1. Introduction
Intracranial aneurysms (IA) have a prevalence of 3 – 5%, with a yearly rate of rupture of around 1%. Aneurysm rupture is a life-threatening disease with high morbidity and mortality. In patients with known non-ruptured IAs - oftentimes incidentally identified during brain examinations for other reasons - precise evaluation of risk factors for rupture and reperfusion after occlusion via ET is crucial for decision making. Close follow up without aneurysm occlusion may be weighted against endovascular or surgical aneurysm occlusion, since aneurysm occlusion is known to be associated with a 2 – 5% complication rate [
1,
2].
Scoring systems like the “PHASES – SCORE” aim to quantify risk of rupture of IAs based on aneurysm morphology and basic patient information, one of the most important deciding parameters being size [
3,
4]. Although size of non-ruptured IAs is a primary deciding factor concerning therapeutic options, recent data showed that also small IAs can rupture [
5]. This leads to the consensus that additional data concerning the stability or instability of IAs is needed.
High – resolution vessel wall imaging (HR – VWI) is an innovative MR imaging tool to visualize the wall of IAs. Multiple studies suggest a correlation between enhancement of vessel walls and inflammation of vessel walls, progression of the size of IAs and a potentially high risk of rupture in incidental IAs [
6,
7]. Chyatte et al. could show that aneurysm formation and rupture is associated with an inflammatory reaction of the vessel wall [
8]. Histological work up of ruptured aneurysm tissue also showed an elevated rate of inflammatory cells, compared to non-ruptured aneurysm tissue [
9,
10]. Inflammatory vasculopathies and atherosclerosis show increased vessel wall enhancement [
11,
12]. HR – VWI can be helpful in identifying IA with increased risk of rupture [
13,
14,
15]. Although recent literature [
16] suggests that AWE of an IA following ET is a common finding and is most possibly associated with the healing process, the prognostic value of this finding is still unclear, yet often encountered in daily practice.
The aim of this study is to investigate if aneurysmal vessel wall enhancement of treated IAs correlates with higher aneurysm reperfusion rates. We hypothesized that AWE is associated with an increased risk of aneurysm reperfusion.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Design
This retrospective imaging study has been approved by the local ethics committee of the Medical University of Innsbruck, Austria (ECS 1089/2021) and was conducted in compliance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
2.2. Patients
Inclusion criteria were age above 18 years, detection of a non-ruptured IA, at least two full MRI studies with designated sequences designed for evaluation of aneurysmal wall enhancement (if available prior to any endovascular intervention and at least one further study after ET), history of at least one diagnostic subtraction angiography study which included endovascular aneurysm occlusion via coiling and clinical history including information of earlier subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) from another aneurysm, history of hypertension and ethnicity in order to calculate the individual PHASES Score. Exclusion criteria were prior history of SAH from a ruptured aneurysm, endovascular treatment via stent or stent - assisted coiling and known history of vasculitis or intracranial vascular malformation.
Patient data were extracted from our Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS) and locally recorded clinical histories, HR - VWI sequences were assessed in the timeframe between Jan. 01st, 2015 and Dec. 31st, 2020.
2.3. Image Acquisition and Analysis
MR images of the brain for each patient were acquired using a 1,5T (Siemens Aera, Siemens Healthcare, Germany) or a 3T MR imaging scanner (Siemens Skyra, Siemens Healthcare, Germany) with a standard 64-element head coil. Similar acquisition protocols were used for all MRI scans. The protocol included DWI and ADC – maps (b-values were 0 and 1000 s/mm²) in an axial plane, T2 turbo spin echo in an axial plane, contrast MR angiography with reconstructions, T1 time of flight angiography. For evaluation of aneurysmal wall enhancement, we used two sequences at our institution in the evaluated timespan. From 2015 to 2018 we used T1 Spin Echo Blood – suppression with fat saturation (T1 SE FS blood-suppression) before and after contrast administration, from 2018 to December 2020 we used T1 sampling perfection with application-optimized contrast using different flip angle evolutions and fat saturation (T1 SPACE FS) before and after contrast administration in sagittal orientation with reconstructions in axial and coronal planes. Gadolinium contrast agent was administered intravenously in a typical dose of 0,1 ml per kg of body weight, 4 minutes prior to acquisition of the contrast enhanced T1 SPACE FS and T1 SE FS blood-suppression sequences. Image quality of our MRI studies was standard, both sequences allow evaluation of AWE, mainly because of excellent spatial resolution and fat saturation.
The specific sequence parameters are summarized in
Table 1.
2.4. Assessment of Intracranial Aneurysms in Imaging Sequences and Clinical History
We assessed the following features and measurements:
Presence and duration of aneurysmal wall enhancement of the electively treated aneurysms on MRI (if available prior to any intervention and every recorded scan after elective intervention including sequences for HR - VWI in the timespan of January 1st 2015 to December 31st 2020.).
