1. Introduction
Accumulating evidence indicates that an excess of nutrients intake is harmful to the heart as a result of its role in cardiac remodeling [
1,
2]. In fact, the cardiovascular diseases (CVD) represent a significant and globally health burden but especially among individuals with obesity and its associated metabolic disturbances including metabolic syndrome and diabetes. Obesity and insulin resistance are recognized inducers of cardiac hypertrophy. While cardiac hypertrophy, which involves the enlargement of heart muscle cells, is the more commonly discussed form of remodeling, cardiac atrophy is also an important aspect.
Interestingly, multiple studies have shown that an atrophic pattern caused by reduced fuel supply to the heart leads to a lower cardiovascular risk profile. This is characterized by a decreased cardiac workload due to enhanced metabolic efficiency and alterations in signaling pathways associated with cardiac remodeling, potentially improving cardiac function and efficiency [
1,
3,
4]. Although the mechanisms behind cardiac atrophy resulting from metabolic unloading are still not well understood, some researchers have suggested that signals from the intermediary metabolism of energy-providing substrates might play significant roles [
1].
Leptin, a hormone predominantly secreted by adipose tissue, is well-known for its role in regulating energy balance by inhibiting hunger, thereby reducing food intake, and promoting energy expenditure. Its levels correlate positively with body mass index (BMI), reflecting the body's fat stores. Beyond its metabolic functions, leptin has been shown to exert complex effects on the cardiovascular system. Notably, leptin influences cardiac structure and function, supported by studies demonstrating its involvement in both hypertrophic and protective mechanisms within the heart [
5,
6].
For instance, studies in obese and leptin deficient mouse models (
ob/
ob and
db/
db) [
7,
8] suggest leptin might protect against LV hypertrophy during the progression of obesity. Importantly, it has been demonstrated that chronic intracerebroventricular (ICV) leptin infusion protects the heart from adverse remodeling and cardiac contractile dysfunction after myocardial infarction (MI) [
9].
Despite these insights, the overall effects of leptin on cardiac remodeling in humans remain largely unknown. Recently, a cross-sectional study by Kamimura et al. [
10] examined the relationship between plasma leptin concentrations and indices of LV structure and function in a community-based cohort of 1172 African-Americans with preserved EF. The study found sex- and BMI-specific associations between leptin levels and LV mass, suggesting that leptin's protective effects against LV hypertrophy might be more pronounced in certain subpopulations.
Similarly, PPARβ/δ plays a significant role as a nuclear receptor acting as a nutrient sensor. Activation of PPARβ/δ regulates various inflammatory processes, lipid metabolism, and energy utilization pathways, which collectively enhance cardiac efficiency and protect against metabolic stress [
9,
10]. Moreover, enhancing PPARβ/δ activity, either through natural means or pharmacological intervention, represents a potential therapeutic approach to mitigate the metabolic complications associated with obesity. Therefore, we propose that PPARβ/δ may interact with leptin signaling pathways, potentially influencing cardiac remodeling and function in response to metabolic stress and nutrient availability.
In fact, recent data from our laboratory support a potential protective role of central leptin signaling against cardiac hypertrophy and provide new insights into the mechanisms by which leptin, acting at a central level, activates PPARβ/δ, harmonizing anti-hypertrophic responses, redox state, proteasome-dependent protein degradation, and autophagy in the heart [
11]. Therefore, balancing their activities could help manage obesity and its comorbidities, which often include insulin resistance and cardiovascular diseases. However, the
in vivo mechanisms underlying the effects of both leptin and PPARβ/δ on cardiac structure and function are not fully understood.
In this study, we focused on investigating the influence of central leptin on heart rate and cardiac output in normoleptinemic rats. Specifically, we aimed to establish in vivo the role of PPARβ/δ on cardiac remodeling when the stimulus applied to induce it was the activation of central leptin signaling. To achieve this, we administered the selective PPARβ/δ antagonist GSK0660.
Our findings support the concept that leptin, acting centrally, induces an atrophic pattern in the heart and contribute to a healthier myocardial profile [
9,
11]. More importantly, our data indicate that administration of the PPARβ/δ antagonist led to a condition resembling left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) in obesity, characterized by an abnormal increase in left ventricular myocardial volume while still maintaining a preserved ejection fraction. This supports the notion that pharmacological inhibition of PPARβ/δ throughout the body abolishes the central actions of leptin in cardiac remodeling.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animals
Experiments were performed in 3-month-old male Wistar rat. All the animals were fed with a standard chow diet and water and maintained in ventilated-controlled quarters (20-25oC temperature, 50-55% humidity, daily 12h-light cycle 7 AM-7 PM). Animals were randomly housed individually, to control their food intake and thereby avoid differences in adipose tissue weight and serum levels of hormones and metabolites that depend on the amount of feed eaten by animals. Body weight and food intake was monitored daily during all the treatments. Animals were handled according to European Union’s laws (2010/63/EU) and following Spanish regulations (RD 53/2013) for laboratory animals’ use. The experimental protocols were approved by the Institutional Scientific Ethics Committee under project license es PR-31-2019. All efforts were made to reduce the number of animals used and minimize animal suffering.
2.2. Intracerebroventricular Leptin Administration
Leptin infusion was performed as previously described [
11,
12]. Rats were anesthetized in an induction chamber with 4% of isoflurane (0.8 liter/min oxygen flow) (Pharmacia-Upjohn, Barcelona, Spain), and then, were placed in a stereotaxic frame (David Kopf, Tujunga California, USA) with a thermal blanket below. Leptin or saline (PBS) was administered during 7 days in the lateral ventricle through a cannula connected to an osmotic minipump (Alzet, Palo Alto, CA), with a releasing rate of 1 µL/h and filled with 0.0082 µg/µL (0.2 µg/day) rat leptin (Sigma), or its vehicle (saline). To analyse the effect of central infusion of leptin, rats were treated with either saline (SS, n=5) or leptin (Lep, n=5) for 7 days. A third group of rats (PF, n=5) was treated with saline and
pair-fed to the amount of food consumed by the leptin-treated group. Body weight and food intake was measured daily during the experiment.
2.3. Pharmacological Administration of the PPARβ/δ Antagonist GSK0660
To analyses the contribution of PPARβ/δ we administer
in vivo GSK0660, a selective antagonist inhibitor of PPARβ/δ, to a group of rats at a dose that does not induce toxic side effects but abolished the effects on body weight mediated either by central leptin infusion or by caloric restriction in
pair-fed rats, as previously described [
11,
12]. Briefly, GSK0660 was diluted first in DMSO (less than 1%) and later in 0.9% NaCl. Then, it was infused daily intraperitoneally (i.p; 1 mg/kg per day) during 7 days to the PF+GSK0660 (n=5) and Lep+GSK0660 (n=5) group of rats. Control groups PF+DMSO (n=5) and Lep+DMSO (n=5) received in parallel an intraperitoneal injection of vehicle at 2 ml/kg (0.062% DMSO). 7 days after minipump implantation, the animals were fasted overnight. Rats were anesthetized by CO
2 inhalation and killed by decapitation. Blood was removed and centrifuged (2000
×g, 15 min), and serum was recovered and frozen in liquid nitrogen at −70°C until use. Hearts were rapidly excised and washed twice in Henseleit buffer at 37°C. After remove the major blood vessels and connective tissue, hearts were dried and weighted. Epididymal (eWAT), perirenal (PrWAT) and brown adipose tissue (BAT) were rapidly excised and weighted. The tibia from each animal was dissected and after removing the muscle the length of the tibia was measured by digital micrometer caliper, and the heart weight/tibial length ratio was calculated. Hereafter, atria were removed and both ventricles were used in all analyses after flash frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at –70°C until use. The hypothalamic regions were carefully dissected as previously described [
13]. After that, hypothalamic regions were frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at −70°C until further processing.
2.4. Biochemical Assessment
Serum hormone and metabolites levels were measured as described [
11,
12] following manufacturer’s instructions. Glucose was measured using an Accutrend Glucose Analyser, (#05050472223, Roche), leptin was quantified using a Rat Elisa Kit (#RD291001200R, Biovendor, Germany) and insulin was determined using a Rat Elisa Kit (#10-1251-01, Mercodia, Sweden).
2.5. Quantitative Transcription Analysis with Real Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
RNA from hypothalamus were obtained using All Prep DNA/RNA/Protein Mini kit (Cat. No. 80004, Qiagen, Venlo, The Netherlands) following manufacturer’s instructions. The cDNA was synthesized from 1.5 µg of DNase-treated RNA. Relative quantification of leptin receptor Ob-Rb, corticotropin releasing hormone (Crh) and thyrotropin releasing hormone (Trh) mRNA levels was performed by real-time PCR according to the manufacturer's protocol on an ABI PRISM 7500 FAST Sequence Detection System instrument and software (PE Applied Biosystem, Foster City, CA). To standardize the amount of cDNA added to the reaction, amplification of endogenous control 18S rRNA was included in separate wells using VIC (TaqMan Assay) or primers as real-time reporter. The ΔΔCT method was used to calculate the relative differences between experimental conditions and control groups as fold of change in gene expression. Details about the genes used in this study are provided in Supplementary Data
Table 1.
