Submitted:
26 June 2024
Posted:
26 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
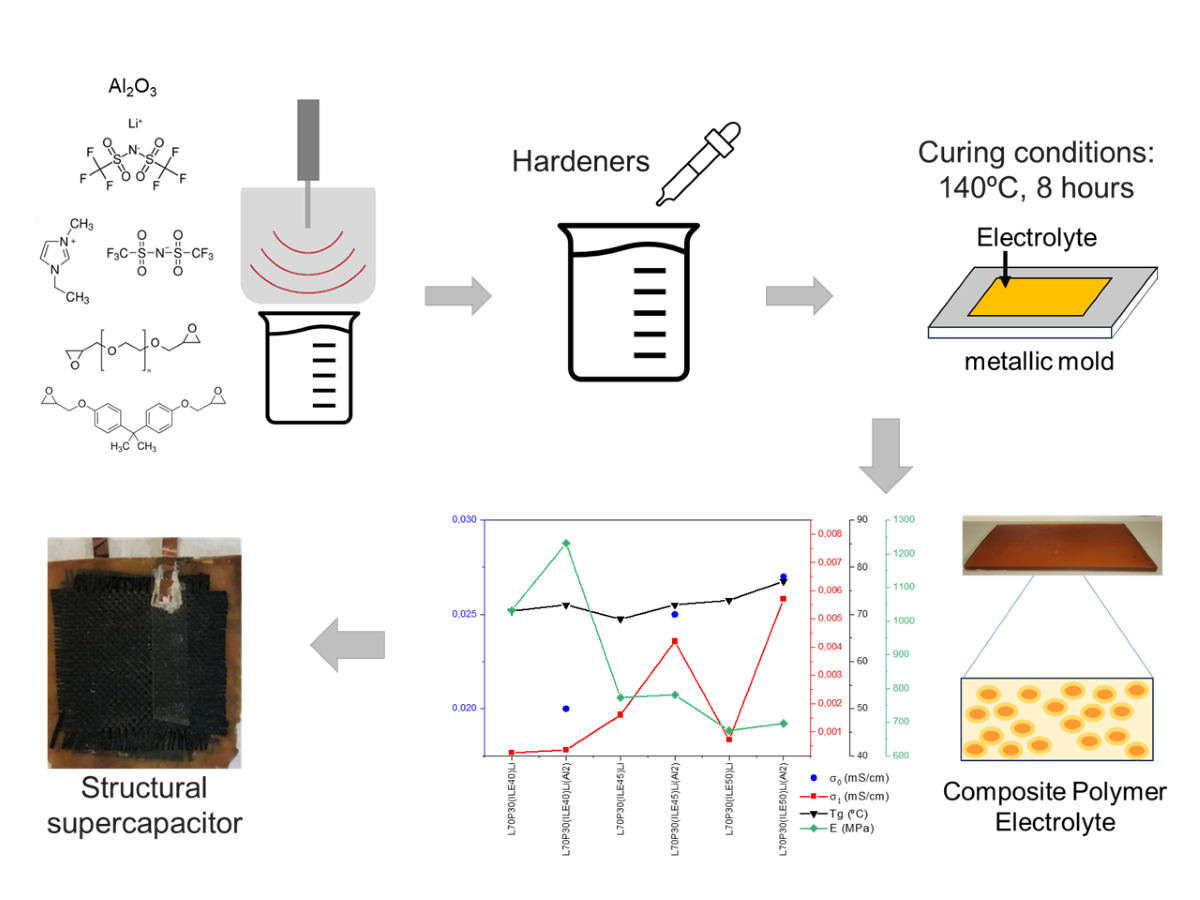
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Dynamic Mechanical Thermal Analysis (DMTA)
2.2.2. Cyclic Voltammetry (CV) and Linear Sweep Voltammetry (LSV)
2.2.3. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS)
2.2.4. Chronoamperometry for lithium transference number calculations (tLi+)
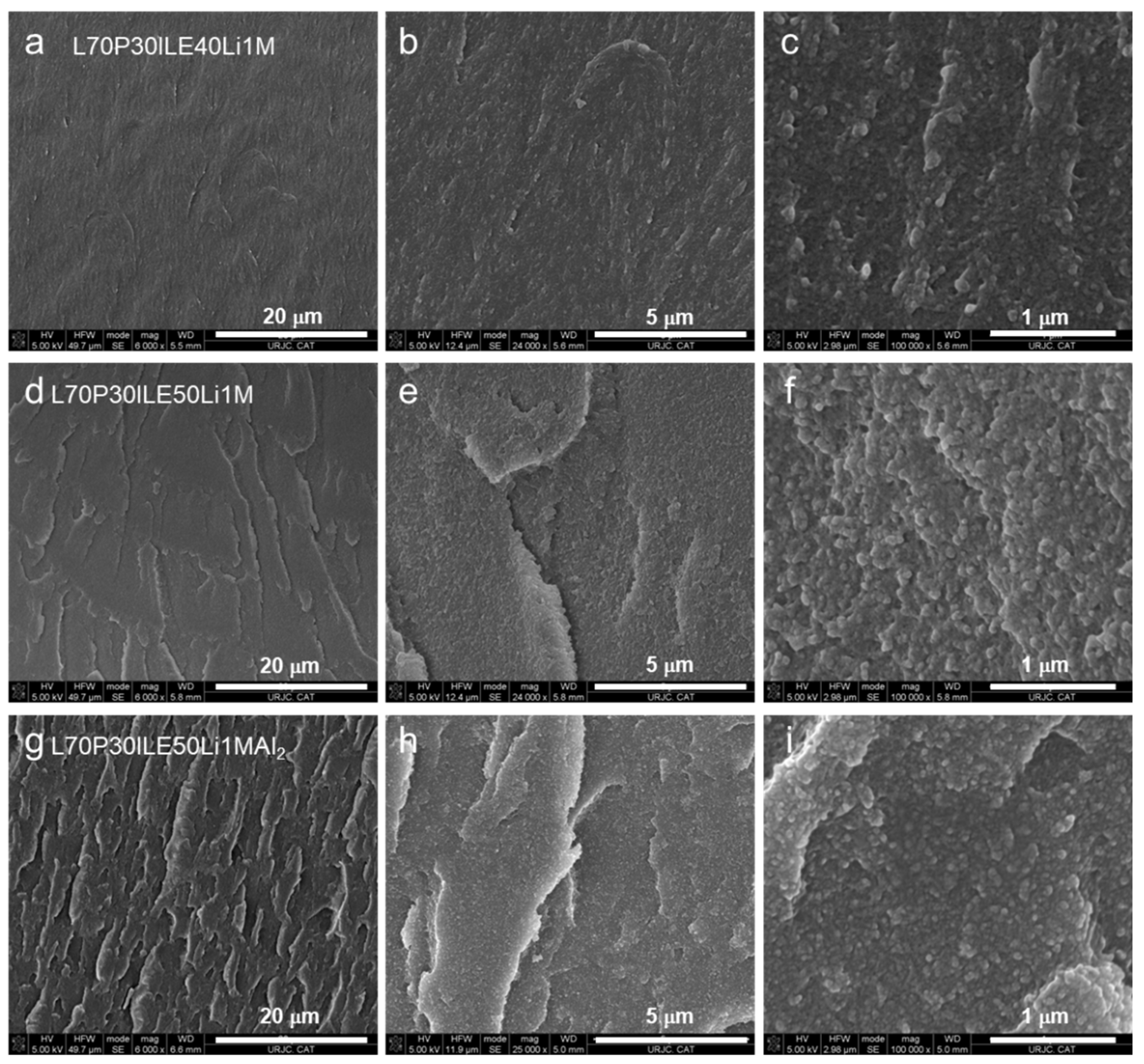
2.2.5. Field-Emission Gun Scanning Electron Microscopy (FEGSEM)
2.3. Solid Polymer Electrolyte Preparation
2.4. Supercapacitor Fabrication
3. Results and Discussion
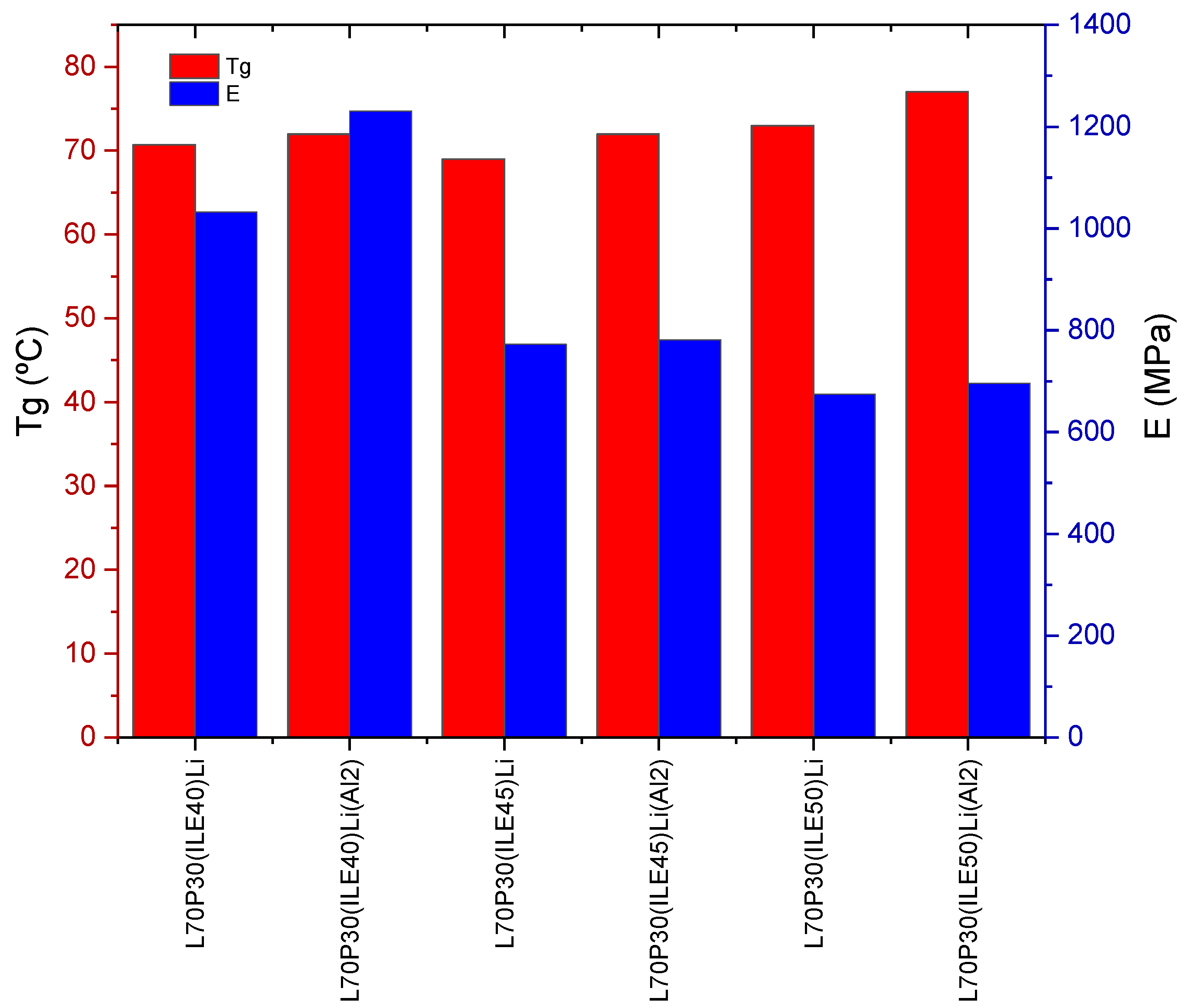
3.1. Thermomechanical and morphologycal characterization of the electrolytes