Analysis of aneurysm location on MRI and DSA.
Grade of AWE
Aneurysm recurrence / reperfusion and retreatment
Size of the aneurysm (maximum diameter in mm)
-
PHASES – Score, which includes
Age
Population (Finnish, Japanese, North American and European)
History of hypertension
Size of aneurysm
Site of aneurysm
Earlier subarachnoid hemorrhage from another aneurysm
One experienced neuroradiologist performed the assessment of IAs in MRI and DSA - studies in a first step, blinded to the written radiological reports, which were consulted in a second step. In case of disagreement, expert opinion was considered. Size parameters were strictly assessed retrospectively on DSA - studies. For the assessment of aneurysm recurrence/reperfusion we applied the Raimond Roy classification [
17] which is based on the evaluation of residual inflow of intracranial aneurysms in DSA - studies. Although this classification is not routinely used for non - invasive depiction of intracranial vessels via MRI, aneurysm recurrence/reperfusion can likewise be distinguished between contrast filling of the aneurysm neck vs. aneurysm sac filling, which has implications concerning further treatment options [
18].
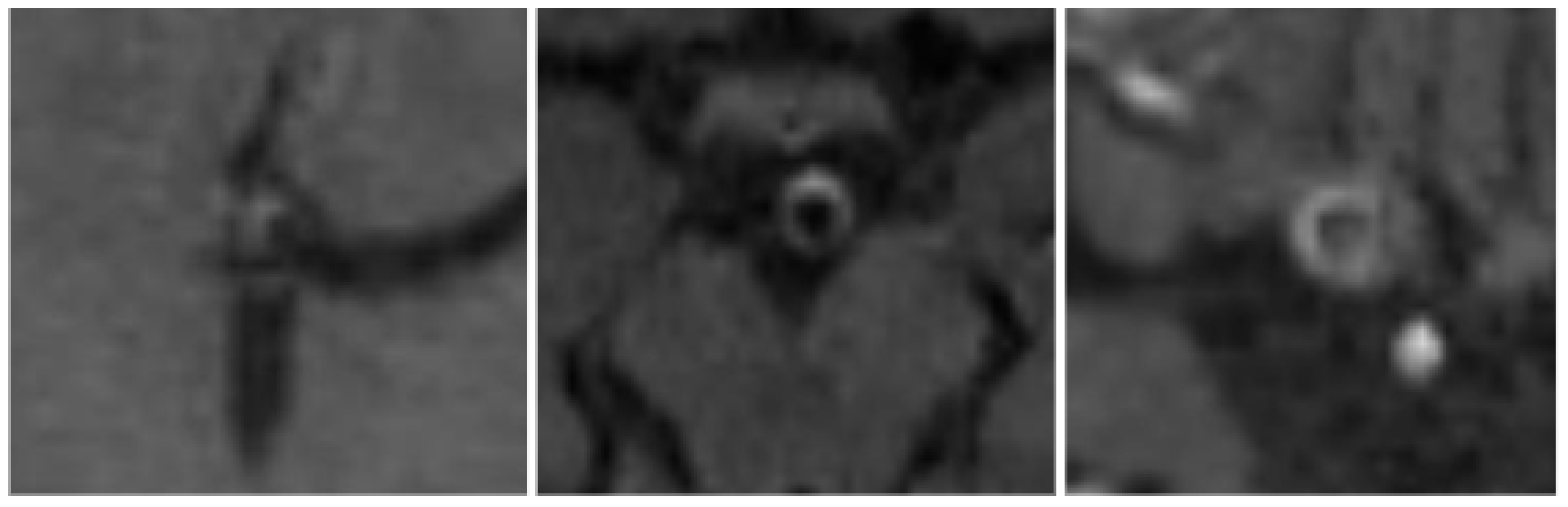
2.5. Grading of AWE
In this study, if present, AWE was categorized into 3 grades, based on the enhancement patterns and enhancement intensity, combined with thickening of the vessel wall of IAs in the follow up examinations after ET, as shown in
Figure 1:
Grade 1: Non – continuous enhancement
Grade 2: Continuous linear enhancement without thickening of the aneurysmal wall
Grade 3: Continuous linear enhancement with thickening of the aneurysmal wall
2.6. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using R (R Core Team v. 3.3.0).
For demographic data, descriptive statistics were applied. Categorical data as count and percentage.
The differences of demographics between the two groups were compared using a non-parametric Mann-Whitney U test. Summary statistics were calculated including median with first and third quartiles (Q1-Q3). Contingency tables were analyzed using Fisher exact test. Statistical significance was defined as p<0.01. Logistic regression was used to model the relationship between reperfusion binary outcome variable and a predictor variable, the p-values were reported. Spearman rank-order correlation between the variables was also checked.
A diagnostic performance was analyzed by a receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curve. The cut-off values were determined using the greatest Youden’s J index in order to calculate sensitivity and specificity.
