Submitted:
21 June 2024
Posted:
24 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Rifampicin Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles
2.3. Experimental Design of Central Composite Design
2.4. Measurement of Particle Size, Polydispersity and ζ Potential
2.5. Determination of Drug Loading and Nanoparticle Yield
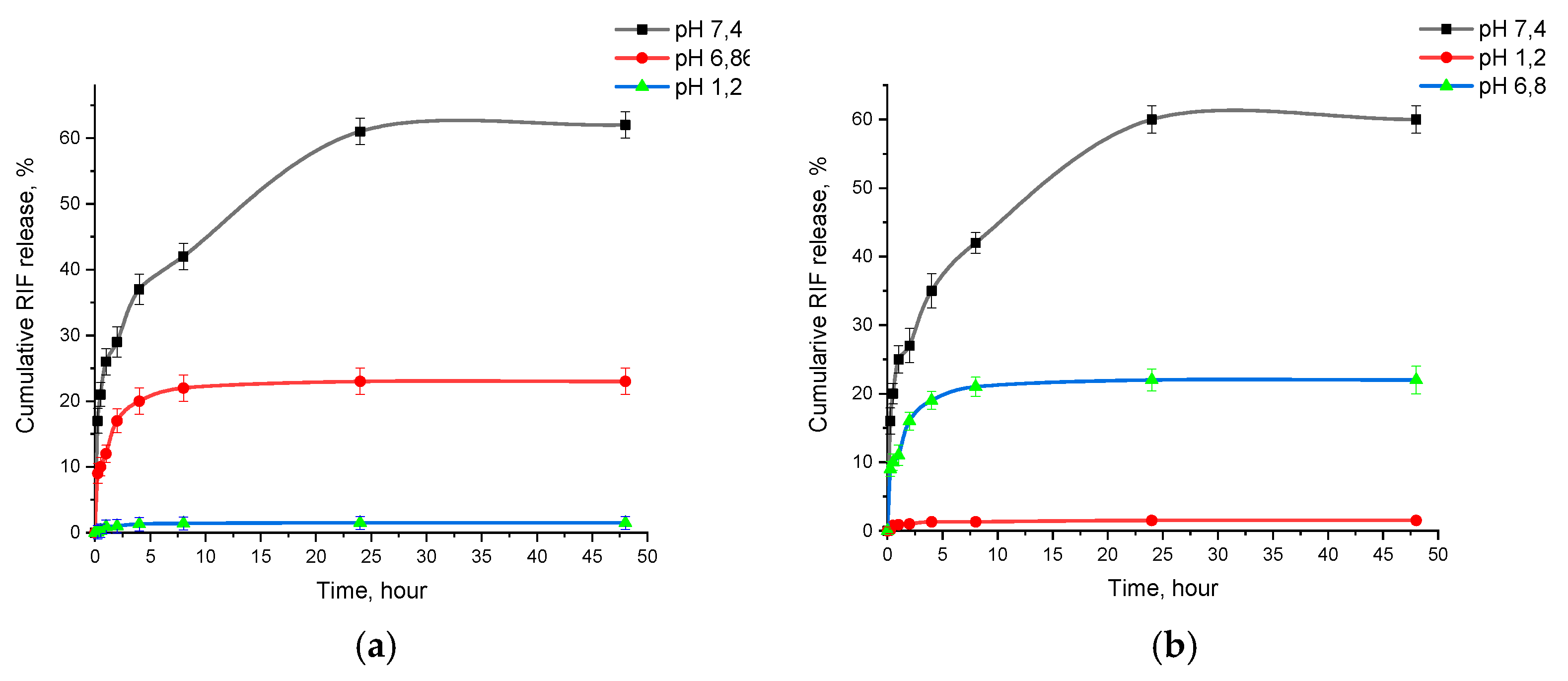
2.6. In Vitro Release of Drug from Polymer Nanoparticles
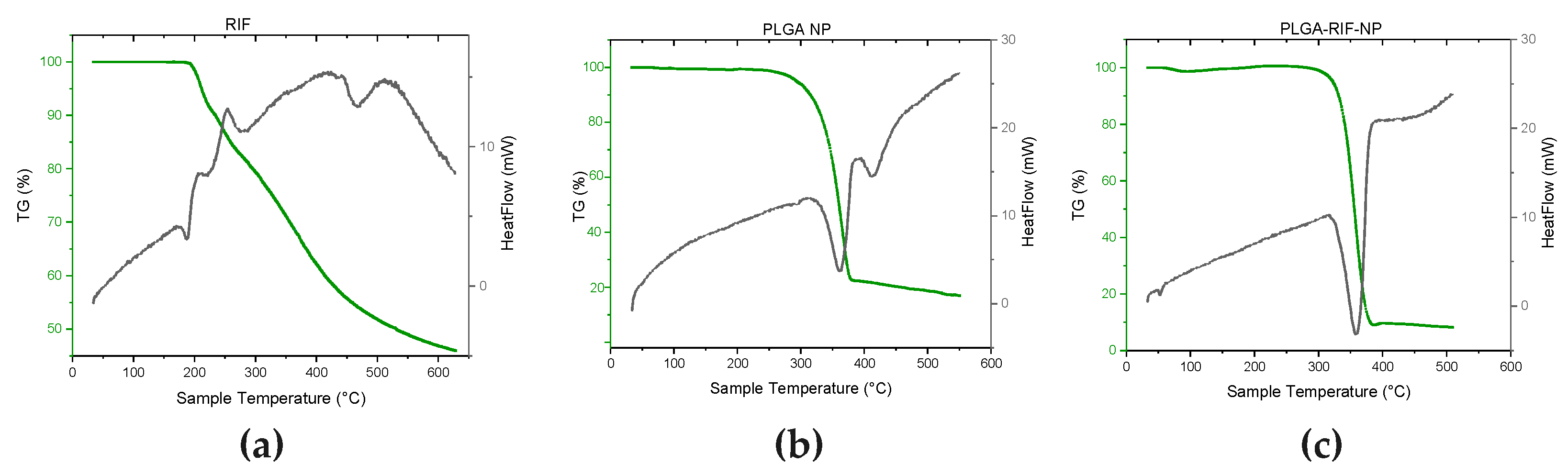
2.7. Thermogravimetric Analysis and Differential Scanning Calorimetry
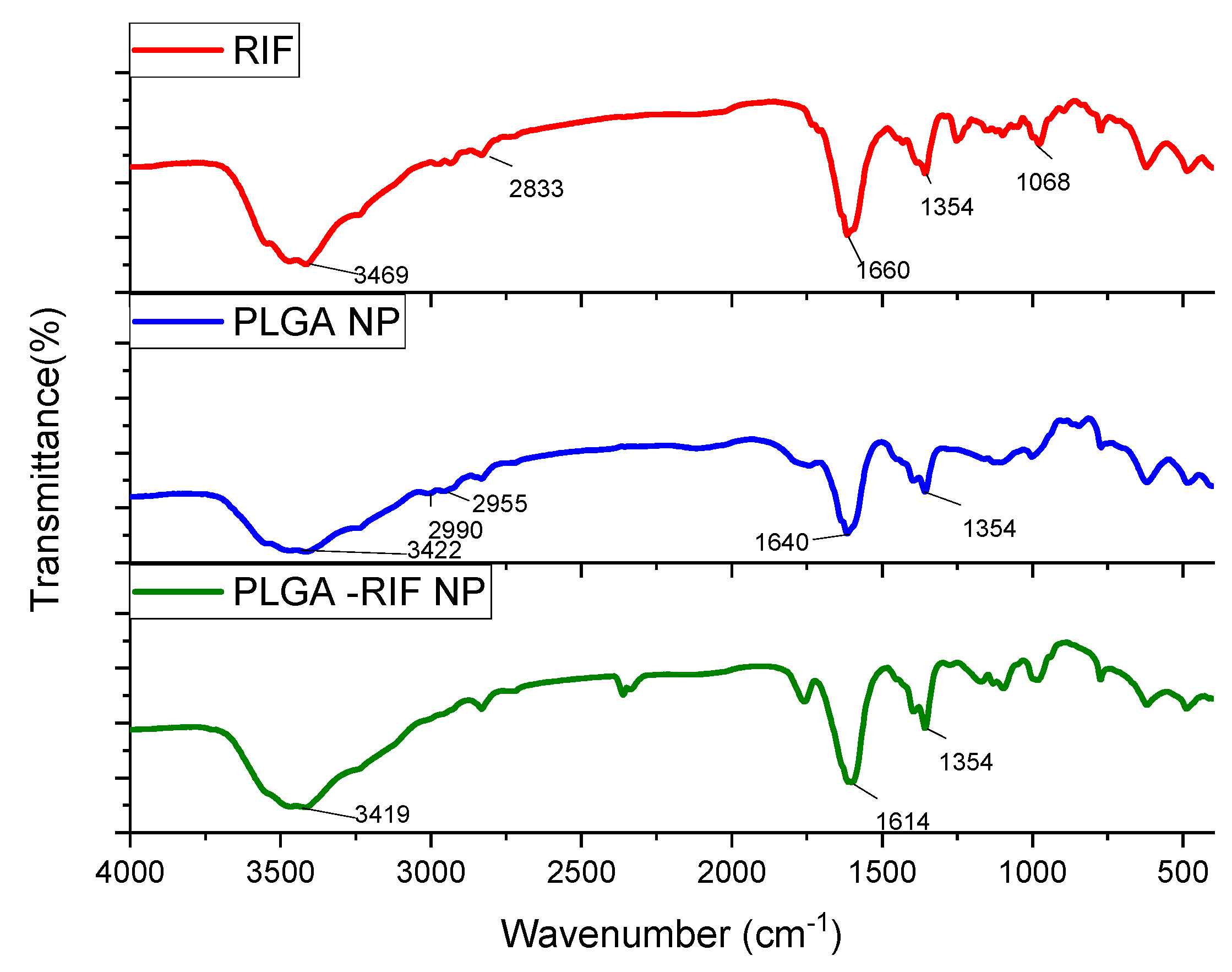
2.8. Study of Prepared Nanoparticles by Infrared Spectroscopy
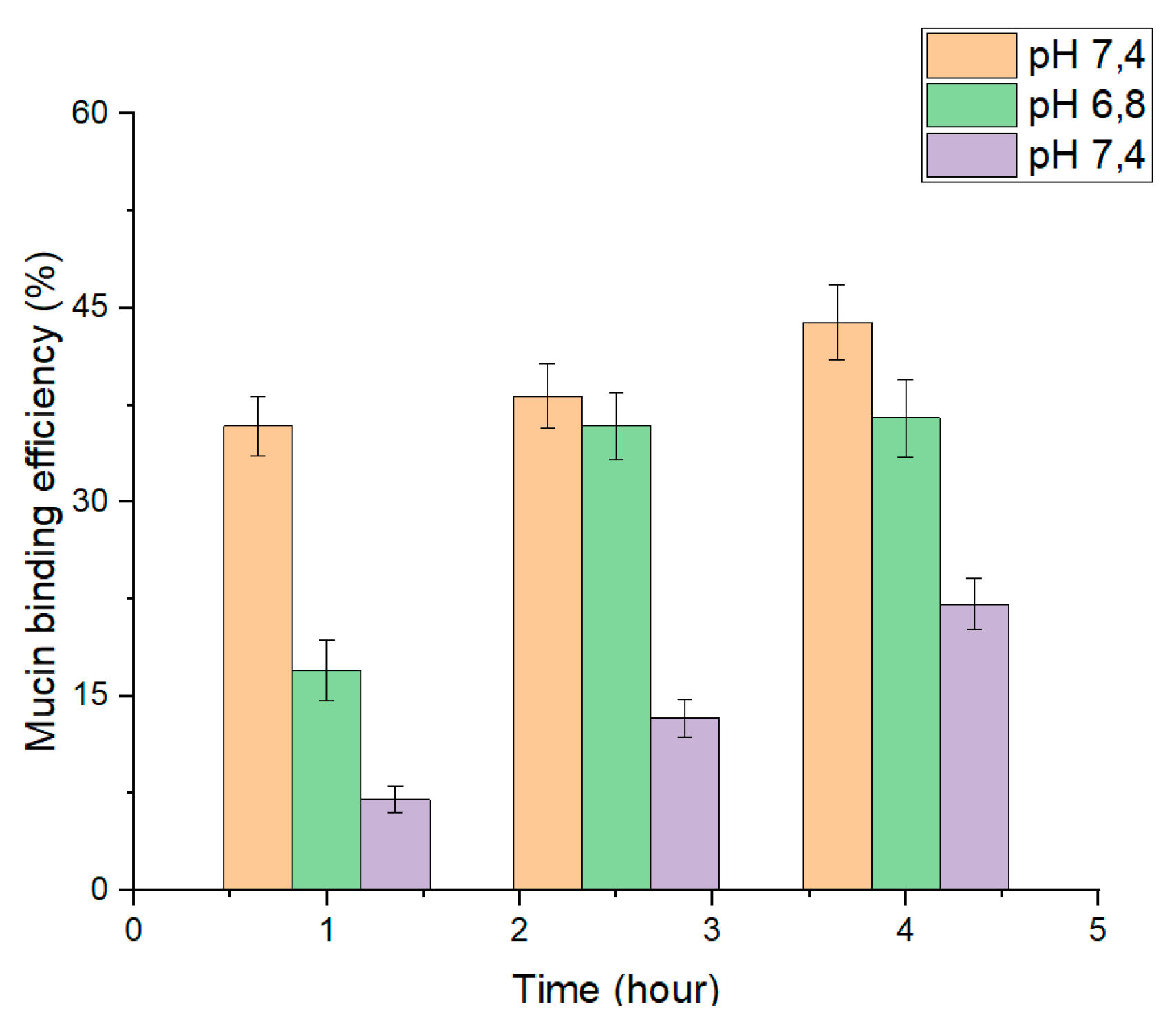
2.9. In Vitro Study of Nanoparticle Mucoadhesion
2.10. Statistical Processing of the Produced Data
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of the PLGA-RIF NPs by the CCD Method
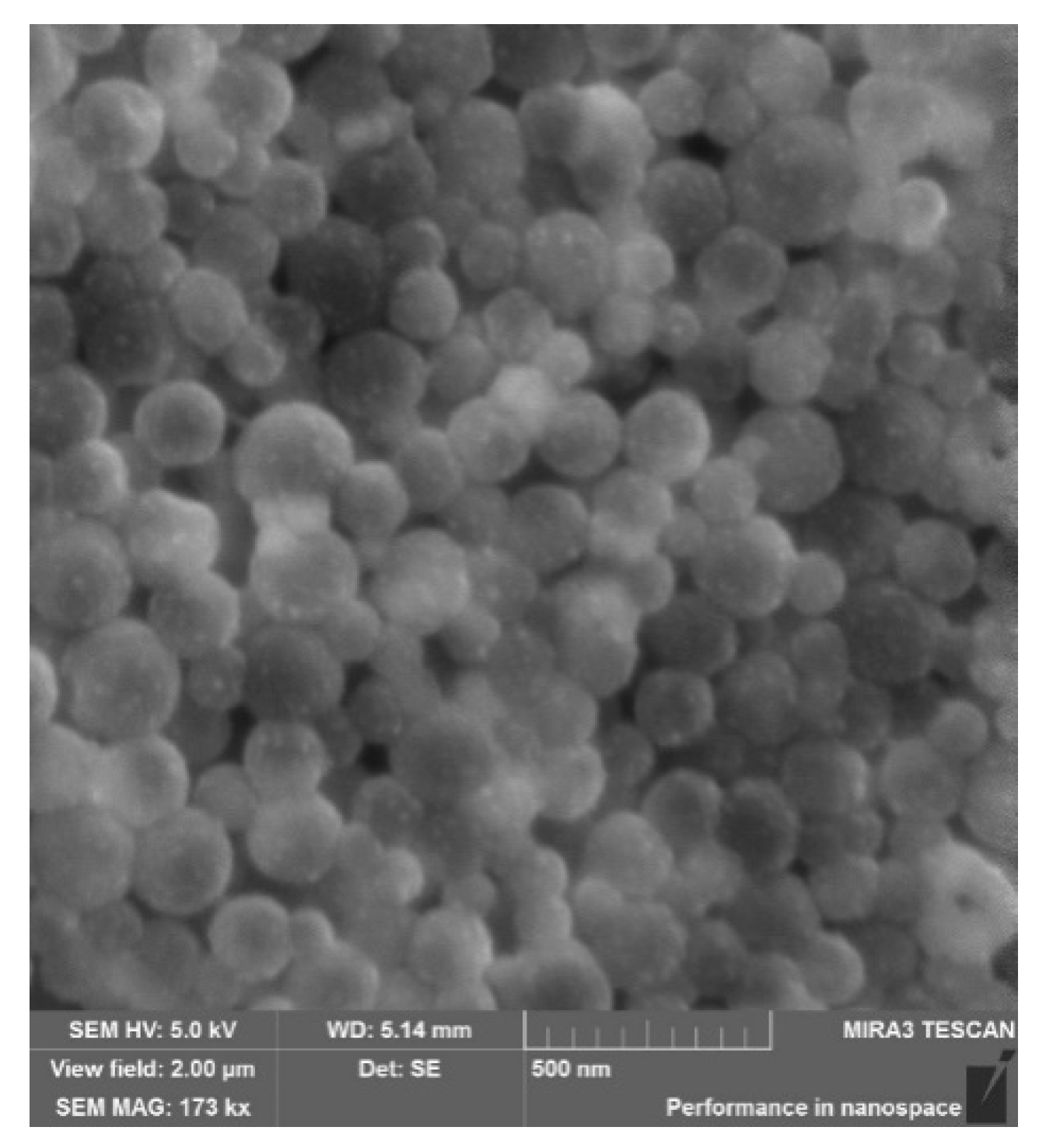
3.2. Physicochemical Characterisation of PLGA-RIF Nanoparticles
3.3. In Vitro Release Profile of PLGA-RIF NPs
3.4. In Vitro Mucoadhesion of PLGA-RIF NPs
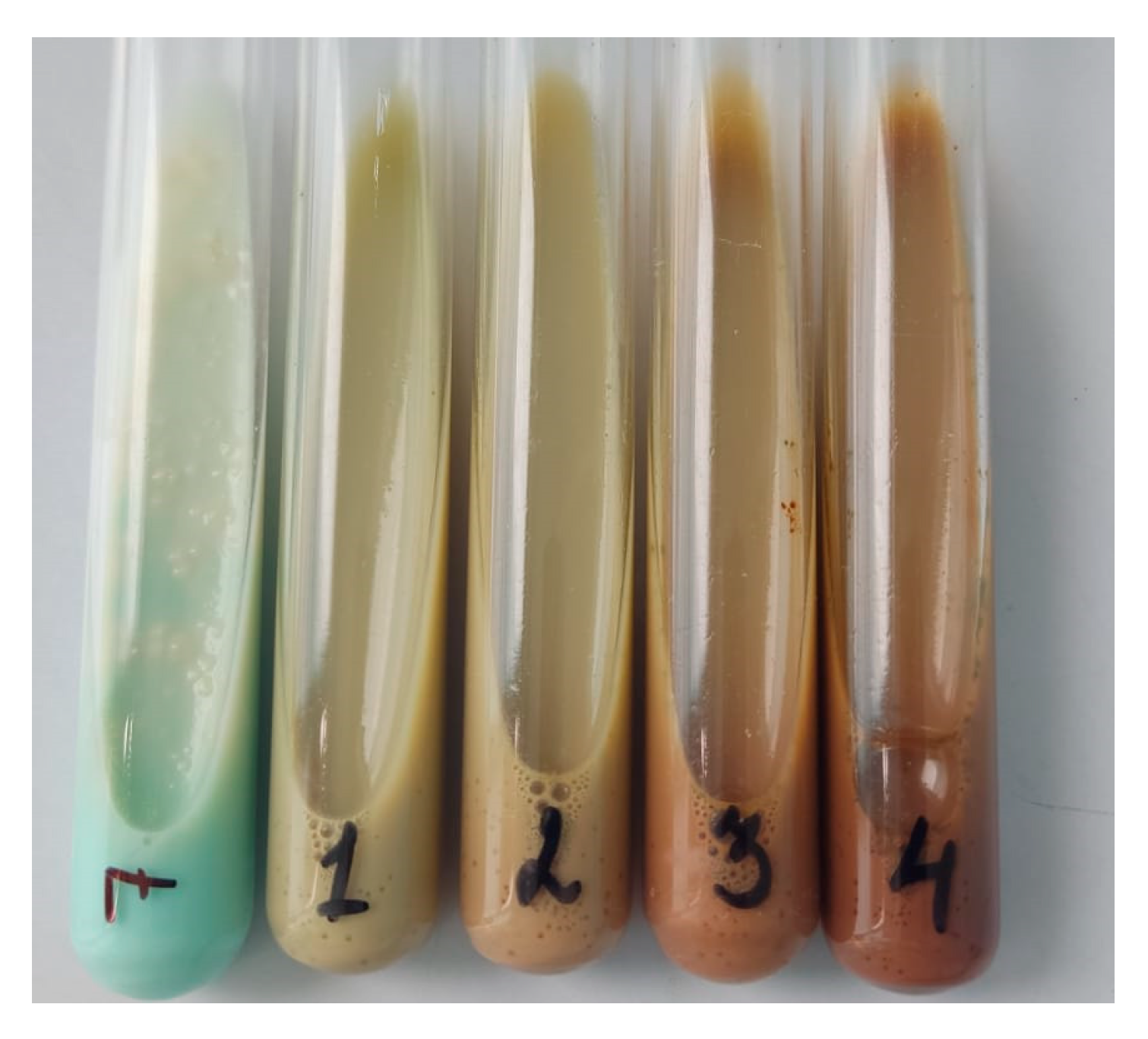
3.5. In Vitro Efficacy of PLGA-RIF NPs against Strain H37Rv
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iacobino, A.; Fattorini, L.; Giannoni, F. Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis 2020: Where We Stand. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tazhbayev, Y.; Galiyeva, A.; Zhumagaliyeva, T.; Burkeyev, M.; Karimova, B. Isoniazid—Loaded Albumin Nanoparticles: Taguchi Optimization Method. Polymers 2021, 13, 3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report 2022; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report 2023; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Glackin, C.A.; Horwitz, M.A.; Zink, J.I. Nanomachines and other caps on mesoporous silica nanoparticles for drug delivery. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 1531–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motiei, M.; Pleno de Gouveia, L.; Šopík, T.; Vícha, R.; Škoda, D.; Císař, J.; Khalili, R.; Domincová Bergerová, E.; Münster, L.; Fei, H.; et al. Nanoparticle-Based Rifampicin Delivery System Development. Molecules 2021, 26, 2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakkimane, S.S.; Shenoy, V.P.; Gaonkar, S.L.; Bairy, I.; Guru, B.R. Antimycobacterial susceptibility evaluation of rifampicin and isoniazid benz-hydrazone in biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles against Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv strain. