1. Introduction
Atypical antipsychotics (AAPs) are the first line of treatment for schizophrenia but are also commonly prescribed for the treatment of other psychiatric disorders, including bipolar disorder and treatment-resistant depression, as well as for the management of community-dwelling persons with Alzheimer’s disease, other forms of dementia [
1], behavior issues associated with autism and intellectual disability [
2] and other behavior-mood disorders including attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) [
3]. The global prevalence of antipsychotic use in adults has been estimated at 1-2%, reported at 1.7 % in the USA in 2020 [
4], with fast-increasing rates in children and adolescents [
5]. AAPs are weak dopamine D2 receptor blockers with variable additional pharmacological targets that commonly involve serotonin (5-HT) receptors [
6]. The ratio of 5-HT2A/D2 and 5-HT2C/D2 receptor affinity and a rapid dissociation constant from the D2 receptor are two important factors that distinguish AAPs in terms of efficacy and side effects [
7]. Other molecular targets additionally characterize the receptor profile of AAPs: 5-HT1 partial agonism, H1 antagonism, α2 antagonism, muscarinic antagonism and positive allosterism, brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) production, and blockade of glycine transporter (GlyT) [
8].
Since AAPs prescriptions are generally life-long, handling side-effects is a relevant concern for physicians and patients [
9]. Although some of these are related to their direct pharmacology targets in the CNS, they are frequently drug-specific and thus likely related to off-target effects or derived from their chemical structures that differentially interfere with cellular physiology.
The most common side-effects are metabolic complications such as dyslipidemia [
10], and impaired glucose homeostasis [
11]. These occur frequently, but not always, along with significant weight gain [
12], and always lead to a relevant increase in cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk [
13]. The fact that the affected groups tend to have, even before treatment starts, a higher prevalence of metabolic syndrome (MetS) and higher CVD risk than the general population further highlights the relevance of the problem [
14].
The mechanisms involved have been extensively investigated but have yet to be clarified. Although some risk derives from the patients themselves, the increased CVD risk is still mainly associated with the treatment [
15]. It has been proposed that the sedative effect of some AAPs and the related increased food intake play a fundamental role [
16]. However, other factors can contribute. AAPs cause hepatotoxicity and inflammation in the liver [
17]. Since the liver is a central metabolic organ, this has an essential impact on the systemic metabolic homeostasis [
18]. The mechanisms involved in liver toxicity are generally regarded as related to AAPs catabolism. AAPs are xenobiotics whose catabolism involves P450 enzymes, leading to enhanced productions of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and, in some cases, the accumulation of reactive intermediate metabolites [
19]. More recently, some studies have investigated the possible role of mitochondria as an alternative source of elevated ROS levels following AAPs administration [
20]. The high hydrophobicity of these molecules can lead to their accumulation in biological membranes, including the mitochondrial inner membrane (IMM), and thus alter cell signaling and bioenergetics; in fact several AAPs have been found to directly alter mitochondrial bioenergetics [
21]. Importantly, mitochondrial damage and oxidative stress have also been shown to play a negative role in neurodegenerative, neurodevelopmental, and behavior disorders [
22]. Furthermore, recent studies suggest that reduced mitochondrial homeostasis, that is, the impairment of mitochondria regulation in terms of activity and turnover, has a negative impact on the cellular capacity to respond to stressors and thus hampers the cellular capacity to prevent the accumulation of cellular damage [
23] and may also dysregulate the activation of cell death related pathways. An early response to mitotoxins is the induction of mitochondrial fission that can enable the elimination of damaged mitochondria through mitophagy [
24]. Fission has been shown to reduce both the mitochondrial oxidative capacity and its sensitivity to mitochondrial-dependent cellular apoptosis, a process that is particularly relevant in the cancer [
25]. In sum, interference with mitochondrial function has been shown to fundamentally alter cell physiology, the cellular capacity to adequately respond to nutrient availability and oxidative stress [
26], to increase metabolic and cardiovascular risk [
27] and to have a negative impact on neurological homeostasis [
24]. Therefore, to minimize the negative side effects of AAPs administration, it is of fundamental importance to evaluate their particular cellular effects and the mechanisms involved.
Clozapine and olanzapine (OLA) are the worst AAPs in terms of increased MetS risk [
28]. OLA is the 4
th most commonly prescribed AAP, accounting for about 10% of the total AAPs prescriptions. Importantly, type 2 diabetes (T2D) is not strictly correlated with adiposity. In fact, 25 % of patients develop hyperglycemia without gaining weight and this metabolic alteration can happen in the early period of the treatment and precede weight gain. Nevertheless, it is important to highlight that weight gain undoubtedly represents an aggravating factor [
29]. On the other hand, OLA reduces both positive and negative psychotic symptoms significantly more than most other AAPs and is associated with a significant reduction of depressive episodes and a more significant improvement in the social functioning [
30]. Therefore, it is one of the most commonly prescribed AAPs [
31].
