Submitted:
28 June 2024
Posted:
01 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
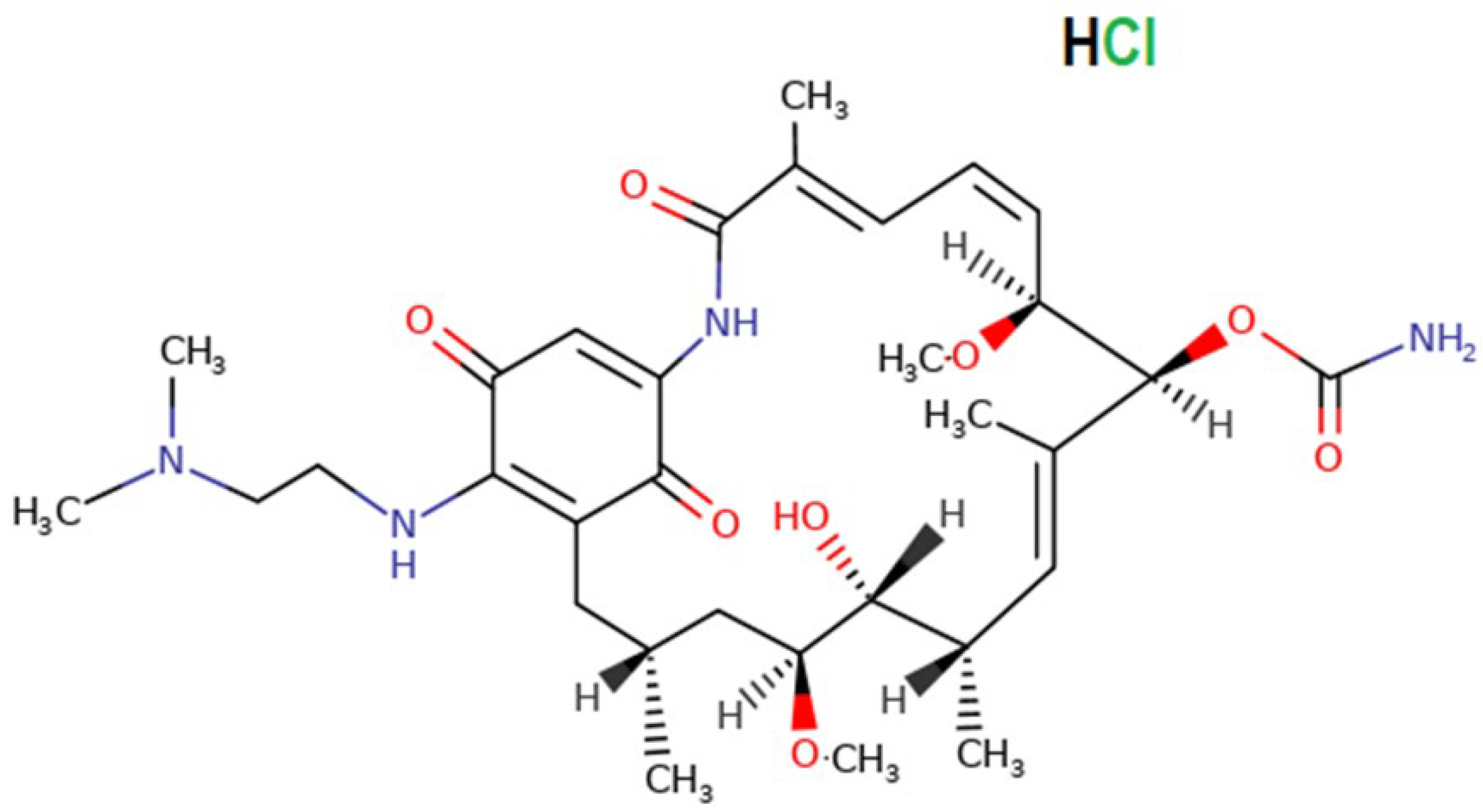
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Parasites
2.3. Isolation and Differentiation of Bone Marrow Precursors into Macrophages (BMMΦ)
2.4. Assessment of the Cytotoxicity of 17-DMAG against BMMΦ In Vitro
2.5. Assessment of the Antileishmanial Efficacy of 17-DMAG against L. braziliensis Promastigotes In Vitro
2.6. Evaluation of the Antileishmanial efficacy of 17-DMAG against Intracellular Amastigote of L. braziliensis In Vitro
2.7. Evaluation of Intraperitoneally Administered 17-DMAG Treatment against L. braziliensis Infection in BALB/c Mice
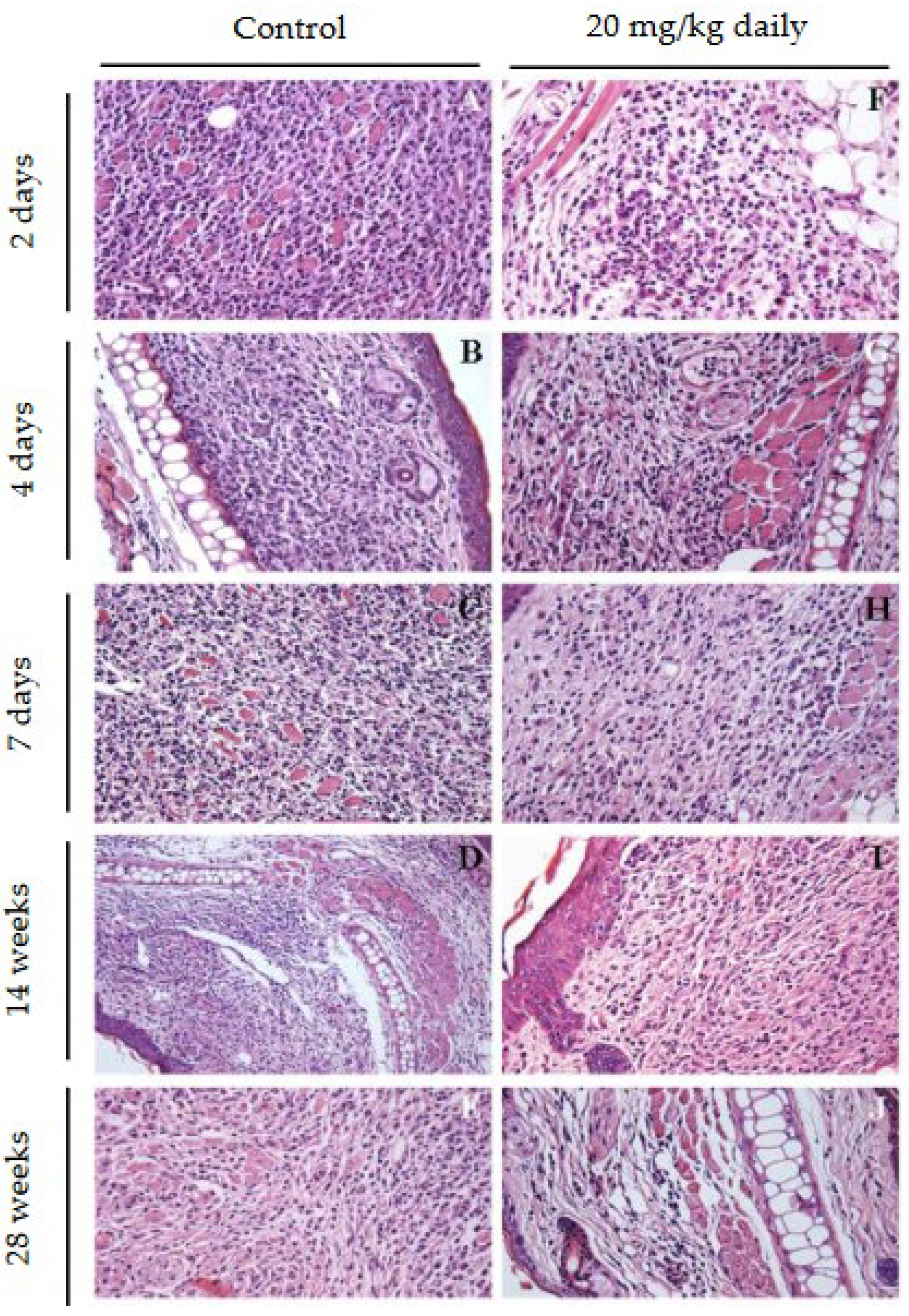
2.8. Evaluation of the Effect of 17-DMAG Treatment on the Inflammatory Infiltrate in Lesions of L. braziliensis-Infected BALB/c Mice
2.9. Evaluation of 17-DMAG Treatment on Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Release by Lymph Node Cells from L. braziliensis-Infected BALB/c Mice
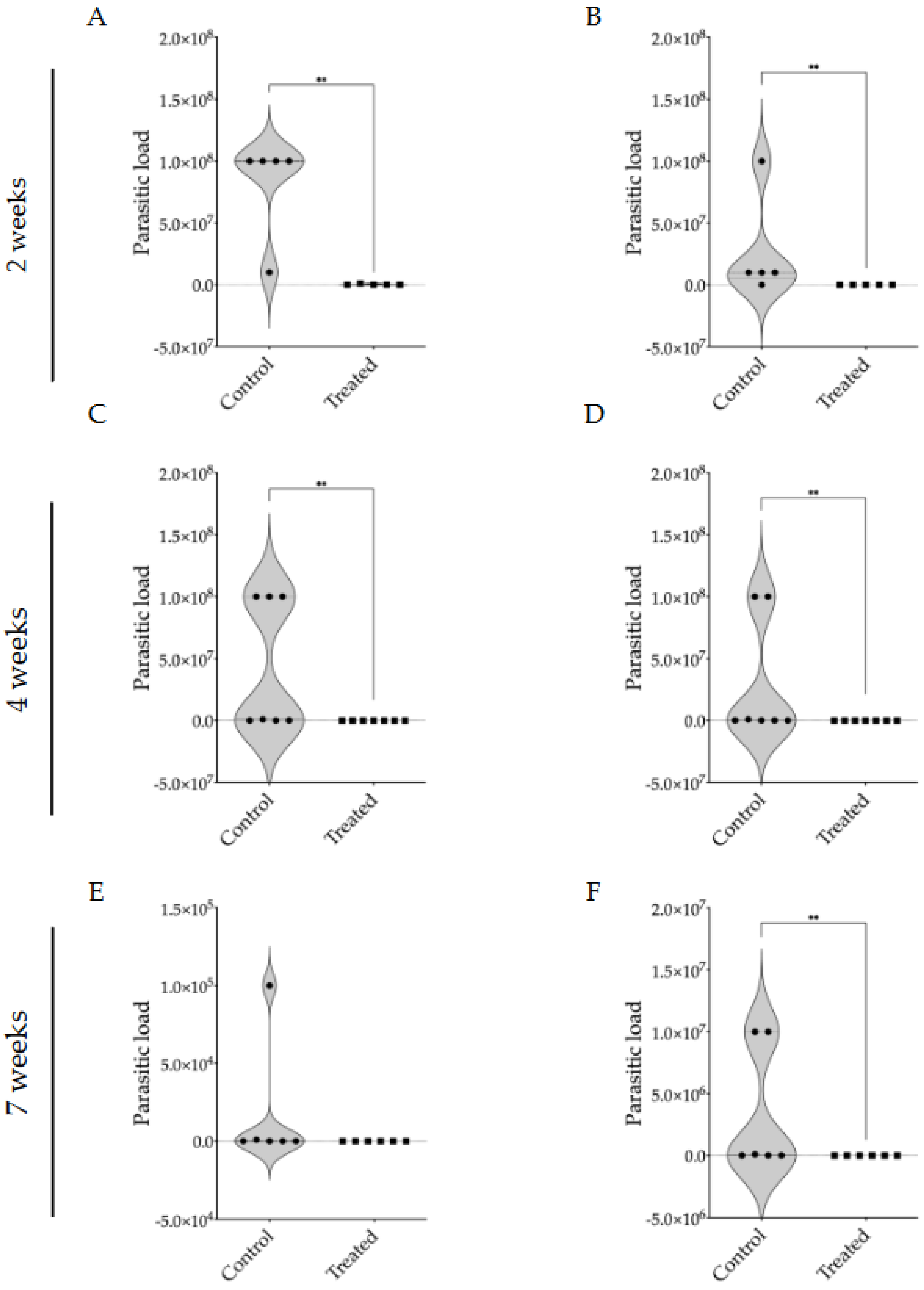
2.10. Quantification of Parasite Burden in BALB/c Mice Infected with L. braziliensis Using Limiting Dilution Assay
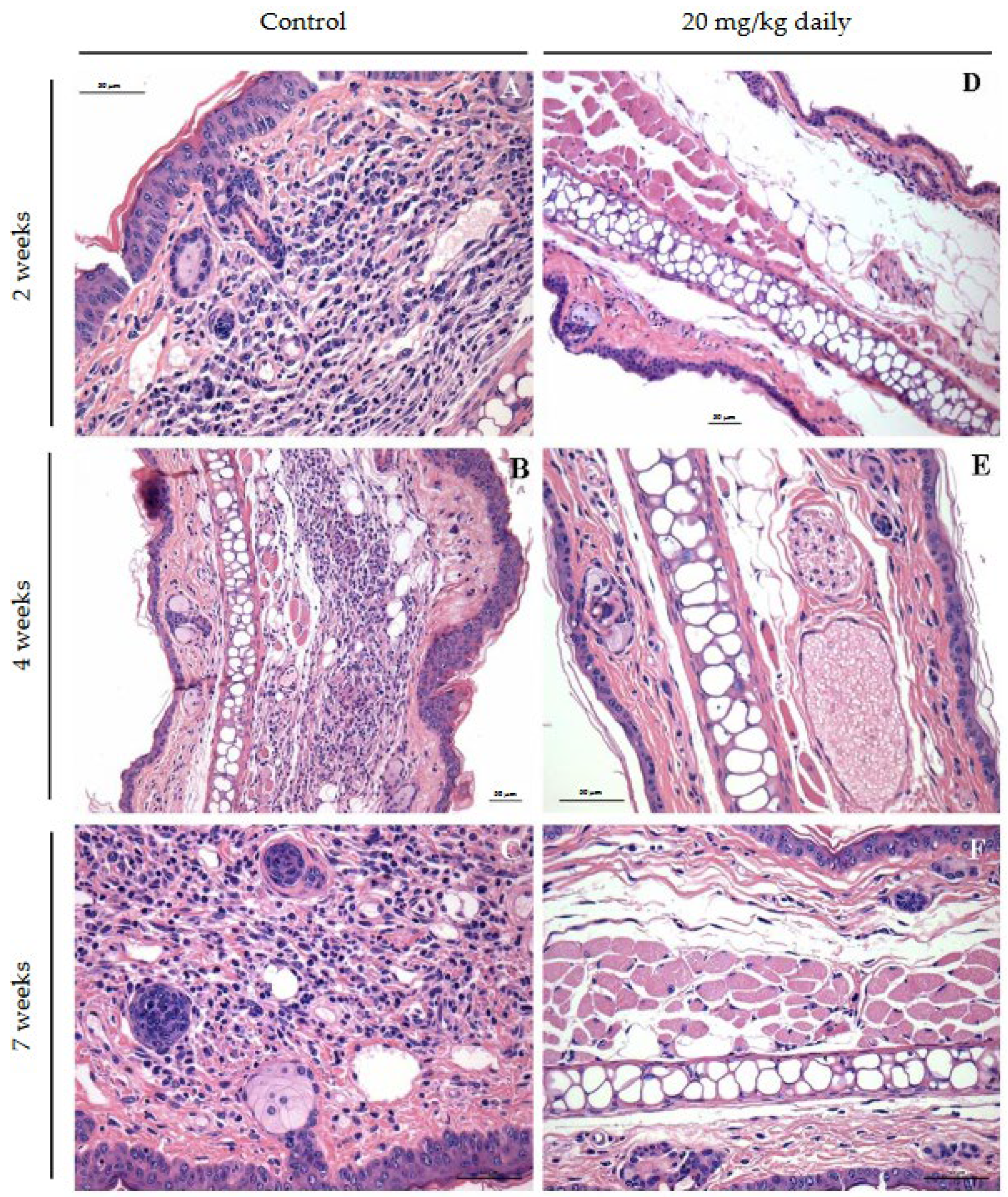
2.11. Histopathological Characterization of Lesions in BALB/c Mice Infected with L. Braziliensis and Treated with 17-DMAG
