Submitted:
26 June 2024
Posted:
26 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Materials and Methods
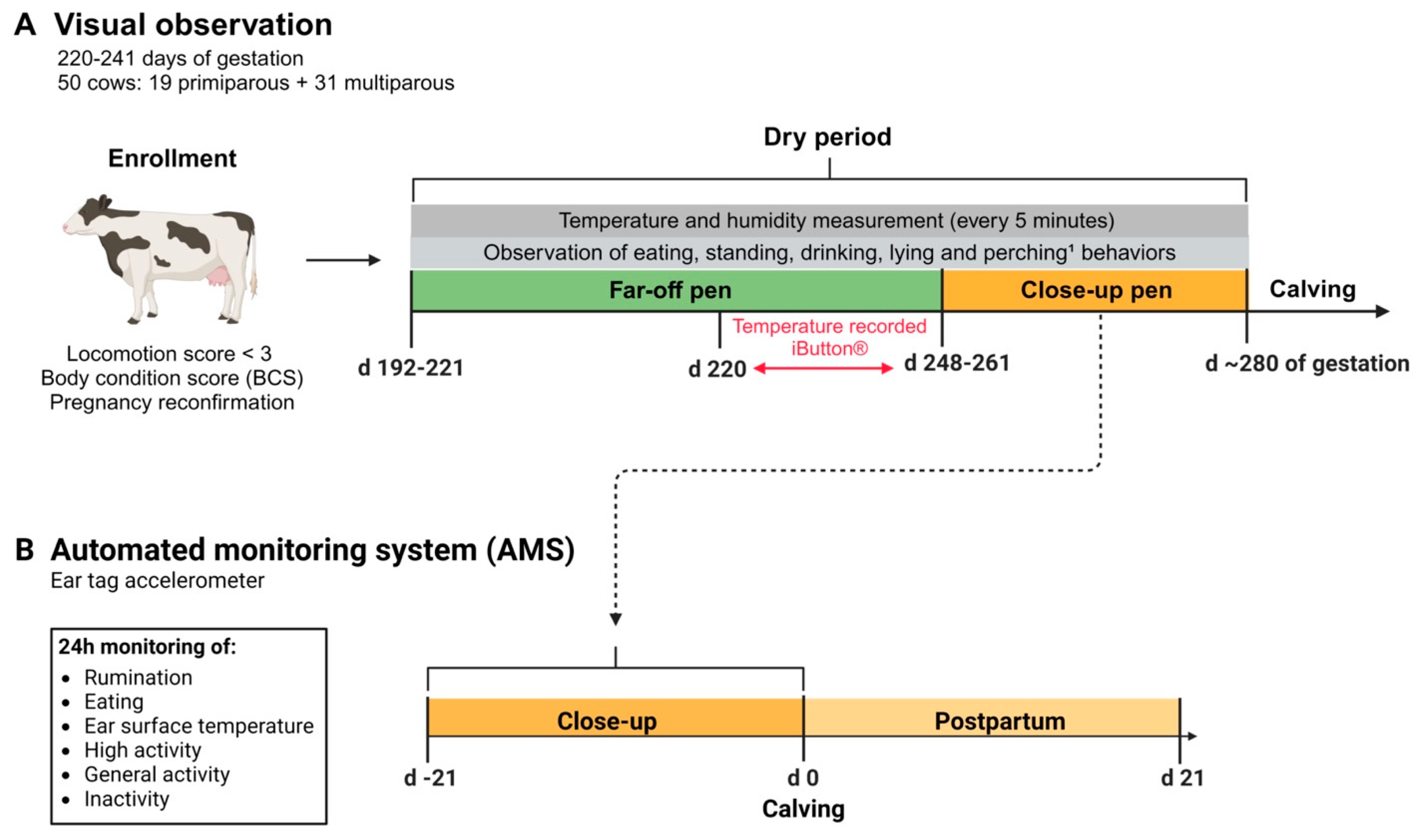
Animals, Facilities, Management, and Enrollment
Temperature Humidity Index (THI) and Assessment of Core Body Temperature (CBT)
Assessment of Dry Cow Behavior
Visual Observations
Automated Behavior Monitoring
Isolation of White Blood Cells for Transcriptome Analysis
Library Preparation and Sequencing – Assessment of WBC Transcriptome
Statistical Analysis
Analysis of Gene Expression in White Blood Cells
Results
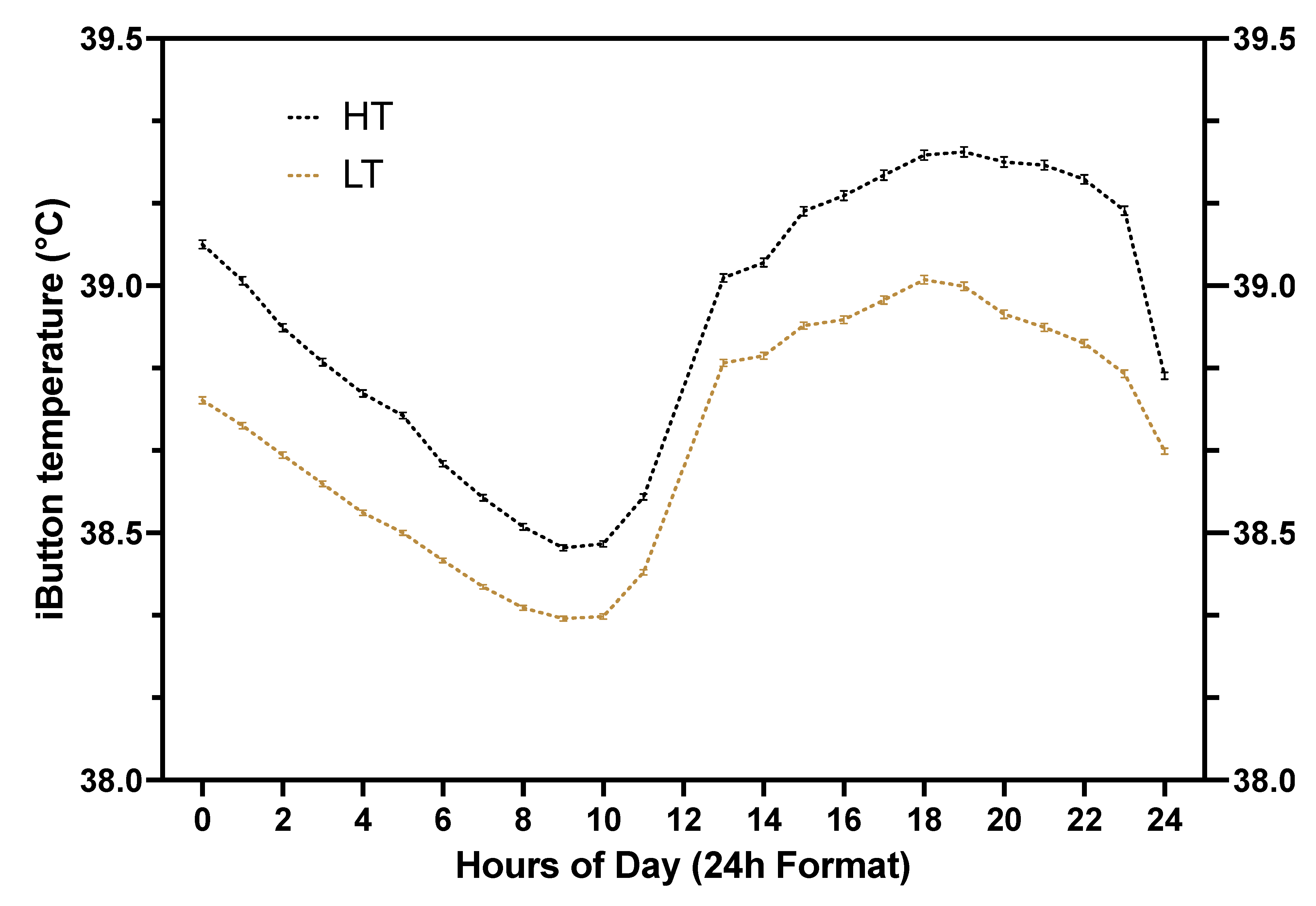
CBT Classification
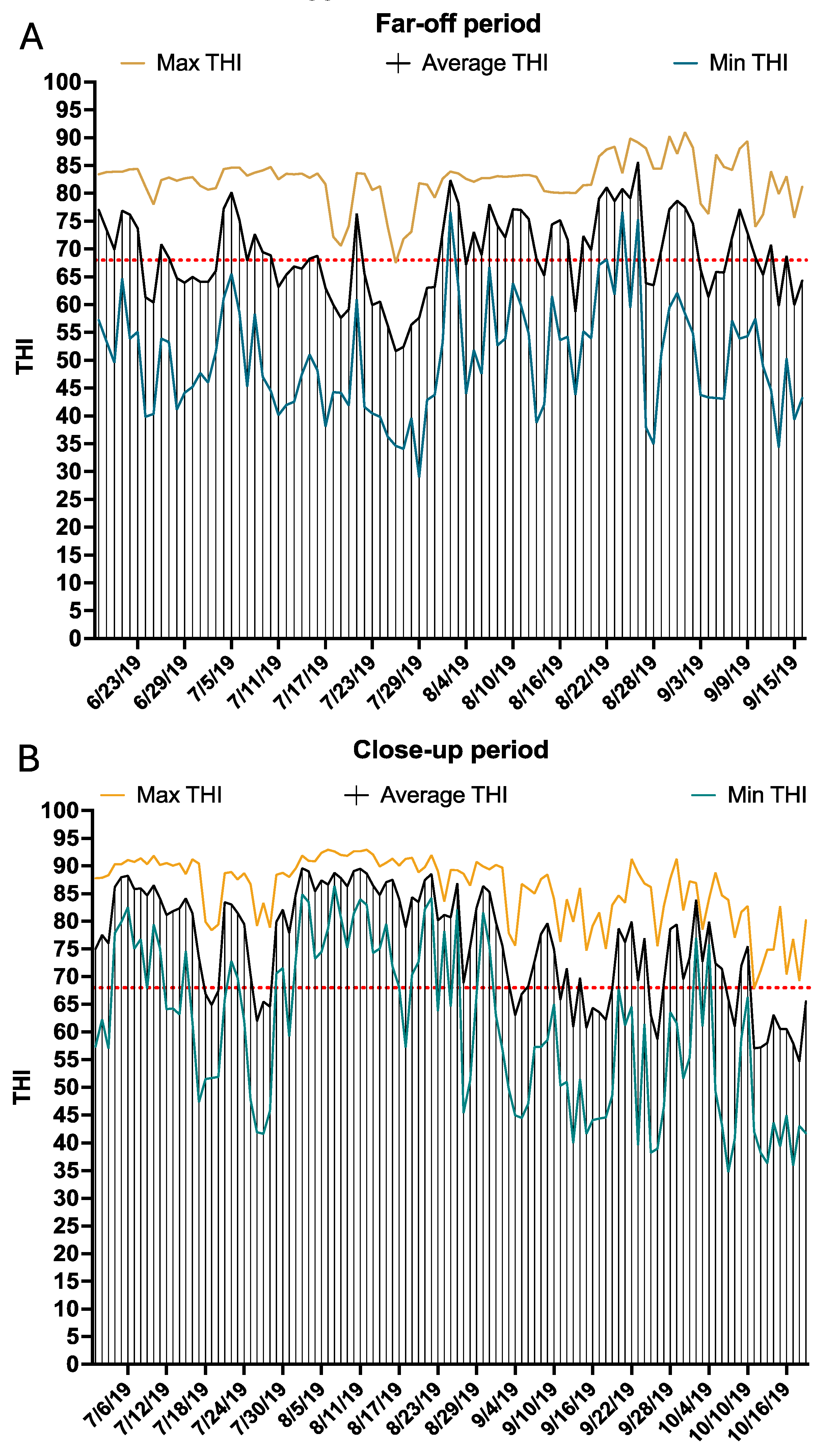
Temperature-Humidity Index in the Far-off and Close-Up Pens and Overall Descriptive Data
Visual Behavior Monitoring
Far-off Period
Close-Up Period
Automated Behavior Monitoring
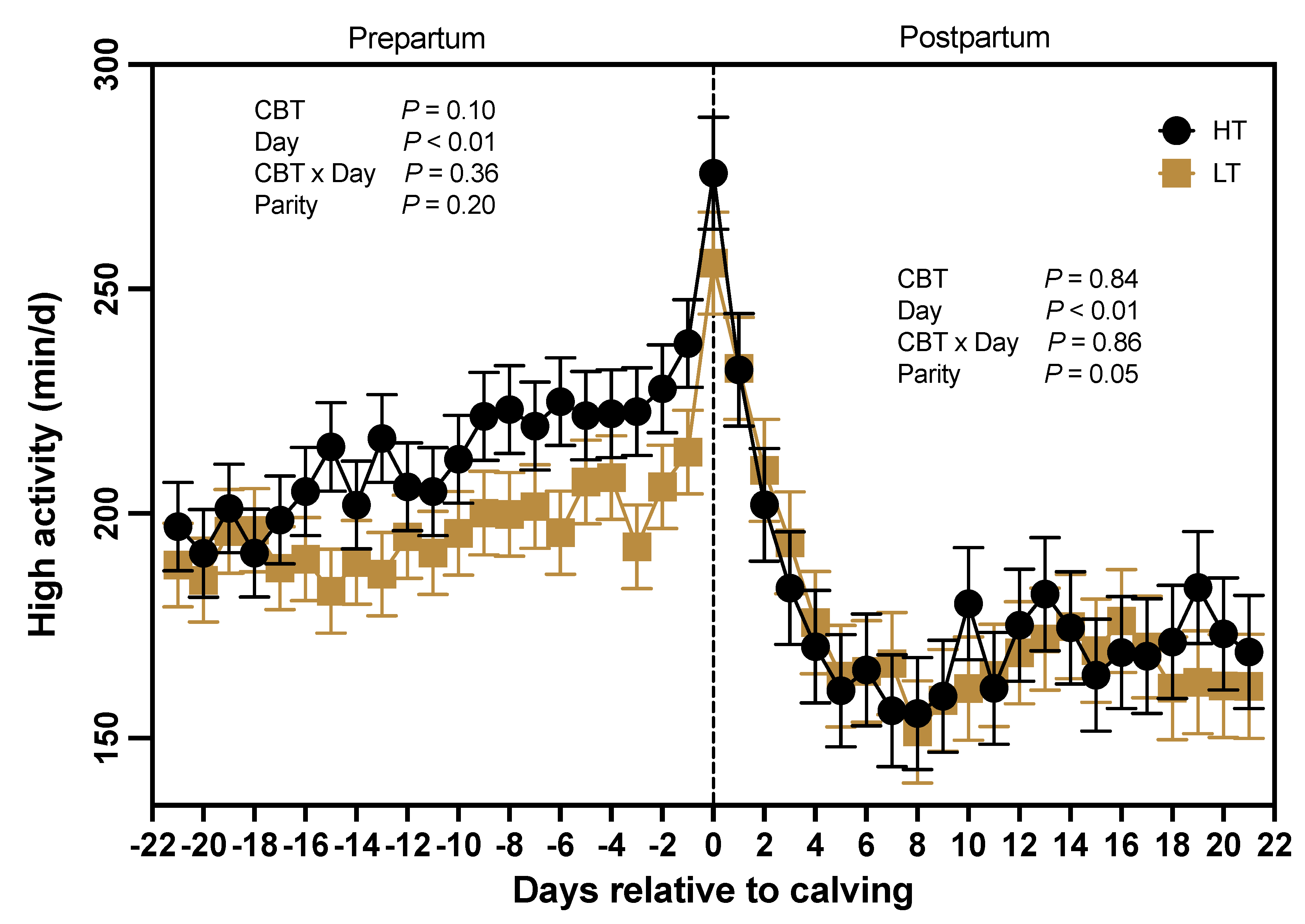
Periods of High Activity
General Activity
Inactive Daily Minutes
Time Eating
Rumination Time
Ear Surface Temperature
Gene Expression Differences in WBC from HT and LT cows
Discussion
Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- St-Pierre, N.R.; Cobanov, B.; Schnitkey, G. Economic Losses from Heat Stress by US Livestock Industries1. Journal of Dairy Science 2003, 86, E52–E77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunn, K.M.; Holly, M.A.; Veith, T.L.; Buda, A.R.; Prasad, R.; Rotz, C.A.; Soder, K.J.; Stoner, A.M.K. Projected heat stress challenges and abatement opportunities for U.S. milk production. PLoS One 2019, 14, e0214665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouraoui, R.; Lahmar, M.; Majdoub, A.; Belyea, R. The relationship of temperature-humidity index with milk production of dairy cows in a Mediterranean climate. Animal Research 2002, 51, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimbelman, R.B.; Rhoads, R.P.; Rhoads, M.L.; Duff, G.C.; Baumgard, L.H.; Collier, R.J. A re-evaluation of the impact of temperature humidity index (THI) and black globe humidity index (BGHI) on milk production in high producing dairy cows. Proceedings of the Southwest Nutrition Conference. USDA Cooperative State Research, Education, and Extension Service (CSREES); 2009:158–169.