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 4303–4318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rather, M.A.; Amin, S.; Maqbool, M.; Bhat, Z.S.; Gupta, P.N.; Ahmad, Z. Preparation and in vitro characterization of albumin nanoparticles encapsulating an anti-tuberculosis drug-levofloxacin. Adv. Sci. Eng. Med. 2016, 8, 912–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keum, C.G.; Noh, Y.W.; Baek, J.S.; Lim, J.H.; Hwang, C.J.; Na, Y.G.; Shin, S.C.; Cho, C.W. Practical preparation procedures for docetaxel-loaded nanoparticles using polylactic acid-co-glycolic acid. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 2225–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, T.S.; Bayindir, Z.S.; Badilli, U. Preparation of polymeric nanoparticles using different stabilizing agents. J. Fac. Pharm. Ank. Univ. 2009, 38, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galiyeva, A.R.; Tazhbayev, Y.M.; Zhumagaliyeva, T.S.; Sadyrbekov, D.T.; Kaikenov, D.A.; Karimova, B.N.; Shokenova, S.S. Polylactide-co-glycolide nanoparticles immobilized with isoniazid: Optimization using the experimental Taguchi method. Bull. Karaganda University. “Chem. ” Ser. 2022, 105, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, J.C.; Pulliam, B.L.; Edwards, D.A. Nanoparticles for drug delivery to the lungs. Trends Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.; Pinheiro, M.; Magalhães, J.; Ribeiro, R.; Seabra, V.; Reis, S.; Sarmento, B. The formulation of nanomedicines for treating tuberculosis. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 102, 102–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shegokar, R.; Al Shaal, L.; Mitri, K. Present status of nanoparticle research for treatment of Tuberculosis. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 14, 100–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Politis, S.N.; Colombo, P.; Colombo, G.; Rekkas, D.M. Design of experiments (DoE) in pharmaceutical development. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2017, 43, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordeeva, D.S.; Sitenkova, A.V.; Moustafine, R.I. New Carriers for Bioadhesive Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems Based on EudragitR EPO/EudragitR L100 Interpolyelectrolyte Complexes. Sci. Pharm. 2024, 92, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timergalieva, V.R.; Gennari, C.G.M.; Cilurzo, F.; Selmin, F.; Moustafine, R.I. Comparative Evaluation of Metformin and Metronidazole Release from Oral Lyophilisates with Different Methods. Sci. Pharm. 