Submitted:
27 June 2024
Posted:
27 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
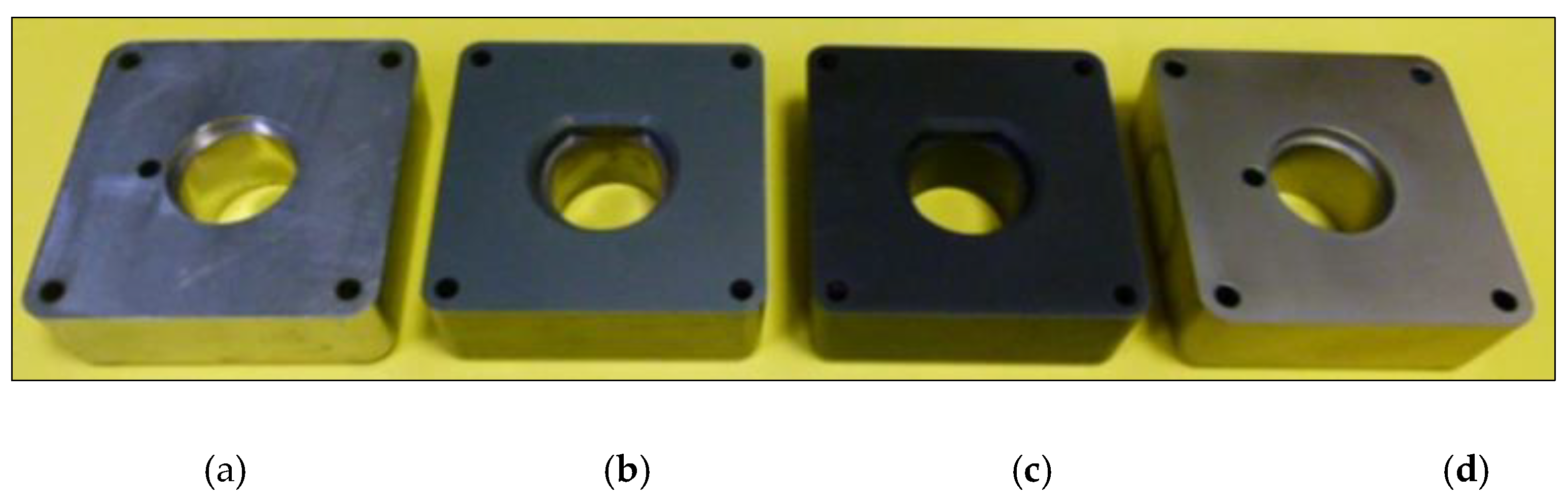
2.1. Material of Inserts and Surface Treatment
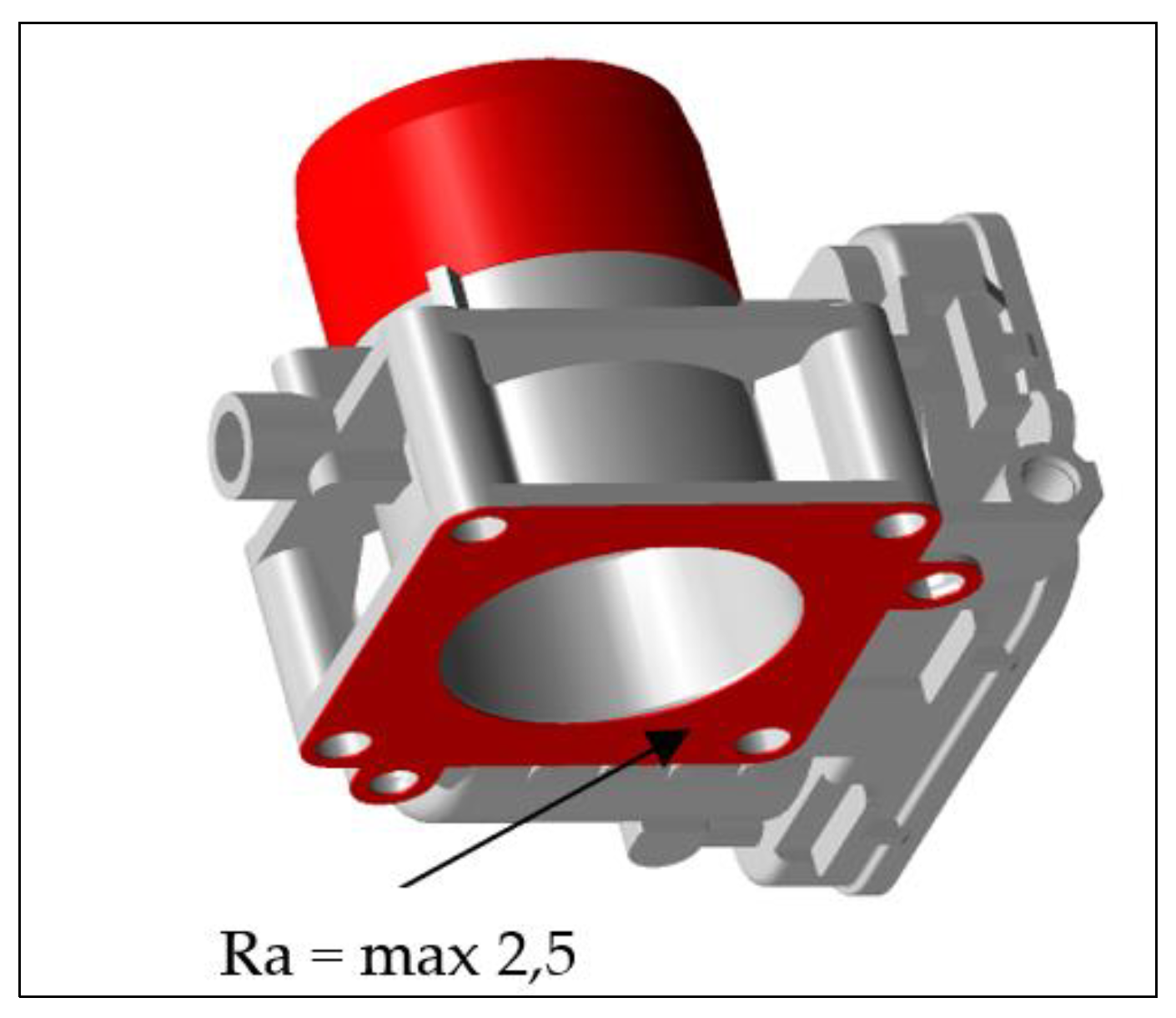
2.2. Casting and Casting Process Conditions
2.3. Estimation of Hardness of Inserts and Roughness of Bearing Surface of Castings