Correlation between variables was also checked.
3. Results
127 patients were included in this retrospective study (median age 58.9 years (47.7 to 65.7)); 94 female (74.0%), 33 male (26.0%). 51 (40.2%) patients showed increased AWE after ET (median age 61.2 years (51.9 to 66.7); 38 female (74.5%), 13 male (25.5%)), 76 (59.8%) patients did not show increased AWE after ET (median age 55.4 years (45.9 to 64.3); 56 female (73.7%), 20 male (26.3%)).
Table 2 and
Table 3 show the population demographics and comparison of PHASES scores and radiological features in patients with reperfusion and AWE (maximum aneurysm diameter is depicted in millimeters).
Seven (13.7%) patients had already shown AWE prior to any intervention in the baseline MRI with AWE persisting in all of them. Six of those seven patients showed reperfusion after endovascular treatment, two patients needed a second endovascular treatment. Unfortunately, the sample size of this group was too small to perform any statistical analysis.
44 of 51 patients (86.3%) firstly showed AWE after ET, with a median timespan of 18 months [1. quartil = 0.06 months (equal to 2 days) / 3. quartil = 67.7 months] after ET.
In the group with AWE after ET, 37 of 51 (72.5%) patients showed reperfusion after ET.
The median difference between the first occurrence of AWE and reperfusion was 0 days, so most patients showed AWE the first time when also reperfusion was visible for the first time [1. quartil = 4.7 months prior to the first showing of AWE / 3. quartil = 24 months after the first showing of AWE].