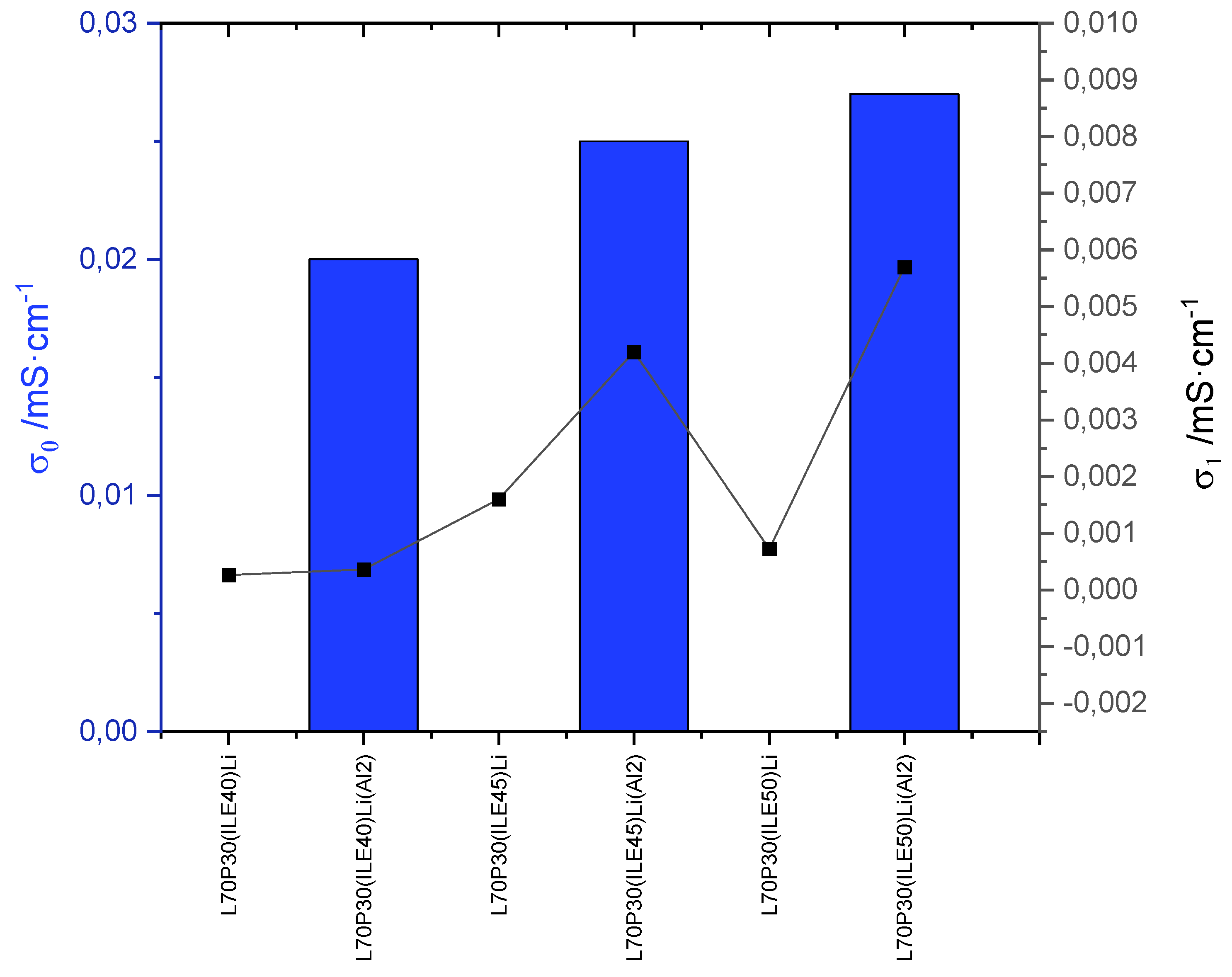
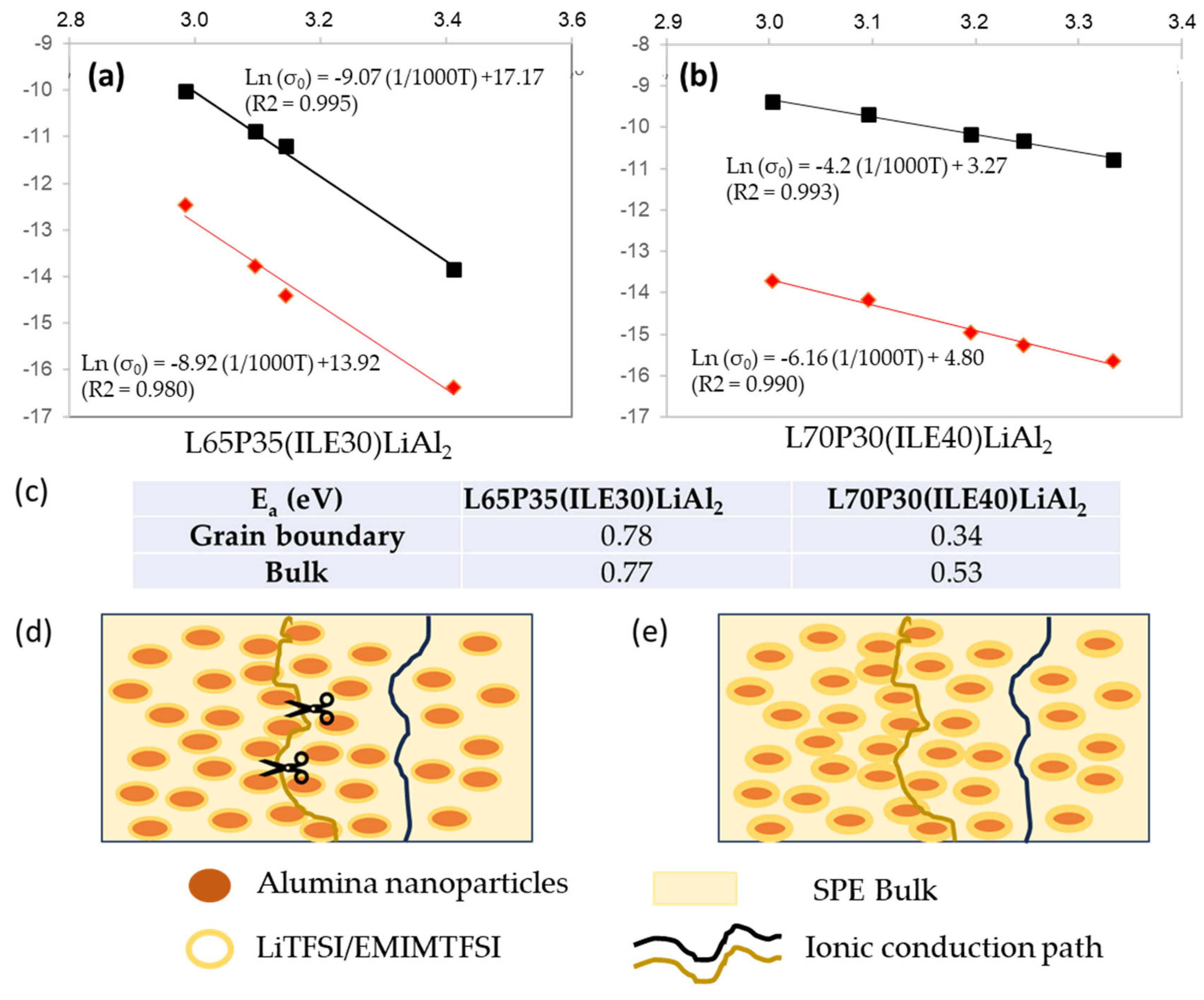
3.2. Electrochemical characterization of electrolytes
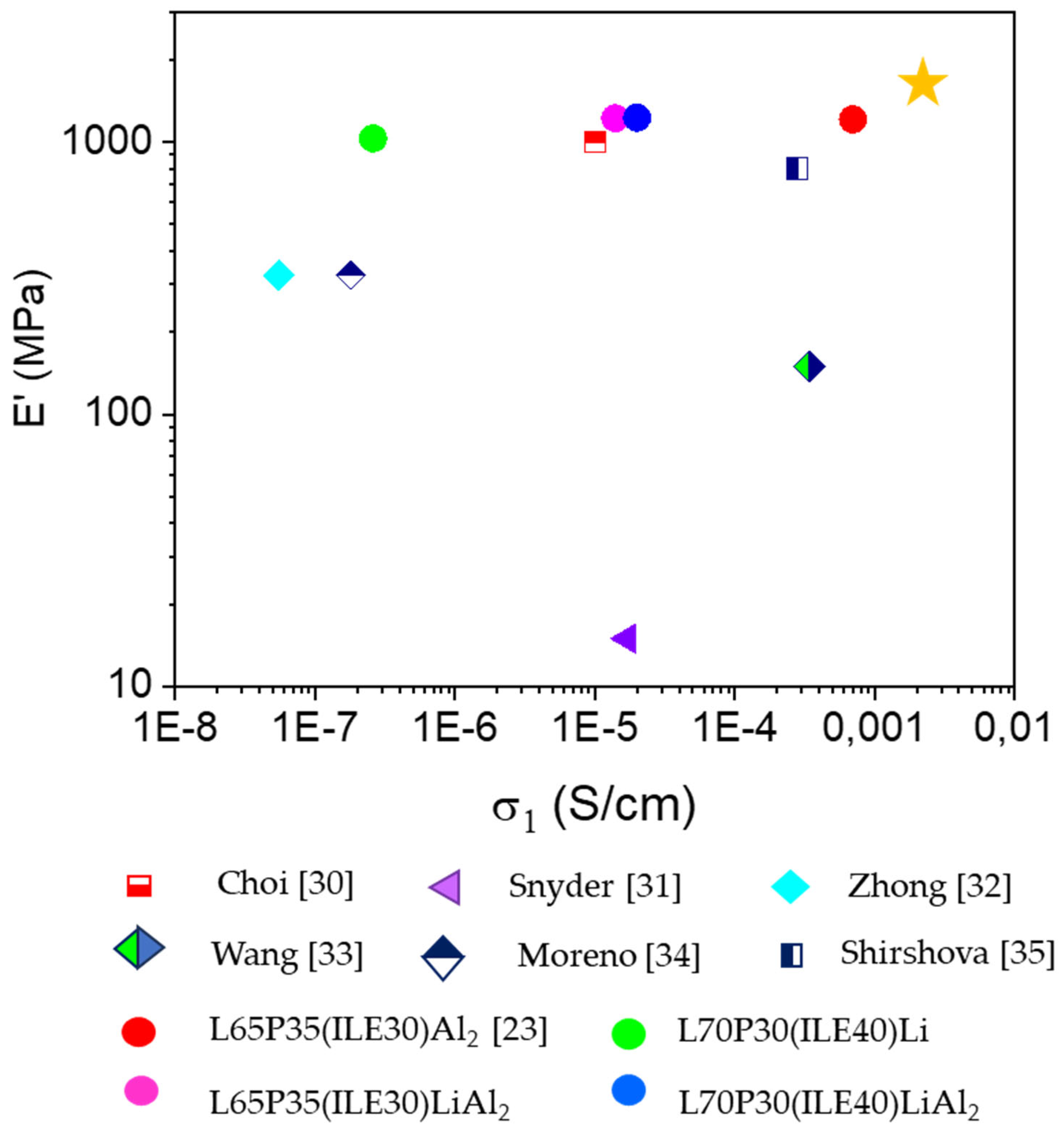
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wazeer, A.; Das, A.; Abeykoon, C.; Sinha, A.; Karmakar, A. Composites for electric vehicles and automotive sector: A review. Green Energy and Intelligent Transportation, 2023, 2, 100043. [CrossRef]
- Cheah, L. Cars on a Diet: The material and energy impacts of passenger vehicle weight reduction in the US. PhD thesis, Massashussets Institute of Technology , USA, 2010. Available: https://dspace.mit.edu/handle/1721.1/62760.
