1. Introduction
As communication technologies and the Internet of Things (IoT) continue to evolve, we are witnessing an expanding array of wireless device applications across diverse sectors. These include autonomous navigation, virtual reality (VR), intelligent urban planning, and telemedicine procedures [
1]. Such applications demand substantial computational resources and are highly sensitive to latency [
2,
3]. However, they are often constrained by the limited processing capabilities and finite battery life of mobile devices [
4]. Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) has emerged as a promising solution to address these constraints, which is a distributed computing paradigm that enhances the computational capabilities of networks. By decentralizing computational and storage resources to the edge of the network, in close proximity to end-users, MEC facilitates the offloading of computation-intensive tasks from wireless devices to nearby servers [
5]. This approach not only conserves energy on mobile devices but also significantly reduces execution latency, thereby enhancing the performance and user experience of latency-sensitive applications[
6].
However, the constraint of limited battery capacity in mobile devices poses a substantial challenge, particularly given the logistical difficulty of regularly replacing batteries in a vast number of devices. To address this challenge, Wireless Power Transfer (WPT) has been proposed as a sustainable energy solution [
7]. In a Wireless Powered Mobile Edge Computing (WPT-MEC) network, a Hybrid Access Point (HAP) serves as the conduit for broadcasting Radio Frequency (RF) energy to wireless devices. Leveraging Energy Harvesting (EH) technology, edge devices can transduce the received RF signals into usable energy to recharge their batteries [
8]. This harvested energy then enables the devices to accomplish computation tasks either locally or by offloading them to MEC servers. By exploiting WPT, it is possible to simultaneously extend the battery lifespan of the devices and significantly enhance their computational capabilities [
9].
In a WPT-MEC network, Energy Efficiency (EE) is a critical performance indicator, defined as the ratio of data processed to the energy consumed by the system [
10,
11]. For instance, the authors in [
11] introduced two iterative-based optimize algorithms aiming to maximize the computational efficiency of MEC system, considering both partial and binary offloading modes. [
10] addressed the EE-delay tradeoff problem in a multi-user WPT-MEC network and proposed an online task offloading algorithm based on Lyapunov optimization method and convex optimization theory. [
12] leveraged stochastic network optimization technique to design a task offloading scheme to optimize the network EE for in the device-to-device (D2D)-aided WPT-MEC system. However, these studies have not considered the double-near-far effect, which can significantly impact edge mobile nodes situated far from the HAP. When a mobile device (MD) is placed at a considerable distance from the HAP, it can result in degraded channel conditions due to the increased communication distance and reduced energy harvesting. This degradation can subsequently cause inefficient data transmission due to signal interference between MDs in close proximity and those further away.
Cooperative computing schemes have been introduced to mitigate the impact of the double-near-far effect [
4,
7,
13,
14,
15]. These schemes leverage relay technology, where devices closer to the AP act as relays to transmit signals for devices situated further away, thereby enhancing data rates under unfavorable channel conditions. For example, [
13] proposed an iterative algorithm to minimize the AP’s total transmit energy, subject to computational task constraints. [
4] tackled the user-cooperation problem for maximize the EE for a WPT-MEC integrated with Backscatter communication. However, these works mainly focused on immediate network performance and usually assume that a priori the load level at the edge node can be obtained, neglecting the dynamics of task arrival, battery level rate, and time-varying wireless channel. In a volatile network environment, the dynamic allocation of resources and task offloading for edge and auxiliary nodes become significantly challenging.
This study focus on the problem of maximizing energy efficiency in a user-cooperation WPT-MEC network by jointly considering stochastic task arrival and dynamic wireless channel variations. Furthermore, we integrate a battery to store the harvested energy for both the MD and the helper node. The problem presents significant challenges in two main aspects. First, the unpredictability of task arrivals and the randomness of channel states on both the data transmission and wireless charging channels result in a stochastic optimization problem. Second, the time coupling among wireless charging duration, task offloading at edge node, and task processing at helper node poses a great challenge in finding the optimal solution. To tackle this problem, we formulate it as a stochastic programming problem. By leveraging Dinkelbach’s method [
16] and Lyapunov optimization technique[
17] , we transform the stochastic optimization problem into a deterministic problem for each slot. This problem, while non-convex, is then converted into a convex problem using variable substitution and convex optimization techniques. We proposed an efficient online control algorithm, the Dynamic Offloading for User Cooperation Algorithm (DOUCA) , which can be easily implemented and operates without prior knowledge of future system information.
1.1. Related Work
WPT-MEC has garnered significant attention from researchers since it helps alleviate energy limitations of IoT nodes while ensuring real-time performance of mobile applications [
18,
19,
20]. The authors of [
19] proposed an energy-saving scheme for a multi-user NOMA-assisted cooperative terahertz single-input multiple-output (SIMO) MEC system that aims to maximize the total user computation energy efficiency (CEE). In [
20], an energy efficiency maximization algorithm based on multi-agent deep reinforcement learning was introduced. This algorithm enhances the computation offloading strategy to achieve maximum energy efficiency in MEC-supported vehicular networks. In [
7], the authors addressed the practical nonlinear energy harvesting (EH) model by jointly optimizing various factors such as computation frequency, execution time of MEC servers and IoT devices, offloading time, EH time, transmission power of each IoT device, and power beacons (PB). Additionally, the authors of [
21] proposed a distributed sleep control method, which autonomously decides whether to enter sleep mode, thereby reducing energy consumption and improving energy efficiency.
To mitigate the double-near-far effect and fully utilize available resources, many researchers focus on user cooperation-assisted WPT-MEC networks [
4,
9,
22,
23]. In [
23], the authors proposed an algorithm to maximize computational efficiency for a user cooperation (UC) and non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) WPT-MEC network, taking into account a nonlinear energy harvesting model. The authors in [
4] propose an innovative UC scheme integrating BackCom and AC to maximize user energy efficiency by leveraging a helper node as a relay between the source node and the HAP. In [
24], a user cooperation scheme for a WPT-assisted NOMA-MEC network is developed to minimize the total energy consumption of the system using the Lagrangian method to convert the non-convex optimization problem into a convex one. In [
25], the authors propose a novel multi-user cooperation scheme to maximize the weighted sum computation rate by considering partial task offloading and orthogonal frequency-division multiple access (OFDMA) communication technology. Due to the constraints of time-varying network environments, achieving a long-term stable optimal solution remains a significant challenge.
In volatile network environments, more and more research focuses on achieving long-term average system performance [
1,
15,
26,
27]. In [
26], the authors proposed an online algorithm to minimize energy consumption based on the Lyapunov optimization framework and meta-heuristic methods. In [
27], the authors introduced a deep reinforcement learning (DRL) algorithm to minimize long-term energy consumption and employed a concave-convex procedure (CCCP) algorithm to solve the computation and communication resource sub-problem for a MEC system with non-complete overlapping non-orthogonal multiple access (NCO-NOMA) technology. In [
28], the authors proposed a dynamic optimization scheme based on queuing theory for a 5G MEC heterogeneous network with multiple energy-harvesting MDs, aiming to minimize the average execution delay of the system. In [
29], the authors proposed a multi-agent reinforcement learning algorithm that combines federated learning and adopts a fine-grained training strategy to accelerate convergence in a dynamic community-based MEC environment. Unlike the aforementioned studies, this paper addresses the challenges of task offloading and user cooperation in dynamic WPT-MEC network environments. We consider the dynamic arrival of tasks, time-varying wireless channel conditions, and the time-slot coupling of battery levels. Additionally, the time coupling between user cooperative communication and wireless charging, as well as the data offloading coupling in cooperative communication, further complicate the problem.
