1. Introduction
Heart transplantation remains the gold standard for End-Stage Heart Failure (ESHF). However, donor shortage limits the utilization of this modality of treatment making it available for only a fraction of the patients on the transplant wait list. Continuous flow left ventricular assist devices (CF-LVADs) have therefore risen in importance as a standard of care for end-stage heart failure. Short, mid and long-term survival rates as well as quality of life have been found to improve with newer and more sophisticated machines [1-6]. Advancements in technology have led to patients remaining on left ventricular support for > 5 years with acceptable quality of life. Durable MCS technology improved following the development of continuous-flow pumps and its FDA approval as a bridge to transplant in 2008 and then its approval for destination therapy in 2010 [
7,
8]. Additionally, the creation of “The Interagency Registry of Mechanically Assisted Circulatory Support” (INTERMACS), sponsored by the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute registry paved the way to improve patient outcomes through research [
8]. Further improvements occurred with advances in VAD technology, reducing device-related adverse events. The most sophisticated line of pumps approved by the FDA uses fully magnetically levitated technology. Data from clinical trials have shown a significant reduction in pump thrombosis in the CF -centrifugal pumps compared to the earlier CF-axial flow pumps that were first approved by the FDA [
1,
9]. With fewer adverse events, there has been a tremendous increase in LVAD implantations. The impact of risk factors on long-term survival projections in patients supported on LVADs is therefore needed with increasing utilization of this technology. Our study has used the TriNetX database to identify risk factors and their impact on the long-term survival of LVAD-supported patients.
2. Materials and Methods
The TriNetX dataset comprises de-identified demographic information, lab results, and diagnoses from 4,705 patients who underwent LVAD implantation between 2002 and 2022 across 80 healthcare organizations. Lab results include 4,771 Logical Observation Identifiers Names and Codes (LOINC) codes which are more specific than Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes for tests, representing over 7 million instances collected from 80,227 encounters preceding implantation. The analysis was focused on the most recent lab results before implantation, with an average interval of 18.0±30.9 days between lab result collection and LVAD insertion.
More than 300,000 instances of primary diagnoses before LVAD implantation were extracted. The diagnosis right before implantation was used, with an average interval of 25.3±34.6 days between diagnosis and implantation.
The study examined the impact of six demographic variables (age, gender, race, ethnicity, marital status, and regional location), 264 lab results, and 326 diagnoses on LVAD patient survival. Lab variables were selected by excluding those with over 90% missing values. The Log-rank test was used to assess post-implant survival effects, while Cox regression was used in univariate analysis to obtain Hazard Ratio (HR). Patients with unknown lab results were removed before the univariate analysis.
Diagnosis variables were chosen by excluding those with fewer than 100 patients with positive diagnoses to mitigate bias. Each diagnosis underwent a log-rank test to compare survival between patients with positive and negative diagnoses, with a significance threshold set at p < 0.001. Unknown diagnoses were excluded from the analysis. Additionally, univariate Cox regression analysis was done to quantify HRs for diagnoses significantly affecting post-implant survival.
The study excluded patients with multiple LVAD implantations and those ≤18 years old at the time of implantation. Patients with recorded death times were classified as deceased, while those without were considered surviving at the time of data collection. Time to event was computed as the duration between LVAD implantation and death or data retrieval. Samples with missing values or data errors (e.g., implantation is after recorded death) were excluded. All analyses were conducted using the Python programming language and the lifelines library.
3. Results
3.1. Demographics
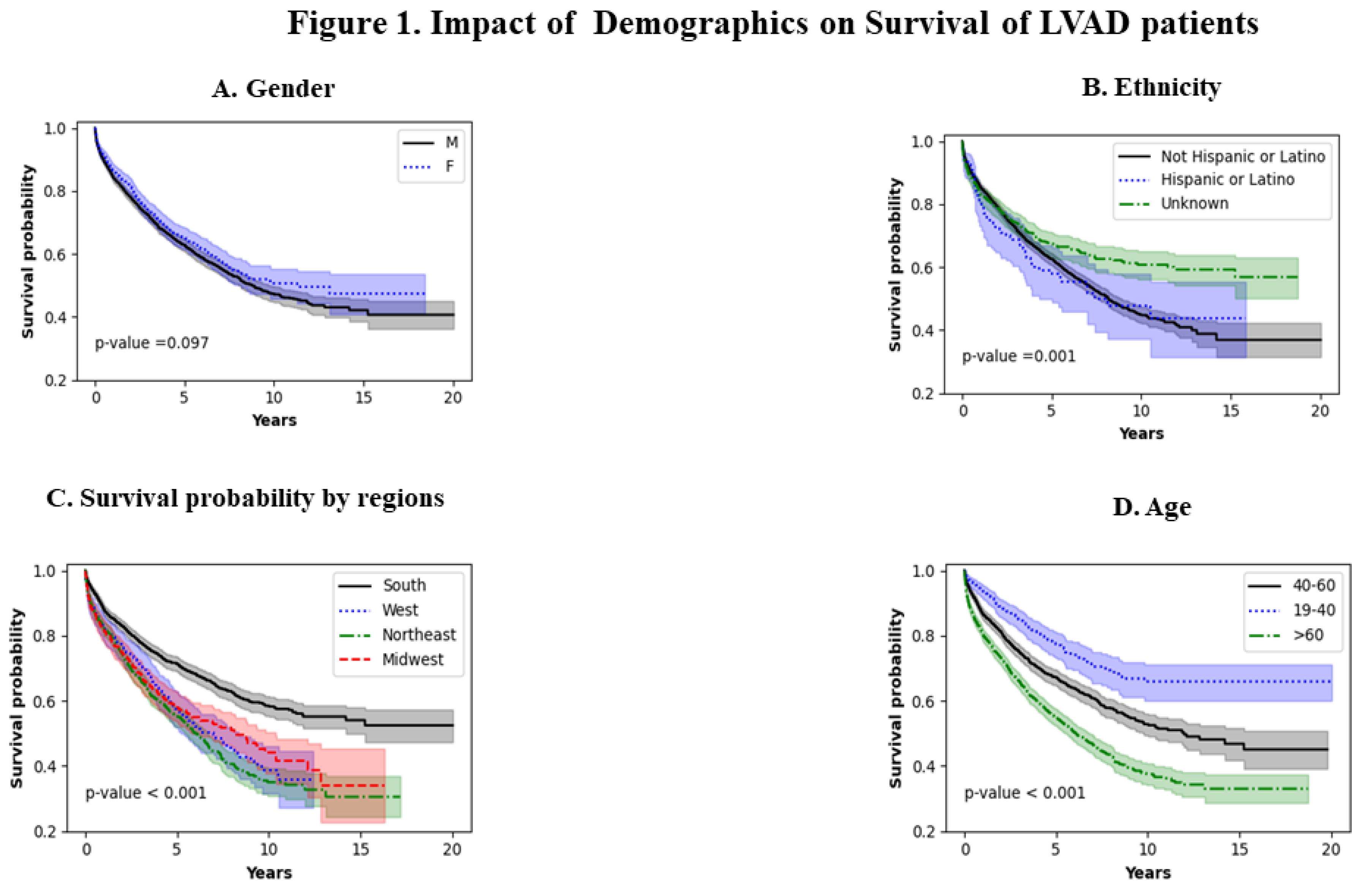
Figure 1A shows the effect of gender. Males and females seem to have similar survival patterns (p=0.097). Figure 1B shows the effect of ethnicity. Non-Hispanic or Latino populations have a worse survival as compared to the Hispanic population (p=0.001). This trend seems to extend throughout the analysis. Figure 1C shows survival probability by region. The northeast population has the worst survival and the southern population has the best survival ( p<0.001). Figure 1D shows the impact of age on LVAD survival. The worst survival was noted in patients >60 years of age and the best survival was noted in the younger population (19-40 years of age) throughout the period analyzed.
