- Levine, D. P. Vancomycin: A History. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 42, S5–S12. [CrossRef]
- Dinu, V.; Lu, Y.; Weston, N.; Lithgo, R.; Coupe, H.; Channell, G.; Adams, G. G.; Torcello Gómez, A.; Sabater, C.; Mackie, A.; Parmenter, C.; Fisk, I.; Phillips-Jones, M. K.; Harding, S. E. The antibiotic vancomycin induces complexation and aggregation of gastrointestinal and submaxillary mucins. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 960. [CrossRef]
- Newman, D. J. Old and modern antibiotic structures with potential for today’s infections. ADMET DMPK, 2022, 10, 131–146. [CrossRef]
- Ottonello, A.; Wyllie, J. A.; Yahiaoui, O.; Sun, S.; Koelln, R. A.; Homer, J. A.; Johnson, R. M.; Murray, E.; Williams, P.; Bolla, J. R.; Robinson, C. V.; Fallon, T.; Soares da Costa, T. P.; Moses, J. E. Shapeshifting bullvalene-linked vancomycin dimers as effective antibiotics against multidrug-resistant gram-positive bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2023, 120, e22087371. [CrossRef]
- Willems, R. P. J.; Van Dijk, K.; Vehreschild, M. J. G. T.; Biehl, L. M.; Ket, J. C. F.; Remmelzwaal, S.; Vandenbroucke-Grauls, C. M. J. E. Incidence of infection with multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria and vancomycin-resistant enterococci in carriers: A systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2023, 23, 719–731. [CrossRef]
- O’Toole, R. F.; Leong, K. W. C.; Cumming, V.; Van Hal, S. Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium and the emergence of new sequence types associated with hospital infection. J. Res. Microbiol 2023, 174, 104046. [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hetjens, L.; Wolter, N.; Li, H.; Shi, X.; Pich, A. Charge-reversible and biodegradable chitosan-based microgels for lysozyme-triggered release of vancomycin. J. Adv. Res. 2023, 43, 87–96. [CrossRef]
- Iglesias-Mejuto, A.; Magariños, B.; Ferreira-Gonçalves, T.; Starbird-Pérez, R.; Álvarez-Lorenzo, C.; Reis, C. P.; Ardao, I.; García-González, C. A. Vancomycin-loaded methylcellulose aerogel scaffolds for advanced bone tissue engineering. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 324, 121536. [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Hu, Y.; Li, X. Polymer mechanochemistry in drug delivery: From controlled release to precise activation. J. Control Release 2024, 365, 259–273. [CrossRef]
- Zakeri-Milani, P.; Loveymi, B. D.; Jelvehgari, M.; Valizadeh, H. The characteristics and improved intestinal permeability of vancomycin PLGA-nanoparticles as colloidal drug delivery system. Colloids Surf. B. 2013, 103, 174–181. [CrossRef]
- Yousry, C.; Elkheshen, S. A.; El-laithy, H. M.; Essam, T.; Fahmy, R. H. Studying the influence of formulation and process variables on Vancomycin-loaded polymeric nanoparticles as potential carrier for enhanced ophthalmic delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 100, 142–154. [CrossRef]
- Hassan, D.; Omolo, C. A.; Fasiku, V. O.; Mocktar, C.; Govender, T. Novel chitosan-based pH-responsive lipid-polymer hybrid nanovesicles (OLA-LPHVs) for delivery of vancomycin against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 147, 385–398. [CrossRef]
- Thamvasupong, P.; Viravaidya-Pasuwat, K. Controlled Release Mechanism of Vancomycin from Double-Layer Poly-L-Lactic Acid-Coated Implants for Prevention of Bacterial Infection. Polymers 2022, 14, 3493. [CrossRef]