1.2. Motivations and Contributions
In this paper, we address the problem of long-term energy efficiency optimization in a user-cooperation WPT-MEC network by taking into account the uncertain load dynamic at edge node and time-varying wireless channel state, which has not been extensively investigated in the literature. The main contributions of our work are summarized as follows:
We formulate the dynamic task offloading problem aiming to maximize the system energy efficiency for a WPT-MEC network. This is achieved by leveraging user cooperation to mitigate the double-near far effect. We extend the existing models in [
4,
13] to accommodate volatile network environments, eliminating the need for prior knowledge of stochastic task arrival and time-varying wireless channel states. Our model deftly balances the stability of the system network with energy efficiency, thereby providing enhanced flexibility and better alignment with real-world application scenarios.
We propose DOUCA, a low-complexity online control algorithm designed to maximize long-term UEE, based on Lyapunov optimization theory. Utilizing the drift-plus-penalty technique, we decouple the stochastic programming problem into a non-convex deterministic optimization sub-problem for each slot. Through the use of variable substitution and convex optimization theory, we transform the sub-problem into a convex problem that contains a small number of variables, enabling efficient solutions. Furthermore, we provide a rigorous theoretical analysis to demonstrate its performance.
We conduct extensive simulations to evaluate the effectiveness and practicality of our proposed algorithm on the impact of control parameter V, network bandwidth, task arrival rate, and geographical distance on energy efficiency and network stability. The results demonstrate that our algorithm achieves 20% higher efficiency than baseline algorithms and can achieve an explicit EE-stability tradeoff.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows. Section II presents the system model of the user-cooperation WPT-MEC network and formulates a stochastic programming problem. In Section III, we employ the Lyapunonv optimizing technique to solve the problem and propose an efficient online algorithm, accompanied by a theoretical performance analysis. In Section IV, simulation results are presented to evaluate the proposed algorithm. Finally, Section V concludes our work and discusses the future directions.
2. System Model
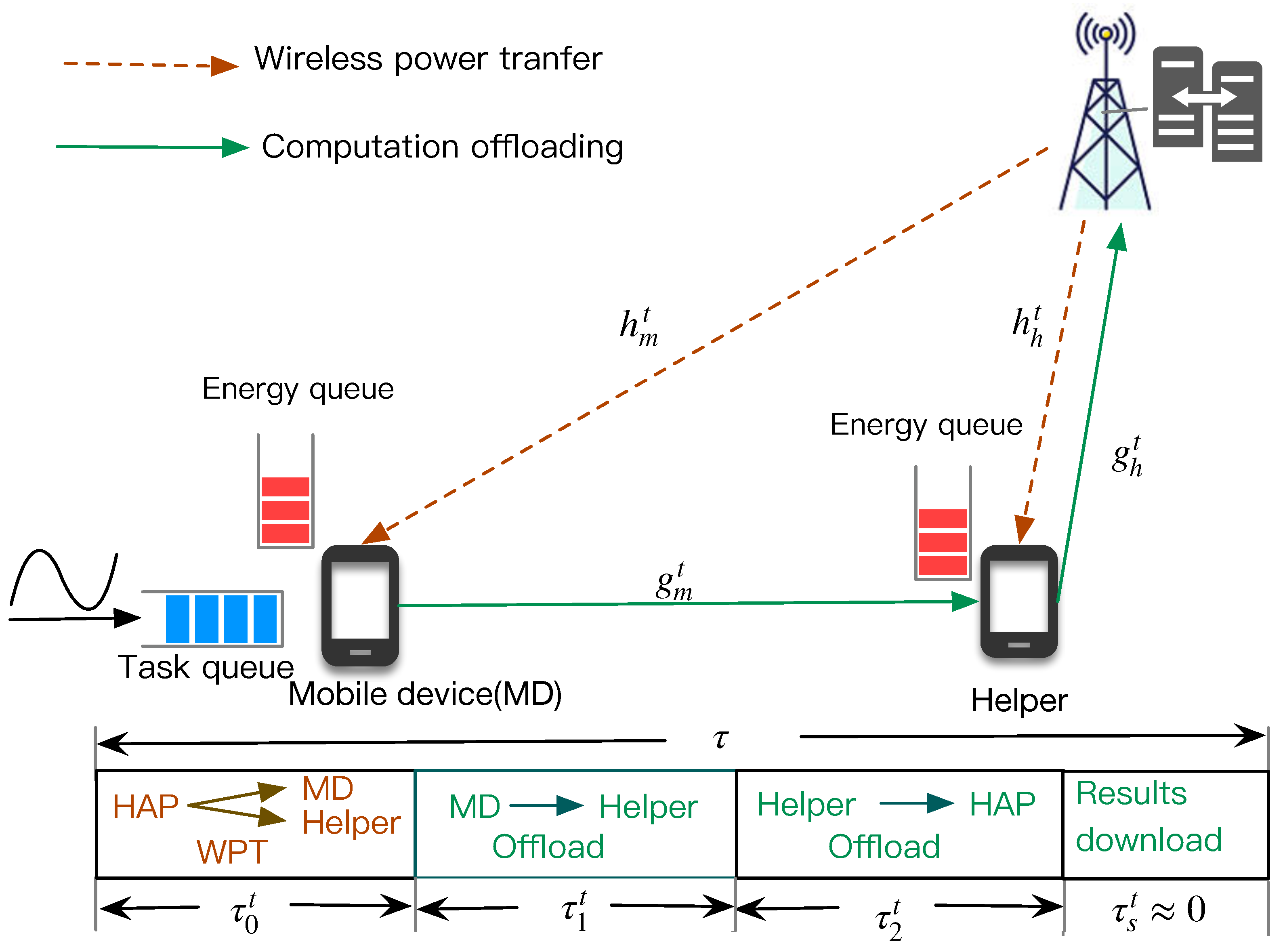
As illustrated in
Figure 1, the WPT-MEC system comprises two MDs and a HAP. One MD, situated at a considerable distance from the HAP, is burdened with a substantial computational workload. The other MD, in proximity to the HAP and in an idle state, acts as a helper. Both MDs operate on the same frequency band and are equipped with integrated batteries for energy storage. The HAP is fitted with a RF energy transmitter and a MEC server, which provide wireless energy and computation offloading services to edge nodes within the base station’s coverage. To mitigate mutual interference, each MD employs a Time-Division Duplexing (TDD) approach to alternate between communication and energy harvesting operations.
We adopt a discrete time-slot model over a time horizon divided into
T time blocks, each of duration
. At the commencement of each time slot, both nodes harvest energy from the RF signals emitted by the HAP, which is then stored in their batteries to facilitate subsequent data transmission or local task execution. A partial offloading strategy is implemented, allowing for the flexible offloading of a portion or the entirety of the computational data to a remote device. Due to poor channel conditions between the distant MD and the HAP, exacerbated by the double near-far effect, direct offloading to the MEC server is infeasible. Consequently, the MD offloads computation data to the helper, which then relays it to the HAP. The helper processes the offloaded tasks or further offloads a segment to the HAP. Upon completion, the HAP returns the computation results to the MD, facilitated by the helper. The key notation and definitions are list in
Table 1.
2.1. Wireless Powered Model
The HAP is equipped with a reliable power source and is responsible for transmitting RF energy to the array of WDs dispersed within its service area. In the first part of each time slot, the HAP broadcasts wireless energy to the MD and the helper for a
amount of time. Let
,
denote the harvested energy of MD and helper from HAP at time slot
t respectively. So we have
and
where
represents the energy conversion efficiency, and
denotes the RF energy transmit power of the HAP.
and
denote the channel gain between the MD and HAP, between the helper and HAP, respectively, which remain constant within the same time slot and vary across different time frames.
2.2. Task Offloading Model
As depicted in
Figure 1, the task data arrival at MD in
tth time slot is denoted as
, which is assumed that
follows an independent and identically distributed (i.i.d.) in different time slots with exponential distribution with mean
, e.g.
. The generated computation task at time slot
t will be placed in the data queue
Q at MD and waiting for process in a First Come First Server(FCFS) manner. Let
denote the backlog of the data queue at slot
t. Thus, the data queue update can be denoted as:
where
denotes the total data process at MD at slot
t.
represents the data of task executed by the MD locally, and
denotes the task offloaded to the helper by wireless transmission.
