1. Introduction
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third most diagnosed cancer. It has the second highest mortality rate worldwide, with the five-year survival rate decreasing significantly in the more advanced stages [
1,
2]. Metastatic CRC in most cases, remains incurable, but treatment has been improved by cytotoxic chemotherapy and targeted therapy [
2]. Cancer cells generally form when gene mutations lead to defects within cellular regulatory systems. This results in cells undergoing continuous, unregulated proliferation and growth and resistance to apoptosis, both with and without growth signals being present [
3,
4,
5]. These characteristics are all features usually controlled through a wide variety of signalling pathways, which can often be dysregulated by being either hyper- or under-activated [
4,
5,
6]. The most commonly dysregulated pathways with or lacking mutations in critical genes or proteins in colorectal cancer are the MAPK-, EGFR-, and Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathways [
7]. These pathways are all involved in various essential cellular processes, such as cell migration, proliferation, angiogenesis, apoptosis, differentiation, and survival, all being implicated in cancer formation and progression [
7,
8].
The epidermal growth factor (EGF) and EGF receptor (EGFR) play an essential role in mammalian cells by regulating cellular growth, differentiation, proliferation, and survival [
9]. EGFR is a member of the receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) family linked to multiple cancers, especially metastatic colorectal cancer [
10]. The activation of the EGFR will lead to the cascade-like activation of various downstream signalling pathways, such as MAPK- and PI3K [
10,
11]. Dysregulated or overexpressed signalling pathways, specifically MAPK, are often present in CRCs, with the inhibition of these pathways being targets for cancer treatment [
7,
12].
Cannabidiol (CBD) is the primary non-psychoactive compound of Cannabis sativa, a plant commonly used as a medicinal agent to provide relief from pain and anxiety. In contrast, the psychotropic compound is ∆9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) [
13]. In vitro studies have previously reported the ability of CBD to treat various cancer types [
14,
15,
16]. Specifically in CRC cells, apoptosis was induced following CBD treatment by regulating pro- and anti-apoptotic proteins. Anti-apoptotic protein expression, such as NOXA, was significantly increased in CRCs due to CBD-facilitated stimulation of the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) [
17]. Although CBD has been shown to induce cytotoxic effects, such as apoptosis in CRC [
17], little is known about the effect of CBD on other properties of cancer cells. As a prelude to in vitro studies, the effect/s of CBD on the proteins involved in the MAPK pathway (EGFR, RAS, RAF, MEK and ERK) are predicted here using a bioinformatic and docking-based study, which could provide information regarding the functioning of these proteins. Similar studies have been conducted to determine if and to which proteins a drug, specifically CBD will bind to, however this approach has not yet been used [
18]. Known protein target prediction and molecular docking software and databases were used to identify which amino acid residues are involved in the predicted interactions [
15,
16].
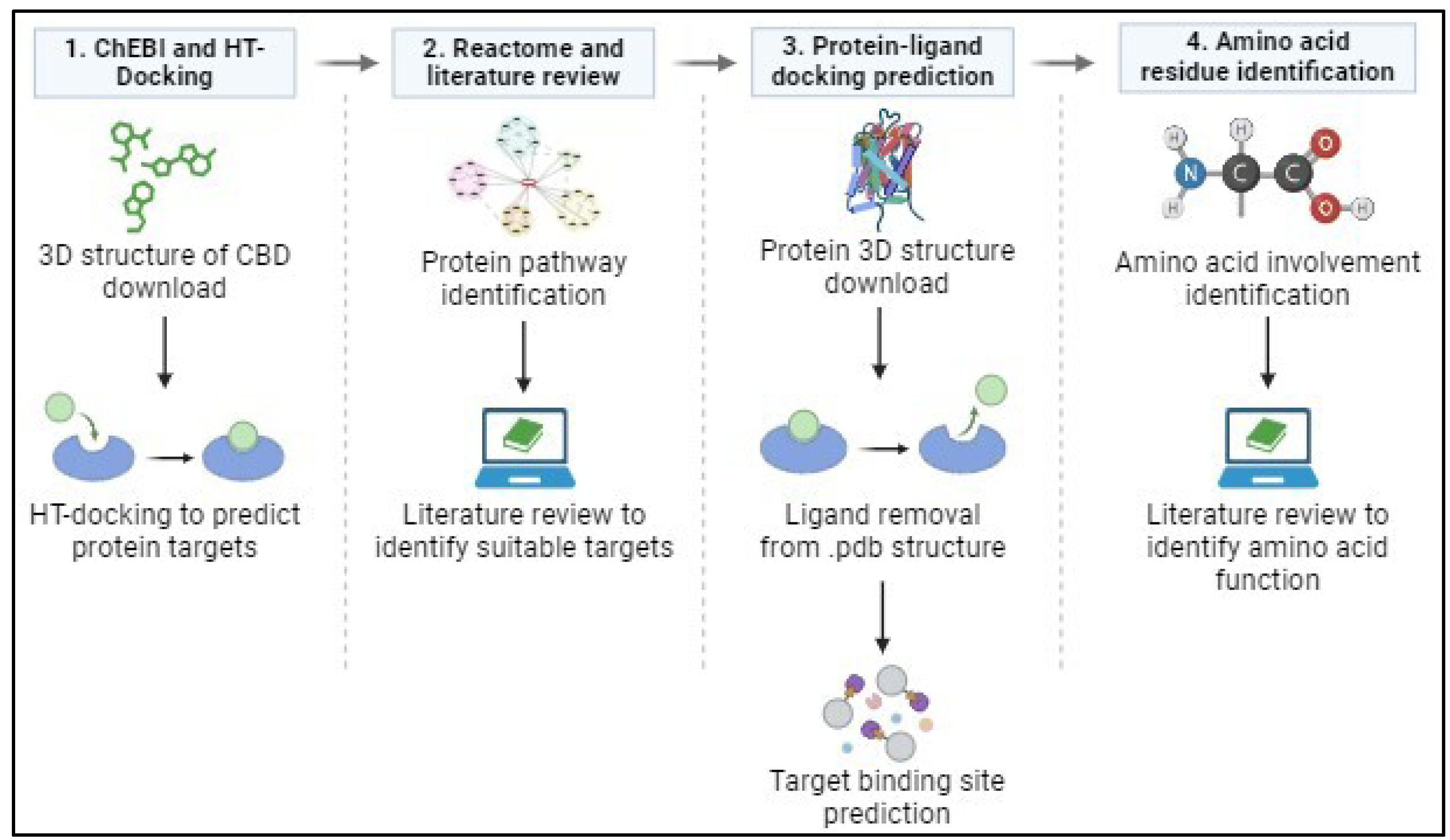
2. Materials and Methods
Chemical Entities of Biological Interest
In the preliminary stages of this in silico analysis, the Chemical Entities of Biological Interest/ChEBI database (
https://www.ebi.ac.uk/chebi/) was used to obtain the 3D structure of CBD. “Cannabidiol” was entered into the database as a search term to generate a list of associated compounds. The 3D structure of CBD, with the correct molecular weight, was downloaded as a spatial data files (.sdf) and used during further analyses using High-Throughput docking.