- Sahiner, M.; Yilmaz, A. S.; Ayyala, R. S.; Sahiner, N. Carboxymethyl Chitosan Microgels for Sustained Delivery of Vancomycin and Long-Lasting Antibacterial Effects. Gels 2023, 9, 708. [CrossRef]
- Liu, W. -B.; Gao, R. -T.; Zhou, L.; Liu, N.; Chen, Z.; Wu, Z.-Q. Combination of vancomycin and guanidinium-functionalized helical polymers for synergistic antibacterial activity and biofilm ablation. Chem. Sci. 2022, 13, 10375-10382. [CrossRef]
- Sezer, A. D.; Kazak Sarılmışer, H.; Rayaman, E.; Çevikbaş A.; Öner, Akbuğa, E. T. J. Development and characterization of vancomycin-loaded levan-based microparticular system for drug delivery. Pharm Dev Technol. 2017, 22, 627-634. [CrossRef]
- Vinod, L. A.; Rajendran, D.; Shivashankar, M.; Chandrasekaran, N. Surface interaction of vancomycin with polystyrene microplastics and its effect on human serum albumin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 256, 128491. [CrossRef]
- Vavasori, A.; Ronchin, L.; Quartarone, G.; Tortato, C. The catalytic copolymerization of ethene with carbon monoxide efficiently carried out in water/dichloromethane/sodium dodecylsulfate emulsion. Modern Research in Catalysis 2013, 2, 93–99. [CrossRef]
- Vavasori, A.; Ronchin, L.; Quartarone, G.; Tortato, C.; The catalytic copolymerization of ethene with carbon monoxide efficiently carried out in water/dichloromethane/sodium dodecylsulfate emulsion. Mod Res Catal. 2013, 2, 93-99. [CrossRef]
- Vavasori, A.; Toniolo, L. Carbon monoxide-ethylene copolymerization catalyzed by a Pd(AcO)2/dppp/TsOH1 system: The promoting effect of water and of the acid. J Mol Catal A Chem. 1996, 110, 13-23. [CrossRef]
- Ataollahi, N.; Girardi, F.; Cappelletto, E.; Vezzù, K.; Di Noto, V.; Scardi, P.; Callone, E.; Di Maggio, R. Chemical modification and structural rearrangements of polyketone-based polymer membrane. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 45485. [CrossRef]
- Ataollahi, N.; Vezzù, K.; Nawn, G.; Pace, G.; Cavinato, G.; Girardi, F.; Scardi, P.; Di Noto, V.; Di Maggio, R. A Polyketone-based Anion Exchange Membrane for Electrochemical Applications: Synthesis and Characterization. Electrochim. Acta. 2017, 226, 148–157. [CrossRef]
- Sole, R.; Gatto, V.; Conca, S.; Bardella, N.; Morandini, A.; Beghetto, V.;Sustainable Triazine-Based Dehydro-Condensation Agents for Amide Synthesis. Molecules, 2021, 26, 191-206. [CrossRef]
- Toncelli, C.; Schoonhoven, M. J.; Broekhuis, A. A.; Picchioni, F. Paal-Knorr kinetics in waterborne polyketone-based formulations as modulating cross-linking tool in electrodeposition coatings. Mater. Des. 2016, 108, 718–724. [CrossRef]
- Scrivanti, A.; Sole, R.; Bortoluzzi, M.; Beghetto, V.; Bardella, N.; Dolmella, A. Synthesis of new triazolyl-oxazoline chiral ligands and study of their coordination to Pd(II) metal centers. Inorganica Chim. Acta 2019, 498, 119129. [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, I. S.; Bettencourt, A. F.; Gonçalves, L. M. D.; Kasper, S.; Bétrisey, B.; Kikhney, J.; Moter, A.; Trampuz, A.; Almeida, A. J. Activity of daptomycin- and vancomycin-loaded poly-epsilon-caprolactone microparticles against mature staphylococcal biofilms. Nanomed. J. 2015, 10, 4351–4366. [CrossRef]