Let
denote local CPU frequency at MD, a constant value, and
represent the CPU cycles required to compute one bit task at MD. The raw data (in bits) processed locally on MD at slot
t is
Note that here
is a constant value, so we rewrite
as
. Meanwhile, the corresponding energy consumed for local computing at slot
t is
where
denotes the computing energy efficiency parameter, which depends on the circuit structure. Here we adopt the partial task offloading strategy, which means a portion of task data will be offloaded the helper. Let
denote the transmit power of MD, which is constrained by the maximum power
, and
is the amount of offloading time for MD. Thus, according to Shannon’s theorem, the offloading data to the helper can be expressed as
where
W denotes the channel bandwidth,
denotes the channel gain from MD to helper at slot
t, and
is additive white Gaussian noise. Here there is an upper bound of
, that is
, The corresponding energy consumption for task offloading is
The MD maintains an energy queue to store the harvested energy from HAP for local computation and task offloading, the energy queue
evolved as follows:
where
, represents the total energy consumption of MD at slot
t and
represents the maximum battery capacity of MD.
2.3. User Helper Model
We assume that the helper also adopts the partial offloading mode, which means the helper can process the offloading task from MD, while offloading computation task to the edge server. After the initial (
) time, offloading task have arrived the helper, the helper should determine the transmission power
to offloading data to edge server. Similar to the MD, the amount of local computing task data and the corresponding energy consumption at helper at slot
t can be derived as
where
denote local CPU frequency at helper, and
represent the CPU cycles required to compute one bit task at helper. The amount of offloading data to edge server and the corresponding energy is
where
denotes the transmit power of helper and
represents the channel gain from helper and HAP at slot
t. Note that here the helper must process the total offloading task data from MD at at each slot
t, so there is not a data queue at the helper, and we have the following constraint
Similar to the MD, the helper also maintains an energy queue
to store the harvested energy from HAP to support the local computing and task offloading, the battery level of helper updates as
where
, represents the amount of energy consumption of helper at slot
t and
represents the maximum energy can be stored in the battery of helper.
2.4. Network stability and Utility
Definition 1.(Queue Stability): The task data queue is strong stable if it satisfies
The network utility here is defined as the ratio of the total achieved computation data to the total energy consumption, The total accomplished computation data and the total energy consumption of user-assisted network at slot
t can be expressed as, respectively
The EE of the network is defined as the time-average achieved computation data by using a unit energy consumption, which is define as the ration of the long term processed data to the total energy consumption as follows:
2.5. Problem Formulation
In this paper, our objective is to design a dynamic control algorithm that maximizes the time-average network EE for a user-assisted WPT-MEC system, all under the constraint of network stability. For each time slot, we make decisions regarding the time allocation for WPT, task offloading time to the helper, task processing time at the helper, and transmit power at MD and helper, without knowing the future channels and data arrivals. Let
denote the time allocation at slot
t and
denote the transmit power of MD and helper. The problem can be formulated a multi-stage stochastic optimization problem as follows:
Constraint (18b) represents the time allocation constraint. Constraints (18c) and (18d) correspond to the battery energy constraints for MD and helper, respectively, indicating that the energy level in the battery must be greater than zero. Constraint (18e) ensures the network stability of the system. (18f) defines the upper bound of the data processed at slot t, meaning that the amount of data processed will not exceed the length of the current data queue Q. Constraint (18g) ensures that the data offloaded to the helper should be completely processed within the current time slot.
Problem P0 is a fractional optimization problem, which is typically non-convex. To handle this, we first utilize the Dinkelbach method [
30] to transform P0 into a more manageable problem, similar to [
31]. We denote the optimal value of
as
and obtain the following Theorem 1.
Theorem 1.
The optimal is achieved if and only if
Proof. For brevity, here we omit the proof details. See Proposition 3.1 of [
32]. □
Since
is unknown during the solution process, (18) is still infeasible to tackle. In accordance with the methodology employed in [
33], we introduce a new parameter
and define it as
We set
at the beginning of the problem. Replacing
in (18), the problem P1 can be transformed into
where
is a given parameter that should be updated through the resolution process. It should be noted that
obtained by (
20) will get closer to
as time goes by [
12]. Therefore, this transformation is reasonable and has the same optimal solution with P0.
3. Algorithm Design
To decouple the battery energy level across time slots and ensure the stability of task queue , we leverage the Lyapunov network optimization technique to transform the long-term average problem in to a deterministic optimization problem for each time slot.
3.1. Lyapunov Optimization Formulation
To simply the battery energy queue at MD and helper, we introduce two virtual queues
and
. Following the Lyapunov optimization framework, we define a combined queue vector
and the quadratic Lyapunov function as:
Then, we obtain the one-period conditional Lyapunov drift [
34] as follows:
Note that
represents the congestion of all queues
,
and
. According to the Lyapunov optimization theory [
34], we derive the one slot drift-plus-penalty expression as
where control parameter
V is a positive value, used to balance the trade-off between network EE and network stability. Actually,
V acts as a weighting factor of the cost optimality in the drift-plus-penalty expression. Increasing the value of V implies algorithm pay more attention to the network EE , that also means resulting in a larger backlog of task queue
Q. We derive an upper bound of
as Lemma 1.
Lemma 1.
For any controlstrategy
at each time slot
t, the one slot Lyapunov
drift-plus-penalty is bounded by the following inequality:
where B is a constant that satisfies the following :
Proof. By using the inequality
,
and combining Eq. (
3), we have
Based on the definition of battery energy queue
and
, we have
Combining the above inequalities (
27), (
28) and (
29), we obtain the upper bound of the Lyapunov drift-plus-penalty. □
According to the drift-plus-penalty technique in Lyapunov optimization theory [
34], we seek to greedily minimize the upper bound of
at each time slot
t, then we can obtain a close-to-optimal solution of problem P2. Therefore, we transform problem P2 to a minimization problem of the RHS (right hand side) of (
25). Note that we can observe the value of
,
,
and
at the beginning of each slot
t, so we can solve the optimizing problem at each slot. Then the one time slot problem can be represented as
The proposed problem P2.1 is a non-convex problem and can not be easily solved by classic convex optimization methods. To address this issue, we first introduce auxiliary variables
and
. Then the problem P2.1 can be simplified as:
where
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
. The problem P2.2 is still a non-convex problem due to the non-convex constraint (31f). In (31f), both sides of the equation is concave that do not satisfy the the conditions for convex constraints. We introduce auxiliary variable
to replace the concave function
.
satisfies
Bring in
and constraint (
32), the problem P2.2 can be transformed into
Lemma 2. when the problem P3 reaches the optimal solution, which is consistent with P2. P3 is a convex optimization problem, which can be efficiently solved by convex optimization tools, such as CVX[35].
Proof.
step1. Assuming that , we can reduce the objective function by simply increasing to . Thus, a better solution is found.
step2. In problem P3, the objective function (
33a) is linear with respect to all variables. Constraints (33b)-(33d) and (33g) are all linear inequality constraints. What’s more, for constraint (33e),
is the perspective of
, which is a concave function of
. Since the perspective operation preserves convexity [
36],
is concave with respect to
and
. It is obvious that
and
are linear functions. Thus, the (33e) is a convex constraint. For the same reason,
in (33f) is concave with respect to
and
so that (33f) is a convex constraint. Thus P3 is proved to be convex. □
According to Lemma 2, at each time slot, we only need to solve a convex problem, P3, which contains a small number of variables. By doing so, we can achieve optimal long-term average EE, even without knowledge of future system information. Our proposed algorithm, the Dynamic Offloading for User Cooperation Algorithm (DOUCA), is summarized as Algorithm 1.
|
Algorithm 1: Dynamic Offloading for User Cooperation Algorithm (DOUCA) |
|
Input: the task arrical queue ; the channel gain , , , .
