1. Introduction
In today's global context, sustainable development has become a top priority for nations across the world. The challenge lies in achieving robust economic growth that is also environmentally friendly. In this context, renewable energy consumption, technological innovation, and export diversification are seen as key drivers of sustainable economic progress. While traditional energy sources can promote economic output, they are a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions and ecological harm (Awodumi & Adewuyi, 2020). This creates a policy dilemma for countries: prioritize pollution reduction or economic growth. Regardless of the source, energy use should be optimized due to its finite nature. Climate change and global warming make renewable energy a highly attractive alternative to fossil fuels, offering significant reductions in CO2 emissions. However, implementing new renewable energy technologies is both time-consuming and expensive. Countries face the dual challenge of maintaining economic growth and tackling climate change. The COVID-19 pandemic has further exacerbated this issue. Governments in both developed and developing nations must carefully balance spending on climate change mitigation with economic stimulus efforts. The E-7 economies—Brazil, China, India, Indonesia, Mexico, Russia, and Turkey—are a varied group that is rapidly growing. While their development stages vary, all face a common challenge: meeting their rising energy demands sustainably. As the world grapples with climate change, these nations' shift towards renewable energy becomes increasingly crucial. Studies have looked into the relationship between renewable energy usage and economic growth, with a particular emphasis on European countries. However, it's important to consider the broader global context and explore this relationship in a wider range of countries. Energy resources remain a fundamental element for economic expansion (Xiong et al., 2014). There's a clear link between economic growth and energy consumption, but this consumption is also highly responsible for greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, particularly CO2 (Gabr and Mohamed, 2020). (Tutak and Brodny, 2022) examined the impact of renewable energy on the economy, the environment, and traditional energy sources. (Smolović et al., 2020) investigated the nexus between renewable energy consumption and economic growth in the European Union, employing a dynamic panel setting. Koengkan et al. (2019) used a panel vector autoregression (PVAR) model to investigate the relationship between financial openness, both renewable and conventional energy use, CO2 emissions, and economic growth in Latin American countries. The established body of economic literature emphasizes innovation and technological advancements as key drivers of economic growthNumerous research endeavours have underscored technological innovation as a pivotal catalyst for economic advancement (Wong et al., 2005; Maradana et al., 2017). There is abundant and coherent evidence available that substantiates the idea that innovation plays a crucial role in driving economic progress (Avila-Lopez et al., 2019; Cantner et al., 2019; Thompson, 2018). Wide-ranging pragmatic investigations underscore the role of innovation in fostering development, often yielding significant ancillary effects. Throughout the study period from 2000 to 2016, the phenomenon of innovation has been acknowledged as the principal driver of economic advancement in developing countries (Sasana and Ghozali, 2017). Both developed and emerging economies are anticipated to shift towards innovative models as they pursue sustainable pathways for economic expansion. The correlation between export diversification and economic growth has attracted considerable interest from academics and policymakers in developing nations. Understanding the factors that influence economic growth has long been a central theme in development studies. Numerous studies have explored the potential impact of economic diversification on a country's growth trajectory (Ali et al., 2022; Lee & Zhang, 2022; Young, 2022). To examine the correlation between economic diversification and economic growth, econometric models are employed. These models quantify the relationship between the IV (diversification) and the DV (economic growth). The measures of economic growth include Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and per capita GDP, while export diversification serves as a common measure of economic diversity. Additionally, these models can incorporate various control variables to account for other influencing factors (Le et al., 2020; Mania & Rieber, 2019). However, there is still inadequate knowledge of all of the essential elements perceived in shifting towards entirely renewable energy sources. This study aims to delve into the intricate interplay between these variables and their collective impact on economic growth, focusing on the E-7 nations. Previous studies have not definitively established a correlation between these factors. As a result, further inquiry into the causal relationship between renewable energy usage and economic advancement is required. Technological innovation stands out as a pivotal element in sustainable economic development, as indicated by various (Rasool et al., 2022; Pradhan et al., 2018; Murad et al., 2019; Anderson et al., 2017; Beneki et al., 2012; Kihombo et al., 2021; Szabo & Herman, 2012). Furthermore, the data shows no clear consensus on this relationship, particularly among the E-7 countries. Our study specifically delves into the link between economic growth and technological innovation in E-7 nations. This research examines the effect of renewable energy consumption, technological advancement, and export diversification on economic development in E-7 nations from 1990 to 2022, given their growing importance to the world economy. It distinguishes itself from previous research in several ways. Firstly, it assesses whether these variables contribute to economic growth for a panel of emerging seven economies such as Brazil, China, Indonesia, India, Mexico, Russia, and Turkey, considering their rapid expansion in these areas. Secondly, it benefits from greater data availability and employs dynamic panel data analysis, allowing for analysis across more countries, variables, and periods. Thirdly, it favours the use of panel data methods for pragmatic investigation. Previous research on the relationship between renewable energy consumption, technological innovation, export diversification, and economic growth has faced challenges with empirical approaches due to the limited availability of annual data, which restricts the number of observations. As a result, panel data approaches are judged appropriate for more reliable and consistent parameter estimation. Therefore, to investigate the cointegration relationship among variables, this study uses the Westerlund panel cointegration test. The long-term impact of export diversification, technical advancement, and renewable energy consumption on economic growth is then ascertained using the PMG-ARDL approach. The robustness of the PMG-ARDL conclusions is then confirmed through the application of fully modified (FMOLS) and DOLS approaches. Fourth, the panel DHL test is employed in this study to investigate the causal link between variables. Additionally, no previous studies have examined the connections between renewable energy consumption, technological innovation, economic growth and export diversification together. Consequently, this study is the first to integrate these factors, as well as other crucial independent variables such as the financial sector and trade openness, into a PMG-ARDL model. Moreover, the authors argue that these variables in E-7 economies have not received enough attention in research. Therefore, this study addresses the gap in the literature regarding the relationship between renewable energy consumption, technological innovation, export diversification, and economic growth in E-7 economies. Based on these discussions, the research objectives are as follows: Firstly, to understand the impact of renewable energy consumption, technological innovation, and export diversification on economic growth in E-7 countries from 1990 to 2022. Secondly, to determine the main driver of economic growth in these nations. The following research questions (RQ) are proposed based on previous studies:
RQ1: Does renewable energy consumption contribute to economic growth in E-7 countries?
RQ2: How does enhancing technological innovation impact economic growth in E-7 countries?
RQ3: What is the relationship between export diversification and economic growth in E-7 countries?
Our empirical findings affirm that renewable energy consumption, technological innovation, and export diversification positively influence economic growth. Moreover, the study reveals a unidirectional causality between foreign direct investment (FDI) and economic growth. These results offer valuable insights for economic policymakers, aiding in informed decision-making. Furthermore, they address gaps in understanding, assisting policymakers of E-7 nations in overcoming barriers to renewable energy consumption, technological innovation, and export diversification, thereby fostering sustainable development.
The structure of the study is outlined as follows: The second step reviews relevant literature on the interaction between renewable energy consumption, technological innovation, export diversification, and economic growth. The third step provides a theoretical overview of the study. Next, the fourth step explains the data sources and the estimation of econometric models. The empirical findings and discussion section presents the explanation of the results. Finally, the concluding section summarizes the implications of the study for policy.
2. Review of Literature
In recent decades, there has been a strong emphasis on understanding the link between renewable energy consumption, technological advancement, export diversification, and economic growth. Numerous studies have investigated this association in different regions, using various economic methods and variables. However, research on the economic dynamics within the E-7 countries, which could have global economic implications, has been limited. As a result, the purpose of this study is to critically analyse the available literature on the relationship between renewable energy consumption, technological advancement, export diversification, and economic growth in this particular setting.
