Submitted:
25 June 2024
Posted:
26 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
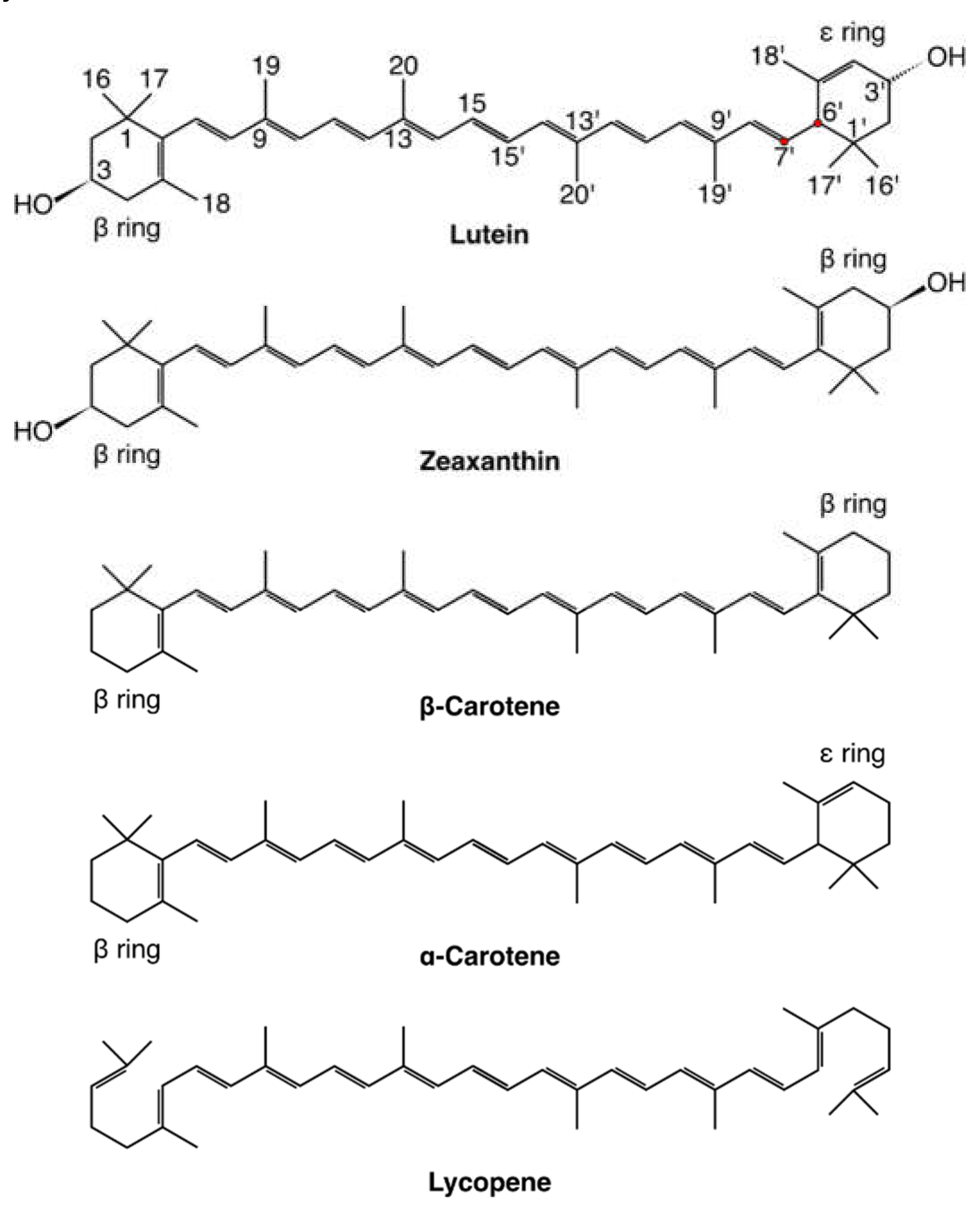
Carotenoids: Basic Information
The Journey of Carotenoids through the Human Body
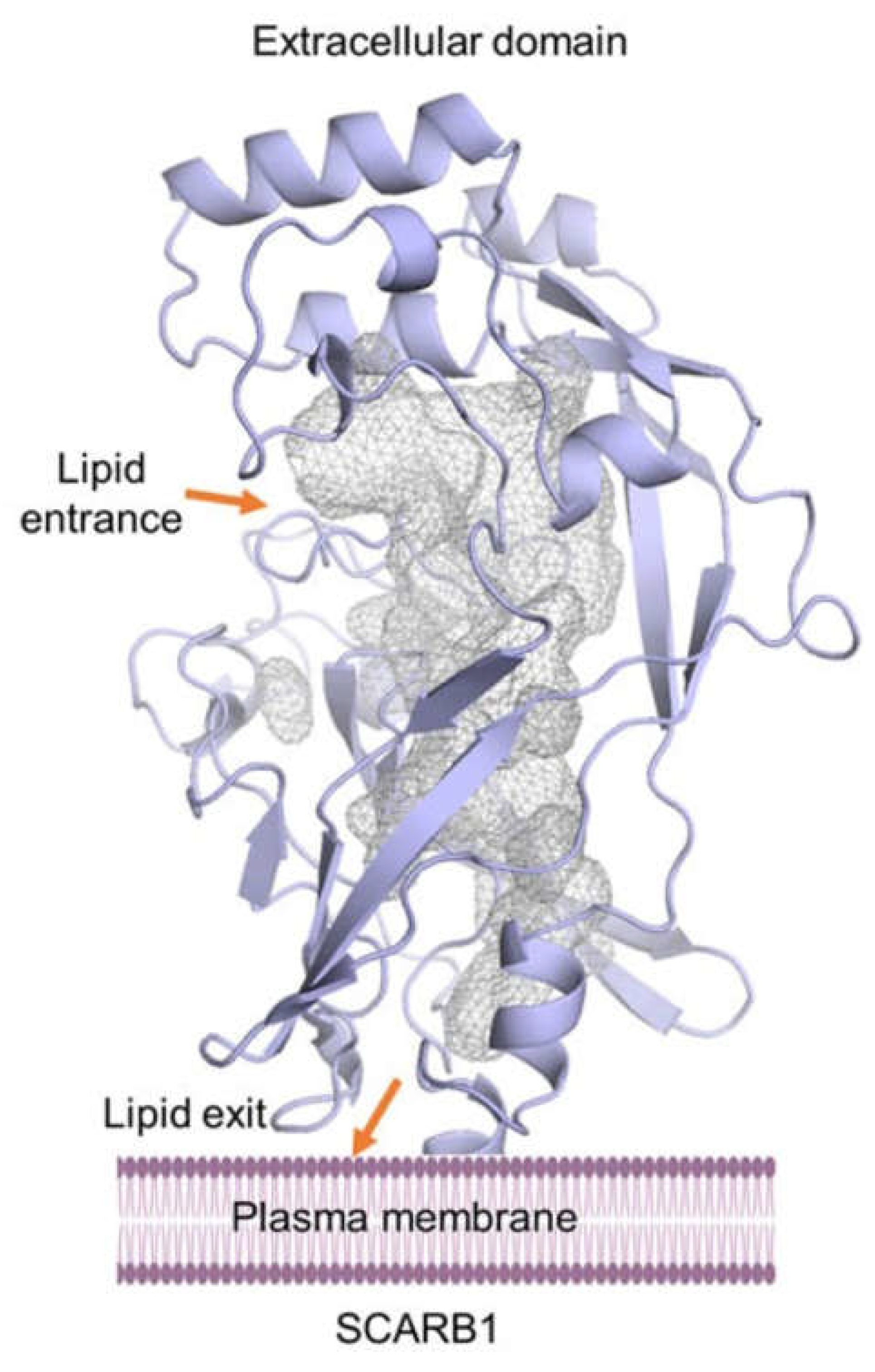
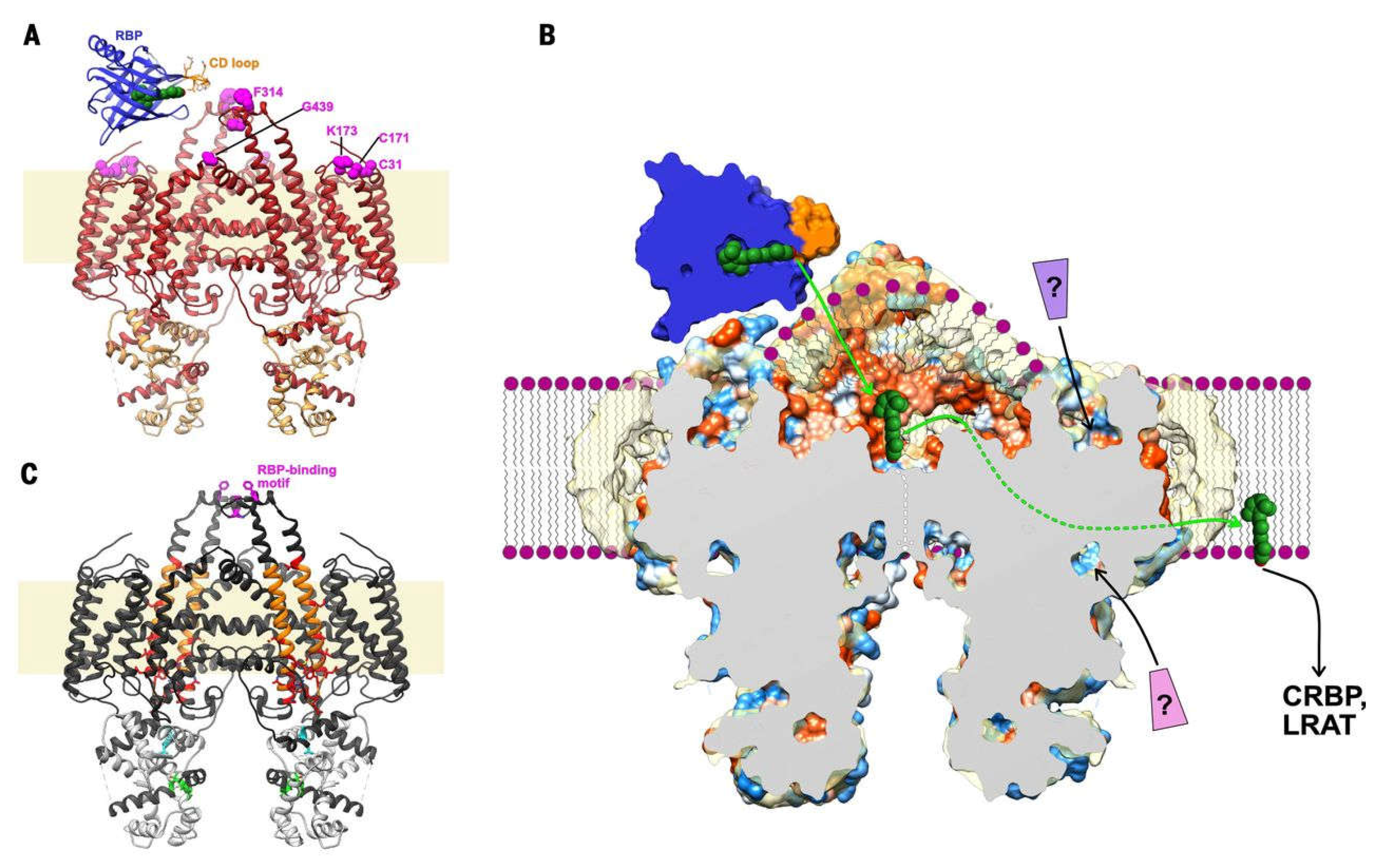
Carotenoid-Receptor Binding: Molecular-Level Studies
Carotenoids: Transfer from Receptor to Membrane
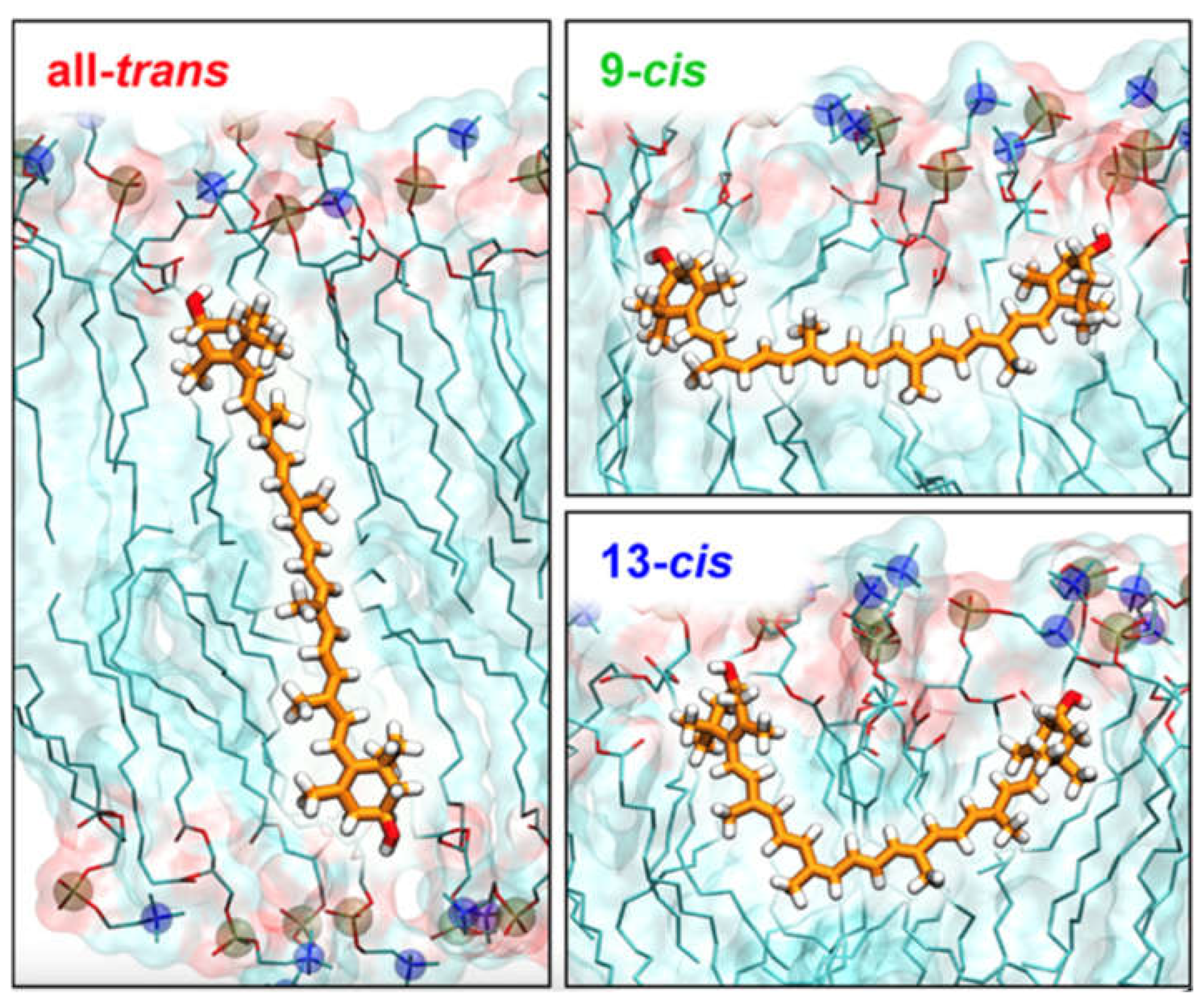
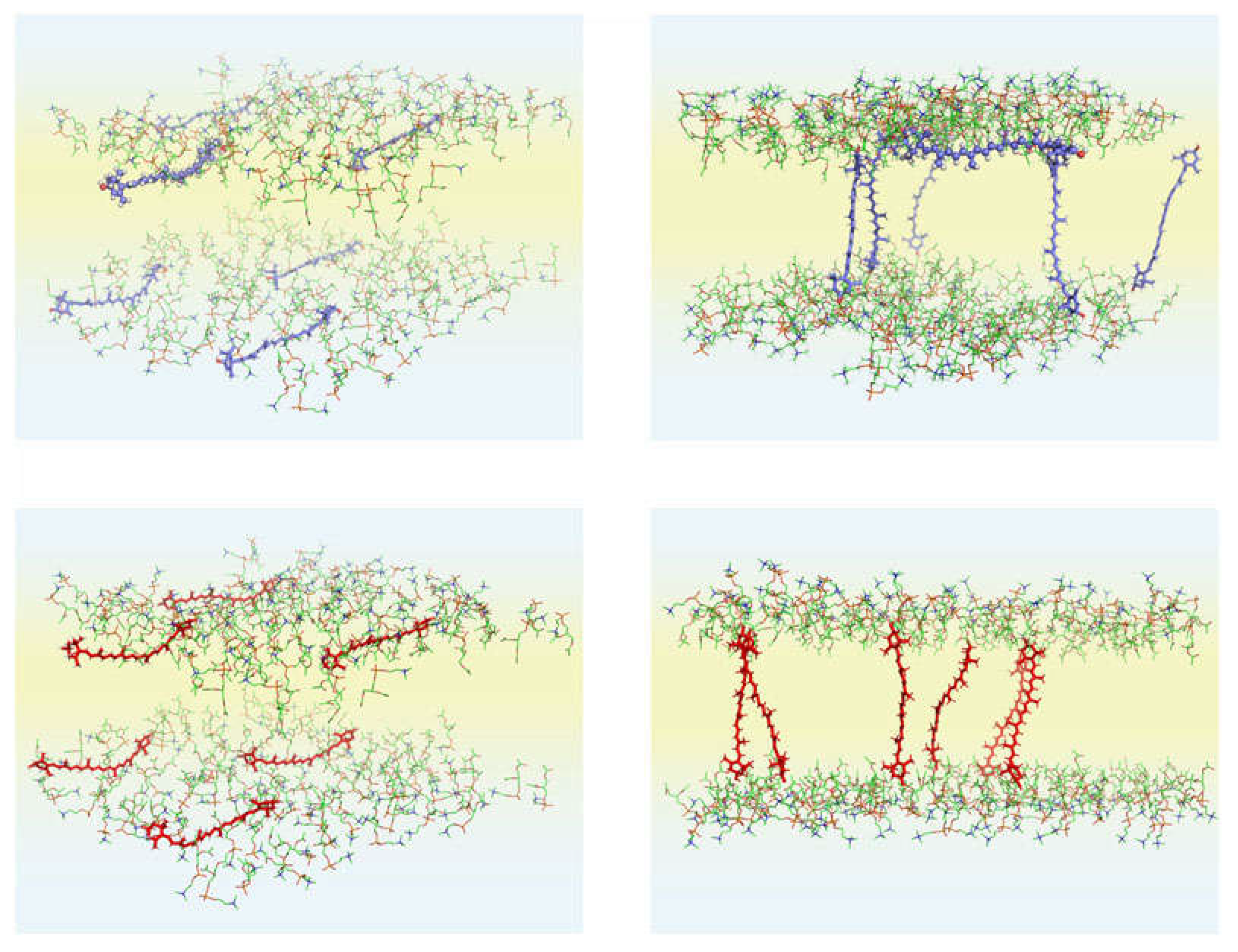
Carotenoids in the Membrane: Atomic-Level Motional Studies
Carotenoids in the Membrane: A Summary of Computational Studies and Their Significance
Author Contributions
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fuentes, P.; Pizarro, L.; Moreno, J.C.; Handford, M.; Rodriguez-Concepcion, M.; Stange, C. Light-dependent changes in plastid differentiation influence carotenoid gene expression and accumulation in carrot roots. Plant Mol Biol 2012, 79, 47-59. [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.H.; Rao, S.M.; Zhou, X.S.; Li, L. Plant carotenoids: recent advances and future perspectives. Mol Hortic 2022, 2, ARTN 3. [CrossRef]
- Ballottari, M.; Mozzo, M.; Girardon, J.; Hienerwadel, R.; Bassi, R. Chlorophyll Triplet Quenching and Photoprotection in the Higher Plant Monomeric Antenna Protein Lhcb5. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 11337-11348. [CrossRef]
- Dall’Osto, L.; Lico, C.; Alric, J.; Giuliano, G.; Havaux, M.; Bassi, R. Lutein is needed for efficient chlorophyll triplet quenching in the major LHCII antenna complex of higher plants and effective photoprotection in vivo under strong light. BMC Plant Biol. 2006, 6, 32.
