Submitted:
22 June 2024
Posted:
24 June 2024
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
| Step | Description |
| Topic | Business Sustainability Model |
| Rationale | There is still a lack of initial description of the Jakarta MRT business model as manager of the TOA area and its development using a value creation approach. |
| Information Sources | Scopus |
| Keywords | Sustainable Business, Sustainable, or Sustainable Value Creation or Public Transportation |
| Inclusion Criteria | Subject categories: Business, Management, Accounting; English; Article type: Journal; Stage: Final |
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
References
- Alvino, F., Di Vaio, A., Hassan, R., & Palladino, R. (2021). Intellectual capital and sustainable development: a systematic literature review. Journal of Intellectual Capital, 22 (1), 76–94. [CrossRef]
- Aldo A, Nurahma T. 2022. Pengaruh Keberadaan MRT Jakarta Terhadap Aktifitas Karyawan Perkantoran di SCBD. Jurnal Muara Sains, Teknologi, Kedokteran, dan Ilmu Kesehatan. 6(1): 1-6. [CrossRef]
- Andersen J. 2011. Resource-based competitiveness: managerial implications of the resource-based view. Strategic Direction. 26(5): 3-5. [CrossRef]
- Anderson JC, Narus JA, van Rossum W. 2006. Customer value propositions in business markets. Harvard Business Review. 84(3): 90-149.
- Ascarya. 2005. Analytic network process (ANP): Pendekatan baru studi kualitatif, Makalah pada Seminar Intern Program Magister Akuntansi Fakultas Ekonomi di Universitas Trisakti, Jakarta.
- Babin BJ, James KW. 2010. A brief retrospective and introspective on value. European Business Review. 22(5): 471–478. [CrossRef]
- Barnes C, Blake H, Pinder D. 2009. Creating & Delivering Your Value Proposition: Managing Customer Experience for Profit. London (UK): Kogan Page.
- Barney & Clark. 2007. Resource Based Theory. Creating and Sustaining Competitive Advantage. Oxford University Press, Oxford.
- BPTJ. 2020. Menuju Integrasi Transportasi di Wilayah Jabodetabek. bptj.dephub.go.id. Retrieved March 12, 2020. https://bptj.dephub.go.id/post/read/menuju-integrasi-transportasi-diwilayah-jabodetabek.
- BPTJ. 2021. Mengembangkan Transportasi Ramah Lingkungan dengan Jalan Kaki dan Bersepeda. bptj.dephub.go.id. Retrieved January 5, 2021, from https://bptj.dephub.go.id/post/read/mengembangkan-transportasi-ramah-lingkungan-dengan-jalan-kaki-dan-bersepeda?language=id.
- Bu Q, Jin Y, Li Z. 2020. How does a customer prefer community or brand? The impacts of customer experience on customer loyalty based on the perspective of value cocreation. The perspective of value co-creation Journal of Contemporary Marketing Science. 3(3): 281-302. [CrossRef]
- Budiawan S.A. 2023. Peningkatan Layanan Transportasi Umum Atasi Kemacetan Ibu Kota. Kompas.id. Retrieved August 17, 2023, from https://www.kompas.id/baca/riset/2023/08/17/peningkatan-layanan-transportasi-umum-atasi-kemacetan-ibu-kota.
- Checkland P, Poulter J. 2010. Systems Approaches to Managing Change: A Practical Guide. Soft Systems Methodology. London (UK): The Open University.
- CNN Indonesia. 2021. Kerugian Ekonomi Akibat Macet Jabodetabek Capai Rp71,4 T. cnnindonesia.com. Retrieved April 28, 2021, from.
- https://www.cnnindonesia.com/ekonomi/20210428120006-92-635840/kerugian-ekonomi-akibat-macet-jabodetabek-capai-rp714-t.
- de Oliviera M, Prest MA, Seabra RD. 2021. Usability evaluation model of an application with emphasis on collaborative security: An approach from social dimensions. Journal of the Brazilian Computer Society. 27(1). [CrossRef]
- Desarbo, W. S., Jedidi, K., & Sinha, I. 2001. Customer value analysis in a heterogeneous market. Strategic Management Journal, 22(9), 845–857. [CrossRef]
- Desarbo WS, Jedidi K, Sinha I. 2013. Customer value analysis in a heterogeneous market. Strategic Management Journal. 22(9): 845–857. [CrossRef]
- Eriyatno. 2012. Meningkatkan Mutu dan Efektifitas Manajemen. Ilmu Sistem. Bogor (ID): IPB Press.