High-Throughput Docking
The 3D structure of CBD was submitted to the HT-Docking website (
https://www.cbligand.org/HTDocking/search_struct.php) to identify proteins that interact with CBD. These were ranked according to their highest to lowest docking scores, indicating the strength of the interaction between CBD and a potential target protein. Proteins with a docking score higher than 6.5 were selected for further analysis from this list.
Reactome
The Reactome Pathway Browser (
https://reactome.org/PathwayBrowser/) was used to identify the subcellular location and pathway(s) of the proteins identified during HT Docking. The proteins were filtered based on the main pathway they are involved in and their function, after which proteins involved in the MAPK pathway were selected for further evaluation.
Protein-Ligand Docking Prediction
Proteins directly involved in the MAPK pathway were chosen, due to the large number of MAPK proteins identified, for further docking studies (see
Table 1 for the list of proteins). The crystal structure of each of these proteins was downloaded from the Protein Data Bank (
https://www.rcsb.org/) as a .pdb file. However, since these structures represent proteins complexed with a ligand, it was necessary to remove these using CCDC GOLD software. The new ligand-free protein structure was downloaded as a .pdb file. Subsequently, this file, together with the 3D structure of CBD, was uploaded to the CB Dock 2 website (
https://cadd.labshare.cn/cb-dock2/index.php), which simulated the binding of CBD to each protein. The three best docking solution files were downloaded, each with their relative Vina scores. Vina scores, like docking scores, indicate the strength of the protein-ligand binding interaction, but whereby the more negative the score, the stronger the interaction between protein and ligand [
17]. The Vina score obtained from the predicted CB docking indicates the strength of the interaction between CBD and the specific protein that CBD is docked onto.
Amino Acid Residue Identification at Docking Sites
The CBD-protein complex from the three optimal docking solutions was uploaded to the LigPlot
+ v.2.2. program obtained from the European Bioinformatic Institute (
https://www.ebi.ac.uk/thornton-srv/software/LigPlus/). This program identified the amino acids involved in the predicted bonds formed between CBD and the docking site of each protein analyzed. The type of bond formed between amino acid residues and atoms from CBD was also identified. From this, a literature review was conducted to determine the possible role these amino acid residues may play in the activity and functioning of the protein and to predict what effect CBD could have on protein activity and, subsequently, the MAPK pathway (
Figure 1).
3. Results
HT-Docking was used to predict which of the 607 proteins available in this database interacted with CBD and the relative strength of this interaction. Of these, 48 proteins linked to CRC were identified to interact strongly with CBD (
Table S1). Reactome-based pathway investigation of these proteins indicated that CBD could interact with a wide variety of MAPK- and MAPK-like proteins and signified that CBD could play an important role in inhibiting or limiting the function of the MAPK pathway. Additional docking analysis using LigPlot revealed that CBD formed strong hydrogen bonds with various amino acid residues in the selected MAPK pathway proteins (
Table 1). These interactions were stabilized by hydrophobic interactions between the atoms of CBD and amino acids found in or near the binding site (
Table 1). The top four scores are represented by BRAF (-8.9), EGFR (-8.8), KRAS (-8.5) and MEK1 (-8.0) (
Table 1). Also represented in
Table 1 are the amino acid residues involved in forming hydrogen bonds with CBD and those amino acids responsible for hydrophobic interactions with CBD. For this study, EGFR, KRAS, BRAF, and MEK are discussed below.