3.2. Infections
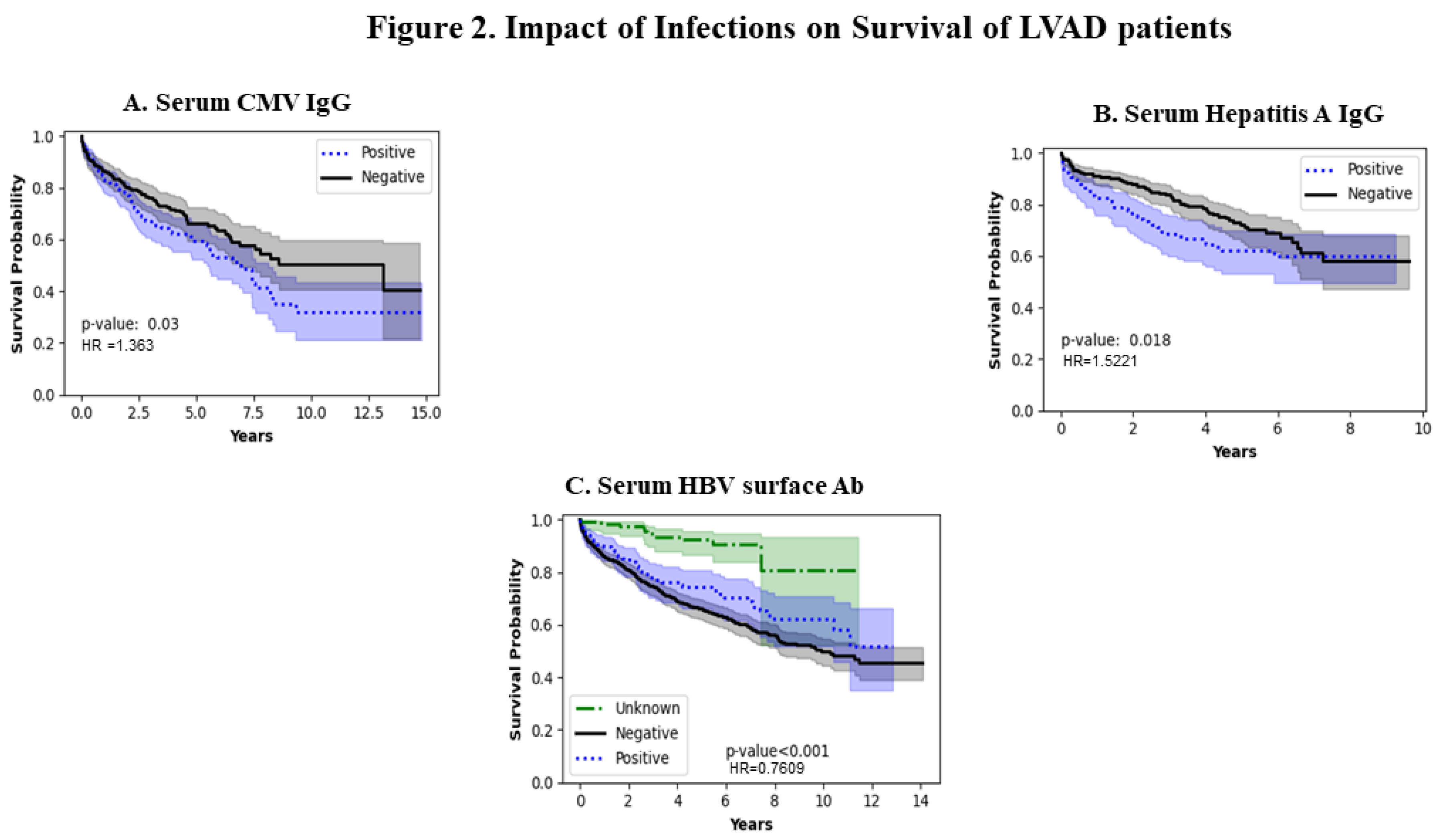
Figure 2A shows the impact of serum CMV IgG levels. In the CMV-negative population, the survival is better and worse in the CMV IgG-positive population (p=0.03) because the population exposed to CMV infection generates CMV IgG antibodies which does not seem to confer any protective effect on survival in the long term. Figure 2B shows the impact of hepatitis A viral infection which shows populations with positive Hepatitis IgG had a worse survival close to approximately 8 years after which the survival rate appears to be similar (p=0.018). Figure 2C shows the impact of the presence /absence of Hepatitis B surface antibody on LVAD survival with better survival in the Hepatitis surface antibody-positive individuals (p-value <0.001).