- Jin, T.; Singer, G.; Liang K.; Yang, Y. Structural batteries: Advances, challenges and perspectives. Materials Today, 2023, 62, 151-167. [CrossRef]
- Greenhalgh, E.S.; Nguyen, S.; Valkova, M.; Shirshova, N.; Shaffer, M.S.P.; Kucernak, A.R.J. A critical review of structural supercapacitors and outlook on future research challenges. Composites Science and Technology, 2023, 235, 109968. [CrossRef]
- Klongkan, S. ; Pumchusak, J. Effects of nano alumina and plasticizers on morphology, ionic conductivity, thermal and mechanical properties of PEO-LiCF3SO3 solid polymer electrolyte. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 161, 171–176. [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Hung, C.; Venkateswarlu, M; Hwang, B. Influence of TiO2 nano-particles on the transport properties of composite polymer electrolyte for lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2005, 146 (1–2), 397–401. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Maeda, S.; Yang, H.; Saito, Y.; Tanase, S.; Sakai, T. All solid-state lithiumpolymer battery using poly (urethane acrylate)/nano-SiO2 composite electrolytes, J. Power Sources 2005, 141 (1) 143–148. [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Yang, J.; Yu, Y.; Tian, F.; Zhang, B.; Feng, M.; Wang, S. The ionic conductivity, mechanical performance and morphology of two-phase structural electrolytes based on polyethylene glycol, epoxy resin and nano-silica. Mater. Sci. Eng. B Solid-State Mater. Adv. Technol., 2017, 219, 37-44. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Gosselink, D.; Chen, P. Synthesis of poly (ethylene-oxide)/nanoclay solid polymer electrolyte for all solid-state lithium/sulfur battery, Ionics 2015, 21, 381–385. [CrossRef]
- Chand, N.; Rai, N.; Agrawal, S.L.; Patel, S.K. Morphology, thermal, electrical and electrochemical stability of nano aluminium-oxide-filled polyvinyl alcohol composite gel electrolyte, Bull. Mater. Sci. 2011, 34, 1297–1304. [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Liu, X.; Ding, J.; Liu, J.; Han, X.; Deng,Y.; Zhong, C.; Hu, W. Poly(Acrylic Acid)-Based Nanocomposite Gel Polymer Electrolyte with High Mechanical Strength and Ionic Conductivity Towards Long-Cycle-Life Flexible Zinc–Air Battery, 2022, (Available at SSRN. 4109010).