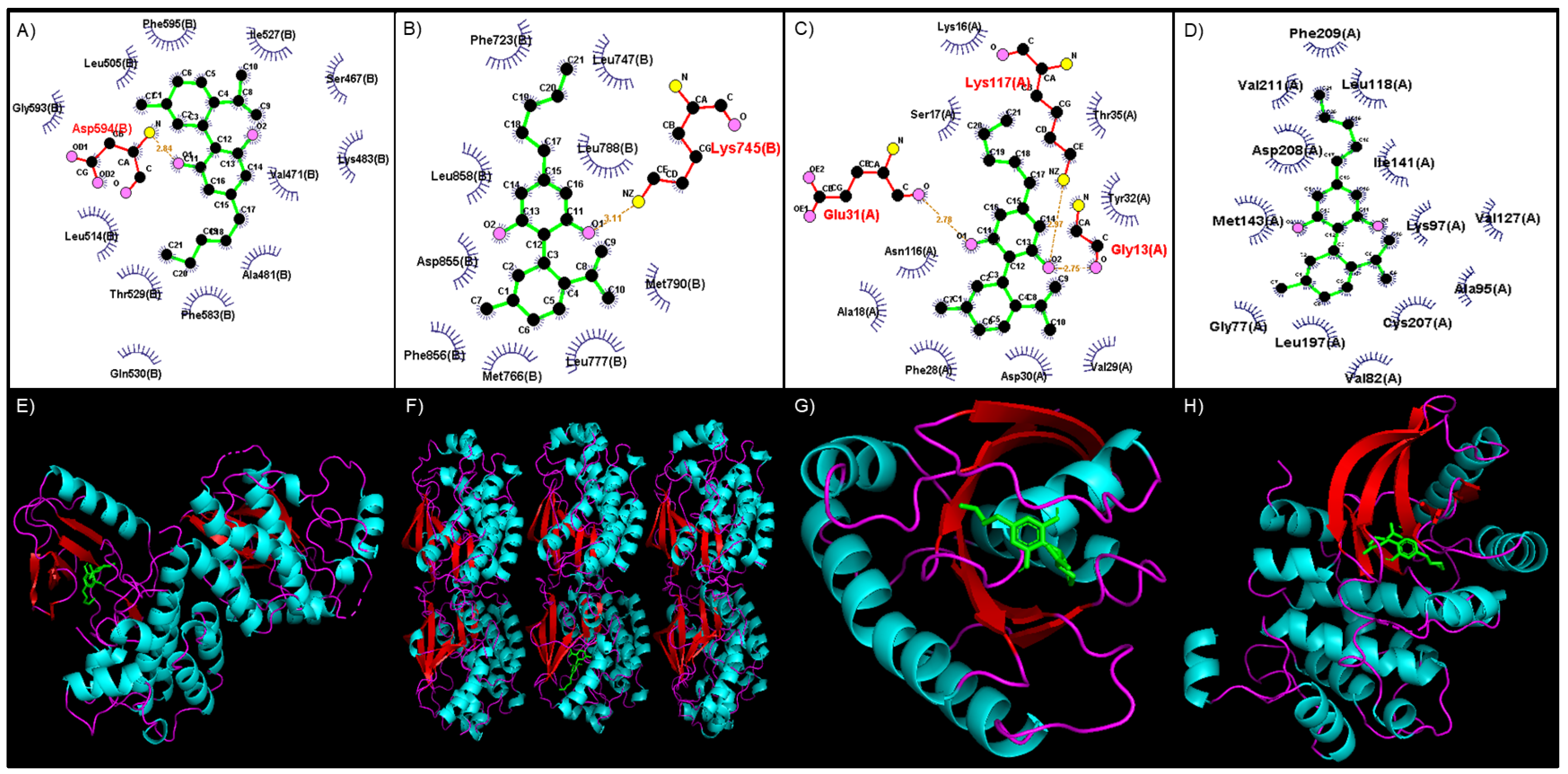
The binding site of CBD to the kinase domain of BRAF indicates that CBD would form a hydrogen bond with the Asp594 residue, which occurs between the amino group (-NH2) of Asp594 and the alcohol group (-OH) side chain of CBD (
Figure 2A). CBD binds to EGFR by forming a hydrogen bond with the Lys745 residue between the -NH2 group of Lys745 and the -OH side chain of CBD (
Figure 2B). The binding of CBD to KRAS involves Gly13, Glu31, and Lys117, which form a hydrogen bond with CBD. These interactions occur between the -NH2 group of Gly13, -OH side chain and Lys117, and the oxygen group of Glu31 and the second oxygen atom of CBD (
Figure 2C). MEK1 interaction with CBD occurs mainly through hydrophobic interactions within the binding site, which includes amino acid residues such as Gly77, Val82, Ala95, Lys97, Leu118, Val127, Ile141, Met143, Leu197, Cys207, Asp208, Phe209, Val211 (
Figure 2D).