2.6. Western Blot Analysis
100 mg of frozen ventricles were grinded under liquid N2 before homogenization (2 mL buffer/g tissue) in Henseleit buffer (1 mM PMSF, 100 mM EDTA, 2 mM Na3VO4, 10 μg/mL leupeptin, 10 μg/mL aprotinin and 1 μg/mL pepstatin), using a manual Dounce homogenizer, followed centrifugation at 800 ×g for 5 min at 4°C to produce a total extract. Protein lysates (equal amounts of 50 µg) were separated under reducing condition (10% polyacrylamide concentration gels) SDS-PAGE. Samples were previously mixed with SDS sample buffer and boiled at 95oC for 10 min. Proteins were transferred to nitrocellulose sheets (0.2µm, Bio-Rad) and incubate overnight (12-16 hours) at 4oC with the appropriate primary antibodies, followed by incubation at room temperature for 2 hours with corresponding secondary antibody conjugated with horseradish peroxidase. Primary polyclonal antibody was anti-PPARβ/δ (1:1000, ab23676) and anti-β-actin (1:1000, ab8226) from Abcam, Cambridge, UK. The secondary antibody used was goat anti-rabbit conjugated with horseradish peroxidase (1:4000, 172-1019) from Bio-Rad, Spain. Blots were repeated 3 times to assure the reproducibility of the results. The immunocomplexes formed were visualized using the ECL Western-blotting detection kit (Amersham Biosciences, Inc, Piscataway, NJ) and the images were subjected to a densitometric analysis with a G-Box Densitometer. Bands were quantified by scanning densitometry with the exposure in the linear range using Gene Tools software (Syngene, Cambridge, UK). Samples from rats infused with vehicle, leptin or GSK0660 in all experimental conditions were run on the same gel to allow a direct comparison. β-actin was used as control for protein loading.
2.7. Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Analysis
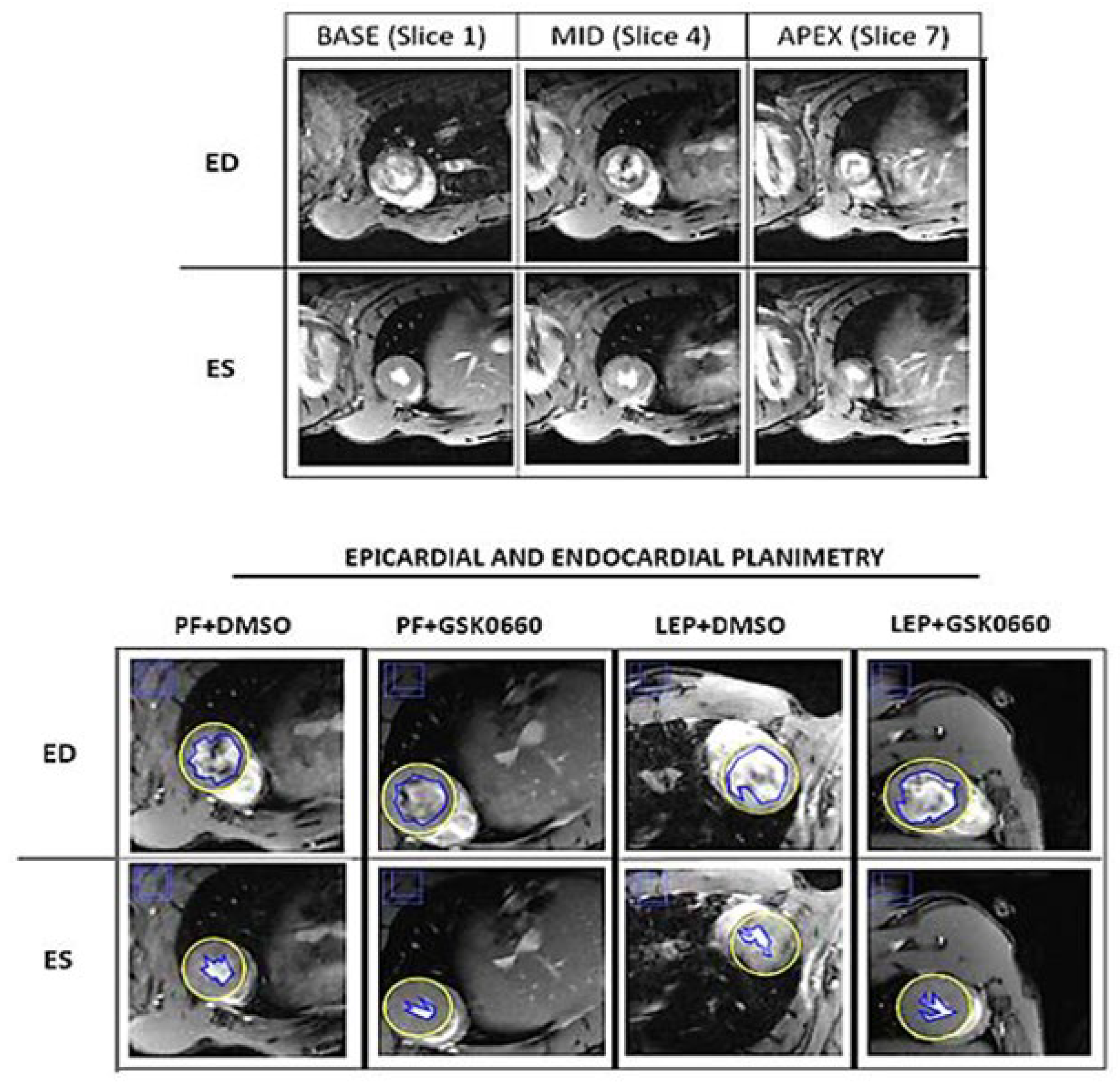
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) studies were performed in a Bruker Biospec 70/30 scanner using a combination of a linear coil (for transmission) with a cardiac phase array coil (for reception). Animals were anesthetized with isoflurane (3% for induction and 1% for maintenance) and placed in an MRI-adapted stereotaxic holder. Respiration rate and ECG were continuously monitored during the scans (SA Instruments). MRI acquisition protocol included an initial flash sequence to center the Field of View (FOV) and plan the short axis (
Table 1). Each short-axis slice (total n=20) was acquired with an integrated sequence.
Table 1.
MRI parameters for LVEF acquisition.
Table 1.
MRI parameters for LVEF acquisition.
| Repetition time |
8 ms |
| Echo time |
2.5 ms |
| Slices thickness |
1.5 mm |
| FOV |
40 x 40 mm |
| Matrix |
256 x 256 |
| Resolution |
0.156 x 0.156 |
Cardiac function and morphology were assessed from the cinema sequences using the freely available software Segment v4.0 R11044b (
http://segment.heiberg.se)[
14]. The primary outcome measure was the LVEF (left ventricular ejection fraction), determined by cardiac MRI. Segmentation of the left ventricle was performed manually. Papillary muscles were included when defining endo- and epicardial borders. Definition of end-diastole and end-systole were calculated by the software. Following manual LV segmentation, the software calculated end-diastolic volume (EDV), end-diastolic left ventricular mass (EDLVM), ejection fraction (EF) and cardiac output (CO) automatically [
15,
16]. Regional wall analyses were performed on a slice-by-slice basis, according to the user manual. In brief, the left ventricle was covered by 5 short-axis slices (1 slice in base/ 3 slices in the middle/ 1 slice in apex) (
Figure 1).
2.8. Statistical Analysis
Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis was performed using the GraphPad Prism version 8.0.2 for Windows (GraphPad Software). Differences between two groups were assessed using the unpaired Student´s t-test. Significant differences between more than two groups were assessed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey test as post-hoc analysis (different letters indicate significant differences). Specific analysis and symbols used have been specified in each figure legend. All differences were considered significant at p≤0.05. The number of rats used per experiments is stated in each figure legend.
3. Results
3.1. Validation of Central Leptin Infusion and Pharmacological Inhibition of PPARβ/δ Activity
In this work, we infused leptin ICV in 3-month old Wistar rat during 7 days to stimulate PPARβ/δ activity in the heart and co-administered GSK0660 (i.p) to abolish the effects of this transcription factor in leptin-treated rats. Initially, we wanted to confirm the ability of exogenous leptin to activate hypothalamic leptin signaling through its own receptor by measuring the hypothalamic mRNA levels of the long form
Ob-Rb leptin receptor and those of
Crh and
Trh, two target genes for the action of leptin, in saline,
pair-fed and leptin treated rats. As expected, leptin induced hypothalamic
Ob-Rb,
Crh and
Trh gene expression compared to the saline and
pair-feeding, indicating that central leptin sensitivity was maintained during the 7 days of leptin treatment and supporting its role in regulating energy balance and metabolic processes (
Table 2).