- Kwon, S.J.; Jung, B.M.; Kim, T.; Byun, J.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.B.; Choi, U.H. Influence of Al2O3 nanowires on ion transport in nanocomposite solid polymer electrolytes. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 10194–10201. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fan, L.; Du, Q.; Jiao, K. Lithium ion transport in solid polymer electrolyte filled with alumina nanoparticles, Energy Adv. 2022, 1, 269. [CrossRef]
- Croce, F.; Persi, L.; Scrosati, B.; Serraino-Fiory, F.; Plichta, E.; Hendrickson, M. A. Role of the Ceramic Fillers in Enhancing the Transport Properties of Composite Polymer Electrolytes. Electrochim. Acta 2001, 46 (16), 2457−2461. [CrossRef]
- Dissanayake, M. A. K. L.; Jayathilaka, P. A. R. D.; Bokalawala, R. S. P.; Albinsson, I.; Mellander, B.-E. Effect of Concentration and Grain Size of Alumina Filler on the Ionic Conductivity Enhancement of the (PEO)9LiCF3SO3:Al2O3 Composite Polymer Electrolyte. J. Power Sources 2003, 119−121, 409−414. [CrossRef]
- Chandra, A.N.; Sungmook, L.; Guk-Hwan,L.; Wonoh, L. Epoxy-based multifunctional solid polymer electrolytes for structural batteries and supercapacitors. a short review. Frontiers in Chemistry, 2024, 12, 1330655. [CrossRef]
- Shirshova, N.; Bismarck, A.; Greenhalgh, E. S.; Johansson, P.; Kalinka, G.; Marczewski, M. J.; Shaffer, M. S. P.; Wienrich, M. Composition as a Means To Control Morphology and Properties of Epoxy Based Dual-Phase Structural Electrolytes. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118 (49), 28377−28387. [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, B. K.; del Bosque, A.; Sánchez, M.; Utrilla, V.; Prolongo, S. G.; Prolongo, M. G.; Ureña, A. Epoxy Resin Systems Modified with Ionic Liquids and Ceramic Nanoparticles as Structural Composites for Multifunctional Applications. Polymer, 2021, 214, 123233. [CrossRef]
- Wendong, Q.; Dent, J.; Arrighi, V.; Cavalcanti, L.; Shaffer, M. S. P.; Shirshova, N. Biphasic Epoxy-Ionic Liquid Structural Electrolytes: Minimising Feature Size through Cure Cycle and Multifunctional Block-Copolymer Addition. Multifunct. Mater. 2021, 4 (3), 035003. [CrossRef]
- Shirshova, N.; Bismarck, A.; Carreyette, S.; Fontana, Q.P.V.; Greenhalgh, E.S.; Jacobsson, P.; Johansson, P.; Marczewski, M.J.; Kalinka, G.; Kucernak, A.R.J.; Scheers, J.; Shaffer, M.S.P.; Steinke, J.H.G.; Wienrich, M. Structural supercapacitor electrolytes based on bicontinuous ionic liquid–epoxy resin systems J. Mater. Chem. A., 2013, 1, 15300-15309. [CrossRef]
- Tu, V.; Asp, L.E.; Shirshova, N.; Larsson, F.; Runesson, K.; Jänicke, R. Performance of bicontinuous structural electrolytes. Multifunct. Mater., 2020, 3, 025001. [CrossRef]
- Choi, U.H., Jung, B.M. Ion Conduction, Dielectric and Mechanical Properties of Epoxy-Based Solid Polymer Electrolytes Containing Succinonitrile. Macromol. Res. 2018, 26, 459–465. [CrossRef]
- Del Bosque,A.; Muñoz, B.K.; Sánchez, M. Ureña, A. Thermomechanically Robust Ceramic/Polymer Nanocomposites Modified with Ionic Liquid for Hybrid Polymer Electrolyte Applications ACS Applied Energy Materials 2022, 5 (4), 4247-4258. [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Romate, X.F. ; Del Bosque, A.; Artigas-Arnaudas, J.; Muñoz, B.K.; Sánchez, M.; A. Ureña. A proof of concept of a structural supercapacitor made of graphene coated woven carbon fibers: EIS study and mechanical performance. Electrochim. Acta, 2021, 370 , 137746. [CrossRef]