- Xiao, F.G.; Shen, L.; Ji, H.F. On photoprotective mechanisms of carotenoids in light harvesting complex. Biochem Bioph Res Co 2011, 414, 1-4. [CrossRef]
- Eggersdorfer, M.; Wyss, A. Carotenoids in human nutrition and health. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2018, 652, 18-26. [CrossRef]
- Milani, A.; Basirnejad, M.; Shahbazi, S.; Bolhassani, A. Carotenoids: biochemistry, pharmacology and treatment. Brit J Pharmacol 2017, 174, 1290-1324. [CrossRef]
- Fiedor, J.; Burda, K. Potential Role of Carotenoids as Antioxidants in Human Health and Disease. Nutrients 2014, 6, 466-488. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.L.; Chen, J.; Ci, F.F.; Pang, H.; Cheng, N.; Xing, A.J. α-Carotene: a valuable carotenoid in biological and medical research. J Sci Food Agr 2022, 102, 5606-5617. [CrossRef]
- Stringham, J.M.; Johnson, E.J.; Hammond, B.R. Lutein across the Lifespan: From Childhood Cognitive Performance to the Aging Eye and Brain. Curr Dev Nutr 2019, 3, ARTN nzz066. [CrossRef]
- Lopresti, A.L.; Smith, S.J.; Drummond, P.D. The Effects of Lutein and Zeaxanthin Supplementation on Cognitive Function in Adults With Self-Reported Mild Cognitive Complaints: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. Front Nutr 2022, 9, ARTN 843512. [CrossRef]