- Gummerus J. 2013. Value creation processes and value outcomes in marketing theory. Marketing Theory. 13(1): 19–46. [CrossRef]
- Haksever C, Chaganti R, Cook RG. 2014. A model of value creation: strategic view. Journal of Business Ethics. 49: 291–305. [CrossRef]
- Hartmann PM, Zaki M, Feldmann N, Neely A. 2016. Capturing value from big data-a taxonomy of data-driven business models used by start-up firms. International Journal of Operations & Production Management. 36(10): 1382–1406. [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim I. 2010. Persiapan teknis pembangunan transportasi cepat masal di Jakarta. Jurnal Sains dan Teknologi Indonesia. 12(3): 197-204. [CrossRef]
- Julienti L, Bakar A, Hartini A. 2010. Assessing the relationship between.
- firm resources and product innovation performance (A resource-based view). Business Process Management Journal. 16(3): 420-435. [CrossRef]
- Klanac NG. 2013. An integrated approach to customer value: A comprehensive-practical approach. Journal of Business Market Management. 1: 22-37.
- Lindic J, da Silva CM. 2011. Value proposition as a catalyst for.
- a customer focused innovation. Management Decision. 49(10): 1694-1708. [CrossRef]
- Lindic J, da Silv, CM. 2011. Value proposition as a catalyst for a customer focused innovation. Management Decision. 49(10): 1694-1708. [CrossRef]
- Lund K, Ordonez R, Nielsen JB, Christiansen S, Houmoller SS, Schmid JH, Gaehede M, Hammershoi D. 2023. Value propositions of public adult hearing rehabilitation in Denmark. Audiol. Res. (13): 254–270. [CrossRef]
- Madhani PM. 2022. Effective marketing strategy with blockchain implementation: Enhancing customer value propositions. IUP Journal of Business Strategy. 19(1): 7-35.
- Marimin. 2009. Teori dan Aplikasi: Sistem Pakar dalam Teknologi Manajerial. Bogor (ID): IPB Press.
- Meirelles DS. e, D’Andrea D. 2021. From private label to co-branded credit card: An assessment of the impact of a change in value proposition over customer value perception and company value capture. Journal of Financial Services Marketin. 26(1): 52-65. [CrossRef]
- Mejtoft T. 2011. Internet of Things and Co-creation of Value. In IEEE International Conference on Internet of Things, and Cyber, Physical and Social Computing. [CrossRef]
- Ng ICL, Smith LA. 2012b. An integrative framework of value. Review of Marketing Research. 9: 207–243. [CrossRef]
- Nurnadhifa H, Latifah HN. 2021. Sistem Mass Rapid Transit (MRT) DKI Jakarta: studi kasus transfer kebijakan pendapatan non-farebox di Indonesia. Public Inspiration: Jurnal Administrasi Publik. 6(2): 97-106. [CrossRef]
- Ortega EMP, Azorin ZFM, Cortes RC. (2018). Competitive strategy, structure and firm performance (A comparison of the resource-based view and the contingency approach). Management Decision. 48(8): 1282-1303. [CrossRef]
- Osterwalder A, Pigneur Y. 2012. Business Model Generation: A Handbook For Visionaries, Game Changers, And Challengers. New Jersey (US): John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
- Osterwalder A, Pigneur. 2012. Business Model Generation. Jakarta (ID): PT Elex Media Komputindo.
- Paananen A, Seppänen, M. (2013). Reviewing customer value literature: Comparing and contrasting customer values perspectives. Intangible Capital. 9(3): 708–729. [CrossRef]
- Paul JK. 2016. Does VRIO help managers evaluate a firm’s resources? Management Decision. 53(8): 1806-1822. [CrossRef]
- Paulo R. Cond et al. (2018). Value proposition: application of value creation activities model in The Supermarket (Vcam-S). Revista de Administração Mackenzie. 19(4). [CrossRef]
- Payne A, Frow P. 2014. Developing superior value propositions: A strategic marketing imperative. Journal of Service Management. 25(2): 213-227. [CrossRef]
- Pemerintah Propinsi DKI Jakarta. 2017. Peraturan Gubernur Nomor 44 Tahun 2017 tentang Pengembangan Kawasan Transit Oriented Development. https://jdih.jakarta.go.id/dokumen/detail/6083.