2.4. Specimen Preparation and Optical Microscopy and SEM
3. Results and Discussion
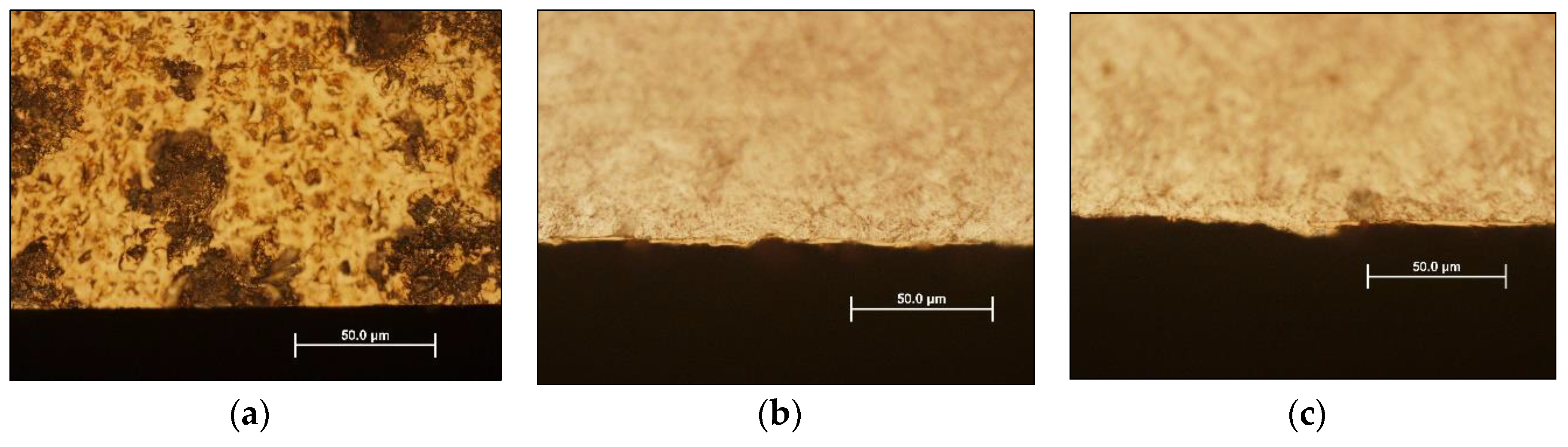
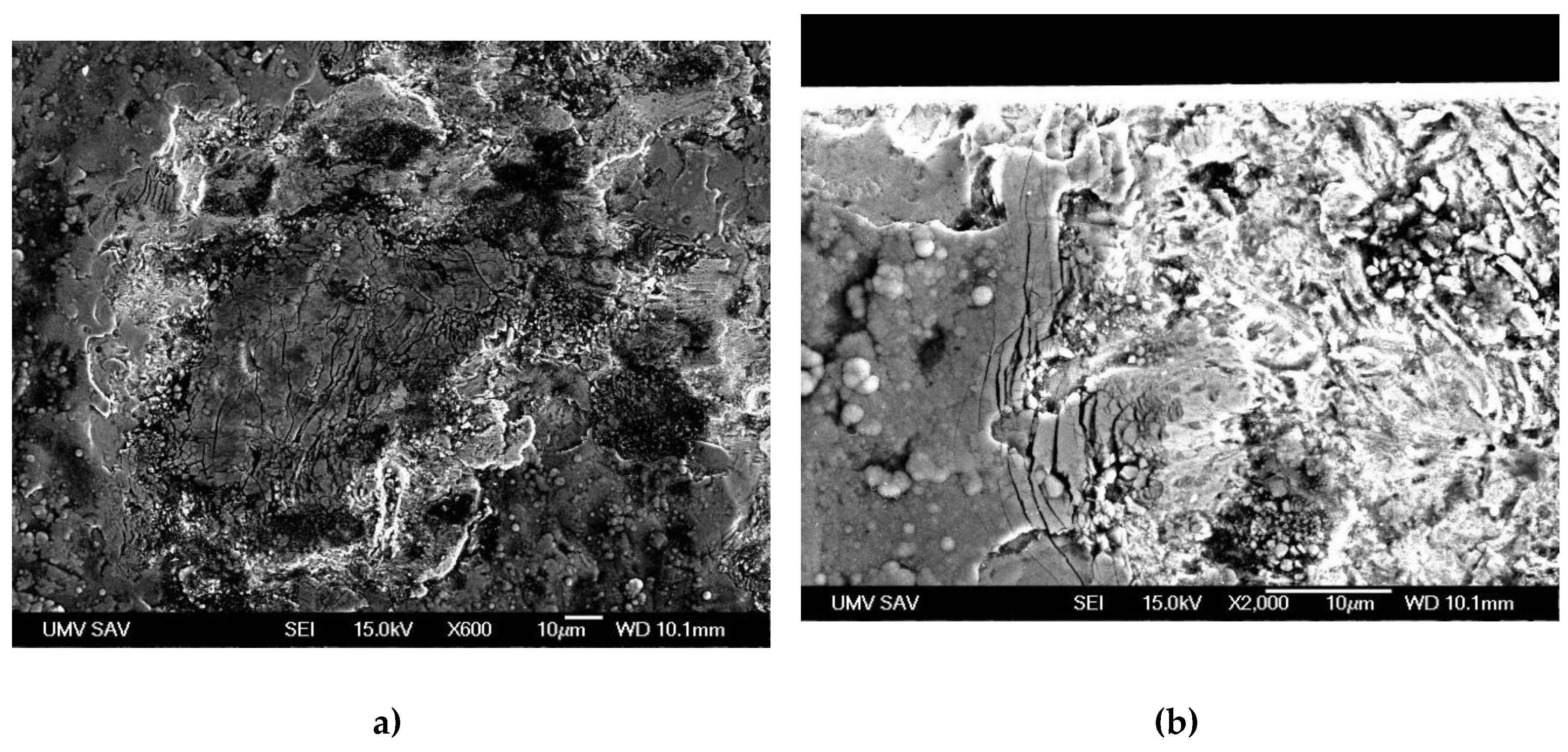
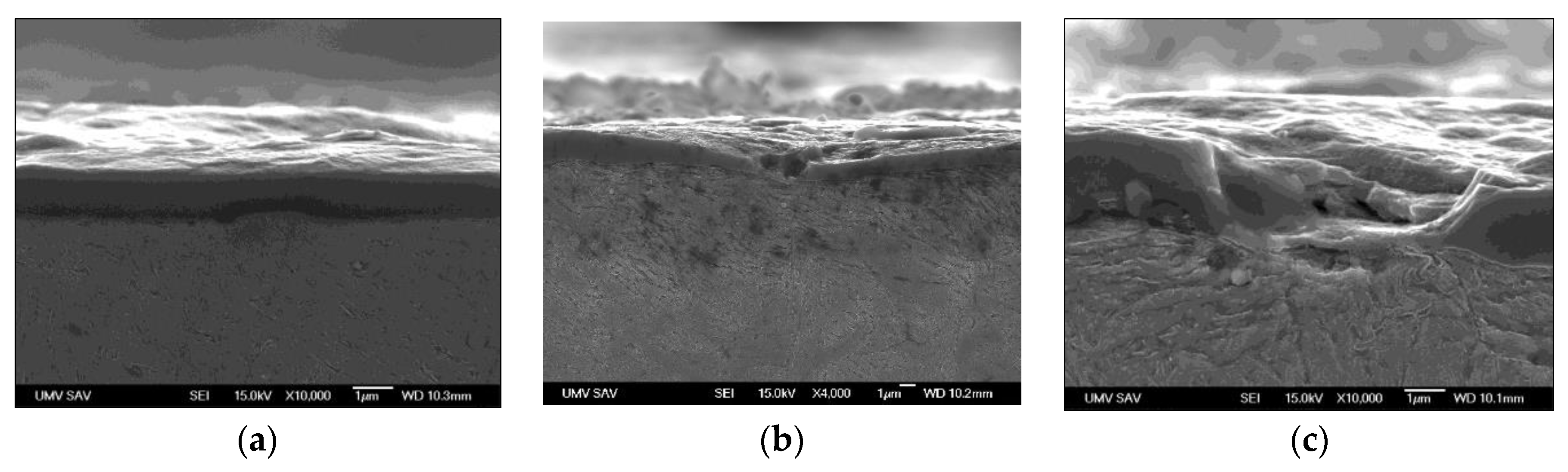
3.1. Optical Microscopy and SEM Analysis
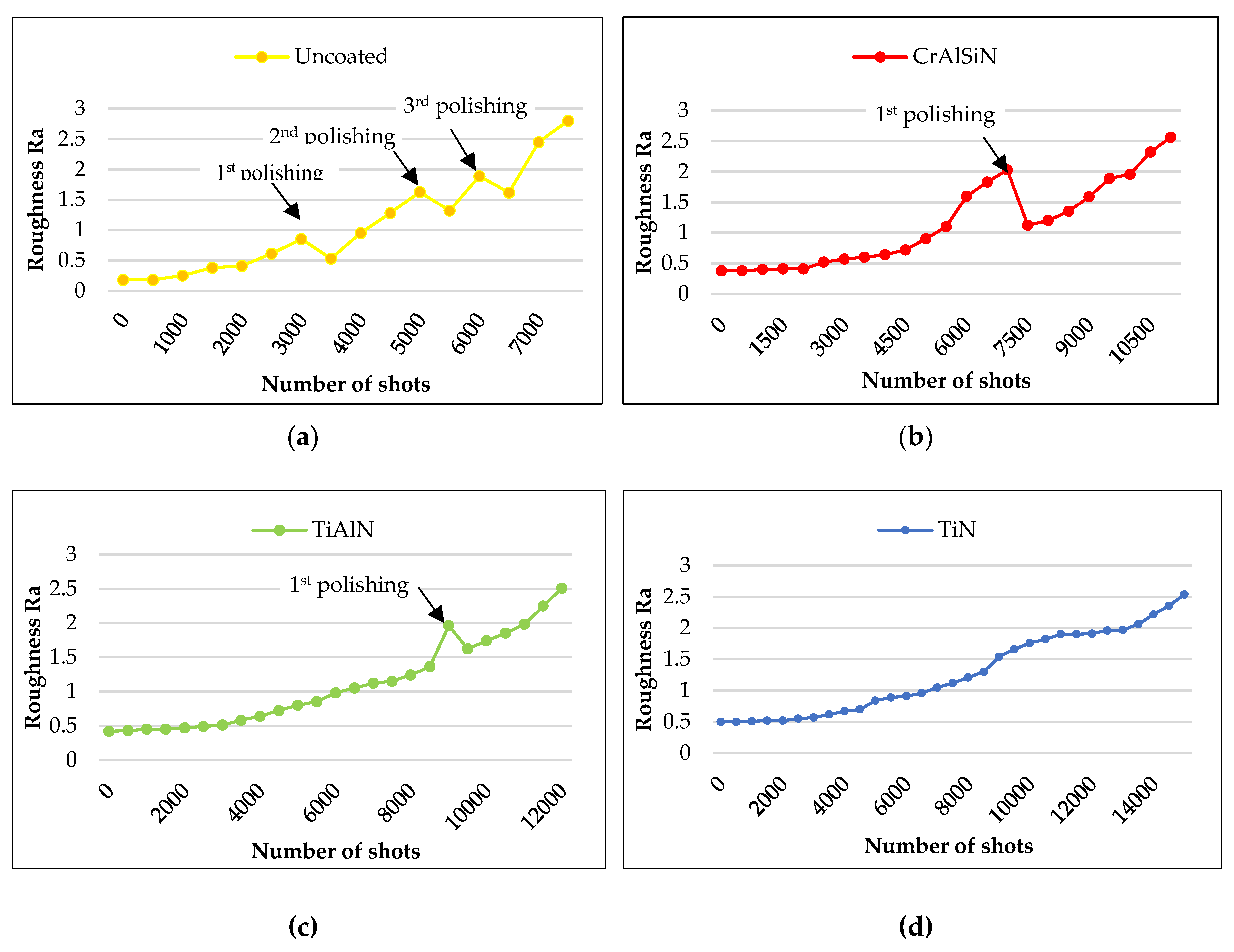
