1. Introduction
Major electronic payment methods rely almost exclusively on financial institutions, which are trusted third parties to process payments. Despite the effectiveness of these systems, they still suffer from inherent weaknesses derived from a trust-based model. Moreover, due to mediation disputes, totally irreversible transactions are not possible. The possibility of reversibility also comes the need for trust, and a certain percentage of fraud is accepted as inevitable. On October 31, 2008, Satoshi Nakamoto, whose identity is still unknown, sent an article entitled
"Bitcoin: an Electronic Peer-to-Peer Cash System" [
1] to a mailing list of cryptography experts. Bitcoin began as an electronic payment system based on cryptography rather than trust, allowing two counterparties to negotiate directly without needing a trusted third party. Cryptography makes transactions computationally irreversible, protecting sellers from fraud attempts. Bitcoin solves the double-spending problem through the use of a peer-to-peer network. Transactions are grouped into blocks, which form a chain called a blockchain. Thanks to the proof-of-work mechanism, Bitcoin guarantees the irreversibility of transactions: once registered in the public blockchain, transactions cannot be changed unless the nodes collaborating to attack the network control most of the computational power, as in the case of the 51% attack [
2]. Identities in the Bitcoin network are pseudo-anonymous: while they are not explicitly linked to real-world individuals or organizations, all transactions are completely transparent. This leads to the concern that the combination of scalable, irrevocable, and anonymous payments is very attractive to criminals involved in fraudulent activities and money laundering. Over the years, several methods have been developed to break the anonymity that Bitcoin is supposed to provide [
3,
4,
5,
6,
7,
8,
9] by identifying clusters of addresses. Such techniques, in any case, run up against the issue of the Bitcoin address controller. The controller of an address may know the corresponding private key, but this does not imply that it is the owner. For example, if a user buys bitcoins from an exchange such as Mt. Gox, his or her funds will be contained in an address generated by the exchange, which knows the corresponding private key and can conduct transactions with it. In this case, Mt. Gox is the controller of the generated address, even though the funds contained in it belong to the user. The study of clusters results in potentially huge groups of addresses, as the number of addresses controlled by a service such as Mt. Gox will be very large. Many studies have focused on a single analysis of clusters of major entities but without studying the complete graph of the entire network divided into groups. Blockchain analysis software based on these results has also been developed, such as BitConduite [
10] and BitExtract [
11]. This paper proposes a tool called Bitcoin Address Clustering based on multiple Heuristics (BACH) that can partition the entire Bitcoin network into groups of addresses using variations of heuristics already known in the literature. BACH allows the visualization of the various clusters found in a 3D graph, thus allowing the overall structure of the clusters to be framed and any patterns within them to be identified. The paper is organized as follows: the
Section 2 details the heuristics that were used in BACH, the
Section 3 describes the operation of BACH and its components, the
Section 4 describes the experiments performed to evaluate the operation of BACH, and finally the conclusions are given in
Section 5.
2. Heuristics employed
Bitcoin address clustering is useful for analyzing transactions occurring in the network. Once a cluster of addresses is found, off-chain information can be combined to trace the identity of the entity related to the cluster. These heuristics were chosen because they are recent and since they have been shown to be particularly effective. Multiple heuristics can be used simultaneously to improve the level of aggregation of the entities found. The three heuristics presented below were used in the present study. Finally, the reliability of the heuristics will be analyzed.
2.1. Multi-Input Address Clustering
The first heuristic presented, which deals with clustering all input addresses to a transaction, is one of the most widely used heuristics for clustering. Androulaki et al. [
12] studied transaction input addresses and developed this heuristic.
Definition 2.1. If two (or more) addresses are inputs to the same transaction, they are controlled by the same user; that is, for each transaction t, each is controlled by the same entity.
The effects of this heuristic are transitive, i.e., if a transaction with addresses
A and
B as input is observed, and then another with addresses
B and
C as input, it can be inferred that addresses
A,
B and
C all belong to the same user. As introduced earlier, it is possible that there are potentially huge clusters due to services such as Mt. Gox that control a large number of addresses belonging to different users; despite this, they will still be clustered into one large cluster. In this case, these are not false positives since these services have access to users’ private keys and control addresses. The heuristic of multi-input clustering is widely used because it is highly accurate: the sender must know all the private keys of the corresponding public keys used in the various inputs to sign a transaction. According to Bitcoin’s protocol, in order to transfer bitcoins from an address, the respective private key must be provided; that is, the transaction must be signed. For this reason, the public keys used as input are unlikely to be controlled by different users since they should know everyone else’s private keys. Furthermore, the transaction is initialized by only one Bitcoin client; therefore, all input addresses can be considered to belong to the same entity. The accuracy of this heuristic can reach 100% if the cases where users use mixing services or CoinJoin transactions [
13] are not considered to intentionally avoid being tracked through clustering. In these situations, the heuristic generates false positives, i.e., addresses not belonging to the same user are clustered together.
2.2. Change Address Clustering
The change address is used in a transaction to return any change to the sender. It is usually a new address generated by the client itself, i.e., the Bitcoin wallet, during the creation of the transaction. In fact, to construct a transaction, the Bitcoin wallet must refer to the currently available set of UTXOs (Unspent Transaction Outputs), that is, the set of outputs that can be spent. In the Bitcoin protocol, a UTXO is indivisible, so it must be used in its entirety. If the UTXO is greater than what the transaction’s sender wants to spend, a new address will be created to receive the change (change address), to which the new UTXO will be sent. In the past, Bitcoin wallets did not generate a new address to receive a change but used the same input address as the sender. To improve anonymity on the network, now the new wallets automatically generate a new address for each transaction to be used as the change address. In the work by Androulaki et al. [
12], in addition to introducing heuristics on multi-input clustering, a heuristic is also presented for identifying the change address of a transaction so that it can be added to the cluster of input addresses and improve the aggregation level. In the article, addresses automatically generated by Bitcoin clients to receive change are called
"shadow addresses." Over the years, many researchers have tried to improve this heuristic to minimize false positives and avoid constructing unreliable clusters. The proposed work uses a variation of this heuristic, proposed by Zhao et al. [
14], in which a method is presented that considers whether the output address is new or already in the blockchain and evaluates the amounts transferred in the transaction. This variant of change address clustering was chosen to be implemented because the heuristic is recent and has a high level of reliability.
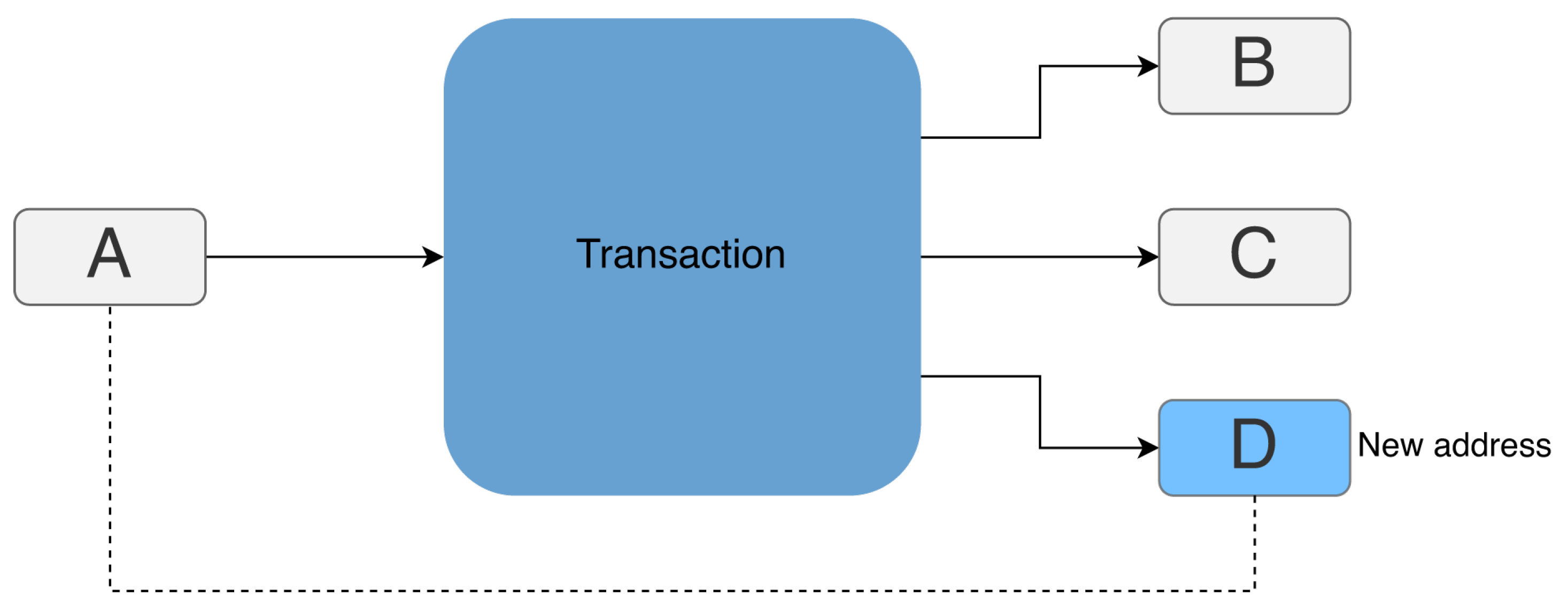
Definition 2.2. Let t be a Bitcoin transaction, A the set of Bitcoin addresses currently in the blockchain:
If address a satisfies conditions 1., 2. and 3. or 1., 2., 4., 5. and 6., then this is the change address of transaction t.
If address
a satisfies conditions 1., 2. and 3., then it is the only new address among all the outputs of
t. In this case, address
a is labeled as the change address and added to the transaction input address cluster, as shown in
Figure 1.
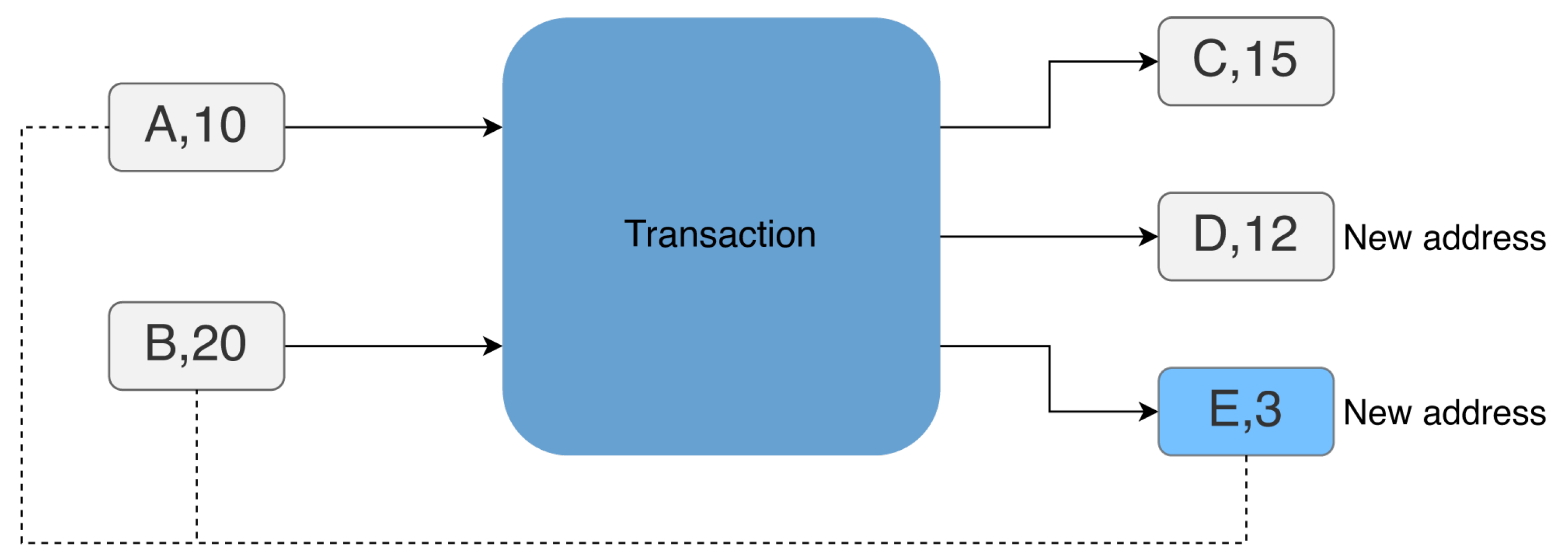
On the other hand, if address
a satisfies conditions 1., 2., 4., 5. and 6., then it means that there is not a single new address in the output of
t, and address
a is the only one among them whose amount is less than all the amounts of the inputs of
t. In this case, address
a is the change address, as shown in
Figure 2.