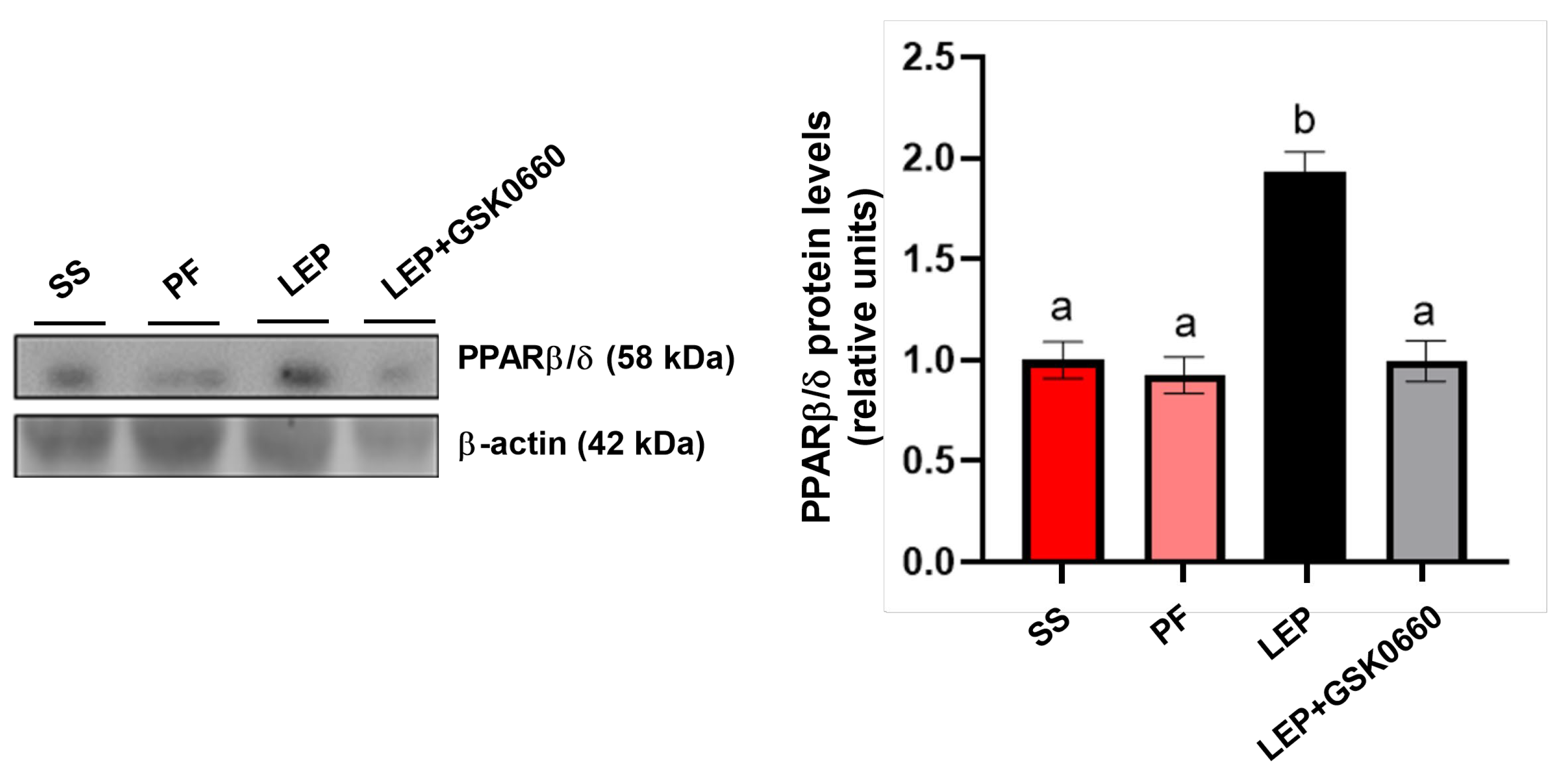
We next confirmed that chronic central infusion of leptin increased PPARβ/δ protein content in the heart, compared to the saline and
pair-feeding (
Figure 2), highlighting its role in leptin's cardiac effects. Moreover, the pharmacological inhibiton of PPARβ/δ, via the
in vivo administration of the selective antagonist GSK0660, blunted the induction of PPARβ/δ in the heart mediated by central leptin (
Figure 2).
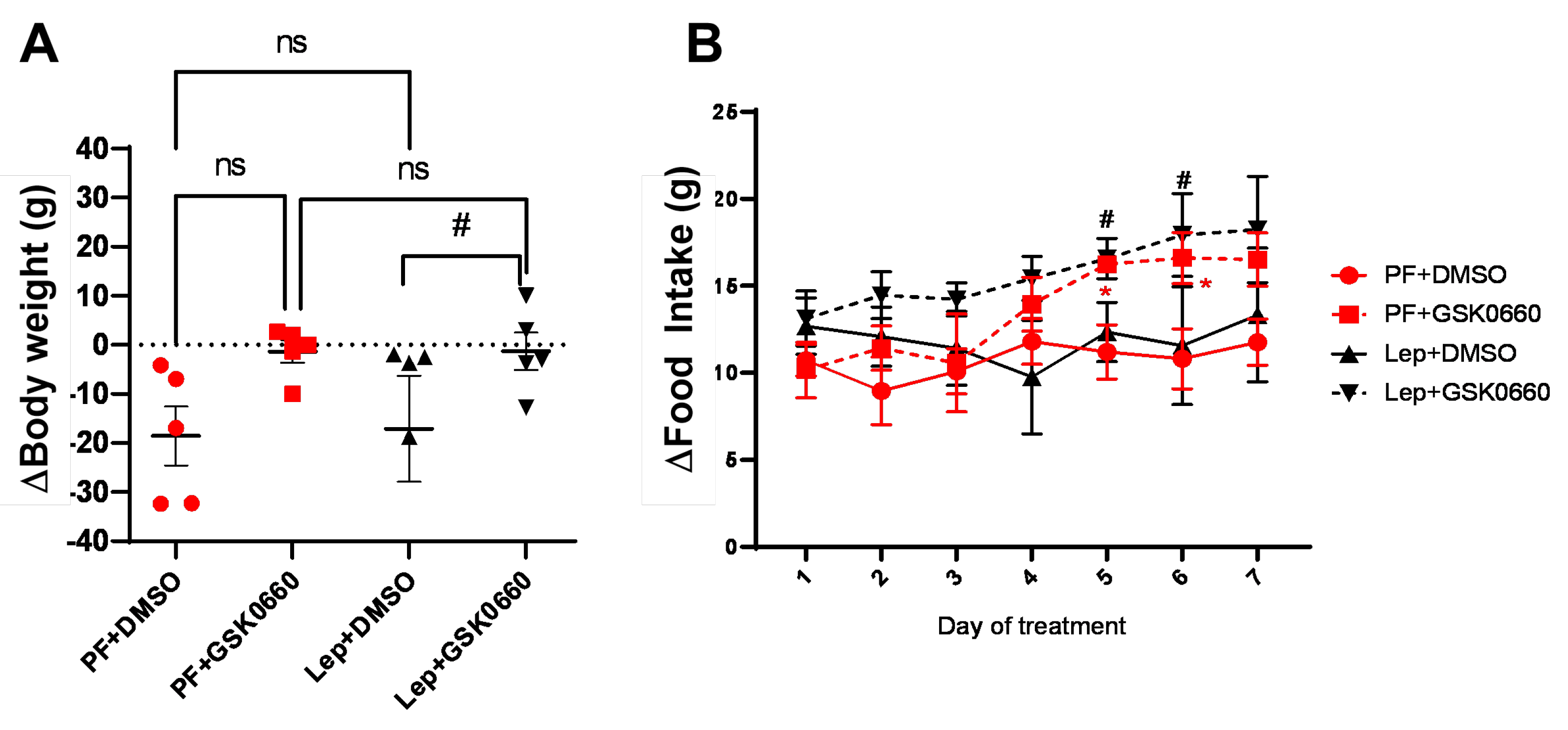
3.2. Effect of Leptin-GSK0660 Co-Treatment on Biological Characteristics of the Rats
Confirming previous data [
12,
17], rats infused with central leptin (Lep+DMSO) did not change significantly their body weight (
Figure 3A), average food consumption (
Figure 3B) and adiposity (
Table 3) compared to
pair-fed groups infused with vehicle (PF+DMSO). The intraperitoneal (i.p) administration of GSK0660 during 7-day (Lep+GSK0660 and PF+GSK0660) abolished the effects on body weight and food intake (
Figure 2A,B) mediated either by central leptin infusion (Lep+GSK0660) or by caloric restriction (PF+GSK0660) in
pair-fed rats.