- De Rensis, F.; Garcia-Ispierto, I.; López-Gatius, F. Seasonal heat stress: Clinical implications and hormone treatments for the fertility of dairy cows. Theriogenology 2015, 84, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, N.B.; Mentink, R.L.; Bennett, T.B.; Burgi, K. The effect of heat stress and lameness on time budgets of lactating dairy cows. J Dairy Sci 2007, 90, 1674–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, N.B. Time budgets for dairy cows: how does cow comfort influence health, reproduction and productivity. Proceedings of the Penn State Dairy Cattle Nutrition Workshop 2008, 12–13. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, I.M.; Dahl, G.E. Dry-period seasonal effects on the subsequent lactation. The Professional Animal Scientist 2012, 28, 628–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanavez, A.L.A.; Voelz, B.E.; Moraes, J.G.N.; Green, J.A.; Mendonça, L.G.D. Physiological, health, lactation, and reproductive traits of cooled dairy cows classified as having high or low core body temperature during the dry period. J Anim Sci 2019, 97, 4792–4802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson, J.S.; Banuelos, S.; Mendonça, L.G.D. Transition dairy cow health is associated with first postpartum ovulation risk, metabolic status, milk production, rumination, and physical activity. J Dairy Sci 2020, 103, 9573–9586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, M.T.; Ghorbani, G.R.; Kargar, S.; Drackley, J.K. Late-gestation heat stress abatement on performance and behavior of Holstein dairy cows. Journal of Dairy Science 2015, 98, 6865–6875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanavez, A.L.A.; Fragomeni, B.; Rocha, L.; Voelz, B.E.; Hulbert, L.E.; Mendonça, L.G.D. Association between 4-day vaginal temperature assessment during the dry period and performance in the subsequent lactation of dairy cows during the warm season1,2. J Anim Sci 2017, 95, 5208–5217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sejian, V.; Bhatta, R.; Gaughan, J.B.; Dunshea, F.R.; Lacetera, N. Adaptation of animals to heat stress. Animal 2018, 12, s431–s444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soriani, N.; Trevisi, E.; Calamari, L. Relationships between rumination time, metabolic conditions, and health status in dairy cows during the transition period. J Anim Sci 2012, 90, 4544–4554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liboreiro, D.N.; Machado, K.S.; Silva, P.R.B.; Maturana, M.M.; Nishimura, T.K.; Brandão, A.P.; Endres, M.I.; Chebel, R.C. Characterization of peripartum rumination and activity of cows diagnosed with metabolic and uterine diseases. J Dairy Sci 2015, 98, 6812–6827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stangaferro, M.L.; Wijma, R.; Caixeta, L.S.; Al-Abri, M.A.; Giordano, J.O. Use of rumination and activity monitoring for the identification of dairy cows with health disorders: Part I. Metabolic and digestive disorders. J Dairy Sci 2016, 99, 7395–7410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stangaferro, M.L.; Wijma, R.; Caixeta, L.S.; Al-Abri, M.A.; Giordano, J.O. Use of rumination and activity monitoring for the identification of dairy cows with health disorders: Part II. Mastitis. J Dairy Sci 2016, 99, 7411–7421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stangaferro, M.L.; Wijma, R.; Caixeta, L.S.; Al-Abri, M.A.; Giordano, J.O. Use of rumination and activity monitoring for the identification of dairy cows with health disorders: Part III. Metritis. Journal of Dairy Science 2016, 99, 7422–7433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merenda, V.R.; Ruiz-Munoz, J.; Zare, A.; Chebel, R.C. Predictive models to identify Holstein cows at risk of metritis and clinical cure and reproductive/productive failure following antimicrobial treatment. Prev Vet Med 2021, 194, 105431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rial, C.; Laplacette, A.; Caixeta, L.; Florentino, C.; Peña-Mosca, F.; Giordano, J.O. Metritis and clinical mastitis events in lactating dairy cows were associated with altered patterns of rumination, physical activity, and lying behavior monitored by an ear-attached sensor. J Dairy Sci 2023, 106, 9345–9365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretti, R.; Biffani, S.; Chessa, S.; Bozzi, R. Heat stress effects on Holstein dairy cows’ rumination. Animal 2017, 11, 2320–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.D.; Hall, L.W.; Collier, R.J.; Smith, J.F. Effect of core body temperature, time of day, and climate conditions on behavioral patterns of lactating dairy cows experiencing mild to moderate heat stress. J Dairy Sci 2015, 98, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordlund, K.V.; Strassburg, P.; Bennett, T.B.; Oetzel, G.R.; Cook, N.B. Thermodynamics of standing and lying behavior in lactating dairy cows in freestall and parlor holding pens during conditions of heat stress. J Dairy Sci 2019, 102, 6495–6507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, J.W. Effects of heat-stress on production in dairy cattle. J Dairy Sci 2003, 86, 2131–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tapkı, İ.; Şahin, A. Comparison of the thermoregulatory behaviours of low and high producing dairy cows in a hot environment. Applied Animal Behaviour Science 2006, 99, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchama, A.; Knochel, J.P. Heat stroke. N Engl J Med 2002, 346, 1978–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchama, A.; Aziz, M.A.; Mahri, S.A.; Gabere, M.N.; Dlamy, M.A.; Mohammad, S.; Abbad, M.A.; Hussein, M. A Model of Exposure to Extreme Environmental Heat Uncovers the Human Transcriptome to Heat Stress. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 9429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprecher, D.J.; Hostetler, D.E.; Kaneene, J.B. A lameness scoring system that uses posture and gait to predict dairy cattle reproductive performance. Theriogenology 1997, 47, 1179–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, J.D.; Galligan, D.T.; Thomsen, N. Principal descriptors of body condition score in Holstein cows. J Dairy Sci 1994, 77, 2695–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borchers, M.R.; Chang, Y.M.; Tsai, I.C.; Wadsworth, B.A.; Bewley, J.M. A validation of technologies monitoring dairy cow feeding, ruminating, and lying behaviors. Journal of Dairy Science 2016, 99, 7458–7466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, M.S.; Moraes, J.G.; Patterson, D.J.; Smith, M.F.; Behura, S.K.; Poock, S.; Spencer, T.E. Influences of sire conception rate on pregnancy establishment in dairy cattle. Biology of Reproduction 2018, 99, 1244–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nature Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. FeatureCounts: An efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Lindsay, H.; Robinson, M.D. Robustly detecting differential expression in RNA sequencing data using observation weights. Nucleic Acids Research, 2014; 42. [Google Scholar]