If no output address in a transaction verifies these conditions, no address will be marked as a change address. In addition, transactions in which an address in the outputs belongs to the transaction’s inputs are not considered since this address is usually just the change address and is already part of the input cluster.
2.3. Coinbase Address Clustering
A coinbase transaction is the first transaction in a block. It is constructed by the miners to receive the mining reward along with the transaction fees in the block. A coinbase transaction is similar to a regular Bitcoin transaction, the only difference being that the coinbase transaction contains a single empty input, called coinbase, and a set of output addresses specified by the miner to receive the reward. Miners often use the
scriptSig field of the coinbase transaction to include a text string. This field unlocks input-related funds within a normal Bitcoin transaction, typically by providing one’s private key. However, for coinbase transactions, there is no need to provide a script to unlock funds, as these are generated by the blockchain and transferred to the miner. Miners typically use this field to include the name of their mining pool, but it can be used to enter any text string. In the early days, when the Bitcoin protocol was launched, individual miners mined blocks. As the technology developed, this phenomenon gradually disappeared, replaced by mining pools. In mining pools, miners collaborate to solve the proof-of-work problem. Once a viable solution is found, the mining pool is responsible for distributing the rewards of the mined block to all the miners who participated in the mining process in proportion to the computational power made available by each of them. As a result, more and more miners are opting for mining pools to reduce energy costs and obtain more stable revenue. Lewenberg et al. [
15] analyzed the operational structure of Bitcoin mining pools. Thus, the last heuristic used in the tool implementation concerns clustering all output addresses in a coinbase transaction.
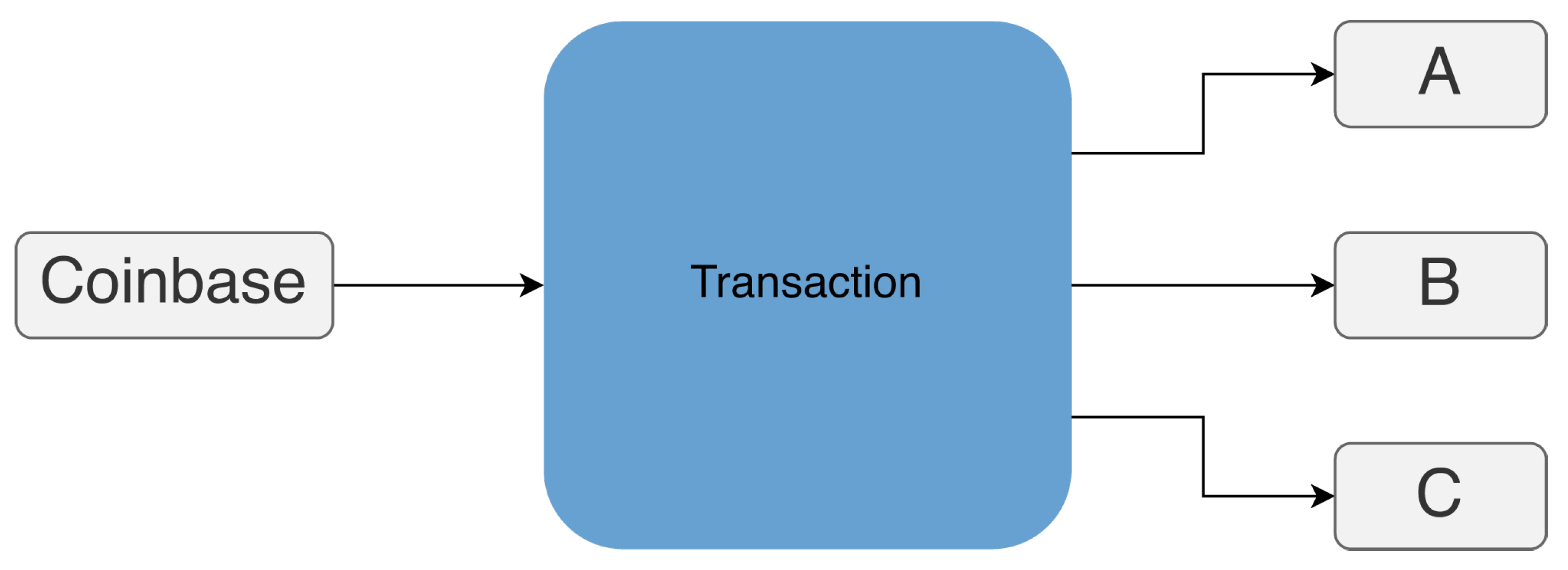
Definition 2.3. If a coinbase transaction contains two (or more) output addresses, they are all controlled by the same entity.
Ordinarily, the output addresses a coinbase transaction unless it is a single miner belonging to a mining pool, as shown in
Figure 3. These addresses will then be tasked with distributing the block rewards to the miners who participated in the pool
The heuristic used in the proposed work adds an additional condition: if the number of output addresses in the coinbase transaction is greater than a certain threshold , then the heuristic is not applied to the transaction. This check is made because some mining pools, such as P2Pool and Eligius, distribute shares to miners directly in the coinbase transaction. It may occur, therefore, that the output addresses of a coinbase transaction refer to different users, and building a cluster with these elements would be incorrect. In the BACH tool, was assigned the value 10, as it was considered a valid compromise based on experimental evidence.
Definition 2.4. If the number of output addresses in a coinbase transaction is less than the γ threshold, then they are all controlled by the same entity.
In this way, many addresses that actually belong to the mining pool are not added to the relevant cluster. It also avoids clustering false positives together, which would contribute to the construction of untrue clusters.
2.4. Accuracy and limitations
Each mining pool has its own internal distribution pattern, which changes frequently. The same considerations can be made for mixing services. For this reason, trying to identify a unique pattern for these services would be meaningless. Rather, heuristics with a certain degree of reliability are used, which can be applied to all Bitcoin services indiscriminately. Several studies have been conducted regarding the accuracy of heuristics used in clustering Bitcoin addresses. Gong Yanan and Chow [
16] analyzed the error rates of some clustering heuristics. Clearly, the accuracy of heuristics does not depend solely on the heuristic itself, but other factors also contribute to determining it, such as the case of CoinJoins for multi-input clustering and the distribution patterns of some mining pools for coinbase clustering. Chang et al. [
17] used the Gini impurity index to measure the homogeneity of the clusters found. To calculate it, information regarding the identity of each cluster must be added, which is not currently present in the BACH tool. Each cluster ideally should contain only addresses belonging to the same entity, but in reality, this is not always the case, and it may happen to have addresses belonging to different entities within the same cluster. Therefore, the following formula is used to calculate cluster homogeneity:
where
m is the number of different tags found within a given cluster,
i is the index of each tag, and
is the fraction of Bitcoin addresses in the cluster belonging to tag i. A tag corresponds to an entity previously found by off-chain information analysis. A pure cluster should contain only addresses belonging to a single entity, and its Gini index would equal 0. But when false positives are included in the cluster, the Gini index can increase to a maximum 1.
3. BACH
BACH is logically composed of three different components:
The database containing the blockchain data;
The server that provides this data through the database;
The client that displays the results.
The network architecture follows a client-server model with a database, whose communication flow between the various nodes is as follows:
The client application accepts an input from the user and sends an HTTP request to the server;
The server opens a connection with the database, performs the query and receives the result;
The server sends the result obtained to the client application that made the request;
The client application displays the cluster data received from the server in a 3D graph.
3.1. Database construction
A script has been developed to retrieve transaction data from the public blockchain and build a database with all addresses divided into clusters using the three heuristics described in the previous section. In addition, all the relationships between addresses created by individual transactions were stored, which will then be used to visualize the cluster within a 3D graph. All addresses found during the scan are stored within the database. In addition, information about the internal structure of the clusters is stored, i.e., the relationships that bind the various addresses within the cluster, which depend on the heuristics used.
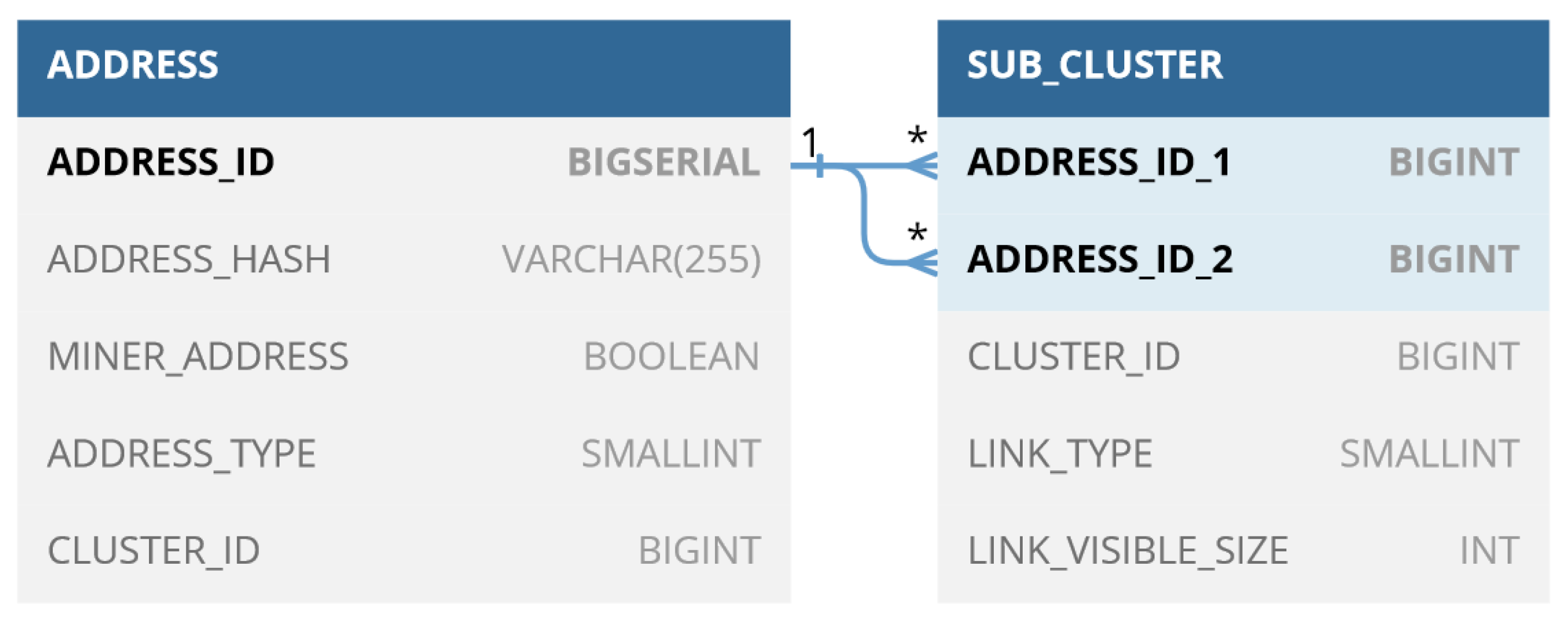
The database schema is shown in
Figure 4.