Output:
|
3.2. Algorithm Complexity Analysis
At each time slot, we are required to solve a simple convex optimization problem, P3, which contains only five decision variables. This can be efficiently solved using mature methods such as the interior point method, which has a computational complexity of approximately , where n is the number of decision variables. In our case, we efficiently solve P3 using CVX.
3.3. Algorithm Performance Analysis
In this section, we analyze that the proposed scheme can achieve the optimal long-term time-average solution. First, we give some assumptions as follows:
then, we can obtain that the expectation can also converge the same solutions
Lemma 3.
Based on (35)–(37), we have
To start with, we give the existence of the optimal solution based on the current queue status.
Lemma 4.
If the problem (P1) is feasible, there exists a policy that satisfies the following conditions :
where * represents the value under optimal solution.
Proof. See the parts 4 and 5 of [
17]. □
Theorem 2. The optimal long-average utility function obtained by P1 is limited by a lower bound that is independent with the time space. The following solutions can be achieved by the algorithm,
-
1.
-
2.
All queues , , are mean rate stable, and thus the constraints are satisfied
Proof. For any
, let us consider the policy and queue state in (42)–(44). Since the result values Em dm are independent of queue status
, we have
By integrating these results to (25) and making
, we have
Note that
is a constant value, which is independent of the current queue status
. Utilizing the iterated expectation and obtaining the sum of the above inequality over time
, we have
Dividing both sides of (63) by
, utilizing the Jensens inequality and the fact that
, we have
Furthermore, letting
, we have
considering
, we have
Furthermore we obtain
□
Theorem 3.
Let be the upper bound of , the time-average sum rate of queue length is bounded by
Proof. By taking iterated expectation and using telescoping sums over
, we have
Dividing both sides of (69) by
, taking
, rearranging terms yield
□
Theorems 2 and 3 provide a rigorous mathematical performance analysis for our proposed algorithm. They demonstrate that the time-average
increases at a rate of
, while the queue length increases at a rate of
. The WPT-MEC system EE
can be improved by adjusting the value of
V.However, the time-average task queue
Q will increases with
V. Therefore, we can tune
V to achieve a
trade-off between
network EE and task queue length. According to Little’s low [
33], the latency is proportional to the time-average task queue length. This also implies that our proposed algorithm can achieve a EE-latency trade-off. This balance is critical in many real-world applications where both efficiency and response time are important.
4. Simulation Results
In this section, we conduct numerical simulation to evaluate the performance of our proposed algorithm. The simulation experiments were executed on a platform equipped with an Intel(R) Xeon(R) Silver 4116 CPU operating at 2.10 GHz, featuring 48 cores, and supplemented by four GeForce RTX 2080 Ti GPUs. We employed a free-space path-loss channel model, and the averaged channel gain
is denoted as
where
denotes the antenna gain,
MHz denotes the carrier frequency,
denotes the path loss exponent, and
in meters denotes the distance between two nodes. The time-varying WPT channel gain and task offloading channel gain
follows Reyleigh fading channel model, where
are the random channel fading factor following an exponential distribution with unit mean. Let
represents
. For simplicity here, we assume that
and the channel gains remain the same in a single slot. The interval between task arrivals follows an exponential distribution with a constant average rate
. The other parameters are set similar to [
37] and listed in
Table 2.
4.1. Impact of System Parameters on Algorithm Performance
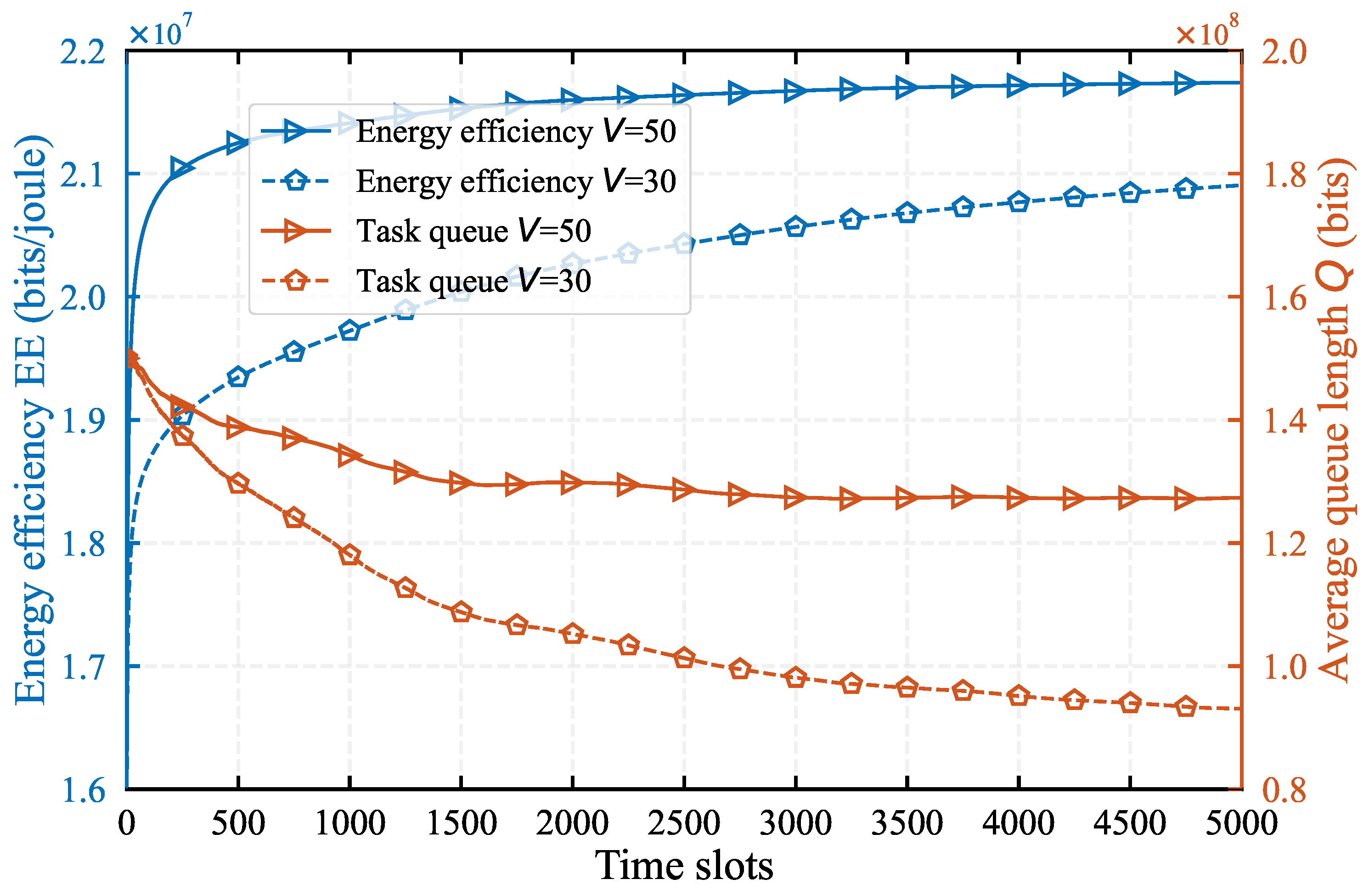
Figure 2, illustrates the variation curves of EE and average task queue length
Q over the 5000 time slots under different control parameters
and the task arrival rate
Mbps. As shown in
Figure 2, the EE exhibits significant fluctuations during the initial phase, but as time goes on, the curve gradually stabilizes and rapid convergence. Meanwhile, the task queue length
Q decreases with time slot
t increasing and becomes stable over time, demonstrating the effectiveness of our proposed algorithm. Furthermore, we observe that larger control parameter
V result in higher EE. However, the average queue length also increases accordingly, which is consistent with the theoretical analysis of algorithm.