4. Discussion
The results of the docking analysis predicted that CBD would bind to a variety of MAPK signalling pathway proteins, with various strengths and types of bonds formed between the protein and CBD. These results indicate that CBD could work in a multifaceted mechanism, binding and potentially inhibiting this signalling cascade in several different ways.
CBD Could Act as a Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor
The in silico analysis of the interaction between CBD and EGFR predicted that CBD would interact with EGFR, a transmembrane receptor involved in the phosphoryl transfer from EGFR to target protein [
21]. EGFR is involved in many signalling pathways, of which the aberrant activation leads to initiation and progression of cancer and CRC [
22,
23,
24,
25]. The hydrogen bond between CBD and EGFR involves the Lys745 residue, which is highly conserved across all types of kinases. A single Lys→Arg mutation leads to a complete loss of catalytic activity of EGFR, which highlights the importance of this residue in phosphate transfer and catalysis [
26,
27]. CBD binding to this residue could diminish the catalytic activity of EGFR due to its importance in the ability of EGFR to function normally. Resistance to first- and second-generation EGFR TKIs arises due to the Thr790→Met mutation [
28,
29]. The Thr790 residue is located in the bottom of the ATP binding pocket, and the Thr790→Met mutation causes a conformational change, which reduces the ability of first- and second-generation TKIs to bind to the ATP pocket [
18,
29]. This Thr790→Met mutation also increases the affinity of the mutant receptor of ATP, which reduces the efficacy of first- and second-generation inhibitors [
18,
27,
28,
29].
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) are compounds which function by inhibiting the tyrosine kinase residues (TKRs) from catalyzing phosphorylation of the target protein’s tyrosine residue, thereby blocking target protein activation [
17,
18]. These TKIs can be grouped into first and second-generation TKIs based on the treatment line into which these inhibitors fall. First-generation inhibitors are the ‘first line’ of treatment used to treat a type of cancer and act as inhibitors to a variety of tyrosine kinases [
32]. Second-generation TKIs are inhibitors used when resistance to first-generation inhibitors has been acquired due to mutations involved in critical sites in the kinases [
33]. Since CBD forms a hydrophobic interaction with Met790 (
Figure 2B) – the mutated isoform, it could potentially hinder the binding of ATP to the binding site, potentially preventing the phosphorylation of downstream target proteins. This indicates that CBD could function as a third-generation TKI, acting against Thr790→Met mutations.
DFG Motif as a Potential Target of CBD
A DFG motif consists of aspartic acid/phenylalanine/glutamine residues, which regulate the catalysis of a protein kinase and play a role in ATP binding to the kinase [
40,
41,
42]. The highly conserved DFG motif is situated in the C-lobe of the catalytic domain of a kinase and is involved in the magnesium binding coordination [
43]. Type 1 inhibitors bind to the DFG motif in an active conformation and bind to the ATP pocket, preventing substrate protein phosphorylation [
44]. In comparison, type 2 kinase inhibitors are ligands that will bind to and occupy the hydrophobic pocket of the kinase, which is adjacent to the ATP binding site [
45].
This in silico analysis revealed that CBD would bind to the kinase domain of BRAF through a hydrogen bond formed with the Asp594 residue of the kinase domain (
Figure 2A). This residue forms part of the larger C-lobe, which is involved in binding substrate proteins [
46] and the DFG motif [
40,
41,
42]. In the active state of BRAF, Asp594 forms a bond with a divalent magnesium ion, stabilizing the phosphate groups of ATP [
46]. CBD also occupies the hydrophobic pocket of BRAF, located between Val471, Cys532, Trp531, Thr529, Leu514, and Ala481 (
Figure 2A) [
37,
42]. As this hydrophobic pocket is next to the catalytic loop, potentially with the binding of CBD to the hydrophobic pocket, the activity of the catalytic loop will be impaired [
46]. This inhibition will consequently prevent the transfer and phosphorylation of BRAF’s downstream target proteins, indicating the potential use of CBD as either a Type 1 or 2 kinase inhibitor.
The present analysis predicted that CBD would interact with MEK1 via hydrophobic interactions with Gly77, Val82, Ala95, Lys97, Leu118, Val127, Ile141, Met143, Leu197, Cys207, Asp208, Phe209, and Val211 (
Figure 2D). Important interactions include CBD with Lys97, Met143, Asp208, and Phe209. Notably, Asp208 and Phe209 are part of the DFG motif in MEK1, which functions similarly to the DFG motif of BRAF [
47]. The Asp208 residue plays a critical role in the active and inactive state of MEK1, the orientation of this residue determining the active and inactive states of BRAF [
48]. Asp208 is the first residue in the MEK1 activation loop, which will bind Mg2+ ions that will subsequently be involved in the coordination of the phosphates of ATP [
49]. If the DFG motif is in the inactive conformation, the Asp208 residue will face away from the active site; while in the active conformation, it will face the active site [
44,
46,
47]. Thus the interaction of CBD with Asp208 and Phe209 will block switching from the inactive to the active state, resulting in the activation loop impeding the binding site of ERK1 on MEK1 [
44,
48].