The address table contains information regarding the addresses found and the clusters to which they belong; there is also a field to specify the type of address (Legacy, Pay To Script Hash, Native SegWit, Taproot), and a field to indicate whether the address is a miner, i.e., appears in output to at least one coinbase transaction. The sub_cluster table, on the other hand, contains information on the relationships between different pairs of addresses within the same cluster; in addition, for each pair, the type of relationship is indicated, i.e., the heuristics used to construct it: this information will be used in the 3D graph to highlight the different relationships with different colors.
After the database construction, to speed up the reading operations in the API, the following indexes were defined:
create index hash_index on address(address_hash);
create index subcluster_index on sub_cluster(address_id_1, address_id_2).
Some additional solutions were adopted to improve the script execution performance and the speed of 3D graph rendering: - All the hashes of the blocks to be parsed are inside a file in the project directory and loaded into memory at the beginning of the script execution to optimize the speed of reading this data. The database connection is left open during the script’s execution, so the queries are executed much faster. In addition, the connection is closed and reopened every 100 blocks to avoid losing data and make a backup. - Replacing the Scanner object with the BufferedReader speeded up the download operation and mapping blocks within objects, greatly improving the overall execution time.
The repository containing the complete code is available on GitHub
1.
3.2. Server architecture
After building the database, REST APIs were implemented to allow external applications to access the data. The technology used is ExpressJS, a NodeJS library for API development. Specifically, endpoints were defined as those that receive GET-type requests via HTTP protocol, query the database, and return data in JSON format, depending on the parameters passed to the request. The endpoints defined are as follows:
GET /{address}: Returns all addresses belonging to the address cluster passed as parameter.
GET /sub/{address}: Returns all links between addresses belonging to the cluster of the address passed as a parameter.
GET /info/{address}: Returns all the links of the address passed as a parameter.
These can then be used by the client application, i.e., the BACH tool, to access the data stored in the database. The repository containing the complete code is available on GitHub
2.
3.3. BACH Webapp
Finally, the web application was implemented, allowing the data on the clusters to be visualized through a 3D graph and tabular structures. The technology used to implement the application is React, a front-end JavaScript library for creating user interfaces. The tool allows the user to set a Bitcoin address in the search bar and display some information about the address cluster. In particular, the tool allows the display of a table of all addresses belonging to the same cluster as the found address and a 3D graph of the cluster, constructed using the heuristics presented above. In addition, by clicking on one of the nodes in the graph, it is possible to visualize in detail all the links of the latter to the other addresses in the cluster. The 3D Force-Directed Graph component has been used to construct the 3D graph. It allows the data structure of a graph to be represented in a three-dimensional space, using ThreeJS/WebGL for 3D rendering. The tool’s homepage provides more information regarding the cluster graph, such as the colors used for the nodes and arcs. The tool allows moving within the 3D graph, zooming in and changing angles, to better visualize certain nodes and links present in the cluster. In addition, clicking on a node within the graph will show all its links to other nodes, with the type of heuristics used for linking. A negative element is the rendering speed of the graph, which on devices with small capacities could take several tens of seconds, especially if the cluster to be displayed is very large. To remedy this problem, the