Central leptin infusion did not induce changes in serum glucose and leptin levels compared to the vehicle-induced rat group (
Table 3), despite showing slightly lower circulating leptin levels in serum, as previously reported [
11]. Nevertheless, GSK0660 treatment notably increased serum levels of insulin (
Table 3), indicating that GSK0660 induced insulin resistance in 3-month-old Wistar rat.
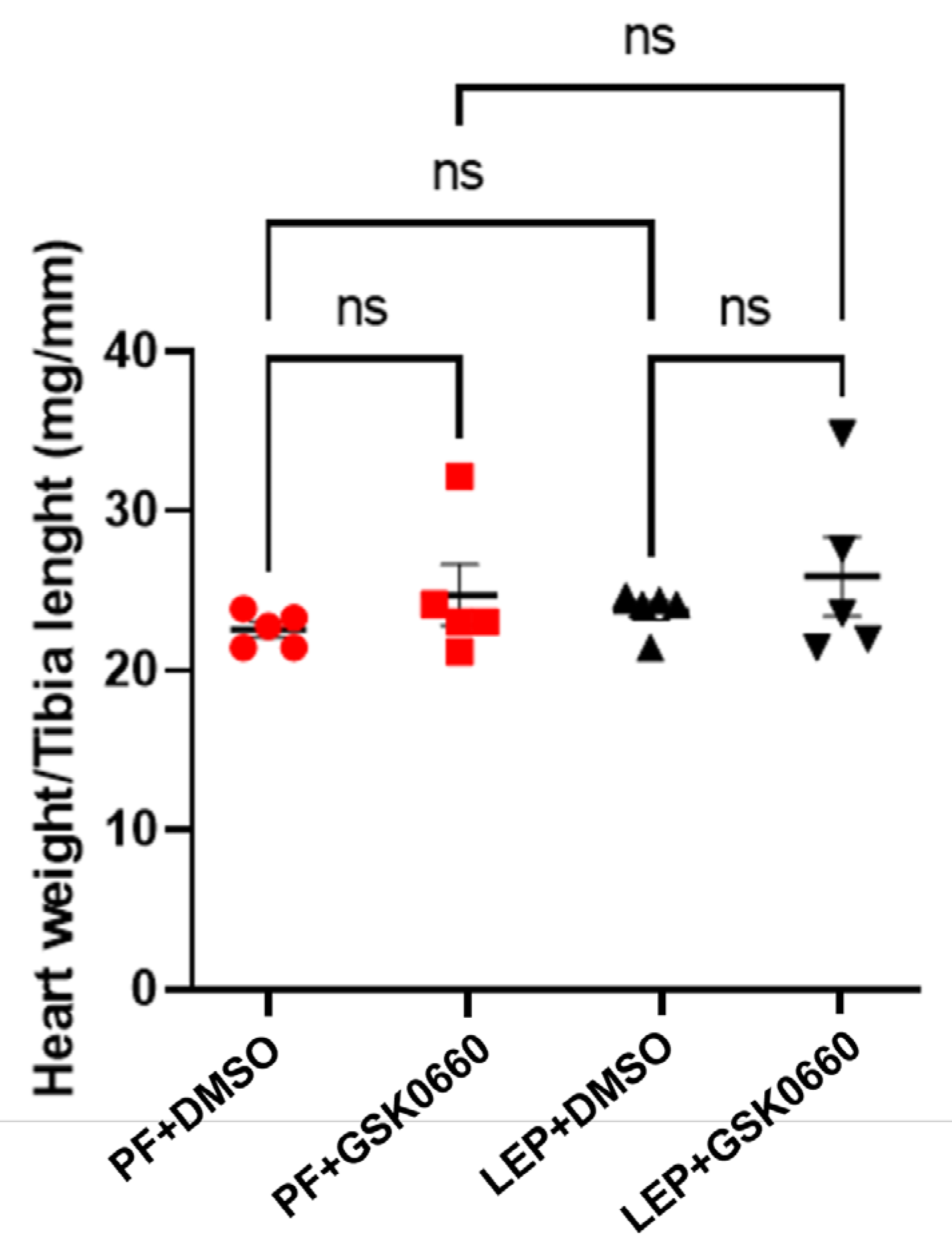
In small animals with rapid changes in body weight, as in rats, the normalization of heart size relative to body weight, is not a good indicator of adverse cardiac remodeling development [
18]. Instead, as the heart weight/tibia length index remains constant after maturity [
18], we used this index to analyze the effects of leptin and GSK0660 on cardiac remodeling. As observed in
Figure 4, this index did not show significant differences between rats treated for 7 days with leptin or vehicle, indicating that leptin treatment did not seem to induce a significant alteration of the ventricular wall. However, in the group of animals treated with GSK0660, the ratio was slightly higher compared to its control group treated with DMSO (
Figure 4).
3.3. Effect of Leptin-GSK0660 Co-Treatment on Cardiac Electrical Properties
To gain a deeper insight on the effects of central leptin on cardiac electrical properties and remodeling, we studied the influence of central leptin treatment in the absence or presence of GSK0660 on cardiac function by analyzing both electrical and physiological patterns.
Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is defined as an increase in left ventricular mass (LVM) associated with structural changes in the myocardium. This occurs in response to mechanical and/or neurohormonal stimuli, leading to increased workload on the myocyte, which, under biomechanical stress, can induce hypertrophy development [
19].
It has previously been reported that ventricular wall thickening is associated with changes in cardiac depolarization and repolarization states, manifested as altered patterns in the duration and amplitude of the QRS complex, as well as QT interval prolongation [
20,
21]. Accordingly, we used this approach to assess cardiac function and electrical activity in our experiments.
Indeed, as presented in
Table 4, we compare the mean values of QRS duration, R wave amplitude as a representation of the QRS complex voltage, and corrected QT duration (QTc) at baseline (t0) and final time points of the treatments (t7) to underscore physiological changes or other alterations in cardiac structure.
The QRS duration and R wave amplitude in lead II voltages, at different times, showed a reduction in the group of animals treated with central leptin, being significant only for the R wave amplitude measurement. These changes suggest a decrease in abnormal ventricular wall growth, which could be indicative of a more atrophic pattern. This is in consonance with previous studies performed in rodents [
9,
11]. Interestingly, these differences were not observed in the group of animals treated with the PPARβ/δ antagonist. By comparison, QTc duration only increased in the group of animals treated with the PPARβ/δ antagonist when comparing baseline (t0) and final time (t7), indicating a potential alteration in ventricular repolarization, which can have implications for arrhythmogenesis and electrical instability.
In fact, the longer QRS duration and higher R wave voltage is used as measures of relative sensitivity and specificity of abnormal ventricular wall growth, which, in combination with other physiological parameters, facilitate the detection of left ventricular hypertrophy. The results presented in this work indicate that rats treated with the PPARβ/δ antagonist present an altered ECG, possibly due to increased ventricular wall thickness, contrasting with the characteristic atrophic pattern observed in rats treated centrally with leptin suggesting that the effects observed with central leptin treatment are mediated by leptin-specific pathways rather than PPARβ/δ signaling.
Given that PPARβ/δ has been implicated in the regulation of ion channels and cellular processes involved in cardiac repolarization [
22,
23,
24], antagonism of PPARβ/δ may disrupt these processes leading to QT prolongation.
Moreover, previous studies have demonstrated the role of disturbed PPARβ/δ activity in the development of metabolic syndrome and its components, including insulin resistance [
25], which are associated with QT interval prolongation and increased cardiovascular risk [
24,
26,
27,
28].
On the other hand, it is known that leptin signaling improves insulin sensitivity, which is important for changing QTc duration and potentially reducing arrhythmogenic risk [
29,
30]. Improved insulin sensitivity through effective leptin signaling can lead to better regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism, thereby stabilizing cardiac electrophysiology and reducing the likelihood of QTc prolongation and related arrhythmias.
In addition to these measures facilitating screening of early-stage pathology development (QRS duration, R amplitude, and long QTc), an increase in heart rate (HR) can be used as an indicator of poor prognosis. Various studies associate increased mortality with an elevated heart rate, finding a positive correlation between the two. Similarly, some authors suggest that reducing HR could be used as a potential target for treating patients with heart failure [
31].
