1. Introduction
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death worldwide, with a significant impact on productivity and quality of life [
1]. Atherosclerosis, a key contributor to CVD, is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized endothelial dysfunction. This dysfunction in conjunction with other pathological events, leads to the formation of atheromas [
2]. This is the pathophysiological cause of coronary artery disease (CAD), which can present as chronic coronary syndrome (CCS) or acute coronary syndrome (ACS), depending on the morphology and inflammatory status of the atheromas [
3]. Acute ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) accounts for 38% of ACS cases, and are associated with the highest mortality rates [
4]. STEMI often exhibits with a completely occluded coronary artery, and primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PPCI) is the gold standard for reopening the vessel. Evidence demonstrated that this approach reduces mortality and enhances patient prognosis [
5,
6].
IL-22 belongs to the IL-10 family and plays diverse roles in regulating cell growth and differentiation, and modulating immunological and inflammatory responses [
7,
8]. T helper cells type 22 (Th22) are the primary IL-22 producers. IL-22 exerts its effects by binding to a heterodimeric receptor complex composed of the primary IL-22R1 receptor and the IL-10R2 coreceptor. This binding induces intracellular signaling through the Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription (JAK/STAT) pathway [
7,
8,
9] Furthermore to the cell surface IL-22 receptor complex, there is a soluble IL-22 binding protein (IL-22BP) that demonstrates higher affinity and specificity for IL-22, being an effective competitive inhibitor of IL-22 in vitro [
10,
11].
Interactions between IL-22 and its receptors trigger adhesion molecule production by endothelial cells, including the intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) and the vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1), which recruit monocytes [
7,
8]. IL-22 also acts in the regulation and proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells, increasing atheroma growth [
12]. These data show that IL-22 may affect atheroma development and instability because the activation of the Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3) protein is directly related to leukocyte activation, endothelial dysfunction progression, and intensified inflammatory cascade [
13]. Nonetheless, the role of IL-22 in STEMI is still unclear due to the scarce literature on this topic.
Thus, the primary objective of this study was to investigate differences in circulating IL-22 levels between patients with STEMI undergoing PPCI and healthy controls; and the secondary objectives were to compare serum IL-22 levels considering the culprit coronary artery, door-to-balloon time (DBT), final angiographic result, CAD classification, and presence of diabetes mellitus (DM).
2. Materials and Methods
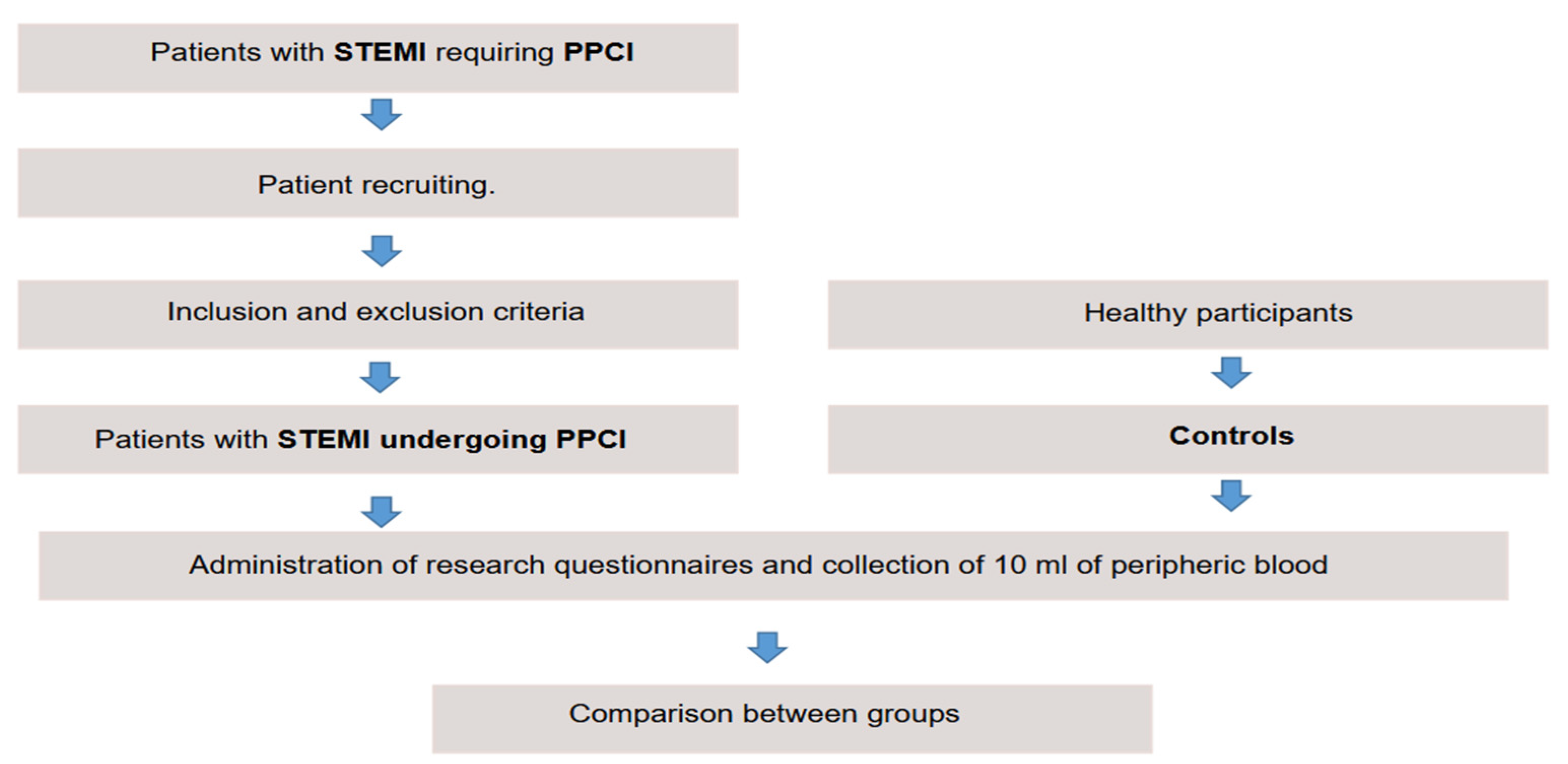