2.1. Nexus Between Renewable Energy Consumption and Economic Growth
Scholars have investigated the connection between economic growth and the use of renewable energy sources. For instance, (Konuk et al. 2021) used panel data from 1970 to 2017 to examine the relationship between the use of biomass energy and economic development in N-11 countries. Their study suggests a beneficial association between economic growth and the utilization of biomass energy in the long term. Similarly, (Jenniches 2018) focused on evaluating the regional economic consequences of transitioning towards renewable energy generation, stressing the significance of clearly defining technologies and assessment periods. (Doytch and Narayan 2021) conducted a study to assess the impact of both renewable and non-renewable energy consumption on the expansion of manufacturing and service sectors. Their results indicate that renewable energy fosters growth in dynamic sectors, such as the services industry in developed economies and the manufacturing sector in middle-income countries. (Acheampong et al., 2021) delved into how renewable energy use, CO2 emissions, and economic development are connected across 45 sub-Saharan African countries from 1960 to 2017. Using the GMM-PVAR approach, they found a relationship between economic growth and the adoption of renewable energy. (Kahia et al. 2022) analysis of a machine learning process to examine the relationship between disaggregated energy consumption, economic growth, and environmental degradation. The studies suggest that to ensure stable economic growth, a decrease in CO2 emissions must be accompanied by an increased utilization of renewable energies. In another study, (Ugur and Sari, 2003) explored how energy consumption affects economic indicators in the top 10 emerging economies and G7 nations. They revealed influence in Argentina, where both GDP and energy consumption influence each other. Additionally, they found that in Korea and Italy, GDP drives energy consumption, while in Turkey, France, Germany, and Japan, energy consumption drives GDP. They also pointed out that countries like Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, Uruguay, and Venezuela have been slow in incorporating renewable energy into their energy mix. Furthermore, during periods of reservoir shortage in these countries, (Koengkan et al., 2020) identified a dynamic link between renewable energy consumption and fossil fuel usage. Conversely, energy conservation measures may lead to economic growth slowdown in four other nations, as suggested by (Soytas and Sari 2003). In various OECD nations, (Ivanovski, et al., 2021) found a strong correlation between increasing economic activity and the use of non-renewable energy. Conversely, a study conducted by Zebra et al. (2021) examined hybrid renewable energy systems (HRES) in underdeveloped countries. They pointed out that Asian developing countries seem to be doing better than their African counterparts when it comes to maintaining and improving the productivity of both renewable and non-renewable mini-grids. Plus, they foresee a continuous drop in the costs of mini-grids, which should make renewable sources more competitive on a larger scale. They highlighted how factors like technology, social factors, and regulations can put the brakes on renewable energy development, though economic constraints surprisingly don't have a direct impact. In certain countries, they found that adopting renewable energy doesn't necessarily hinder or significantly boost economic development. (Islam, et al., 2022) examined the effect of rising incomes on the use of non-renewable and renewable energy sources in their study. Their research uncovered a complex relationship in which income growth occasionally encourages rising renewable energy usage but occasionally has little or no effect. Some industrialized nations still prefer fossil fuel consumption over renewable energy for economic development (Shrinkhal, 2019; Islam et al., 2021; Kahia, et al. 2019; Charfeddine & Kahia 2019). This is at the cost of the environment (Doytch and Narayan, 2016). Renewable energy may have little impact on economic development in industrialised countries, however, the share of renewable energy in total energy use is increasing in some EU countries, regardless of economic conditions (Ogonowski, 2021). The cost of entirely switching to renewable energy is not feasible for South Korea (Park et al., 2016). However, Chinese investments in renewable energy projects in sub-Saharan Africa could bring economic benefits to the region, such as job opportunities, production boosts, and stronger local ties (Lema et al., 2021). A study in Kenya found that a majority of people are in favour of renewable energy and believe it will save them money on electricity bills (Oluoch et al., 2020). These results point to a positive relationship between the use of renewable energy and economic expansion. Based on this understanding, Hypothesis 1 is formulated for the present study:
HI: Renewable energy consumption affects economic growth in E-7 countries.
2.2. The Connection Between Technological Advancement and Economic Growth
In the early days, macroeconomic growth theories primarily focused on capital and labour, almost disregarding technology. However, the work of Romer (1986) and Lucas (1988) has revealed that technology is an integral part of the production process. With the emergence of endogenous growth models, researchers have explored the impact of technological innovation on economic growth. Numerous studies have indicated that innovation drives economic expansion. For example, Santra (2017) found a clear link between embracing innovation and flourishing economies in BRICS nations. Avila-Lopez et al. (2019) revealed a positive connection between technological progress and economic growth in Latin American nations. Maradana et al. (2017) examined 19 European nations and highlighted a strong correlation between innovation and economic development. Their work shed light on the complex causal links between innovation and growth.
Hu and Png (2013) analysed manufacturing data from 72 countries to understand how patent rights affect economic prosperity. They discovered that quicker growth was linked to stronger patent rights, especially in countries with higher incomes and industries with a high patent concentration. Hasan and Tucci (2010) investigated the impact of technological innovation on economic growth in 58 different countries. They demonstrated the positive connection between economic development and patent quality and stressed the significance of strong patent regimes in promoting faster growth. Kahia et al. (2023) revealed that Saudi Arabia acknowledges the need to shift its economy towards energy-intensive industries and services, while also promoting the development of high technology. The literature consistently indicates a favourable correlation between the variables, resulting in the following hypothesis:
Hypothesis 2: Higher technological innovation leads to higher economic growth in E-7 countries.
2.3. Nexus Between Export Diversification and Economic Growth
The literature on export diversification lacks a consistent definition. This definition is based on how diversification is measured. For example, Balavac (2012) employed concentration indices to determine how diverse a country's exports are. These indices show whether a country's export revenues are predominantly derived from a few products (showing export concentration) or are distributed more evenly across a range of goods (representing export diversification). A diverse economy goes through structural transformation and has multiple revenue streams, allowing for long-term growth and development. This diversification and expansion provide the stability, security, and dependability that emerging countries require rather than relying largely on the production of primary goods, which is typically unpredictable and vulnerable to fluctuations (Abu Wadi and Bashayreh, 2018). Jednak et al. (2016) investigated the effects of economic diversification on Serbia's development from 2007 to 2012. They discovered that the structure and diversification of economic activities promote economic growth and development. Esu and Udonwa (2015) investigated the impact of diversifying Nigeria's economy using time series data from 1980 to 2011. The findings demonstrated that Nigeria could achieve long-term gains through diversification by encouraging large-scale industrialization in the non-oil sector, emphasising the use of technology in all trade and investment discussions, and maintaining recent improvements in the agricultural sub-sector, among other factors. Ayeni (2013) studied how tourism could help diversify Nigeria's economy. Using a linear model and multivariate regression analysis, he concluded that tourism would significantly boost the Nigerian economy. Gozgor and Can (2016) used system-GMM estimations to assess the effects of the Theil index, extensive margin, and intensive margin on real GDP per capita in 158 countries. They discovered that export diversification boosts real GDP per capita in low-income nations. McIntyre et al. (2018) investigated economic diversification through exports for 34 small nations from 1990 to 2015. The study discovered that more diversified countries had fewer production swings and greater average growth than most other small countries.