The precise mechanism of OLA action is unknown since it exhibits a wide array of receptor affinities that may explain the clinical and adverse effects. Efficacy in schizophrenia may be by a combination of dopamine D2 and serotonin 5-HT2A receptor antagonism in the mesolimbic pathway [
32]. OLA shows a higher affinity for serotonin 5-HT 2A receptors than dopamine D2 receptors with selectivity for dopamine receptor subtypes in the mesolimbic and mesocortical systems over the nigrostriatal and tuberoinfundibular systems; perhaps the reason for the reduced risk of extrapyramidal side effects and hyperprolactinemia. Antagonism at muscarinic, histaminic, and alpha-adrenergic receptors leads to side effects, such as dry mouth, micturition difficulty, constipation, weight gain, somnolence, dizziness, and hypotension [
33]. OLA is well absorbed when taken orally with 80 % bioavailability although undergoing first-pass metabolism, and reaches peak plasma concentrations after 6 h where it is predominantly bound to albumin (90 %) and α1-acid glycoprotein (77 %). It has linear kinetics with an elimination half-life of 21–54 h reaching steady-state concentration after one week [
34]. In the liver, OLA is metabolized to its 10- and 4′- N-glucuronides, 4′-N-desmethyl olanzapine [cytochrome P450(CYP) 1A2] and olanzapine N-oxide [flavin monooxygenase 3], and then cleared. Metabolism to 2-hydroxymethyl olanzapine via CYP2D6 is a minor pathway. Furthermore, OLA does not inhibit CYP isozymes [
7]. However, OLA has been shown to increase plasma transaminases levels, suggesting drug-induced liver damage, liver steatosis, and even non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (a pathological development of simple liver steatosis) in some cases, the effects that could be related to its impact on whole-body metabolism [
35]. Some
in vitro studies have evaluated the effect of OLA on the mitochondria and its impact on redox homeostasis. For example, OLA has been shown to induce mitochondrial fission [
36], the down-regulation of electron transport chain (ETC) genes as well as to decrease mitochondrial enzyme activity, ATP synthesis, and oxygen consumption rate (OCR) in circulating leukocytes of patients at elevated risk for MetS [
37]. Furthermore, increased oxidative stress and glutathione depletion was detected in hepatocytes treated with OLA in one study, and implicated both mitochondrial toxicity and CYP450 activity [
38]. Other studies on the mitochondrial toxicity of AAPs imply that OLA has very little or no direct mitochondrial toxicity, while other AAPs, and in particular, aripiprazole (ARI), have been shown to reduce mitochondrial OCR [
39] in liver cells, an effect that may be related to the inhibition of ETC Complex I (CI) or CV activity [
40]. Although a clear picture of AAPs interference on mitochondria has not emerged yet, available data suggest that it may trigger mitochondrial dysfunction and lead to the development of MetS.
ARI is the 2
nd most widely prescribed AAP, accounting for about 20 % of the total number of AAPs prescriptions. It is a partial agonist of D2 receptors [
41], a partial 5-HT1A receptor agonist, and a 5-HT2A receptor antagonist. Its unique pharmacological properties compared to other AAPs, along with the resulting lack of the sedative and hyperphagic effects, have prompted physicians to recommend its prescription in patients at risk of or with MetS. ARI has been shown to induce debilitating extrapyramidal syndromes (EPS) in ~ 5 to 15 % of patients likely due to off-target effects. ARI is catabolized in the liver by N-dealkylation, hydroxylation, and dehydrogenation by the cytochrome P450 (CYP)3A4 and 2D6 enzymes, thus polymorphisms in these genes can reduce drug tolerance [
42,
43]. However, LiverTox NIH publication notes, updated in 2023 indicates that ARI’s hepatotoxicity likelihood score falls under the D category, namely, possible rare cause of clinically apparent liver injury [
44]. Nevertheless, a literature search reveals that several cases related to ARI-induced liver injury have been reported [
45] but, there are no large-scale epidemiological studies to provide sufficient pharmacoepidemiology evidence [
46]. Of note, chronic feeding of adult
Drosophila melanogaster with ARI has been shown to result in structural damage of brain and thoracic muscle mitochondria, along with locomotor dysfunction [
47], supporting the notion that ARI mitotoxicity occurs
in vivo and can have a significant pathologic role.