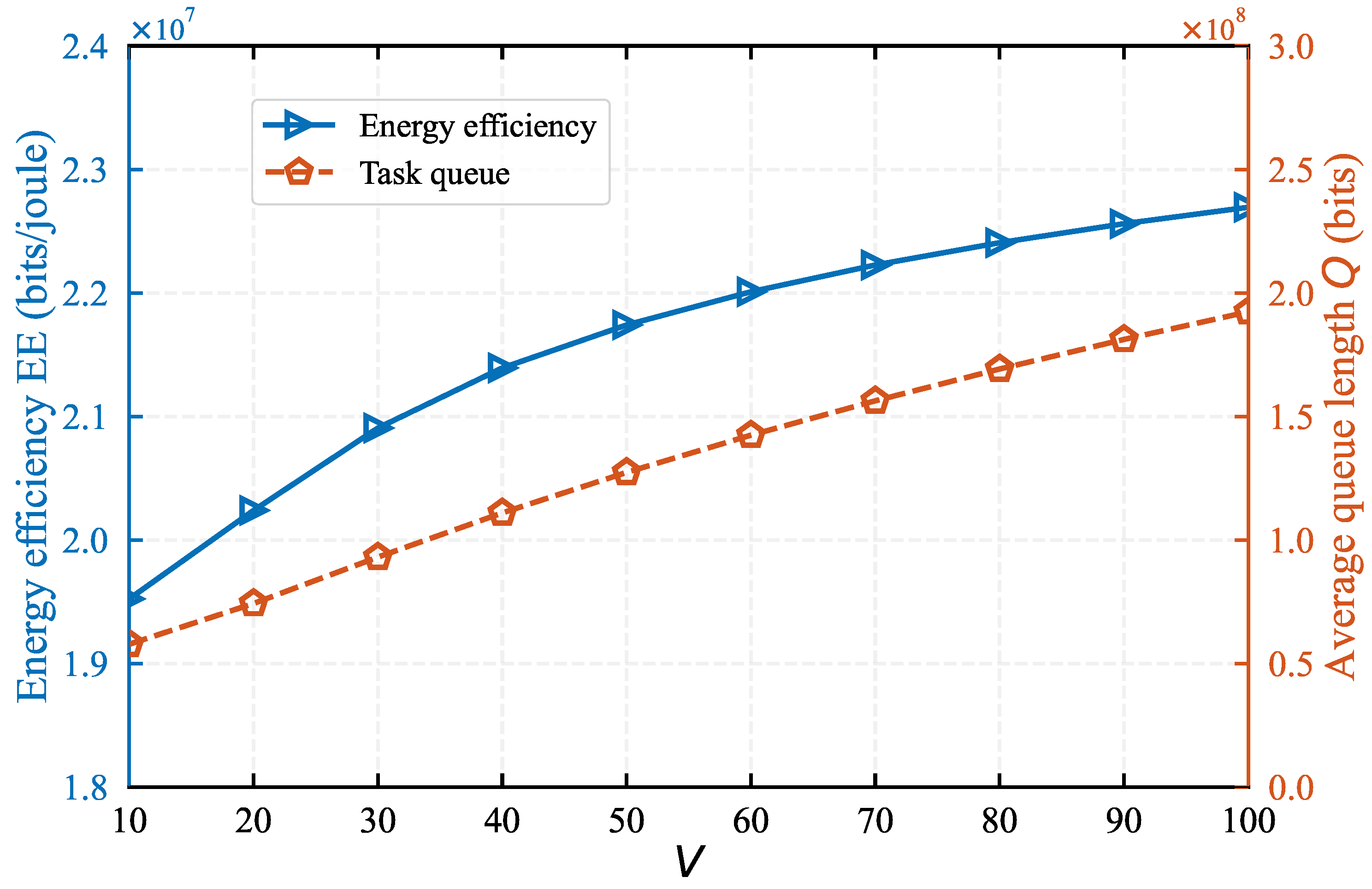
Figure 3 demonstrates the influence of control parameter
V on EE and average task queue length. We find that as
V increases from 10 to 100, the EE escalates from
bits/joule to
bits/joule, while the backlog of queue
Q expands from
bits to
bits. This trend signifies that both EE and queue length augment with an increasing
V. This is because with the increasing of the value of
V, our algorithm will focus towards to optimize EE, and paying less attention to the network queue stability. Here,
V acts as a knob to balance the trade-off between EE and network queue stability.
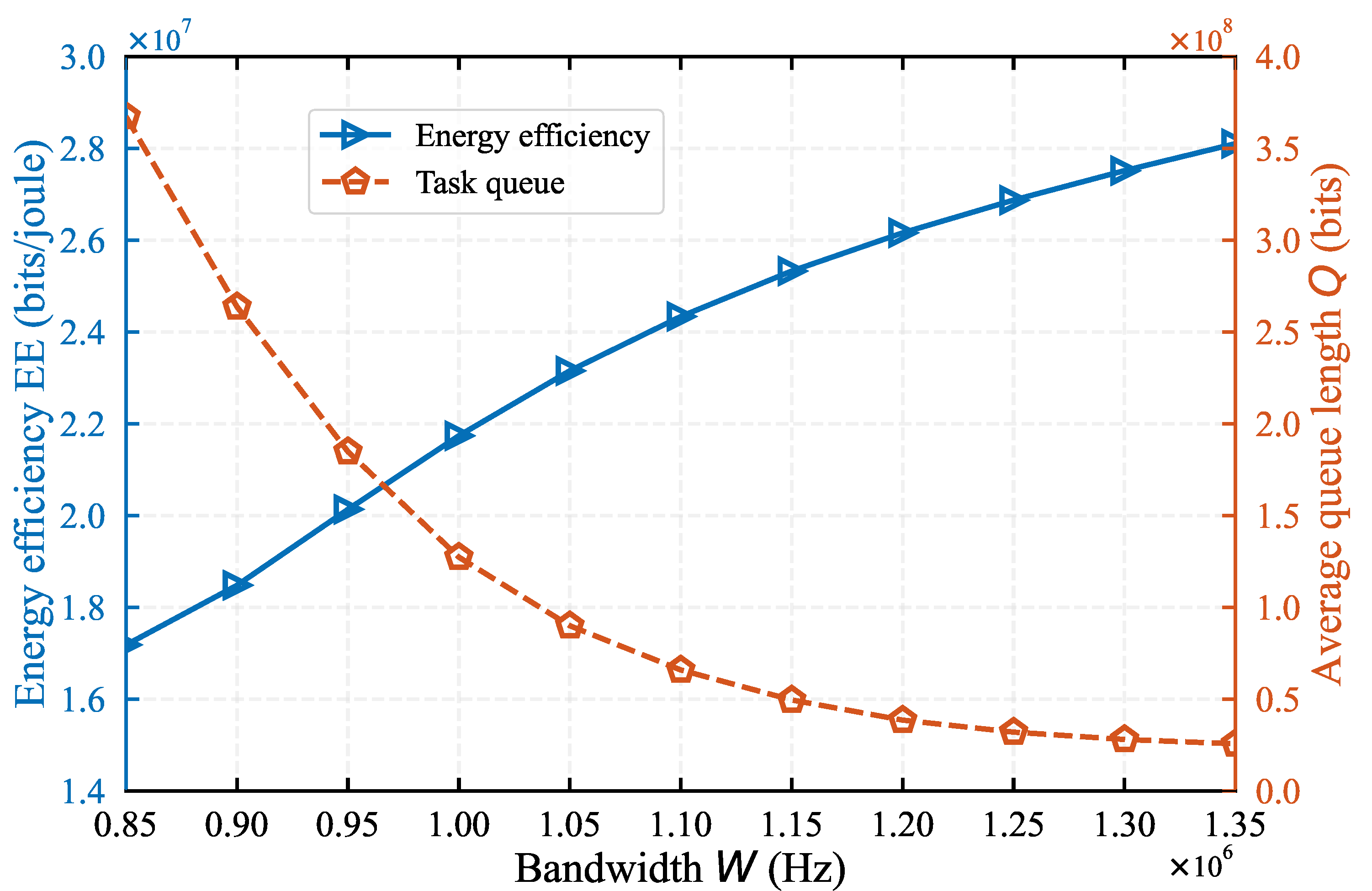
In
Figure 4, we evaluate the the impact of network bandwidth
W on system performance under
. As the network bandwidth
W increases from
Hz to
Hz, the EE rises from
bits/joule to
bits/joule, while the task queue length
Q decreases from
bits to
bits. This is because the increase in network bandwidth improves the speed of task data upload, enabling more tasks to be offloaded to the helper and HAP. Consequently, the amount of tasks processed at MD also increases, leading to a rise in energy efficiency. Additionally, the increased network bandwidth enhances the MD’s data processing rate, contributing to the reduction in task queue length. Moreover,
Figure 4 shows that when the network bandwidth is below 1, the variation in bandwidth has a more significant impact on the task queue length than on EE. Conversely, when the bandwidth exceeds 1, its variation has a greater impact on EE. This analysis indicates that appropriately increasing the network bandwidth can significantly enhance system performance.
