Introduction
Russell’s Viper (Daboia russelii) is occasionally found in Pakistan, India, Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh, and Sri Lanka (Uetz et al. 2019). A couple of decades ago, it was listed as a Critically Endangered species in Bangladesh (IUCN Bangladesh 2000). The previous distribution was confined to the areas along the Padma River and its tributaries. Russell's viper reappeared prominently in Bangladesh after a long absence. Beginning in 2012, the appearance of Russell's viper has been reported in the Barind tract. It came to the limelight in 2013 when one Indigenous (Shawtal) female died due to Russell’s viper bite in the Shibrampur village under Tanore Upazila of Rajshahi district (Ahsan and Saeed 2018). The recent rise in snakebite from Russell’s viper in different districts of the country is a matter of considerable public concern. Incidents and deaths involving bites from Russell's vipers have recently surged in many districts, leading to widespread panic among the citizens of the country. Hence, the study aims to update the distributional map of Russell’s Viper (Daboia russelii) across the country and to find out the causal factors of the surges.
Methodology
Both primary and secondary data were collected in this study. The secondary data was collected from national and local newspapers, online news portals, and social media outlets. A total number of 10 key informants were interviewed to identify the causal factors of increasing the abundance of this snake. Content analysis was done to interpret the data.
Results and Discussions
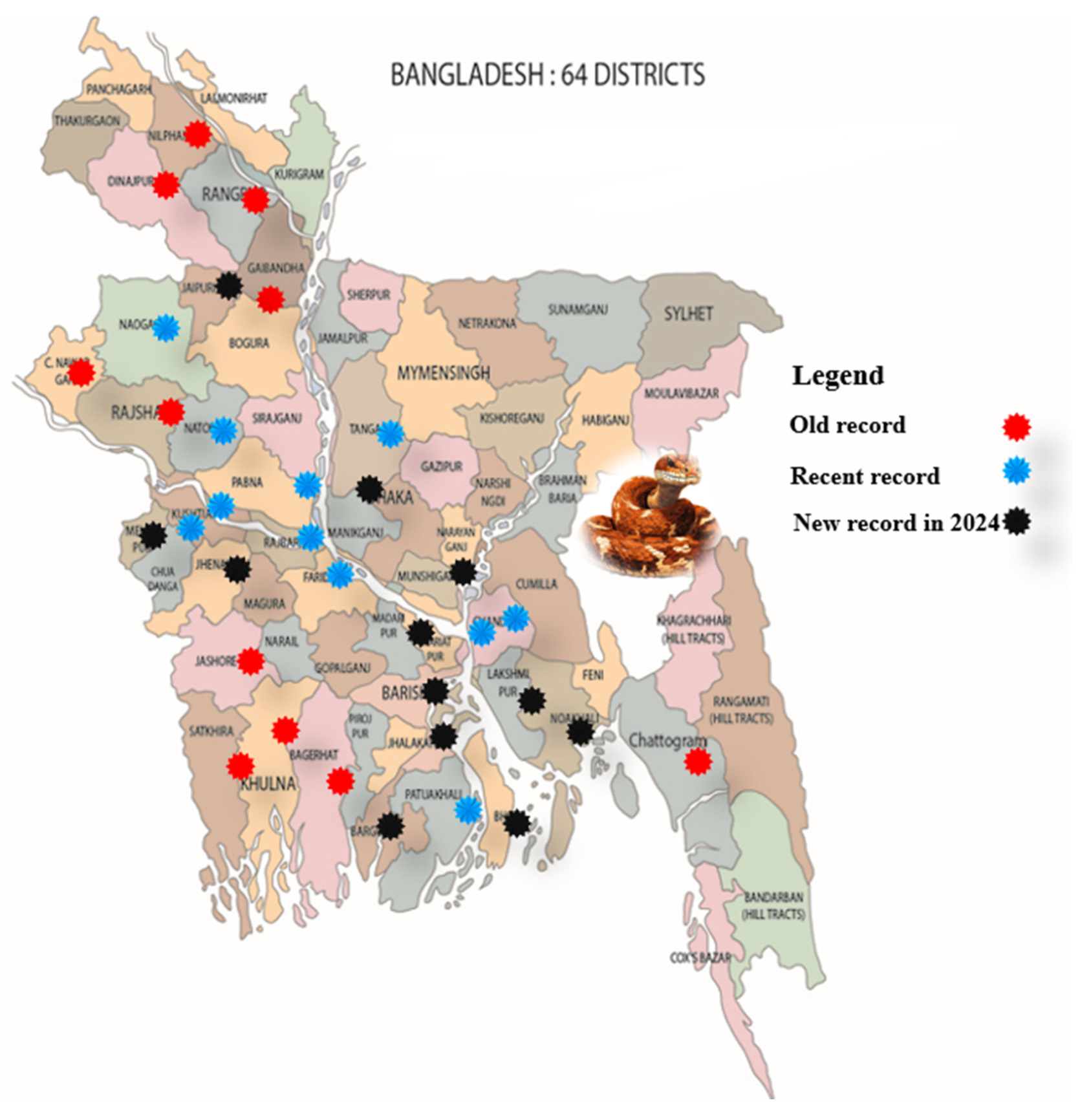
Increased distributional areas
The result showed that the viper spread to 12 new districts:
Jhalakathi,
Jaipurhat, Dhaka,
Munshiganj,
Barishal,
Barguna,
Bhola,
Meherpur,
Jhenaidah,
Shariatpur,
Laxmipur and
Noakhali (
Figure 1). It revealed that the distributional range of this snake was expanded drastically in 2024. Out of 64 districts of the country, the snake was found in 33 districts. Ahsan & Saeed (2018) revealed that its distribution was increased from 11 to 17 districts. Khandakar & Jeny (2020) added another new 05 districts to the distributional map of Russell’s Vipers in Bangladesh.