As seen in
Table 5, animals treated with central leptin were able to reduce heart rate, which was not observed in animals additionally treated with the PPARβ/δ antagonist. In the GSK0660-treated groups (PF+GSK0660 and Lep+GSK0660), an increase in heart rate was induced compared to their controls (PF+DMSO and Lep+DMSO). Surprisingly, a significant increase in R-R interval duration (ms) occurred in control animals treat-ed with the vehicle.
This result indicates that central leptin signaling may act as a regulator against the development of cardiac arrhythmias, probably due to its ability to impact cardiomyocyte size [
32,
33], to improve insulin sensitivity, and to modulate the autonomic nervous system activity and the expression of ion channels involved in cardiac repolarization [
29,
30]. Interestingly, Lin et al. [
34] have suggested that circulating leptin directly modulates cardiac electrical properties, including heart rate and QT interval, via its receptors expressed in cardiac tissue. These findings suggest a mechanism by which leptin may influence cardiovascular function independently of the central pathways, indicating the potential implications of dysregulated leptin signaling in cardiovascular disorders, including the development of bradycardia, QT interval prolongation, and ventricular arrhythmias.
Table 5.
Sinus rhythm (R-R interval, R-R) and mean heart rate (HR) for treated-groups.
Table 5.
Sinus rhythm (R-R interval, R-R) and mean heart rate (HR) for treated-groups.
| |
R-R INTERVAL (ms) |
∆R-R (ms) |
Heart Rate (bpm) |
∆HR (bpm) |
| |
t0 |
t7 |
t0 |
t7 |
| PF+DMSO |
136±6 |
159±7*
|
23±4.1a
|
210±22 |
274±30*
|
64±16.64a
|
| PF+GSK0660 |
145±4 |
196±31*
|
51±14.0b
|
205±12 |
275±34*
|
70±16.12a
|
| LEP+DMSO |
135±5 |
139±4 |
4±2.9c
|
231±30 |
219±20 |
-12±16.12b
|
| LEP+GSK0660 |
141±4 |
142±6 |
1±3.2c
|
199±4 |
224±14*
|
25±6.51c
|
Therefore, while the precise role of leptin in protecting against cardiac arrhythmias is still being elucidated, our data suggests that central leptin actions may have beneficial effects on cardiac electrophysiology and rhythm regulation
3.4. Effect of Leptin-GSK0660 Co-Treatment on Cardiac Remodeling and Function
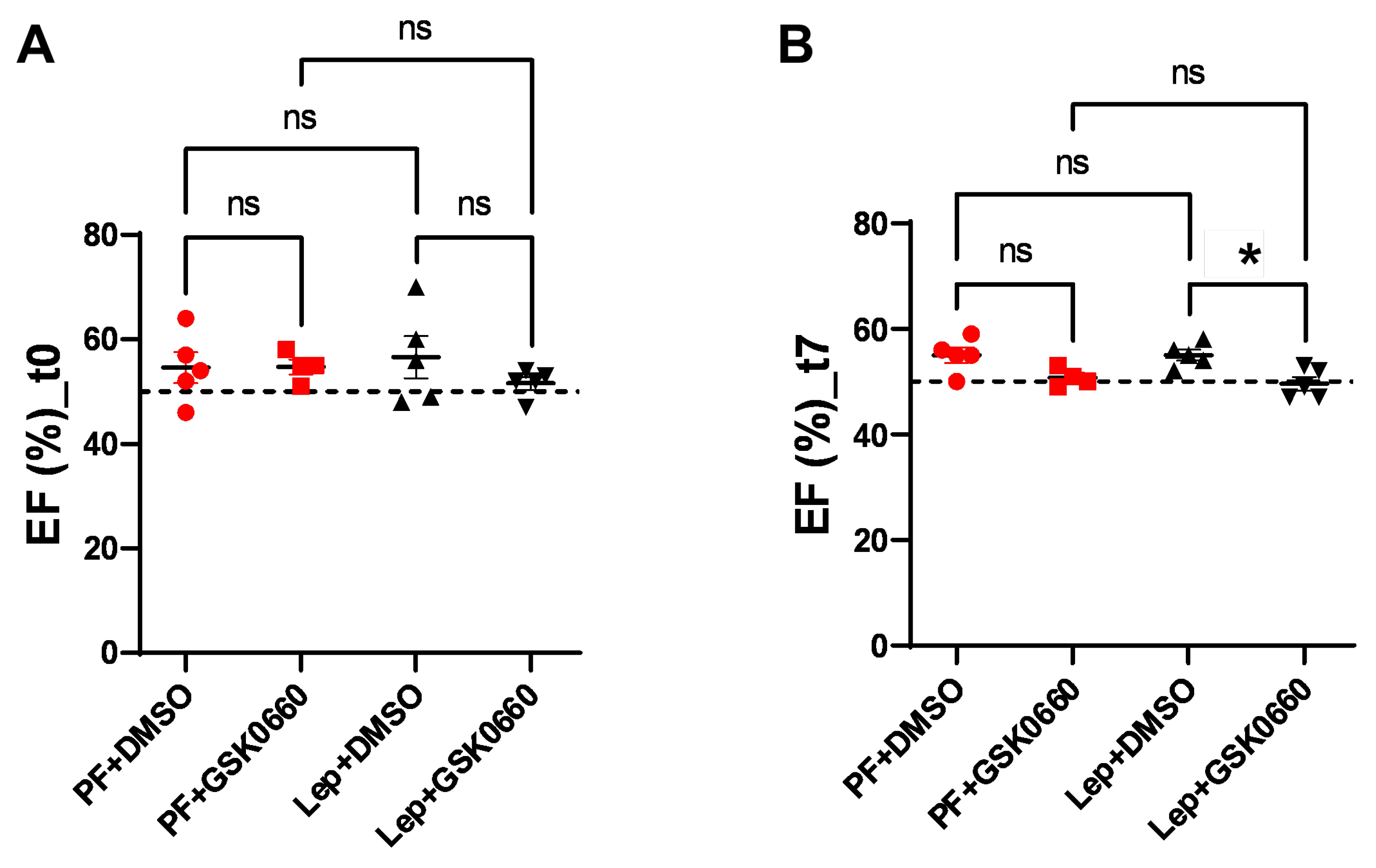
Next, we evaluated alterations in cardiac function using Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) to monitor the response to the progression of central leptin or vehicle treatment. As expected, at baseline (t0) there were not differences in ejection fraction (EF, %) between groups (
Figure 5). However, a decrease in EF was induced at the final time (t7) in the Lep+GSK0660 group which was statistically significant compared to its control group (Lep+DMSO). This decrease only fell below the 50% threshold when the PPARβ/δ activity was inhibited in the central leptin-treated group (Lep+GSK0660). Although EF% values are considered borderline between 41 and 49% [
35,
36,
37] this should not be considered an indicator of heart failure development; instead, it indicates a loss of contractile capacity.
Studies in animal models and some human studies have shown that high-fat diets can lead to cardiac dysfunction, including reduced ejection fraction, as evidenced [
38,
39]. These effects appear to be mediated by various mechanisms, including inflammation, oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and insulin resistance, all of which can impair cardiac contractility and function. While these studies primarily focus on insulin resistance and mitochondrial dynamics in heart disease, there could be implications for the role of leptin signaling in cardiac function. Importantly, vehicle-treated, and centrally leptin-treated groups showed preserved ejection fraction after 7 days of treatment (
Figure 5).