8 of 37 patients (21.6%) needed a second endovascular treatment; three patients (8.1%) needed a third endovascular treatment.
In the group without AWE in any follow up after ET, 26 of 76 (34.2%) patients exhibited reperfusion. Three of 26 (11.5%) patients needed a second endovascular treatment, no patient needed a third endovascular treatment.
Table 2 and
Table 3 show the population demographics and comparison of PHASES - Scores and radiological features in patients with reperfusion and AWE (median aneurysm maximum diameter).
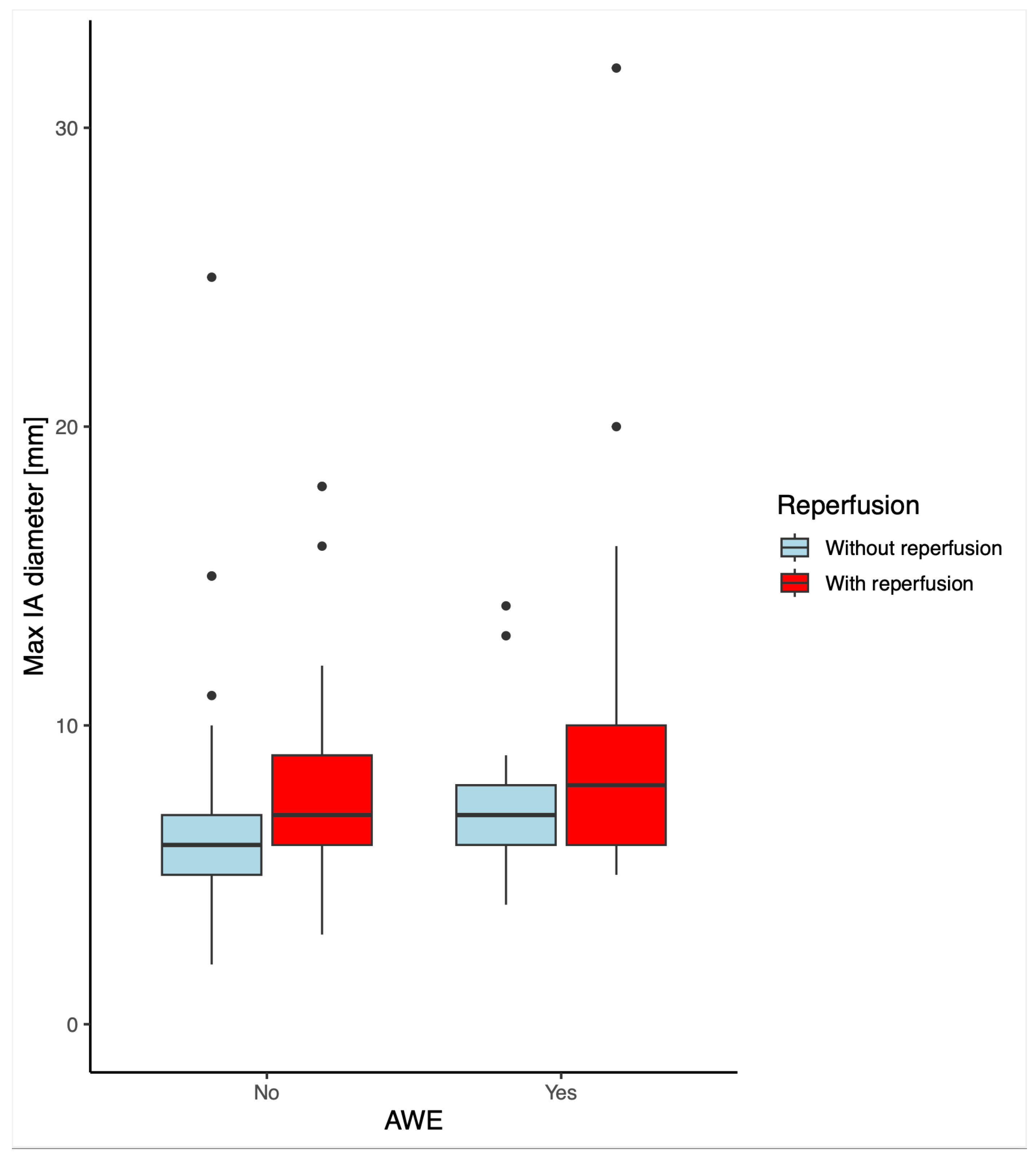
Demographics showed significant group-wise differences in age concerning AWE. Aneurysmal wall enhancement was statistically significantly different for patients with and without reperfusion (p<0.001). The single maximum diameter was significantly higher for patients with reperfusion or AWE, this is visualized in the boxplots in
Figure 2. The groups categorized for three grades of AWE showed statistically significant differences in all three AWE grade groups. However, there was no correlation between the AWE grade and reperfusion. There were also no statistically significant differences in PHASES scores for patients with or without AWE or reperfusion.
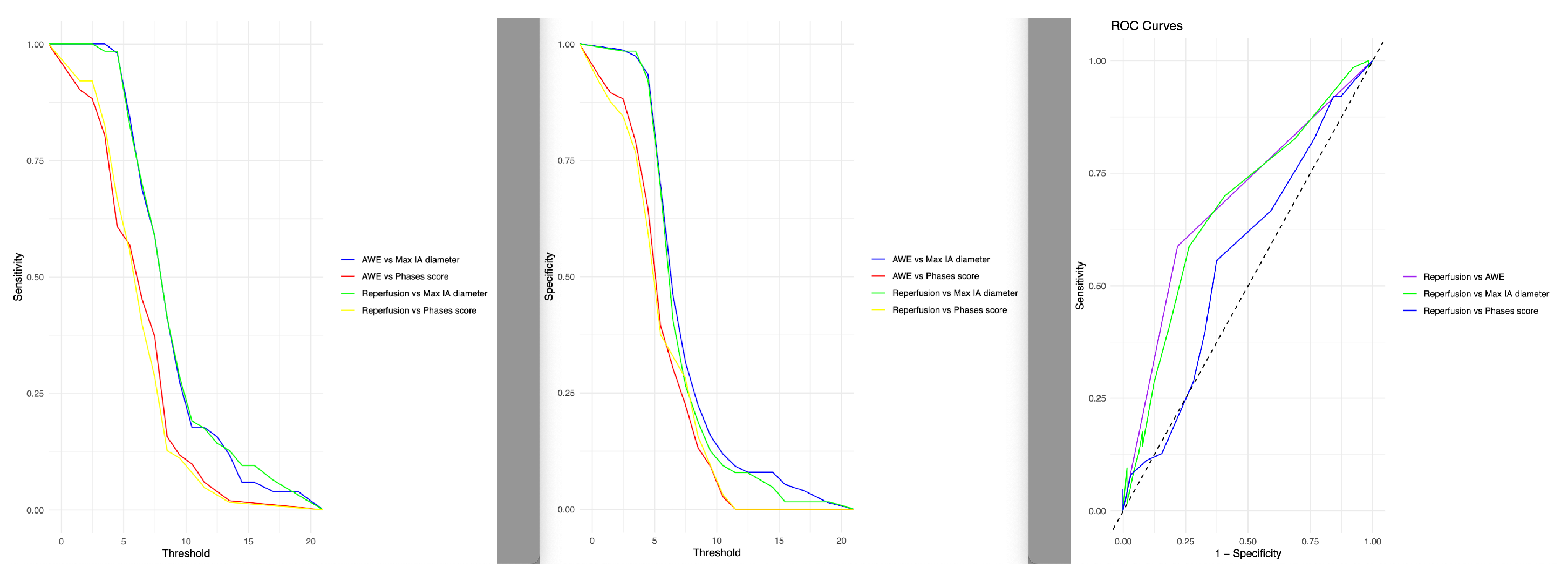
The ROC curve analysis results (
Table 4) indicates that AWE is not a complete biomarker for reperfusion. Although the sensitivity was very high (78.1%), the specificity is low (58.7%).
Figure 3 shows the relation of the sensitivity and specificity of the maximum IA diameter, AWE, PHASES score and reperfusion.