In the inactive conformation of the DFG motif, an allosteric binding site or hydrophobic pocket will be formed next to the DFG motif. This pocket will be separated from the DFG motif by Lys97 and Met143 [
52]. Importantly, Lys97 is part of a conserved region of three amino acids that forms a Lys-Asp-Asp motif, which plays a key role in phosphoryl transfer [
48]. This is an essential catalytic residue involved in coupling the ATP phosphates, forming a salt bridge with a Glu114, an occurrence that signals that the kinase is in the active catalytic state [
43,
44,
49]. The binding of CBD to this residue will prevent the formation of the salt bridge, limiting the transfer of a phosphoryl group, so trapping the kinase in an inactive state. Type 1 MEK1 inhibitors have a similar chemical structure to ATP and will compete with it for the catalytic binding site on MEK1 [
48]. Type 2 inhibitors function in occupying the hydrophobic pocket next to the ATP binding pocket when the DFG motif is in its inactive state. These inhibitors will form hydrogen bonds with Glu114 and Asp208, forming van der Waals interactions between other residues in this region [
44,
46].
Additional Targets for CBD-Induced Inhibition
The in silico analysis identified additional MAPK-pathway proteins that also interact with CBD; however, theses predicted interactions are slightly weaker than those described above, and MEK1. These CBD-PR interactions include cRAF, NRAS, HRAS, MEK2, ERK1 and ERK2, which form the MAPK signalling cascade.
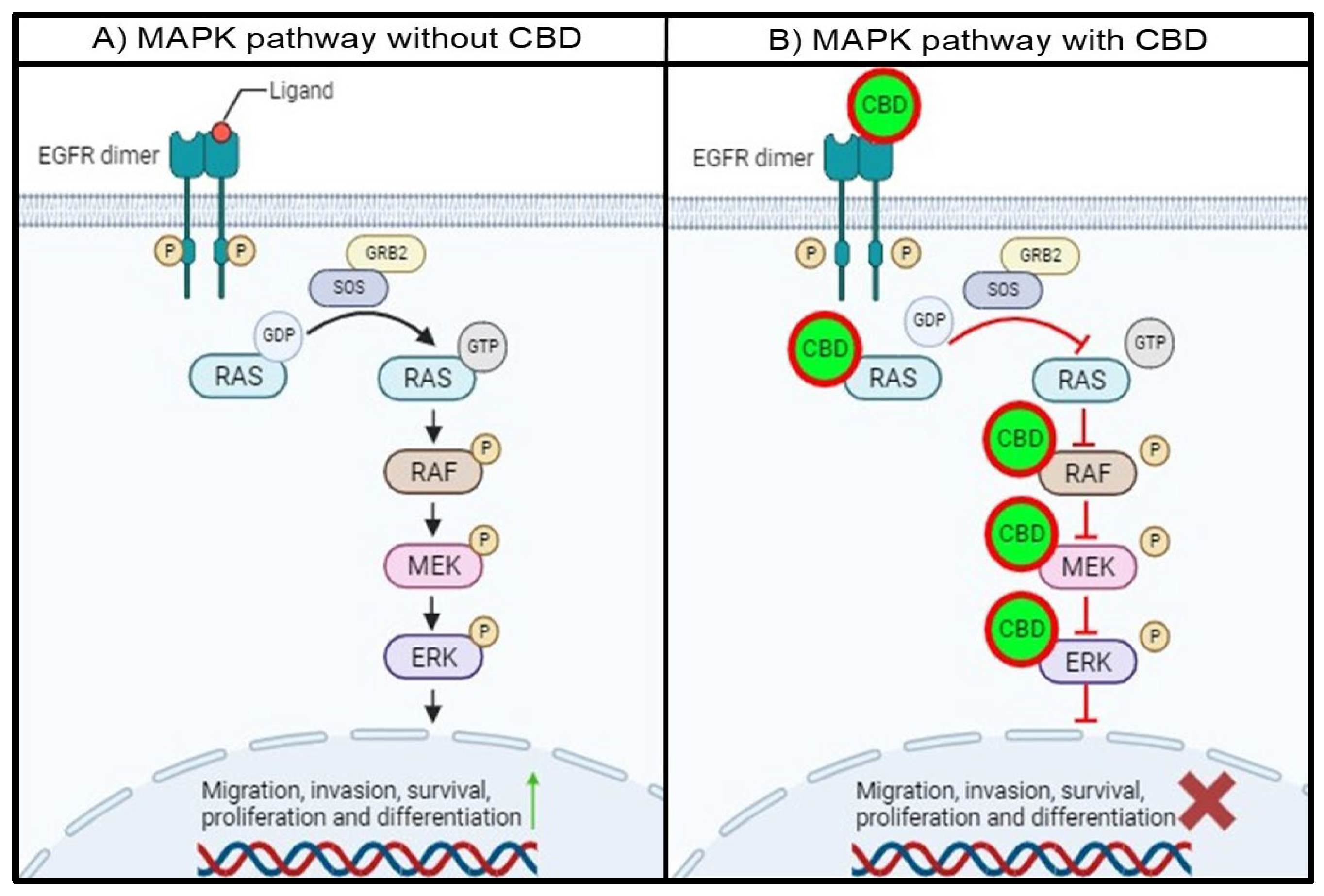
The interaction between CBD and proteins involved in each step of the MAPK pathway could potentially be used as a novel method to treat CRC. Since CBD interacts with almost all proteins involved in the pathway, it will not only inhibit the activity of a single protein but in this pathway Thus as depicted in
Figure 3, CBD can inhibit the activity of multiple MAPK pathway proteins.
