1. Introduction
Zinc and its alloys have a low melting point, fine fluidity, easy brazing, plastic processing, and other excellent properties, so they are widely used in thermal spraying, capacitor spraying gold, hardware, electronics, industrial equipment, and automotive industries [
1,
2,
3]. The current method of manufacturing rods or wires for the preparation of zinc and its alloys is mainly casting followed by extrusion. The low elongation of cast zinc alloy rods or wires makes them more difficult to machine, which greatly limits their application [
4,
5,
6,
7]. However, the conventional hot extrusion process for the production of zinc alloy rods or wires is long, mainly because most zinc alloys have a hexagonal crystal structure that makes plastic deformation at room temperature quite difficult. The process of continuous or semi-continuous casting of zinc and its alloy ingots, followed by heating of the extrusion barrel and die, has so far been the common process used at home and abroad for zinc alloy rods or wires [
8,
9,
10]. The strength and plasticity of zinc alloy can be greatly improved after deformation, but the process is long and the production cost is high. Therefore, it has become one of the hot spots for research to reduce the production cost and efficiency of zinc alloys while ensuring the performance of the products.
The continuous casting and extrusion process has been successfully applied to the industrial production of Al alloy and Mg alloy bars and wires. This has successfully demonstrated the feasibility of continuous casting and extrusion in the production of alloys and has achieved great economic benefits [
11,
12,
13]. Recently, it has been found that continuous casting and extrusion process has been successfully applied to the preparation of zinc alloys. However, the current study focuses on the microstructure and room temperature mechanical properties of the Zn-15Al alloys [
14,
15]. The Al and Cu are common alloying elements in zinc alloys [
16,
17,
18,
19]. Therefore, the effect of different Al or Cu content on the microstructure and room temperature mechanical properties of Zn alloy by continuous casting and extrusion was discussed. This can provide a new idea for processing Zn alloy with low cost and high efficiency.
2. Materials and Methods
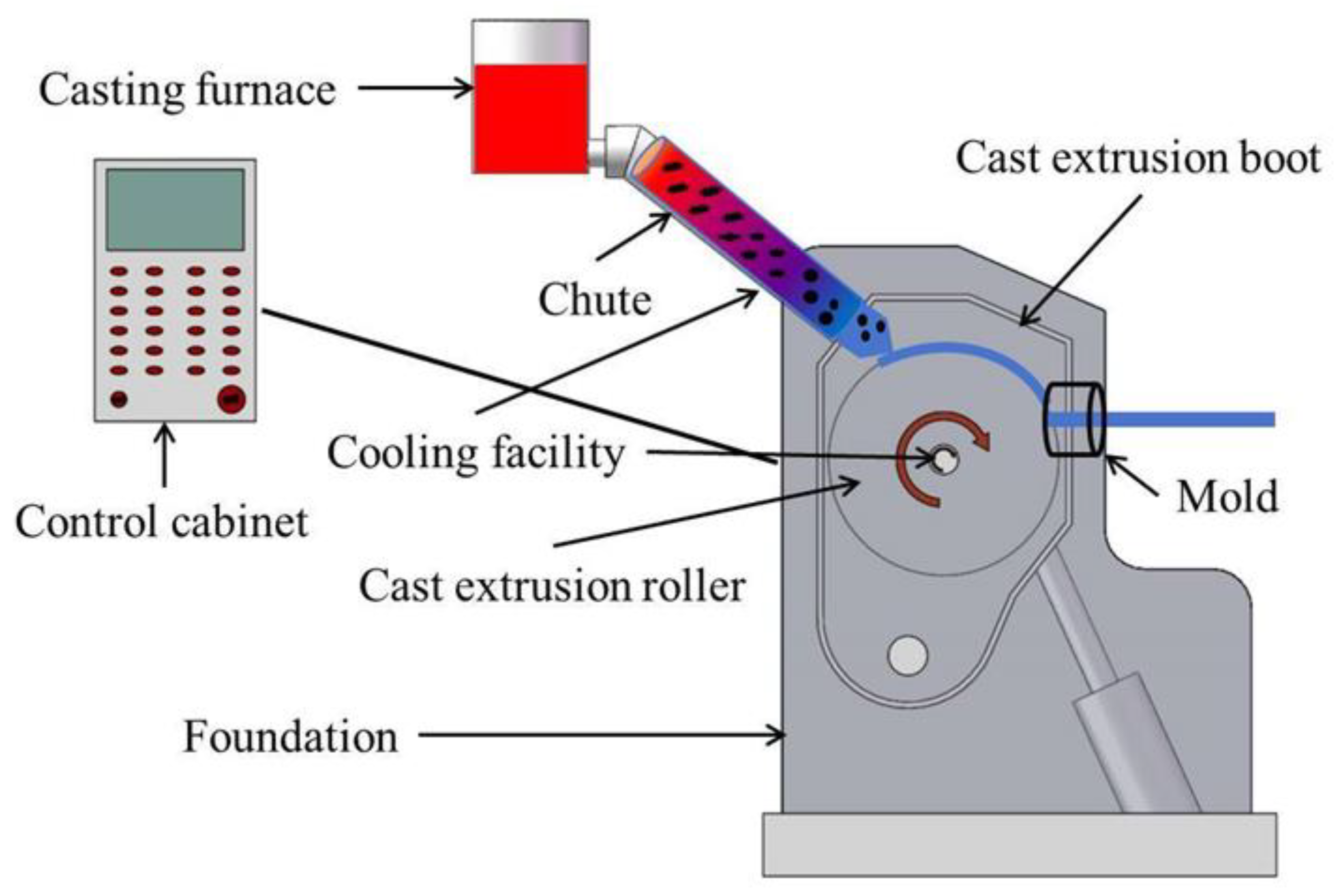