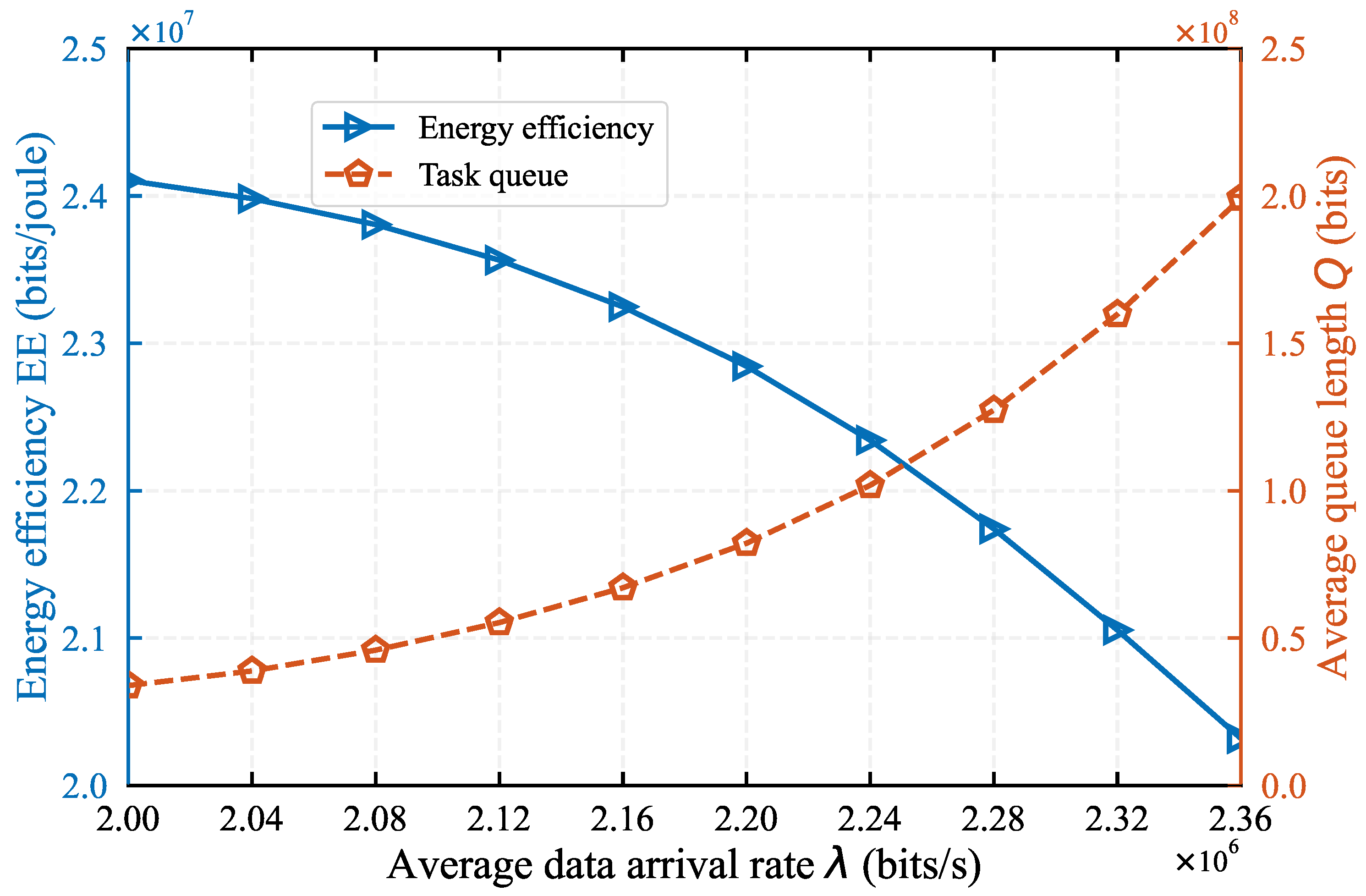
In
Figure 5, we evaluate the impact of task arrival rate
on system performance when
. As observed in
Figure 5, an increase in task load corresponds to a decrease in EE while the task queue length
Q exhibits an increasing trend, which is consistent with real-world expectations. The reason is that as the task arrival load increases, the processing efficiency of both MD and helper remains unchanged, causing an accumulation of task data in the MD’s task queue. Furthermore,
Figure 5 indicates that when
exceeds
bits/s, the queue length
Q increases rapidly, while energy efficiency continues to decrease linearly. This analysis implies that an excessive load can negatively impact system performance. Consequently, it is crucial to either expand the bandwidth or improve the processing capacity of the MD to address this issue.
4.2. Comparing with Baseline Algorithms
To evaluate the performance of our algorithm we consider the following three representative benchmarks:
Edge computing scheme: The MD does not perform local computation and offloading all task to the helper and HAP.
Random offloading scheme: The MD randomly selects part of tasks to offload to the helper and HAP.
Equalized time allocation scheme: Allocate task offloading time equally to the MD and helper, which means in our model.
For fairness, it is essential to maintain network queue stability across all methods. Therefore, the three baseline approaches mentioned above are implemented based on the Lyapunov optimization framework.