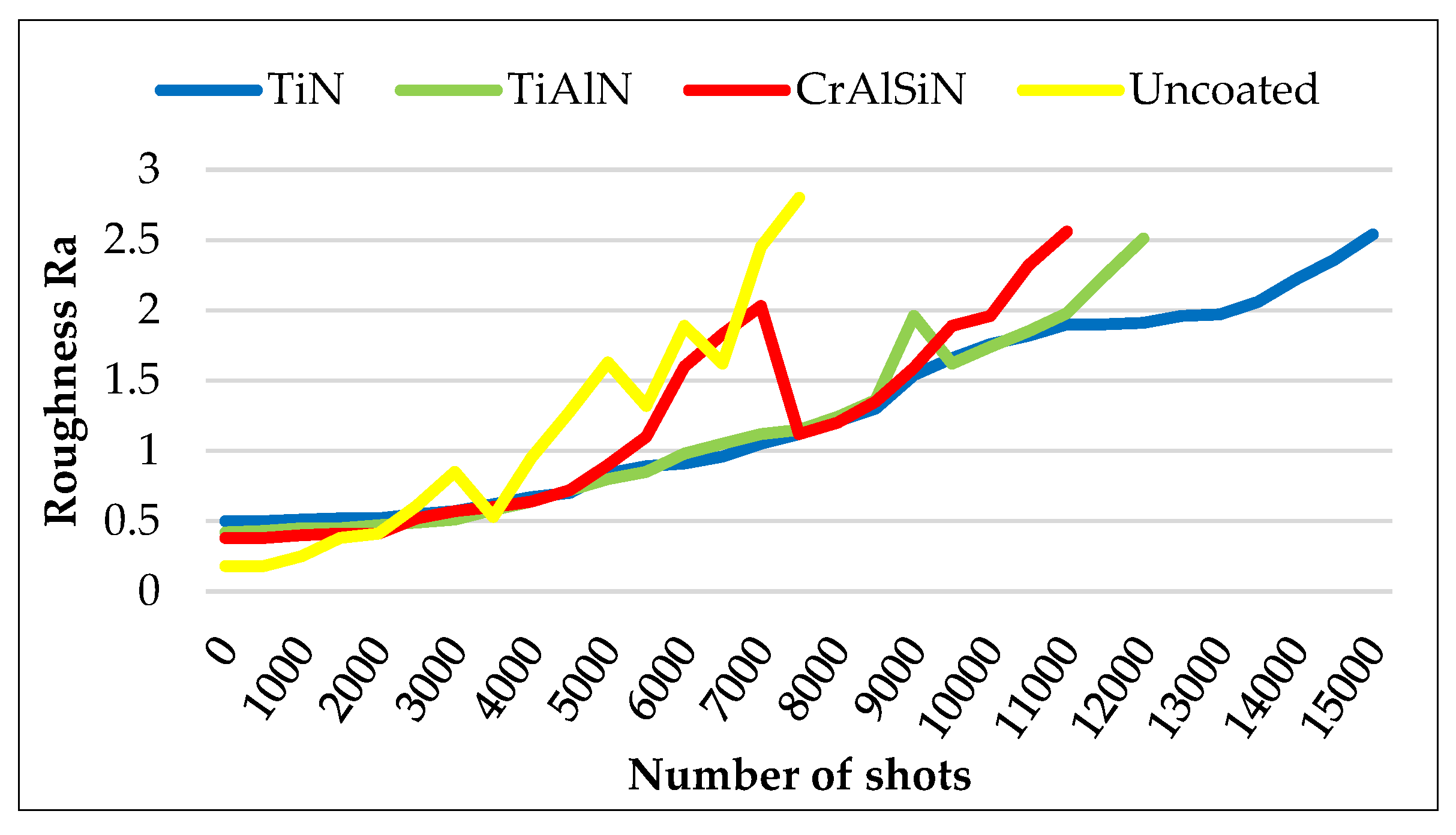
3.2. Hardness and Surface Roughness
4. Conclusions
- The optical and SEM analysis showed wear and formation of craters at the bottom of which the uncovered basic material of the insert is visible. The study of surface morphology revealed the presence of cracks probably caused by the cyclic thermomechanical effect. These failures can be prerequisites for the formation of intermetallic Fe-Al layers. They negatively affect the surface quality of castings manifesting by increasing average roughness (Ra).
- The PVD-coated inserts achieved a significantly longer lifetime than uncoated inserts concerning the requirements on casting surface roughness (Ra), while the TiN-coated insert performed the best in comparison with TiAlN and CrAlSiN-coated inserts. The difference in lifetime using TiAlN and CrAlSiN coated inserts was only 10000 shots with an advantage for TiAlN.
- Polishing performed to prolong the inserts’ lifetime has a low effect on uncoated insert (brought prolongation of lifetime by 500 shots). It was applied also in the case of TiAlN and CrAlSiN coated inserts when they were approaching the critical value of Ra and the prolongation of lifetime ranged from 2000 – 3000 shots.