2023, 91, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samprasit, W.; Opanasopit, P.; Chamsai, B. Alpha-mangostin and resveratrol, dual-drugs-loaded mucoadhesive thiolated chitosan-based nanoparticles for synergistic activity against colon cancer cells. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2021, 110, 1221–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galiyeva, A.; Daribay, A.; Zhumagaliyeva, T.; Zhaparova, L.; Sadyrbekov, D.; Tazhbayev, Y. Human Serum Albumin Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Optimization and Immobilization with Antituberculosis Drugs. Polymers 2023, 15, 2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tazhbayev, Y.M.; Galiyeva, A.R.; Zhumagaliyeva, T.S.; Burkeyev, M.Z.; Kazhmuratova, A.T.; Zhakupbekova, E.Z.; Zhaparova, L.Z.; Bakibayev, A.A. Synthesis and characterization of isoniazid immobilized polylactide-co-glycolide nanoparticles. Bull. Karaganda University. “Chem. ” Ser. 2021, 101, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, H.P.; Cesar, C.L.; Barjas-Castro, M. de L.Electrical properties of the red blood cell membrane and immunohematological investigation. Rev. Bras. De Hematol. E Hemoter. 2011, 33, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, N.; Ahmad, R.; Al Qatifi, S.; Alessa, M.; Al Hajji, H.; Sarafroz, M. A bioanalytical UHPLC based method used for the quantification of Thymoquinone-loaded-PLGA-nanoparticles in the treatment of epilepsy. BMC Chem. 2020, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.; Ashokraj, Y.; Bharatam, P.V.; Pillai, O.; Panchagnula, R. Solid-state characterization of rifampicin samples and its biopharmaceutic relevance. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2004, 22, 127–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, R.; Reis, T.V.d.S.; da Silva, L.C.C.; Storpírtis, S.; Mercuri, L.P.; Matos, J.d.R. Thermal behavior and decomposition kinetics of rifampicin polymorphs under isothermal and non-isothermal conditions. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 46, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Feng, S.; Liu, X.; Xing, L.; Chen, D.; Xiong, C. Morphology, thermal properties, mechanical property and degradation of PLGA/PTMC composites. J. Polym. Res. 2020, 27, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.T.C.R.; Cardoso, B.C.O.; e Silva, M.E.S.R.; Freitas, R.F.S.; Sousa, R.G. Synthesis, Characterization, and Study of PLGA