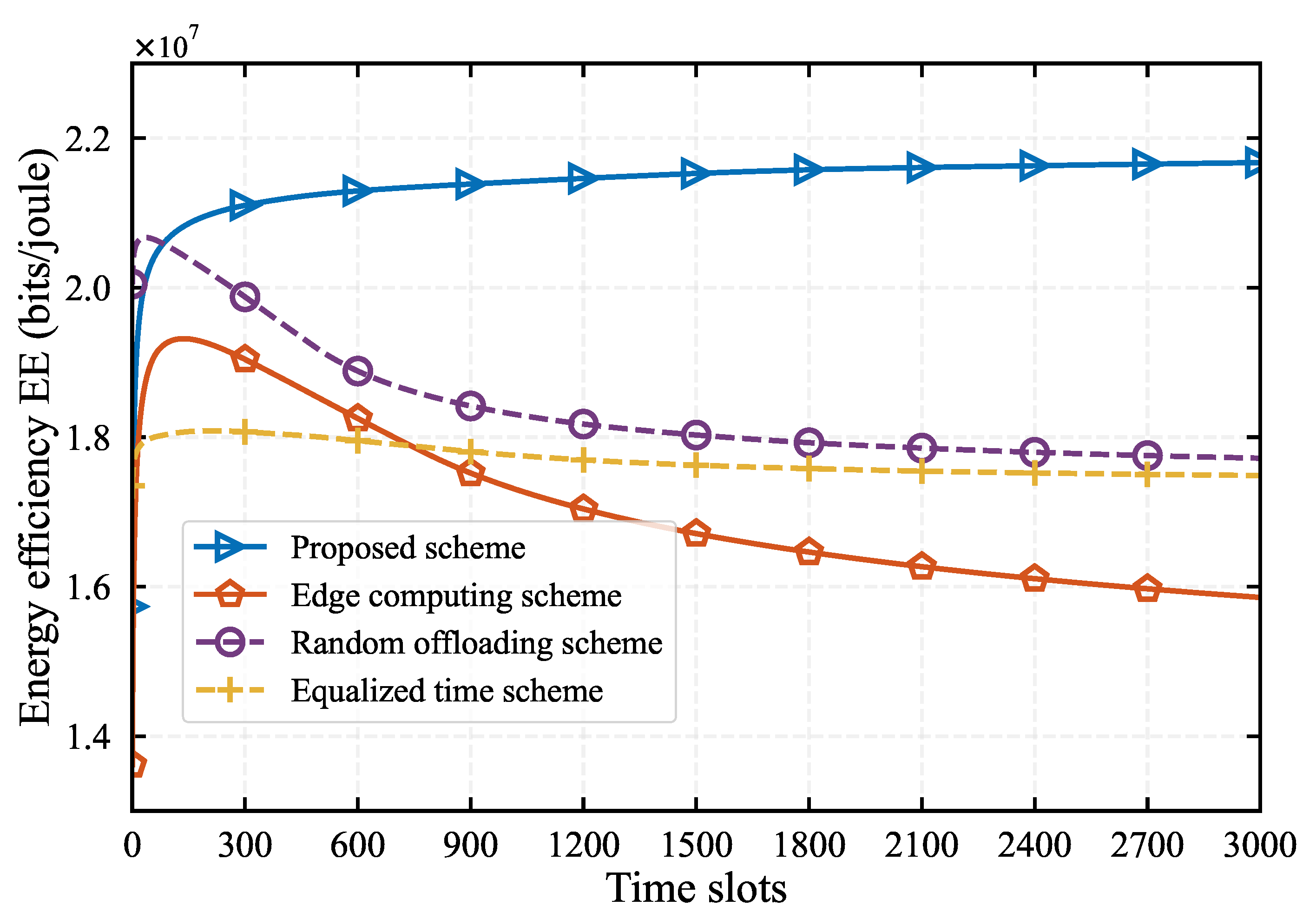
In
Figure 6, we evaluate the performance of our algorithm and the three baseline algorithms with the whole time period 3000 time slots under
. All algorithm converge after 1000 time slots. Our algorithm achieves the best EE, followed by the random offloading approach, with the equalized time allocation scheme ranking third, and the edge computing method performing the worst. Our algorithm outperforms the other three by 10%, 10%, and 20% respectively. This superior performance can be attributed to our algorithm’s consideration of the relationship among charging time, offloading time, and the helper’s cooperative time. It also leverages both the local computing resources of MD and the computing resources of the edge server. The edge computing method, which offloads all tasks to the edge server, only considers edge computing resources and overlooks the computing resources of the MD endpoint, resulting in inferior performance. The random offloading algorithm, which can utilize both edge server and local resources, ranks second in performance.Furthermore, the equalized time allocation method ignores priority of MD and Helper when offloading tasks, leading to an inefficient offloading process, and thus reducing the overall system performance.
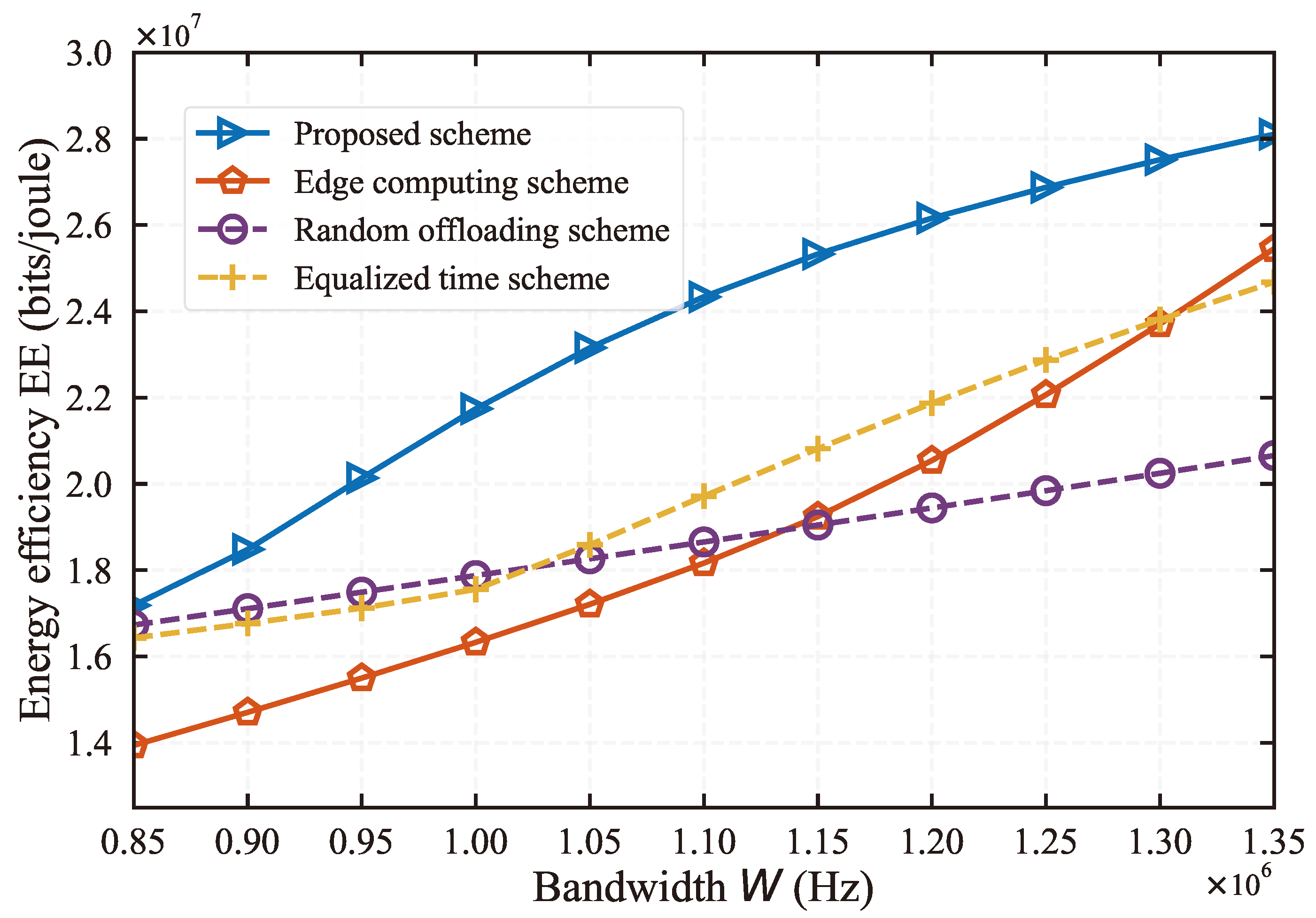
Figure 7 shows the impact of network bandwidth changes, ranging from
Hz to
Hz, on network performance across different algorithms. As can be seen from the figure, the EE achieved by all schemes increases with the growth of network bandwidth. This is because all schemes utilize edge computing resources for task computation, and an increase in bandwidth means more tasks can be uploaded to the edge server. This demonstrates the significant influence of network bandwidth on mobile edge networks. Furthermore, our algorithm consistently achieves the best EE across different bandwidths, demonstrating its superiority. Also, it can be seen from the figure that when the network bandwidth is around 1.0Mbps, the superiority of our algorithm is most evident, far exceeding that of other baseline algorithms.
In
Figure 8, we evaluate the system performance under different distance between MD and helper for all different algorithms, where the distance varies in
. We find that the EE of all algorithms decreases as the distance increases. Across all distances, our algorithm achieves the best EE. When the distance
m, our algorithm’s performance improves by 17%, 17%, and 31% compared to the other three algorithms, demonstrating that our algorithm can more effectively utilize network resources and edge computing resources. Additionally, it can be seen from
Figure 8 that as the distance increases, the advantages of EE achieved by our algorithm tends to decline. This suggests that in practical environments, the distance between edge node devices and relays should not be too large, as it could lead to a rapid decline in network performance.