Conversely, (Al-Marhubi, 2000) conducted a comparative analysis of export diversification benefits across developed and developing countries, finding a positive correlation between export diversification and economic growth, particularly for developing nations. (Onodugo et al., 2013) evaluated the relationship between non-oil exports and economic growth in Nigeria, finding a modest and negligible contribution. (Hamed et al. 2014) found a positive association between exports and foreign direct investment (FDI) in terms of economic growth. (Adewuyi and Arawomo 2016) investigated export diversification patterns in Nigeria amidst market price fluctuations, identifying key factors influencing export earnings variability, and offering insights for policymakers aiming to bolster export stability. The literature assessment reveals differing viewpoints on the relationship between export diversification and economic growth. Some research indicates a favourable correlation, whereas others do not. As a result of the preceding observations, the following hypothesis is proposed:
Hypothesis 3: Export diversification impacts economic growth in E-7 countries.
Previous research has mostly focused on the impact of renewable energy consumption, technological advancement, and export variety on economic growth on a national scale. Thus, there is a considerable research vacuum in determining the impact of renewable energy consumption, innovation in technology, and export diversification on economic growth in E-7 countries. This inconsistency presents a challenge for stakeholders aiming to develop effective economic strategies relating to these 7 economies. Further the
Furthermore, the use of novel econometric methods such as cross-sectional dependence, panel unit root test, panel cointegration, robustness tests FMOLS and DOLS, and DHL causality testing remains limited in the current literature. As a result, this study seeks to fill this gap by studying the linkages between renewable energy usage, technological innovation, export diversification, and economic growth, with a focus on E-7 countries.
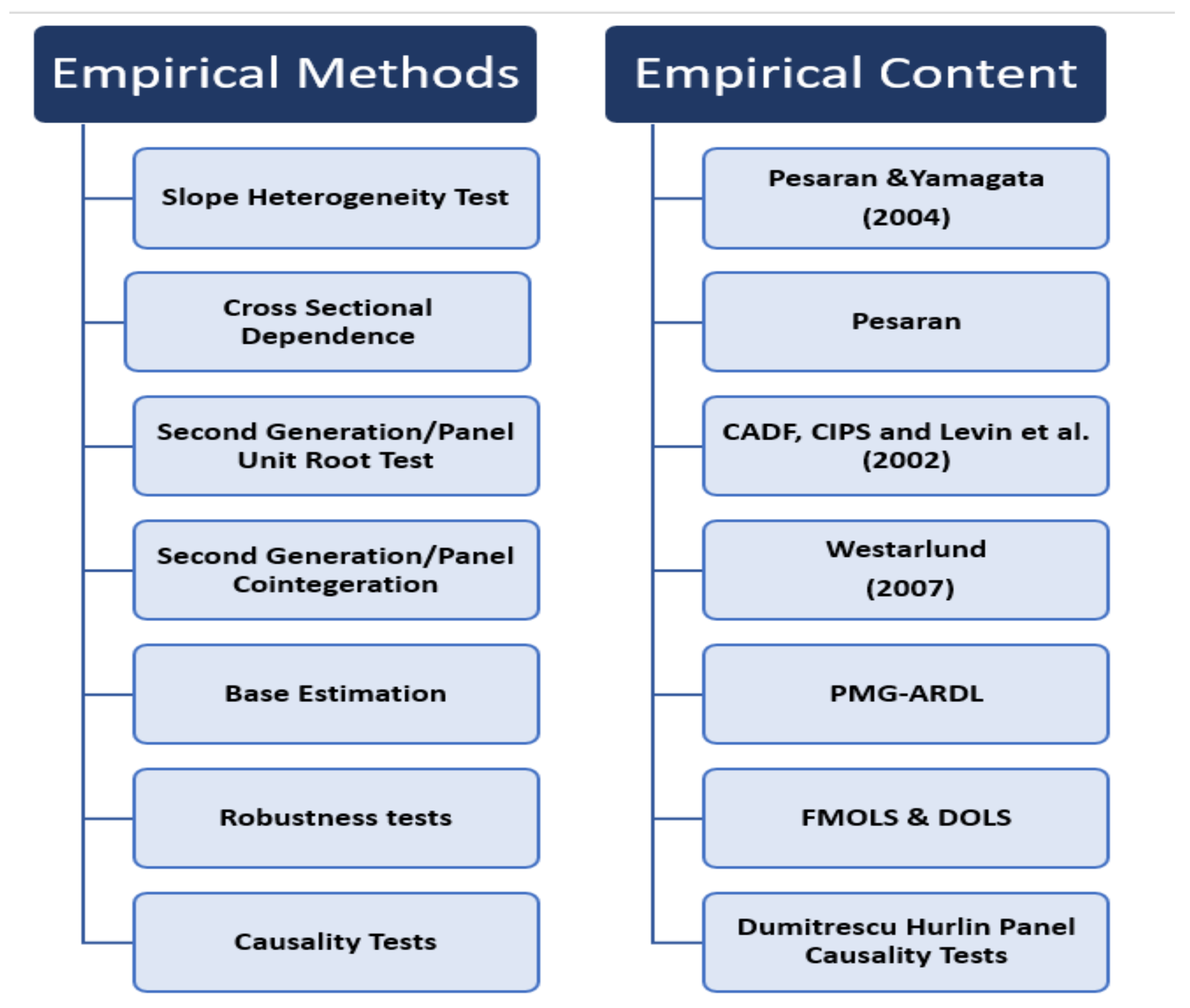
3. Data and Methodology
This study investigates how renewable energy consumption, innovation in technology, and export diversification affect economic growth in seven emerging countries: Brazil, China, Indonesia, India, Mexico, Russia, and Turkey. The study uses data from the World Bank and World Development Indicator (WDI 2023) for the period from 1990 to 2022, focusing on the most recent available data. Renewable energy consumption, technical innovation, and export diversification are among the independent variables examined, while control variables such as the financial sector and trade openness are also taken into account. GDP is the dependent variable. The study employs a deductive research approach and uses secondary data sources to examine the endogenous growth theory and other explanatory variables. Hypotheses are formulated based on the theory, and relevant data are collected accordingly. To reach correct findings on the effects of efficient economic policies, a variety of econometric techniques are used, including cross-sectional dependency, panel cointegration, PMG-ARDL, FMOLS, DOLS, and DHL causality tests. The study builds on previous research conducted by Mohanty and Sethi 2021) and Iqbal et al. (2022).
Table 1 summarises the variables, including their symbols, measurement units, data sources, and expected effects on economic development.
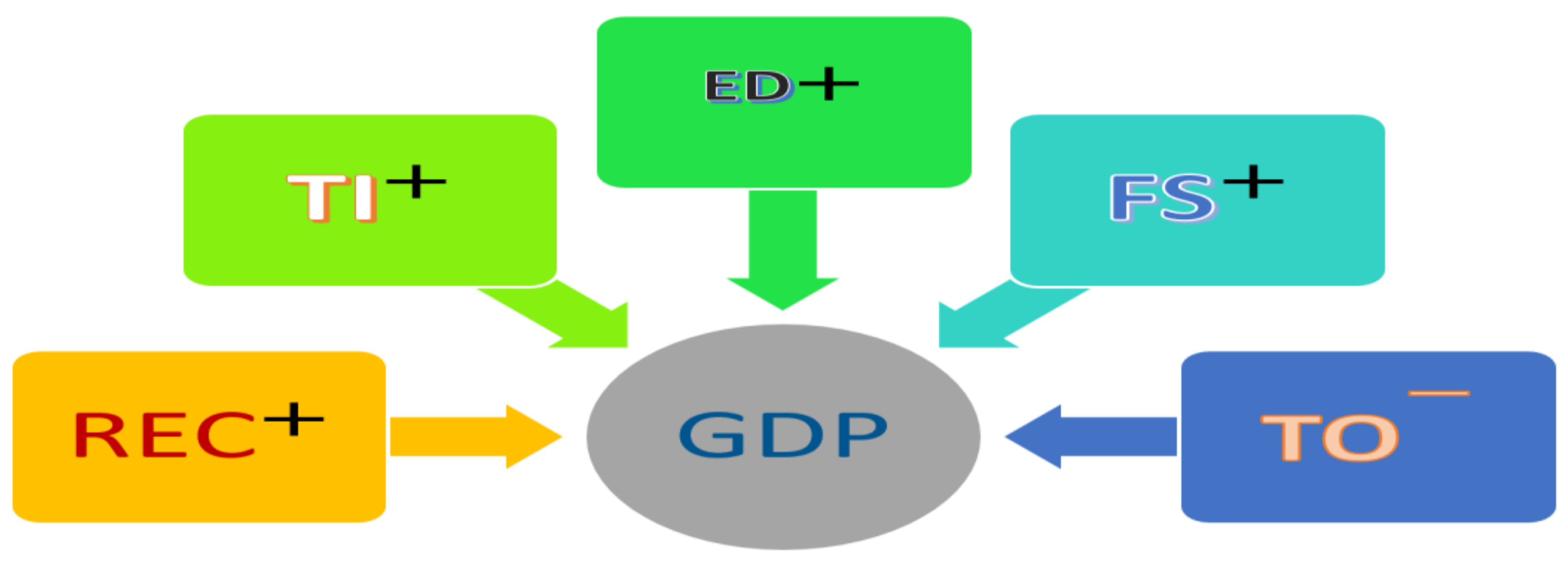
Figure 1 depicts the study's theoretical framework, whereas
Figure 2 and
Figure 3 show trend and boxplot analyses of the variables.