- Parekh, R.; Hammond, B.R.; Chandradhara, D. Lutein and Zeaxanthin Supplementation Improves Dynamic Visual and Cognitive Performance in Children: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Parallel, Placebo-Controlled Study. Adv Ther 2024. [CrossRef]
- Yabuzaki, J. Carotenoids Database: structures, chemical fingerprints and distribution among organisms. Database-Oxford 2017, ARTN bax004. [CrossRef]
- Amengual, J. Bioactive Properties of Carotenoids in Human Health. Nutrients 2019, 11, ARTN 2388. [CrossRef]
- Pitts, S.B.J.; Johnson, N.S.; Wu, Q.; Firnhaber, G.C.; Kaur, A.P.; Obasohan, J. A meta-analysis of studies examining associations between resonance Raman spectroscopy-assessed skin carotenoids and plasma carotenoids among adults and children. Nutr Rev 2022, 80, 230-241. [CrossRef]
- Fiedor, L.; Dudkowiak, A.; Pilch, M. The origin of the dark S state in carotenoids: a comprehensive model. J R Soc Interface 2019, 16, ARTN 20190191. [CrossRef]
- Moise, A.R.; Al-Babili, S.; Wurtzel, E.T. Mechanistic Aspects of Carotenoid Biosynthesis. Chem Rev 2014, 114, 164-193. [CrossRef]
- Harrison, E.H. Mechanisms involved in the intestinal absorption of dietary vitamin A and provitamin A carotenoids. Bba-Mol Cell Biol L 2012, 1821, 70-77. [CrossRef]
- Lemmens, L.; Colle, I.; Van Buggenhout, S.; Palmero, P.; Van Loey, A.; Hendrickx, M. Carotenoid bioaccessibility in fruit- and vegetable-based food products as affected by product (micro) structural characteristics and the presence of lipids: A review. Trends Food Sci Tech 2014, 38, 125-135. [CrossRef]