- Le Ray, A.- M.; Chiffoleau, S.; Iooss, P.; Grimandi, G.; Gouyette, A.; Daculsi, G.; Merle, C. Vancomycin encapsulation in biodegradable poly(ε-caprolactone) microparticles for bone implantation. Influence of the formulation process on size, drug loading, in vitro release and cytocompatibility. Biomaterials. 2003, 24, 443-449. [CrossRef]
- Honary, S.; Ebrahimi, P.; Hadianamrei, R. Optimization of particle size and encapsulation efficiency of vancomycin nanoparticles by response surface methodology. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2014, 19, 987-998. [CrossRef]
- Kalhapure, R. S.; Mocktar, C.; Sikwal, D. R.; Sonawane, S. J.; Kathiravan, M. K.; Skelton, A.; Govender, T. Ion pairing with linoleic acid simultaneously enhances encapsulation efficiency and antibacterial activity of vancomycin in solid lipid nanoparticles. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2014,117, 303-311. [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, J. C.; Alvarez-Lorenzo, C.; Taboada, P.; Burillo, G.; Bucio, E.; De Prijck, K.; Nelis, H. J.; Coenye, T.; Concheiro, A. Polypropylene grafted with smart polymers (PNIPAAm/PAAc) for loading and controlled release of vancomycin. Eur J Pharm Biopharm . 2008, 70, 467–477. [CrossRef]
- Takacs-Novak, K.; Noszal, B.; Tòkés-Kovesdi, M.; Sz6sz, G. Acid-base properties and proton-speciation of vancomycin. Int. J. Pharm. 1993, 89, 261-263. [CrossRef]
- Flores-Rojas, G. G.; Vázquez, E.; López-Saucedo, F.; Buendia-Gonzalez, L.; Vera-Graziano, R.; Mendizabal, E.; Bucio, E. Lignocellulosic membrane grafted with 4-vinylpiridine using radiation chemistry: Antimicrobial activity of loaded vancomycin. Cellulose. 2023, 30, 3853–3868. [CrossRef]
- Bil, M., Jurczyk-Kowalska, M.; Kopeć, K.; Heljak, M. Study of Correlation between Structure and Shape-Memory Effect/Drug-Release Profile of Polyurethane/Hydroxyapatite Composites for Antibacterial Implants. Polymers 2023, 15, 938. [CrossRef]
- Avila-Novoa, M. G.; Solis-Velazquez, O. A.; Guerrero-Medina, P. J.; González-Gómez, J. P.; González-Torres, B.; Velázquez-Suárez, N. Y.; Martínez-Chávez, L.; Martínez-Gonzáles, N. E.; De la Cruz-Color, L.; Ibarra-Velázquez, L. M.; Cardona-López, M. A.; Robles-García, M. A.; Gutiérrez-Lomelí, M. Genetic and compositional analysis of biofilm formed by Staphylococcus aureus isolated from food contact surfaces. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13. [CrossRef]
- Beghetto, V.; Gatto, V.; Samiolo, R.; Scolaro, C.; Brahimi, S.; Facchin, M.; Visco, A. Plastics today: Key challenges and EU strategies towards carbon neutrality: A review. Environmental Pollution, 2023, 334, 122102. [CrossRef]

| Sample | pH | Elementals(%) | EE% | LC% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | S | ||||
| PKSK | - | 4.02±0.01 | 9.31±0.02 | - | - |
| PKSK-VCM | 2.3 | 4.36±0.02 | 7.67±0.01 | 41.25±0.03 | 23.08±0.01 |
| PKSK-VCM | 5.0 | 7.13±0.01 | 2.37±0.03 | 75.00±0.02 | 31.03±0.01 |
| PKSK-VCM | 8.8 | 5.86±0.01 | 5.10±0.01 | 66.66±0.01 | 25.00±0.02 |
| PKT | - | 1.66±0.03 | 4.23±0.02 | - | - |
| PKT-VCM | 2.3 | 2.10±0.01 | 3.75±0.03 | 23.08±0.01 | 10.71±0.02 |
| PKT-VCM | 5.0 | 7.73±0.02 | 1.12±0.01 | 80.00±0.02 | 31.58±0.01 |
| PKT-VCM | 8.8 | 3.66±0.03 | 3.41±0.03 | 42.67±0.02 | 15.15±0.03 |
| Sample | pH | MIC (µg/ml) |
|---|---|---|
| PKSK-VCM | 2.3 | 1.44 |
| PKSK-VCM | 5.0 | 0.23 |
| PKSK-VCM | 8.8 | 1.56 |
| PKT-VCM | 2.3 | 2.68 |
| PKT-VCM | 5.0 | 0.24 |
| PKT-VCM | 8.8 | 3.79 |
| VCM | 1.54 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