3.1. Model Specifications
The model is based on prior research findings (Saidi and Hammami 2017; Dinh et al. 2019; Sahoo and Sethi 2020; Yusuf et al. 2020; Ali et al. 2022; Iqbal et al. 2022). GDP was the dependent variable in this study, while the explanatory factors included R.E.C., T.I., E.D., F.S., and T.O. The following shows a representation of the basic regression model:
The authors opted to transform all variables into logarithmic form for this study. To make the comprehension of the estimated outcomes easier, this approach was chosen. Natural logarithms are used in the following conversion of the basic regression model:
In this equation, we use various variables to represent different aspects. The variable "t" represents the time period, "i" represents the country, and "LNGDP" is the natural logarithm of GDP, which serves as a proxy for economic growth. Similarly, "LNREC" represents the natural logarithm of renewable energy consumption, measured as a percentage of total final energy consumption. "LNTI" signifies the natural logarithm of technological innovation, which is calculated by summing up residents' patent applications. "LNED" represents the natural logarithm of exports of goods and services, also as a percentage of GDP. "LNFS" indicates the natural logarithm of domestic credit to the private sector by banks, as a percentage of GDP. "LNTO" depicts the natural logarithm of trade as a percentage of GDP. Lastly, "ε" represents the error term.
3.2. Methods of Estimation
We use the panel data technique for empirical analysis since prior research on the relationship between renewable energy consumption, technological innovation, export diversification, the financial sector, trade openness, and economic growth has weaknesses in its empirical methodology. Because statistics on renewable energy, innovations in technology, export diversification, the financial sector, and trade openness are collected every year, the number of observations is restricted, limiting the period. As a result, the panel data approach is appropriate for empirical analysis since it allows for more accurate and consistent parameter estimates. Hence, in this study, we employed the panel data methodology on panel data from E-7 countries and followed a systematic procedure consisting of five steps to empirically assess Eq. (2).
3.3. The Slope Homogeneity Test
The issue of varying slopes is important in panel data econometrics. We address this by using a method introduced by Pesaran and Yamagata (2008). This method allows us to assess the variation in weighted slopes for each entity, providing insights into slope heterogeneity. The test results are derived using specific equations.
3.4. The Cross-Section Dependence Test
To assess cross-sectional dependence, we utilized the CD test (Pesaran, 2015). The test statistics are presented as follows:
3.5. Panel Unit Root Test
Traditional unit root tests used in econometrics include the Augmented Dickey-Fuller (ADF), Phillips-Perron, Breitung, Maddala, and Hadri tests. However, these tests may not be appropriate for dealing with cross-sectional dependence (CSD) and slope heterogeneity (SH) in the data. These issues can impact the reliability of the results obtained from these traditional tests. To address these issues, Pesaran (2007) devised an improved unit root test known as the Cross-Sectional Augmented Dickey-Fuller (CADF) and Cross-Sectional (CIPS) test. These advanced methods are specifically developed to evaluate the stationarity of variables in panel data, even when there is cross-sectional dependency and slope heterogeneity. Equation (5) plays a crucial role in the CIPS test, as it involves calculating the cross-sectional mean of "ti." This means the calculation is an essential component of the CIPS test technique, as it aids in determining variable stationarity while addressing cross-sectional dependence and slope heterogeneity.
The Cross-Sectional Augmented Dickey-Fuller (CADF) test is widely used in academia to address concerns like cross-sectional dependence (CSD) and heterogeneity. This method begins with a unit-root test to generate its initial hypothesis. If the test results show that the variable is stationary at I (I), a cointegration test is performed before proceeding with parameter estimation. The CADF method is used to generate the data needed for the CIPS test. Additionally, Equation (6) for CADF, which stands for Cross-Augmented Dickey-Fuller, can be represented as follows:
This equation serves as the basis for the Cross-Sectional Augmented Dickey-Fuller Test method. It allows researchers to calculate the necessary statistics required for the CIPS test. This equation uses Yt-1 and ΔYit-1 to represent the level (I(0)) and first difference (I(I)) of each cross-sectional series.
3.6. Co-integration Test
Investigating cointegration is important in econometric research because many economic theories involve long-term implications. This study seeks to determine whether there is a long-term relationship between integrated series. To address the issue of cross-sectional dependency, we utilize the method proposed by Pesaran and Yamagata (2008), which is known for its robust and reliable results, as endorsed by Pesaran (2015). Westerlund's (2007) cointegration test outperforms previous tests in terms of cross-sectional dependence. This test has the distinct advantage of employing the bootstrap approach, which is very helpful in addressing cross-sectional dependence.
Pesaran and Yamagata (2008) created a second-generation technique with four equations (Eqs. 7, 8, 9, and 10). It serves as the foundation for cointegration analysis in circumstances when panel data has complicated properties like cross-sectional dependence, heterogeneity, and non-stationarity.
In the field of statistical analysis for panel data, there are several forms of group means statistics designated as Gt and Ga, as well as panel means statistics represented by Pt and Pa. Each of these statistical measures has a specific function and is abbreviated accordingly. When assuming that the model variables are independent, often referred to as the "null" hypothesis, and the alternative hypothesis suggests the presence of co-integration among the variables, test statistics are calculated for this purpose These statistics aid in determining whether the data supports the presence of co-integrating relationships or the null hypothesis that no relationship exists between the variables. Essentially, these statistics are crucial for assessing the strength and significance of potential co-integration among the variables under study.
In this study, the robustness of the estimation results obtained using the PMG-ARDL approach was tested using FMOLS and DOLS tests. Additionally, panel causality testing was performed to investigate the causal links between the variables. The DHC test, a variant of the Granger causality test created especially for heterogeneous panel datasets with fixed coefficients, was used for this purpose (Ahmed et al., 2022). According to Dumitrescu and Hurlin (2012), the DHC test uses the Wbar test to determine the mean and the Zbar test to evaluate the normal distribution. It is shown by the equation that follows:
In this case, represents the autoregressive parameters where j represents the lag length.