3.3. Co-Morbidities
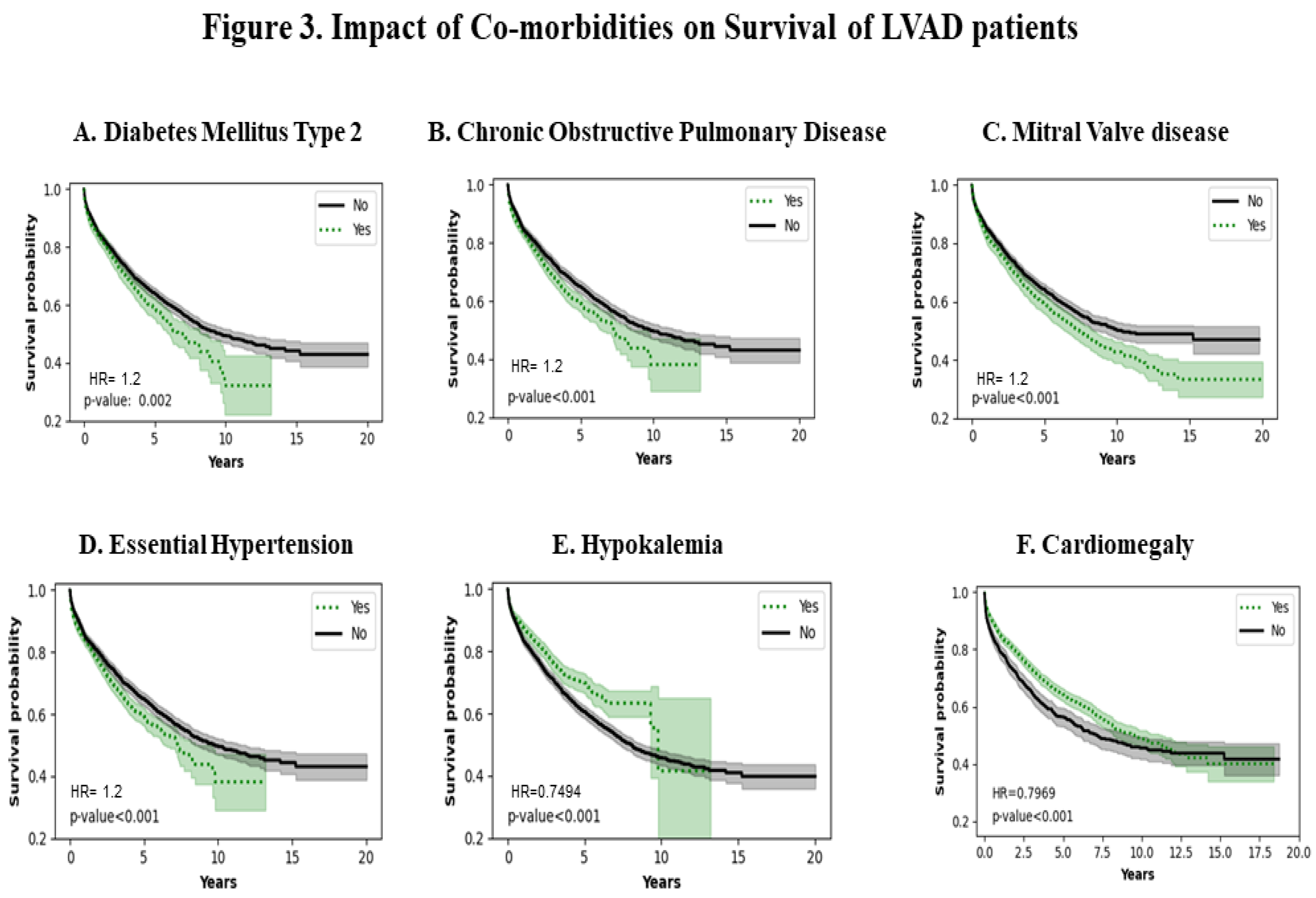
Figure 3A shows the effect of Diabetes Mellitus type 2 (DM type 2). Patients with a history of DM type 2 have a poorer survival (p=0.002). Figure 3B shows the effect of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). COPD patients have a lower survival probability (p<0.001). Figure 3C shows that mitral valve disease decreases survival probability (p<0.001). Figure 3D shows that essential hypertension also decreases survival probability in the patients who carry the diagnosis(p<0.001). Figure 3E shows that persistent hypokalemia can increase survival probability up to approximately 10 years (p<0.001). Figure 3F shows that cardiomegaly has a protective effect on survival up approximately to 10 years (HR = 0.79 ; p<0.001).
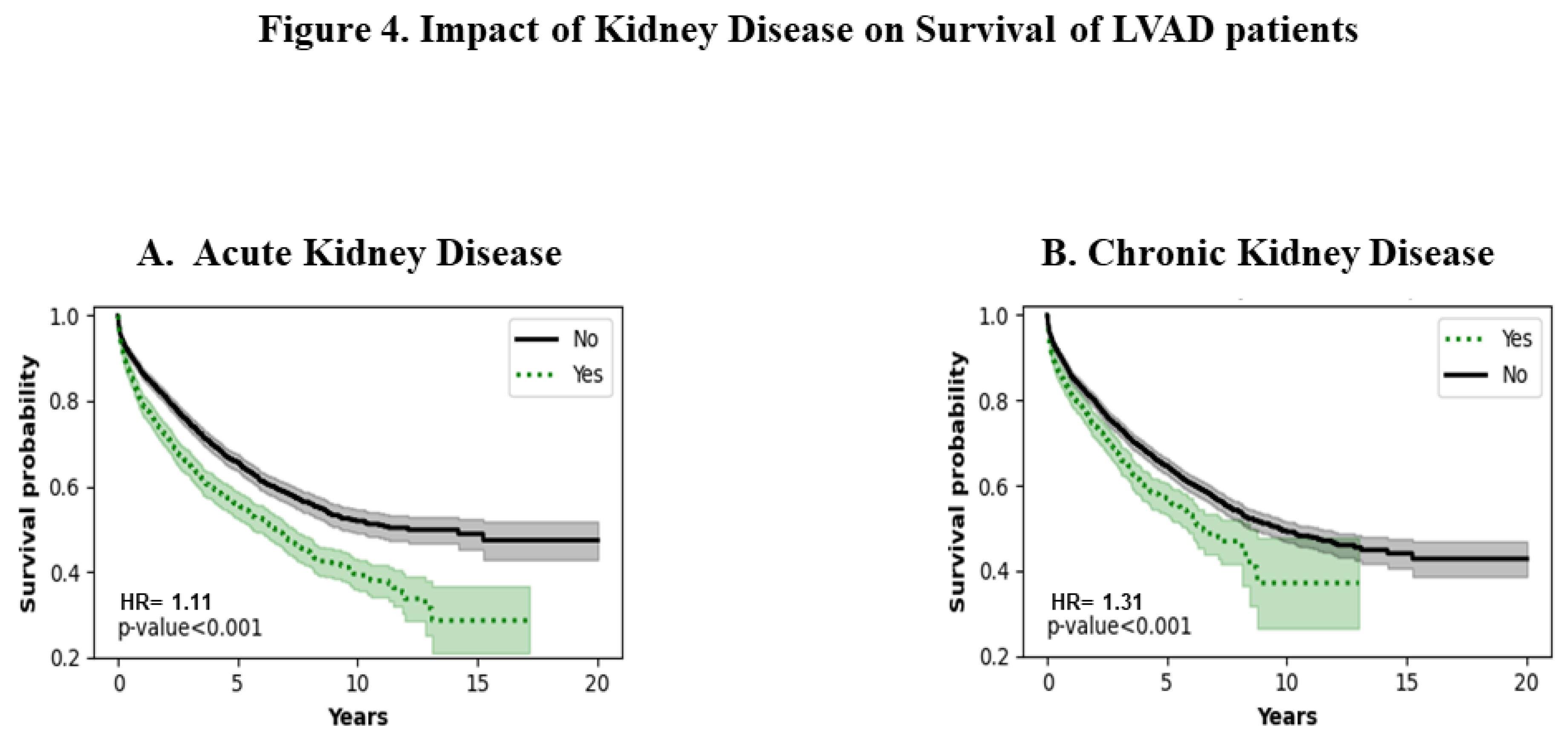
3.4. Acute and Chronic Kidney Disease
Figures 4A and 4B show the effect of acute and chronic kidney disease respectively. Patients with a history of acute and chronic kidney disease have poorer survival ( p<0.001). The trend remains consistent throughout the entire period of analysis.