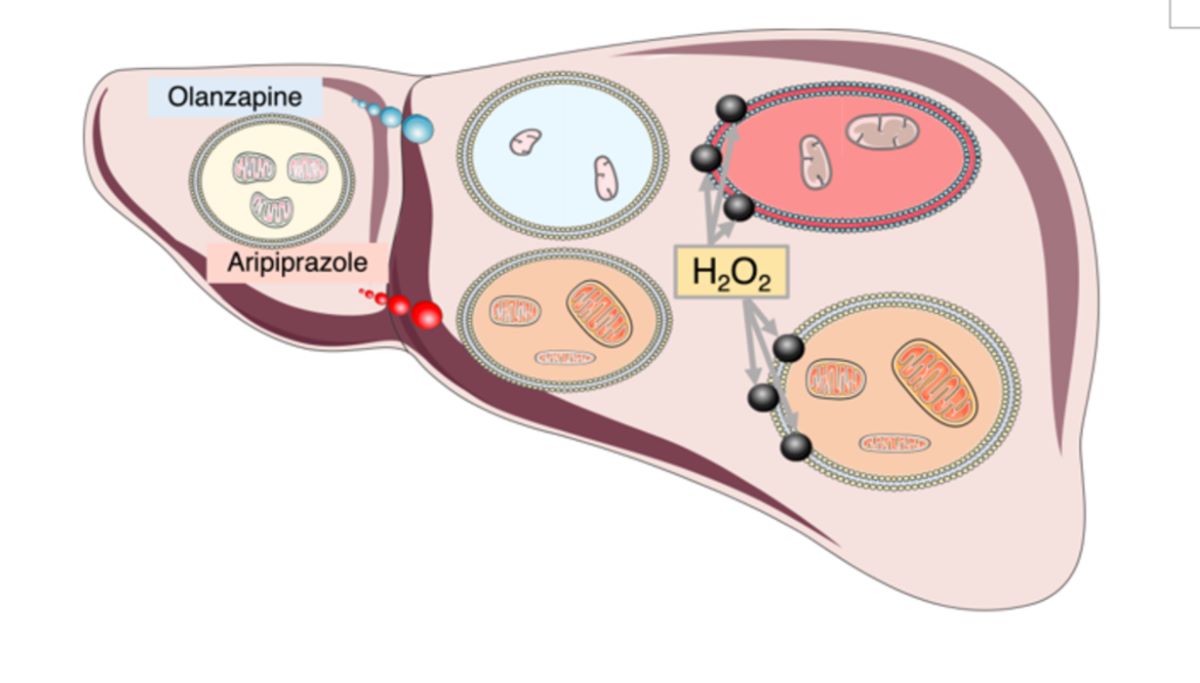
In order to shed some light on the mechanisms involved in ARI and OLA secondary effects, we used Fao cells, a rat hepatocarcinoma (HCC) cell line with well-preserved metabolic plasticity and ROS sensing and tested how ARI and OLA 24 h single treatment, as well as daily treatments for several weeks, modified the cellular response to an oxidative challenge. Our results imply that ARI mitotoxicity reduces the cellular sensitivity to MAPK activation and as a result show reduced cell death rates following an oxidative challenge.
2. Materials and Methods
Reagents were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) unless otherwise indicated.
Cell culture. The rat hepatoma cell line Fao (#89042701, ECACC) was grown at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere with 5 % CO2, in Coon’s F-12 Modified Liquid Medium (#MBC-F0855) supplemented with 10 % fetal bovine serum (#10270-106, Gibco, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Whaltham, MA, USA), 1 % penicillin/streptomycin (#15140-122, Gibco, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Whaltham, MA, USA) and 1 % GlutaMAX supplement (#35050038, Gibco, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Whaltham, MA, USA). Cells were seeded on 96-well flat-bottom cell culture plate (40.000 cells/well) for cytotoxicity assessments, Collagen coated (5 μg/cm2) 1 cm2 glass cover slips positioned on 24-well plates (200.000 cells/well) for MitoSOX assessment, 12-well cell culture plates (500.000 cells/well) for caspase activity determination, 6-well cell culture plates (1 million cells/well) for proteasomal activity measurement, 6-well cell culture plates (1 million cells/well) and T25 flasks (3 million cells/flask) for gene and protein expression analyses. To test ARI and OLA effects Fao cells were grown in the presence of a control vehicle, 0.12 % DMSO (#67-68-5, Acros Organics, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Whaltham, MA, USA), ARI (#PHR1784) or OLA (#PHR1825) at doses corresponding to laboratory alert levels in patients’ sera (2.23 μM ARI and 0.32 μM OLA) and at 6μM ARI/OLA. Different batches of cells were tested in parallel. Cells were exposed to ARI/OLA for 24 h (single treatment) or 4-8 weeks (repeated treatment), with media changes every 24 h, prior to being challenged with 1.5/3 mM H2O2 for 3 h and harvested.