For this test, the following are the alternative and null hypotheses:
Unidirectionally causality
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Descriptive Statistics on Study Variables
For the variables in our investigation,
Table 2 shows the values of the mean, maximum, minimum, and standard deviation. To simplify the dataset and ensure consistent and reliable results, we chose to use the logarithmic form for all variables. For LNGDP, the average value is 1.33 per cent with a standard deviation of 0.91 per cent, and the maximum value is 2.65 per cent. This implies a continuous growth pattern among the E-7 economies, with minimal difference amongst the nations investigated. LNREC has a mean of 2.93 per cent, a standard deviation of 0.88 per cent, and a maximum of 4.08 per cent. This demonstrates an emphasis on biogas services to boost overall economic strength. LNED has an average value of 3.04 per cent, a standard deviation of 0.42 per cent, and a maximum of 4.13 per cent. The higher maximum and minimum values suggest a gap in export diversification among the E-7 countries, emphasizing the need for increased trade activities to stimulate economic growth. LNTI has an average value of 8.24%, a standard deviation of 2.24%, and a maximum value of 14.17%. This reveals a considerable innovation gap across the E-7 countries, emphasising the significance of boosting innovation to promote economic growth. LNFS has an average of 1.52%, a standard deviation of 0.73%, and a maximum of 2.65%. Finally, LNTO has a mean value of 3.73 per cent, a standard deviation of 0.73 per cent, and a maximum value of 4.70 per cent, illustrating the favourable impact of trade openness on economic growth. Among all variables, technological innovation exhibits the highest standard deviation (2.24 per cent), indicating greater variability, while trade openness has the lowest standard deviation (0.8 per cent), suggesting more stability in its measurements.
4.2. Correlation Between Variables
Table 2 shows the correlation between variables as numerical values that indicate their relationships. The correlation coefficient between gross domestic product (LNGDP) and renewable energy consumption (LNREC) is 0.22. For technological innovation (LNTI) and gross domestic product (LNGDP), it is 0.04. The correlation coefficient between export diversification (LNED) and gross domestic product (LNGDP) is 0.07, while for the financial sector (LNFS) and gross domestic product (LNGDP), it is 0.61. The correlation coefficient between trade openness (LNTO) and gross domestic product (LGDP) is 0.08.
A correlation below -0.01 or close to 0 suggests a weak correlation. Specifically, the correlation between trade openness (LNTO), export diversification, and technological innovation (TO) is 0.08, 0.07, and 0.04, respectively.
In this research, we analyse cross-sectional dependence among a group of E-7 emerging economies using all six CD tests. Additionally, (Breitung, 2005) investigated the possibility of misleading estimates resulting from the assumption of "slope homogeneity" when the data includes slope heterogeneity. To solve this issue, we use the slope homogeneity test given by Pesaran and Yamagata (2008).
Table 3's results show that the null hypothesis of slope homogeneity was rejected at the 1% significance level, showing the presence of slope heterogeneity in the datasets.
Table 4 provides a summary of cross-sectional dependence (CSD) testing. To achieve proper regression analysis, Chudik and Pesaran (2015) advocate examining cross-sectional dependencies with classic unit root tests. More recent studies, such as those by Breusch and Pagan (1980), have highlighted the bias in infinite-sample adjustments, as addressed by Pesaran et al. (2008). Pesaran (2015) conducted a CD test on cross-sectional dependence, confirming its presence in the panel data. As such, it is imperative to use an approach that takes into account the cross-sectional dependency and slope heterogeneity in panel data. We will use second-generation panel unit root tests to address this, more precisely cointegration techniques recommended by Pesaran (2007), Levin et al. (2002), and Pesaran (2015).
The next step in this research involves confirming the correct order of steps for integrating multiple datasets.
Table 5 displays the outcomes of the CIPS, CADF, and Levin panel unit root tests. The results indicate that certain variables exhibit stationarity at the level, denoted as I (0), while others demonstrate stationarity in first differences, indicating first-order integration, denoted as I (1). Given the mixed integration characteristics of the variables, we employ both the linear and nonlinear ARDL cointegration methods.
After doing panel unit root tests, the next step is to see if the variables have a long-term co-integration connection. The results of the co-integration assessments, using the methodology proposed by Westerlund (2007), have been presented in
Table 6.
Table 6 shows that statistics reject the non-cointegration hypothesis more frequently at the panel level than at the individual level, demonstrating the presence of a long-term link between two or more variables. Once long-term cointegration among variables is confirmed, the next step is to assess the long-term impact of the selected variables. To do this, the PMG-ARDL approach is used to calculate the long-term effects of renewable energy consumption, innovations in technology, export diversification, the financial sector, and trade openness on economic growth. The selection of the PMG-ARDL estimator is motivated by the limited sample size, as it provides consistent and reliable estimates. The findings resulting from the PMG-ARDL analysis can be found in
Table 7.
4.3. Pooled Mean Group Autoregressive Distributed Lag (PMG- ARDL) Analysis
The results are presented in
Table 7, which shows that renewable energy consumption (LNREC) has a significant positive impact on economic growth at the 1% significance level. This suggests that as renewable energy consumption rises, so will economic growth. The coefficient estimates of 0.71 indicate that for every 1% increase in renewable energy consumption, economic growth is predicted to increase by 0.71%. This underscores the significance of implementing flexible and cost-effective policies to promote renewable energy consumption in E-7 countries, particularly in light of climate change and global warming concerns. Renewable energy not only offers an appealing alternative to fossil fuels but also holds the potential to curb CO2 emissions and support economic development. Kahia et al. (2019) and Charfeddine and Kahia (2019) conducted a study on renewable energy. Their research highlights the potential for countries to mitigate the impacts of climate change by shifting away from carbon-intensive development models. Emphasising the importance of renewable energy sources, like as solar and wind power, can help MENA countries reduce their dependency on fossil fuels while stimulating economic growth. However, technological innovation plays a crucial role in boosting economic growth. The positive coefficient confirms that advancements in technology drive national economic development. Based on the estimated coefficient of 0.07, each additional per cent of technological innovation is projected to increase economic growth by 0.07%. This highlights the importance of E-7 nations giving priority to technological innovation to accelerate economic development, as previous studies have also found a positive correlation between the two. These results confirm the conclusions of studies by Thompson (2018), Cantner et al. (2019), Iqbal et al. (2022), Santra (2017), and others, which show a positive correlation between economic growth and innovations in technology. Moreover, the positive coefficient for export diversification (ED) suggests that as the value of export diversification increases, economic growth also rises. The magnitude of 2.12 indicates that for each additional percentage of export diversification, economic development is estimated to increase by 2.12%. This underscores the importance of promoting export diversification strategies to stimulate economic growth in E-7 countries. These results are consistent with other studies by Sadorsky (2012), Jednak et al. (2016), and McIntyre et al. (2018), which highlight the positive connection between economic growth and export diversification. Based on the findings, it is clear that E-7 countries have to remove barriers to foreign trade to attain better levels of economic growth. Policymakers should implement favourable policies that stimulate export diversification, which in turn facilitates and encourages technological innovation within these nations. Furthermore, governments of E-7 countries should formulate policies that provide incentives for economic growth through export diversification, the acceptance of renewable energy sources, and the promotion of technological innovation. Regarding the control variable in the long run, the financial sector (FS) demonstrates a positive albeit insignificant relationship with economic growth. However, it is important to recognise the financial sector's key role in mobilising and distributing savings for productive initiatives, particularly in developing economies. These studies suggest that the E-7 countries have not made significant progress in terms of financial sector development. According to a similar study conducted by Charfeddine and Kahia (2019), financial development and the renewable energy sectors in MENA countries continue to make minimal contributions to enhancing environmental quality and economic growth. The findings show that an increase of 1% in financial sector development (FSD) corresponds to a 0.10% rise in economic growth. This empirical result is consistent with similar research undertaken in other economic circumstances, including Gautam (2015), Paudel and Acharya (2020), Shahbaz and Rahman (2012), and Thangavelu et al. (2004). However, trade openness has a negative and statistically significant influence on economic growth in the E-7 countries. This finding contradicts previous research, specifically that undertaken by Bastola and Sapkota (2015) on trade dynamics. It appears that trade is not the key driver of economic progress in these countries. The results of the PMG-ARDL analysis indicate a strong connection between long-term economic growth and renewable energy consumption, technological innovation, and export diversification. Additionally, energy consumption has a notable influence on short-term economic growth. On the other hand, the effect of technological innovation and trade openness on short-term economic growth is determined to be insignificant. Similarly, (Alomari & Bashayreh, 2020) found that PMG-ARDL models show a strong positive long-run link between export diversification and real GDP growth, but no significant impact of export diversification in the short run. Instead, variables like renewable energy consumption, innovation in technology, and export diversification are more significant in supporting economic growth. These results have been validated by Ali and Malik (2017), Iqbal et al. (2022), Nistor (2014), Rao et al. (2020), and Yusuf et al. (2020).