- Pemerintah Propinsi DKI Jakarta. 2021. Peraturan Gubernur Nomor 65 Tahun 2021 tentang Perubahan Atas Peraturan Gubernur Nomor 15 Tahun 2020 tentang Penugasan Perseroan Terbatas Mass Rapid Transit Jakarta Sebagai Pengelola Kawasan Berorientasi Transit Koridor Utara-selatan Mass Rapid Transit Jakarta. https://jdih.jakarta.go.id/dokumen/detail/5894.
- Pemerintah Propinsi DKI Jakarta. 2021. Peraturan Gubernur Nomor 50 Tahun 2021 tentang Perubahan Atas Peraturan Gubernur Nomor 67 Tahun 2019 tentang Penyelenggaraan Kawasan Berorientasi Transit. https://jdih.jakarta.go.id/dokumen/detail/1772/peraturan-gubernur-nomor-50-tahun-2021-tentang-perubahan-atas-peraturan-gubernur-nomor-67-tahun-2019-tentang-penyelenggaraan-kawasan-berorientasi-transit.
- Pemerintah Propinsi DKI Jakarta. 2022. Peraturan Gubernur Nomor 31 Tahun 2022 tentang Rencana Detail Tata Ruang Wilayah Perencanaan Provinsi Daerah Khusus Ibukota Jakarta. https://jdih.jakarta.go.id/ dokumen/detail/4933/peraturan-gubernur-nomor-31-tahun-2022-tentang-rencana-detail-tata-ruang-wilayah-perencanaan-provinsi-daerah-khusus-ibukota-jakarta.
- Pennie F, Payne A. 2011. A stakeholder perspective of the value proposition concept. European Journal of Marketing. 45(1/2): 223-240. [CrossRef]
- PT MRT Jakarta. 2019. Together We Create More Value (Laporan Tahunan 2019) PT. MRT Jakarta (Perseroda)). https://jakartamrt.co.id/sites/default/ files/2020-09/Annual-Report-MRT-Jakarta-2019.pdf.
- PT MRT Jakarta. 2020. Growing In Sustainability (Laporan Keberlanjutan 2020 Sustainability Report). MRT Jakarta. https://jakartamrt.co.id/sites/ default/files/2021/08/MRT%20SR2020_Esig%20Dekom_290721.pdf.
- PT MRT Jakarta. 2021. Synergi and Innovation to Develop The Nation. (Laporan Keberlanjutan 2021 Sustainability Report). MRT Jakarta. https://jakartamrt.co.id/sites/default/files/2022-06/AR%20MRT%202021-L6-9jun-compressed.pdf.
- PT MRT Jakarta. 2022. Thriving Trough Transformation. (Laporan Keberlanjutan 2022 Sustainability Report). MRT Jakarta. https://jakartamrt.co.id/sites/default/files/2023-08/Annual%20Report%20 MRT%20Jakarta%202022.pdf.
- Rahardyan A. 2020. MRT Jakarta Siapkan 4 Skenario Bertahan dari Pandemi Covid-19. Ekonomi Bisnis.com. Retrieved November 25, 2021, from https://ekonomi.bisnis.com/read/20200429/98/1234683/mrt-jakarta-siapkan-4-skenario-bertahan-dari-pandemi-covid-19 R.
- Rusli C, Gusti AKS 2009. Penduduk dan Pembangunan Perumahan di Jabodetabek: Tantangan Pengembangan Megapolitan Jakarta. Jurnal Kependudukan Indonesia. 4(1): 55-72.
- Saaty TL, Vargas LG. 2012. Models, Methods, Concepts Applications of the Analytic Hierarchy Process: 175. Springer Science and Business Media.
- Sembiring LJ. 2021. Cek Guys! Daftar Wilayah Bisa Mudik, Ada Jakarta sampai Medan. CNBC Indonesia. Retrieved November 25, 2021, from https://www.cnbcindonesia.com/news/20210411131129-4-236918/cek-guys-daftar-wilayah-bisa-mudik-ada-jakarta-sampaimedan.