Copolymer In Vitro Degradation. J. Biomater. Nanobiotechnology 2015, 6, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yessentayeva, N.A.; Galiyeva, A.R.; Daribay, A.T.; Sadyrbekov, D.T.; Zhumagalieva, T.S.; Marsel, D.T. Synthesis and Optimization of Bovine Serum Albumin Nanoparticles Immobilized with Antituberculosis Drugs. EURASIAN JOURNAL OF CHEMISTRY 2024, 29, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Puri, V.; Kumar, P.; Singh, I.; Huanbutta, K. Development and Evaluation of Rifampicin Loaded Alginate–Gelatin Biocomposite Microfibers. Polymers 2021, 13, 1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivashchenko, O.; Tomila, T.; Ulyanchich, N.; Yarmola, T.; Uvarova, I. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy of Antibiotic Loaded Ag-Free and Ag-Doped Hydroxyapatites. Adv. Sci. Eng. Med. 2014, 6, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portaccio, M.; Menale, C.; Diano, N.; Serri, C.; Mita, D.G.; Lepore, M. Monitoring production process of cisplatin-loaded PLGA nanoparticles by FT-IR microspectroscopy and univariate data analysis. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwer, M.K.; Al-Mansoor, M.A.; Jamil, S.; Al-Shdefat, R.; Ansari, M.N.; Shakeel, F. Development and evaluation of PLGA polymer based nanoparticles of quercetin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 92, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, M.G.; Dutta, S.; Al Hinai, A.T.; Feroz, S. Studies on encapsulation of Rifampicin and its release from chitosan-dextran sulfate capsules. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2014, 32, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N. Rasagiline-encapsulated chitosan-coated PLGA nanoparticles targeted to the brain in the treatment of parkinson’s disease. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Amp; Relat. Technol. 2017, 40, 677–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.; Alam, M.A.; Ahmad, R.; Naqvi, A.A.; Ahmad, F.J. Preparation and characterization of surface-modified PLGA-polymeric nanoparticles used to target treatment of intestinal cancer. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2017, 46, 432–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, N.; Alam, M.A.; Ahmad, R.; Umar, S.; Jalees Ahmad, F. Improvement of oral efficacy of Irinotecan through biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles through in vitro and in vivo investigations. J. Microencapsul. 