- Xavier, A.A.O.; Mercadante, A.Z. The bioaccessibility of carotenoids impacts the design of functional foods. Curr Opin Food Sci 2019, 26, 1-8. [CrossRef]
- Parker, R.S. Carotenoids .4. Absorption, metabolism, and transport of carotenoids. FASEB J. 1996, 10, 542-551. [CrossRef]
- Chacón-Ordóñez, T.; Carle, R.; Schweiggert, R. Bioaccessibility of carotenoids from plant and animal foods. J Sci Food Agr 2019, 99, 3220-3239. [CrossRef]
- Reboul, E. Proteins involved in fat-soluble vitamin and carotenoid transport across the intestinal cells: New insights from the past decade. Prog. Lipid Res. 2023, 89, ARTN 101208. [CrossRef]
- Furr, H.C.; Clark, R.M. Transport, uptake, and target. Tissue storage of carotenoids. In Carotenoids in Health and Disease, Krinsky, N.I., Mayne, S.T., Sies, H., Eds.; Marcel Dekker: New York, 2004; pp. 229-278.
- Gugliucci, A. The chylomicron saga: time to focus on postprandial metabolism. Front Endocrinol 2024, 14, ARTN 1322869. [CrossRef]
- Shmarakov, I.O.; Yuen, J.J.; Blaner, W.S. Carotenoid Metabolism and Enzymology. In Carotenoids and Human Health, Tanumihardjo, S.A., Ed.; Humana Press (Springer): New York, 2013; pp. 29-56.
- Canene-Adams, K.; Erdman Jr., J.W. Absorption, transport, distribution in tissues and bioavailability. In Carotenoids, Nutrition and Health, Britton, G., Liaaen-Jensen, S., Pfander, H., Eds.; Birkhäuser Verlag: Basel, 2009; Volume 5, pp. 115-144.