- TomTom. (n.d.). DKI Jakarta, Kota Termacet 10 Dunia. databoks. https://databoks.katadata.co.id/ datapublish/2020/02/20/dki-jakarta-kota-termacet-10-dunia.
- Turban E, McLean E, Wetherbe J. 2005. Information Technology for Management – Transforming Business in the Digital Economy. 3 rd Edition. New York (US): John Wiley & Son, Inc.
- Widyanto, U. (2018). MRT Jakarta Tiru Jepang, Genjot Pendapatan Non-Tiket | Tempo.co. LINE TODAY. Retrieved November 27, 2021, from https://today.line.me/id/v2/article/L2VJVG.
- Wiryono, S. (2021a,). Kasatpol PP DKI: Berangkat Kerja dari Bodetabek ke Jakarta Harus Ada Surat Tugas Kantor Halaman all - Kompas.com. Megapolitan Kompas.com. Retrieved November 25, 2021, from https://megapolitan.kompas.com/read/2021/05/07/14080621/kasatpol-pp-dki-berangkat-kerja-dari-bodetabek-ke-jakarta-harus-ada-surat?page=all W.
- Zikmund, William G. (1997). Business Research Methods, Fifth Ed., New York (US): The Dryden Press, Harcourt Brace College Publishers.
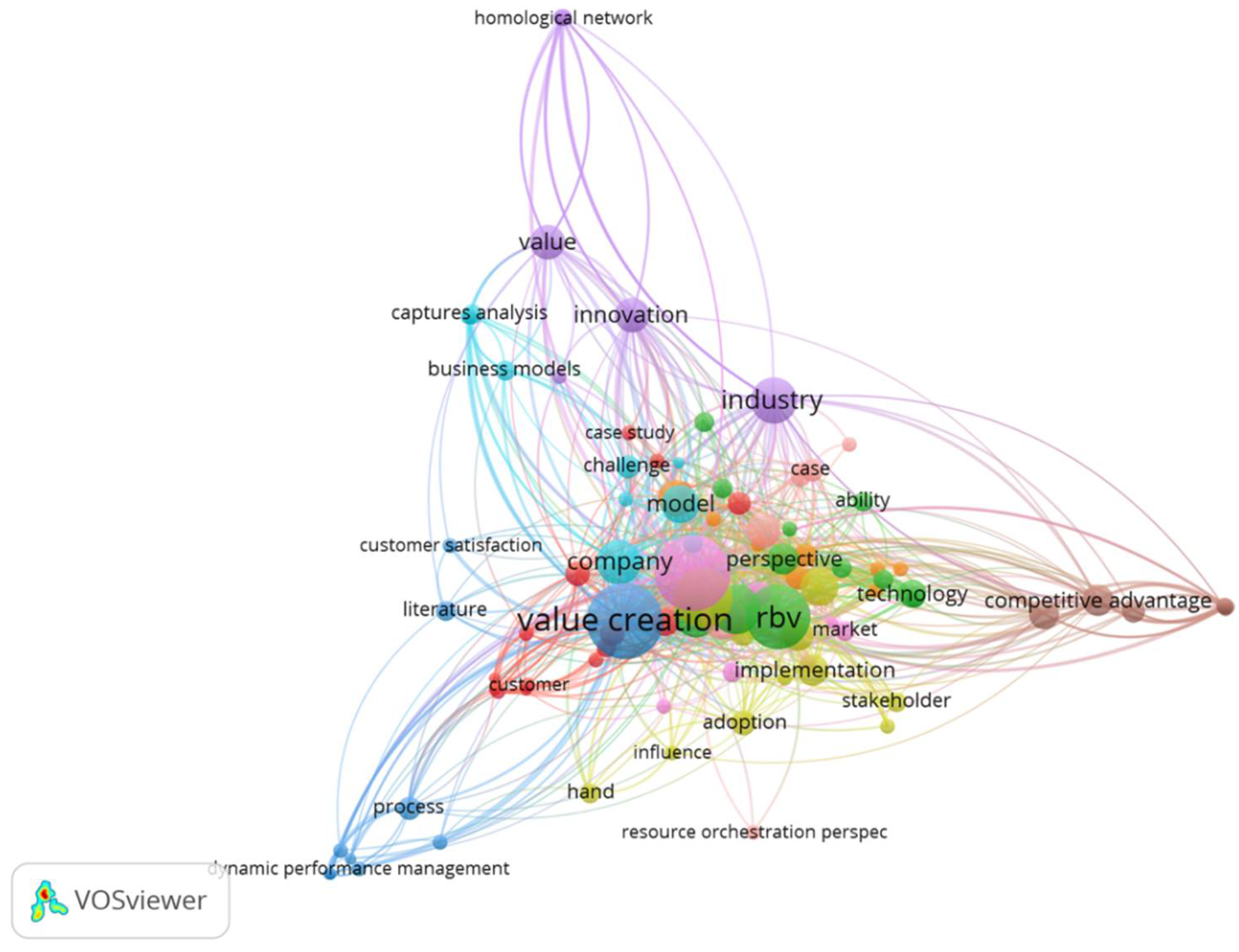
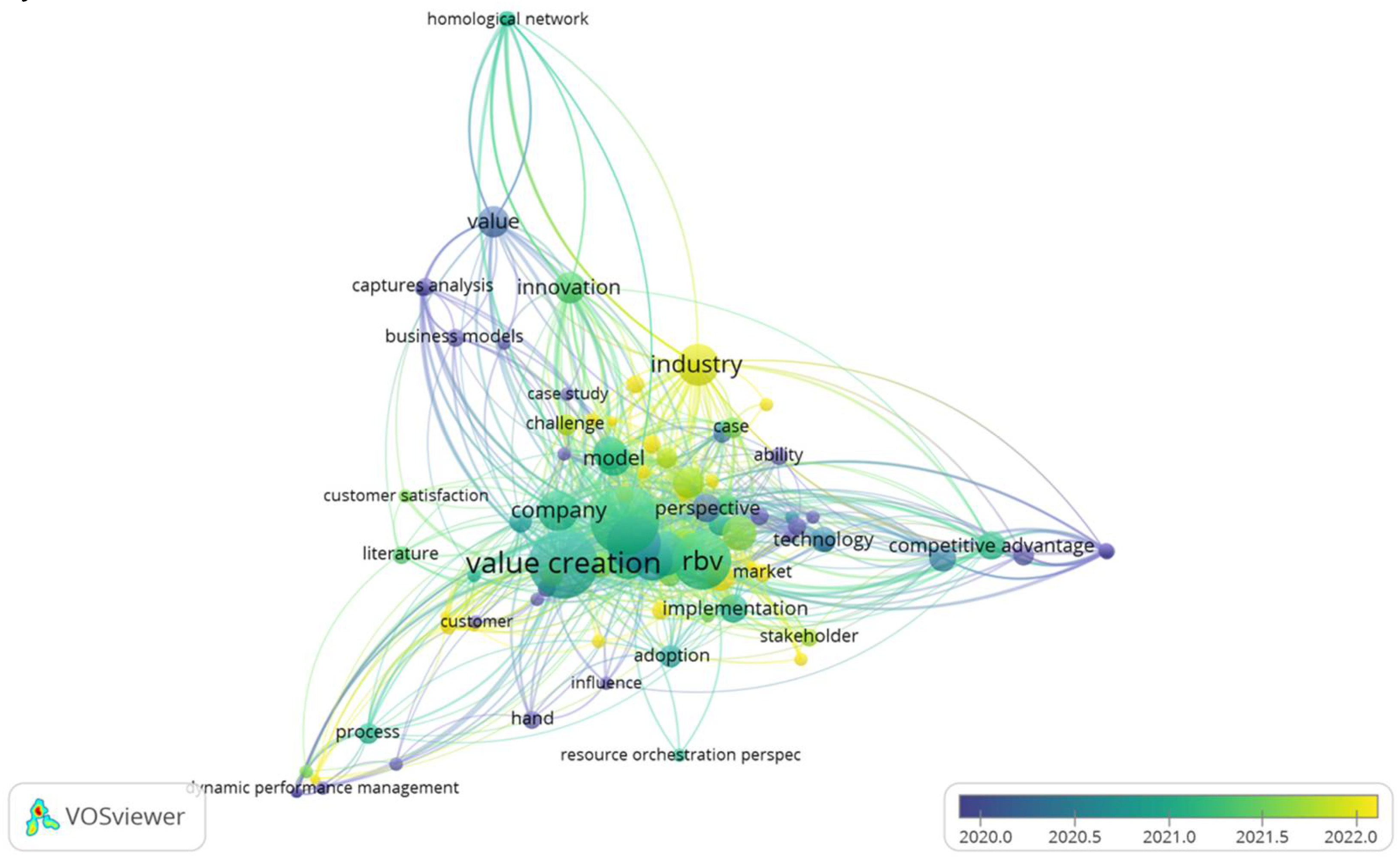
| No. | Topic | Author | Objective | Findings | Theory | Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | A Model of ValueCreation: Strategic View. | Cengiz et al. (2014) | The main aim of the research is to propose a model of value creation in three dimensions: financial, non-financial and time. |
The research presents the following key findings: a. Stakeholder Values. b. Multidimensional Approach. c. Time Dimension. d. Value Creation Practices. e. The challenge of maintaining a broad value perspective during a crisis. |
The theoretical background used in this article mainly focuses on the concept of value creation and stakeholder theory. | The methodology used in the research involves a proposed value creation model in three dimensions: financial, nonfinancial, and time. |
| 2. | A stakeholder perspective of the value proposition concept. | Pennie and Adrian (2011) | The aim of this research is to explore the concept of value proposition (VP) and its role as a stakeholder alignment mechanism in marketing systems. | The main finding of this research is that value propositions play an important role in creating shared value between various stakeholders and act as a valuable alignment mechanism in marketing systems. | The theoretical background used is to integrate insights from the relationship marketing literature, which emphasizes the role of various stakeholders in creating and capturing value. |
The methodology used in this research is a literature review combined with conceptual analysis. The author critically analyzes existing literature and concepts related to value propositions from various sources to develop a comprehensive understanding of stakeholder perspectives on the value proposition concept. |