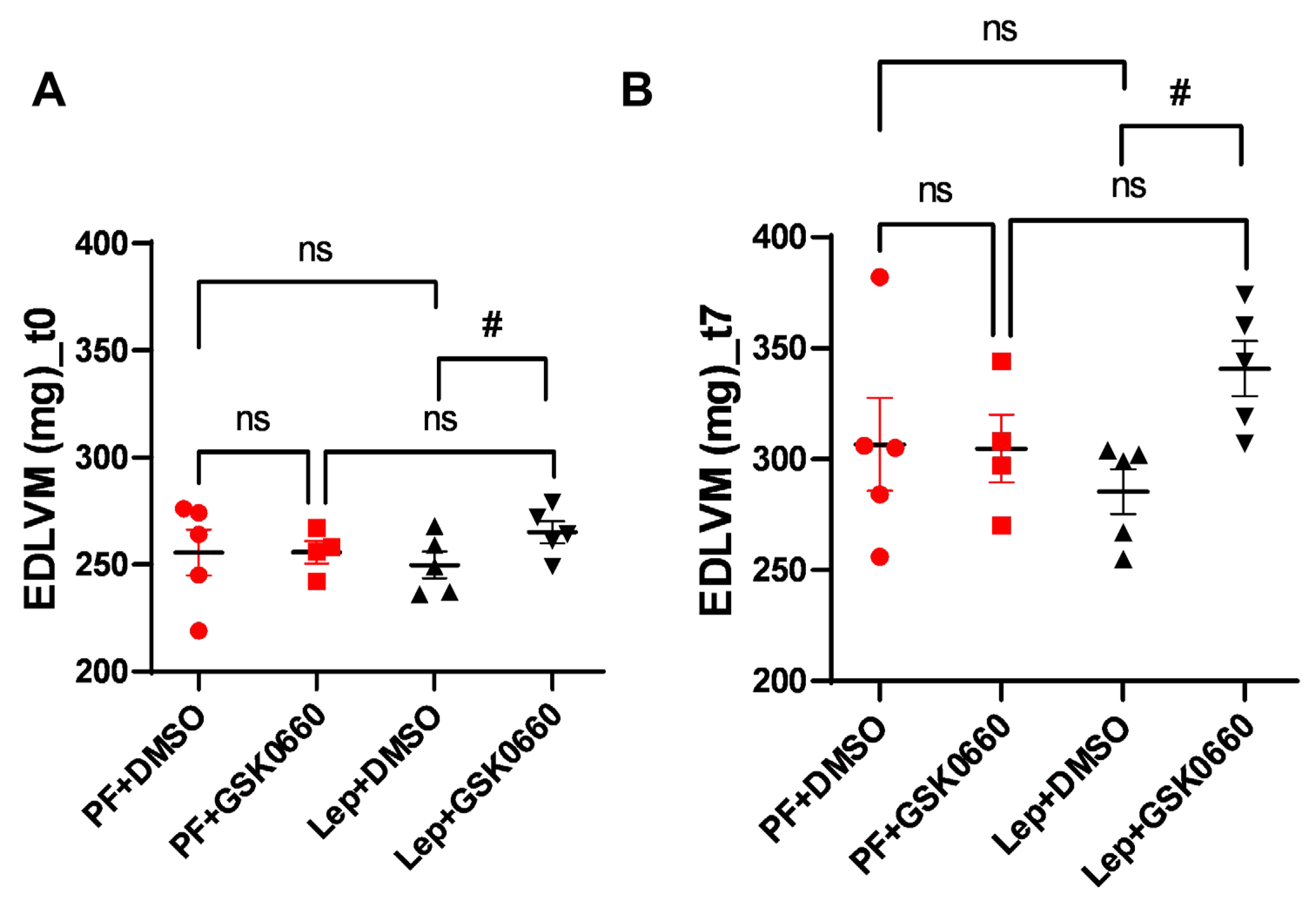
As already mentioned, analysis of MRI allows for more effective estimation of variations in ventricular mass. We observed that animals treated with the vehicle did not present differences in end-diastolic left ventricular mass (EDLVM) (
Figure 6) at baseline and post-treatment times. However, in animals treated centrally with leptin, EDLVM was significantly greater in the group where PPARβ/δ action was blocked using GSK0660. Surprisingly, these animals already showed differences in ventricular mass at baseline. These differences increased at the final time (t7), with EDLVM being significantly greater in this group (Lep+GSK0660).
Thus, this study supports that central leptin treatment at a low dose (0,2 µg/day) promote an atrophic pattern in the myocardium and that PPARβ/δ is required for leptin signaling to remodel cardiac tissue in rats with normal leptin sensitivity.
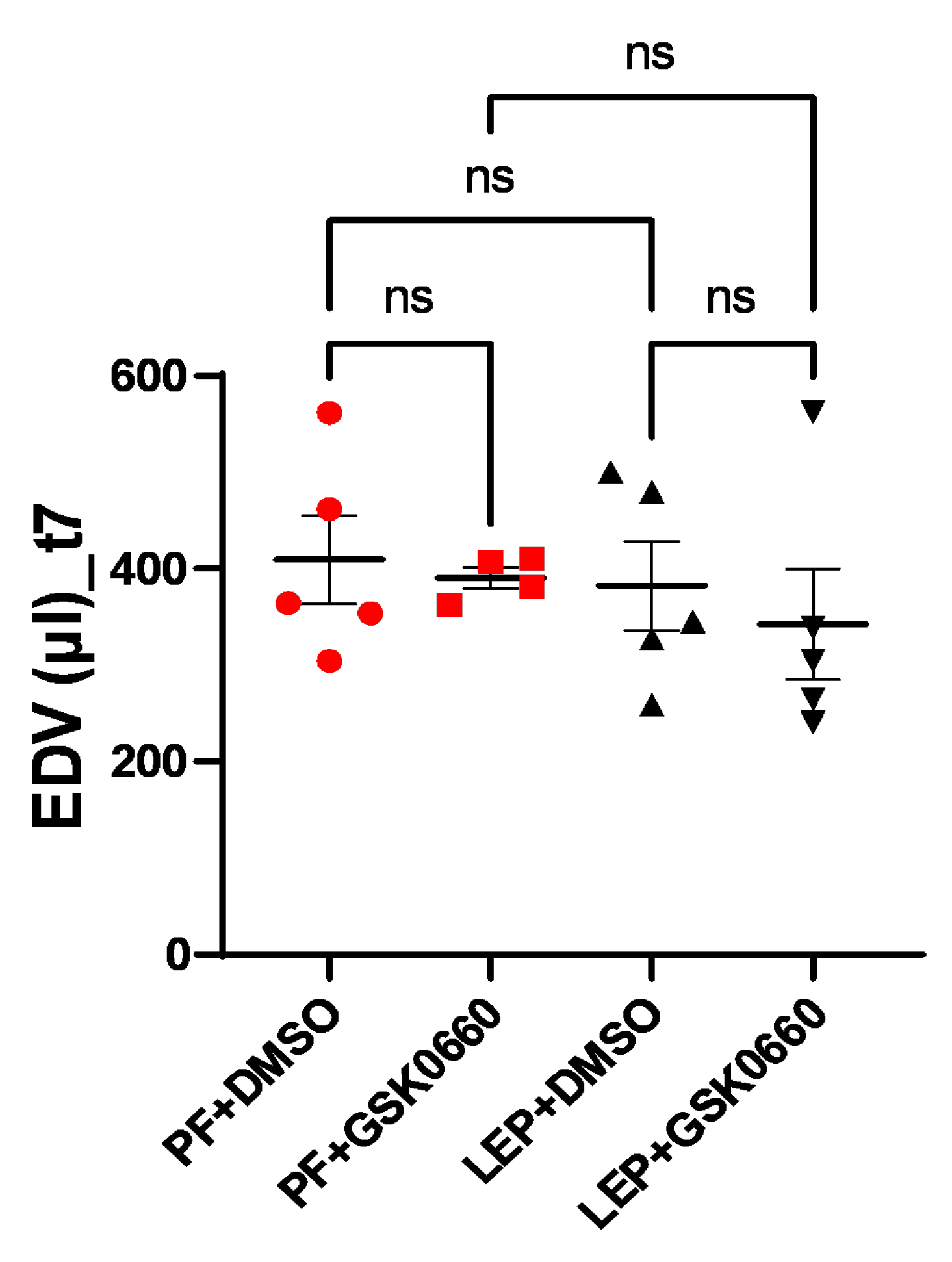
To measure the potential impact of increased ventricular mass on ventricular filling volume, end-diastolic volume (EDV) was measured at the final time (t7). Although differences were not significant, a slight decrease in final ventricular filling volume was observed for the group of animals with dual treatment (ICV-Leptin and IP-GSK0660) (
Figure 7).