- Li, B.X.; Vachali, P.; Chang, F.Y.; Gorusupudi, A.; Arunkumar, R.; Shi, L.J.; Rognon, G.T.; Frederick, J.M.; Bernstein, P.S. HDL is the primary transporter for carotenoids from liver to retinal pigment epithelium in transgenic ApoA-I/Bco2 mice. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2022, 716, ARTN 109111. [CrossRef]
- Arunkumar, R.; Gorusupudi, A.; Bernstein, P.S. The macular carotenoids: A biochemical overview. Bba-Mol Cell Biol L 2020, 1865, ARTN 158617. [CrossRef]
- Krinsky, N.I.; Cornwell, D.G.; Oncley, J.L. The Transport of Vitamin-a and Carotenoids in Human Plasma. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1958, 73, 233-246. [CrossRef]
- Böhm, V.; Lietz, G.; Olmedilla-Alonso, B.; Phelan, D.; Reboul, E.; Bánati, D.; Borel, P.; Corte-Real, J.; de Lera, A.R.; Desmarchelier, C.; et al. From carotenoid intake to carotenoid blood and tissue concentrations - implications for dietary intake recommendations. Nutr Rev 2021, 79, 544-573. [CrossRef]
- Elvira-Torales, L.I.; García-Alonso, J.; Periago-Castón, M.J. Nutritional Importance of Carotenoids and Their Effect on Liver Health: A Review. Antioxidants-Basel 2019, 8, ARTN 229. [CrossRef]
- Bohn, T.; Desmarchelier, C.; El, S.N.; Keijer, J.; van Schothorst, E.; Rühl, R.; Borel, P. β-Carotene in the human body: metabolic bioactivation pathways - from digestion to tissue distribution and excretion. P Nutr Soc 2019, 78, 68-87. [CrossRef]
- Landrum, J.T. Reactive Oxygen and Nitrogen Species in Biological Systems: Reactions and Regulation by Carotenoids. In Carotenoids and Human Health, Tanumihardjo, S.A., Ed.; Humana Press (Springer) New York, 2013; Volume 1, pp. 57-101.