| 3. | Value Proposition: Application of Value Creation Activities Model In the Supermarket (Vcam-S). | Paulo et al. (2018) | The aim of this article is to explore the application of the Value Creation Activity Model in a supermarket context (VCAM-S). The author aims to investigate and present the value proposition in the supermarket industry, specifically focusing on the value creation activity model. | The main findings of this research are as follows: a. As a theoretical basis for value propositions, loyalty, innovation, expectations, strategies, and tendencies in identifying value activities and their respective value sources. b. Identify various value creation activities in the supermarket sector, such as providing convenience in finding products, offering a mix of products with welfare attributes, launching product novelties, and providing a product mix with practicality attributes. c. The Value Proposition Framework is based on research findings and provides a structure for understanding and applying value propositions in a supermarket context. |
The theoretical basis used in the research is to explore the concept of value proposition as a position statement that defines target customers, why customers buy, and what the company sells. | The methodology used in this research involves two main stages. a. The first stage consisted of a bibliographic review, where articles in the field of marketing and supermarket retail were researched and analyzed. b. The second stage involved collecting primary data through personal interviews with 12 professionals from the supermarket sector. |
| 4. | Modeling An Organizational Sustainable Competitive Advantage. | Sunje and Pasic (2011) |
The aim of this research is to develop a model that describes the process of building sustainable competitive advantage for organizations, including static and dynamic aspects. | The main finding of this research is the development of a model of sustainable competitive advantage in organizations. This model consists of static and dynamic aspects. | The theoretical background of this research revolves around developing a model for building sustainable competitive advantage in organizations. It is based on the VRIO (Value, Rareness, Imitability, Organization) strategic tool framework, which is an extension of internal analysis. | The methodology used in this research is the development of a model that describes the process of building sustainable competitive advantage, both static and dynamic aspects. The model developed is based on the strategic tool framework VRIO (Value, Rareness, Imitability, Organization). |
| 5. | Competitive strategy, structure and firm performance (A comparison of the resource-based view and the contingency approach). | Eva et al. (2018) | The purpose of this research is to examine the relationship between organizational structure, competitive strategy, and company performance. This research aims to contribute to the understanding of how these factors interact and impact company performance. | The main finding of this research is that the relationship between organizational structure and company performance is influenced by competitive strategy. This study emphasizes the importance of considering the fit between strategy, structure, and performance, and suggests that the Resource-Based View (RBV) model provides valuable insights in this context. |