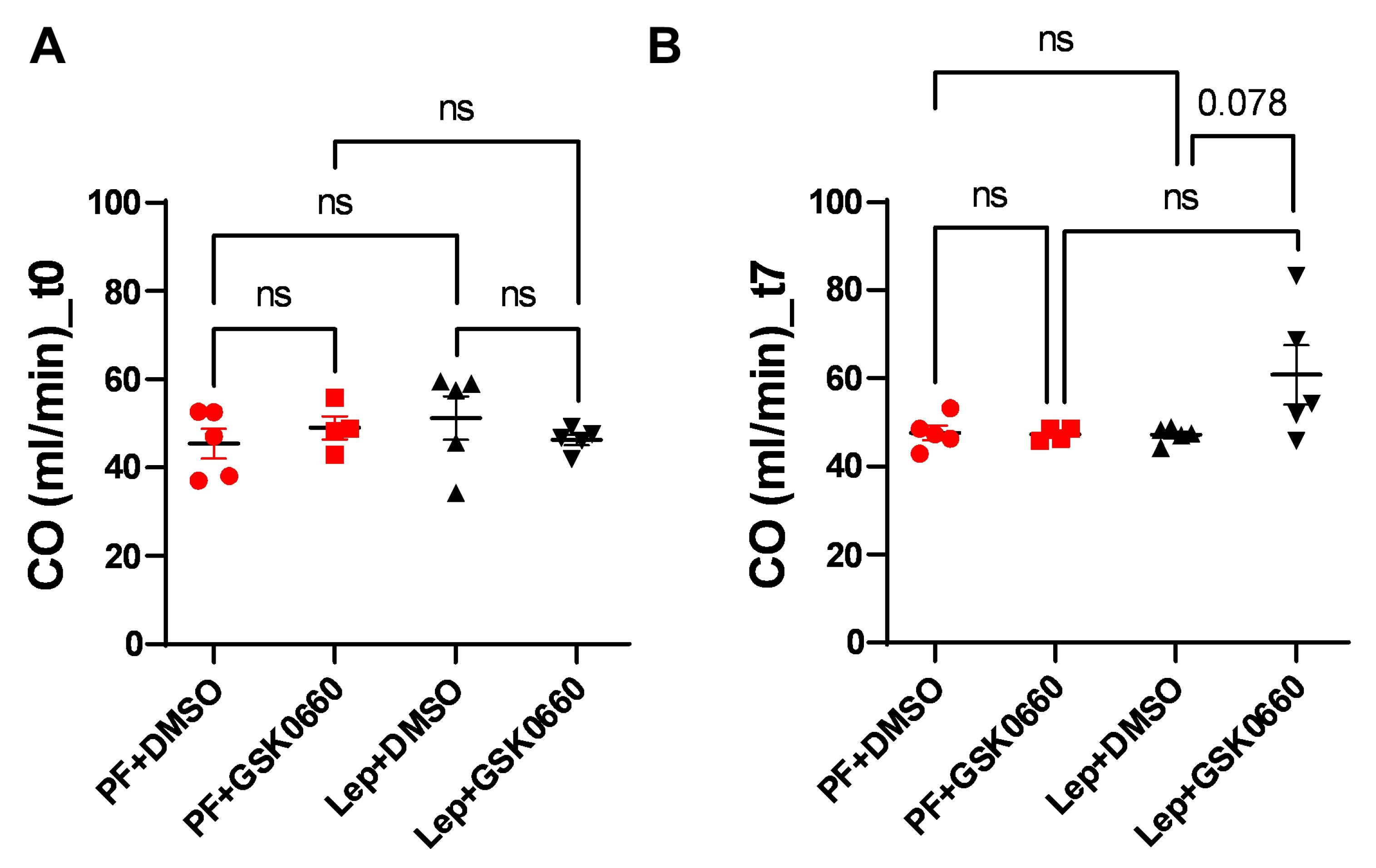
Finally, possible changes in cardiac output (CO) were studied. As seen in
Figure 8, the differences in ventricular mass did not induce changes in CO pre- and post-treatment, despite an increase in the Lep+GSK0660 group (t7) being observed, which was not significant (p=0.078). The lack of significant changes in CO may be attributed, at least in part, to compensatory mechanisms that were initially induced during the development of hypertrophy to prevent an increase in CO [
40]. These compensatory mechanisms could involve various physiological adaptations aimed at maintaining cardiac output despite changes in ventricular mass. One such mechanism could involve an increase in heart rate (HR), which was observed in the animal treated with leptin and the PPARβ/δ antagonist (Lep+GSK0660), as depicted in
Figure 8.
In summary, this study examines the impact of central leptin infusion and the pharmacological inhibition of PPARβ/δ on cardiac remodeling and cardiac function in Wistar rat. We confirm that leptin may have protective effects against abnormal ventricular growth, while PPARβ/δ antagonism might lead to changes in cardiac electrical activity indicative of left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH). Our results provide new insights on the physiological mechanisms by which the leptin-PPARβ/δ crosstalk impact cardiac remodeling and cardiac function in rats.
Furthermore, building upon the findings presented in this study and our prior research, we suggest that central leptin treatment may exert cardioprotective effects by facilitating atrophic remodeling, potentially linked with metabolic unloading. This process could involve the induction of FoxO1/3 and the inhibition of mTORC1 pathways [
11].
In contrast, treatment with the PPARβ/δ antagonist GSK0660 resulted in increased QTc duration, indicating potential alterations in ventricular repolarization and an increased risk of arrhythmias. Hence, antagonists like GSK0660 could potentially be used to study metabolic pathways but might also have implications for disrupting energy balance if not used appropriately.
4. Conclusions and Future Directions
This study explores the specific interactions between leptin and PPARβ/δ in cardiac function. The observed cardioprotective effects of leptin suggest its therapeutic potential for managing cardiac conditions. It was conducted using animal models. Further research in clinical settings is needed to validate our findings and assess their clinical relevance.
However, it is important to note that inhibition of PPARβ/δ-associated pathways may interfere with leptin's beneficial effects, which may be relevant in patients with conditions like generalized lipodystrophy where leptin therapy is used to mitigate cardiac hypertrophy [
41].
Future research into the effects of PPARβ/δ modulation on cardiac electrophysiology may inform the development of targeted therapies for arrhythmias and other cardiovascular conditions. Indeed, further research is needed to explore the long-term effects of leptin and PPARβ/δ modulation on cardiac health.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org; Table S1: Primers sequences of genes used for quantification of mRNAs by qRT-PCR; Figure S1: Representative Red Ponceau staining of the nitrocellulose membrane for total protein normalization prior to immunodetection; Table S2: Quantitative densitometry analysis of PPARβ/δ protein bands from the Western-Blot.
Author Contributions
For research articles with several authors, a short paragraph specifying their individual Conceptualization, N.G. and A.A.; Methodology, B.R., C.P., L.M., and M.B.; Software, B.R. and M.B.; Validation, N.G., A.A., C.P.; Investigation, B.R., C.P., L.M.; Resources, N.G., A.A.; Writing – Original Draft Preparation, B.R. and N.G.; Writing – Review & Editing, N.G. and A.A.; Visualization, B.R., C.P., L.M.; Supervision, N.G. and A.A.; Project Administration, N.G. and A.A.; Funding Acquisition, N.G. and A.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Ministerio de Ciencia, Innovación y Universidades, Spain under project grants RTI2018-098643-B-I00. Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación, Spain, under project grants PID2021-128243OB-I00. University of Castilla-La Mancha, Spain and the European Regional Development Fund (FEDER) under project grants 2021 GRIN-30987.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge their gratitude to Sergio Moreno for the excellent technical assistance.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Baskin, K.K.; Taegtmeyer, H. Taking Pressure off the Heart: The Ins and Outs of Atrophic Remodelling. Cardiovasc. Res. 2011, 90, 243–250. [CrossRef]
- Gibb, A.A.; Hill, B.G. Metabolic Coordination of Physiological and Pathological Cardiac Remodeling. Circ. Res. 2018, 123, 107–128. [CrossRef]
- Sudi, S.B.; Tanaka, T.; Oda, S.; Nishiyama, K.; Nishimura, A.; Sunggip, C.; Mangmool, S.; Numaga-Tomita, T.; Nishida, M. TRPC3-Nox2 Axis Mediates Nutritional Deficiency-Induced Cardiomyocyte Atrophy. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9785. [CrossRef]
- Bacova, B.S.; Andelova, K.; Sykora, M.; Egan Benova, T.; Barancik, M.; Kurahara, L.H.; Tribulova, N. Does Myocardial Atrophy Represent Anti-Arrhythmic Phenotype? Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2819. [CrossRef]
- Karmazyn, M.; Purdham, D.M.; Rajapurohitam, V.; Zeidan, A. Leptin as a Cardiac Hypertrophic Factor: A Potential Target for Therapeutics. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2007, 17, 206–211. [CrossRef]
- Hall, M.E.; Harmancey, R.; Stec, D.E. Lean Heart: Role of Leptin in Cardiac Hypertrophy and Metabolism. World J. Cardiol. 2015, 7, 511–524. [CrossRef]
- Me, H.; Mw, M.; Je, H.; De, S. Rescue of Cardiac Leptin Receptors in Db/Db Mice Prevents Myocardial Triglyceride Accumulation. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 307. [CrossRef]
- Barouch, L.A.; Berkowitz, D.E.; Harrison, R.W.; O’Donnell, C.P.; Hare, J.M. Disruption of Leptin Signaling Contributes to Cardiac Hypertrophy Independently of Body Weight in Mice. Circulation 2003, 108, 754–759. [CrossRef]
- Gava, F.N.; da Silva, A.A.; Dai, X.; Harmancey, R.; Ashraf, S.; Omoto, A.C.M.; Salgado, M.C.; Moak, S.P.; Li, X.; Hall, J.E.; et al. Restoration of Cardiac Function After Myocardial Infarction by Long-Term Activation of the CNS Leptin-Melanocortin System. JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 2021, 6, 55–70. [CrossRef]
- D, K.; T, S.; W, W.; M, deShazo; Je, H.; Md, W.; Ij, K.; Th, M.; Kr, B.; Me, H. Higher Plasma Leptin Levels Are Associated with Reduced Left Ventricular Mass and Left Ventricular Diastolic Stiffness in Black Women: Insights from the Genetic Epidemiology Network of Arteriopathy (GENOA) Study. Hypertens. Res. Off. J. Jpn. Soc. Hypertens. 2018, 41. [CrossRef]
- Rubio, B.; Mora, C.; Pintado, C.; Mazuecos, L.; Fernández, A.; López, V.; Andrés, A.; Gallardo, N. The Nutrient Sensing Pathways FoxO1/3 and mTOR in the Heart Are Coordinately Regulated by Central Leptin through PPARβ/δ. Implications in Cardiac Remodeling. Metabolism. 2020, 115, 154453. [CrossRef]