- Su, C.-T.; Urban, Z. LTBP4 in Health and Disease. Genes (Basel) 2021, 12, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubiczkova, L.; Sedlarikova, L.; Hajek, R.; Sevcikova, S. TGF-β – an excellent servant but a bad master. Journal of Translational Medicine 2012, 10, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naryzny, S.N.; Legina, O.K. Haptoglobin as a Biomarker. Biochem Mosc Suppl B Biomed Chem 2021, 15, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luppe, J.; Sticht, H.; Lecoquierre, F.; Goldenberg, A.; Gorman, K.M.; Molloy, B.; Agolini, E.; Novelli, A.; Briuglia, S.; Kuismin, O.; Marcelis, C.; Vitobello, A.; et al. Heterozygous and homozygous variants in STX1A cause a neurodevelopmental disorder with or without epilepsy. Eur J Hum Genet 2023, 31, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuho, I.; Balaji, S.; Muntean, B.S.; Skamangas, N.K.; Chavali, S.; Tesmer, J.J.G.; Babu, M.M.; Martemyanov, K.A. A Global Map of G Protein Signaling Regulation by RGS Proteins. Cell 2020, 183, 503–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Bounkari, O.; Guria, A.; Klebba-Faerber, S.; Claußen, M.; Pieler, T.; Griffiths, J.R.; Whetton, A.D.; Koch, A.; Tamura, T. Nuclear localization of the pre-mRNA associating protein THOC7 depends upon its direct interaction with Fms tyrosine kinase interacting protein (FMIP). FEBS Letters 2009, 583, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.A.; Sudi, J.; Babatz, T.D.; Brune, C.W.; Oswald, D.; Yen, M.; Nowak, N.J.; Cook, E.H.; Christian, S.L.; Dobyns, W.B. A de novo 1p34.2 microdeletion identifies the synaptic vesicle gene RIMS3 as a novel candidate for autism. Journal of Medical Genetics 2010, 47, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, J.; Miyazono, K.; Ehata, S. Decreased TGFBR3/betaglycan expression enhances the metastatic abilities of renal cell carcinoma cells through TGF-β-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Oncogene 2018, 37, 2197–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higa, L.A.; Wardley, J.; Wardley, C.; Singh, S.; Foster, T.; Shen, J.J. CNKSR2-related neurodevelopmental and epilepsy disorder: a cohort of 13 new families and literature review indicating a predominance of loss of function pathogenic variants. BMC Med Genomics 2021, 14, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietzsch, A.N.; Al-Hasani, H.; Altschmied, J.; Bottermann, K.; Brendler, J.; Haendeler, J.; Horn, S.; Kaczmarek, I.; Körner, A.; Krause, K.; Landgraf, K.; Le Duc, D.; et al. Dysfunction of the adhesion G protein-coupled receptor latrophilin 1 (ADGRL1/LPHN1) increases the risk of obesity. Sig Transduct Target Ther 2024, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukic, M.; Chouaref, J.; Della Chiara, V.; Dogan, S.; Ratner, F.; Hogenboom, J.Z.M.; Epp, T.A.; Chawengsaksophak, K.; Vonk, K.K.D.; Breukel, C.; Ariyurek, Y.; San Leon Granado, D.; et al. CDCA7-associated global aberrant DNA hypomethylation translates to localized, tissue-specific transcriptional responses. Science Advances 2024, 10, eadk3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, R.; Kobayashi, S.; Wagatsuma, H.; Aisaka, K.; Kohda, T.; Kaneko-Ishino, T.; Ishino, F. A retrotransposon-derived gene, PEG10, is a novel imprinted gene located on human chromosome 7q21. Genomics 2001, 73, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, A.; Cook, N.B. Time budgets of lactating dairy cattle in commercial freestall herds. J Dairy Sci 2010, 93, 5772–5781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, E.I.; LeBlanc, S.J.; McBride, B.W.; Duffield, T.F.; DeVries, T.J. Association of rumination time with subclinical ketosis in transition dairy cows. J Dairy Sci 2016, 99, 5604–5618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufman, E.I.; Asselstine, V.H.; LeBlanc, S.J.; Duffield, T.F.; DeVries, T.J. Association of rumination time and health status with milk yield and composition in early-lactation dairy cows. J Dairy Sci 2018, 101, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanjanapruthipong, J.; Junlapho, W.; Karnjanasirm, K. Feeding and lying behavior of heat-stressed early lactation cows fed low fiber diets containing roughage and nonforage fiber sources. J Dairy Sci 2015, 98, 1110–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antanaitis, R.; Džermeikaitė, K.; Bespalovaitė, A.; Ribelytė, I.; Rutkauskas, A.; Japertas, S.; Baumgartner, W. Assessment of Ruminating, Eating, and Locomotion Behavior during Heat Stress in Dairy Cattle by Using Advanced Technological Monitoring. Animals (Basel) 2023, 13, 2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanjanapruthipong, J.; Junlapho, W.; Karnjanasirm, K. Feeding and lying behavior of heat-stressed early lactation cows fed low fiber diets containing roughage and nonforage fiber sources. J Dairy Sci 2015, 98, 1110–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rulquin, H.; Caudal, J.P. Effects of lying or standing on mammary blood flow and heart rate of dairy cows. Ann Zootech 1992, 41, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munksgaard, L.; Jensen, M.B.; Pedersen, L.J.; Hansen, S.W.; Matthews, L. Quantifying behavioural priorities—effects of time constraints on behaviour of dairy cows, Bos taurus. Applied Animal Behaviour Science 2005, 92, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, H.; Lietzau, M.; Tichy, A.; Herzog, K. Investigations of mammary and uterine blood flow in relation to milk yield, postpartum disease, and pregnancy result in dairy cows. Theriogenology 2016, 86, 1906–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McWilliams, C.J.; Schwanke, A.J.; DeVries, T.J. Is greater milk production associated with dairy cows who have a greater probability of ruminating while lying down? JDS Commun 2022, 3, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piñeiro, J.M.; Menichetti, B.T.; Barragan, A.A.; Relling, A.E.; Weiss, W.P.; Bas, S.; Schuenemann, G.M. Associations of pre- and postpartum lying time with metabolic, inflammation, and health status of lactating dairy cows. J Dairy Sci 2019, 102, 3348–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proudfoot, K.L.; Huzzey, J.M. A first time for everything: The influence of parity on the behavior of transition dairy cows*. JDS Communications 2022, 3, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suthar, V.; Burfeind, O.; Bonk, S.; Voigtsberger, R.; Keane, C.; Heuwieser, W. Factors associated with body temperature of healthy Holstein dairy cows during the first 10 days in milk. J Dairy Res 2012, 79, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutjens, M.F. Feed Efficiency-Impact on Economics. 2008.