The theoretical background of this research is mainly based on strategic management and organizational theory. This article draws on various theoretical frameworks such as the resource-based view of the firm, core competencies, strategic fit, environmental fit, and contingency theory. | The methodology used in this research involved collecting data from companies with 250 or more employees, using opinion scales to assess organizational structure and competitive strategy, and using subjective performance measures. |
| 6. | Does VRIO help managers evaluate a firm’s resources? | Paul (2016) | The aim of research on the VRIO method is to evaluate whether the method helps managers analyze company resources. | A key finding from research on VRIO methods and their impact on strategic actions and analysis of corporate resources is that although VRIO encourages users to evaluate resources relative to competitors and competitive dynamics, VRIO also has limitations. | The research focuses on the theoretical background of the VRIO (Value-Rarity-Imitability-Organization) method and its impact on strategic actions and corporate resource analysis. | Research papers on VRIO methods and their impact on strategic actions and enterprise resource analysis use experimental methods to directly evaluate user analyzes guided by VRIO relative to those that are not. |
| 7. | Assessing the relationship between firm resources and product innovation performance (A resource-based view). | Lily and Hartini (2018) | The aim of this research is to investigate the relationship between firm resources and product innovation performance in the context of manufacturing firms. | This research emphasizes the importance of intangible resources, especially product reputation, in driving product innovation performance in the context of manufacturing firms in Malaysia. | The theoretical background in this research is based on the Resource-Based View (RBV) of strategic management. The RBV focuses on the firm as a unique collection of resources and emphasizes that not all resources have the potential to provide a firm with a sustainable competitive advantage. | The methodology used in this research involved developing a questionnaire based on accepted scale development methods for business research. The questionnaire was then distributed via a mail survey to technology entrepreneurs. |
| 8. | Value proposition as a catalyst for a customer focused innovation. | Lindic and Marques (2011) | The aim of this research is to investigate the role of value propositions as innovation catalysts. This research focuses on identifying value proposition elements and their relationships in different contexts, such as product, industry, or customer life cycles. | The main findings of this article include a comprehensive list of novelties and general characteristics discovered through research. | This research draws on various theoretical backgrounds to support its research, including: a. Business Model Innovation. b. Value Proposition Theory. c. Innovation Theory. d. This research uses a case study approach. e. Interdisciplinary Perspective. |