The logistic regression analysis reported that the maximum aneurysm diameter is associated with increased odds of reperfusion. For the maximum diameter as a predictor, the coefficient estimates with a p-value of 0.015, suggesting that it is significantly associated with reperfusion (p ). For AWE as a predictor, the coefficient estimates a p-value of , indicating a highly significant association with reperfusion. These results suggest that AWE has a stronger association with reperfusion than maximum aneurysm size.
No significant correlation was detected between the variables. There was no significant correlation between AWE and the grading of reperfusion.
4. Discussion
The understanding of the patophysiology of aneurysmal wall enhancement in IAs is crucial to identify unstable IAs and to plan further treatment options [
19].
The results of this study show that increased AWE in non-ruptured IAs is common after ET, affecting 40% of patients and that increased AWE after ET is associated with reperfusion.
Although increased AWE in an untreated IA is widely regarded as a factor indicating aneurysm instability, there is still no clear consensus of its interpretation after ET, with some authors suggesting that for example in ET with stent – implantation, it might be due to flow diversion effects [
20]. A recent study by Elsheikh et al. [
16] proposed that increased AWE after endovascular treatment might reflect the healing process. Larsen et al. [
21] showed that increased enhancement inside the aneurysmal cavity after ET is associated with stability and could be interpreted as a sign of aneurysm healing.
Although we cannot dispute these propositions and results, this study indicates that increased AWE after endovascular treatment is significantly associated with higher reperfusion rates after endovascular treatment in large aneurysms, so it might not be feasible to interpret it as a benign process. A recent study by Leber et al. [
22] could also show that AWE after ET is associated with aneurysm recanalization/reperfusion, which is similar to our results. However, their patient cohort did also include patients who had initially suffered a subarachnoid hemorrhage in contrast to our study which is exclusively based on unruptured intracranial aneurysms.
The results of this study show that increased AWE could be considered as sign of persistent inflammation and consequent instability and at least trigger high alertness in assessing the adjacent angiography images.
The typical follow - up procedure for patients after endovascular treatment of IAs includes repeated MRI – scans to rule out and assess for possible complications after treatment and investigate for reperfusion or occurrence of new IAs. At our institution, patients usually receive several MRI – scans after ET, with usual intervals being in the initial first days after ET and subsequently after 6 and 12 months, followed by scans every 12 months. The decision to consider further DSA or retreatment is mainly based on the results of these scans.
If reperfusion is present, the rates of retreatment were comparable in patients with increased AWE and without increased AWE (28.6% in group 1 and 25% in group 2). This might be due to the fact that in the current evaluation and decision – making in interdisciplinary meetings, increased AWE is not considered and the indication for retreatment on MRI - angiography images and DSA studies.
However, in the subsequent statistical analysis, the data demonstrates that reperfusion after ET is only associated with AWE in large aneurysms.
This leads to the question: "What is a small and what is a large aneurysm?". First of all we have to define which size parameters we include in our assessment. A lot of studies use the single maximum diameter; this is also the base and most important factor for calculationg the PHASES score [
3]. In order to compare our results we also only assessed the single maximum diameter.
The exact threshold between large and small IAs is not yet clear and should be subject of further, preferably prospective studies. However, our data suggests that concerning the effects of AWE an initial size over 7.5mm might be a sensible cut - off value, as based on our ROC analysis in
Figure 3.
We also evaluated the AUC for different parameters, including reperfusion vs. the maximum aneurysm diameter (sensitivity of 71.6%, specificity of 60.0%), reperfusion vs. AWE (sensitivity of 73.4%, specificity of 58.7%, this further underlines that AWE after ET should trigger high alertness in assessing the subsequent angiography sequences (time of flight angiography or contrast MR angiography) but is not very specific as a single parameter.
Furthermore, these findings might suggest that the assessment of increased AWE is only feasible if the initially untreated IA is considered to be of a large caliber. Consequently follow - up examinations after ET should include VWI including contrast agents, which lengthens the imaging protocol but might ultimately contribute data in the difficult decision - making process of potential re-treatment after ET.
This finding is not entirely unexpected, since bigger IAs can be challenging to treat via ET and might therefore be more prone to aneurysm reperfusion.
In smaller aneurysms however, increased AWE does not seem to contribute information concerning possible reperfusion (as a marker for instability) and should be interpreted as an indeterminate parameter. Especially in these IAs, further research is highly warranted. This finding could lead to the conclusion that VWI after ET can be omitted in subsequent follow up scans, reducing scanning time and cost. Furthermore, a larger patient group could be examined which is not eligible for contrast agents (e.g. pregnancy or severe kidney dysfunction or allergies to MRI contrast agents).
However, aneurysms are in no way bound to a specific geometrical shape which leads to the conclusion that two aneurysms can have the same single maximum diameter but differ significantly in their shape and volume.