- Adin, G.; Gelman, A.; Solomon, R.; Flamenbaum, I.; Nikbachat, M.; Yosef, E.; Zenou, A.; Shamay, A.; Feuermann, Y.; Mabjeesh, S.J.; Miron, J. Effects of cooling dry cows under heat load conditions on mammary gland enzymatic activity, intake of food and water, and performance during the dry period and after parturition. Livestock Science 2009, 124, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grummer, R.R.; Mashek, D.G.; Hayirli, A. Dry matter intake and energy balance in the transition period. Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract 2004, 20, 447–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huzzey, J.M.; Veira, D.M.; Weary, D.M.; von Keyserlingk M a, G. Prepartum behavior and dry matter intake identify dairy cows at risk for metritis. J Dairy Sci 2007, 90, 3220–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar, D.; Kaim, M.; Flamenbaum, I.; Hanochi, B.; Toaff-Rosenstein, R.L. Technical note: Accelerometer-based recording of heavy breathing in lactating and dry cows as an automated measure of heat load. J Dairy Sci 2019, 102, 3480–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovács, D.; Sigmond, T.; Hotzi, B.; Bohár, B.; Fazekas, D.; Deák, V.; Vellai, T.; Barna, J. HSF1Base: a comprehensive database of HSF1 (heat shock factor 1) target genes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2019, 20, 5815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Åkerfelt, M.; Morimoto, R.I.; Sistonen, L. Heat shock factors: integrators of cell stress, development and lifespan. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology 2010, 11, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huzzey, J.M.; Duffield, T.F.; LeBlanc, S.J.; Veira, D.M.; Weary, D.M.; von Keyserlingk, M.A.G. Short communication: Haptoglobin as an early indicator of metritis. Journal of Dairy Science 2009, 92, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moraes, J.G.N.; Gull, T.B.; Ericsson, A.C.; Caldeira, M.O.; Evans, T.J.; Poock, S.E.; Lucy, M.C. Systemic antibiotic treatment of cows with metritis early postpartum does not change the progression of uterine disease or the uterine microbiome at 1 month postpartum. Res Sq 2024:rs.3.rs-4233045.