link_visible_size field in the
sub_cluster table has been introduced in the database, which avoids rendering all the links within a cluster. This allows even less powerful devices to view the entire cluster graph without experiencing major slowdowns. In the client code, it is possible to modify this field so that if a node contains more links than the set limit, they are not rendered within the graph. This aspect is useful in cases where there are fairly large groups of addresses in which each has a link to every other address in the group: this is the case with groups that are formed using multi-input clustering heuristics; indeed, all input addresses to the same transaction have a link to all others. If the number of input addresses is
N, then the relationships between them will be
, i.e., a significantly larger number and growing factorially with
N. It is important to note that although these links are not shown in the graph, the nodes are still displayed correctly, as shown in
Figure 5 and
Figure 6.
The repository containing the complete code is available on GitHub
3.
4. Experimentation
This section reports the experiments carried out to validate the functionality of BACH. The experiments were performed considering the first 130,000 blocks of the Bitcoin blockchain. The script for building the database ran on a Windows 10 machine with 16 GB RAM and AMD Ryzen 7 4700U processor. The first 130,000 blockchain blocks were parsed over a runtime of about a week. The final size of the database is 6454 MB. After the first 100,000 blocks, the execution slowed down considerably. This was due to the increasing number of transactions within the blocks and, more importantly, to the increasing database size. In addition to reading and inserting operations, editing operations are also required on existing records, such as updating the ClusterID of an address group. Since some fields are changed frequently, it is impossible to define indexes on them to speed up reading.
4.1. Detection of peeling chains
The peeling chain is a transactional pattern, used mainly by mixing services, that allows large sums of money to be laundered through a long series of small transactions. This process is illustrated in
Figure 7. Basically, the peeling chain starts with one address receiving a certain amount of money. This address then sends the money to two (or more) addresses: one still belongs to the transaction’s sender, representing the changed address. The change address repeats the peeling process until all the money runs out.
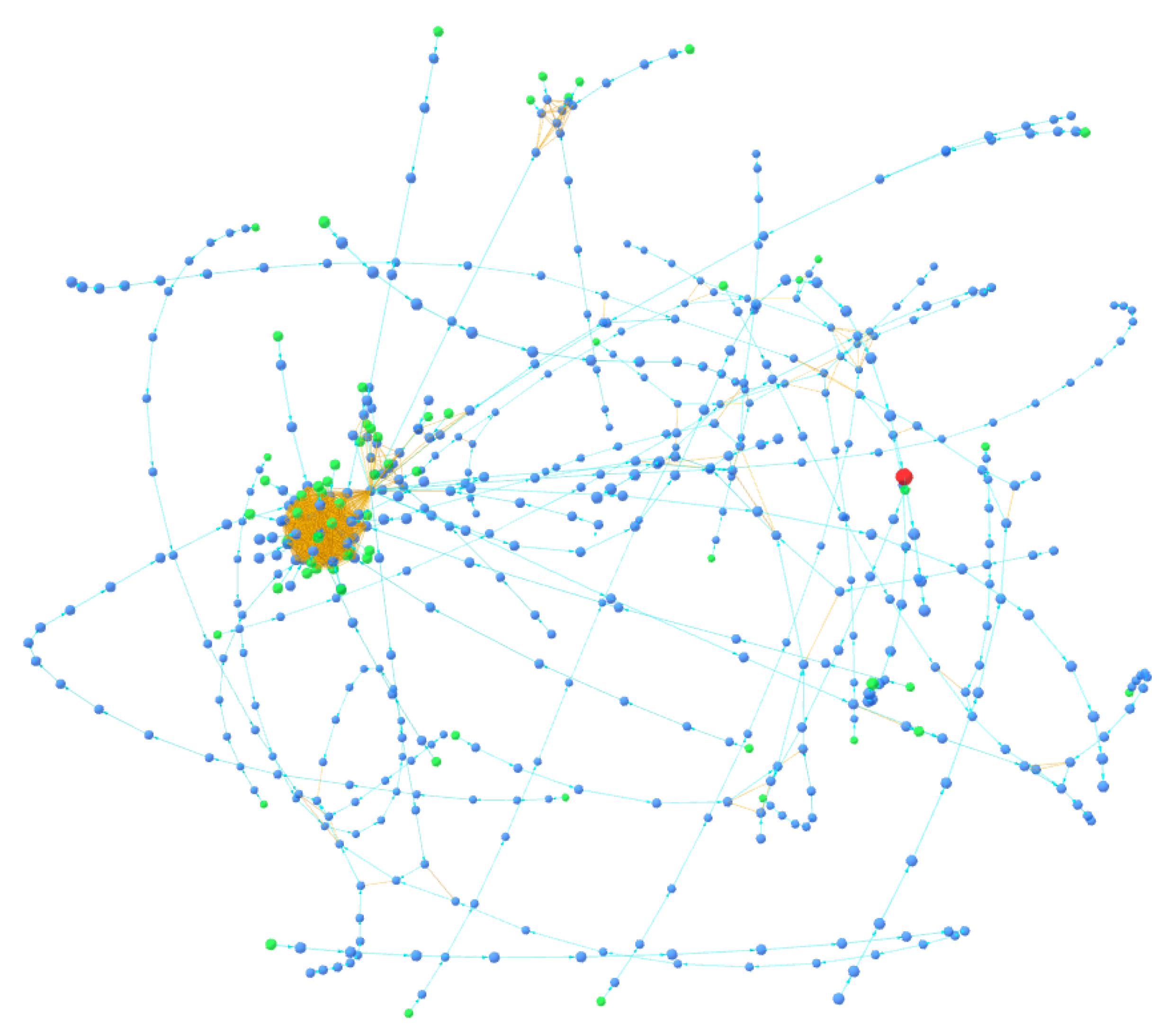
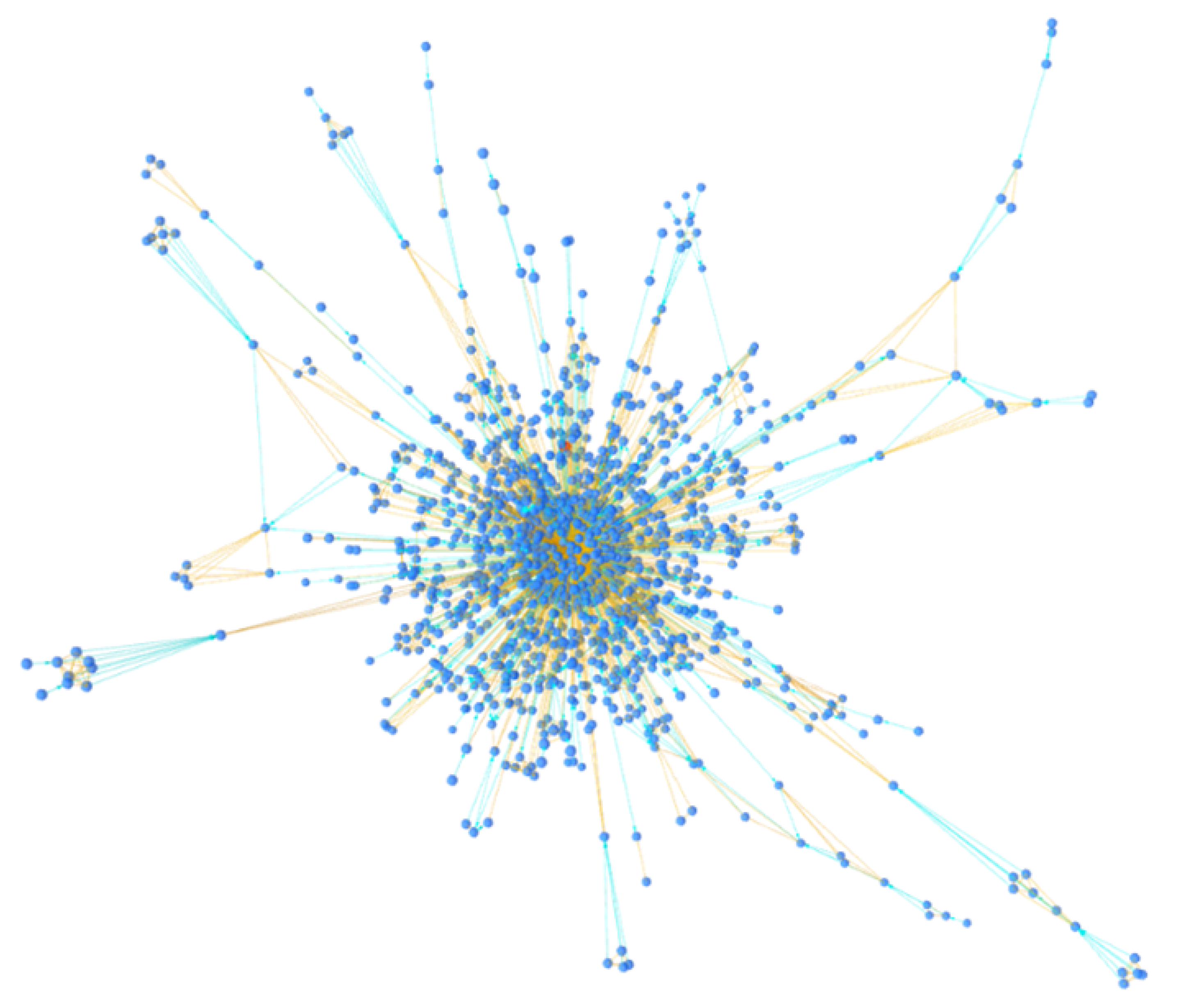
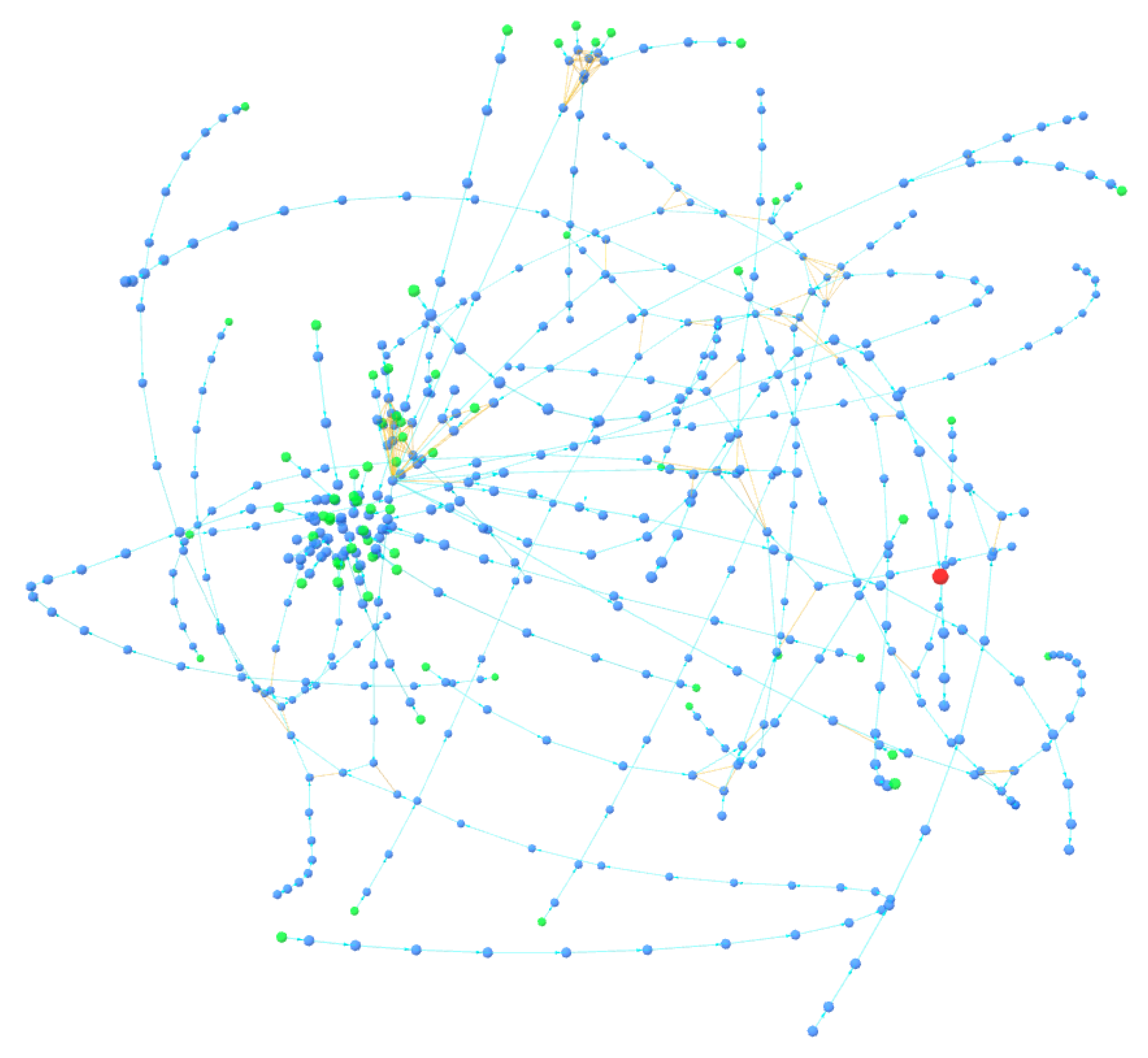
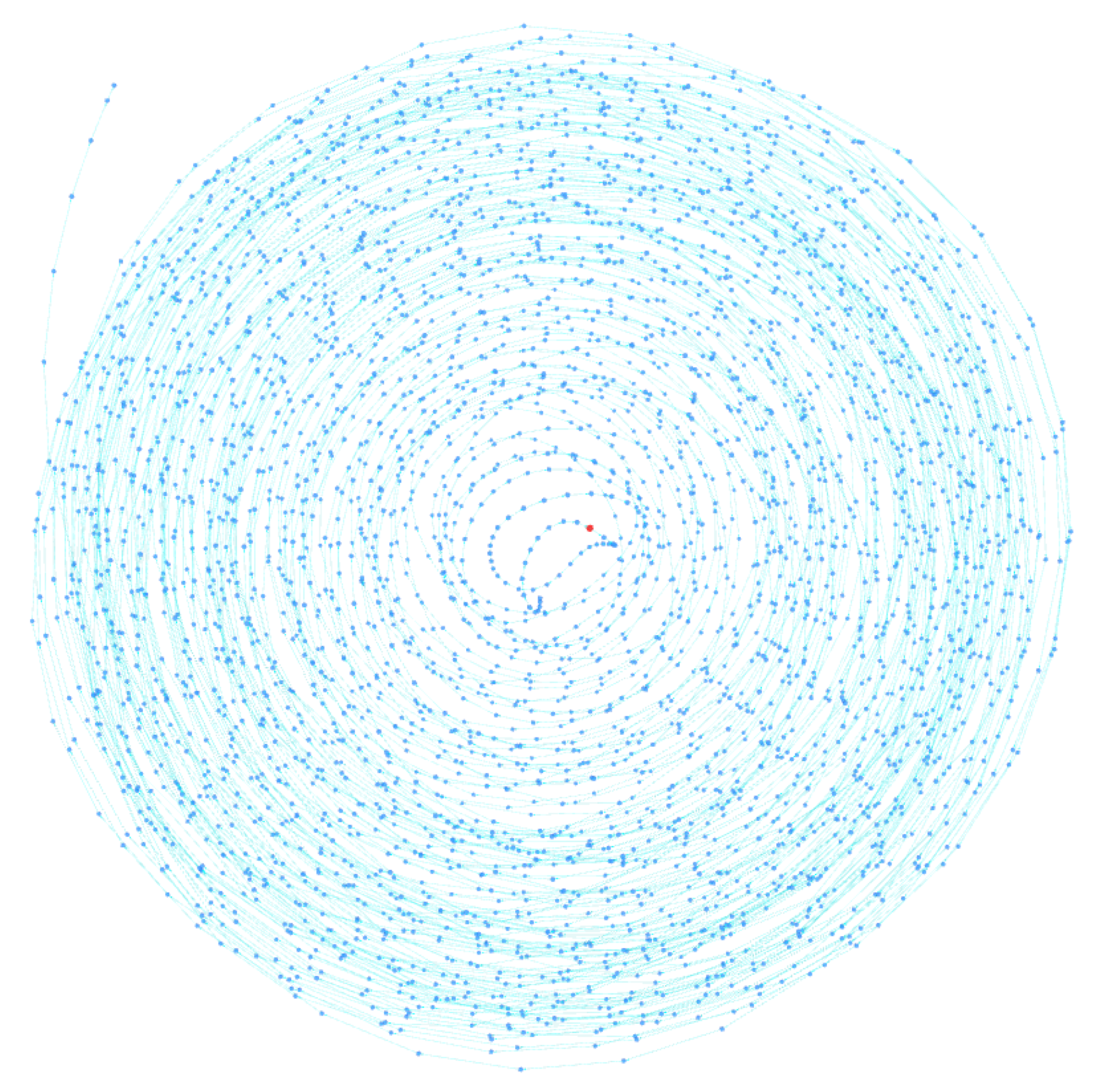
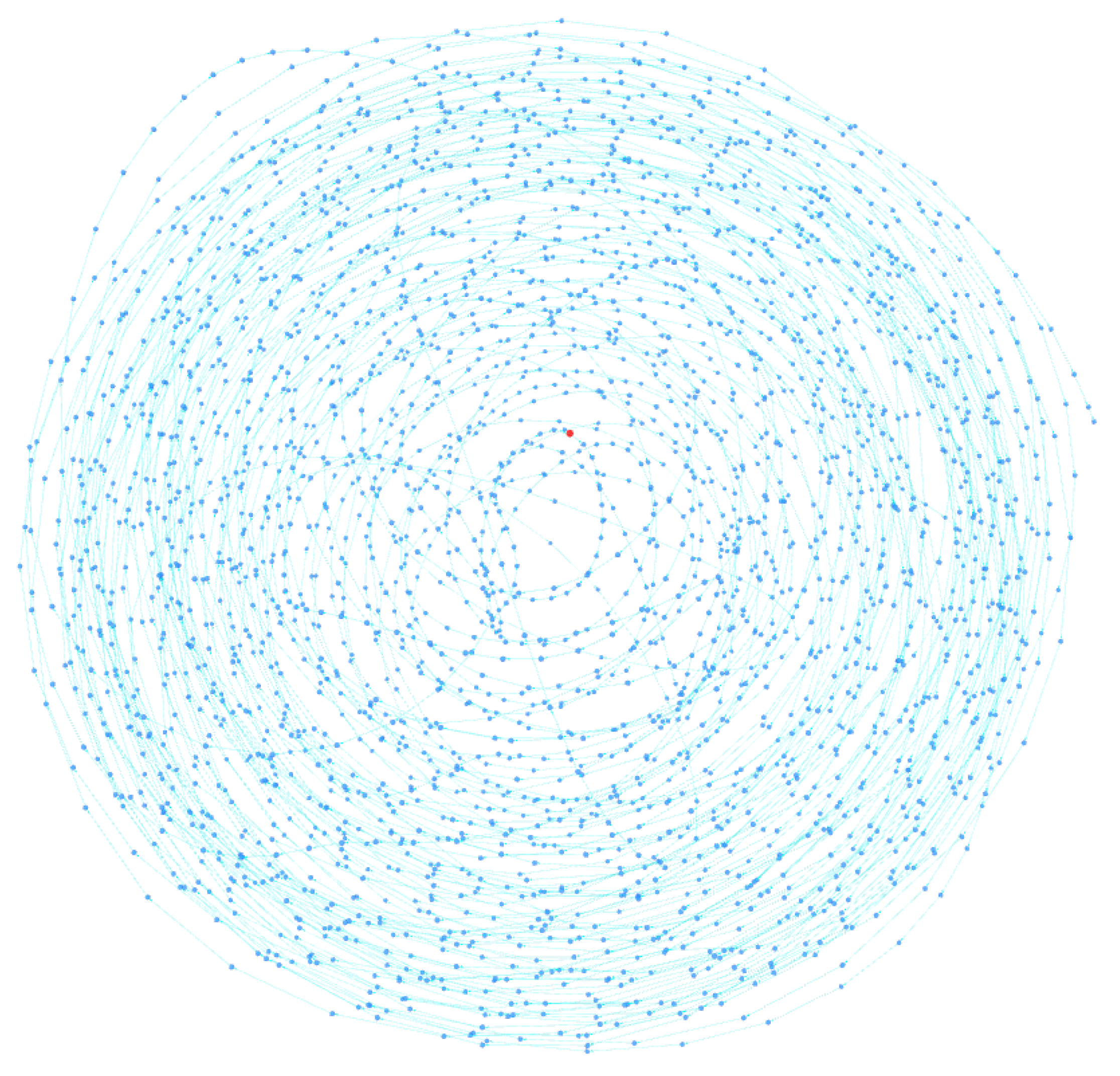
Typically, the address to which peels are sent belongs to an exchange, where they are usually converted into fiat currency or other types of assets. Criminals typically use very long and complex peeling chains to lose track of their funds. Note that this pattern does not have to be attributed to money laundering activities but can also be used by ordinary users who wish to maintain privacy and avoid being tracked by clustering tools. Through the BACH tool, some clusters were identified that could be the result of a peeling chain. In fact, as can be seen in
Figure 8 and
Figure 9, they exhibit a spiral shape in which each cluster address represents the change address of another. The tool, in fact, thanks to the 3D visualization of the cluster graph, makes it easy to identify any patterns present within it. They are very similar and are shown in the figure from the same angle. Each address is linked to another through change address heuristics, as seen by the light blue colored links between the various nodes. This type of structure often indicates the presence of a peeling chain.