The Zn-2Al and Zn-4Al alloys were conducted using pure Zn and Al with a purity of over 99.9 wt.% (mass fraction). Similarly, The Zn-2Cu and Zn-4Cu alloys were made using pure Zn and Cu with purities exceeding 99.9 wt.%. As shown in
Figure 1, the pure zinc was first heated to 600 °C for melting and then pure aluminum or pure copper was added. After all the metal had been melted, a graphite bell was pressed into the alloy with 2 wt.% C
2Cl
6 for degassing. The temperature was lowered to 550 °C and then left to stand for 20 minutes to obtain the Zn alloy melt. The alloy melt was poured into the CASTEX-300 continuous casting and extrusion machine. The rotational speed of the casting and extrusion wheel was 8 r/min, and the cooling water flow rate was 15 L/min.
After sanding with 200 # to 2000 # sandpaper, the Zn alloy was mechanically polished to a mirror shape. The corrosion solution was a 9% HNO3+91% H2O solution. The metallographic observation of the alloy was examined by the GX71 inverted optical microscope. The microstructure and fracture morphology of the alloy were observed under a JSM-6510 scanning electron microscope. The X-ray diffraction (XRD) was conducted on the PW3040/60 X-ray analyzer with Cu target Kα Line and a scanning speed of 3 °/min. The room temperature tensile specimen was machined from Zn-Al alloy with a gauge length of 25 mm and a diameter of 5 mm. The tensile tests at room temperature were enforced at a strain rate of 10-3 s-1 on a microcomputer- controlled AG-X electronic universal experimental machine. Five specimens were carried out to check the repeatability of the results.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. X-Ray Diffraction
According to the Zn-Al phase diagram, during the solidification process of Zn-Al alloy with a mass fraction of 1-5%, rich Zn phases first precipitate. As the temperature decreases to 381 °C (eutectic point), a eutectic structure composed of rich Al and rich Zn phases begins to precipitate. The temperature continues to decrease, and the eutectic structure undergoes a dissolution process. Secondary rich Al and rich Zn phases precipitate in the rich Zn and Al phases [
20]. From the Zn-Cu phase diagram, it can be seen that the maximum solubility of copper in Zn is 2.75 wt.% at 425 °C. The first intermetallic phase formed by Cu addition in Zn is CuZn
4 phase [
21].