This cross-sectional, descriptive and analytical study was conducted in a reference hospital in cardiology. A total of 210 patients with STEMI undergoing PPCI and 70 healthy controls were recruited between January 2022–August 2023.
The inclusion criteria were age ≥ 18 years and a clinical diagnosis of STEMI treated with PPCI. The exclusion criteria were previous or current oncologic disease, severe liver disease, blood dyscrasia, inability to respond to the questionnaire, or refusal to participate in the study. The controls were healthy volunteers ≥ 18 years old.
Patients meeting these criteria were invited to participate in the study. Those who accepted signed the informed consent form (
Figure 1).
After admission, the participants answered a clinical questionnaire. Clinical and socioeconomic parameters were self-declared, and documented in a research-specific clinical record that was stored in a database.
The culprit vessel was defined as the coronary artery causing STEMI and undergoing PPCI. Multivessel CAD was defined as two or more obstructed vessels (≥ 70%); and single-vessel CAD as only one vessel affected. DBT was classified as > 60 minutes or ≤ 60 minutes. The final coronary flow was measured according to the criteria proposed by the Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction (TIMI) Study Group [
14]. Angiographic success was determined by TIMI 3 final coronary flow, residual lesion < 10%, and absence of thrombi and dissections.
2.1. Serum IL-22 Analysis
The standard technique was used to collect 10 ml of peripheral blood for measuring IL-22 levels. This collection occurred immediately after PPCI in the patient group, and electively in the control group.
The blood was centrifuged, and the supernatant was collected and stored at -80 °C. Sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) quantified serum IL-22 levels using the Human IL-22 DuoSet® kit (R&D Systems Inc, USA & CAN), according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. This kit has a minimum detection level of 50 pg/ml.
2.2. Statistical Analysis
The data included the descriptive analysis of clinical and angiographic characteristics of the patients, and the comparative analysis of serum IL-22 levels between cases and controls. Numeric parameters were analyzed by the Shapiro-Wilk normality test. Normal parameters were presented as mean and standard deviation, and non-normal parameters as median and 25th and 75th percentiles. Categorical parameters were presented as absolute values and percentages.
The Student’s t-test, Mann-Whitney test, and analysis of variance (ANOVA) were used to analyze numerical parameters, depending on their normality. Categorical parameters were analyzed using the chi-square test or the Fisher’s exact test. Statistical analyses were prepared by an independent statistician using the SPSS software version 23. P-values < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
All participants were comparatively analyzed. Subsequently, the cases were divided into five subgroups, considering the culprit vessel, CAD classification, DBT, angiographic success of PPCI, and DM. These subgroups were distributed by sex, age, clinical status, and angiographic profile. IL-22 levels were also compared.