In the absence of CBD, the intracellular tyrosine kinase domain of EGFR will be phosphorylated with ligand binding, resulting in the dimerization of EGFR. This phosphorylated residue will provide a docking site for GRB2, which will interact with SOS. This complex will allow GDP-bound RAS to release GDP and hydrolyze GTP to activate RAS, leading subsequent RAF, MEK1/2, and ERK1/2 activation. Activation of ERK1/2 will lead to the activation and transcription of target proteins and genes associated with migration, invasion, survival, proliferation, and differentiation (
Figure 3A).
The proposed mechanism for the interaction between CBD and the MAPK pathway proteins indicates that the entire MAPK pathway will be affected in the presence of CBD. CBD binding to EGFR will prevent the transfer of a phosphoryl group to GDP, which is bound to RAS, leaving RAS inactive. Secondly, the interaction between CBD and RAS will either prevent the release of GDP and hydrolysis of GTP and occupy the ATP binding pocket in the RAS isoforms. This will prevent RAS from phosphorylating RAF, leaving RAF inactive. Thirdly, CBD can also interact with RAF, specifically BRAF, and impair the catalytic activity by binding to the hydrophobic pocket and ATP binding site. This will inhibit the activity of BRAF, and MEK downstream of BRAF will not be activated. Finally, the interaction of CBD with MEK1 will also trap MEK1 in an inactive state by binding to the DFG motif and hydrophobic pocket. Subsequently, the MAPK pathway will be impaired, and the activation and transcription of proteins involved in cell migration, invasion, survival, proliferation, and differentiation will be either decreased or inhibited (
Figure 3B). This can also be useful since proteins in the MAPK pathway can often be mutated and become resistant to conventional treatments. With the multi-protein inhibition of the MAPK pathway, treatment resistance can be overcome.
5. Conclusions
This in silico study predicts that CBD could play a pivotal role in inhibiting the EGFR and MAPK pathways since almost all the proteins involved in this pathway interact with CBD. The most notable interactions occur between CBD and EGFR, KRAS, BRAF, and MEK1, as reflected by docking scores and being the most critically mutated or dysregulated proteins in colorectal cancer. CBD is proposed to act as an inhibitor of these proteins mainly by binding to the ATP catalytic binding site, which prevents phosphotransfer and subsequent downstream activation of the substrate proteins. Secondly, CBD can act by binding to the DFG, which is adjacent to the hydrophobic pocket. The catalytic activity of this target protein is inhibited by this mechanism. Since the effect of CBD on these proteins has not yet been investigated, future studies should aim to determine if CBD indeed binds to these predicted target sites in these proteins and if the expected inhibitory effect occurs. Further, n-vitro phosphorylation studies on the selected proteins may determine if the phosphorylation of these proteins is affected by CBD treatment. In conclusion, CBD is predicted to interact with multiple role-players in the EGFR and MAPK pathways, potentially inhibiting these pathways and proteins.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at
Preprints.org. Table S1: Proteins identified during interaction with CBD and their docking scores and gene names. Table S2: CB dock results of CBD binding to EGFR. Table S3: CB dock results of CBD binding to KRAS. Table S4: CB dock results of CBD binding to HRAS. Table S5: CB dock results of CBD binding to NRAS. Table S6: CB dock results of CBD binding to BRAF. Table S7: CB dock results of CBD binding to cRAF. Table S8: CB dock results of CBD binding to MEK1. Table S9: CB dock results of CBD binding to MEK2. Table S10: CB dock results of CBD binding to ERK1. Table S11: CB dock results of CBD binding to ERK2.
Author Contributions
J du Plessis conducted the in silico work and collected and analyzed the data. J du Plessis wrote the manuscript with assistance from A Omar. C Penny and A Deroubaix conceived the idea to determine protein binding to CBD using bioinformatic analysis. A Omar, C Penny, and A Deroubaix edited the manuscript, and all authors have reviewed the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Wits/MRC Common Epithelial Cancer Research Centre and the Faculty Research Council (FRC) of the Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Witwatersrand. The funders’ role was financial support; and had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or in manuscript preparation.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study and the data not shown here are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request. As the data files are Excel spreadsheets, they have not been included in the
Supporting Information document. Data required to replicate the study can be found in the
Supporting Information document.
Conflicts of Interest
There are no conflicts of interest to declare. The authors have no affiliation with any organization with direct or indirect financial interests in the subject matter discussed in the manuscript.