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mayer, A.R.; et al. Die soldering and corrosion failure of high temperature tool steel for high-pressure die casting Al alloy. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2024, 161, 108314. [CrossRef]
- Nunes, V.; Silva, F.J; Andrade, M.F; Alexandre, R.; Baptista, A.P. Increasing the lifespan of high-pressure die cast molds subjected to severe wear. Surf. and Coat. Techn. 2017, 332, 319–331. [CrossRef]
- Terek, P.; et al. Effects of die core treatments and surface finishes on the sticking and galling tendency of Al–Si alloy casting during ejection, Wear 2016, 356–357, 122–134. [CrossRef]
- Markežič, R.; Naglič, I.; Mole, N.; Šturm, R. Experimental and numerical analysis of failures on a die insert for high pressure die casting. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2019, 95, 171–180. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.W.; Jahedi, M.Z. Die erosion and its effect on soldering formation in high pressure die casting of aluminium alloy. Mat. & Des. 1999, 6, 303–309. [CrossRef]
- Kohlhepp, M.; Uggowitzer, P.J.; Hummel, M.; Höppel, H.W. Formation of Die Soldering and the Influence of Alloying Elements on the Intermetallic Interface. Mat. 2021, 14, 1580. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.W. Formation and progression of die soldering during high pressure die casting. Mat. Science and Eng. 2005, 397, 356–369. [CrossRef]
- Domkin, K.; Hattel, J.H.; Thorborg, J. Modeling of high temperature- and diffusion-controlled die soldering in aluminum high pressure die casting. J. of Mat. Proc. Techn. 2009, 4051–4061. [CrossRef]
- Salem, M.; et al. Effect of aluminizing and oxidation on the thermal fatigue damage of hot work tool steels for high pressure die casting applications. Intern. J. of Fat. 2019, 119, 126–138. [CrossRef]
- Teplická, K. Comparison of Using Managerial Instruments in Industry Companies in Slovakia and the Czech Republic. TEM J. 2019, 8, s. 1191–1197. [CrossRef]
- J. Brezinová; et al., “Use of Duplex PVD Coatings to Increase the Life of Moulds and Cores for die Casting of Aluminium Alloys in the Automotive Industry”, Acta Mech. Slov. 2022, 26, 42–51. [CrossRef]
- Sütőová, A.; Grzinčič, M. Creation of Defects Catalogue for Nonconforming Product Identification in the Foundry Organization. QIP J. 2013, 17, 52–58. [CrossRef]
- Bhaskar, M.; Anand, G.; Nalluswamy, T.; Suresh, P. Die Life in Aluminium High-Pressure Die Casting Industries. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. D 2022, 103, 117–123. [CrossRef]
- Gulizia, S.; Jahedi, M.Z; Doyle, E.D. Performance evaluation of PVD coatings for high pressure die casting. Surf. and Coat. Techn. 2001, 140, 200–205. [CrossRef]
- Rosso, M.; Ugues, D.; Torres, E.; Perucca, M; Kapranos, P. Performance enhancements of die casting tools trough PVD nanocoatings. Int. J. Mater. Form. 2008, 1, 1259–1262. [CrossRef]
- Paiva, J.; et al. Tribological and Wear Performance of Nanocomposite PVD Hard Coatings Deposited on Aluminum Die Casting Tool. Mat. 2018, 11, 358. [CrossRef]
- Midson, S.P; De Campos Neto, N.D.; May, W; Korenyi-Both, A.L; Kaufman, M.J. Laboratory Testing to Characterize the Use of PVD Coatings and Alternate Die Materials for Reducing Soldering and Erosion for Aluminum Die Casting Applications. Inter Met. 2024. [CrossRef]
- Campos Neto, N.D.; Korenyi-Both, A.L.; Vian, C.; Midson, S.P; Kaufman, M.J. The development of coating selection criteria to minimize die failure by soldering and erosion during aluminum high pressure die casting. J. of Mat. Proc. Tech. 2023, 316, 117954. [CrossRef]
- Torres, E.; Ugues, D.; Brytan, Z.; Perucca, M. Development of multilayer coatings for forming dies and tools of aluminium alloy from liquid state. J. of Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2009, 42. [CrossRef]