2018, 35, 327–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galiyeva, A.R.; Tazhbayev, Y.M.; Yessentayeva, N.A.; Daribay, A.T.; Marsel, D.T.; Sadyrbekov, D.T.; Zhaparova, L.Z.; Arystanova, Z.T. PEGylation of Albumin Nanoparticles Immobilized with the Anti-Tuberculosis Drug “Isoniazid”. Eursian J. Chem. 2023, 110, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, R.; Shaikh, R.; Raj Singh, T.; Garland, M.; Woolfson, A. Mucoadhesive drug delivery systems. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2011, 3, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boddupalli, B.; Mohammed Zulkar, N.K.; Nath, R.; Banji, D. Mucoadhesive drug delivery system: An overview. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2010, 1, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brannigan, R.P.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Progress and Current Trends in the Synthesis of Novel Polymers with Enhanced Mucoadhesive Properties. Macromol. Biosci. 2019, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaldybekov, D.B.; Tonglairoum, P.; Opanasopit, P.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Mucoadhesive maleimide-functionalised liposomes for drug delivery to urinary bladder. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 111, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Advances in Mucoadhesion and Mucoadhesive Polymers. Macromol. Biosci. 2010, 11, 748–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
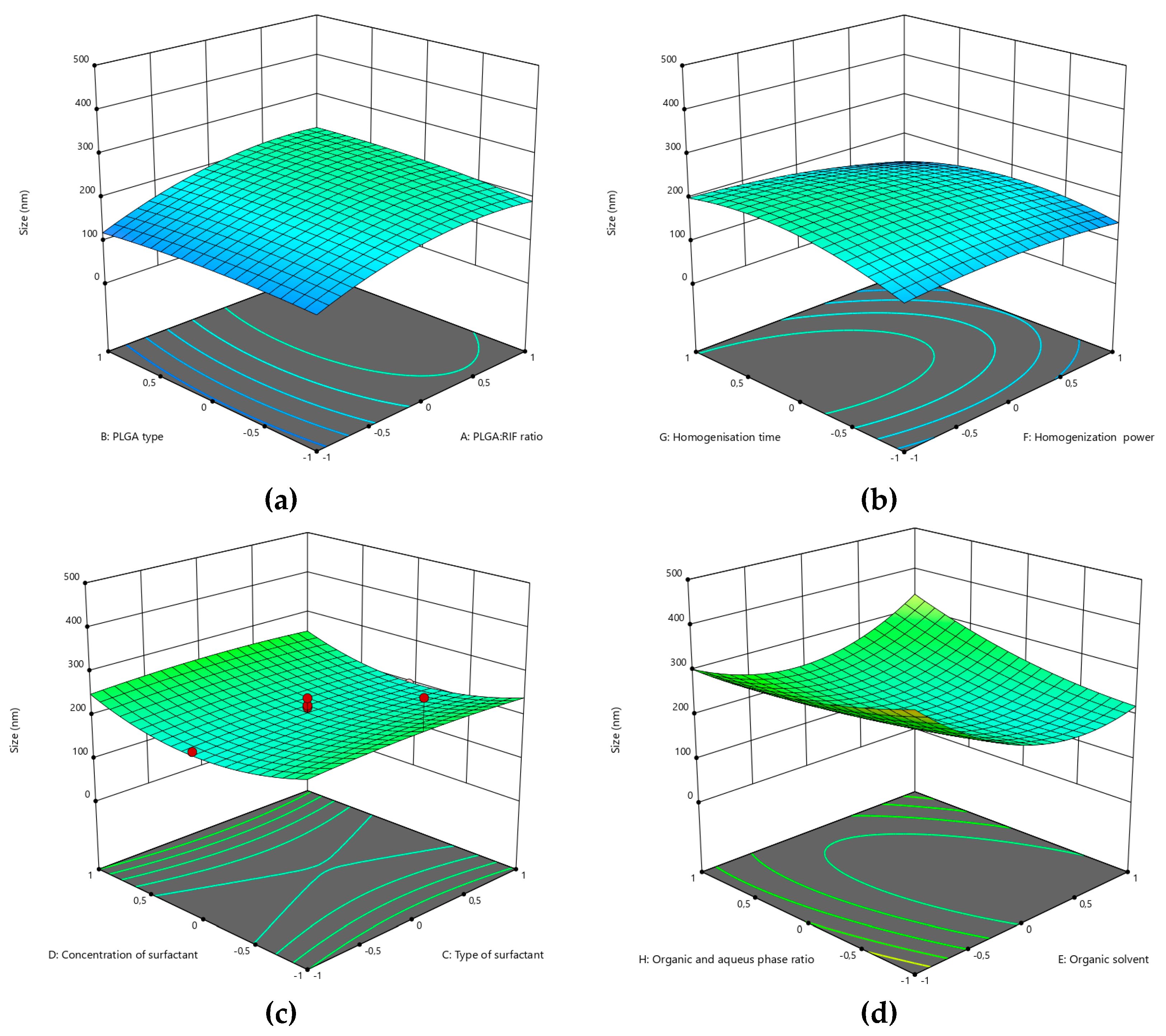
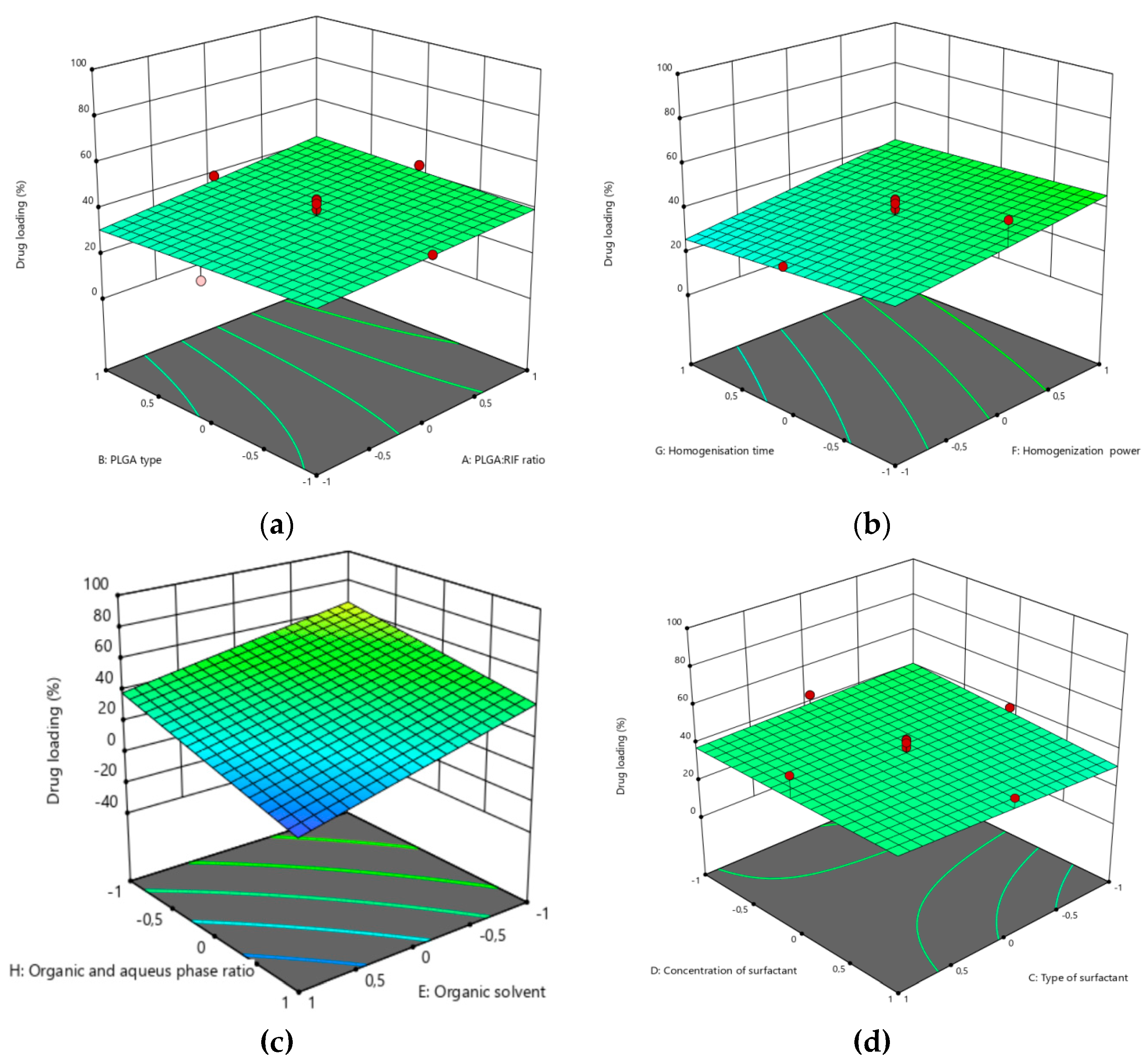
| Independent variable | Variable level | ||
| Low -1 |
Center 0 |
High 1 |
|
| PLGA:RIF | 1:1 | 2:1 | 3:1 |
| Type of PLGA | Mw 7 000-17 000 | Mw 24 000-38 000 | Mw 30 000-60 000 |
| Surfactant type | PVA | Tween 80 | Pluronic F127 |
| Concentration of surfactant | 0,5% | 1% | 2% |
| Organic solvent | DCM | DMSO | EA |
| Organic phase: aqueous phase | 1:1 | 1:5 | 1:10 |
| Homogenization power | 15 W | 35 W | 70 W |
| Homogenization time | 5 min | 10 min | 15 min |
| NPs | PLGA:RIF | PLGA type | Surfactant type | Surfactant concentration, % | Organic solvent | Organic phase: aqueous phase | Homogenization power, W | Homogenization time, min | Average size of NP, nm | PDI | Z potential, mV | Drug loading, % | NPs yield, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| NP1 | 3:1 | PLGA30 | PVA | 0,5 | EA | 1:1 | 15 | 5 | 189±2 | 0.046±0.003 | -30.9±3.4 | 58 | 75 |
| NP2 | 3:1 | PLGA30 | PVA | 2 | DCM | 1:1 | 15 | 5 | 422±2 | 0.280±0.013 | -13.1±1.8 | 64 | 59 |