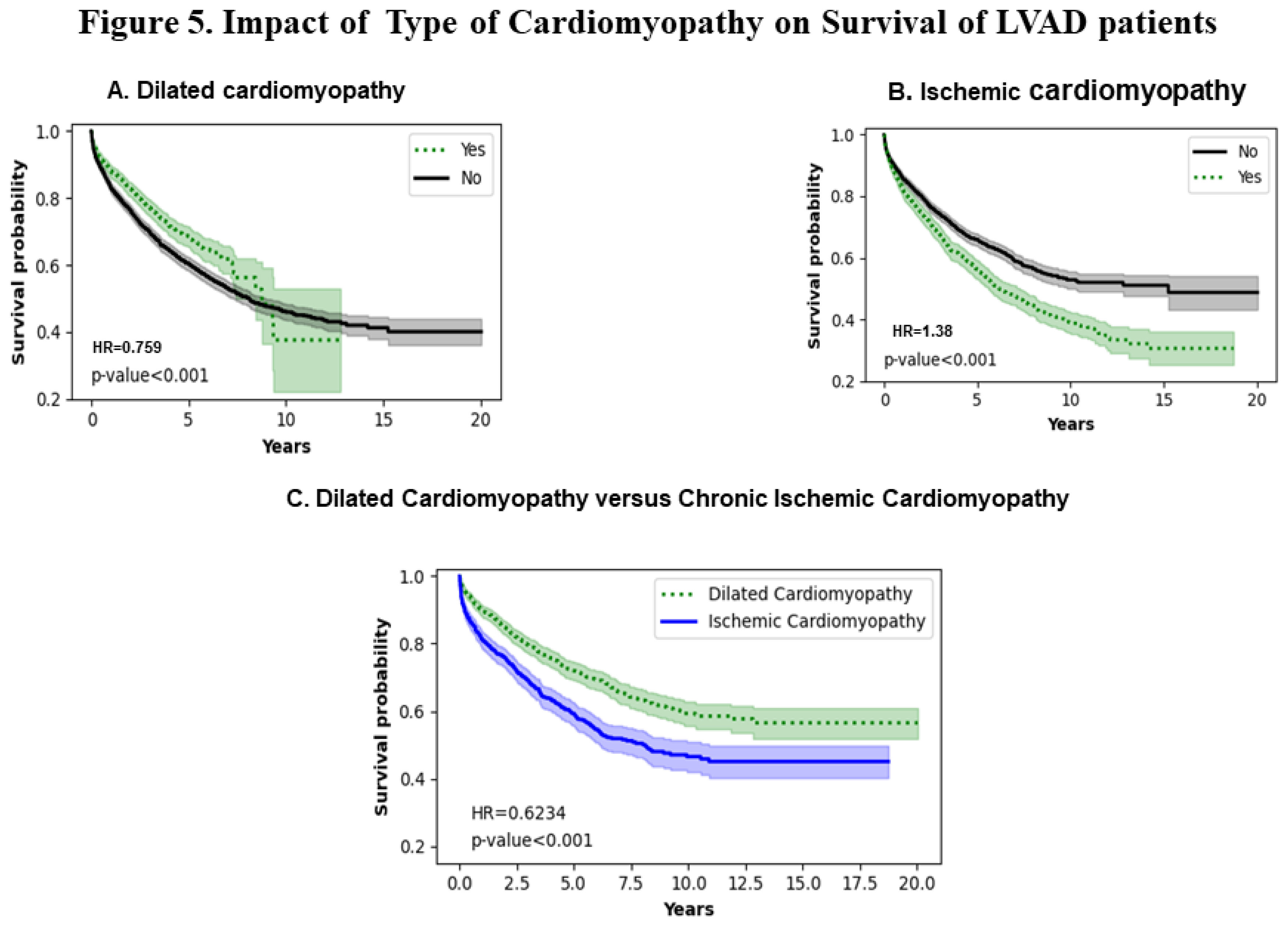
3.5. Type of Cardiomyopathy
Figures 5A and 5B show the effect of dilated and ischemic cardiomyopathy respectively. Patients with a history of ischemic cardiomyopathy have poorer survival (p<0.001). The trend remains consistent throughout the entire analysis. Interestingly, 50 % of dilated cardiomyopathy patients are alive at 10 years and about 40 % remain alive at 12 years. However, 50 % of ischemic cardiomyopathy patients remain alive for close to 7.5 years with a consistent decrease to 20 % at 12 to 18 years. Figure 5C shows a comparison of dilated versus ischemic cardiomyopathy that shows that there is a statistically significant difference in the survival probabilities of the two types of cardiomyopathies with dilated cardiomyopathy patients have a higher survival probability throughout the entire period of analysis ( HR =0.6234 ;p<0.001).