- Tianwei Jin, Gerald Singer, Keyue Liang, Yuan Yang, Structural batteries: Advances, challenges and perspectives, Materials Today, 2023, 62, 151-167. [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, B.K.; González-Banciella, A.; Ureña, D.; Sánchez, M.; Ureña, A. Electrochemical Comparison of 2D-Flexible Solid-State Supercapacitors Based on a Matrix of PVA/H3PO4. Polymers 2023, 15, 4036. [CrossRef]
- S. Seki, Y. Ohno, Y. Kobayashi, H. Miyashiro, A. Usami, Y. Mita, H. Tokuda, M. Watanabe, K. Hayamizu, S. Tsuzuki, M. Hattori, N. Terada, Imidazolium-based room-temperature ionic liquid for lithium secondary batteries, J. Electrochem. Soc. 2007, 154, A173–A177. [CrossRef]
- Z.P. Rosol, N.J. German, S.M. Gross, Solubility, ionic conductivity and viscosity of lithium salts in room temperature ionic liquids, Green Chem. 2009, 11, 1453–1457. [CrossRef]
- Y.H. Song, T. Kim, U.H. Choi, Tuning morphology and properties of epoxy-based solid-state polymer electrolytes by molecular interaction for flexible all-solid-state supercapacitors, Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 3879–3892. [CrossRef]
- U.H. Choi, B.M. Jung. Ion conduction, dielectric and mechanical properties of epoxy-based solid polymer electrolytes containing succinonitrile Macromol. Res., 2018, 26, 459-465. [CrossRef]
- J.F. Snyder, R.H. Carter, E.D. Wetzel Electrochemical and mechanical behavior in mechanically robust solid polymer electrolytes for use in multifunctional structural batteries. Chem. Mater., 2007, 19, 3793-3801. [CrossRef]
- J. Ji, B. Li, W.-H. Zhong. Simultaneously enhancing ionic conductivity and mechanical properties of solid polymer electrolytes via a copolymer multi-functional filler. Electrochim. Acta, 2010, 55, 9075-9082. [CrossRef]
- Y.J. Wang, D. Kim. Crystallinity, morphology, mechanical properties and conductivity study of in situ formed PVdF/LiClO4/TiO2 nanocomposite polymer electrolytes. Electrochim. Acta, 2007, 52, 3181-3189. [CrossRef]
- M. Moreno, R. Quijada, M.A. Santa Ana, E. Benavente, P. Gomez-Romero, G. González. Electrical and mechanical properties of poly(ethylene oxide)/intercalated clay polymer electrolyte. Electrochim. Acta, 2011, 58, 112-118.
- Q. Wendong, J. Dent, V. Arrighi, L. Cavalcanti, M.S.P. Shaffer, N. Shirshova Biphasic epoxy-ionic liquid structural electrolytes : minimising feature size through cure cycle and multifunctional block-copolymer addition Multifunct. Mater., 2021, 4, 035003. [CrossRef]
- W. Zaman,N. Hortance,M. B. Dixit,V. De Andrade,K. B. Hatzell, J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 23914–23921.
- Tan, SJ., Zeng, XX., Ma, Q. et al. Recent Advancements in Polymer-Based Composite Electrolytes for Rechargeable Lithium Batteries. Electrochem. Energ. Rev. 2018, 1, 113–138. [CrossRef]
- Mengyang Jia, Muhammad Khurram Tufail, Xiangxin Guo. Insight into the Key Factors in High Li+ Transference Number Composite Electrolytes for Solid Lithium Batteries. ChemSusChem 2023, 16, e2022018. [CrossRef]
- K. Pożyczka, M. Marzantowicz, J.R. Dygas, F. Krok, Ionic conductivity and lithium transference number of poly(ethylene oxide):litfsi system, Electrochimica Acta, 2017, 227, 127-135. [CrossRef]