- Mitani, K.; Fujita, H.; Kappas, A.; Sassa, S. Heme Oxygenase Is a Positive Acute-Phase Reactant in Human Hep3B Hepatoma Cells. Blood 1992, 79, 1255–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, A.W.Y.; McFarlane, A.; Verhovsek, M. Haptoglobin testing in hemolysis: measurement and interpretation. Am J Hematol 2014, 89, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberghina, D.; Piccione, G.; Casella, S.; Panzera, M.; Morgante, M.; Gianesella, M. The effect of the season on some blood metabolites and haptoglobin in dairy cows during postpartum period. Archives Animal Breeding 2013, 56, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.-L.; Chen, S.-Y.; Qin, C.; Jia, X.; Deng, F.; Wang, J.; Lai, S.-J. Clinical Ketosis-Associated Alteration of Gene Expression in Holstein Cows. Genes (Basel) 2020, 11, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, A.; Sawai, M.; Sakurai, H. Stress-induced transcription of regulator of G protein signaling 2 (RGS2) by heat shock transcription factor HSF1. Biochimie 2013, 95, 1432–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehwinkel, J.; Herold, A.; Gari, K.; Köcher, T.; Rode, M.; Ciccarelli, F.L.; Wilm, M.; Izaurralde, E. Genome-wide analysis of mRNAs regulated by the THO complex in Drosophila melanogaster. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2004, 11, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libri, D.; Dower, K.; Boulay, J.; Thomsen, R.; Rosbash, M.; Jensen, T.H. Interactions between mRNA export commitment, 3’-end quality control, and nuclear degradation. Mol Cell Biol 2002, 22, 8254–8266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strässer, K.; Masuda, S.; Mason, P.; Pfannstiel, J.; Oppizzi, M.; Rodriguez-Navarro, S.; Rondón, A.G.; Aguilera, A.; Struhl, K.; Reed, R.; Hurt, E. TREX is a conserved complex coupling transcription with messenger RNA export. Nature 2002, 417, 304–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zenklusen, D.; Vinciguerra, P.; Wyss, J.-C.; Stutz, F. Stable mRNP formation and export require cotranscriptional recruitment of the mRNA export factors Yra1p and Sub2p by Hpr1p. Mol Cell Biol 2002, 22, 8241–8253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.