- Bandara, S.; von Lintig, J. Aster la vista: Unraveling the biochemical basis of carotenoid homeostasis in the human retina. Bioessays 2022, 44, ARTN e2200133. [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.E.; Harrison, E.H. Mechanisms of selective delivery of xanthophylls to retinal pigment epithelial cells by human lipoproteins. J Lipid Res 2016, 57, 1865-1878. [CrossRef]
- Harrison, E.H. Mechanisms of Transport and Delivery of Vitamin A and Carotenoids to the Retinal Pigment Epithelium. Mol Nutr Food Res 2019, 63, ARTN 1801046. [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.J.; Asthana, S.; Kraemer, F.B.; Azhar, S. Scavenger receptor B type 1: expression, molecular regulation, and cholesterol transport function. J Lipid Res 2018, 59, 1114-1131. [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.Y.; Anishchenko, I.; Park, H.; Peng, Z.L.; Ovchinnikov, S.; Baker, D. Improved protein structure prediction using predicted interresidue orientations. P Natl Acad Sci USA 2020, 117, 1496-1503. [CrossRef]
- Powers, H.R.; Sahoo, D. SR-B1’s Next Top Model: Structural Perspectives on the Functions of the HDL Receptor. Curr Atheroscler Rep 2022, 24, 277-288. [CrossRef]
- Quadro, L.; Giordano, E.; Costabile, B.K.; Nargis, T.; Iqbal, J.; Kim, Y.; Wassef, L.; Hussain, M.M. Interplay between β-carotene and lipoprotein metabolism at the maternal-fetal barrier. Bba-Mol Cell Biol L 2020, 1865, ARTN 158591. [CrossRef]
- Borel, P.; Moussa, M.; Reboul, E.; Lyan, B.; Defoort, C.; Vincent-Baudry, S.; Maillot, M.; Gastaldi, M.; Darmon, M.; Portugal, H.; et al. Human plasma levels of vitamin E and Carotenoids are associated with genetic polymorphisms in genes involved in lipid metabolism. J Nutr 2007, 137, 2653-2659. [CrossRef]
- Reboul, E. Mechanisms of Carotenoid Intestinal Absorption: Where Do We Stand? Nutrients 2019, 11, ARTN 838. [CrossRef]
- Steinhoff, J.S.; Lass, A.; Schupp, M. Biological Functions of RBP4 and Its Relevance for Human Diseases. Front Physiol 2021, 12, ARTN 659977. [CrossRef]
- Ask, N.M.; Leung, M.; Radhakrishnan, R.; Lobo, G.P. Vitamin A Transporters in Visual Function: A Mini Review on Membrane Receptors for Dietary Vitamin A Uptake, Storage, and Transport to the Eye. Nutrients 2021, 13, ARTN 3987. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Clarke, O.B.; Kim, J.; Stowe, S.; Kim, Y.K.; Assur, Z.; Cavalier, M.; Godoy-Ruiz, R.; von Alpen, D.C.; Manzini, C.; et al. Structure of the STRA6 receptor for retinol uptake. Science 2016, 353, ARTN aad8266. [CrossRef]
- Petkovich, M.; Chambon, P. Retinoic acid receptors at 35 years. J Mol Endocrinol 2022, 69, T13-T24. [CrossRef]
- Riabroy, N.; Dever, J.T.; Tanumihardjo, S.A. α-Retinol and 3,4-didehydroretinol support growth in rats when fed at equimolar amounts and α-retinol is not toxic after repeated administration of large doses. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 111, 1373-1381. [CrossRef]
- Likkei, K.; Moldenhauer, M.; Tavraz, N.N.; Maksimov, E.G.; Sluchanko, N.N.; Friedrich, T. Lipid composition and properties affect protein-mediated carotenoid uptake efficiency from membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomem. 2024, 1866, ARTN 184241. [CrossRef]
- Shyam, R.; Vachali, P.; Gorusupudi, A.; Nelson, K.; Bernstein, P.S. All three human scavenger receptor class B proteins can bind and transport all three macular xanthophyll carotenoids. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2017, 634, 21-28. [CrossRef]
- Bandara, S.; Ramkumar, S.; Imanishi, S.; Thomas, L.D.; Sawant, O.B.; Imanishi, Y.; von Lintig, J. Aster proteins mediate carotenoid transport in mammalian cells. P Natl Acad Sci USA 2022, 119, ARTN e2200068119. [CrossRef]
- Slonimskiy, Y.B.; Egorkin, N.A.; Friedrich, T.; Maksimov, E.G.; Sluchanko, N.N. Microalgal protein AstaP is a potent carotenoid solubilizer and delivery module with a broad carotenoid binding repertoire. Febs J 2022, 289, 999-1022. [CrossRef]
- Bandara, S.; Moon, J.; Ramkumar, S.; von Lintig, J. ASTER-B regulates mitochondrial carotenoid transport and homeostasis. J Lipid Res 2023, 64, ARTN 100369. [CrossRef]
- Powers, H.R.; Jenjak, S.E.; Volkman, B.F.; Sahoo, D. Development and validation of a purification system for functional full-length human SR-B1 and CD36. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2023, 299, ARTN 105187. [CrossRef]
- Sluchanko, N.N.; Slonimskiy, Y.B.; Egorkin, N.A.; Varfolomeeva, L.A.; Kleymenov, S.Y.; Minyaev, M.E.; Faletrov, Y.V.; Moysenovich, A.M.; Parshina, E.Y.; Friedrich, T.; et al. Structural basis for the carotenoid binding and transport function of a START domain. Structure 2022, 30, 1647-+. [CrossRef]