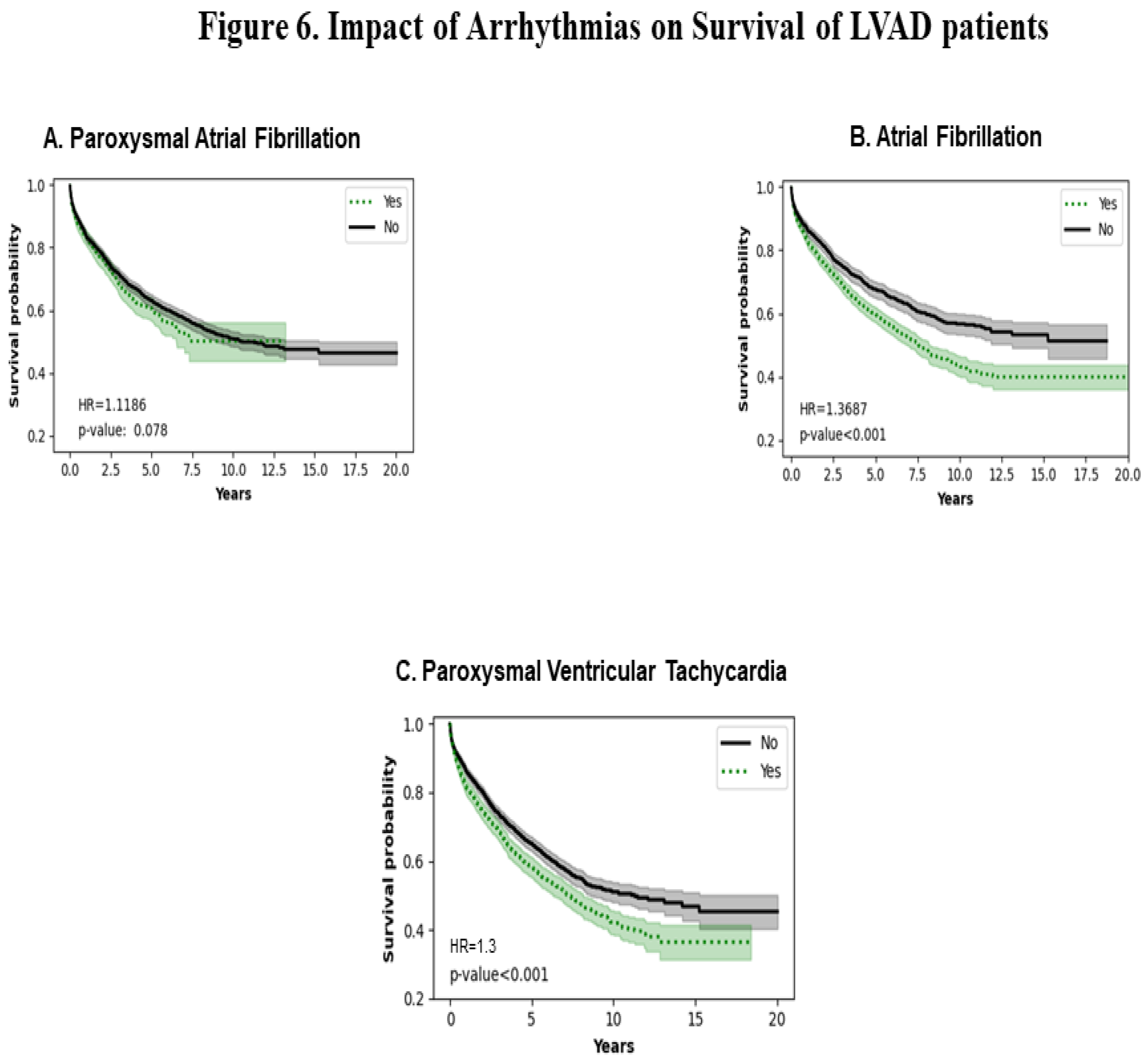
3.6. Impact of Type of Arrhythmias
Figure 6A shows that paroxysmal atrial fibrillation does not affect the survival probability of LVADs in the long term (HR=1.11; p=0.078). Figure 6B shows a statistically significant decrease in survival probability in atrial fibrillation (HR =1.37; p<0.001). Figure 6C shows that paroxysmal ventricular tachycardia decreases survival probability (p<0.001).
All risk factors are summarized in
Table 1. The number of positive and negative diagnoses is also depicted in this table.
4. Discussion
4.1. Demographics
The impact of gender is not statistically significant in our study through the duration of the analyses. Though women in general are fewer in number to receive VADs their survival is not different in short-term studies conducted in a small number of patients up to 5 years [
10]. This effect seems to be consistent with the results obtained in this study. Though perioperative differences in morbidity and mortality have been noted the long-term effects do not seem to portray that trend. Though women supported on an LVAD are at a greater risk of neurologic events as compared to their male counterparts both men and women have similar all-cause mortality post any neurological events thus implying no significant differences in survival [
11]. In the current literature decision-making and emotional factors affect women differently than men which in turn can impact a worse survival in the short term in women [
12]. Further studies are needed to compare gender-based short and long-term quality of life in people and its impact on survival.
Our study shows that the non-Hispanic white race has a worse survival than the Hispanics in the long term. The utilization of VADs has been assumed to be equal in all races when adjusted for other confounding factors in some studies [
13]. Many other studies have shown that utilization of VADS needs more diversity in terms of race and gender and other socioeconomic issues. More studies are needed to assess race-based effects on long-term LVAD survival in the setting of improving diversity [
14,
15].
In our study, we have shown that the northeast had the worst survival consistently throughout the analysis while the south had the best survival. Studies using the INTERMACS data showed early on in 2015 that the South had a lower survival as compared to other regions [
16]. However, such regional differences can be attributed to changes in acuity of the patients, and improvements in utilization of bridging techniques to stabilize patients before implanting LVADs which could have changed in centers contributing data to the TriNetX database and that we have extracted more current data. The data represented in the paper by Krim et al was > 10 years old and hence differences may be explained by changes in the utilization of newer pumps in different centers in the various regions studied across the United States [
16]. Long-term survival appears to be affected by older age >60 years which is consistent with earlier findings that age >60 is an independent risk factor for mortality in the short term at 1 year [
17]
4.2. Infections
Different infections have varied effects on survival in the LVAD-supported population. CMV IgG does not seem to confer any protection in terms of long-term survival in our study. It has also been shown in other studies that CMV reactivation occurs in the post-VAD implant period and could contribute to poor outcomes. CMV reactivation can occur in immunocompetent patients who are critically ill [
14]. Impaired cellular immunity in LVAD patients leads to dysfunctional CD4-positive T cells resulting in apoptosis until approximately 4 weeks post-implantation [18-20]. Our studies show positive Hepatitis A IgG patients have poorer survival at least up to 8 years post-implant. This observation is difficult to explain as this is the first report and more studies are needed to determine the implication. It is unclear if this has any link to impaired cell-mediated immunity in this population. The protection conferred by hepatitis B surface antibody can be explained by the fact that it indicates immunity acquired via an immune response to vaccination, or the presence of passively acquired antibody or prior infection [
21].
4.3. Comorbidities
Diabetes has been noted to be an important risk factor in our study for the long-term survival of LVAD patients. However, it has been noted that diabetes is not a short-term and intermediate risk factor but impacts long-term survival [
22]. Such variations may be the effect of differential pre and post-implant diabetes control. A meta-analysis showed that diabetes did not increase all-cause mortality in LVAD-supported patients [
23]. COPD patients and LVAD appear to have lower survival in our study at least up to 10 years. Other studies show no significant direct impact on survival in the short term but do have an impact on gastrointestinal bleeding which is a risk factor for short-term survival [
24,
25]. Mitral valve disease in general seems to affect long-term survival in our study. This is consistent with earlier studies showing that greater than moderate mitral regurgitation is consistent with worse survival in the short and mid-terms [
26]. Most recently a meta-analysis showed that post-operative mortality is not affected by moderate to severe MR [
27]. However residual post-operative mitral regurgitation though corrected to a certain extent can impact prognosis via deterioration of right ventricular function and pulmonary pressures. Repair of mitral regurgitation may improve prognosis [
28]. Additionally, residual mitral regurgitation may be influenced by differences in gene expression of inflammatory markers which have been reported in ischemic mitral regurgitation [
29].