Cluster A contains 3659 addresses, while Cluster B contains 2781 addresses. You can analyze them in detail with the BACH tool by entering the following Bitcoin addresses:
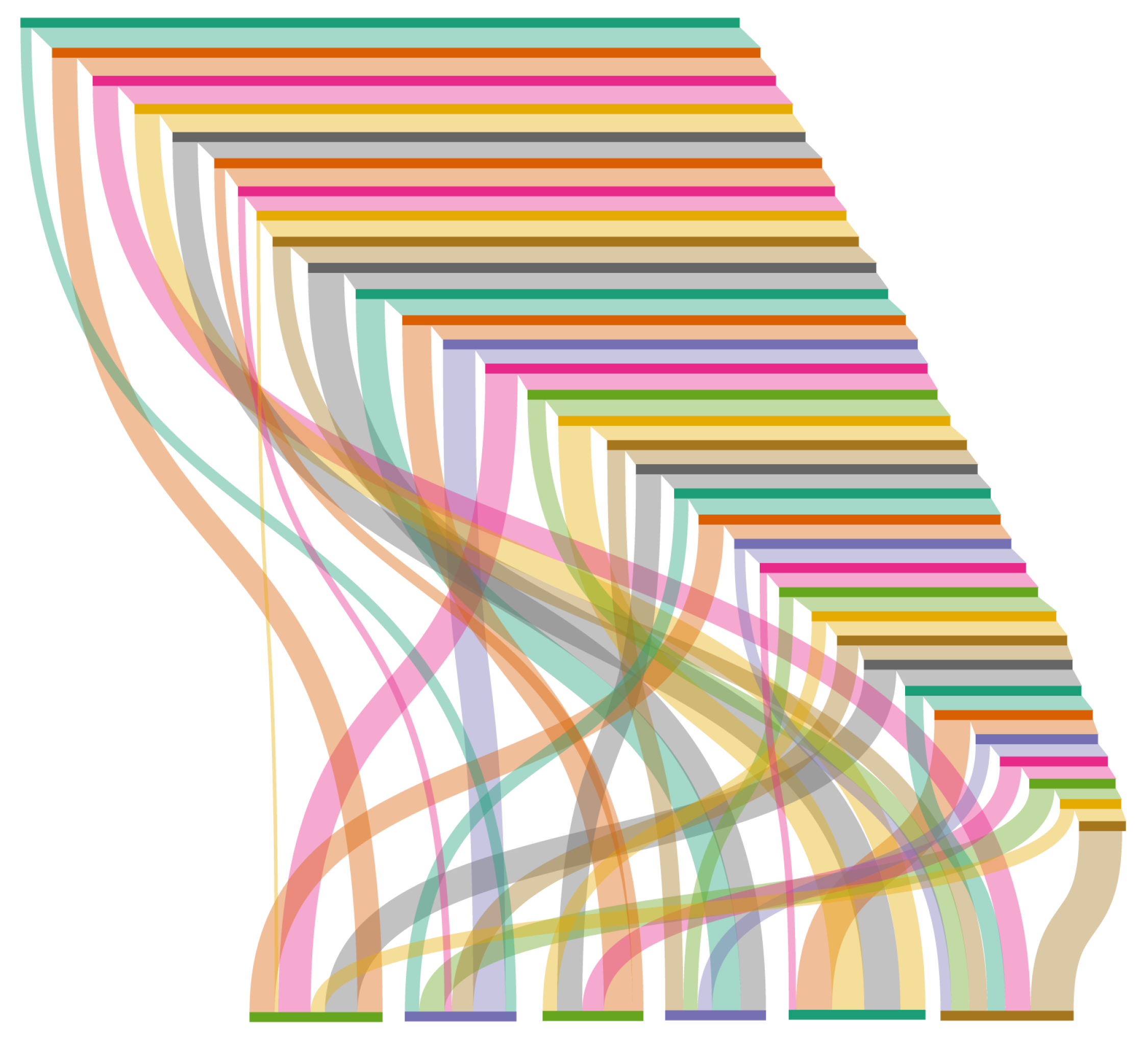
The patterns were represented by a Sankey diagram, a special flow chart in which the width of the arrows is drawn proportionally to the amount of flow. Sankey diagrams, drawn using the online tool SankeyMatic, are very useful for visualizing the money flow between addresses. The spiral-shaped clusters identified by the BACH tool represent peeling chains. Each address in the chain, as it first appears in the blockchain, is identified as the change address of the transaction. This way, all addresses in the peeling chain are correctly placed in the same cluster. On the other hand, a limitation of the tool is that the addresses where peels are sent are not included in the cluster. The first pattern identified uses only one address to which the peel is sent and can be schematized as in
Figure 10. Each node in the peeling chain always sends the peel to the same address, eventually containing the same amount of money as the address that starts the chain. This is the simplest configuration of a peeling chain. The other two patterns identified instead use multiple peeling addresses in a way that increases their complexity. Specifically, the second uses about ten peeling addresses, while the third uses hundreds.
Figure 11 summarizes the process used by these patterns: in the example, only six peeling addresses were included, which will eventually contain the amount of money from the address that started the chain, but the process used by the patterns described is identical.
Analyzing the spiral clusters identified by the BACH tool, it was found that cluster B, shown in
Figure 9, uses a peeling chain with multiple peeling addresses, similar to the pattern shown in
Figure 11. The same cluster has been investigated by Zhao et al. [
14], in which a peeling chain pattern was identified by studying 166 mixing transactions. Specifically, 125 BTC were transferred from an address to eight peeling addresses. At the end of the process, the amount of money in the eight destination addresses matched the amount contained in the source address. BACH provides several useful information regarding the cluster, but a limitation of the tool is that the peeling addresses are not placed in the same cluster as the peeling chain addresses.
4.2. Comparison to Wallet Explorer
This section highlights the differences between the clusters found by BACH and those found instead by Wallet Explorer. To perform this type of analysis, the database was reconstructed using only the heuristic on multi-input clustering, i.e., the only heuristic used by Wallet Explorer for constructing clusters. In this way, the results obtained by the two tools after analyzing the same dataset will be compared since Wallet Explorer also analyzes transactions after the block at a height of 130,000. Next, some of the limitations of Wallet Explorer are listed:
Uses only multi-input clustering heuristic, thus not allowing aggregate clusters with a good probability to belong to the same entity.
Does not allow visualization of relationships between addresses in the same cluster but merely displays them all in the same table.
Because of the previous point, it is impossible to visualize the cluster’s internal structure graphically since the relationships have not been stored.
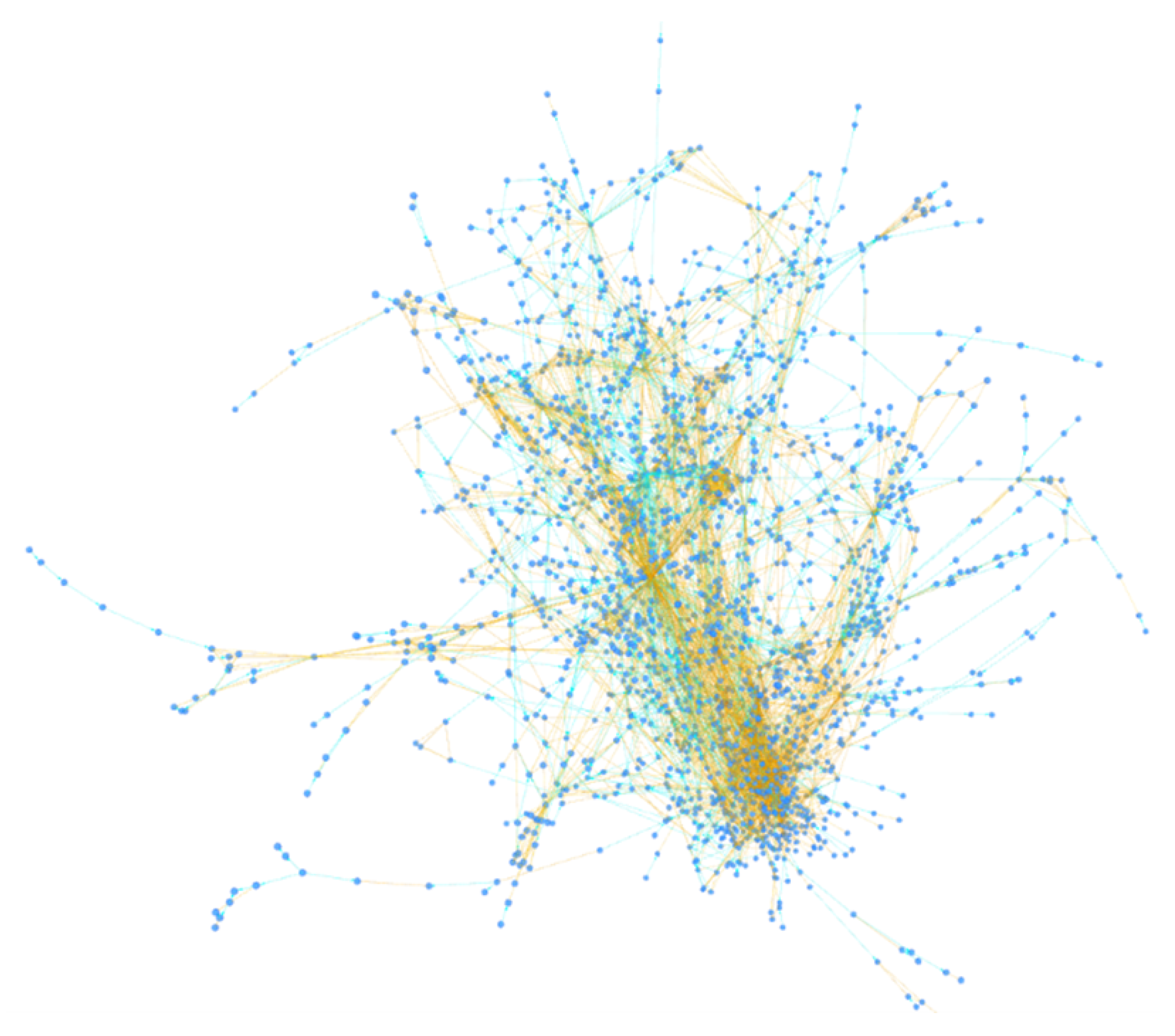
BACH aims to solve these problems by using three clustering heuristics and storing all the relationships between addresses for each analyzed transaction, indicating the heuristics used to find them. This information allows one to trace the internal structure of the cluster, which is illustrated in a 3-D graph. The clusters were analyzed by reconstructing the Wallet Explorer database with the same scheme used by BACH but exclusively implementing heuristics on multi-input clustering. This method also allows comparison of the internal structure of the clusters obtained by the two tools. The following images show a comparison of the identified clusters.