-W.; Wang, L.; Huang, D.; Chen, H.; Li, B.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, A.; Zhang, J.; Zuo, F. Inheritance patterns of leukocyte gene expression under heat stress in F1 hybrid cattle and their parents. Journal of Dairy Science 2020, 103, 10321–10331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
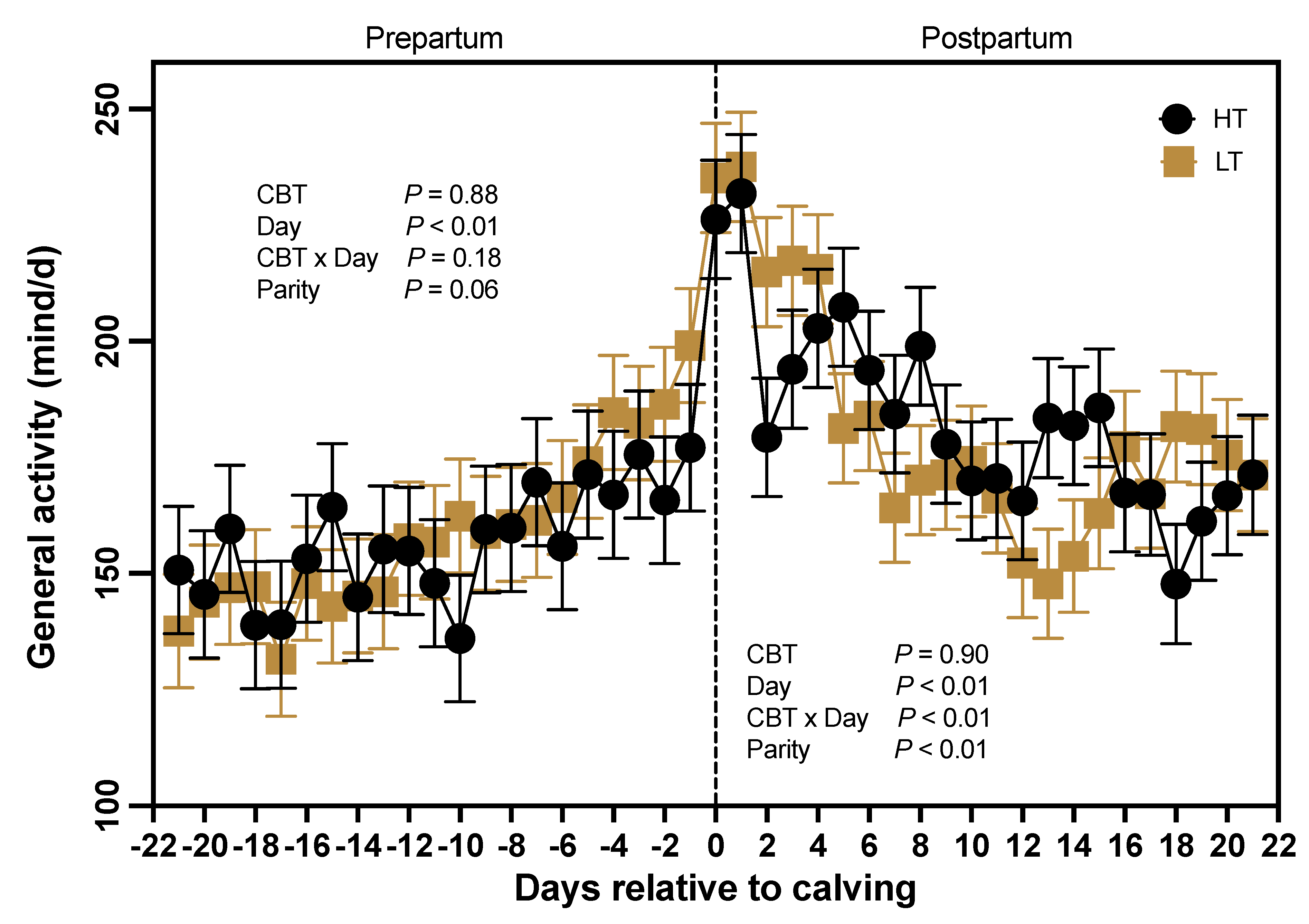
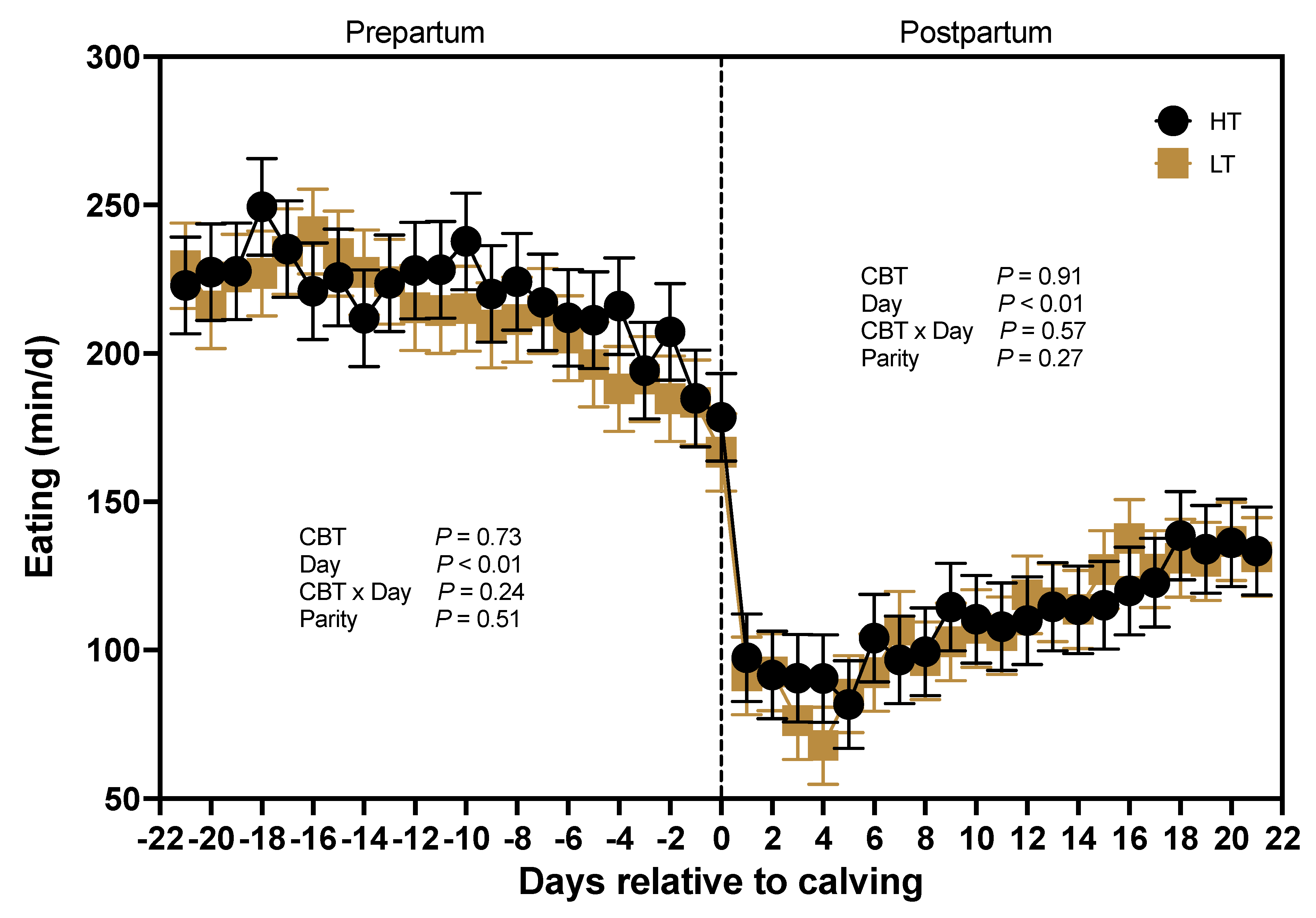
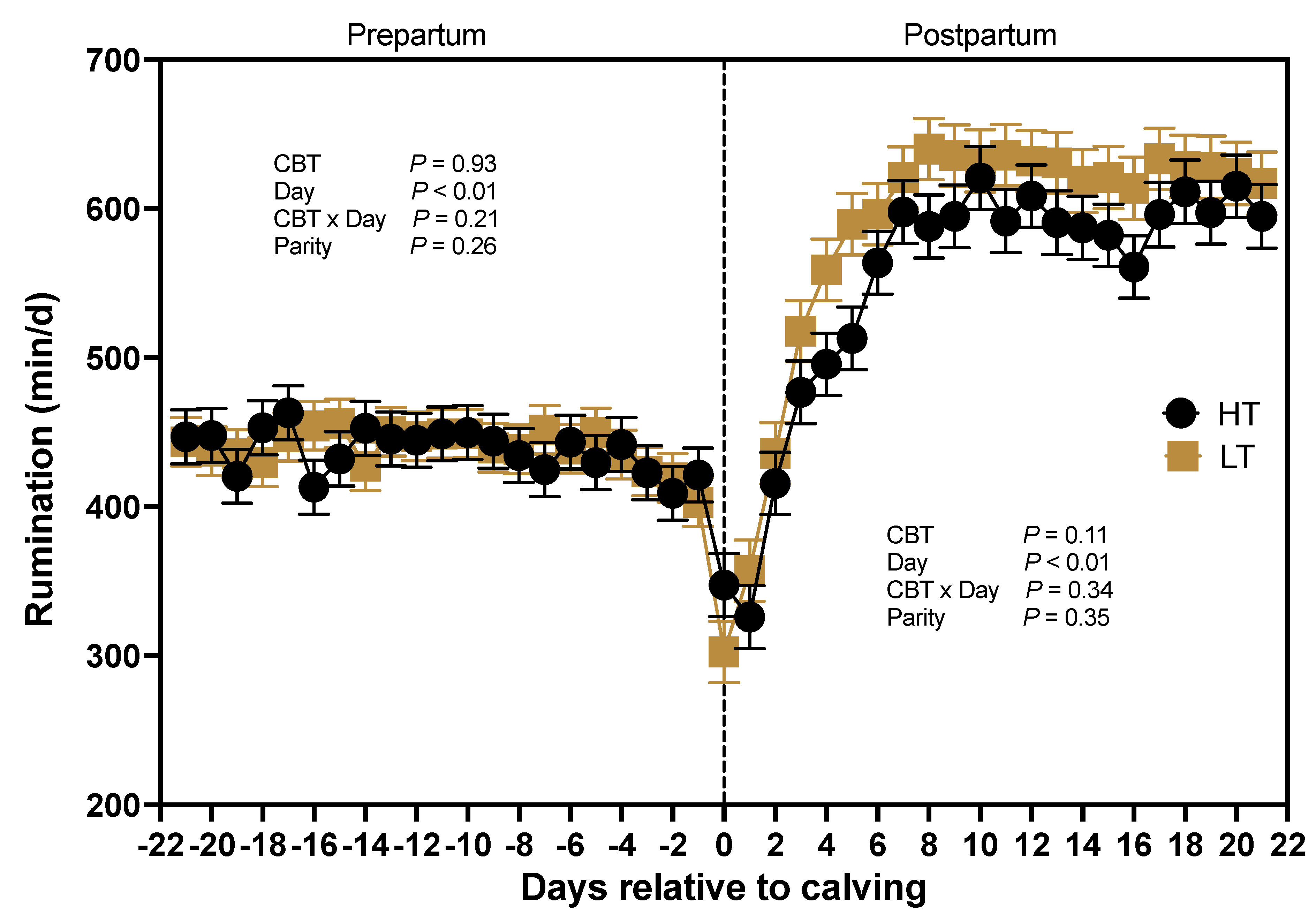
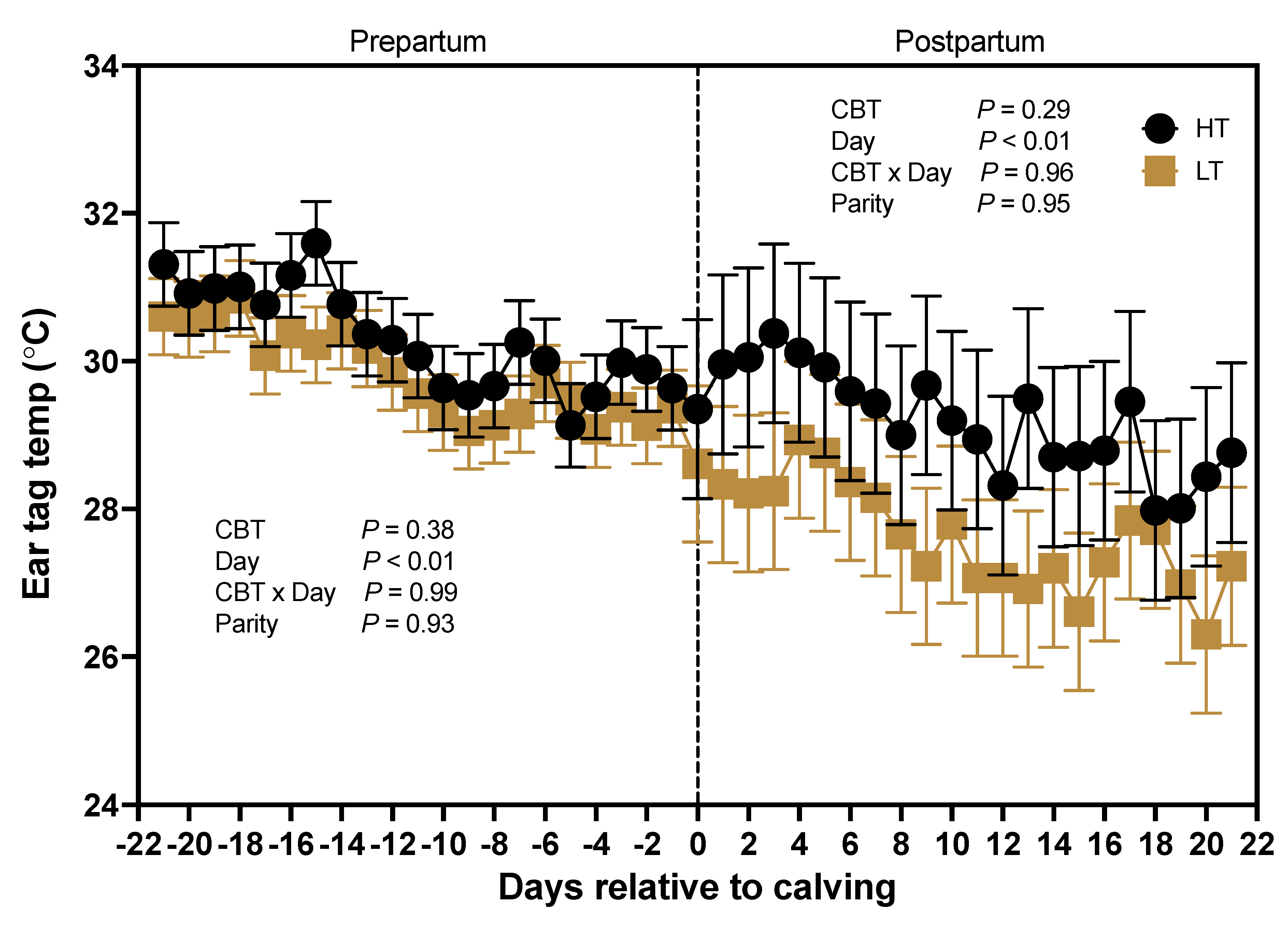
| Core body temperature (CBT)1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Item | LT | HT | P-value |
| Number of cows | 25 | 25 | |
| Percentage of multiparous cows | 52.0 | 72.0 | 0.15 |
| Lactation number at enrollment | 1.7 ± 0.1 | 2.2 ± 0.1 | 0.05 |
| Average core body temperature, °C | 38.70 ± 0.03 | 38.94 ± 0.03 | < 0.01 |
| Days in milk at dry off | 316.8 ± 9.2 | 315.8 ± 9.2 | 0.94 |
| Days of gestation at enrollment | 225.8 ± 1.1 | 229.0 ± 1.1 | 0.04 |
| Days spent in close-up pen | 26.7 ± 1.1 | 23.8 ± 1.1 | 0.05 |
| Gestation length, d | 280.1 ± 0.8 | 278.0 ± 0.8 | 0.09 |
| Core Body Temperature2 | P-value | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Item | Low Temperature (LT) | High Temperature (HT) | CBT | Time3 | CBT x Time | Parity | CBT x Parity | |
| Far-off | ||||||||
| Lying, % | 46.5 ± 2.8 | 41.6 ± 3.1 | 0.24 | < 0.01 | 0.48 | 0.21 | 0.15 | |
| Standing, % | 26.7 ± 2.7 | 27.6 ± 3.1 | 0.85 | < 0.01 | 0.39 | 0.81 | 0.81 | |
| Eating, % | 15.3 ± 1.6 | 18.6 ± 1.8 | 0.18 | < 0.01 | 0.96 | 0.69 | 0.96 | |
| Drinking, %4 | 2.24 ± 0.4 | 1.8 ± 0.5 | 0.18 | < 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.67 | 0.91 | |
| Perching, %4 | 10.1 ± 1.6 | 11.5 ± 1.8 | 0.66 | 0.37 | 0.67 | 0.85 | 0.59 | |
| Close-up | ||||||||
| Lying, % | 47.2 ± 2.1 | 49.5 ± 2.5 | 0.49 | < 0.01 | 0.31 | 0.84 | 0.21 | |
| Standing, % | 36.2 ± 2.4 | 29.7 ± 2.7 | 0.35 | < 0.01 | 0.34 | 0.15 | 0.37 | |
| Eating, % | 16.1 ± 1.3 | 17.0 ± 1.6 | 0.66 | < 0.01 | 0.61 | 0.32 | < 0.01 | |
| Drinking, %4 | 1.8 ± 0.3 | 2.1 ± 0.3 | 0.09 | < 0.01 | 0.50 | 0.01 | 0.04 | |
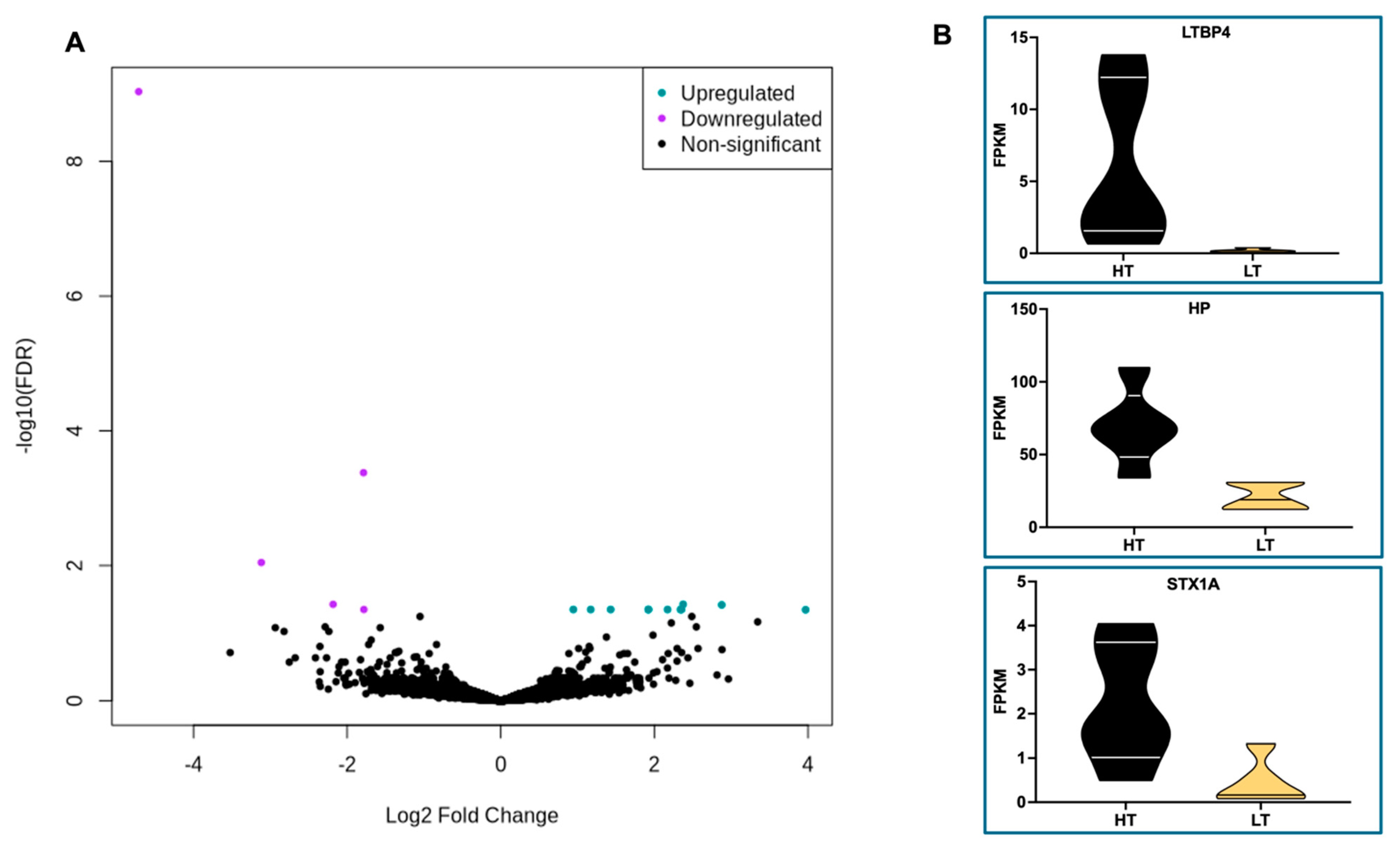