Essential hypertension influences pump flows causing them to decrease and thereby promoting stasis which predisposes to pump thrombosis as well as strokes. Additionally, chronically low pulsatility leads to reduced endothelial function due to the absence of the routine cardiac cycle. Under such a milieu, small changes in blood pressure may deteriorate endothelial structure/function in the cerebral microvasculature and predispose the local area to progressive vessel damage and rupture therefore causing hemorrhagic strokes also [
30,
31]. This could explain the significant impact of essential hypertension on long-term LVAD survival seen in our study. Further studies are needed to elucidate this aspect of the physiological impact of LVADs. In a small study, hypokalemia showed a non-significant protective effect on the survival of LVAD patients 1-month post-LVAD implant [
32]. In our study hypokalemia seems to confer a survival benefit in the long-term. The effect of cardiomegaly on survival may be the end effect of molecular signaling pre and post-LVAD implant resulting in changes in myocyte size and regression of hypertrophy. This phenomenon needs further investigation [
33].
4.4. Renal function
The long-term success and survival of LVAD patients are dependent on preserving end-organ function. Hence it is not surprising that any insult to the kidneys whether acute or chronic has an impact on LVAD survival as shown in our study. Additionally, LVAD support can mitigate or worsen renal function depending on the stage and acuity of heart failure which impacts long-term survival [
34,
35].
4.5. Type of cardiomyopathy
In our study, dilated cardiomyopathy patients did better than their ischemic counterparts in terms of long-term survival. Existing literature shows that in the short or long term, there is no significant decrease in mortality in ischemic cardiomyopathy patients [
36,
37]. Our findings can be explained by the higher burden of comorbidities they may carry such as older age, higher myocardial damage, and other structure /function issues that would impair the physiology of the heart and predispose to more arrhythmias. In a small study, 12 dilated cardiomyopathy patients were explanted after fully functional recovery of the myocardium at 10 months post-implantation with no complications [
38]. Larger studies are needed to compare the impact of etiologies of heart failure on LVAD survival.
4.6. Arrhythmias
Our study showed that paroxysmal atrial fibrillation did not confer significant mortality on LVAD patients but atrial fibrillation in general had a significant effect on mortality in this population. Similar observations have been made in other studies in the short and mid-terms [39-42]. Additional atrial fibrillation can also lead to ventricular tachyarrhythmias which is an independent risk factor noted in our study [
43]. Electrical storms impact short-term survival significantly [
44].
5. Conclusions
This is the first report of a detailed long-term survival assessment of several risk factors that impact the LVAD population Our study shows that older individuals, non-Hispanic/Latino race, and the northeast populations had a worse survival in terms of the demographics of the population. Exposure to CMV and hepatitis A does not confer a survival advantage but patients who had Hepatitis surface antibodies had a significant survival advantage. Comorbidities such as diabetes, COPD, mitral valve disease, and essential hypertension showed a worse survival. Hypokalemia and cardiomegaly conferred a survival advantage for up to 10 years in our study. Both acute and chronic kidney disease significantly worsen long-term survival. In our study, dilated cardiomyopathy patients consistently showed better survival in the long term with LVAD. In our study, paroxysmal ventricular tachycardia and persistent atrial fibrillation patients showed poor long-term survival but there was no significant change in survival in the paroxysmal atrial fibrillation population.
This study is limited by the fact that it is retrospective and uses diagnosis codes.
Future directions would include internal and external validation of risk factors in different databases to evolve a risk factor assessment model for this population. Future studies are also needed to classify risk factors as short, mid, or long-term. The use of AI-driven technologies may reveal risk factors which may help increase the sensitivity and specificity of the risk factor models to better predict survival of LVAD patients.
Institutional Review Board Statement.
NONE.
Through TriNetX
users search for patients meeting specified criteria in a de-identified database, without prior Institutional Review Board (IRB) approval No IRB approval is required.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.N., D.D., and B.M.; methodology, D.D.; software, D.D.; validation, N.N. and D.D.; formal analysis, D.D.; investigation, N.N., B.M, D.D, data curation, N.N.; writing—original draft preparation, N.N; writing—review and editing, N.N; visualization, N.N.; supervision, N.N, D.D, B.M; project administration, N.N. and D.D.; funding acquisition, none for this project.
Informed Consent Statement
NOT applicable as this is a retrospect decoded database analysis.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Conflicts of Interest
NONE of the authors have any conflicts of interest to disclose.
References
- Mehra MR, Uriel N, Naka Y, Cleveland JC Jr., Yuzefpolskaya M, Salerno CT, et al. A Fully Magnetically Levitated Left Ventricular Assist Device - Final Report. N Engl J Med, 2019;380(17):1618–27. [CrossRef]
- Milano CA, Rogers JG, Tatooles AJ, Bhat G, Slaughter MS, Birks EJ, et al. HVAD: The ENDURANCE Supplemental Trial. JACC Heart Fail, 2018;6(9):792–802. [CrossRef]
- Rogers JG, Pagani FD, Tatooles AJ, Bhat G, Slaughter MS, Birks EJ, et al. Intrapericardial Left Ventricular Assist Device for Advanced Heart Failure. N Engl J Med, 2017;376(5):451–60. [CrossRef]
- Molina EJ, Shah P, Kiernan MS, Cornwell WK 3rd, Copeland H, Takeda K, et al. The Society of Thoracic Surgeons Intermacs 2020 Annual Report. Ann Thorac Surg, 2021;111(3):778–92. [CrossRef]
- Kirklin JK, Pagani FD, Kormos RL, Stevenson LW, Blume ED, Myers SL, et al. Eighth annual INTERMACS report: Special focus on framing the impact of adverse events. J Heart Lung Transplant, 2017;36(10):1080–6. [CrossRef]
- Cowger J, Sundareswaran K, Rogers JG, Park SJ, Pagani FD, Bhat G, et al. Predicting survival in patients receiving continuous flow left ventricular assist devices: the HeartMate II risk score. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2013;61(3):313–21. [CrossRef]
- Starling RC, Naka Y, Boyle AJ, et al.: Results of the post-U.S. Food and Drug Administration-approval study with a continuous flow left ventricular assist device as a bridge to heart transplantation: a prospective study using the INTERMACS (Interagency Registry for Mechanically Assisted Circulatory Support). Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 2011;57:1890–8.