- Mazuecos, L.; Pintado, C.; Rubio, B.; Guisantes-Batán, E.; Andrés, A.; Gallardo, N. Leptin, Acting at Central Level, Increases FGF21 Expression in White Adipose Tissue via PPARβ/δ. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4624. [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, M.; Pintado, C.; Torrillas-de la Cal, R.; Moltó, E.; Gallardo, N.; Andrés, A.; Arribas, C. Ageing Alters the Lipid Sensing Process in the Hypothalamus of Wistar Rat. Effect of Food Restriction. Nutr. Neurosci. 2022, 25, 1509–1523. [CrossRef]
- Heiberg, E.; Sjögren, J.; Ugander, M.; Carlsson, M.; Engblom, H.; Arheden, H. Design and Validation of Segment--Freely Available Software for Cardiovascular Image Analysis. BMC Med. Imaging 2010, 10, 1. [CrossRef]
- Schweins, M.; Gäbel, R.; Raitza, M.; Vasudevan, P.; Lemcke, H.; Joksch, M.; Schildt, A.; Kurth, J.; Lindner, T.; Meinel, F.G.; et al. Multi-Modal Assessment of a Cardiac Stem Cell Therapy Reveals Distinct Modulation of Regional Scar Properties. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 187. [CrossRef]
- Lang, C.I.; Vasudevan, P.; Döring, P.; Gäbel, R.; Lemcke, H.; Lindner, T.; Steinhoff, G.; Krause, B.J.; Vollmar, B.; Meinel, F.G.; et al. Expedient Assessment of Post-Infarct Remodeling by Native Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Mice. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11625. [CrossRef]
- Mora, C.; Pintado, C.; Rubio, B.; Mazuecos, L.; López, V.; Fernández, A.; Salamanca, A.; Bárcena, B.; Fernández-Agulló, T.; Arribas, C.; et al. Central Leptin Regulates Heart Lipid Content by Selectively Increasing PPAR β/δ Expression. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 236, 43–56. [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.C.; Spurgeon, H.A.; Rakusan, K.; Weisfeldt, M.L.; Lakatta, E.G. Use of Tibial Length to Quantify Cardiac Hypertrophy: Application in the Aging Rat. Am. J. Physiol. 1982, 243, H941-947. [CrossRef]
- Samak, M.; Fatullayev, J.; Sabashnikov, A.; Zeriouh, M.; Schmack, B.; Farag, M.; Popov, A.-F.; Dohmen, P.M.; Choi, Y.-H.; Wahlers, T.; et al. Cardiac Hypertrophy: An Introduction to Molecular and Cellular Basis. Med. Sci. Monit. Basic Res. 2016, 22, 75–79. [CrossRef]
- Domain, G.; Chouquet, C.; Réant, P.; Bongard, V.; Vedis, T.; Rollin, A.; Mandel, F.; Delasnerie, H.; Voglimacci-Stephanopoli, Q.; Mondoly, P.; et al. Relationships between Left Ventricular Mass and QRS Duration in Diverse Types of Left Ventricular Hypertrophy. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2022, 23, 560–568. [CrossRef]
- Okin, P.M.; Roman, M.J.; Devereux, R.B.; Kligfield, P. Gender Differences and the Electrocardiogram in Left Ventricular Hypertrophy. Hypertens. Dallas Tex 1979 1995, 25, 242–249. [CrossRef]
- Papatheodorou, I.; Galatou, E.; Panagiotidis, G.-D.; Ravingerová, T.; Lazou, A. Cardioprotective Effects of PPARβ/δ Activation against Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Rat Heart Are Associated with ALDH2 Upregulation, Amelioration of Oxidative Stress and Preservation of Mitochondrial Energy Production. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6399. [CrossRef]
- Planavila, A.; Rodríguez-Calvo, R.; Jové, M.; Michalik, L.; Wahli, W.; Laguna, J.C.; Vázquez-Carrera, M. Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Beta/Delta Activation Inhibits Hypertrophy in Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes. Cardiovasc. Res. 2005, 65, 832–841. [CrossRef]
- Barish, G.D.; Narkar, V.A.; Evans, R.M. PPAR Delta: A Dagger in the Heart of the Metabolic Syndrome. J. Clin. Invest. 2006, 116, 590–597. [CrossRef]
- Manickam, R.; Wahli, W. Roles of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor β/δ in Skeletal Muscle Physiology. Biochimie 2017, 136, 42–48. [CrossRef]
- DeBoer, M.D.; Gurka, M.J.; Woo, J.G.; Morrison, J.A. Severity of Metabolic Syndrome as a Predictor of Cardiovascular Disease Between Childhood and Adulthood: The Princeton Lipid Research Cohort Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 66, 755–757. [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-H.; Olson, P.; Evans, R.M. Minireview: Lipid Metabolism, Metabolic Diseases, and Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 2201–2207. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-X. PPARs: Diverse Regulators in Energy Metabolism and Metabolic Diseases. Cell Res. 2010, 20, 124–137. [CrossRef]
- Morrison, C.D.; Huypens, P.; Stewart, L.K.; Gettys, T.W. Implications of Crosstalk between Leptin and Insulin Signaling during the Development of Diet-Induced Obesity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1792, 409–416. [CrossRef]
- Sierra-Johnson, J.; Romero-Corral, A.; Lopez-Jimenez, F.; Gami, A.S.; Sert Kuniyoshi, F.H.; Wolk, R.; Somers, V.K. Relation of Increased Leptin Concentrations to History of Myocardial Infarction and Stroke in the United States Population. Am. J. Cardiol. 2007, 100, 234–239. [CrossRef]
- Hori, M.; Okamoto, H. Heart Rate as a Target of Treatment of Chronic Heart Failure. J. Cardiol. 2012, 60, 86–90. [CrossRef]
- Fraley, M.A.; Birchem, J.A.; Senkottaiyan, N.; Alpert, M.A. Obesity and the Electrocardiogram. Obes. Rev. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Obes. 2005, 6, 275–281. [CrossRef]
- Wiegerinck, R.F.; Verkerk, A.O.; Belterman, C.N.; van Veen, T.A.B.; Baartscheer, A.; Opthof, T.; Wilders, R.; de Bakker, J.M.T.; Coronel, R. Larger Cell Size in Rabbits with Heart Failure Increases Myocardial Conduction Velocity and QRS Duration. Circulation 2006, 113, 806–813. [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-C.; Huang, J.; Hileman, S.; Martin, K.H.; Hull, R.; Davis, M.; Yu, H.-G. Leptin Decreases Heart Rate Associated with Increased Ventricular Repolarization via Its Receptor. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2015, 309, H1731-1739. [CrossRef]
- Lang, R.M.; Badano, L.P.; Mor-Avi, V.; Afilalo, J.; Armstrong, A.; Ernande, L.; Flachskampf, F.A.; Foster, E.; Goldstein, S.A.; Kuznetsova, T.; et al. Recommendations for Cardiac Chamber Quantification by Echocardiography in Adults: An Update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. Off. Publ. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2015, 28, 1-39.e14. [CrossRef]
- Savarese, G.; Stolfo, D.; Sinagra, G.; Lund, L.H. Heart Failure with Mid-Range or Mildly Reduced Ejection Fraction. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2022, 19, 100–116. [CrossRef]
- Golla, M.S.G.; Hajouli, S.; Ludhwani, D. Heart Failure and Ejection Fraction. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island (FL), 2024.
- Abel, E.D.; O’Shea, K.M.; Ramasamy, R. Insulin Resistance: Metabolic Mechanisms and Consequences in the Heart. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 2068–2076. [CrossRef]
- Dorn, G.W. Mitochondrial Dynamics in Heart Disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1833, 233–241. [CrossRef]
- Saheera, S.; Krishnamurthy, P. Cardiovascular Changes Associated with Hypertensive Heart Disease and Aging. Cell Transplant. 2020, 29, 963689720920830. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.-L.; Sachdev, V.; Burklow, T.R.; Li, W.; Startzell, M.; Auh, S.; Brown, R.J. Leptin Attenuates Cardiac Hypertrophy in Patients With Generalized Lipodystrophy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, e4327–e4339. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).