After studying the results of FMOLS and DOLS, it was shown that there is a positive association between renewable energy consumption (REC) and economic growth (GDP). A 1% increase in REC corresponds to a 0.20-0.25% increase in GDP. These findings are consistent with the results of the PMG-ARDL analysis.
The FMOLS data show that technological innovation (TI) has a significant positive influence on EG at the 1% level of significance. This observation is backed by the DOLS results. Furthermore, the FMOLS estimator results show that export diversification (ED) has a positive and statistically significant impact on EG. Furthermore, both FMOLS and DOLS results emphasise the positive and highly significant effect of financial sector development (FS) on GDP.
On the other hand, the PMG-ARDL analysis reveals a negative and significant relationship between trade openness (TO) and EG at a 5% level of significance, as indicated by the FMOLS results. However, the DOLS results suggest that the relationship between TO and GDP is negative but not statistically significant.
5. Panel Causality Test Results
The DHC test, which is based on the Granger causality test, can be used to assess both linear and nonlinear causal links. Its objective is to determine causation between series. The DHC test results are reported in
Table 9.
Table 9 shows that the TI series has a unidirectional causality relationship with the GDP series. Technological advancements and the adoption of innovations into economic growth are beneficial to economic development. These findings are congruent with those obtained by Maradana et al. (2022), who also found a unidirectional causality association between TI and economic growth in 19 European nations. Furthermore, our findings indicate a unidirectional causal link between ED and GDP. Hinlo and Arranguez (2017) observed similar results across ASEAN countries. Furthermore, while there is a one-way causality relationship between EF and trade openness, no causal relationship has been found between REC and GDP.
6. Conclusions and Policy Implications
This study investigates at the impact of renewable energy consumption, innovation in technology, and export diversification on economic growth in E-7 countries from 1990 to 2022. The dependent variable in the study is GDP, while the independent variables are renewable energy consumption, innovation in technology, and export diversification. Several tests, including CSD, CIPS, IPS, and CADF unit root tests, were used to evaluate cross-section dependency and series stationarity. The study also explores long-term relationships between variables through Westerlund residual co-integration tests. The PMG-ARDL approach is used to assess the long-term impact of renewable energy consumption, innovation in technology, and export diversification on economic growth. The DHL causality test is used to investigate causal directions among the variables. Key findings confirm a long-term association among the variables and indicate that renewable energy consumption, technological innovation, and export diversification have a significantly positive long-term impact on economic growth. The study also employs FMOLS and DOLS models, which yield consistent results. The DHL test indicates a unidirectional causal association between renewable energy consumption, innovation in technology, export diversification, the financial sector, and trade openness and economic growth. These findings offer valuable insights for economic policymakers in the E-7 countries. By eliminating obstacles to the adoption of renewable energy, fostering technological innovation, and diversifying exports, policymakers can effectively promote sustainable economic development.
Specifically, the study recommends promoting renewable energy consumption to positively contribute to economic growth and suggests that policymakers in E-7 economies should prioritize enhancing renewable energy consumption. The findings highlight the benefits of renewable energy sources in combating climate change and fostering environmental sustainability. Therefore, efforts should be focused on enhancing reliability and sustainability in the adoption of renewable energy technologies. In the context of emerging economies like the E-7 countries, it is crucial to prioritize technologically advanced and environmentally friendly solutions, especially in the environmental sector, to encourage clean, environmentally friendly, sustainable economic development. Furthermore, the positive effects of export diversification highlight how important exports are in the long run for economic growth, especially in the E-7 countries. Export diversification not only provides trade opportunities but also promotes domestic investment, job creation, and the transfer of advanced technology. Therefore, these countries should establish an investment-friendly environment, attract trade, and implement policies that encourage technological innovation. Governments should develop measures to stimulate economic growth through trade, renewable energy usage, and innovations in technology. It is crucial to highlight that this study only examines the E-7 countries; future research could look into similar dynamics in a larger spectrum of developing and emerging economies. Furthermore, this analysis ignores other issues such as corruption, R&D spending, carbon emissions, and infrastructure. Future studies could incorporate these variables to improve the analysis. Finally, while this study looks at the relationship between renewable energy use, innovation in technology, export diversification, and economic growth, future research could focus on related themes such as environmental quality.
References
- Aali Bujari, A., & Venegas Martínez, F. (2016). Technological innovation and economic growth in Latin America. Revista mexicana de economía y finanzas, 11(2), 77-89.
- Abu Wadi, R.M., Bashayreh, A. (2018), Economic diversification in Bahrain. International Journal of Economics and Financial Issues, 8(4), 120-125.
- Acheampong, A. O., Dzator, J., & Savage, D. A. (2021). Renewable energy, CO2 emissions and economic growth in sub-Saharan Africa: does institutional quality matter?. Journal of Policy Modeling, 43(5), 1070-1093.
- Adewuyi, A. O., & Arawomo, D. F. (2014). Export Diversification in the Context of Price Uncertainty: Empirical Analysis of Nigeria’s Case. The Nigerian Journal of Economics and Social Studies, 56(3), 419-443.
- Adewuyi, A.O. and Arawomo D.F. (2016). Export Diversification in the Context of Price Uncertainty: Empirical Analysis of Nigeria’s Case. The Nigerian Journal of Economic and Social Studies. 56(3) 419 – 443.
- Ahmed N, Sheikh AA, Hamid Z, Senkus P, Borda RC, Wysokińska-Senkus A, Glabiszewski W (2022) Exploring the causal relationship among green taxes, energy intensity, and energy consumption in nordic countries: Dumitrescu and Hurlin causality approach. Energies 15(14):5199. [CrossRef]
- Akcali BY, Sismanoglu E (2015) Innovation and the effect of research and development (R&D) expenditure on growth in some developing and developed countries. Procedia Soc Behav Sci 195:768–775.
- Ali N, Phoungthong K, Techato K, Ali W, Abbas S, Dhanraj JA, Khan A (2022) FDI, green innovation and environmental quality nexus: new insights from BRICS economies. Sustainability 14(4):2181.
- Al-Marhubi, F. (2000). Export diversification and growth: an empirical investigation. Applied economics letters, 7(9), 559-562.
- Al-Marhubi, F. (2018). Export diversification and growth: an empirical investigation, Applied Economics Letters 7: 559 – 562.
- Alomari, M. W., & Bashayreh, A. G. (2020). Modeling the exports diversification in the oil countries growth: The case of gulf cooperation council countries. International Journal of Energy Economics and Policy, 10(3), 119-129.