- Vetter, J.; Eriksson, A. O; Reiter, A.; Derflinger, V.; Kalss, W. Quo Vadis: AlCr-Based Coatings in Industrial Applications”, Coat. 2021, 11, 344. [CrossRef]
- Ugues, D.; Torres, E.; Perucca, M.; Albertinazzi, M.; Rosso, M. Hard coatings to prevent the washout phenomena in high pressure die casting tools. Berg Huett. Monatsh, 151, 109–112. [CrossRef]
- Gurada, C.; Mundotia, R.; Mhatre, R.; Kale, A.; Kothari, D. Thermal Fatigue Resistance Studies of Multilayer CrN and AlTiN Coatings Deposited on Plasma Nitrided H-13 Hot Work Steel. Lub. 2023, 11. [CrossRef]
- Matei, A.A.; Turcu, R.N.; Pencea, I.; Herghelegiu, E.; Petrescu, M.I.; Niculescu, F. Comparative Characterization of the TiN and TiAlN Coatings Deposited on a New WC-Co Tool Using a CAE-PVD Technique. Crys. 2023, 13, 112. [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Guha, S.; Ghadai, R.; Swain, B.P. A comparative analysis over different properties of TiN, TiAlN and TiAlSiN thin film coatings grown in nitrogen gas atmosphere. Mat. Chem. and Phys. 2021, 258, 123866. [CrossRef]
- Obrosov, A.; et al. XPS and AFM Investigations of Ti-Al-N Coatings Fabricated Using DC Magnetron Sputtering at Various Nitrogen Flow Rates and Deposition Temperatures. Met. 2017, 7, 52. [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.Y.; Lee, K.O.; Kang, S.S.; Kim, K.H. Comparison for mechanical properties between TiN and TiAlN coating layers by AIP technique. J. of Mat. Proc. Tech. 2002, 130–131, 260–265. [CrossRef]
- Liew, W.Y.; Jie, J.L.; Yan, L.Y.; Dayou, J.; Sipaut, C.S.; Madlan, M.F. Frictional and Wear Behaviour of AlCrN, TiN, TiAlN Single-layer Coatings, and TiAlN/AlCrN, AlN/TiN Nano-multilayer Coatings in Dry Sliding. Proc. Eng. 2013, 68, 512–517. [CrossRef]
- Valleti, P.C.; Venu Gopal, A.; Joshi, S.V. CrAlSiN nanocomposite thin films for high-speed machining applications, Mat. and Man, Proc. 2018, 33, 371–377. [CrossRef]
- Wang. Q. et al. Comparison of tribological and electrochemical properties of TiN, CrN, TiAlN and a-C:H coatings in simulated body fluid. Mat. Chem. and Phys. 2015, 158, 74–81. [CrossRef]
- Berger, C.; Scheerer, H.; Ellermeier, J. Modern materials for forming and cutting tools – overview”, Mat. Werkst 2010, 41, 5–16. [CrossRef]
- Tošenovský, F.; Tošenovský, J.; Blaštíková, M. Selected Problems in Statistical Modelling of Metallurgical Processes. In Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Metallurgy and Materials, Brno, Czech Republic, 22. 5. 2019. 10.37904/metal.2019.776.
- Ding, R.; et al. Failure analysis of H13 steel die for high pressure die casting Al alloy. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2021, 124, 105330. [CrossRef]
- IATF. IATF 16949:2015 Quality Management System. International Automotive Task Force, 2016.
- Mitterer, C.; Holler, F.; Üstel, F.; Heim, F.D. Application of hard coatings in aluminium die casting — soldering, erosion and thermal fatigue behaviour. Surf. and Coat. Tech. 2000, 125, mec233–239. [CrossRef]
| C | Si | Mn | Cr | Mo | V | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0,38 | 0,90 | 0,40 | 5,20 | 1,30 | 0,45 | balance |
| Fe | Si | Mn | Ni | Cr | Ti | Cu | Pb | Mg | Zn | Sn | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| max 1.1 |
10 - 12 |
max 0.55 | max 0.45 | max 0.15 | max 0.25 | 1.5 - 2.5 |
max 0.25 | max 0.3 | max 1.7 | max 0.15 | balance |
| Measured Parameters |
Uncoated | CrAlSiN Coated |
TiAlN Coated |
TiN Coated |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (HRC) | 48 | 52 | 53 | 50 |
| Roughness (Ra) | 0,10 | 0,34 | 0,39 | 0,46 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