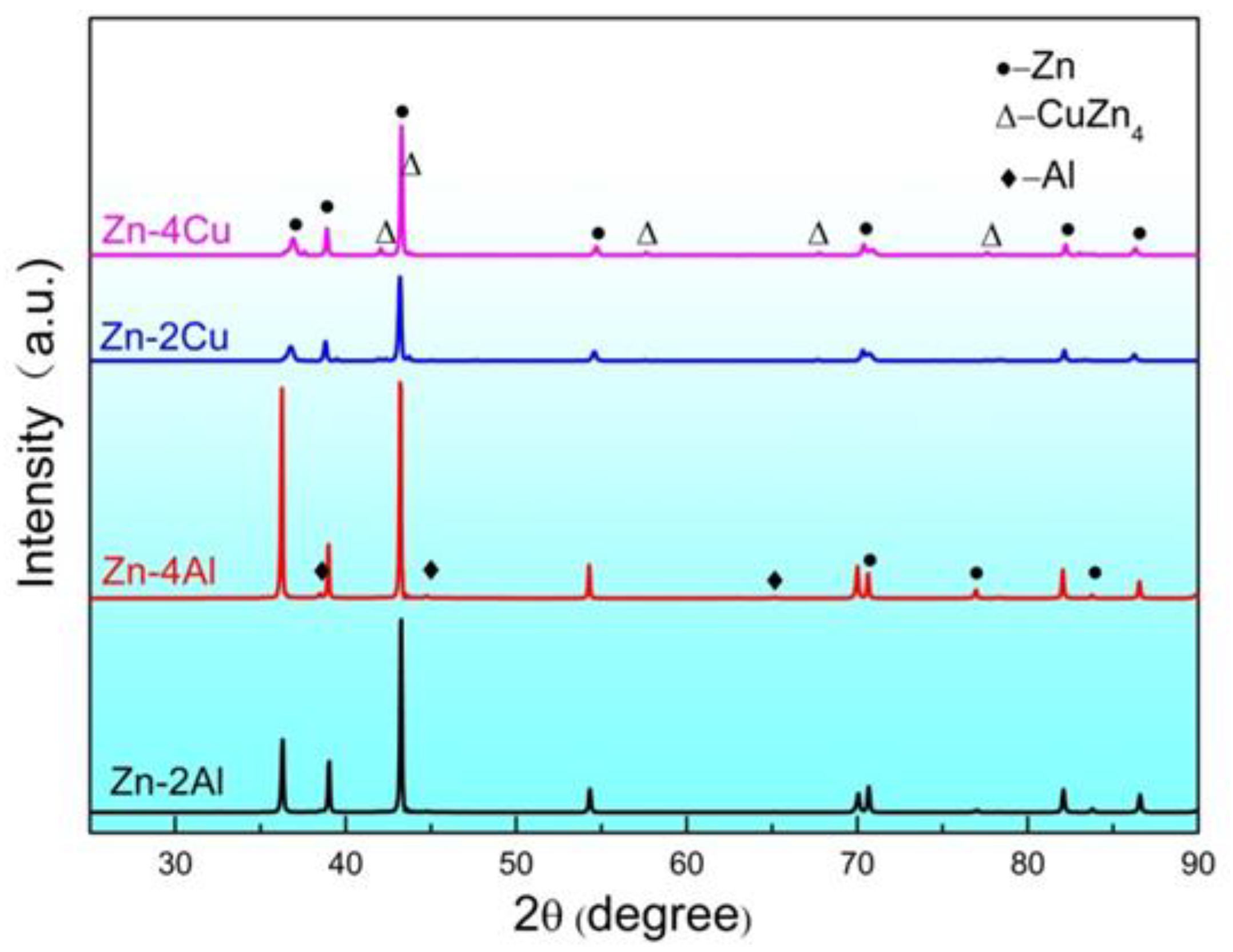
Figure 2 shows the XRD patterns of continuous casting and extrusion Zn alloys. It can be seen that the Zn-Al alloys with different Al contents are mainly composed of rich Zn phase and rich Al phase. With the Al content increases, there is no significant change in the phase composition of the alloy, but the diffraction peak intensity of the Al-rich phase slightly increases, which agrees with the observation of the Zn-Al alloys [
22]. The Zn-Cu alloys have similar phenomena as Zn-Al alloys.
3.2. Microstructure
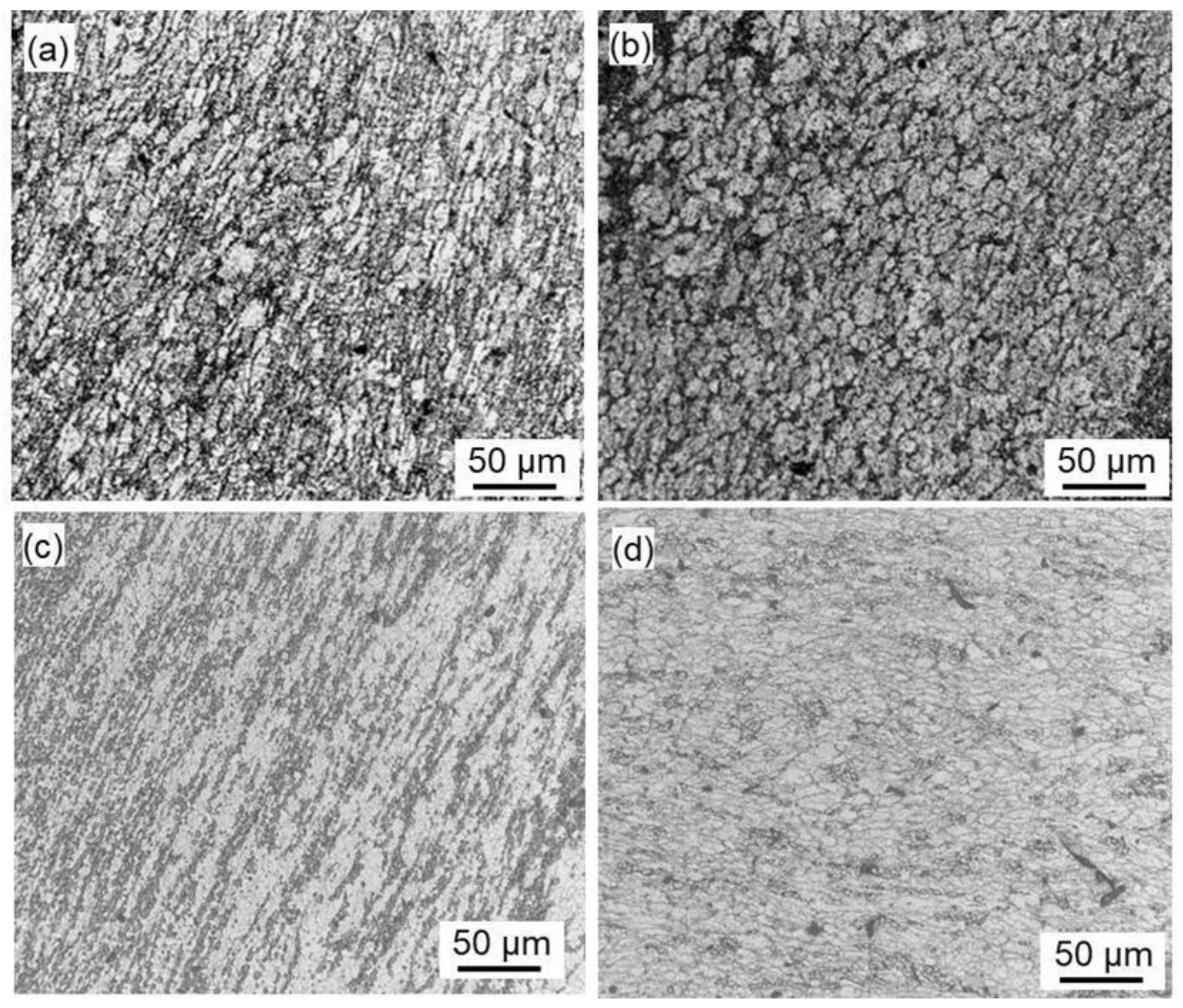
The metallographic images of Zn alloys with different Al or Cu contents after continuous casting and extrusion are shown in
Figure 3. It is clear from the figure that the Zn-2Al alloy uses Zn-based solid solutions as the matrix, with a certain amount of Al-based solid solutions distributed. Among them, white