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin [Internet]. 2021. n/a(n/a). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modest, D.P.; Pant, S.; Sartore-Bianchi, A. Treatment sequencing in metastatic colorectal cancer. Eur J Cancer [Internet]. 2019, 109, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouad, Y.A.; Aanei, C. Revisiting the hallmarks of cancer. Am J Cancer Res [Internet]. 2017, 7, 1016–1036. [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sever, R.; Brugge, J.S. Signal transduction in cancer. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med [Internet]. 2015, 5, a006098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. The Hallmarks of Cancer. Cell [Internet]. 2000, 100, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koveitypour, Z.; Panahi, F.; Vakilian, M.; Peymani, M.; Seyed Forootan, F.; Nasr Esfahani, M.H.; et al. Signaling pathways involved in colorectal cancer progression. Cell Biosci [Internet]. 2019, 9, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabana, Y.M.; Dahham, S.S.; Shah, A.M.; Majid, A. Major signaling pathways of colorectal carcinogenesis. Recent Adv Colon Cancer. 2016, 1, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Oda, K.; Matsuoka, Y.; Funahashi, A.; Kitano, H. A comprehensive pathway map of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling. Mol Syst Biol [Internet]. 2005/05/25. 2005, 1, 2005–0010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krasinskas, A.M. EGFR Signaling in Colorectal Carcinoma. Yantiss RK, editor. Patholog Res Int [Internet]. 2011, 2011, 932932. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Pan, W.; Liu, S.; Shen, Z.; Xu, Y.; Hu, L. ERK/MAPK signalling pathway and tumorigenesis (Review). Exp Ther Med [Internet]. 2020, 19, 1997–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittaker, S.; Marais, R.; Zhu, A.X. The role of signaling pathways in the development and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene [Internet]. 2010, 29, 4989–5005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atakan, Z. Cannabis, a complex plant: different compounds and different effects on individuals. Ther Adv Psychopharmacol [Internet]. 2012, 2, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerretani, D.; Collodel, G.; Brizzi, A.; Fiaschi, A.I.; Menchiari, A.; Moretti, E.; et al. Cytotoxic Effects of Cannabinoids on Human HT-29 Colorectal Adenocarcinoma Cells: Different Mechanisms of THC, CBD, and CB83. Int J Mol Sci. 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sreevalsan, S.; Joseph, S.; Jutooru, I.; Chadalapaka, G.; Safe, S.H. Induction of apoptosis by cannabinoids in prostate and colon cancer cells is phosphatase dependent. Anticancer Res [Internet]. 2011, 31, 3799–3807. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Qin, Y.; Pan, Z.; Li, M.; Liu, X.; Chen, X.; et al. Cannabidiol Induces Cell Cycle Arrest and Cell Apoptosis in Human Gastric Cancer SGC-7901 Cells. Biomolecules [Internet]. 2019, 9, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, S.; Yun, H.K.; Jeong, Y.A.; Jo, M.J.; Kang, S.H.; Kim, J.L.; et al. Cannabidiol-induced apoptosis is mediated by activation of Noxa in human colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Lett [Internet]. 2019, 447, 12–23. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0304383519300230. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, Y.-M.; He, X.-B.; Jing, Y.-K.; Wang, L.-R.; Wang, J.-M.; Xie, X.-Q. Computational systems pharmacology analysis of cannabidiol: a combination of chemogenomics-knowledgebase network analysis and integrated in silico modeling and simulation. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2019, 40, 374–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.-Y.; Zhang, H.-X.; Mezei, M.; Cui, M. Molecular docking: a powerful approach for structure-based drug discovery. Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2011, 7, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, Y.Y.; Li, W.-H. Evolutionary approach to predicting the binding site residues of a protein from its primary sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci [Internet]. 2011, 108, 5313–5318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zámečníkova, A. Novel approaches to the development of tyrosine kinase inhibitors and their role in the fight against cancer. Expert Opin Drug Discov [Internet]. 2014, 9, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayati, A.; Moghimi, S.; Salarinejad, S.; Safavi, M.; Pouramiri, B.; Foroumadi, A. A review on progression of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitors as an efficient approach in cancer targeted therapy. Bioorg Chem [Internet]. 2020, 99, 103811. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0045206819319406. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, T.; Gerber, D.E. Newer-Generation EGFR Inhibitors in Lung Cancer: How Are They Best Used? Cancers 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santarpia, L.; Lippman, S.M.; El-Naggar, A.K. Targeting the MAPK-RAS-RAF signaling pathway in cancer therapy. Expert Opin Ther Targets [Internet]. 2012, 16, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markowitz, S.D.; Bertagnolli, M.M. Molecular origins of cancer: Molecular basis of colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2009, 361, 2449–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrera, A.C.; Alexandrov, K.; Roberts, T.M. The conserved lysine of the catalytic domain of protein kinases is actively involved in the phosphotransfer reaction and not required for anchoring ATP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A [Internet]. 1993, 90, 442–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spellmon, N.; Li, C.; Yang, Z. Allosterically targeting EGFR drug-resistance gatekeeper mutations. J Thorac Dis [Internet]. 2017, 9, 1756–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, C.-H.; Mengwasser, K.E.; Toms, A.V.; Woo, M.S.; Greulich, H.; Wong, K.