- Kornilov, F.D.; Slonimskiy, Y.B.; Lunegova, D.A.; Egorkin, N.A.; Savitskaya, A.G.; Kleymenov, S.Y.; Maksimov, E.G.; Goncharuk, S.A.; Mineev, K.S.; Sluchanko, N.N. Structural basis for the ligand promiscuity of the neofunctionalized, carotenoid-binding fasciclin domain protein AstaP. Commun Biol 2023, 6, ARTN 471. [CrossRef]
- Horvath, M.P.; George, E.W.; Tran, Q.T.; Baumgardner, K.; Zharov, G.; Lee, S.; Sharifzadeh, H.; Shihab, S.; Mattinson, T.; Li, B.X.; et al. Structure of the lutein-binding domain of human StARD3 at 1.74 angstrom resolution and model of a complex with lutein. Acta Crystallogr F 2016, 72, 609-618. [CrossRef]
- Shyam, R.; Gorusupudi, A.; Nelson, K.; Horvath, M.P.; Bernstein, P.S. RPE65 has an additional function as the lutein to meso-zeaxanthin isomerase in the vertebrate eye. P Natl Acad Sci USA 2017, 114, 10882-10887. [CrossRef]
- Varfolomeeva, L.A.; Slonimskiy, Y.B.; Egorkin, N.A.; Minyaev, M.E.; Faletrov, Y.V.; Boyko, K.M.; Sluchanko, N.N. Preparation and Structural Studies of the Silkworm Carotenoid-Binding Protein Complexed with a New Pigment. Crystallogr Rep+ 2022, 67, 909-917. [CrossRef]
- Hazai, E.; Bikádi, Z.; Zsila, F.; Lockwood, S.F. Molecular modeling of the non-covalent binding of the dietary tomato carotenoids lycopene and lycophyll, and selected oxidative metabolites with 5-lipoxygenase. Bioorgan Med Chem 2006, 14, 6859-6867. [CrossRef]
- Neculai, D.; Schwake, M.; Ravichandran, M.; Zunke, F.; Collins, R.F.; Peters, J.; Neculai, M.; Plumb, J.; Loppnau, P.; Pizarro, J.C.; et al. Structure of LIMP-2 provides functional insights with implications for SR-BI and CD36. Nature 2013, 504, 172-176. [CrossRef]
- Molteni, C.; La Motta, C.; Valoppi, F. Improving the Bioaccessibility and Bioavailability of Carotenoids by Means of Nanostructured Delivery Systems: A Comprehensive Review. Antioxidants-Basel 2022, 11, ARTN 1931. [CrossRef]
- Widjaja-Adhi, M.A.K.; Lobo, G.P.; Golczak, M.; Von Lintig, J. A genetic dissection of intestinal fat-soluble vitamin and carotenoid absorption. Hum Mol Genet 2015, 24, 3206-3219. [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, A.; Bertoni, M.; Bienert, S.; Studer, G.; Tauriello, G.; Gumienny, R.; Heer, F.T.; de Beer, T.A.P.; Rempfer, C.; Bordoli, L.; et al. SWISS-MODEL: homology modelling of protein structures and complexes. Nucleic Acids Res 2018, 46, W296-W303. [CrossRef]
- Fiser, A.; Sali, A. MODELLER: Generation and refinement of homology-based protein structure models. Method Enzymol 2003, 374, 461-491. [CrossRef]
- Rizzuti, B. Molecular simulations of proteins: From simplified physical interactions to complex biological phenomena. Bba-Proteins Proteom 2022, 1870, ARTN 140757. [CrossRef]
- Jemiola-Rzeminska, M.; Pasenkiewicz-Gierula, M.; Strzalka, K. The behaviour of β-carotene in the phosphatidylcholine bilayer as revealed by a molecular simulation study. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2005, 135, 27-37. [CrossRef]
- Pasenkiewicz-Gierula, M.; Baczynski, K.; Murzyn, K.; Markiewicz, M. Orientation of lutein in a lipid bilayer - revisited. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2012, 59, 115-118.
- Makuch, K.; Markiewicz, M.; Pasenkiewicz-Gierula, M. Asymmetric Spontaneous Intercalation of Lutein into a Phospholipid Bilayer, a Computational Study. Comput Struct Biotec 2019, 17, 516-526. [CrossRef]
- Torrie, G.M.; Valleau, J.P. Nonphysical sampling distributions in Monte Carlo free-energy estimation: Umbrella sampling. J. Comput. Phys. 1977, 23, 187-199. [CrossRef]
- Cerezo, J.; Zuniga, J.; Bastida, A.; Requena, A.; Ceron-Carrasco, J.P. Conformational changes of beta-carotene and zeaxanthin immersed in a model membrane through atomistic molecular dynamics simulations. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 6527-6538. [CrossRef]
- Grudzinski, W.; Nierzwicki, L.; Welc, R.; Reszczynska, E.; Luchowski, R.; Czub, J.; Gruszecki, W.I. Localization and Orientation of Xanthophylls in a Lipid Bilayer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9619. [CrossRef]
- Luchowski, R.; Grudzinski, W.; Welc, R.; Pinto, M.M.M.; Sek, A.; Ostrowski, J.; Nierzwicki, L.; Chodnicki, P.; Wieczor, M.; Sowinski, K.; et al. Light-Modulated Sunscreen Mechanism in the Retina of the Human Eye. J. Phys. Chem. B 2021, 125, 6090-6102. [CrossRef]
- Semenov, A.N.; Gvozdev, D.A.; Zlenko, D.V.; Protasova, E.A.; Khashimova, A.R.; Parshina, E.Y.; Baizhumanov, A.A.; Lotosh, N.Y.; Kim, E.E.; Kononevich, Y.N.; et al. Modulation of Membrane Microviscosity by Protein-Mediated Carotenoid Delivery as Revealed by Time-Resolved Fluorescence Anisotropy. Membranes-Basel 2022, 12, ARTN 905. [CrossRef]
- Johnson, Q.R.; Mostofian, B.; Gomez, G.F.; Smith, J.C.; Cheng, X.L. Effects of carotenoids on lipid bilayers. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 3795-3804. [CrossRef]