is the Al-rich phase, and black is the Zn-rich phase. At the same time, it has deformation characteristics and presents fibrous characteristics along the extrusion direction (
Figure 3 (a)). The Zn-4Al alloy is composed of Zn-based solid solution and eutectic structure. After continuous casting and extrusion, it undergoes complete recrystallization, and its grain size is relatively uniform (
Figure 3 (b)). As the Al or Cu content increases, the deformation degree of Zn alloy weakens and the fibrous structure decreases (
Figure 3).
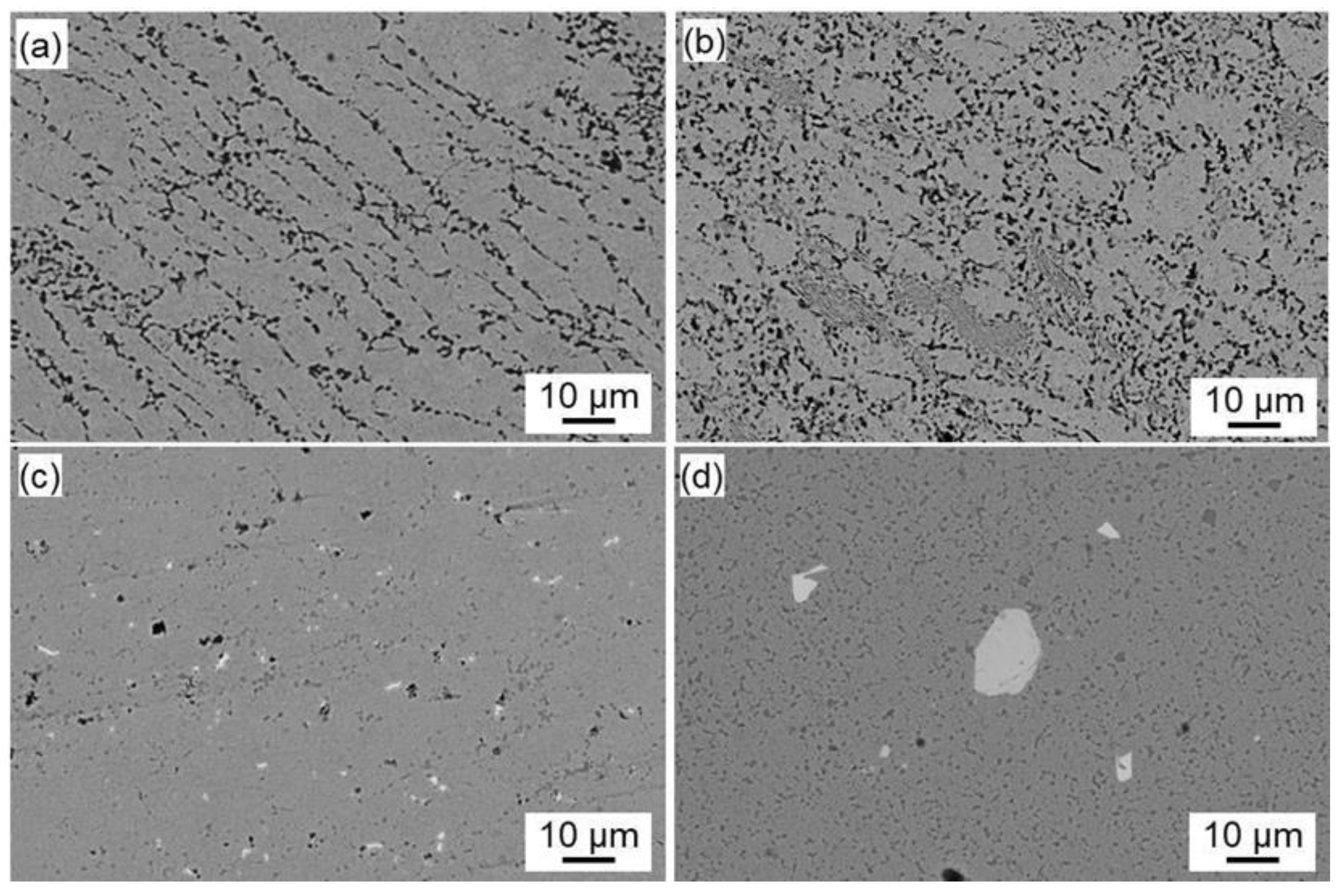
The SEM microstructure of continuous casting and extrusion Zn alloys with different Al or Cu contents is shown in
Figure 4. The bright ones are rich Zn phase, while the dark ones are rich Al phase. The microstructure of Zn-2Al alloy by continuous casting and extrusion is composed of Zn-based solid solutions as the matrix, with a certain amount of Al-based solid solutions distributed. At the same time, there is a certain degree of deformation along the extrusion direction (
Figure 4 (a)). From
Figure 4 (b), it can be seen that the continuous casting and extrusion Zn-4Al alloy is composed of Zn-based solid solution and lamellar eutectic structure, which also produces a certain degree of deformation along the extrusion direction. This microstructure is similar to other preparation methods of Zn-Al alloy [
23,
24,
25]. With the increasing of Al content, the lamellar eutectic structure in the Zn-Al alloys increases and the microstructure appears slightly coarse, but the degree of structural deformation weakens. The SEM microstructure of the Zn-Cu alloy is presented in
Figure 4 (c) and 4 (d). The micrometer-sized second phase (bright phases) gradually increases with increasing Cu content in the Zn-Cu alloys [
26].