-K.; et al. The T790M mutation in EGFR kinase causes drug resistance by increasing the affinity for ATP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A [Internet]. 2008, 105, 2070–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.M.; Syn, N.L.; Cho, B.C.; Soo, R.A. Acquired resistance to EGFR targeted therapy in non-small cell lung cancer: Mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Cancer Treat Rev [Internet]. 2018, 65, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Jiang, S.; Shi, Y. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors for solid tumors in the past 20 years (2001–2020). J Hematol Oncol [Internet]. 2020, 13, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, P.L.; Gray, N.S. Targeting cancer with small molecule kinase inhibitors. Nat Rev Cancer [Internet]. 2009, 9, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oehler, V.G. First-generation vs second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors: which is best at diagnosis of chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia? Hematology [Internet]. 2020, 2020, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breccia, M.; Alimena, G. Second-Generation Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors (Tki) as Salvage Therapy for Resistant or Intolerant Patients to Prior TKIs. Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis. 2014, 6, e2014003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Bryan, J.P. Pharmacological targeting of RAS: Recent success with direct inhibitors. Pharmacol Res [Internet]. 2019, 139, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, A.T.; Carracedo, A.; Locasale, J.W.; Anastasiou, D.; Takeuchi, K.; Kahoud, E.R.; et al. Ubiquitination of K-Ras enhances activation and facilitates binding to select downstream effectors. Sci Signal [Internet]. 2011, 4, ra13–ra13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hobbs, G.A.; Der, C.J.; Rossman, K.L. RAS isoforms and mutations in cancer at a glance. J Cell Sci [Internet]. 2016, 129, 1287–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Bera, A.K.; Gondi, S.; Westover, K.D. KRAS Switch Mutants D33E and A59G Crystallize in the State 1 Conformation. Biochemistry [Internet]. 2018, 57, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantsar, T. The current understanding of KRAS protein structure and dynamics. Comput Struct Biotechnol J [Internet]. 2019, 18, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klaus, S.; Reza, A.M.; Wolfgang, K.; Lisa, W.; Alfred, L.; Frank, S.; et al. The Ras-RasGAP Complex: Structural Basis for GTPase Activation and Its Loss in Oncogenic Ras Mutants. Science (80- ) [Internet]. 1997, 277, 333–339. [Google Scholar]
- Bollag, G.; Tsai, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Ibrahim, P.; Nolop, K.; et al. Vemurafenib: the first drug approved for BRAF-mutant cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov [Internet]. 2012, 11, 873–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, T.; Lee, J.T.; Weiru, W.; Jiazhong, Z.; Hanna, C.; Shumeye, M.; et al. Discovery of a selective inhibitor of oncogenic B-Raf kinase with potent antimelanoma activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci [Internet]. 2008, 105, 3041–3046. [Google Scholar]
- Bollag, G.; Hirth, P.; Tsai, J.; Zhang, J.; Ibrahim, P.N.; Cho, H.; et al. Clinical efficacy of a RAF inhibitor needs broad target blockade in BRAF-mutant melanoma. Nature [Internet]. 2010, 467, 596–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ung, P.M.-U.; Schlessinger, A. DFGmodel: predicting protein kinase structures in inactive states for structure-based discovery of type-II inhibitors. ACS Chem Biol. 2015, 10, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roskoski, R.J. Classification of small molecule protein kinase inhibitors based upon the structures of their drug-enzyme complexes. Pharmacol Res. 2016, 103, 26–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kufareva, I.; Abagyan, R. Type-II kinase inhibitor docking, screening, and profiling using modified structures of active kinase states. J Med Chem [Internet]. 2008, 51, 7921–7932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanks, S.K.; Hunter, T. The eukaryotic protein kinase superfamily: kinase (catalytic) domain structure and classification1. FASEB J [Internet]. 1995, 9, 576–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornev, A.P.; Haste, N.M.; Taylor, S.S.; Ten Eyck, L.F. Surface comparison of active and inactive protein kinases identifies a conserved activation mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A [Internet]. 2006, 103, 17783–17788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu., P.-K.; Park, J.-I. MEK1/2 Inhibitors: Molecular Activity and Resistance Mechanisms. Semin Oncol [Internet] 2015, 42, 849–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roskoski, RJ. MEK1/2 dual-specificity protein kinases: Structure and regulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012, 417, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gray, N.S. Rational design of inhibitors that bind to inactive kinase conformations. Nat Chem Biol [Internet]. 2006, 2, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pargellis, C.; Tong, L.; Churchill, L.; Cirillo, P.F.; Gilmore, T.; Graham, A.G.; et al. Inhibition of p38 MAP kinase by utilizing a novel allosteric binding site. Nat Struct Biol. 2002, 9, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohren, J.F.; Chen, H.; Pavlovsky, A.; Whitehead, C.; Zhang, E.; Kuffa, P.; et al. Structures of human MAP kinase kinase 1 (MEK1) and MEK2 describe novel noncompetitive kinase inhibition. Nat Struct Mol Biol [Internet]. 2004, 11, 1192–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Xie, L.; Bourne, P. Insights into the binding mode of MEK type-III inhibitors. A step towards discovering and designing allosteric kinase inhibitors across the human kinome. PLoS One. 2017, 12, e0179936. [Google Scholar]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).