Unfortunately, it was not possible to retrieve 3 standardised dimensions for modeling the aneurysms as volumes in our data - set (which might be more accurate), as they were not always uniformly measured in more than the single biggest diameter in the DSA - studies of our cohort. However, we believe that adding a second or third dimension would also not entirely reflect the true specific geometrical shape of each aneurysm, given that they are often deformed and not uniformly shaped in standardised geometrical forms like cylinders or ellipsis.
To our knowledge, there is no internationally established grading system concerning AWE after treatment or prior to any treatment. In their study from 2020, Elsheikh et al. propose a grading system, ranging from faint to strong enhancement [
16] but do not comment further on its clinical significance. We tried to further categorize AWE into 3 grades in this study, based on reproducible imaging characteristics. Although Grade 2 and 3 of AWE were significantly different concerning patients with and without aneurysm reperfusion, there was no correlation between the AWE grade and aneurysm reperfusion. This finding indicates that it is not only necessary to assess whether AWE is present but also its extent.
Since vessel walls of IAs are of a very small caliber, in our experience it can be difficult to assess AWE if faint and non linear (Grade 1 in our study) which is partly based on voxel size or suboptimal image quality. This might lead to diagnostic inaccuracy and inter-rater variability in reporting. However, the data of this study suggests that all grades of AWE were strongly associated with aneurysm reperfusion.
Although the PHASES score is very helpful concerning initial risk stratification of IAs, it does not predict which IAs are prone to reperfusion, although the biggest aneurysm diameter is an important contributing factor in calculating the score. This could lead to the conclusion that additional risk factors, which are reflected in the PHASES - Score (such as age, hypertension, site of aneurysm, population, history of SAH) are important criteria in initial assessment but lose their diagnostic value in decision making concerning re - treatment options, although it has to noted that only IAs that did not rupture were included in this study, which do not reflect the whole population of patients with IAs.
Our two main focus - groups concerning AWE showed significant differences in age, which we cannot fully explain. One possible contributing factor might be that athersclerosis (which can lead to increased AWE [
12]) is more common in an older age - group. This should be further explored in a much larger patient cohort.
Limitations include the retrospective design, which includes no fixed time points for follow-up scans of each patient. Although usually a fixed schedule for follow-up scans is applied after ET (one day, 6 months, 12 months, 24 months, 48 months) the amount of scans can be increased based on the clinical course of each patient including newly arising symptoms or complications such as reperfusion or decreased if patients don’t comply with their fixed appointments. These facts cause heterogeneity of the intervals and number of follow - up scans after ET and also the time intervals from the initial treatment to the first MRI study including sequences for assessment of AWE. HR - VWI MRI sequences were introduced late in 2014 at our institution, with our analysis of HR- VWI starting with January 1st of 2015, but our database includes patients who received treatment earlier to introduction of these sequences. This leads to slight inaccuracies in the comparison of the first time AWE and reperfusion occured. Although these dates were fairly parrallel in most patients (median of 0 days difference between the first occurence of AWE and reperfusion) some patients already showed reperfusion prior to the introduction of HR - VWI in our institution. Moreover, in our clinical routine patients are not continually scanned on the same MRI - scanner, so the analyzed scans were performed on 2 different scanners (1.5 and 3T), which also contributes to heterogeneity of image acquisition and image data. However, a study by Roa et al. [
23] showed that there are no significant differences between different manufacturers or different field strengths (comparing 3T and 7T though, which differs from our study setting) concerning HR – VWI of IAs. 31 of 51 patients (60.8%) which showed AWE after treatment received their baseline and first post - treatment MRI - scan on the same MRI - scanner though, with no recognizable difference in enhancement characteristics. In conclusion, to our knowledge there is no difference in diagnostic sensitivity concerning HR – VWI in IAs due to field strength. Image quality of our MRI studies allowed evaluation of AWE in both sequence - types (T1 SPACE FS and T1 SE FS blood-suppression). The main limitation of T1 – SPACE FS sequences is that they can be susceptible to motion artifacts due to the long acquisition time. The main limitation of T1 SE FS blood-suppression sequences is that they are only available in an axial plane. The two sequence types differ in their characteristics though, which also contributes to heterogeneity of the data.
Although our results clearly suggest that AWE is associated with reperfusion in large aneurysms, we believe that our results should be validated further in a prospective setting with fixed time points and on a single MRI - scanner.
Since only endovascularly treated IAs were included, there is a lack of correlation with histopathological data, which would have been helpful in interpreting increased AWE. This data might always be challenging to acquire though, since most patients with IAs receive endovascular treatment at our institution and also patients who do receive surgical clipping as a treatment option do not receive histopathological workup since the treated IAs are not resected.