3.3. Mechanical Properties
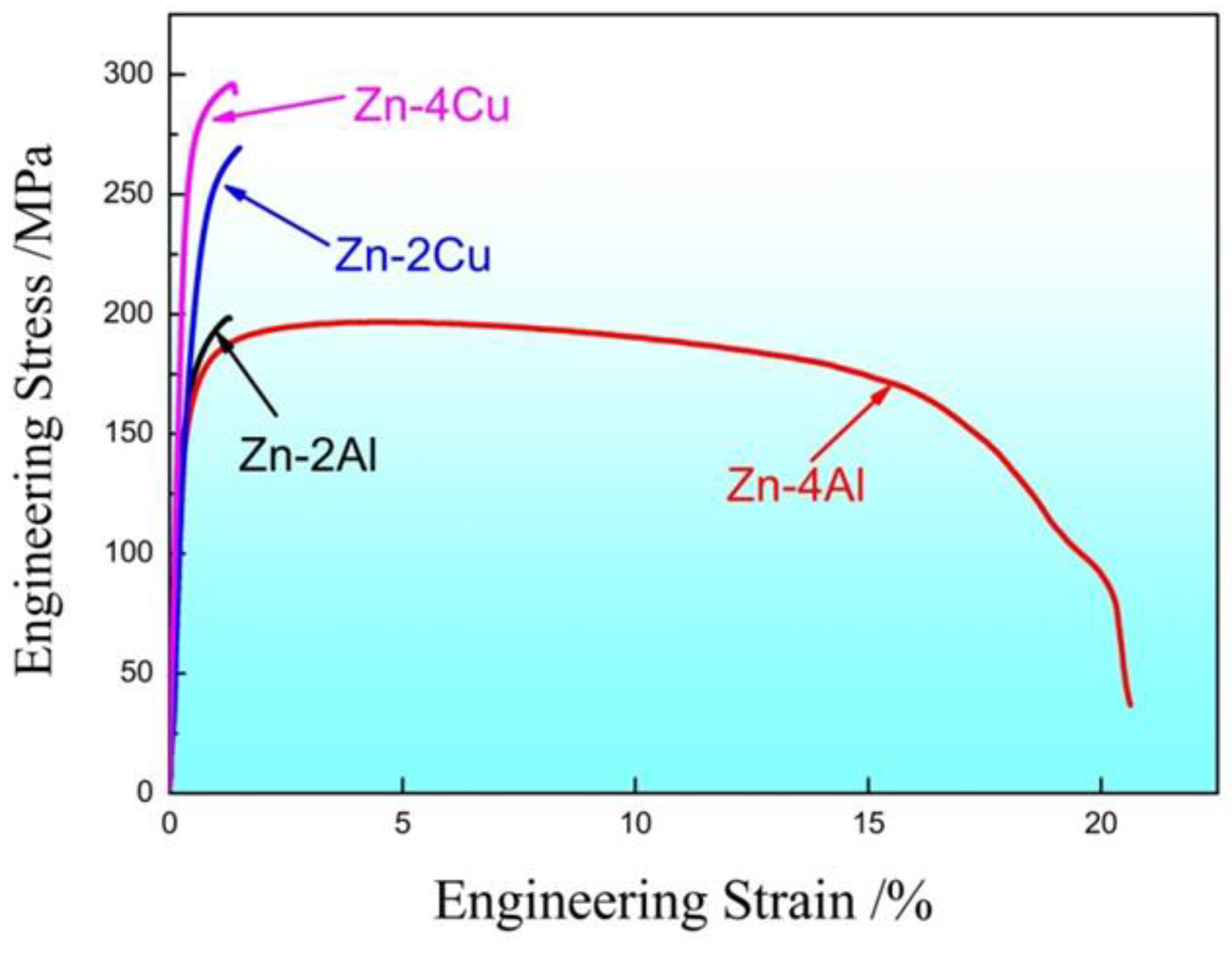
Figure 5 shows the tensile engineering stress-strain curves at room temperature of continuous casting and extrusion Zn alloys with different Al or Cu contents. The strength of the Zn alloy increases significantly with the addition of Cu compared to the addition of Al. With the increase of Cu content, the strength of the alloy gradually increases, but the elongation does not change much, basically around 2%. The tensile strength of continuous casting and extrusion Zn-Al alloy slightly decreases with the increase of Al content, from 199 MPa to 197 MPa. The yield strength decreases with the increase of Al content, from 164 MPa to 148 MPa. The room elongation increases from 1.2% to 20% with the increase of Al content. Generally speaking, with the increase of Al or Cu content, the strength and plasticity of Zn alloy increase simultaneously, because the increase of Al or Cu content refines the microstructure of Zn alloy [
26,
27,
28]. In this experiment, continuous casting and extrusion is a process that integrates casting and extrusion, so Zn alloy has both casting and extrusion microstructures [
29]. This results in an increase in Al content in Zn-Al alloy from 2 wt.% to 4 wt.%, with a slight decrease in strength and a significant increase in plasticity. However, the strength and plasticity of the alloy are slightly enhanced as the Cu content is increased from 2 wt.% to 4 wt.%.
In the present experiments the mechanical properties of continuous casting and extrusion Zn alloys were altered due to grain refinement and the combined effect of the second phase content and morphology. With the increase of Al content, the size of Zn-rich phase in the matrix of the Zn-Al alloys increases slightly, and the increase of lamellar eutectic. The combined effect of the above microstructural factors leads to a slight decrease in the strength of the Zn-Al alloys with the increase of Al content and a substantial increase in the elongation. For the Zn-Cu alloys, the second phase plays a decisive role in increasing its strength.
4. Conclusions
Continuous casting and extrusion process is a forming method that combines casting and extrusion. It is a short process and low-cost processing method, which can greatly improve the performance of alloys. Therefore, this article conducted the effect of Al or Cu contents on the microstructure and room temperature tensile properties of continuous casting and extrusion Zn alloys. The following conclusions are obtained:
(1) The Zn alloy with a lower Al or Cu contents can be prepared by continuous casting and extrusion.