- Jorde UP, Kushwaha SS, Tatooles AJ, Naka Y, Bhat G, Long JW, Horstmanshof DA, Kormos RL, Teuteberg JJ, Slaughter MS, Birks EJ, Farrar DJ, Park SJ; HeartMate II Clinical Investigators. Results of the destination therapy post-food and drug administration approval study with a continuous flow left ventricular assist device: a prospective study using the INTERMACS registry (Interagency Registry for Mechanically Assisted Circulatory Support). J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014 ;63(17):1751-7. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehra MR, Naka Y, Uriel N, Goldstein DJ, Cleveland JC Jr, Colombo PC, Walsh MN, Milano CA, Patel CB, Jorde UP, Pagani FD, Aaronson KD, Dean DA, McCants K, Itoh A, Ewald GA, Horstmanshof D, Long JW, Salerno C; MOMENTUM 3 Investigators. A Fully Magnetically Levitated Circulatory Pump for Advanced Heart Failure. N Engl J Med. 2017 ;376(5):440-450. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zubarevich A, Szczechowicz M, Osswald A, Arjomandi Rad A, Vardanyan R, Pompeu Bo Sá M, Van den Eynde J, Schmack B, Wendt D, Koch A, Pizanis N, Kamler M, Ruhparwar A, Weymann A, Zhigalov K. Impact of gender in patients with continuous-flow left ventricular assist device therapy in end-stage heart failure. Int J Artif Organs. 2021 ;44(12):990-997. [CrossRef]
- Sherazi S, Kutyifa V, McNitt S, Papernov A, Hallinan W, Chen L, Storozynsky E, Johnson BA, Strawderman RL, Massey HT, Zareba W, Alexis JD. Effect of Gender on the Risk of Neurologic Events and Subsequent Outcomes in Patients With Left Ventricular Assist Devices. Am J Cardiol. 2017 ;119(2):297-301. [CrossRef]
- Kim JM, Maqsood MH, Makuvire T, McIlvennan CK, Thompson JS, Matlock DD, Allen LA, Warraich HJ. Gender-based differences in decision making, quality of life and survival among patients undergoing left ventricular assist device evaluation. PLoS One. 2023 ;18(10):e0293121. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones MM, McElroy LM, Mirreh M, Fuller M, Schroeder R, Ghadimi K, DeVore A, Patel CB, Black-Maier E, Bartz R, Thomas K. The impact of race on utilization of durable left ventricular assist device therapy in patients with advanced heart failure. J Card Surg. 2022 ;37(11):3586-3594. [CrossRef]
- Breathett K, Allen LA, Helmkamp L, Colborn K, Daugherty SL, Blair IV, Jones J, Khazanie P, Mazimba S, McEwen M, Stone J, Calhoun E, Sweitzer NK, Peterson PN. Temporal Trends in Contemporary Use of Ventricular Assist Devices by Race and Ethnicity. Circ Heart Fail. 2018 ;11(8):e005008. [CrossRef]
- Cascino TM, Colvin MM, Lanfear DE, Richards B, Khalatbari S, Mann DL, Taddei-Peters WC, Jeffries N, Watkins DC, Stewart GC, Aaronson KD; REVIVAL Investigators. Racial Inequities in Access to Ventricular Assist Device and Transplant Persist After Consideration for Preferences for Care: A Report From the REVIVAL Study. Circ Heart Fail. 2023 Jan;16(1):e009745. [CrossRef]
- Krim SR, Vivo RP, Campbell P, Estep JD, Fonarow GC, Naftel DC, Ventura HO. Regional differences in use and outcomes of left ventricular assist devices: Insights from the Interagency Registry for Mechanically Assisted Circulatory Support Registry. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2015 ;34(7):912-20. [CrossRef]
- Muslem R, Caliskan K, Akin S, Yasar YE, Sharma K, Gilotra NA, Kardys I, Houston B, Whitman G, Tedford RJ, Hesselink DA, Bogers AJJC, Manintveld OC, Russell SD. Effect of Age and Renal Function on Survival After Left Ventricular Assist Device Implantation. Am J Cardiol. 2017 ;120(12):2221-2225. [CrossRef]
- Lundgren SW, Florescu DF, Zolty R. Reactivation of Cytomegalovirus Following Left Ventricular Assist Device Implantation: A Case-Control Study. ASAIO J. 2021 Apr 1;67(4):405-410. [CrossRef]
- Cowley NJ, Owen A, Shiels SC, et al. Safety and efficacy of antiviral therapy for prevention of cytomegalovirus reactivation in immunocompetent critically ill patients: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med. 2017;177:774–783.
- Kimball PM, Flattery M, McDougan F, Kasirajan V. Cellular immunity impaired among patients on left ventricular assist device for 6 months. Ann Thorac Surg.2008; 85:1656–1661.
- Jeng WJ, Papatheodoridis GV, Lok ASF. Hepatitis B. Lancet. 2023 ;401(10381):1039-1052. [CrossRef]
- Kogan A, Frogel J, Ram E, Jamal T, Peled-Potashnik Y, Maor E, Grupper A, Morgan A, Segev A, Raanani E, Sternik L. The impact of diabetes on short-, intermediate- and long-term mortality following left ventricular assist device implantation. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2022 ;61(6):1432-1437. [CrossRef]
- Zhou P, Xiao Z, Zhu P, Nie Z, Pavan D, Zheng S. Diabetes Mellitus Is Not a Risk Factor for Patients Supported With Left Ventricular Assist Device. Ann Thorac Surg. 2020 May;109(5):1614-1622. [CrossRef]
- Ebner B, Grant JK, Vincent L, Maning J, Olarte N, Olorunfemi O, Colombo R, Chaparro S. Evaluating the impact of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease on in-hospital outcomes following left ventricular assist device implantation. J Card Surg. 2020 Dec;35(12):3374-3380. [CrossRef]
- Thohan V, Shi Y, Rappelt M, Yousefzai R, Sulemanjee NZ, Hastings TE, Cheema OM, Downey F, Crouch JD. The association between novel clinical factors and gastrointestinal bleeding among patients supported with continuous-flow left ventricular assist device therapy. J Card Surg. 2019 Jun;34(6):453-462. [CrossRef]
- Okoh A, Yanagida R, Schultheis M, Chaudari S, Fugar S, Nnaoma C, Chan O, Zucker MJ, Karanam R, Russo MJ, Camacho M. Impact of Baseline Mitral Regurgitation on Postoperative Outcomes After Left Ventricular Assist Device Implantation as Destination Therapy. Transplant Proc. 2019 ;51(3):859-864. [CrossRef]
- Arjomandi Rad A, Zubarevich A, Shah V, Yilmaz O, Vardanyan R, Naruka V, Moorjani N, Ruhparwar A, Punjabi PP, Weymann A. Prognostic value of mitral regurgitation in patients undergoing left ventricular assist device deployment: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Artif Organs. 2023 Aug;47(8):1250-1261. [CrossRef]
- Ertugay S, Kemal HS, Kahraman U, Engin C, Nalbantgil S, Yagdi T, et al. Impact of residual mitral regurgitation on right ventricular systolic function after left ventricular assist device implantation. Artif Organs, 2017; 41(7): 622–7.
- S, Khalighi AH, Gorman RC, et al. Mitral valve leaflet response to ischaemic mitral regurgitation: from gene expression to tissue remodelling. J R Soc Interface, 2020; 17(166):20200098.