Aneurysm reperfusion does also not always imply need for further endovascular retreatment - it would be interesting to launch a study with a longer period of observation (e.g. 10 years). In this current study the observation period was limited to up to 5 years. Furthermore, a study concerning reperfusion including patients who demonstrate increased AWE prior to any treatment and patients who do not might be interesting. Due to our small sample size of patients with increased AWE prior to any intervention, this could not be achieved in this study. Studies including radiomics – associated feature assessment of increased AWE in IAs could also be of great interest.
5. Conclusions
In contrast to other studies, we could show that commonly occurring increased AWE after ET of large IAs is associated with higher rates of aneurysm reperfusion, implying that AWE is a marker of instability after ET. However, in small IAs, increased AWE after ET is not associated with higher rates of aneurysm reperfusion.
Based on these results, in patients with large IAs it might be feasible to consider diagnostic re - angiography or early re-treatment if increased AWE is present after ET.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Valentin Ladenhauf, Malik Galijasevic, Ondra Petr, Johannes Deeg, Leonhard Gruber, Elke Gizewski and Astrid Grams; Data curation, Raimund Helbok, Verena Rass, Christian Freyschlag, Ondra Petr and Johannes Deeg; Formal analysis, Malik Galijasevic, Milovan Regodic and Johannes Deeg; Methodology, Valentin Ladenhauf, Milovan Regodic, Verena Rass, Christian Freyschlag, Leonhard Gruber, Elke Gizewski and Astrid Grams; Project administration, Valentin Ladenhauf and Astrid Grams; Resources, Raimund Helbok, Elke Gizewski and Astrid Grams; Software, Malik Galijasevic and Milovan Regodic; Supervision, Raimund Helbok, Christian Freyschlag, Ondra Petr, Leonhard Gruber, Elke Gizewski and Astrid Grams; Validation, Valentin Ladenhauf and Astrid Grams; Writing – original draft, Valentin Ladenhauf, Malik Galijasevic and Astrid Grams; Writing – review & editing, Valentin Ladenhauf, Malik Galijasevic, Milovan Regodic, Raimund Helbok, Verena Rass, Christian Freyschlag, Johannes Deeg, Leonhard Gruber, Elke Gizewski and Astrid Grams.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This retrospective imaging study has been approved by the local ethics committee of the Medical University of Innsbruck, Austria (ECS 1089/2021) and was conducted in compliance with the Declaration of Helsinki. The patients consent was collected.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data will be made available upon a request.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank our patients and their families for agreeing to participate in this research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AWE |
aneurysmal wall enhancement |
| IA |
IA |
| ET |
endovascular treatment |
| MRI |
magnetic resonance imaging |
| MRA |
magnetic resonance angiography |
| HR-VWI |
high-resolution vessel-wall imaging |
| TR |
time of repetition |
| TE |
echo time |
| FOV |
field of view |
| FA |
flip angle |
| PACS |
Picture Archiving and Communication System |
| TOF |
time of flight |
| T1- SE FS BS |
T1 Spin Echo blood – suppression with fat saturation |
| T1-SPACE FS |
T1 sampling perfection with application-optimized contrast using different flip angle evolutions and fat saturation |
References
- Etminan, N.; Rinkel, G. Unruptured intracranial aneurysms: development, rupture and preventive management. Nature Reviews Neurology 2016, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, A.; Kirino, T.; Hashi, K.; Aoki, N.; Fukuhara, S.; Hashimoto, N.; Takeo, N.; Sakai, M.; Teramoto, A.; Tominari, S.; et al. The Natural Course of Unruptured Cerebral Aneurysms in a Japanese Cohort. The New England journal of medicine 2012, 366, 2474–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greving, J.; Wermer, M.; Brown, R.; Morita, A.; Juvela, S.; Yonekura, M.; Ishibashi, T.; Torner, J.; Takeo, N.; Rinkel, G.; et al. Development of the PHASES score for prediction of risk of rupture of intracranial aneurysms: A pooled analysis of six prospective cohort studies. Lancet neurology 2013, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bijlenga, P.; Gondar, R.; Schilling, S.; Morel, S.; Hirsch, S.; Cuony, J.; Corniola, M.; Perren, F.; Rüfenacht, D.; Schaller, K. PHASES Score for the Management of Intracranial Aneurysm: A Cross-Sectional Population-Based Retrospective Study. Stroke 2017, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikawa, F.; Morita, A.; Tominari, S.; Nakayama, T.; Shiokawa, Y.; Date, I.; Nozaki, K.; Miyamoto, S.; Kayama, T.; Arai, H. Rupture risk of small unruptured cerebral aneurysms. Journal of Neurosurgery 2020, 132, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etminan, N.; Rinkel, G. Cerebral aneurysms: Cerebral aneurysm guidelines—more guidance needed. Nature reviews. Neurology 