The methodology used in this research involved an embedded design, which aims to reduce the limitations of single case studies by allowing for more in-depth analysis through examination of subunits. The unit of analysis chosen is individual novelty, making it possible to carry out systematic and detailed case analysis. |
| 9. | Value Propositions of Public Adult Hearing Rehabilitation in Denmark. | Katja (2023) | The aim of this article on adult community hearing rehabilitation in Denmark is to identify and evaluate the value proposition of the hearing rehabilitation process in the Danish public health system. | Key findings from this research include the following: 1. Identify the Value Proposition. 2. The Importance of the Diagnostic Process. 3. Involvement of Closest Family. 4. Characteristics of Human Practitioners. 5. Physical Presence. 6. Methodological Approach. 7. Research Population. These findings provide insight into the factors that patients consider important in the hearing rehabilitation process of Danish adults. |
The theoretical background used in research on adult community hearing rehabilitation in Denmark involves exploring value propositions in the context of the Danish public health system. This research applies 2-step inductive and deductive theme-based analysis to identify 21 value propositions relevant to the hearing rehabilitation process. | The methodology used in this research involves two main steps: 1. Harvesting Value Proposition. 2. 2-step inductive and deductive theme-based analysis was used to identify 21 value propositions deemed relevant for further assessment. |
| 10. | Resource-based competitiveness: managerial implications of the resource-based view. | Jim (2010) | The purpose of this research is to discuss the shift in strategic management research from focusing on company products to focusing on internal factors such as resources and capabilities. | The main finding of research discussing the shift in strategic management research is that there has been a transition from focusing on a company's products to concentrating on internal factors such as resources and capabilities. | This research discusses the shift in strategic management research from a focus on company products to internal factors such as resources and capabilities. This shift is based on the theoretical framework of the resource-based view, which emphasizes the importance of a company's internal resources and capabilities in achieving sustainable competitive advantage. |
The methodology used in the research addressing this shift in strategic management research is not mentioned explicitly in the context provided. This research primarily focuses on the practical implications of the resource-based view and discusses how companies can benefit from adopting a more resource-based approach in their strategic management practices. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