- Troutman GS, Genuardi MV. Left Ventricular Assist Devices: A Primer for the Non-Mechanical Circulatory Support Provider. J Clin Med. 2022 ;11(9):2575. [CrossRef]
- Wasson LT, Yuzefpolskaya M, Wakabayashi M, Takayama H, Naka Y, Uriel N, Jorde UP, Demmer RT, Colombo PC. Hypertension: an unstudied potential risk factor for adverse outcomes during continuous flow ventricular assist device support. Heart Fail Rev. 2015 May;20(3):317-22. [CrossRef]
- Imamura T, Narang N, Combs P, Siddiqi U, Stonebraker C, Jeevanandam V. Hyperkalemia in Patients With Left Ventricular Assist Devices. Circ Rep. 2021 Sep 29;3(11):647-653. [CrossRef]
- George I, Bish LT, Kamalakkannan G, Petrilli CM, Oz MC, Naka Y, Sweeney HL, Maybaum S. Myostatin activation in patients with advanced heart failure and after mechanical unloading. Eur J Heart Fail. 2010 ;12(5):444-53. [CrossRef]
- Hariri IM, Dardas T, Kanwar M, Cogswell R, Gosev I, Molina E, Myers SL, Kirklin JK, Shah P, Pagani FD, Cowger JA. Long-term survival on LVAD support: Device complications and end-organ dysfunction limit long-term success. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2022 Feb;41(2):161-170. [CrossRef]
- Givens RC, Topkara VK. Renal risk stratification in left ventricular assist device therapy. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2018 Jan;15(1):27-33. [CrossRef]
- Tsiouris A, Borgi J, Karam J, Nemeh HW, Paone G, Brewer RJ, Morgan JA. Ischemic versus nonischemic dilated cardiomyopathy: the implications of heart failure etiology on left ventricular assist device outcomes. ASAIO J. 2013;59(2):130-5. [CrossRef]
- Ivanov B, Djordjevic I, Sabashnikov A, Sindhu D, Hink S, Eghbalzadeh K, Gerfer S, Gaisendrees C, Schlachtenberger G, Rustenbach C, Seuthe K, Regnier K, Mader N, Pfister R, Zeriouh M, Rahmanian P, Wahlers T. Impact of Ischaemic and Dilated Cardiomyopathy on Short-Term and Long-Term Survival After Ventricular Assist Device Implantation: A Single-Centre Experience. Heart Lung Circ. 2022 Mar;31(3):383-389. [CrossRef]
- Gyoten T, Amiya E, Kinoshita O, Tsuji M, Kimura M, Hatano M, Ono M. Myocardial recovery evaluation from ventricular assist device in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. ESC Heart Fail. 2022 Aug;9(4):2491-2499. [CrossRef]
- Enriquez AD, Calenda B, Gandhi PU, Nair AP, Anyanwu AC, Pinney SP. Clinical impact of atrial fibrillation in patients with the HeartMate II left ventricular assist device. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014 Nov 4;64(18):1883-90. [CrossRef]
- Sisti N, Mandoli GE, Sciaccaluga C, Valente S, Mondillo S, Cameli M. Insight into Atrial Fibrillation in LVAD Patients: From Clinical Implications to Prognosis. Pulse (Basel). 2020 Aug;8(1-2):2-14. [CrossRef]
- Antonides CFJ, Yalcin YC, Veen KM, Muslem R, De By TMMH, Bogers AJJC, Gustafsson F, Caliskan K. Survival and adverse events in patients with atrial fibrillation at left ventricular assist device implantation: an analysis of the European Registry for Patients with Mechanical Circulatory Support. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2022 ;61(5):1164-1175. [CrossRef]
- Oezpeker C, Zittermann A, Pühler T, Ensminger S, Gummert JF, Morshuis M. Permanent Atrial Fibrillation and 2 Year Clinical Outcomes in Patients with a Left Ventricular Assist Device Implant. ASAIO J. 2017 Jul/Aug;63(4):419-424.
- Hickey KT, Colombo PC, Naka Y, Garan AR, Yuzefpolskaya M, Garan H, Wan EY, Sciacca RR, Goldenthal I, Biviano AB. Atrial Fibrillation Is Associated with Recurrent Ventricular Arrhythmias After LVAD Implant: Incidence and Impact in a Consecutive Series. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2020 Apr;13(2):199-203. [CrossRef]
- Rehorn MR, Black-Maier E, Loungani R, Sen S, Sun AY, Friedman DJ, Koontz JI, Schroder JN, Milano CA, Khouri MG, Katz JN, Patel CB, Pokorney SD, Daubert JP, Piccini JP. Electrical storm in patients with left ventricular assist devices: Risk factors, incidence, and impact on survival. Heart Rhythm. 2021 Aug;18(8):1263-1271. [CrossRef]
Table 1.
Risk Factor Assessment.
Table 1.
Risk Factor Assessment.
| Code |
Risk Factor |
Number positive |
Number negative |
p-value |
Hazard Ratio |
| 13949-3 |
Serum CMV IgG |
268 |
286 |
0.031 |
1.363 |
| 32018-4 |
Serum Hepatitis A IgG |
159 |
364 |
0.0184 |
1.52 |
| 22322-2 |
Serum HBV surface Ab |
188 |
785 |
0.001 |
0.7609 |
| E11.9 |
Diabetes |
2985 |
1037 |
0.002 |
1.2 |
| 416.8 |
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease |
3018 |
1004 |
0.001 |
1.21 |
| 424 |
Mitral Valve disease |
3061 |
961 |
0.001 |
1.21 |
| 110 |
Essential Hypertension |
2442 |
1580 |
<0.001 |
1.21 |
| E87.6 |
Hypokalemia |
2854 |
1168 |
<0.001 |
0.749 |
| I51.7 |
Cardiomegaly |
2522 |
1500 |
<0.001 |
0.799 |
| N17.9 |
Acute Kidney Disease |
2191 |
1831 |
<0.001 |
1.11 |
| N18.9 |
Chronic kidney Disease |
3060 |
962 |
<0.001 |
1.31 |
| I142.0 |
Dilated Cardiomyopathy |
2685 |
1337 |
<0.001 |
0.759 |
| I25.5 |
Ischemic Cardiomyopathy |
2689 |
1333 |
<0.001 |
1.38 |
| 427.1 |
Paroxysmal Ventricular Tachycardia |
2779 |
1243 |
<0.001 |
1.3 |
| 427.31 |
Atrial Fibrillation |
2075 |
1624 |
<0.001 |
1.37 |
| I48 |
Paroxysmal atrial ifibrillation |
980 |
2778 |
0.078 |
1.1186 |
| 272.4 |
Hyperlipidemia |
2761 |
1261 |
<0.001 |
1.5 |
| 414 |
Coronary atheosclerosis of native vessel or graft |
3069 |
953 |
<0.001 |
1.5 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).