| NP3 | 3:1 | PLGA7 | Pluronic | 2 | EA | 1:10 | 15 | 5 | 316±2 | 0.349±0.051 | -28.2±3.3 | 24 | 22 |
| NP4 | 2:1 | PLGA24 | Tween 80 | 1 | DMSO | 1:5 | 35 | 10 | 220±2 | 0.177±0.023 | -20.1±0.6 | 45 | 33 |
| NP5 | 3:1 | PLGA7 | Pluronic | 2 | EA | 1:1 | 70 | 5 | 94±1 | 0.285±0.067 | -22.8±2.3 | 88 | 26 |
| NP6 | 1:1 | PLGA7 | PVA | 0,5 | EA | 1:1 | 70 | 15 | 219±2 | 0.489±0.035 | -0.61±2.1 | 78 | 41 |
| NP7 | 2:1 | PLGA24 | Tween 80 | 1 | DMSO | 1:5 | 35 | 15 | 175±2 | 0.191±0.046 | -15.6±3.7 | 29 | 67 |
| NP8 | 3:1 | PLGA30 | PVA | 2 | EA | 1:10 | 15 | 15 | 452±3 | 0.499±0.086 | -15.8±2.9 | 31 | 66 |
| NP9 | 2:1 | PLGA24 | Tween 80 | 1 | DMSO | 1:5 | 35 | 10 | 170±2 | 0.358±0.008 | -23.2±4.2 | 40 | 34 |
| NP10 | 2:1 | PLGA24 | Tween 80 | 1 | DMSO | 1:5 | 35 | 10 | 172±2 | 0.178±0.008 | -21.6±2.8 | 37 | 37 |
| NP11 | 3:1 | PLGA7 | PVA | 0,5 | DCM | 1:1 | 15 | 5 | 443±3 | 0.261±0.034 | -14.5±3.4 | 52 | 69 |
| NP12 | 1:1 | PLGA30 | Pluronic | 0,5 | DCM | 1:10 | 70 | 5 | 260±2 | 0.262±0.045 | -24.3±2.2 | 30 | 33 |
| NP13 | 2:1 | PLGA24 | Tween 80 | 1 | DMSO | 1:5 | 35 | 10 | 184±2 | 0.186±0.08 | -23.2±2.1 | 33 | 31 |
| NP14 | 3:1 | PLGA7 | Pluronic | 2 | DCM | 1:10 | 70 | 5 | 219±2 | 0.248±0.065 | -20.3±3.1 | 23 | 36 |
| NP15 | 1:1 | PLGA7 | PVA | 2 | EA | 1:1 | 15 | 5 | 119±2 | 0.217±0.013 | -11.2±2.7 | 44 | 41 |
| NP16 | 1:1 | PLGA7 | Pluronic | 2 | EA | 1:1 | 15 | 15 | 166±3 | 0.556±0.039 | -20.1±1.4 | 16 | 3 |
| NP17 | 3:1 | PLGA7 | PVA | 0,5 | EA | 1:10 | 70 | 5 | 356±3 | 0.474±0.023 | -12.8±1.3 | 48 | 68 |
| NP18 | 2:1 | PLGA24 | Tween 80 | 1 | DMSO | 1:1 | 35 | 10 | 291±2 | 0.373±0.034 | -15.4±0.3 | 37 | 55 |
| NP19 | 2:1 | PLGA24 | PVA | 1 | DMSO | 1:5 | 35 | 10 | 206±3 | 0.135±0.023 | -13.2±1.3 | 39 | 33 |
| NP20 | 1:1 | PLGA30 | Pluronic | 2 | DCM | 1:10 | 15 | 15 | 271±1 | 0.508±0.056 | -9.5±1.5 | 27 | 31 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| NP21 | 1:1 | PLGA30 | PVA | 0,5 | DCM | 1:1 | 70 | 5 | 282±2 | 0.145±0.034 | -16.4±2.3 | 65 | 61 |
| NP22 | 2:1 | PLGA24 | Tween 80 | 2 | DMSO | 1:5 | 35 | 10 | 193±4 | 0.224±0.006 | -18.5±3.3 | 40 | 28 |
| NP23 | 2:1 | PLGA24 | Tween 80 | 1 | DMSO | 1:5 | 70 | 10 | 167±3 | 0.276±0.013 | -15,6±1.3 | 41 | 17 |
| NP24 | 1:1 | PLGA7 | Pluronic | 0,5 | EA | 1:1 | 15 | 5 | 94±2 | 0.206±0.043 | -13.9±1.6 | 48 | 32 |
| NP25 | 1:1 | PLGA30 | Pluronic | 0,5 | EA | 1:1 | 70 | 15 | 95±3 | 0.238±0.023 | -20.7±3.1 | 55 | 30 |
| NP26 | 3:1 | PLGA7 | Pluronic | 0,5 | DCM | 1:1 | 70 | 15 | 271±4 | 0.116±0.032 | -17.5±0,7 | 53 | 65 |