- Mostofian, B.; Johnson, Q.R.; Smith, J.C.; Cheng, X.L. Carotenoids promote lateral packing and condensation of lipid membranes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 12281-12293. [CrossRef]
- Makuch, K.; Hryc, J.; Markiewicz, M.; Pasenkiewicz-Gierula, M. Lutein and Zeaxanthin in the Lipid Bilayer-Similarities and Differences Revealed by Computational Studies. Front Mol Biosci 2021, 8, ARTN 768449. [CrossRef]
- Ri, J.S.; Choe, C.S.; Choe, S.H.; Jong, K.H.; Hong, S.N.; Schleusener, J.; Lademann, J.; Darvin, M.E. Lycopene, but not zeaxanthin, serves as a skeleton for the formation of an orthorhombic organization of intercellular lipids within the lamellae in the stratum corneum: Molecular dynamics simulations of the hydrated ceramide NS bilayer model. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomem. 2023, 1865. [CrossRef]
- Flieger, J.; Raszewska-Famielec, M.; Radzikowska-Büchner, E.; Flieger, W. Skin Protection by Carotenoid Pigments. Int J Mol Sci 2024, 25, ARTN 1431. [CrossRef]
- Gastaldo, I.P.; Himbert, S.; Ram, U.; Rheinstädter, M.C. The Effects of Resveratrol, Caffeine, β-Carotene, and Epigallocatechin Gallate (EGCG) on Amyloid-β Aggregation in Synthetic Brain Membranes. Mol Nutr Food Res 2020, 64, ARTN 2000632. [CrossRef]
- Hachlica, N.; Stefanska, M.; Mach, M.; Kowalska, M.; Wydro, P.; Domagala, A.; Kessler, J.; Zajac, G.; Kaczor, A. Organization of Carotenoid Aggregates in Membranes Studied Selectively using Resonance Raman Optical Activity. Small 2024. [CrossRef]
- Pasenkiewicz-Gierula, M.; Markiewicz, M. Orientation of lutein in a lipid bilayer – revisited. In Proceedings of the 16th International Symposium on Carotenoids., Krakow, Poland,, 2012; pp. 105-105.
- Sujak, A.; Okulski, W.; Gruszecki, W.I. Organisation of xanthophyll pigments lutein and zeaxanthin in lipid membranes formed with dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomem. 2000, 1509, 255-263. [CrossRef]
- Sujak, A.; Mazurek, P.; Gruszecki, W.I. Xanthophyll pigments lutein and zeaxanthin in lipid multibilayers formed with dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2002, 68, 39-44. [CrossRef]
- Fukuoka, H.; Gali, H.E.; Bu, J.J.; Sella, R.; Afshari, N.A. Ultraviolet light exposure and its penetrance through the eye in a porcine model. Int J Ophthalmol-Chi 2023, 16, 172-177. [CrossRef]
- Snodderly, D.M.; Auran, J.D.; Delori, F.C. The Macular Pigment .2. Spatial-Distribution in Primate Retinas. Invest Ophth Vis Sci 1984, 25, 674-685.
- Schalch, W.; Landrum, J.T.; Bone, R.A. The Eye. In Carotenoids, Nutrition and Health, Britton, G., Liaaen-Jensen, S., Pfande, H., Eds.; Birkhäuser Verlag Basel, 2009; Volume 5, pp. 301-330.
- O’Connell, E.; Neelam, K.; Nolan, J.; Eong, K.G.A.; Beatty, S. Macular carotenoids and age-related maculopathy. Ann Acad Med Singap 2006, 35, 821-830.
- Ahmed, S.; Lott, M.; Marcus, D. The macular xantophyls. Survey of Ophthalmology 2005, 50, 183-193.
- Vishwanathan, R.; Johnson, E.J. Lutein and Zeaxanthin and Eye Disease. In Carotenoids and Human Health, Tanumihardjo, S.A., Ed.; Humana Press (Springer): New York, 2013; Volume 1, pp. 215-235.
- Welc-Stanowska, R.; Pietras, R.; Mielecki, B.; Sarewicz, M.; Luchowski, R.; Widomska, J.; Grudzinski, W.; Osyczka, A.; Gruszecki, W.I. How Do Xanthophylls Protect Lipid Membranes from Oxidative Damage? J Phys Chem Lett 2023. [CrossRef]
- Cantrell, A.; McGarvey, D.J.; Truscott, T.G.; Rancan, F.; Böhm, F. Singlet oxygen quenching by dietary carotenoids in a model membrane environment. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2003, 412, 47-54. [CrossRef]
- Subczynski, W.K.; Wisniewska, A.; Widomska, J. Location of macular xanthophylls in the most vulnerable regions of photoreceptor outer-segment membranes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2010, 504, 61-66. [CrossRef]
- Widomska, J.; Gruszecki, W.I.; Subczynski, W.K. Factors Differentiating the Antioxidant Activity of Macular Xanthophylls in the Human Eye Retina. Antioxidants-Basel 2021, 10, Artn 601. [CrossRef]
- Widomska, J.; Zareba, M.; Subczynski, W.K. Can Xanthophyll-Membrane Interactions Explain Their Selective Presence in the Retina and Brain? Foods 2016, 5, ARTN 7. [CrossRef]
- Wisniewska, A.; Subczynski, W.K. Distribution of macular xanthophylls between domains in a model of photoreceptor outer segment membranes. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2006, 41, 1257-1265.
- Polívka, T.; Sundström, V. Ultrafast dynamics of carotenoid excited states -: From solution to natural and artificial systems. Chem Rev 2004, 104, 2021-2071. [CrossRef]
- Accomasso, D.; Arslancan, S.; Cupellini, L.; Granucci, G.; Mennucci, B. Ultrafast Excited-State Dynamics of Carotenoids and the Role of the S State. J Phys Chem Lett 2022, 13, 6762-6769. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