3. Results
The study included 280 participants, 210 cases of STEMI undergoing PPCI and 70 healthy controls. Descriptive analysis exhibited a higher prevalence of men in the case group (63.8% men, 36.2% women). The most prevalent risk factors were systemic arterial hypertension (SAH) (76.2%), smoking history (55.2%), and DM (38.1%) (
Table 1).
In the subgroups, descriptive analysis showed that 83.3% of cases had a DBT > 60 minutes, and that the anterior descending artery (LAD) was affected in 53.8% of cases. Multivessel CAD was preset in 71.4% of cases, with an angiographic success rate of 84.8% (
Table 2).
Serum IL-22 levels were lower in cases (149.63, 84.99–294.56) than in controls (482.67, 344.33–641.00), with p < 0.001.
Serum IL-22 levels were compared by subgroup, according to the culprit coronary artery, CAD classification, DBT, angiographic success, and DM (
Table 3).
4. Discussion
Herein, the results demonstrated lower circulating IL-22 in patients with STEMI undergoing PPCI than in healthy controls. In the subgroups, cases with DBT < 60 minutes and with the RCA as culprit artery had lower IL-22 levels. CAD classification, angiography success, and DM showed no influence on IL-22 levels.
Some studies indicate that high IL-22 levels have an atherogenic effect, especially in stable disease. However, it is unclear if this is a specific cause or part of an immune-inflammatory response [
15,
16].
Conversely, animal studies had different results. IL-22 had a protective effect against myocardial remodeling and unfavorable cardiovascular outcomes after AMI induction in rats, which may be linked to atheroma stabilization. Differently from most human studies, which evaluate CCS, that study analyzed an ACS model [
17,
18].
Yamamoto et al. [
18] assessed the role of endogenous IL-22 in mice. That study induced AMI by ligating the left coronary artery in wild-type and IL-22 knock-out mice, with a significantly lower survival rate in IL-22 knock-out animals due to a higher rate of cardiac rupture. Tang et al. [
19] assessed the effect of exogenous IL-22 in rats. They induced AMI by ADA ligation, followed by subcutaneous injection of 100 µg/kg/day of recombinant IL-22 (IL-22R) for seven days. Animals treated with IL-22R exhibited attenuated adverse ventricular remodeling and improved post-AMI cardiac function. It is noteworthy that the pharmacological inhibition of STAT3 also inhibited IL-22 [
19].
Zhang et al. [
17] evaluated 26 patients with non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI), 16 patients with unstable angina, 16 patients with stable angina, and 16 healthy controls. They reported significantly higher plasma IL-22 levels in AMI patients with NSTEMI (33.09 ± 6.53 pg/ml) than in patients with unstable angina (29.86 ± 3.49 pg/ml, p = 0.02), patients with stable angina (26.96 ± 3.09 pg/ml, p < 0.001), and healthy controls (24.16 ± 2.46 pg/ml, p < 0.001).
Opposing with the study by Zhang et al. [
17], this study exhibited lower IL-22 levels in patients with ACS. However, the clinical profile of our patients was also different. We analyzed STEMI cases undergoing PCCI, while Zhang et al. [
17] studied patients with NSTEMI and CCS. On the one hand, IL-22 levels may differ irrespective of total vessel occlusion or PPCI.
On the other hand, animal studies associated higher IL-22 levels with positive remodeling effects and increased survival, but the animals analyzed in those studies had no coronary reperfusion after AMI induction, which hinders comparisons with our model. The impact of coronary reperfusion on circulating IL-22 levels needs further clarification.
IL-22 is part of the IL-10 family and acts at a cellular level, mainly through the Jak/STAT pathway. It has a pro-atherogenic effect by inducing endothelial cells to produce ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 and stimulating monocyte recruitment [
7,
8]. STAT3 phosphorylation is induced after IL-22 binds with its receptors (IL-22R1 and IL-10R2) [
8].
After activation, STAT3 translocates to the nucleus, modulating the expression of its target genes [
20]. In humans, STAT3 pathway signaling directly relates to the expression of inflammatory mediators, which act in leukocyte activation and endothelial dysfunction progression [
13]. In animals, blocking this pathway may be associated with improved clinical prognosis [
13,
19].
To summarize, IL-22 appears to have an atherogenic effect in a stable coronary disease model in humans, and patients with NSTEMI had higher serum IL-22 levels than patients with CCS and healthy controls. In AMI-induced animal models, higher IL-22 levels were associated with better survival. This study confirmed that patients with STEMI undergoing PPCI had lower circulating IL-22 levels than healthy controls.