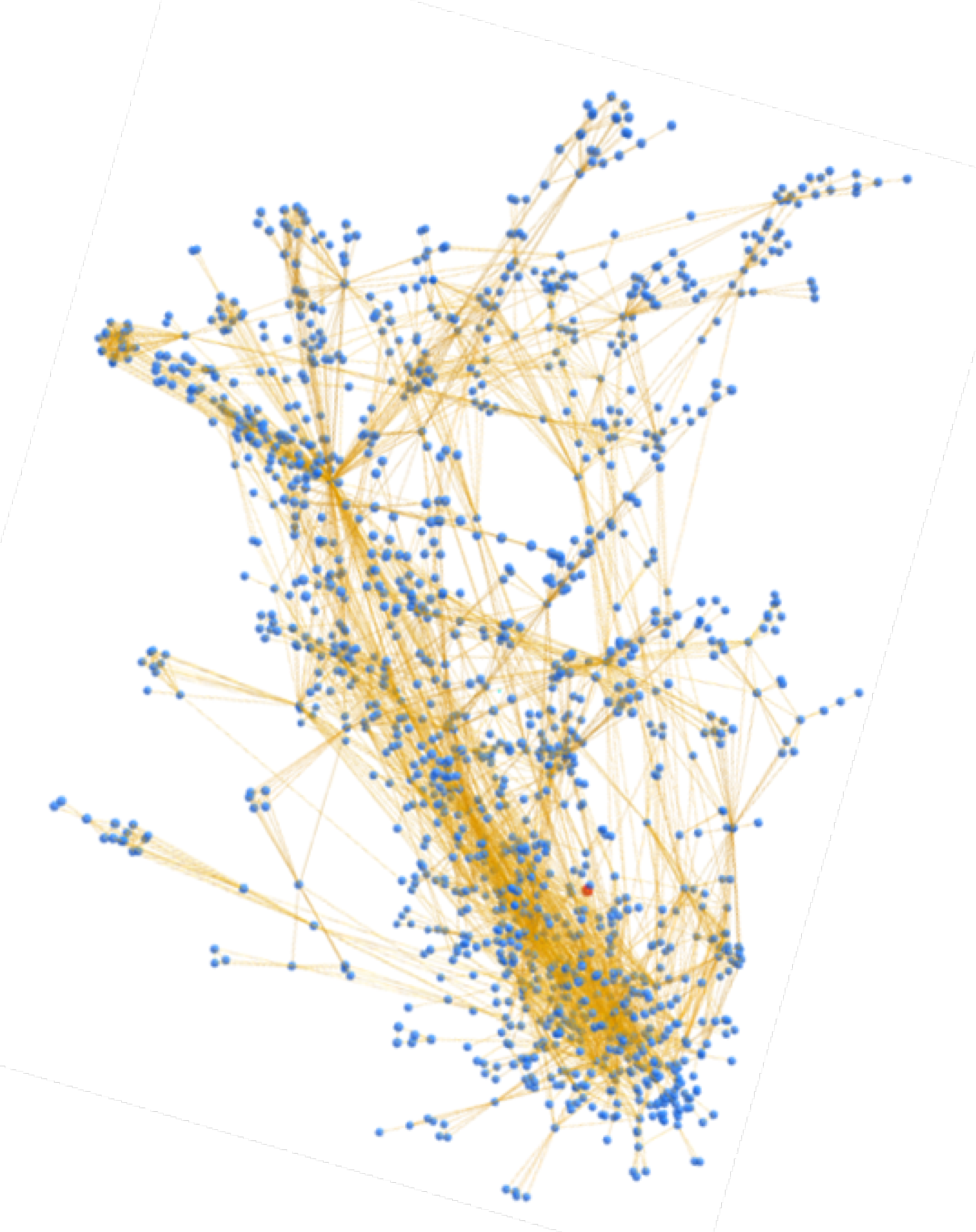
Figure 12 displays a cluster obtained exclusively using the multi-input clustering heuristic; in fact, all its links are orange, i.e., the various nodes are related to each other with the only relationship of multi-input.
Figure 13, on the other hand, shows the same cluster but constructed using the BACH tool: in fact, it is possible to visually notice the difference in the number of nodes and relationships between the two clusters. In addition, other types of links are also present, which indicate the use of the new clustering heuristics introduced in the tool. It is important to note that some small clusters obtained with the heuristics on multi-input are not clustered together in Wallet Explorer, while the BACH tool aggregates some of them to the main cluster using the other two heuristics. The following address can be searched in the BACH tool to analyze the cluster shown in the figure:
1wEmdvd75rGsTiR8myP1F9os8yPUySUKJ. Di seguito viene mostrato un ulteriore esempio, questa volta utilizzando il cluster di Slush Pool [
18]. Anche in quest caso possono essere effettuate le medesime considerazioni.
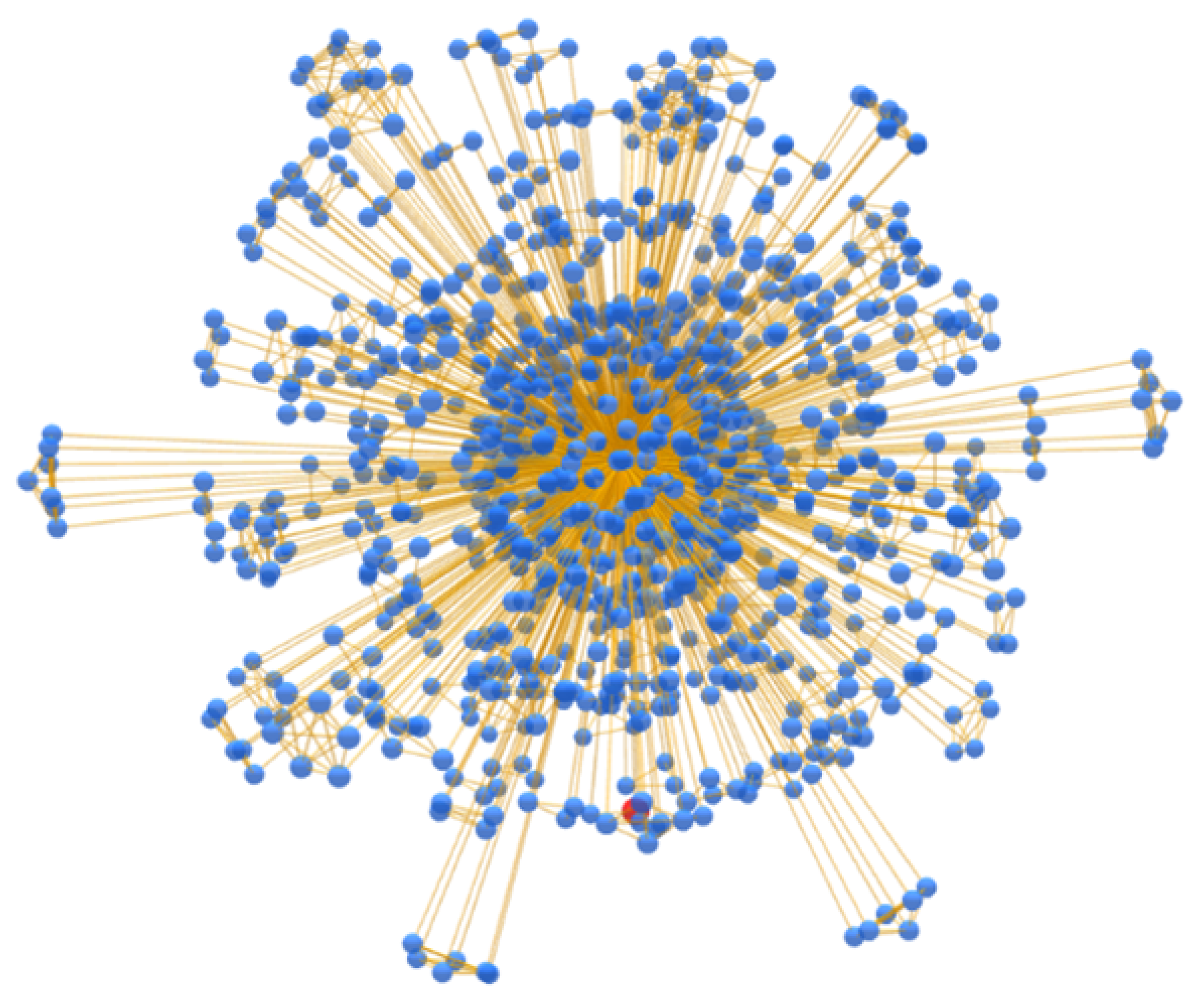
In
Figure 14, the cluster contains only the nodes linked to the central address, while in
Figure 15, it is possible to see how these addresses are also linked to others through new relationships, which in most cases are identified by heuristics on change address clustering. Ultimately, this analysis has shown how BACH favors an increase in address aggregation within clusters compared to Wallet Explorer and introduced a novel feature to observe the cluster from a new point of view.
Table 1 shows some information about the results obtained by the two tools.
In contrast to expectations, the number of total clusters turns out to be higher in the case of BACH, which is expected to contain a smaller number of clusters as it aims to aggregate smaller clusters into larger ones. This goal was indeed achieved by BACH, but the larger number of clusters identified can be attributed to the use of the new heuristic on coinbase clustering, which identifies a large number of clusters by analyzing coinbase transactions. In fact, there are a total of 11,006 clusters consisting solely of miners, as many of the initial blocks of the blockchain contain multiple output addresses in coinbase transactions; as a result, many clusters are formed due to the heuristic on coinbase clustering. By removing these clusters from the figure shown in the table, a total of 51,859 clusters are obtained. This is a lower number than that of Wallet Explorer, which shows how the introduction of the two new heuristics improved the degree of address aggregation in the network. In addition, the table shows data on the number of total relationships, which is obviously higher in BACH’s case, and the number of addresses from which the largest cluster is composed. Finally, the size of the databases containing the data used by the two tools is shown: in this case, most of the space is clearly occupied by information about the relationships within the various clusters. Thus, the database will be significantly larger in the case of BACH, which contains many more relationships than Wallet Explorer. It is important to emphasize that the size given for the Wallet Explorer database does not correspond to the actual size of the database used by the service since the database has been reconstructed to carry out these analyses: in fact, Wallet Explorer does not store the internal relationships for each cluster, greatly reducing its size.