| NP27 | 3:1 | PLGA7 | Pluronic | 2 | EA | 1:10 | 70 | 15 | 377±4 | 0.393±0.051 | -23.9±1.9 | 31 | 35 |
| NP28 | 2:1 | PLGA24 | Tween 80 | 1 | EA | 1:5 | 35 | 10 | 225±2 | 0.269±0.042 | -17.8±1.7 | 41 | 49 |
| NP29 | 2:1 | PLGA7 | Tween 80 | 1 | DMSO | 1:5 | 35 | 10 | 182±3 | 0.157±0.023 | -15.7±2.3 | 38 | 30 |
| NP30 | 1:1 | PLGA7 | PVA | 2 | DCM | 1:10 | 15 | 15 | 165±4 | 0.263±0.015 | -12.5±0.4 | 4 | 6 |
| NP31 | 1:1 | PLGA7 | Pluronic | 2 | EA | 1:10 | 70 | 5 | 345±3 | 0.393±0.045 | -12.1±1.1 | 13 | 28 |
| NP32 | 3:1 | PLGA24 | Tween 80 | 1 | DMSO | 1:5 | 35 | 10 | 202±2 | 0.179±0.035 | -22.6±3.9 | 44 | 37 |
| NP33 | 1:1 | PLGA7 | Pluronic | 0,5 | DCM | 1:10 | 15 | 15 | 232±2 | 0.198±0.024 | -23.5±1.2 | 14 | 26 |
| NP34 | 3:1 | PLGA30 | PVA | 0,5 | EA | 1:1 | 70 | 15 | 173±3 | 0.118±0.021 | -9.2±1.1 | 36 | 57 |
| NP35 | 1:1 | PLGA30 | Pluronic | 2 | EA | 1:1 | 15 | 5 | 93±2 | 0.275±0.053 | -7.9±1.4 | 24 | 17 |
| NP36 | 1:1 | PLGA24 | Tween 80 | 1 | DMSO | 1:5 | 35 | 10 | 152±3 | 0.235±0.014 | -16.7±1.2 | 27 | 9 |
| NP37 | 3:1 | PLGA7 | PVA | 0,5 | EA | 1:10 | 15 | 15 | 239±2 | 0.164±0.032 | -9.1±0.3 | 11 | 65 |
| NP38 | 2:1 | PLGA24 | Tween 80 | 1 | DMSO | 1:10 | 35 | 10 | 178±2 | 0.226±0.035 | -13.3±2.5 | 15 | 29 |
| NP39 | 1:1 | PLGA30 | PVA | 2 | DCM | 1:10 | 70 | 5 | 221±2 | 0.164±0.003 | -13.5±1.9 | 8 | 29 |
| NP40 | 1:1 | PLGA30 | PVA | 2 | EA | 1:1 | 70 | 15 | 118±3 | 0.187±0.013 | -8.1±0.9 | 35 | 25 |
| NP41 | 3:1 | PLGA7 | Pluronic | 2 | DCM | 1:10 | 15 | 15 | 418±5 | 0.468±0.022 | -11.4±4.1 | 32 | 38 |
| NP42 | 3:1 | PLGA30 | Pluronic | 0,5 | DCM | 1:1 | 15 | 5 | 337±4 | 0.144±0.006 | -21.3±1.1 | 37 | 55 |
| NP43 | 2:1 | PLGA24 | Tween 80 | 1 | DMSO | 1:5 | 35 | 10 | 242±2 | 0.238±0.011 | -20.1±0.9 | 43 | 44 |
| NP44 | 3:1 | PLGA30 | Pluronic | 2 | EA | 1:10 | 70 | 5 | 315±3 | 0.473±0.018 | -16.4±0.4 | 35 | 36 |
| NP45 | 2:1 | PLGA24 | Tween 80 | 1 | DMSO | 1:5 | 35 | 5 | 175±2 | 0.184±0.023 | -20.2±0.6 | 52 | 23 |
| NP46 | 3:1 | PLGA30 | PVA | 0,5 | DCM | 1:10 | 70 | 15 | 216±3 | 0.155±0.046 | -9.7±1.1 | 36 | 52 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| NP47 | 3:1 | PLGA30 | Pluronic | 2 | DCM | 1:1 | 70 | 15 | 327±2 | 0.271±0.007 | -3.4±1.4 | 66 | 35 |
| NP48 | 1:1 | PLGA7 | PVA | 0,5 | DCM | 1:10 | 70 | 5 | 162±2 | 0.288±0.016 | -16.7±5.6 | 30 | 8 |
| NP49 | 2:1 | PLGA24 | Tween 80 | 1 | DMSO | 1:5 | 15 | 10 | 225±3 | 0.205±0.018 | -15.7±1.6 | 32 | 27 |
| NP50 | 2:1 | PLGA24 | Tween 80 | 1 | DCM | 1:5 | 35 | 10 | 354±4 | 0.416±0.023 | -19.9±1.5 | 34 | 43 |