2015, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Texakalidis, P.; Hilditch, C.; Lehman, V.; Lanzino, G.; Pereira, V.; Brinjikji, W. Vessel Wall Imaging of Intracranial Aneurysms: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. World Neurosurgery 2018, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chyatte, D.; Bruno, G.; Desai, S.; Todor, D.R. Inflammation and intracranial aneurysms. Neurosurgery 1999, 45, 1137–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frösen, J.; Piippo, A.; Paetau, A.; Kangasniemi, M.; Niemelä, M.; Hernesniemi, J.; Jääskeläinen, J. Remodeling of Saccular Cerebral Artery Aneurysm Wall Is Associated With Rupture Histological Analysis of 24 Unruptured and 42 Ruptured Cases. Stroke; a journal of cerebral circulation 2004, 35, 2287–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, K.; Taneda, M.; Asai, T.; Kinoshita, A.; Ito, M.; Kuroda, R. Structural fragility and inflammatory response of ruptured cerebral aneurysms: a comparative study between ruptured and unruptured cerebral aneurysms. Stroke 1999, 30, 1396–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mossa-Basha, M.; Hwang, W.; de Havenon, A.; Hippe, D.; Balu, N.; Becker, K.; Tirschwell, D.; Hatsukami, T.; Anzai, Y.; Yuan, C. Multicontrast High-Resolution Vessel Wall Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Its Value in Differentiating Intracranial Vasculopathic Processes. Stroke 2015, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skarpathiotakis, M.; Mandell, D.; Swartz, R.; Tomlinson, G.; Mikulis, D. Intracranial atherosclerotic plaque enhancement in patients with ischemic stroke. American Journal of Neuroradiology 2013, 34, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergouwen, M.; Backes, D.; Schaaf, I.; Hendrikse, J.; Kleinloog, R.; Algra, A.; Rinkel, G. Gadolinium Enhancement of the Aneurysm Wall in Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms Is Associated with an Increased Risk of Aneurysm Instability: A Follow-Up Study. American Journal of Neuroradiology 2019, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartman, J.; Watase, H.; Sun, J.; Hippe, D.; Kim, L.; Levitt, M.; Sekhar, L.; Balu, N.; Hatsukami, T.; Yuan, C.; et al. Intracranial aneurysms at higher clinical risk for rupture demonstrate increased wall enhancement and thinning on Multi-Contrast 3d vessel wall MRI. The British Journal of Radiology 2019, 92, 20180950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edjlali, M.; Guédon, A.; Ben Hassen, W.; Boulouis, G.; Joseph, B.; Rodriguez-Régent, C.; Trystram, D.; Nataf, F.; Meder, J.; Turski, P.; et al. Circumferential Thick Enhancement at Vessel Wall MRI Has High Specificity for Intracranial Aneurysm Instability. Radiology 2018, 289, 172879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsheikh, S.; Urbach, H.; Meckel, S. Contrast Enhancement of Intracranial Aneurysms on 3T 3D Black-Blood MRI and Its Relationship to Aneurysm Recurrence following Endovascular Treatment. American Journal of Neuroradiology 2020, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mascitelli, J.R.; Moyle, H.; Oermann, E.K.; Polykarpou, M.F.; Patel, A.A.; Doshi, A.H.; Gologorsky, Y.; Bederson, J.B.; Patel, A.B. An update to the Raymond–Roy occlusion classification of intracranial aneurysms treated with coil embolization. Journal of neurointerventional surgery 2015, 7, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, C.Y.; Peterson, R.B.; Howard, B.M.; Zygmont, M.E. Imaging intracranial aneurysms in the endovascular era: surveillance and posttreatment follow-up. RadioGraphics 2022, 42, 789–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, A. Wall enhancement in stable aneurysms needs to be understood first to be able to identify instable and culprit aneurysms. European Radiology 2023, pp. 1–3. [CrossRef]
- Zwarzany. ; Owsiak, M.; Tyburski, E.; Poncyljusz, W. High-Resolution Vessel Wall MRI of Endovascularly Treated Intracranial Aneurysms. Tomography 2022, 8, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, N.; Flueh, C.; Madjidyar, J.; Synowitz, M.; Jansen, O. Visualization of Aneurysm Healing: Enhancement Patterns and Reperfusion in Intracranial Aneurysms after Embolization on 3T Vessel Wall MRI. Clinical Neuroradiology 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leber, S.L.; Hassler, E.M.; Michenthaler, M.; Renner, W.; Deutschmann, H.; Reishofer, G. Wall Enhancement of Coiled Intracranial Aneurysms is Associated with Aneurysm Recanalization: A Cross-Sectional Study. American Journal of Neuroradiology 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roa, J.A.; Zanaty, M.; Osorno-Cruz, C.; Ishii, D.; Bathla, G.; Ortega-Gutierrez, S.; Hasan, D.M.; Samaniego, E.A. Objective quantification of contrast enhancement of unruptured intracranial aneurysms: a high-resolution vessel wall imaging validation study. Journal of neurosurgery 2020, 134, 862–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).