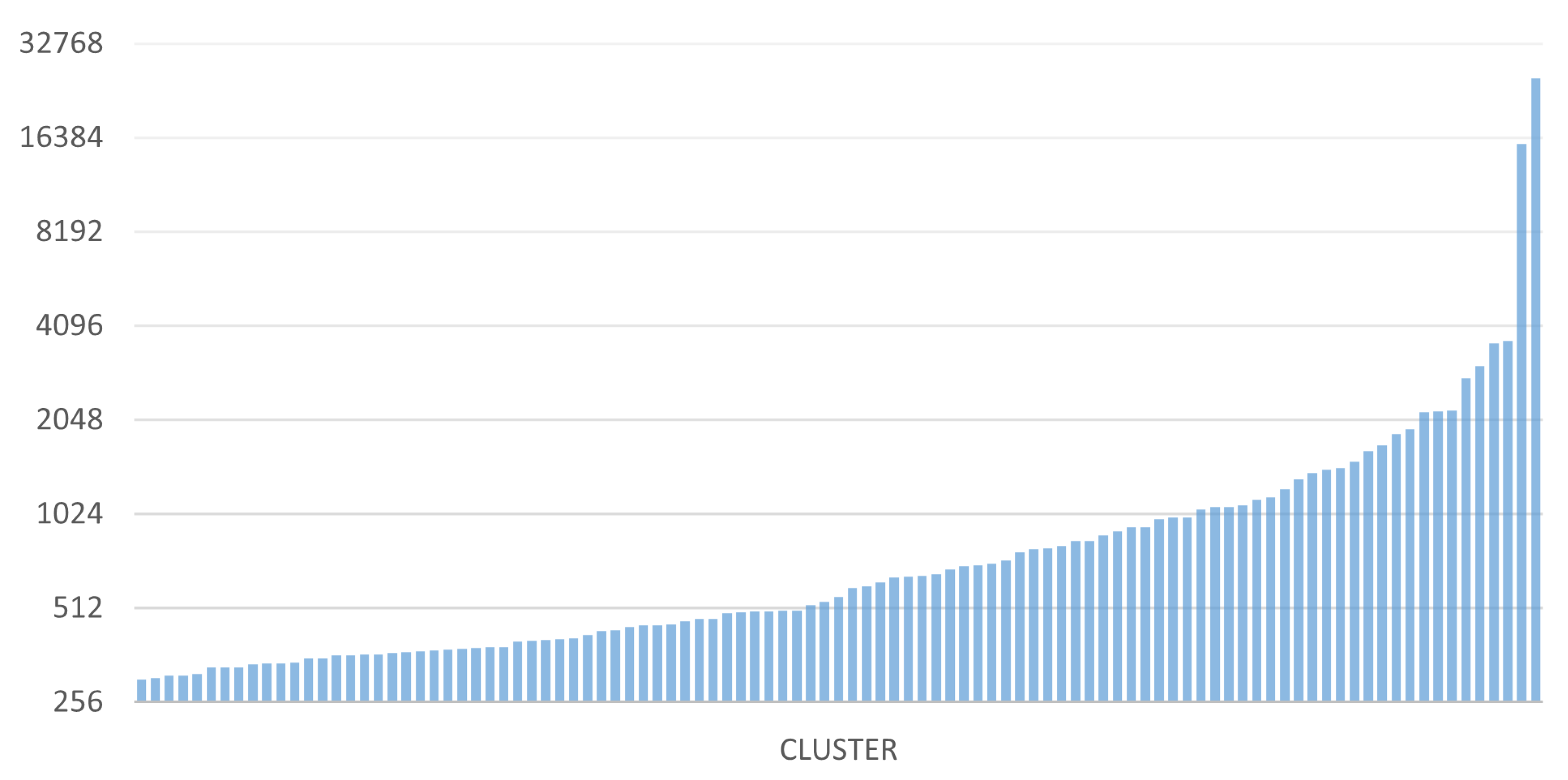
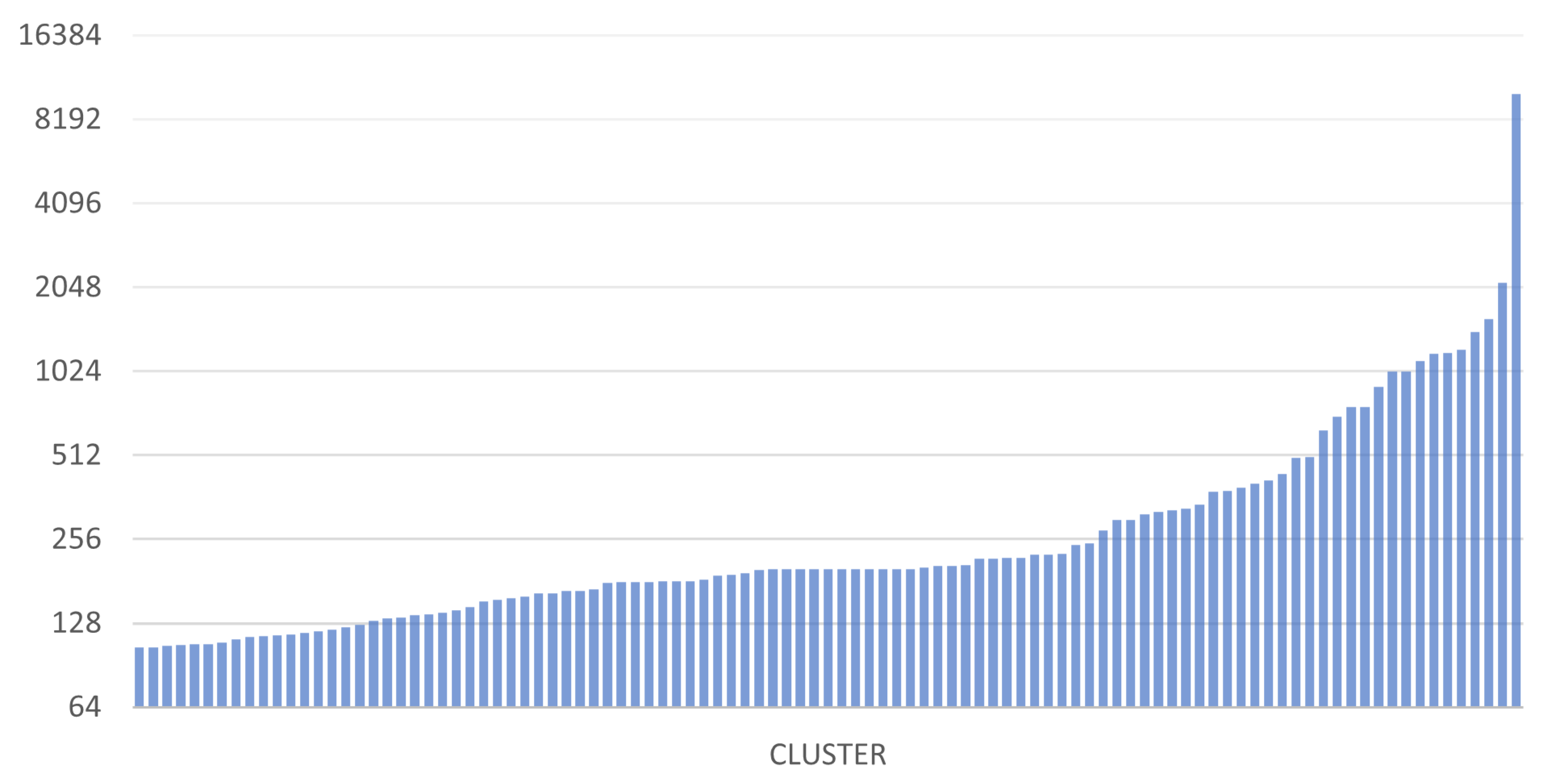
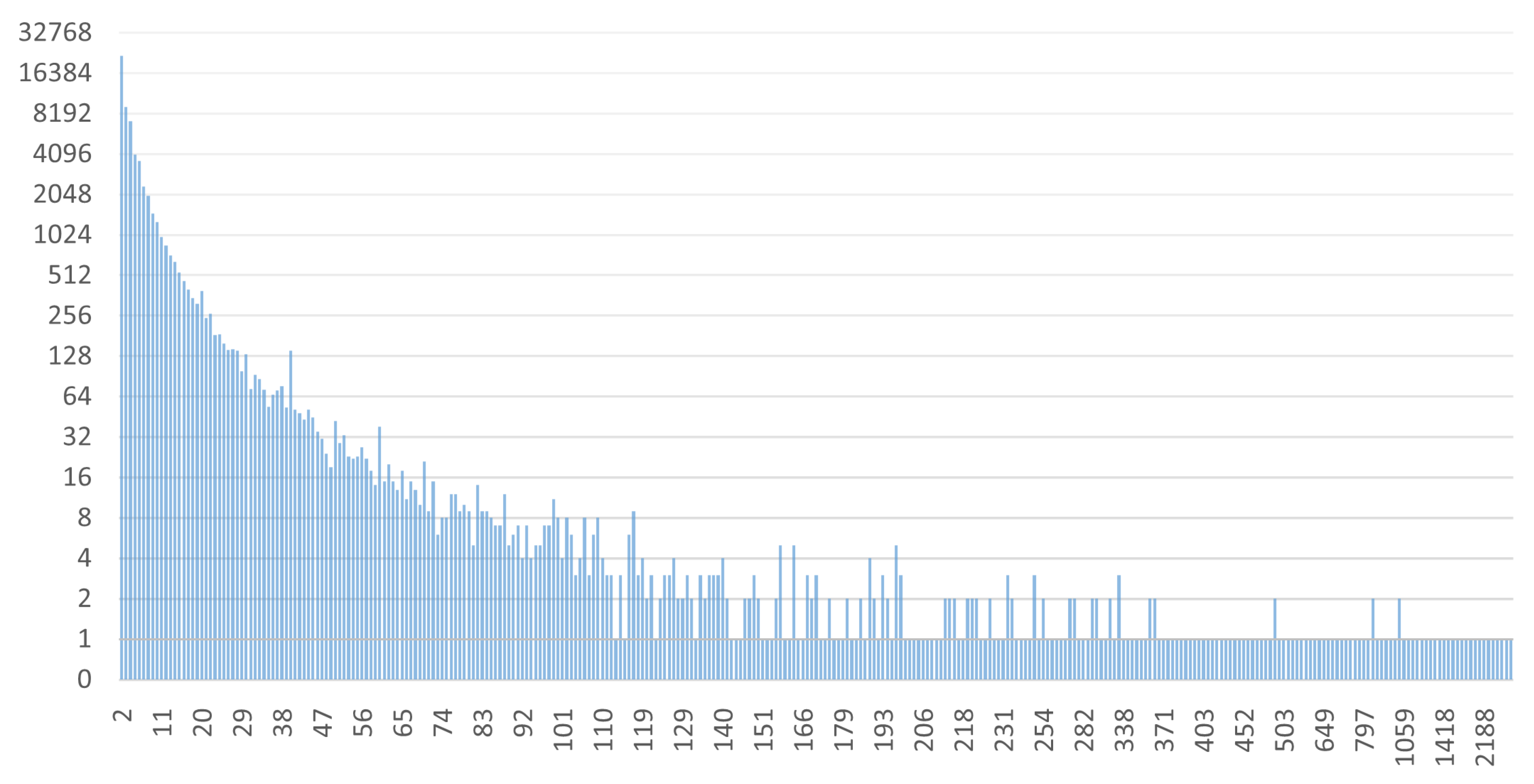
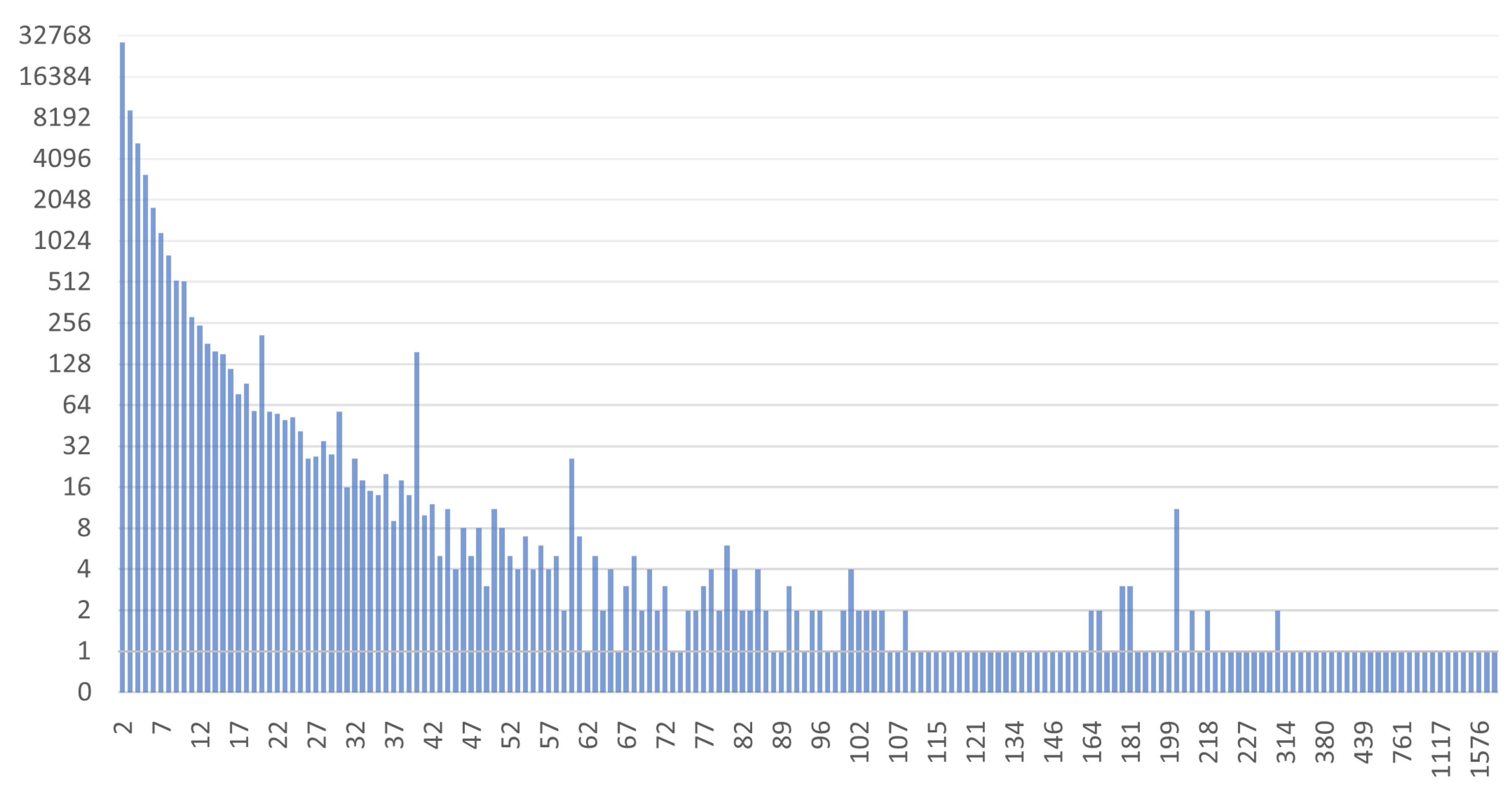
Some interesting data regarding the size of the clusters found and the distribution of addresses in the various clusters are now shown. The two graphs in
Figure 16 and
Figure 17 show the sizes of the 100 largest clusters obtained from BACH and Wallet Explorer analysis, respectively.