- Avila-Lopez LA, Lyu C, Lopez-Leyva S (2019) Innovation and growth: evidence from Latin American countries. J Appl Econ 22(1):287–303.
- Awodumi, O. B., & Adewuyi, A. O. (2020). The role of non-renewable energy consumption in economic growth and carbon emission: Evidence from oil producing economies in Africa. Energy Strategy Reviews, 27, 100434.
- Ayeni, D.A. (2013), Predicting the effects of economic diversification on sustainable tourism development in Nigeria. American Journal of Tourism Management, 2(1), 15-21.
- Balavac, M. (2012), Determinants of Export Diversification at the Export Margins: Reference to Transition Economies. In ETSG 2012 Annual Conference Paper.
- Cantner U, Dettmann E, Giebler A, Guenther J, Kristalova M (2019) The impact of innovation and innovation subsidies on economic development in German regions. Reg Stud 53(9):1284–1295.
- Cao, X., Kannaiah, D., Ye, L., Khan, J., Shabbir, M. S., Bilal, K., & Tabash, M. I. (2022). Does sustainable environmental agenda matter in the era of globalization? The relationship among financial development, energy consumption, and sustainable environmental-economic growth. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29(21), 30808-30818.
- Charfeddine, L., & Kahia, M. (2019). Impact of renewable energy consumption and financial development on CO2 emissions and economic growth in the MENA region: a panel vector autoregressive (PVAR) analysis. Renewable energy, 139, 198-213.
- Dinh TT-H, Vo DH, Nguyen TC (2019) Foreign direct investment and economic growth in the short run and long run: empirical evi dence from developing countries. Journal of Risk and Financial Management 12(4):176.
- Doytch, N., & Narayan, S. (2016). Does FDI influence renewable energy consumption? An analysis of sectoral FDI impact on renewable and non-renewable industrial energy consumption. Energy Economics, 54, 291-301.
- Doytch, N., & Narayan, S. (2021). Does transitioning towards renewable energy accelerate economic growth? An analysis of sectoral growth for a dynamic panel of countries. Energy, 235, 121290.
- Dumitrescu EI, Hurlin C (2012) Testing for Granger non-causality in heterogeneous panels. Econ Model 29(4):1450 1460. [CrossRef]
- Esu, G.E., Udonwa, U. (2015), Economic diversification and economic growth: Evidence from Nigeria. Journal of Economic and Sustainable Development, 6(16), 56-63.
- Feentra, R. and Kee H. (2018). Export variety and Country Productivity: estimating the monopolistic competition model with endogenous productivity. Journal of International Economics, 74(2), 500 – 516.
- Ferreira, G. F., & Harrison, R. W. (2012). From Coffee Beans to Microchips: Export Diversification and Economic Growth in Costa Rica. Journal of Agricultural and Applied Economics, 44(4), 517-531.
- Forgha, N.G., Sama M.C. and Atangana E.M. (2018). The Effects of Export Diversification on Economic Growth in Cameroon. International Invention Journal of Arts and Social Sciences. 1(3), 54 – 69.
- Fu, Q., Wang, J., Xiang, Y., Yasmeen, S., & Zou, B. (2022). Does financial development and renewable energy consumption impact on environmental quality: A new look at China’s economy. Frontiers in Psychology, 13, 905270.
- Gabr, E. M., and Mohamed, S. M. (2020). Energy Management Model to Minimize Fuel Consumption and Control Harmful Gas Emissions. Int. J. Energ Water Res. 4 (4), 453–463. [CrossRef]
- Garces, E., & Daim, T. U. (2012). Impact of renewable energy technology on the economic growth of the USA. Journal of the Knowledge Economy, 3, 233-249.
- Gozgor, G., Can, M. (2016), Effects of the product diversification of exports on income at different stages of economic development. Eurasian Business Review, 6(2), 215-235.
- Hamed, K., Hadi, D., & Hossein, K. (2014). Export diversification and economic growth in some selected developing countries. African Journal of Business Management, 8(17), 700-704.
- Hasan I, Tucci CL (2010) The innovation–economic growth nexus: global evidence. Res Policy 39(10):1264–1276.
- Hesse, H. (2009), Export Diversification and Economic Growth. The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development, Working Paper. Washington: The World Bank. p55-80.
- Hesse, H. (2009). Export diversification and economic growth. Breaking into new markets: emerging lessons for export diversification, 2009, 55-80.
- Hu AG (2015) Innovation and economic growth in East Asia: an over view. Asian Economic Policy Review 10(1):19–37.
- Hu AG, Png IP (2013) Patent rights and economic growth: evidence from cross-country panels of manufacturing industries. Oxford Economic Studys 65(3):675–698.
- Hu Y, Xiao J, Deng Y, Xiao Y, Wang S (2015) Domestic air passenger traffic and economic growth in China: Evidence from heterogeneous panel models. J Air Transp Manag 42:95–100.
- Iqbal A, Tang X, Rasool SF (2022) Investigating the nexus between CO2 emissions, renewable energy consumption, FDI, exports and economic growth: evidence from BRICS countries. Environment, Development and Sustainability 1–30.
- Iqbal, A., Tang, X., Jahangir, S., & Hussain, S. (2022). The dynamic nexus between air transport, technological innovation, FDI, and economic growth: evidence from BRICS-MT countries. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29(45), 68161-68178.
- Islam, M. M., Khan, M. K., Tareque, M., Jehan, N., & Dagar, V. (2021). Impact of globalization, foreign direct investment, and energy consumption on CO2 emissions in Bangladesh: Does institutional quality matter?. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(35), 48851-48871.
- Ivanovski, K., Hailemariam, A., & Smyth, R. (2021). The effect of renewable and non-renewable energy consumption on economic growth: Non-parametric evidence. Journal of Cleaner Production, 286, 124956.
- Jednak, S., Nikolic, D.M., Kragulj, D., Vujosevic, M. (2016), The effects of economic activities diversification on development: The perspective of Serbia. Industrija, 44(2), 23-42.
- Jenniches, S. (2018). Assessing the regional economic impacts of renewable energy sources–A literature review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 93, 35-51.
- Kahia, M., & Ben Jebli, M. (2021). Industrial growth, clean energy generation, and pollution: evidence from top ten industrial countries. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28, 68407-68416.
- Kahia, M., Ben Jebli, M., & Belloumi, M. (2019). Analysis of the impact of renewable energy consumption and economic growth on carbon dioxide emissions in 12 MENA countries. Clean Technologies and Environmental Policy, 21, 871-885.
- Kahia, M., Jarraya, B., Kahouli, B., & Omri, A. (2022). The role of environmental innovation and green energy deployment in environmental protection: Evidence from Saudi Arabia. Journal of the Knowledge Economy, 1-27.
- Kahia, M., Jarraya, B., Kahouli, B., & Omri, A. (2023). Do environmental innovation and green energy matter for environmental sustainability? Evidence from Saudi Arabia (1990–2018). Energies, 16(3), 1376.
- Kahia, M., Moulahi, T., Mahfoudhi, S., Boubaker, S., & Omri, A. (2022). A machine learning process for examining the linkage among disaggregated energy consumption, economic growth, and environmental degradation. Resources Policy, 79, 103-104.
- Kahia, M., Omri, A., & Jarraya, B. (2020). Does green energy complement economic growth for achieving environmental sustainability? evidence from Saudi Arabia. Sustainability, 13(1), 180.
- Koengkan, M., Fuinhas, J. A., & Santiago, R. (2020). The relationship between CO2 emissions, renewable and non-renewable energy consumption, economic growth, and urbanisation in the Southern Common Market. Journal of Environmental Economics and Policy, 9(4), 383-401.