(2) With the increase of Al content, the strength of the Zn-Al alloy slightly decreases and the elongation of the Zn-Al alloy significantly increases, from 1.2% to 20%., which is due to the combined effect of microstructure refinement, deformation degree, eutectic microstructure morphology, and content.
(3) The strength and elongation of the Zn-Cu alloy are slightly enhanced as the Cu content is attributed to the size and content of the second phase.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.W. and S.S.; methodology, C.W., S.S. and J.Y.; software, C.W., S.S. and J.Y.; validation, C.W.; formal analysis, S.S., J.Y. and C.W.; investigation, C.W., S.S. and J.Y.; resources, C.W.; data curation, S.S. and J.Y..; writing—original draft preparation, S.S.; writing—review and editing, C.W., S.S. and J.Y.; visualization, J.Y.; supervision, C.W. and S.S.; project administration, S.S.; funding acquisition, S.S. All authors read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Support Program for Liaoning Provincial Department of Education Basic Research Program (Grant No. JYTMS20231163).
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
We sincerely appreciate the support provided by Shenyang University in the preparation of this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Sun, S.N.; Ren, Y.P.; Wang, L.Q.; Yang, B.; Qin, G.W. Room temperature quasi-superplasticity behavior of backward extruded Zn-15Al alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 2016, 676, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kustra, P.; Wróbel, M.; Byrska-Wójcik, D.; Paćko, M.; Płonka, B.; Wróbel, M.; Sulej-Chojnacka, J.; Milenin, A. Manufacture technology, mechanical and biocorrosion properties of the Zn and ZnMg0.008 alloy wires designed for biodegradable surgical threads. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 67, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.J.; Wang, Q.Z.; Jiao, Z.X.; Cui, C.X.; Yin, F.X.; Yao, C. Effects of combined use of inoculation and modification heat treatment on microstructure, damping and mechanical properties of Zn–Al eutectoid alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 2020, 790, 139740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.N.; Wang, H.L.; Yang, B.; Qin, G.W. Effect of extrusion temperature on mechanical properties of as-extruded Zn–22Al alloys. Mater. Sci. Tech. 2020, 36, 805–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, C.; Zhang, J.C. Strain rate and anisotropic effects on incipient plastic deformation of Zn–Cu–Ti alloy sheets. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 2024, 890, 145909. [Google Scholar]
- Azad, B.; Eivani, A.R.; Salehi, M.T. An investigation of microstructure and mechanical properties of as-cast Zn–22Al alloy during homogenizing and equal channel angular pressing. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 22, 3255–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.D.; Zhu, X.L.; Guo, P.S.; Zhang, Y. D.; Xu, Y.; Pang, Y.; Song, Z. L.; Yang, L.J. Effects of Li addition on the properties of biodegradable Zn–Fe–Li alloy: Microstructure, mechanical properties, corrosion behavior, and cytocompatibility. Mater. Today. Commun. 2024, 39, 108661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liang, W.L.; Ban, C.Y.; Suo, Y.S.; Lv, G.C.; Liu, T.; Wang, X.J.; Zhang, H.; Cui, J.Z. Effects of a high-voltage pulsed magnetic field on the solidification structures of biodegradable Zn-Ag alloys. Mater. Char. 2020, 163, 110274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.Z.; Li, H.Y.; Xu, J.Y.; Gao, X.X. Liu, X.F. Microstructure evolution of a high-strength low-alloy Zn-Mn-Ca alloy through casting, hot extrusion and warm caliber rolling. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 2020, 771, 138626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.L.; Yang, L.; Lai, Y.L.; Liu, Y. The effects of Zr content and hot rolling on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Zn-1.5Cu-1.0Ag-xZr alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 912, 165116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.W.; Gao, M.Q.; Liu, Y.; Pan, S.; Meng, S.C.; Fu, Y.; Guan, R.G. Formation mechanism of refined Al6(Mn, Fe) phase particles during continuous rheo-extrusion and its contribution to tensile properties in Al-Mg-Mn-Fe alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 2023, 872, 144952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.R.; Yin, B.; Liu, S.Y.; Shi, L.; Wang, S.C.; Wen, J.L. Microstructural evolution, flow stress and constitutive modeling of Al-1.88Mg-0.18Sc-0.084Er alloy during hot compression. Trans. Nonferrous. Met. Soc. China. 