These graphs show that the number of addresses per cluster has increased evenly, improving the level of address aggregation. The average number of addresses per cluster in BACH has also grown compared to Wallet Explorer. This aspect can be seen even more clearly in the two graphs in
Figure 18 and
Figure 19, in which the values on the y-axis indicate the size of the clusters, while those on the x-axis indicate the number of clusters with a given size.
In
Figure 18, it is possible to observe how the curve settles around the value 100, while in
Figure 19, this happens around the value 50. This finding indicates that BACH can detect many more clusters larger than Wallet Explorer, where most of the clusters found contain a maximum of about 50 addresses. The number of addresses analyzed is the same for both tools, but the distribution of these within the various clusters has changed dramatically. In fact, in the case of BACH, the number of addresses not belonging to any cluster decreased by about 60% compared to the Wallet Explorer analysis.
5. Conclusions
This work proposed BACH, a tool that can analyze Bitcoin transactions and identify clusters of addresses that can potentially belong to a single entity. Such a tool is more effective than those already known, using multiple combined heuristics to identify the address cluster. BACH works on Bitcoin but is still extendable to other cryptocurrencies operating via blockchain. The operation of BACH is superior to other already known tools because it uses multiple heuristics simultaneously. Experiments have shown that BACH is particularly effective in detecting transactional patterns and that the clusters detected are more complete and substantial. Such a tool thus proves useful when deanonymizing transactions on the blockchain, particularly where illicit activity or money laundering is suspected.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Violante F., Galantucci, S., and De Lucci F.; methodology, Costantini, M., Galantucci, S., and Violante F.; software, Violante F., De Lucci F., and Caringella, M.; validation, Violante F., De Lucci F., and Galantucci, S.; formal analysis, Costantini, M., Galantucci, S., and Violante F.; investigation, Costantini, M., Galantucci, S., and Violante F.; resources, Violante F., Caringella, M., and De Lucci F.; data curation, Violante F., Caringella, M., and Galantucci, S.; writing—original draft preparation, Costantini, M., Galantucci, S., and Violante F.; writing—review and editing, Costantini, M., Galantucci, S., and De Lucci F.; visualization, Violante F., Galantucci, S., and Costantini, M.; supervision, Violante F., Caringella, M., and Galantucci, S.; project administration, Violante F., Caringella, M., and De Lucci F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Regione Puglia - Progetto ACROSS - AcCounting & payROll Software cloud converSion - POR PUGLIA FESR 2014-2020 - Grant number: THA48Y5
Data Availability Statement
Data used in this work is public
AI or AI-assisted tools were not used in drafting any aspect of this manuscript
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Nakamoto, S. Bitcoin: A peer-to-peer electronic cash system 2008.
- Raju, R.S.; Gurung, S.; Rai, P. An overview of 51% attack over Bitcoin network. Contemporary Issues in Communication, Cloud and Big Data Analytics: Proceedings of CCB 2020 2022, pp. 39–55.
- Kaminsky, D. Some Thoughts on Bitcoin. https://dankaminsky.com/2011/08/05/bo2k11/ Accessed on June 25th, 2024.
- Irwin, A.S.; Turner, A.B. Illicit Bitcoin transactions: challenges in getting to the who, what, when and where. Journal of money laundering control 2018, 21, 297–313. [Google Scholar]
- Meiklejohn, S.; Pomarole, M.; Jordan, G.; Levchenko, K.; McCoy, D.; Voelker, G.M.; Savage, S. A fistful of bitcoins: characterizing payments among men with no names. Proceedings of the 2013 conference on Internet measurement conference, 2013, pp. 127–140.
- Shojaeinasab, A.; Motamed, A.P.; Bahrak, B. Mixing detection on bitcoin transactions using statistical patterns. IET Blockchain 2023, 3, 136–148. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Y.; Kwon, H.; Lee, J.; Hur, J. A practical de-mixing algorithm for bitcoin mixing services. Proceedings of the 2nd ACM Workshop on Blockchains, Cryptocurrencies, and Contracts, 2018, pp. 15–20.
- Wu, J.; Liu, J.; Chen, W.; Huang, H.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, Y. Detecting mixing services via mining bitcoin transaction network with hybrid motifs. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems 2021, 52, 2237–2249. [Google Scholar]
- De Balthasar, T.; Hernandez-Castro, J. An analysis of bitcoin laundry services. Secure IT Systems: 22nd Nordic Conference, NordSec 2017, Tartu, Estonia, November 8–10, 2017, Proceedings 22. Springer, 2017, pp. 297–312.
- Kinkeldey, C.; Fekete, J.D.; Isenberg, P. Bitconduite: Visualizing and analyzing activity on the bitcoin network. EuroVis 2017-Eurographics Conference on Visualization, Posters Track, 2017, p. 3.
- Yue, X.; Shu, X.; Zhu, X.; Du, X.; Yu, Z.; Papadopoulos, D.; Liu, S. Bitextract: Interactive visualization for extracting bitcoin exchange intelligence. IEEE transactions on visualization and computer graphics 2018, 25, 162–171. [Google Scholar]
- Androulaki, E.; Karame, G.O.; Roeschlin, M.; Scherer, T.; Capkun, S. Evaluating user privacy in bitcoin. Financial Cryptography and Data Security: 17th International Conference, FC 2013, Okinawa, Japan, April 1-5, 2013, Revised Selected Papers 17. Springer, 2013, pp. 34–51.
- Maxwell, G. Coinjoin: Bitcoin Privacy for the Real World. https://bitcointalk.org/?topic=279249 Accessed on June 25th, 2024.
- Zhao, Z.; Wang, J.; Shi, K.; Zhang, H. Improving Address Clustering in Bitcoin by Proposing Heuristics. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management 2022, 19, 3737–3749. [Google Scholar]
- Lewenberg, Y.; Bachrach, Y.; Sompolinsky, Y.; Zohar, A.; Rosenschein, J.S. Bitcoin mining pools: A cooperative game theoretic analysis. Proceedings of the 2015 international conference on autonomous agents and multiagent systems, 2015, pp. 919–927.
- Gong, Y.; Chow, K.P.; Ting, H.F.; Yiu, S.M. Analyzing the error rates of bitcoin clustering heuristics. IFIP International Conference on Digital Forensics. Springer, 2022, pp. 187–205.
- Chang, T.H.; Svetinovic, D. Improving bitcoin ownership identification using transaction patterns analysis. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems 2018, 50, 9–20. [Google Scholar]
- Hercog, U.; Povše, A. Taint analysis of the Bitcoin network. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.01538. [Google Scholar]
Figure 1.
Change Address example: output address D is the change address
Figure 1.
Change Address example: output address D is the change address
Figure 2.
Change Address example: output address E is the change address
Figure 2.
Change Address example: output address E is the change address
Figure 3.
Coinbase Address example: addresses A, B, and C belong to a mining pool
Figure 3.
Coinbase Address example: addresses A, B, and C belong to a mining pool
Figure 4.
Schema of the Database used by BACH
Figure 4.
Schema of the Database used by BACH
Figure 5.
Viewing with no limitation in the display of links
Figure 5.
Viewing with no limitation in the display of links
Figure 6.
Viewing with active link display limit
Figure 6.
Viewing with active link display limit
Figure 7.
Peeling chain process. Each node in the peeling chain uses only two addresses for each transaction: one is the address where the peel is sent (in grey), and the other is the change address, where the remaining amount of money is sent (in blue). The address chain in blue represents the peel chain.
Figure 7.
Peeling chain process. Each node in the peeling chain uses only two addresses for each transaction: one is the address where the peel is sent (in grey), and the other is the change address, where the remaining amount of money is sent (in blue). The address chain in blue represents the peel chain.
Figure 8.
Cluster A graph
Figure 8.
Cluster A graph
Figure 9.
Cluster B graph
Figure 9.
Cluster B graph
Figure 10.
Peeling chain with single peeling address
Figure 10.
Peeling chain with single peeling address
Figure 11.
Peeling chain with multiple peeling addresses
Figure 11.
Peeling chain with multiple peeling addresses
Figure 12.
Cluster obtained using Wallet Explorer
Figure 12.
Cluster obtained using Wallet Explorer
Figure 13.
Cluster obtained using BACH
Figure 13.
Cluster obtained using BACH
Figure 14.
Cluster obtained using Wallet Explorer
Figure 14.
Cluster obtained using Wallet Explorer
Figure 15.
Cluster obtained using BACH
Figure 15.
Cluster obtained using BACH
Figure 16.
Size of the 100 largest clusters obtained with BACH
Figure 16.
Size of the 100 largest clusters obtained with BACH
Figure 17.
Size of the 100 largest clusters obtained with Wallet Explorer
Figure 17.
Size of the 100 largest clusters obtained with Wallet Explorer
Figure 18.
Distribution of addresses in clusters obtained with BACH
Figure 18.
Distribution of addresses in clusters obtained with BACH
Figure 19.
Distribution of addresses in clusters obtained with Wallet Explorer
Figure 19.
Distribution of addresses in clusters obtained with Wallet Explorer
Table 1.
Comparison of the results obtained by the two tools
Table 1.
Comparison of the results obtained by the two tools
| Indicators |
Wallet Explorer |
BACH |
| Number of total clusters |
54441 |
62865 |
| Number of total relations |
3597427 |
4315813 |
| Size of the largest cluster |
10084 |
25377 |
| Database size |
4074 MB |
6454 MB |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).