| NP51 | 2:1 | PLGA30 | Tween 80 | 1 | DMSO | 1:5 | 35 | 10 | 220±2 | 0.175±0.018 | -24.5±1.1 | 39 | 37 |
| NP52 | 1:1 | PLGA30 | PVA | 0,5 | DCM | 1:10 | 15 | 5 | 209±3 | 0.212±0.024 | -16.9±0.6 | 25 | 49 |
| NP53 | 2:1 | PLGA24 | Tween 80 | 0,5 | DMSO | 1:5 | 35 | 10 | 323±4 | 0.248±0.017 | -16.1±4.7 | 45 | 45 |
| NP54 | 3:1 | PLGA7 | PVA | 2 | DCM | 1:1 | 70 | 15 | 302±5 | 0.166±0.05 | -15.0±2.1 | 34 | 59 |
| NP55 | 1:1 | PLGA30 | PVA | 0,5 | EA | 1:10 | 70 | 15 | 163±3 | 0.234±0.08 | -17.1±1.1 | 16 | 22 |
| NP56 | 1:1 | PLGA7 | Pluronic | 2 | DCM | 1:1 | 15 | 5 | 257±2 | 0.176±0.02 | -17.8±2.1 | 50 | 20,6 |
| NP57 | 2:1 | PLGA24 | Pluronic | 1 | DMSO | 1:5 | 35 | 10 | 197±4 | 0.212±0.03 | -15.6±4.6 | 49 | 55 |
| NP58 | 3:1 | PLGA30 | Pluronic | 0,5 | EA | 1:10 | 15 | 15 | 373±3 | 0.479±0.05 | -24.5±2.3 | 6 | 20 |
| NP59 | 2:1 | PLGA24 | Tween 80 | 1 | DMSO | 1:5 | 35 | 10 | 225±3 | 0.207±0.03 | -22.4±2.9 | 44 | 30 |
| NP60 | 1:1 | PLGA30 | PVA | 0,5 | DCM | 1:1 | 15 | 15 | 311±3 | 0.15±0.05 | -18.2±1.6 | 63 | 67 |
| Response | Source | Sum of Squares | Degree of Freedom | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Size | Model | 4.293E+05 | 44 | 9757.75 | 3.33 | 0.0071 | significant |
| Pure error | 4664.39 | 5 | 932.88 | ||||
| Residual | 43955.54 | 15 | 2930.37 | ||||
| Lack of fit | 39291.15 | 10 | 3929.11 | 4.21 | 0.0630 | ||
| Cor total | 4.733E+05 | 59 | |||||
| Drug loading | Model | 15793.89 | 36 | 438.72 | 8.98 | < 0.0001 | significant |
| PureError | 100.33 | 5 | 20.07 | ||||
| Residual | 1124.08 | 23 | 48.87 | ||||
| LackofFit | 1023.75 | 18 | 56.88 | 2.83 | 0.1263 | ||
| CorTotal | 16917.98 | 59 |
| Name | Goal | Lower Limit | Upper Limit |
|---|---|---|---|
| PLGA:RIF ratio | Is in range | 1:1 | 1:3 |
| PLGA type | Is in range | 7 000-17 000 | 30 000-60 000 |
| Type of surfactant | Is in range | PVA | Tween80 |
| Organic solvent | Is equal to DCM | DCM | EA |
| Homogenization power | Is equal to 70 W | 15W | 70W |
| Homogenization time | Is in range | 5 min | 15 min |
| Organic and aqueous phase ratio | Is equal to 1:1 | 1:1 | 1:10 |
| Size | minimize | 93,4 | 451,8 |
| Drug loading | maximize | 4 | 88,2 |
| Size, nm | PDI | Zeta potencial, mV | Encapsulation efficiency, % | Drug loading, % | Yield, % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Predicted | 228 | 0,120 | -24 | 93 | 70 | 45 |
| Experimental | 223±2 | 0,110±0,01 | -26±2 | 91±2 | 67±1 | 47±2 |
| Error, % | 2,2 | 8,3 | 8,3 | 2,2 | 4,3 | 4,4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