- Koengkan, M., Fuinhas, J. A., and Marques, A. C. (2019). “The Relationship between Financial Openness, Renewable and Nonrenewable Energy Consumption, CO2 Emissions, and Economic Growth in the Latin American Countries: an Approach with a Panel Vector Auto Regression Model,” in The Extended Energy-Growth Nexus. Editors J A Fuinhas and A Marques (Cambridge: Academic Press), 199–229. [CrossRef]
- Konuk, F., Zeren, F., Akpınar, S., & Yıldız, Ş. (2021). Biomass energy consumption and economic growth: Further evidence from NEXT-11 countries. Energy Reports, 7, 4825-4832.
- Kugler, M. (2006). Does foreign investment facilitate exports? Evidence from Venezuelan manufacturing. Theoretical & Applied Economics, 23(3), 18-33.
- Lema, R., Bhamidipati, P. L., Gregersen, C., Hansen, U. E., and Kirchherr, J. (2021). China’s Investments in Renewable Energy in Africa: Creating Co-benefits or Just Cashing-in?World Development. World Develop. 141 (May), 105365. [CrossRef]
- Levin, A., Lin, C. F., & Chu, C. S. J. (2002). Unit root tests in panel data: asymptotic and finite-sample properties. Journal of econometrics, 108(1), 1-24.
- Maradana RP, Pradhan RP, Dash S, Gaurav K, Jayakumar M, Chat terjee D (2017) Does innovation promote economic growth? Evidence from European countries. J Innov Entrep 6(1):1–23.
- McIntyre, A., Li, M.X., Wang, K., Yun, H. (2018), Economic Benefits of Export Diversification in Small States. International Monetary Fund. Working Paper.
- Mohanty S, Sethi N (2021) The energy consumption-environmental quality nexus in BRICS countries: the role of outward foreign direct investment.
- Ogonowski, P. (2021). Application of VMCM, to Assess of Renewable Energy Impact in European Union Countries. Proced. Comput. Sci. 192, 4762–4769. [CrossRef]
- Oluoch, S., Lal, P., Susaeta, A., and Vedwan, N. (2020). Assessment of Public Awareness, Acceptance and Attitudes towards Renewable Energy in Kenya. Scientific Afr. 9 (September), e00512. [CrossRef]
- Omri, A., & Kahia, M. (2024). Environmental sustainability and health outcomes: Do ICT diffusion and technological innovation matter?. International Review of Economics & Finance, 89, 1-11.
- Onodugo, V. A., IKPE MARIUS, I. K. P. E., & Anowor, O. F. (2013). Non-oil export and economic growth in Nigeria: A time series econometric model. International Journal of Business Management & Research (IJBMR), 3(2).
- Osei-Assibey Bonsu, M., & Wang, Y. (2022). The triangular relationship between energy consumption, trade openness and economic growth: new empirical evidence. Cogent Economics & Finance, 10(1), 2140520.
- Park, S.-H., Jung, W.-J., Kim, T.-H., and Lee, S.-Y. T. (2016). Can Renewable Energy Replace Nuclear Power in Korea? an Economic Valuation Analysis. Nucl. Eng. Techn. 48 (2), 559–571. [CrossRef]
- Pesaran, M.H. (2007). A simple panel unit root test in the presence of cross-section dependence. Journal of applied econometrics, 22(2), 265-312.
- Pesaran, M.H. (2015). Testing weak cross-sectional dependence in large panels. Econometric reviews, 34(6-10), 1089-1117.
- Pesaran, M. H., & Yamagata, T. (2008). Testing slope homogeneity in large panels. Journal of econometrics, 142(1), 50-93.
- Pradhan RP, Arvin MB, Bahmani S (2018) Are innovation and financial development causative factors in economic growth? Evi dence from a panel granger causality test. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 132:130–142.
- Rasool SF, Chin T, Wang M, Asghar A, Khan A, Zhou L (2022) Exploring the role of organizational support, and critical suc cess factors on renewable energy projects of Pakistan. Energy 243:122765.
- Rasool SF, Samma M, Wang M, Zhao Y, Zhang Y (2019) How human resource management practices translate into sustainable organizational performance: the mediating role of product, process and knowledge innovation. Psychol Res Behav Manag 12:1009.
- Romer PM (1986) Increasing returns and long-run growth. J Polit Econ 94(5):1002–1037 Romer PM (1990) Endogenous technological change. J Polit Econ 98(5, Part 2): S71-S102.
- Sadorsky, P. (2012), Energy consumption, output and trade in South America. Energy Economics, 34(2), 476-488.
- Sahoo M, Sethi N (2021) The intermittent effects of renewable energy on ecological footprint: evidence from developing countries.
- Saidi S, Hammami S (2017) Modeling the causal linkages between transport, economic growth and environmental degradation for 75 countries. Transp Res Part d: Transp Environ 53:415–427.
- Santra S (2017) The effect of technological innovation on production-based energy and CO2 emission productivity: evidence from BRICS countries. Afr J Sci Technol Innov Dev 9(5):503–512.
- Sasana H, Ghozali I (2017) The impact of fossil and renewable energy consumption on the economic growth in Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa. International Journal of Energy Eco nomics and Policy 7(3):194–200.
- Sharma, R., Sinha, A., & Kautish, P. (2021). Examining the nexus between export diversification and environmental pollution: evidence from BRICS nations. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(43), 61732-61747.
- Shrinkhal, R. (2019). Economics, technology, and environmental protection: a critical analysis of phytomanagement. In Phytomanagement of polluted sites (pp. 569-580). Elsevier.
- Smolović, J. C., Muhadinović, M., Radonjić, M., and Đurašković, J. (2020). How Does Renewable Energy Consumption Affect Economic Growth in the Traditional and New Member States of the European Union? Energ. Rep. 6 (November), 505–513. [CrossRef]
- Soytas, U., & Sari, R. (2003). Energy consumption and GDP: causality relationship in G-7 countries and emerging markets. Energy economics, 25(1), 33-37.
- Sun, H., Clottey, S.A., Geng, Y., Fang, K., Amissah, J.C.K. (2019), Trade openness and carbon emissions: Evidence from belt and road countries. Sustainability, 11(9), 2682.
- Thompson M (2018) Social capital, innovation and economic growth. J Behav Exp Econ 73:46–52.
- Tutak, M., and Brodny, J. (2022). Renewable Energy Consumption in Economic Sectors in the EU-27. The Impact on Economics, Environment and Conventional Energy Sources. A 20-Year Perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 345 (April), 131076. [CrossRef]
- Wahab, S., Zhang, X., Safi, A., Wahab, Z., & Amin, M. (2021). Does energy productivity and technological innovation limit trade-adjusted carbon emissions?. Economic Research-Ekonomska Istraživanja, 34(1), 1896-1912.
- Westerlund, J. (2008). Panel cointegration tests of the Fisher effect. Journal of applied econometrics, 23(2), 193-233.
- Wong PK, Ho YP, Autio E (2005) Entrepreneurship, innovation and economic growth: evidence from GEM data. Small Bus Econ 24(3):335–350.
- Xiong, P.-p., Dang, Y.-g., Yao, T.-x., and Wang, Z.-x. (2014). Optimal Modeling and Forecasting of the Energy Consumption and Production in China. Energy 77, 623–634. [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, H. A., Shittu, W. O., Akanbi, S. B., Umar, H. M., & Abdulrahman, I. A. (2020). The role of foreign direct investment, financial development, democracy and political (in) stability on economic growth in West Africa. International Trade, Politics and Development, 4(1), 27-46.
- Zebra, E. I. C., van der Windt, H. J., Nhumaio, G., & Faaij, A. P. (2021). A review of hybrid renewable energy systems in mini-grids for off-grid electrification in developing countries. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 144, 111036.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).