5. Conclusions
The joint optimization of computation offloading and resource allocation in WPT-MEC systems poses a significant challenge due to the time-varying network environments and the time-coupling nature of battery charging and discharging. In this study, we concentrate on maximizing the long-term EE of a WPT-MEC system through user collaboration. We formulated an EE maximization problem that takes into account the uncertainty of load dynamics and the time-varying wireless channel. This problem presents substantial difficulties due to the coupling of multiple parameters. To address this issue, we propose an efficient online control algorithm, termed DOUCA. This algorithm employs Dinkelbach’s method and Lyapunov optimization theory to decouple the sequential decision problem into a deterministic optimization problem for each time slot. Extensive simulation results validate the effectiveness of our proposed algorithm, which achieves a remarkable improvement in energy efficiency compared to benchmark methods, striking a balance between EE and system stability. An intriguing direction for future research is to investigate scenarios with multiple MDs, which could further enhance the practicality and applicability of the system in real-world settings.
Author Contributions
Methodology, H.H.; Validation, Z.C. and L.S.; Formal analysis, H.H.; Investigation, H.H. and H.F.; Resources, H.H.; Data curation, H.H. and S.H.; Writing—original draft, H.H. and H.F.; Writing—review and editing, H.H.; Supervision, L.S. and S.H.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province, China (No.2021A0101180005).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
We thank all of the reviewers for their valuable comments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Wang, X.; Li, J.; Ning, Z.; Song, Q.; Guo, L.; Guo, S.; Obaidat, M.S. Wireless powered mobile edge computing networks: A survey. ACM Computing Surveys 2023, 55, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; He, H.; Shen, H.; Tian, H. Energy-Efficiency Maximization for Relay-Aided Wireless-Powered Mobile Edge Computing. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2024, 11, 18534–18548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, X.; He, H.; Shen, H. A Multi-Agent RL Algorithm for Dynamic Task Offloading in D2D-MEC Network with Energy Harvesting. Sensors 2024, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Wu, X.; He, Z.; Guizani, M. Energy efficiency maximization of backscatter-assisted wireless-powered MEC with user cooperation. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Sun, W.; Kato, N. Mobile-edge computation offloading for ultradense IoT networks. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2018, 5, 4977–4988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.C.; Patel, M.; Sabella, D.; Sprecher, N.; Young, V. Mobile edge computing—A key technology towards 5G. ETSI white paper 2015, 11, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, L.; Ye, Y.; Chu, X.; Lu, G. Computation energy efficiency maximization for a NOMA-based WPT-MEC network. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2021, 8, 10731–10744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zeng, M.; Mishra, D.; Hao, L.; Ma, Z.; Dobre, O.A. Latency minimization for IRS-aided NOMA MEC systems with WPT-enabled IoT devices. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, S.; Wu, J.; Liu, L.; Lan, D.; Taherkordi, A. Energy-efficient cooperative communication and computation for wireless powered mobile-edge computing. IEEE Systems Journal 2020, 16, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, S.; Leng, S.; Maharjan, S.; Zhang, Y. Energy Efficiency and Delay Tradeoff for Wireless Powered Mobile-Edge Computing Systems With Multi-Access Schemes. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 2019, PP, 1–1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Hu, R.Q. Computation efficiency maximization in wireless-powered mobile edge computing networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 2020, 19, 3170–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Xu, X.; Huang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Tao, X.; Zhang, P. Resource management for computation offloading in D2D-aided wireless powered mobile-edge computing networks. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2020, 8, 8005–8020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Wong, K.K.; Yang, K. Wireless powered cooperation-assisted mobile edge computing. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 2018, 17, 2375–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Bi, S.; Xing, H.; Lin, X. Collaborative Computation Offloading in Wireless Powered Mobile-Edge Computing Systems. 2019 IEEE Globecom Workshops (GC Wkshps), 2019, pp. 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Song, W.; Wang, Q.; Hu, R.Q.; Zhu, H. Energy Efficiency and Delay Tradeoff in an MEC-Enabled Mobile IoT Network. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2022, 9, 15942–15956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, S.P.; Vandenberghe, L. Convex optimization; Cambridge university press, 2004.
- Neely, M. Stochastic network optimization with application to communication and queueing systems; Springer Nature, 2022.
- Zhou, F.; Hu, R.Q. Computation Efficiency Maximization in Wireless-Powered Mobile Edge Computing Networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 2020, 19, 3170–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MEC, N.A.C.T.S. Energy-Efficient Optimization of Multi-User NOMA-Assisted Cooperative THz-SIMO MEC Systems 2023.
- Ernest, T.Z.H.; Madhukumar, A. Computation Offloading in MEC-Enabled IoV Networks: Average Energy Efficiency Analysis and Learning-Based Maximization. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lim, Y. Bio-inspired sleep control for improving the energy efficiency of a mec system. Applied Sciences 2023, 13, 2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Bi, S.; Xing, H.; Lin, X. Collaborative Computation Offloading in Wireless Powered Mobile-Edge Computing Systems. 2019 IEEE Globecom Workshops (GC Wkshps), 2019.
- Su, B.; Ni, Q.; Yu, W.; Pervaiz, H. Optimizing computation efficiency for NOMA-assisted mobile edge computing with user cooperation. IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking 2021, 5, 858–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Chen, J.; He, B.; Lv, L.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, L. Energy consumption minimization for wireless powered NOMA-MEC with user cooperation. 2021 13th International Conference on Wireless Communications and Signal Processing (WCSP). IEEE, 2021, pp. 1–5.
- Wu, X.; He, Y.; Saleem, A. Computation rate maximization in multi-user cooperation-assisted wireless-powered mobile edge computing with OFDMA. China Communications 2023, 20, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Chen, S.; Cui, Y.; Du, J. Efficient Trajectory Planning and Dynamic Resource Allocation for UAV-Enabled MEC System. IEEE Communications Letters 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Lin, S.; Hong, X.; Shi, J. DRL-Assisted Resource Allocation for Non-Completely Overlapping NOMA Based Dynamic MEC Systems. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Yuan, X.; Chen, D.; Zhang, N.; Sun, H.; Taherkordi, A. Multi-User Dynamic Computation Offloading and Resource Allocation in 5G MEC Heterogeneous Networks With Static and Dynamic Subchannels. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, W.; Guo, B.; Xu, L.; Duong, T.Q. Accelerating convergence of federated learning in mec with dynamic community. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinkelbach, W. On nonlinear fractional programming. Management science 1967, 13, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Bu, X.; Yang, K.; Wu, Z.; Han, Z. Green large-scale fog computing resource allocation using joint benders decomposition, Dinkelbach algorithm, ADMM, and branch-and-bound. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2018, 6, 4106–4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zappone, A.; Jorswieck, E.; others. Energy efficiency in wireless networks via fractional programming theory. Foundations and Trends® in Communications and Information Theory 2015, 11, 185–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, S.; Leng, S.; Maharjan, S.; Zhang, Y. Energy efficiency and delay tradeoff for wireless powered mobile-edge computing systems with multi-access schemes. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 2019, 19, 1855–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neely, M.J. Stochastic network optimization with non-convex utilities and costs. 2010 Information Theory and Applications Workshop (ITA). IEEE, 2010, pp. 1–10.
- Diamond, S.; Boyd, S. CVXPY: A Python-embedded modeling language for convex optimization. Journal of Machine Learning Research 2016, 17, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zawawi, Z.B.; Huang, Y.; Clerckx, B. Multiuser wirelessly powered backscatter communications: Nonlinearity, waveform design, and SINR-energy tradeoff. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 2018, 18, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, S.; Huang, L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.J.A. Lyapunov-guided deep reinforcement learning for stable online computation offloading in mobile-edge computing networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 2021, 20, 7519–7537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).