Causes of the comeback
Climate change
The respondents noted that excessive humidity along with hot weather emerging from climate change is preferable for this viper. Consequently, the volume of water in the river in the monsoon was increasing. The salinity of the country was heightening due to climate change. Such environmental variables were congenial for its survival and reproduction. Rahman (2020) reported that increased salinity due to climate change facilitated the invasion of the alien species. The respondents also added that the frequency of flooding increased in Bangladesh. Consequently, it entered Bangladesh from India in a larger number by hitching rides on hyacinth mats carried downstream during the monsoon season. Venomous snake habitat in Bangladesh is highly modulated by environmental and climatic factors (Chowdhury et al. 2022).
Killing of the predators
The respondents opined that the killing of natural predators such as foxes, monitor lizards and mongoose led to the rise in the snake population. The abundance of prey is highly correlated with the predator’s abundance and distribution (Rahman 2023 a, b).
Higher fertility and increased abundance of food
The respondents argued that one of the reasons for the increase in the number of Russell's vipers is that this snake gives birth directly, does not lay eggs and its survival rate is high. This snake was already present in the Barind tract. The cropping pattern and crop diversification have been increased. The single-cropped area has been turned into a multi-cropped area. Consequently, the abundance of rats, its main prey increased.
Alteration of the past habitat
The respondents added that the destruction of vegetation coverage in the upper part of the Padma Basin is also a contributing factor. This alteration in habitat has facilitated the movement of Russell's vipers downstream. The natural vegetation coverage of Bangladesh is decreasing at an alarming rate due to high population density, sharply skewed distribution of lands, and the overexploitation of forest resources. The natural forests have become critically fragmented to the point where they are considered unlikely to maintain a rich level of biodiversity, nor support viable populations of natural and native species (Rahman et al. 2009; Rahman 2021). The altered microclimate becomes unsuitable for many animals, which forces them to migrate (Rahman 2023c).
References
- Chowdhury, M. A. W., S. Varela, S. Roy, M.M. Rahman, M. Noman, M., I. K. Al Haidar, and J. Müller. 2022. Favourable climatic niche in low elevations outside the flood zone characterises the distribution pattern of venomous snakes in Bangladesh. Journal of Tropical Ecology 38(6), 437-450.
- Khandakar, N. and K. N. Jeny.2020. New distributional records of Russell’s Vipers, Daboia russelii (Shaw and Nodder 1797), in Bangladesh. Reptiles & Amphibians 27(1), 81-82.
- Rahman, M. M., A. Nishat, and H. Vacik. 2009. Anthropogenic disturbances and plant diversity of the Madhupur Sal forests (Shorea robusta C.F. Gaertn) of Bangladesh. International Journal of Biodiversity Science Management 5(3), 162–173.
- Rahman, M.M. 2020. Impact of increased salinity on the plant community of the Sundarbans Mangrove of Bangladesh. Community Ecology 21, 273–284. [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M. 2021. Achieving Sustainable Development Goals of Agenda 2030 in Bangladesh: the crossroad of the governance and performance. Public Administration and Policy: An Asia-Pacific Journal 24 (2): 195-211. [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M. 2023a. Threats to the Critically Endangered Leopard (Panthera pardus) in Bangladesh: Conservation Approaches. SSRN Electronic Journal. [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M. 2023b. Threats to the Bengal tiger (Panthera tigris) in Bangladesh (November 28, 2023). SSRN Electronic Journal. [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M. 2023c. Impact of Habitat Fragmentation on the Diversity of Flora and Fauna of Bangladesh. SSRN Electronic Journal. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).