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
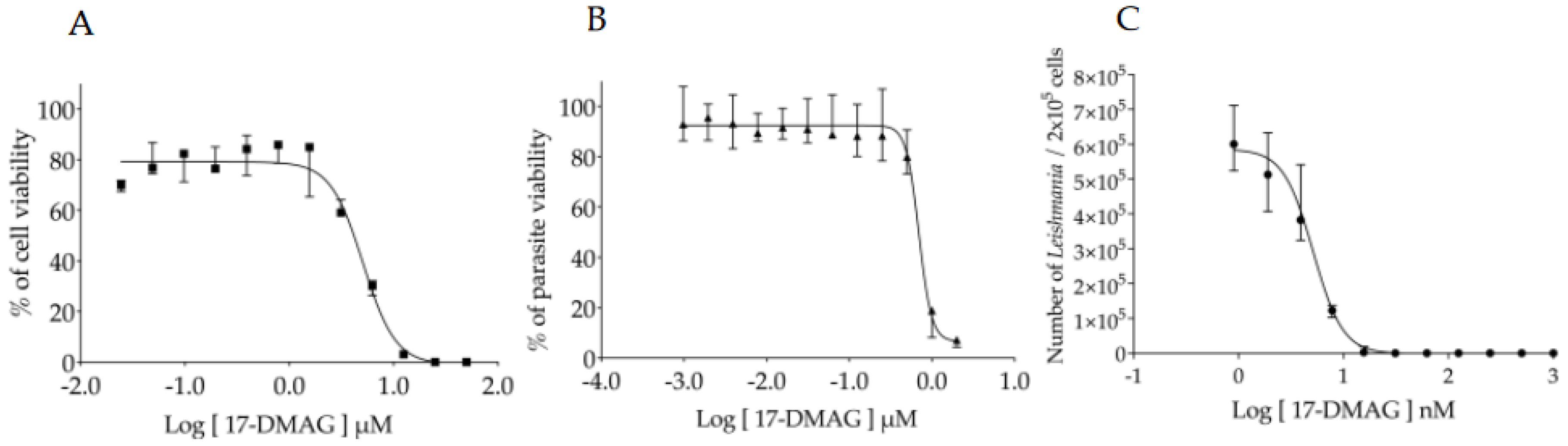
3.1. Assessment of the 17-DMAG Effectiveness against L. braziliensis In Vitro
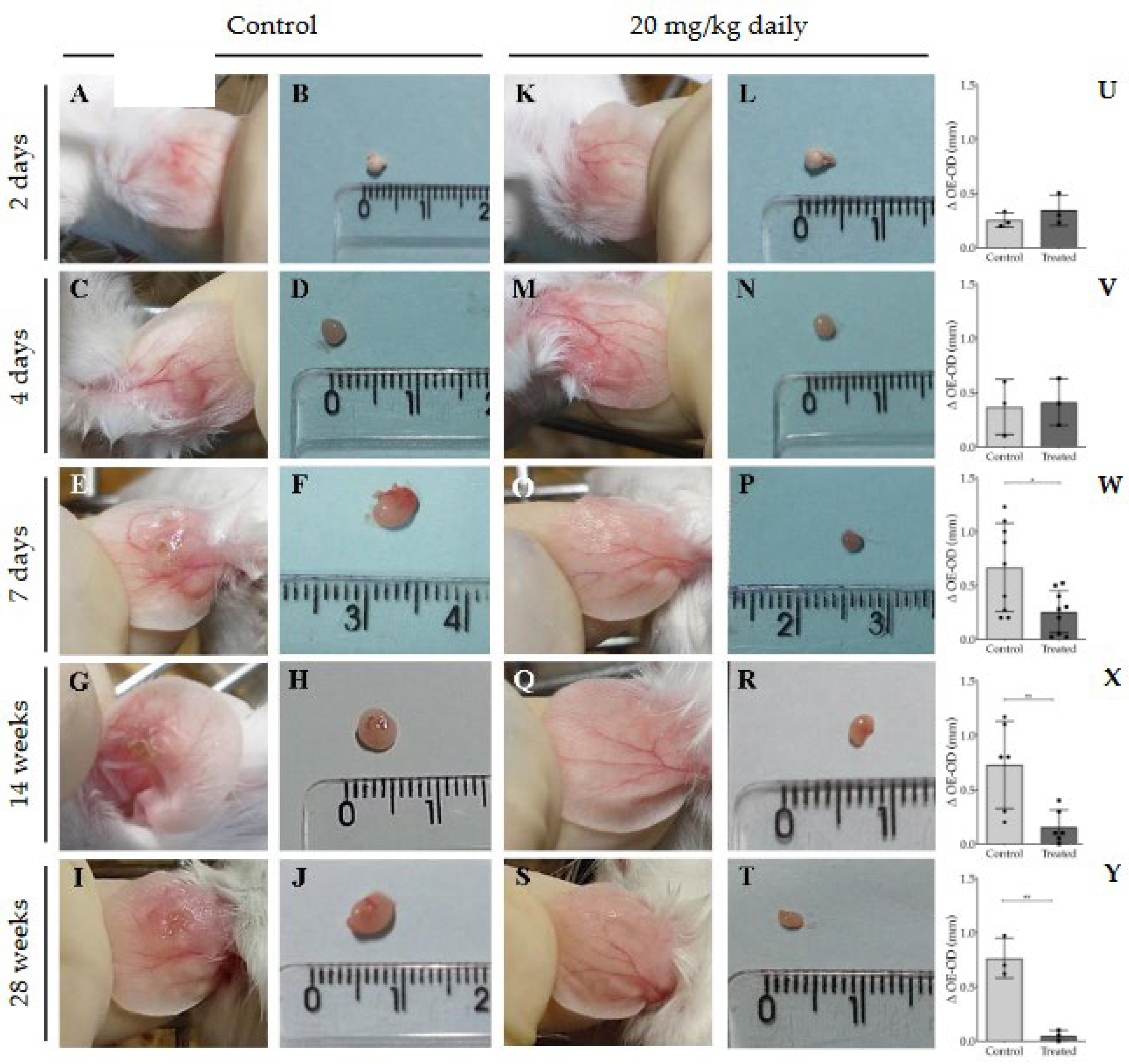
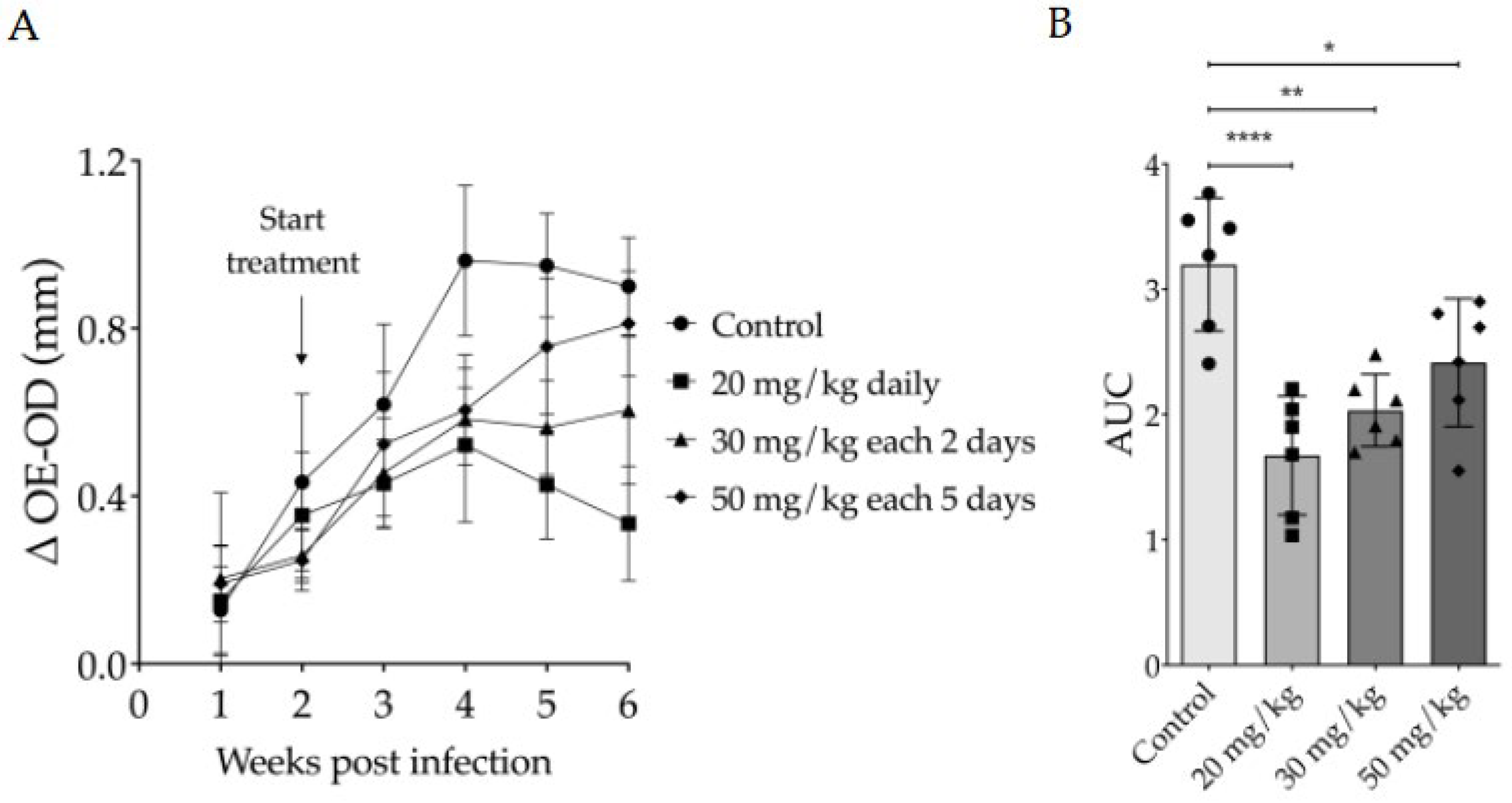
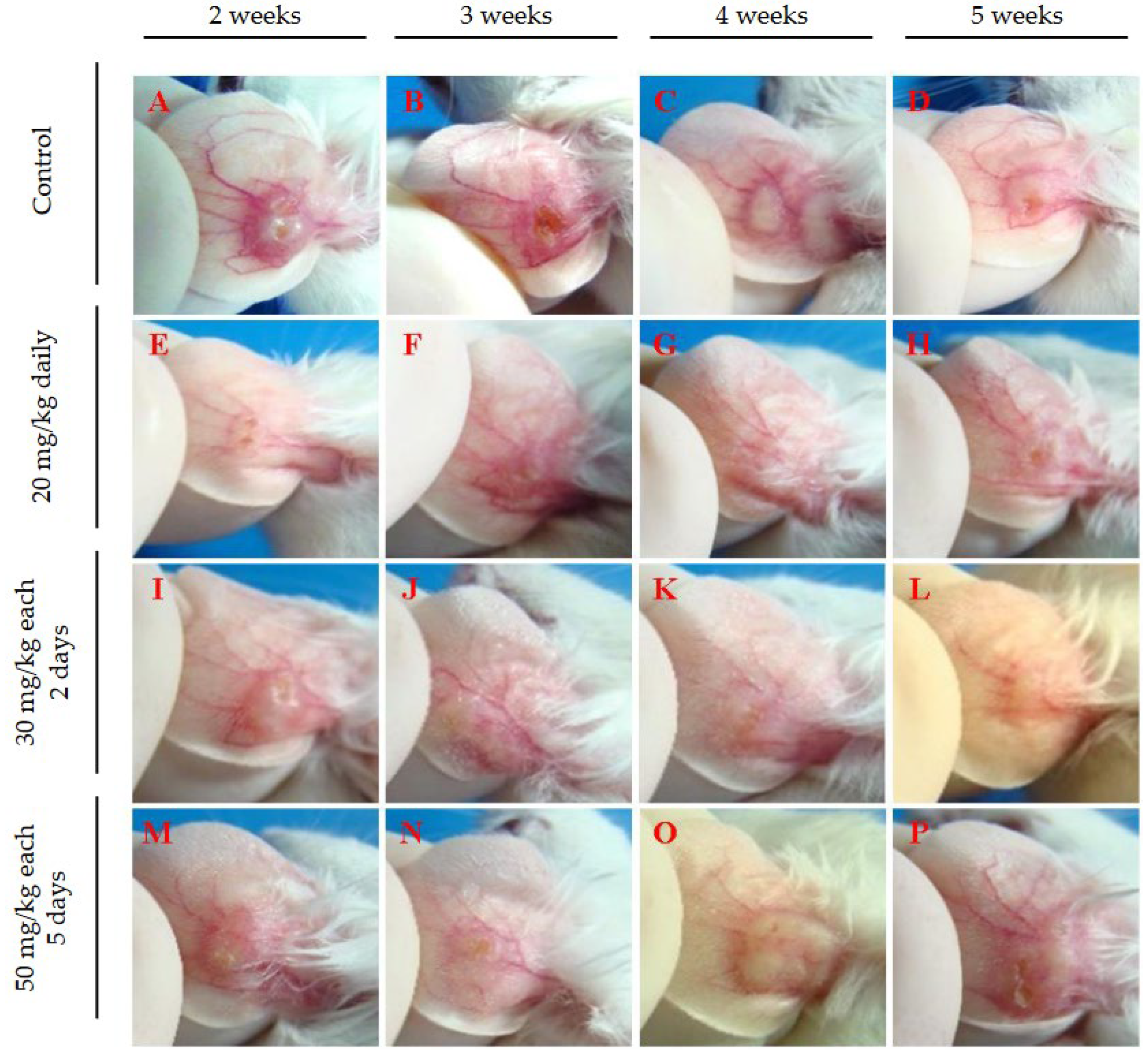
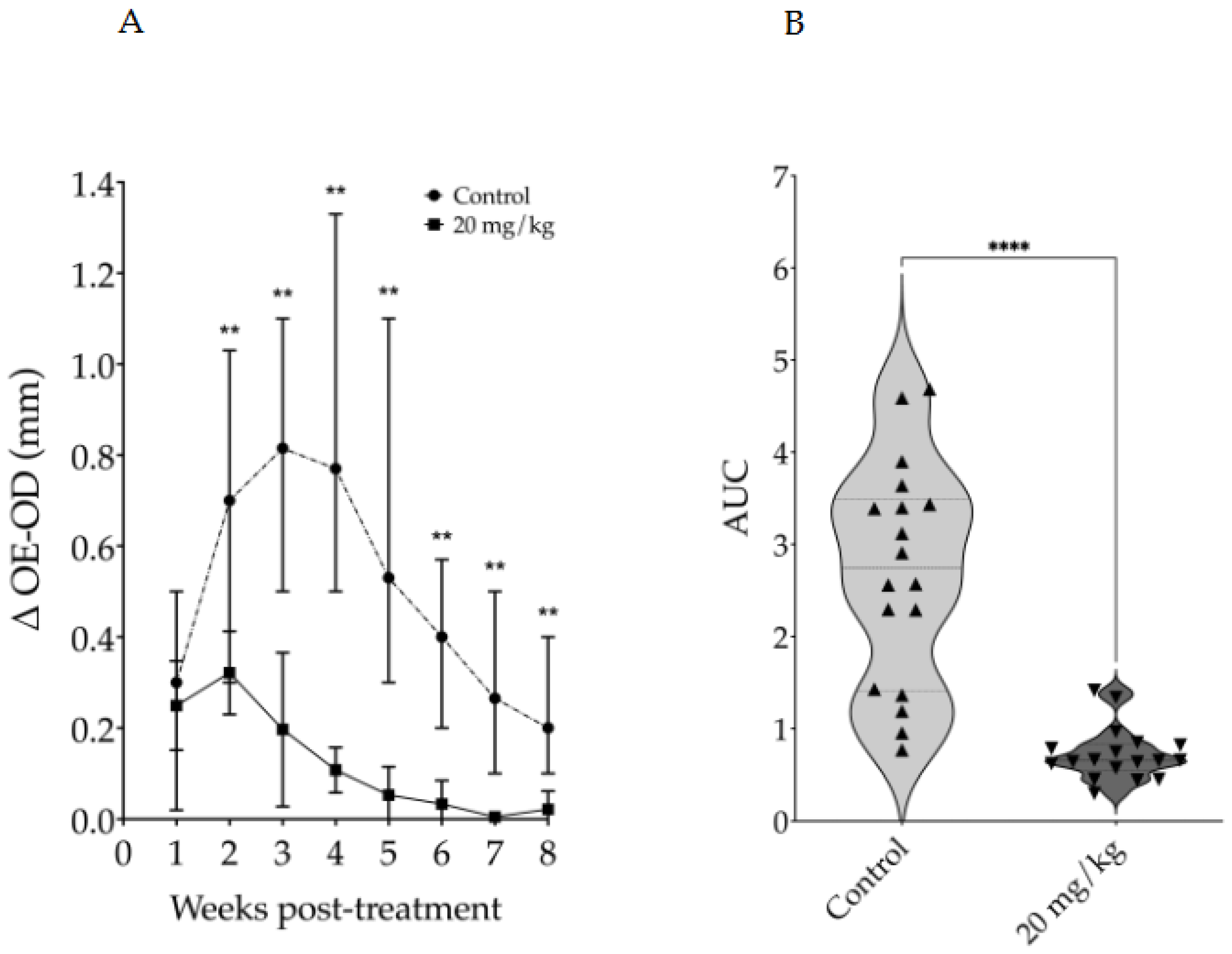
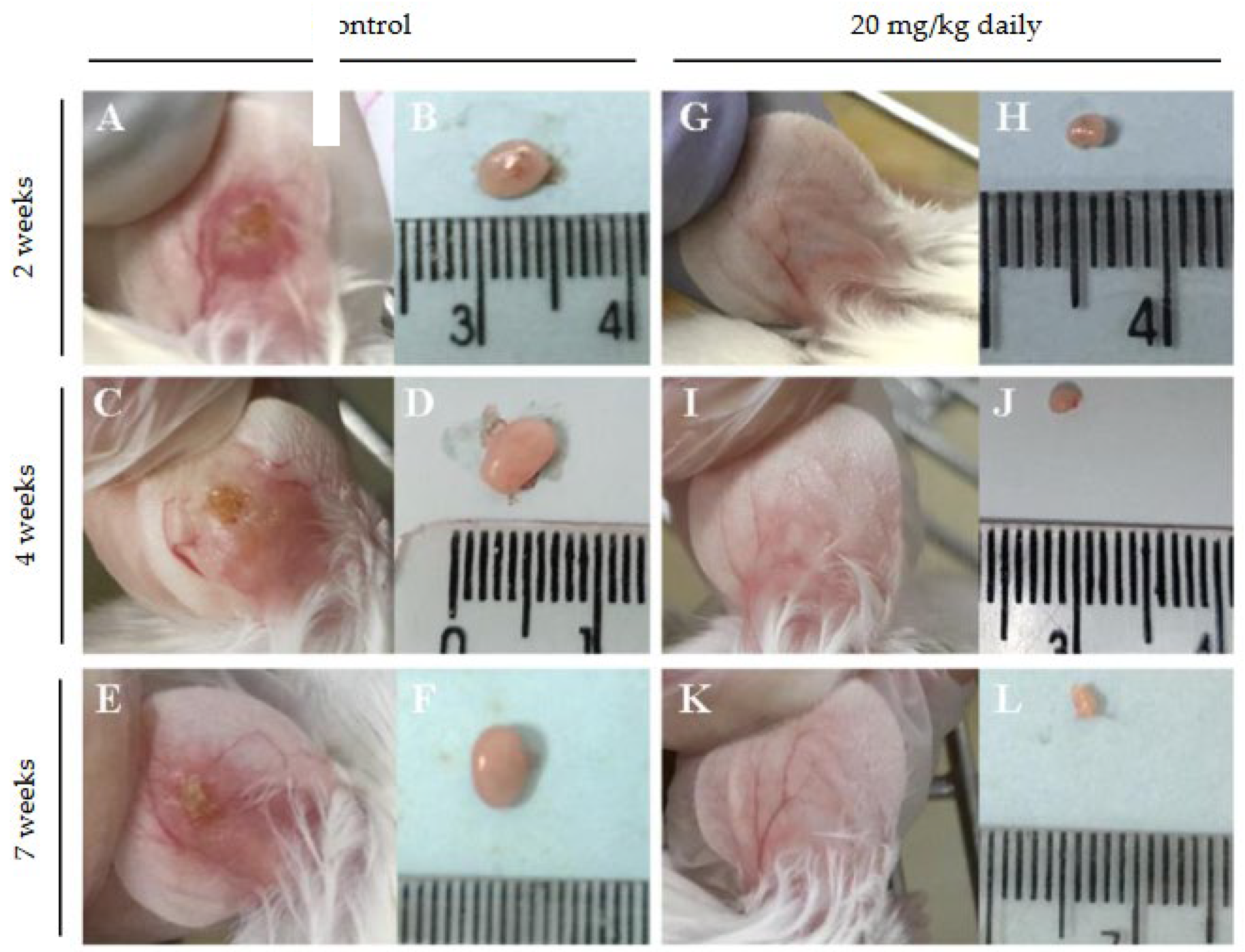
3.2. Evaluation of Intraperitoneally Administered 17-DMAG Treatment Against L. braziliensis Infection in BALB/c Mice
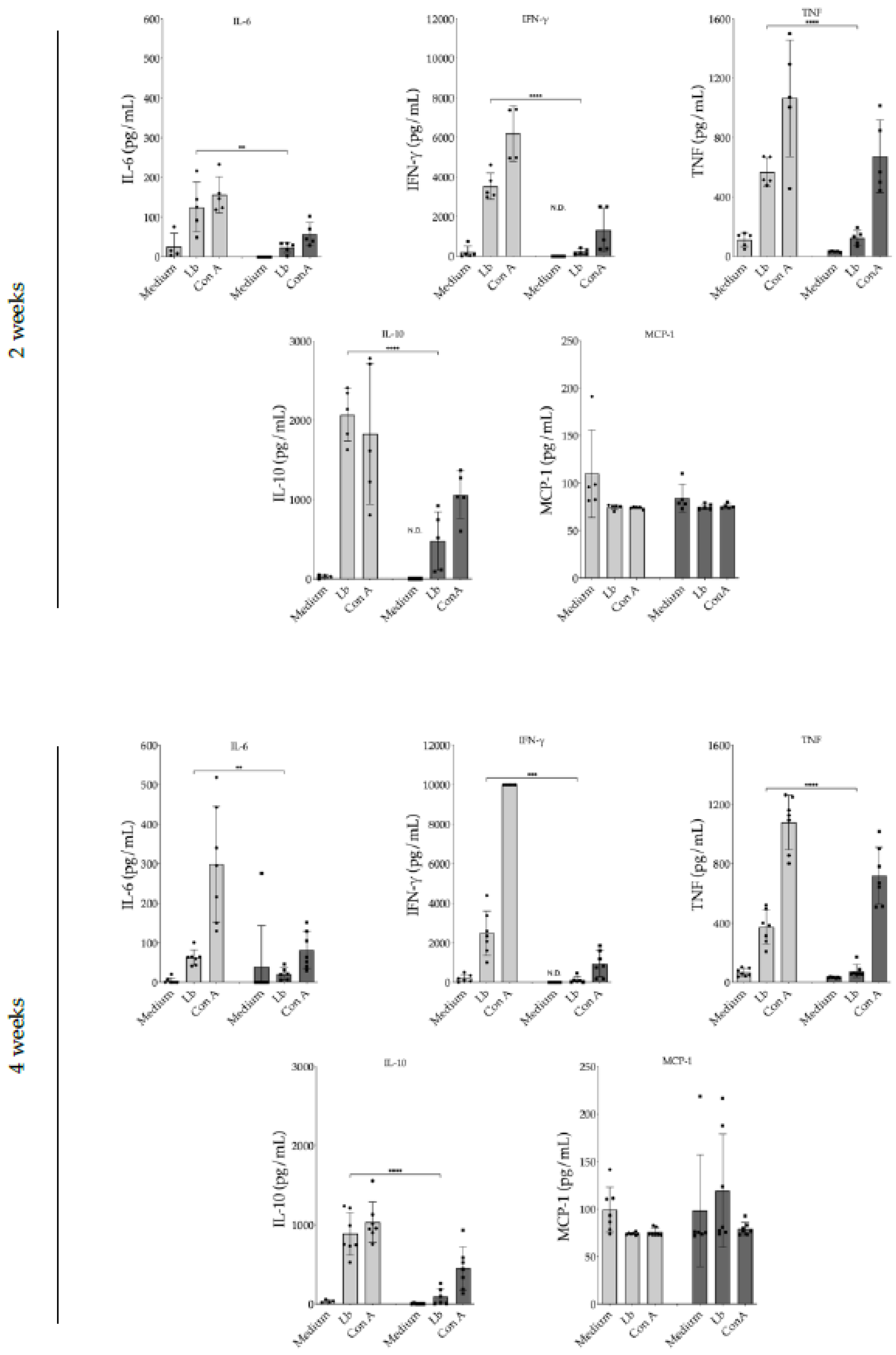
3.3. Evaluation of 17-DMAG Treatment on Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines Released by Lymph Node Cells from L. braziliensis-Infected BALB/c Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO Weekly Epidemiological Record. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 91, 441–460.
- mondiale de la Santé, O.; Organization, W.H. Weekly Epidemiological Record, 2016, Vol. 91, 39 [Full Issue]. Weekly Epidemiological Record= Relevé épidémiologique hebdomadaire 2016, 91, 441–460. [Google Scholar]
- de Menezes, J.P.B.; Guedes, C.E.S.; de O.A. Petersen, A.L.; Fraga, D.B.M.; Veras, P.S.T. Advances in Development of New Treatment for Leishmaniasis. Biomed Res Int 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solit, D.B.; Chiosis, G. Development and Application of Hsp90 Inhibitors. Drug Discov Today 2008, 13, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schopf, F.H.; Biebl, M.M.; Buchner, J. The HSP90 Chaperone Machinery. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2017, 18, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallavi, R.; Roy, N.; Nageshan, R.K.; Talukdar, P.; Pavithra, S.R.; Reddy, R.; Venketesh, S.; Kumar, R.; Gupta, A.K.; Singh, R.K. Heat Shock Protein 90 as a Drug Target against Protozoan Infections: Biochemical Characterization of HSP90 from Plasmodium Falciparum and Trypanosoma Evansi and Evaluation of Its Inhibitor as a Candidate Drug. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2010, 285, 37964–37975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zilberstein, D.; Shapira, M. The Role of PH and Temperature in the Development of Leishmania Parasites. Annu Rev Microbiol 1994, 48, 449–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graefe, S.E.B.; Wiesgigl, M.; Gaworski, I.; Macdonald, A.; Clos, J. Inhibition of HSP90 in Trypanosoma Cruzi Induces a Stress Response but No Stage Differentiation. Eukaryot Cell 2002, 1, 936–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, N.; Nageshan, R.K.; Ranade, S.; Tatu, U. Heat Shock Protein 90 from Neglected Protozoan Parasites. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular Cell Research 2012, 1823, 707–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hombach, A.; Ommen, G.; MacDonald, A.; Clos, J. A Small Heat Shock Protein Is Essential for Thermotolerance and Intracellular Survival of Leishmania Donovani. J Cell Sci 2014, 127, 4762–4773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guswanto, A.; Nugraha, A.B.; Tuvshintulga, B.; Tayebwa, D.S.; Rizk, M.A.; Batiha, G.E.-S.; Gantuya, S.; Sivakumar, T.; Yokoyama, N.; Igarashi, I. 17-DMAG Inhibits the Multiplication of Several Babesia Species and Theileria Equi on in Vitro Cultures, and Babesia Microti in Mice. Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist 2018, 8, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murillo-Solano, C.; Dong, C.; Sanchez, C.G.; Pizarro, J.C. Identification and Characterization of the Antiplasmodial Activity of Hsp90 Inhibitors. Malar J 2017, 16, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, K.J.; Shapiro, T.A. Potent Antitrypanosomal Activities of Heat Shock Protein 90 Inhibitors in Vitro and in Vivo. J Infect Dis 2013, 208, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palma, L.C.; Ferreira, L.F.G.R.; Petersen, A.L. de O.A.; Dias, B.R.S.; Menezes, J.P.B. de; Moreira, D.R. de M.; Hernandes, M.Z.; Veras, P.S.T. A Docking-Based Structural Analysis of Geldanamycin-Derived Inhibitor Binding to Human or Leishmania Hsp90. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 14756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, A.L. de O.A.; Guedes, C.E.S.; Versoza, C.L.; Lima, J.G.B.; de Freitas, L.A.R.; Borges, V.M.; Veras, P.S.T. 17-AAG Kills Intracellular Leishmania Amazonensis While Reducing Inflammatory Responses in Infected Macrophages. PLoS One 2012, 7, e49496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva Santos, C.; Brodskyn, C.I. The Role of CD4 and CD8 T Cells in Human Cutaneous Leishmaniasis. Front Public Health 2014, 2, 102244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egorin, M.J.; Lagattuta, T.F.; Hamburger, D.R.; Covey, J.M.; White, K.D.; Musser, S.M.; Eiseman, J.L. Pharmacokinetics, Tissue Distribution, and Metabolism of 17-(Dimethylaminoethylamino)-17-Demethoxygeldanamycin (NSC 707545) in CD 2 F 1 Mice and Fischer 344 Rats. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 2002, 49, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sausville, E.A. Geldanamycin Analogs. Journal of chemotherapy 2004, 16, 68–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitesell, L.; Lin, N.U. HSP90 as a Platform for the Assembly of More Effective Cancer Chemotherapy. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular Cell Research 2012, 1823, 756–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, C.I. de; Barral Netto, M. O Modelo Experimental Nas Infecções Causadas Por L. Amazonensis e L. Braziliensis. 2005.