| wt.% | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | L | P | ILE | Li(1M) | PC | Al |
| L65P35(ILE30)Li | 41.82 | 22.52 | 30 | 5.7 | - | - |
| L70P30(ILE40)Li | 36.71 | 15.74 | 40 | 7.6 | - | - |
| L65P35(ILE40)Li | 34.2 | 18.3 | 40 | 7.6 | - | - |
| L60P40(ILE40)Li | 34.47 | 20.98 | 40 | 7.6 | - | - |
| L70P30(ILE45)Li | 35.55 | 13.95 | 45 | 8.5 | - | - |
| L65P35(ILE45)Li | 30.22 | 16.27 | 45 | 8.5 | - | - |
| L60P40(ILE45)Li | 27.9 | 18.6 | 45 | 8.5 | - | - |
| L70P30(ILE50)Li | 28.44 | 12.19 | 50 | 9.4 | - | - |
| L65P35(ILE50)Li | 26.41 | 14.22 | 50 | 9.4 | - | - |
| L60P40(ILE50)Li | 24.38 | 16.25 | 50 | 9.4 | - | - |
| L70P30(ILE40)(PC5)Li | 33.21 | 14.23 | 40 | 7.6 | 5 | - |
| L65P35(ILE40)(PC5)Li | 30.84 | 16.60 | 40 | 7.6 | 5 | - |
| L65P35(ILE30)Li(Al2) | 40.52 | 21.8 | 30 | 5.7 | - | 2 |
| L70P30(ILE40)Li(Al2) | 35.31 | 15.13 | 40 | 7.6 | - | 2 |
| L70P30(ILE45)Li(Al2) | 31.15 | 13.35 | 40 | 8.5 | - | 2 |
| L70P30(ILE50)Li(Al2) | 27.04 | 11.59 | 40 | 9.4 | - | 2 |
| Entry | Sample | Tg (ᴼC) | E’ (MPa) (T = 30ºC) |
E’’ (MPa) (T = 30ºC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | L70P30(ILE40)Li | 70.7 ± 0.9 | 1032 ± 41 | 94 ± 6 |
| 2 | L65P35(ILE40)Li | 57 ± 2 | 659 ± 27 | 108 ± 8 |
| 3 | L60P40(ILE40)Li | 55 ± 2 | 539 ± 87 | 104 ± 17 |
| 4 | L70P30(ILE45)Li | 69 ± 2 | 773 ± 127 | 71 ± 2 |
| 5 | L65P35(ILE45)Li | 56 ± 3 | 506 ± 93 | 82 ± 4 |
| 6 | L60P40(ILE45)Li | 44.8 ± 0.5 | 222 ± 19 | 72 ± 3 |
| 7 | L70P30(ILE50)Li | 73 ± 1 | 675 ± 81 | 61,8 ± 0,9 |
| 8 | L65P35(ILE50)Li | 57 ± 4 | 530 ± 145 | 73 ± 14 |
| 9 | L60P40(ILE50)Li | 50 ± 2 | 328 ± 79 | 74 ± 12 |
| 10 | L70P30(ILE40)(PC5)Li | 63 ± 2 | 603 ± 122 | 76 ± 7 |
| 11 | L65P35(ILE40)(PC5)Li | 50 ± 1 | 504 ± 26 | 101 ± 5 |
| 12 | L70P30(ILE40)Li(Al2) | 72 ± 2 | 1231 ± 84 | 112 ± 5 |
| 13 | L70P30(ILE45)Li(Al2) | 72 ± 2 | 781 ± 77 | 74 ± 3 |
| 14 | L70P30(ILE50)Li(Al2) | 76.6 ± 0.8 | 696 ± 18 | 69 ± 1 |
| Entry | Sample |
σ0 (S·cm−1) |
σ1 (S·cm−1) |
Csp (μF/cm2) |
Stability range (V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | L70P30(ILE40)Li | 0.30 | 0.3 | ||
| 2 | L65P35(ILE40)Li | 1.74 | 0.3 | ||
| 3 | L60P40(ILE40)Li | 3.76 | 0.8 | ||
| 4 | L70P30(ILE45)Li | 21.22 | 1.2 | ||
| 5 | L65P35(ILE45)Li | 44.03 | 1.0 | ||
| 6 | L60P40(ILE45)Li | 109.39 | 1.7 | ||
| 7 | L70P30(ILE50)Li | 29.64 | 2.2 | ||
| 8 | L65P35(ILE50)Li | 18.44 | 1.1 | ||
| 9 | L60P40(ILE50)Li | 67.57 | 1.8 | ||
| 10 | L70P30(ILE40)(PC5)Li | 7.50 | 1.4 | ||
| 11 | L65P35(ILE40)(PC5)Li | 30.44 | 1.2 | ||
| 12 | L70P30(ILE40)Li(Al2) | 4.61 | 2.4 | ||
| 13 | L70P30(ILE45)Li(Al2) | 9.11 | 2.6 | ||
| 14 | L70P30(ILE50)Li(Al2) | 2.95 | 2.3 |
| Entry | Sample | Tg (ᴼC) | E’ (MPa) (T = 30ºC) |
σ0 (S·cm−1) |
σ1 (S·cm−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11,2 | L65P35(ILE30) | 65 ± 2 | 1202 ± 10 | - | |
| 21 | L65P35(ILE40) | 68 ± 2 | 495 ± 60 | - | |
| 31 | L65P35(ILE45) | 63 ± 3 | 401 ± 80 | - | |
| 41,2 | L65P35(ILE30)Al2 | 83 ± 1 | 1213 ± 164 | ||
| 51 | L65P35(ILE40)Al2 | 70 ± 2 | 461 ± 62 | ||
| 61 | L65P35(ILE45)Al2 | 65 ± 3 | 469 ± 89 | ||
| 7 | L65P35(ILE30)Li | 68 ± 1 | 1235 ± 20 | - | |
| 8 | L65P35(ILE30)Li(Al2) | 85 ± 1 | 1224 ± 103 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