In the case of STEMI and PPCI, acute arterial occlusion causes myocardial ischemia and necrosis, triggering an inflammatory cascade whose severity depends on the anatomical territories involved [
6,
15,
21,
22]. We found no studies in the literature on IL-22 levels in patients with STEMI undergoing PPCI.
DM is a well-known risk factor for CAD. It is associated with a pro-inflammatory status that accelerates the onset of atherosclerosis. It is also an independent predictor of worse prognosis in patients with ACS [
23,
24]. Despite this, IL-22 levels had no correlation with DM in this study.
The role of IL-22 in patients with DM and STEMI is not clear. However, we can infer a crosstalk between these mediators because IL-22 is part of the IL-10 family. IL-10 decreases inflammation, potentially improving the treatment of DM2 by inhibiting pro-inflammatory factors and increasing peripheral sensitivity to insulin [
25]. Thus, new studies should investigate the synergism between IL-22 and IL-10 actions. Considering the lack of data on IL-22 in some subgroups of STEMI patients undergoing PPCI, future studies need to confirm our findings that patients with DBT < 60 minutes and with the RCA as culprit artery have lower IL-22 than controls.
The main limitations of this study include its single-center design, the inclusion of patients treated for STEMI with medications that can affect with IL-22 levels, the analysis of only a single IL22 dosage, and the lack of evaluation of the association between IL-22 levels and prognosis due to the low rate of clinical events after PPCI.
5. Conclusions
This study demonstrated that IL-22 levels were significantly lower in patients with STEMI compared to healthy controls.
Within the subgroups, patients with a door-to-balloon time (DBT) of less than 60 minutes and those with the right coronary artery (RCA) as the culprit artery exhibited lower IL-22 levels. However, CAD classification, angiography success, and the presence of diabetes mellitus (DM) did not influence serum IL-22 levels.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.F.C. and D.C.O.; methodology, A.F.C. and D.C.O.; formal analysis, all authors; investigation, all authors; data curation, A.F.C. and D.C.O.; writing—original draft preparation, A.F.C. and D.C.O; writing—review and editing, A.F.C. and D.C.O; validation, all authors; visualization, A.F.C. and D.C.O.; supervision, D.C.O.; project administration, D.C.O. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee of Cardiology Emergency Room of Pernambuco - University of Pernambuco (protocol code 29969220500005192 – January 4, 2022) for studies involving humans.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study .
Data Availability Statement
The data generated and analyzed during this study are included in this published article and are available from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the staff at the cardiological hospital and at the clinical research laboratory for supporting this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Lloyd-Jones, D.; Adams, R.; Carnethon, M.; De Simone, G.; Ferguson, T. B.; Flegal, K.; Ford, E.; Furie, K.; Go, A.; Greenlund, K.; et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics -2009 update: a report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation 2009, 119, e21–e181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libby, P. Mechanisms of acute coronary syndromes and their implications for therapy. N Engl J Med 2013, 368, 2004–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pober, J.S.; Sessa, W.C. ; Evolving functions of endothelial cells in inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol 2007, 7, 803–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, B.; Claessen, B. E.; Arnold, S. V.; Chan, D.; Cohen, D. J.; Giannitsis, E.; Gibson, C. M.; Goto, S.; Katus, H. A.; Kerneis, M.; et al. ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2019, 5, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergmark, B.A.; Mathenge, N.; Merlini, P.A.; Lawrence-Wright, M.B.; Giugliano, R.P. Acute coronary syndromes. Lancet 2022, 399, 1347–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, J. P.; Tan, L. L.; Zheng, H.; Lau, Y. H.; Chan, S. P.; Tan, K. B.; Chua, T.; Tan, H. C.; Foo, D.; Lee, C.W.; et al. First Medical Contact-to-Device Time and Heart Failure Outcomes Among Patients Undergoing Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes 2018, 11, e004699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.W.; Hu, Y.; Liu, J.; Yang, H.; Huang, P. Interleukin-22: a potential therapeutic target in atherosclerosis. Mol Med 2021, 27, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, Y.; Su, Z.; Xia, L. Effects of IL-22 on cardiovascular diseases. Int Immunopharmacol 2020, 81, 106277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutz, S.; Eidenschenk, C.; Ouyang, W. IL-22, not