- Debnath, A.; Shahinas, D.; Bryant, C.; Hirata, K.; Miyamoto, Y.; Hwang, G.; Gut, J.; Renslo, A.R.; Pillai, D.R.; Eckmann, L. Hsp90 Inhibitors as New Leads to Target Parasitic Diarrheal Diseases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2014, 58, 4138–4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannini, G.; Battistuzzi, G. Exploring in Vitro and in Vivo Hsp90 Inhibitors Activity against Human Protozoan Parasites. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2015, 25, 462–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zininga, T.; Shonhai, A. Small Molecule Inhibitors Targeting the Heat Shock Protein System of Human Obligate Protozoan Parasites. Int J Mol Sci 2019, 20, 5930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murillo-Solano, C.; Dong, C.; Sanchez, C.G.; Pizarro, J.C. Identification and Characterization of the Antiplasmodial Activity of Hsp90 Inhibitors. Malar J 2017, 16, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, A.L. de O.A.; Cull, B.; Dias, B.R.S.; Palma, L.C.; Luz, Y. da S.; de Menezes, J.P.B.; Mottram, J.C.; Veras, P.S.T. 17-AAG-Induced Activation of the Autophagic Pathway in Leishmania Is Associated with Parasite Death. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palma, L.C.; Ferreira, L.F.G.R.; Petersen, A.L. de O.A.; Dias, B.R.S.; Menezes, J.P.B. de; Moreira, D.R. de M.; Hernandes, M.Z.; Veras, P.S.T. A Docking-Based Structural Analysis of Geldanamycin-Derived Inhibitor Binding to Human or Leishmania Hsp90. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 14756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansfield, C.R.; Quan, B.; Chirgwin, M.E.; Eduful, B.; Hughes, P.F.; Neveu, G.; Sylvester, K.; Ryan, D.H.; Kafsack, B.F.C.; Haystead, T.A.J. Selective Targeting of Plasmodium Falciparum Hsp90 Disrupts the 26S Proteasome. Cell Chem Biol 2024, 31, 729–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiang, J.G.; Agravante, N.G.; Smith, J.T.; Bowman, P.D. 17-DMAG Diminishes Hemorrhage-Induced Small Intestine Injury by Elevating Bcl-2 Protein and Inhibiting INOS Pathway, TNF-α Increase, and Caspase-3 Activation. Cell Biosci 2011, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-L.; Shen, H.-H.; Cheng, P.-Y.; Chu, Y.-J.; Hwang, H.-R.; Lam, K.-K.; Lee, Y.-M. 17-DMAG, an HSP90 Inhibitor, Ameliorates Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome via Induction of HSP70 in Endotoxemic Rats. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0155583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tukaj, S.; Węgrzyn, G. Anti-Hsp90 Therapy in Autoimmune and Inflammatory Diseases: A Review of Preclinical Studies. Cell Stress Chaperones 2016, 21, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tukaj, S.; Zillikens, D.; Kasperkiewicz, M. Inhibitory Effects of Heat Shock Protein 90 Blockade on Proinflammatory Human Th1 and Th17 Cell Subpopulations. Journal of Inflammation (United Kingdom) 2014, 11, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimp, S.K.; Chafin, C.B.; Regna, N.L.; Hammond, S.E.; Read, M.A.; Caudell, D.L.; Rylander, M.N.; Reilly, C.M. Heat Shock Protein 90 Inhibition by 17-DMAG Lessens Disease in the MRL/Lpr Mouse Model of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Cell Mol Immunol 2012, 9, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimp, S.K.; Parson, C.D.; Regna, N.L.; Thomas, A.N.; Chafin, C.B.; Reilly, C.M.; Nichole Rylander, M. HSP90 Inhibition by 17-DMAG Reduces Inflammation in J774 Macrophages through Suppression of Akt and Nuclear Factor-ΚB Pathways. Inflammation research 2012, 61, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimmanapalli, R.; O’Bryan, E.; Kuhn, D.; Yamaguchi, H.; Wang, H.G.; Bhalla, K.N. Regulation of 17-AAG-Induced Apoptosis: Role of Bcl-2, Bcl-XL, and Bax Downstream of 17-AAG-Mediated down-Regulation of Akt, Raf-1, and Src Kinases. Blood 2003, 102, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