2021, 31, 53–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.J.; Qin, J.; Lü, S.L.; Li, J.Y.; Guo, W.; Wu, S.S.; Zhang, Y.H. Mechanisms of extrusion-ratio dependent ultrafine-grain fabrication in AZ31 magnesium alloy by continuous squeeze casting-extrusion. J. Mater. Process Tech. 2022, 310, 117755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.N.; Li, D.Y.; Liu, D.Y.; Yang, B.; Ren, Y.P.; Qin, G.W. Microstructure and mechanical properties of continuous casting and extrusion Zn-15 wt% Al alloys. Mater. Lett. 2020, 261, 127090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.N.; Li, D.Y.; Liu, D.Y.; Yang, B.; Ren, Y.P.; Liu, J.T.; Xie, H.B. Effects of Bi and Ce addition on tensile properties and corrosion resistance of Zn-15Al alloys by continuous casting and extrusion. Mater. Lett. 2020, 275, 128027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.F.; Sun, C.; Zhuo, X.R.; Liu, H.; Ju, J.; Xue, F.; Bai, J.; Jiang, J.H.; Xin, Y.C. Evolution of grain size and texture of Zn-0.5Cu ECAP alloy during annealing at 200 ℃ and its impact on mechanical properties. J. Alloy. Compd. 2022, 919, 165871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, Y.K.; Ge, Q.Q.; Liu, Z.X.; Qiao, A.K.; Mu, Y.L. Mechanical characteristics and in vitro degradation of biodegradable Zn-Al alloy. Mater. Lett. 2021, 300, 130181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.T.; Jia, B.; Zhang, Z.C.; Qu, X.H.; Li, G.N.; Lin, W.J.; Zhu, D.H.; Dai, K.R.; Zheng, Y.F. Alloying design of biodegradable zinc as promising bone implants for load-bearing applications. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.K.; Xiao, S.J.; He, W.Q.; Wang, J.J.; Ma, Y.M.; Zhang, H.H. Effect of melt overheating treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Zn–Al alloy. Vacuum 2022, 201, 111071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.Z.; Niu, R.M.; Cui, X.Y.; Bobruk, E.V.; Murashkin, M.Y.; Enikeev, N.A.; Gu, J.; Song, M.; Bhatia, V.; Ringer, S.P.; Valiev, R.Z.; Liao, X.Z. Mechanism of room-temperature superplasticity in ultrafine-grained Al-Zn alloys. Acta Mater. 2023, 246, 118671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.M.; Huang, H.; Niu, J.L.; Jin, Z.H.; Dargusch, M.; Yuan, G.Y. Characterization of nano precipitate phase in an as-extruded Zn-Cu alloy. Scripta Mater 2021, 200, 113907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez-Menchaca, J.; Torres-Torres, D.; Garay-Tapia, A.M. Microstructural, mechanical and thermodynamic study of the as-cast Zn-Al-Sr alloys at high Sr content. J. Alloy. Compd. 2020, 829, 154511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.N.; Liu, J.T.; Li, X.L.; Ye, G.; Weng, Y.M.; Lu, Z.T.; Lou, D.F. High ductility Zn-6Al alloys with fine-grained microstructure processed by low temperature backward extrusion. Rare Metal. Mat. Eng. 2021, 50, 2263–2267. [Google Scholar]
- Farabi, E.; Sharp, J.A.; Valid, A.; Fabijanic, D.M.; Barnett, M.R.; Gallo, S.C. Development of high strength and ductile Zn-Al-Li alloys for potential use in bioresorbable medical devices. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 2021, 122, 111897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.C.; Sandlobes, S.; Wu, L.; Hu, W.P.; Gottstein, G.; Korte-kerzel, S. Mechanical behaviour of Zn-Al-Cu-Mg alloys: Deformation mechanisms of as-cast microstructures. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 2016, 651, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirtas, M.; Kawasaki, M.; Yanar, H.; Purcek, G. High temperature superplasticity and deformation behavior of naturally aged Zn-Al alloys with different phase compositions. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 2018, 730, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.B.; Niu, J.L.; Huang, H.; Zhang, H.; Pei, J.; Ou, J.M.; Yuan, G.Y. Potential biodegradable Zn-Cu binary alloys developed for cardiovascular implant applications. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. 2017, 72, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Liang, W.L.; Yang, L.; Cao, F.L.; Sun, K.; Ban, C.Y.; Cui, J.Z. Structure refinement and homogenization of Zn-Cu alloys induced by a high-voltage pulsed magnetic field during the solidification process. Int. J. Metal. Cast. 2023, 17, 399–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.Z.; Gao, X.X.; Zhang, H.J.; Liu, X.F.; Li, H.Y.; Zhou, C.; Yin, Y.X.; Wang, L.N. Design biodegradable Zn alloys: Second phases and their significant influences on alloy properties. Bioact. Mater. 2020, 5, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).