| Stable IDs2 | Gene name | Gene Description | FPKM (HT)3 | FPKM (LT)3 | P-value | FDR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Increased in HT | ||||||
| ENSBTAG00000004757 | LTBP4 | Latent transforming growth factor beta binding protein 4 | 6.1 ± 2.6 | 0.2 ± 0.05 | 6.41 x 10^-14 | 9.23 x 10^-10 |
| ENSBTAG00000006354 | HP | Haptoglobin | 69.0 ± 12.1 | 20.9 ± 4.1 | 5.83 x 10^-8 | 0.0004 |
| ENSBTAG00000017075 | STX1A | Syntaxin 1A | 2.2 ± 0.6 | 0.43 ± 0.24 | 1.88 x 10^-6 | 0.009 |
| ENSBTAG000000586334 | - | Immunoglobulin-like domain-containing protein5 | 10.8 ± 3.2 | 4.3 ± 2.3 | 1.30 x 10^-5 | 0.038 |
| ENSBTAG000000343664 | RGS25 | Regulator of g-protein signaling 25 | 24.6 ± 7.0 | 7.1 ± 1.8 | 3.19 x 10^-5 | 0.045 |
| Increased in LT | ||||||
| ENSBTAG000000091104 | THOC76 | THO complex subunit 7 homolog6 | 0.6 ± 0.1 | 3.5 ± 1.0 | 1.27 x 10^-5 | 0.038 |
| ENSBTAG00000044202 | CNKSR2 | Connector enhancer of kinasesuppressor of Ras 2 | 0.02 ± 0.02 | 0.09 ± 0.02 | 1.59 x 10^-5 | 0.038 |
| ENSBTAG000000540864 | - | Immunoglobulin V-set domain-containing protein5 | 6.9 ± 1.6 | 34.4 ± 11.6 | 4.06 x 10^-5 | 0.045 |
| ENSBTAG00000003458 | CDCA7 | Cell division cycle associated 7 | 17.8 ± 2.6 | 34.5 ± 3.0 | 3.60 x 10^-5 | 0.045 |
| ENSBTAG00000040088 | SLC9B2 | solute carrier family 9 member B2 | 4.9 ± 2.0 | 13.3 ± 2.6 | 3.54 x 10^-5 | 0.045 |
| ENSBTAG000000484234 | - | Ig-like domain-containing protein5 | 4.8 ± 2.3 | 12.12 ± 1.9 | 4.66 x 10^-5 | 0.045 |
| ENSBTAG00000024269 | TGFBR3 | Transforming growth factor beta receptor 3 | 2.7 ± 0.5 | 6.1 ± 0.8 | 4.43 x 10^-5 | 0.045 |
| ENSBTAG00000003675 | ADGRL1 | Adhesion G protein-coupled receptor L1 | 2.5 ± 0.7 | 5.2 ± 0.3 | 2.64 x 10^-5 | 0.045 |
| ENSBTAG00000059156 | PEG10 | Paternally expressed 10 | 1.2 ± 0.7 | 3.1 ± 0.8 | 4.54 x 10^-5 | 0.045 |
| ENSBTAG00000018726 | RIMS3 | Regulating synaptic membrane exocytosis 3 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 1.5 ± 0.4 | 3.43 x 10^-5 | 0.045 |
| ENSBTAG00000007772 | SLC29A4 | Solute carrier family 29 member 4 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 1.3 ± 0.5 | 5.02 x 10^-5 | 0.045 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