simply a Th17 cytokine. Immunol Rev. 2013, 252, 116–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, B.C.; Logsdon, N.J.; Walter, M.R. Structure of IL-22 bound to its high-affinity IL-22R1 chain. Structure 2008, 16, 1333–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mühl, H.; Bachmann, M. IL-18/IL-18BP and IL-22/IL-22BP: Two interrelated couples with therapeutic potential. Cell Signal 2019, 63, 109388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camaré, C.; Pucelle, M.; Nègre-Salvayre, A.; Salvayre, R. Angiogenesis in the atherosclerotic plaque. Redox Biol 2017, 12, 18–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Lv, J.; Yang, W.; Xu, B.; Wang, Z.; Yu, Z.; Wu, J.; Yang, Y.; Han, Y. Targeted inhibition of STAT3 as a potential treatment strategy for atherosclerosis. Theranostics. 2019, 9, 6424–6442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chesebro, J. H.; Knatterud, G.; Roberts, R.; Borer, J.; Cohen, L. S.; Dalen, J.; Dodge, H. T.; Francis, C. K.; Hillis, D.; Ludbrook, P. Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction (TIMI) Trial, Phase I: A comparison between intravenous tissue plasminogen activator and intravenous streptokinase. Clinical findings through hospital discharge. Circulation 1987, 76, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torquati, L.; Coombes, J. S.; Murray, L.; Hasnain, S. Z.; Mallard, A. R.; McGuckin, M. A.; Fassett, R. G.; Croci, I.; Ramos, J. S. Fibre Intake Is Independently Associated with Increased Circulating Interleukin-22 in Individuals with Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrients 2019, 11, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Tang, R.; Lu, Y.; Wang, W.; Xiao, C.; Meng, T.; Ao, X.; Li, X.; Peng, L.; Kwadwo Nuro-Gyina, P.; Zhou, Q. Irbesartan may relieve renal injury by suppressing Th22 cells chemotaxis and infiltration in Ang II-induced hypertension. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020, 87, 106789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, T.; Wang, X. Q.; Du, R. Z.; Zhang, K. N.; Liu, X. G.; Ma, D. X.; Yu, S.; Su, G. H.; Li, Z. H.; Guan, Y. Q.; Du, N. L. Elevated frequencies of circulating Th22 cell in addition to Th17 cell and Th17/Th1 cell in patients with acute coronary syndrome. PLoS One 2013, 8, e71466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, M.; Yasukawa, H.; Takahashi, J.; Nohara, S.; Sasaki, T.; Shibao, K.; Akagaki, D.; Okabe, K.; Yanai, T.; Shibata, T.; Fukumoto, Y. Endogenous interleukin-22 prevents cardiac rupture after myocardial infarction in mice. PLoS One 2023, 18, e0286907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, T. T.; Li, Y. Y.; Li, J. J.; Wang, K.; Han, Y.; Dong, W. Y.; Zhu, Z. F.; Xia, N.; Nie, S. F.; Zhang, M.; et al. Liver-heart crosstalk controls IL-22 activity in cardiac protection after myocardial infarction. Theranostics 2018, 8, 4552–4562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linton, M.F.; Moslehi, J.J.; Babaev, V.R. Akt Signaling in Macrophage Polarization, Survival, and Atherosclerosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2019, 20, 2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazel, R.; Joseph, T. I.; Sankardas, M. A.; Pinto, D. S.; Yeh, R. W.; Kumbhani, D. J.; Nallamothu, B. K. Comparison of Reperfusion Strategies for ST-Segment-Elevation Myocardial Infarction: A Multivariate Network Meta-analysis. J Am Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e015186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D. W.; Clare, R. M.; Schulte, P. J.; Pieper, K. S.; Shaw, L. K.; Califf, R. M.; Ohman, E. M.; Van de Werf, F.; Hirji, S.; Harrington, R. A.; et al. Extent, location, and clinical significance of non-infarct-related coronary artery disease among patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction. JAMA 2014, 312, 2019–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faludi, A. A.; Izar, M. C. O.; Saraiva, J. F. K.; Chacra, A. P. M.; Bianco, H. T.; Afiune, A.; Neto, A.A.; Bertolami, A. , Pereira, A. C., Lottenberg, A. M., et al. Atualização da Diretriz Brasileira de Dislipidemias e Prevenção da Aterosclerose – 2017. Arq Bras Cardiol 2017, 109 (2 Supl 1), 1–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, K.; Wang, S.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, L. The association between interleukin family and diabetes mellitus and its complications: An overview of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2024, 210, 111615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, E. G.; Ko, H. J.; Cho, Y. R.; Kim, H. J.; Ma, Z.; Yu, T. Y.; Friedline, R. H.; Kurt-Jones, E.; Finberg, R.; Fischer, M. A.; et al. Interleukin-10 prevents diet-induced insulin resistance by attenuating macrophage and cytokine response in skeletal muscle. Diabetes 2009, 58, 2525–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).