MitoSOX. Cells were seeded on Collagen-coated glass coverslip glasses 24 h prior to treatment. Following treatment, cells were washed with 1x PBS and labeled with 3 μM MitoSOX in HBSS (1.26 mM CaCl2, 0.49 mM MgCl2 × 6H2O, 0.41 mM MgSO4 × 7H2O, 5.33 mM KCl, 0.44 mM KH2PO4, 4.17 mM NaHCO3, 137.93 mM NaCl, 0.34 mM Na2HPO4, 5.56 mM D-glucose) in the darkness for 10 min at 37 °C. Then, the cells were washed with 1x PBS, fixed with 4 % paraformaldehyde for 15 min at room temperature, washed again with 1x PBS and stored at 4 °C 1x PBS in the darkness prior to mounting on slides with ProLong Diamond Antifade Mountant (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA). Slides were stored in the dark at 4 °C. Images were captured using a fluorescence inverted microscope (Olympus IX81F, Olympus Corporation, Japan). The images’ scale bar is 50 μm.
Cell viability. Cytotoxicity was evaluated using 0.04 mg/mL Neutral Red (NR, 3-Amino-7-dimethylamino- 2-methylphenazine hydrochloride; N4638) staining as previously described [
48]. NR assay was performed for single ARI/OLA treatments. Dehydrogenase activity was determined using the Thiazolyl Blue Tetrazolium Bromide assay (MTT, #M5655). The extracellular release of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) was measured using the LDH Cytotoxicity Detection Kit (#MK401, Takara Bio Europe, Saint-Germain-en-Laye, France) as previously described [
49]. Cells’ images were captured using an inverted microscope (Leica, Wetzlar, Germany). Representative images are included in
Supplementary Figure S1. The images scale bar is 50 μm.
Caspase activity. Caspase 3/7 and 9 activities were assessed using Caspase-Glo reagents (#G810C, (#G811C #G816C, #G822C, Promega, Madison, WI, USA) following the manufacture’s instructions. Caspase cleavage releases an active luciferase substrate whose luminescence signal is proportional to caspase activity and is detectable in a Luminometer. This assay was used following ARI and OLA treatments with and without the 3 h H2O2 challenge, as well as with cells treated for 3 h with 1 μM staurosporine (STS), a powerful inductor of apoptosis through the mitochondrial pathway, prior to harvesting. The cells were washed with 1x PBS and stored at –80 °C. Cells were next lysed in CCLR lysis buffer (# E1531, Promega, Madison, WI, USA), centrifuged and the supernatant was saved, diluted with CCLR and Caspase-Glo 9 or Caspase-Glo 3/7 reagent were added. Following 20 min incubation, the luminescence signal was captured with a luminometer 20/20n (Turner Biosystems Corp., Promega, Madison, WI, USA). Protein concentration in the extract was determined using the Pierce 660 nm Protein Assay Reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA) and used to determine the luminescence/μg of protein in the sample.
mRNA analysis. Total RNA was isolated and retro-transcribed as previously described [
48]. Gene expression was assessed by qPCR analysis using TaqMan probes in a 7500 Real-Time PCR System using the SDS v1.3.1 software (Applied Biosystems, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Genes expression was calculated relative to the expression of the reference gene, 18S rRNA (#Rn18s) using the equation: target/reference=(E(reference)Ct(reference))/(E(target)Ct(target)). Biological replicate values were then divided by the average of all samples in the replicate to account for multi-plate experiments variability and expressed as logarithmic fold change normalized to the baseline sample without a probe. The following TaqMan probes labelled with the FAM dye (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Whaltham, MA, USA) were used: the reference gene Rn18s (#Rn03928990_g1),
Cas3 (#Rn00563902_m1),
Cas9 (#Rn00581212_m1),
p38 (#Rn00578842_m1),
Stat3 (#Rn00680715_m1),
Bax (#Rn01509178_m1),
Bcl2 (#Rn99999125_m1),
BclXL (#Rn00437783_m1),
Mcl1 (#Rn00821024_g1),
Bid (#Rn01459517_m1),
Diablo (#Rn01480487_g1).
Protein extraction and western blotting (WB). Whole-cell lysates were obtained as described [
50]. In brief, 20 μg of whole protein extracts, were loaded onto 10 % and 12 % acrylamide gels to be separated by standard sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). The gel was stained with Coomassie blue (#27813Fluka,) to control for equal loading and proteins were transferred onto PVDF Immobilon-P membranes (#IPVH00010) using a semi-dry transfer system (BioRad Hercules, CA, USA). Membranes blocked with 3 % BSA in TBS-T were incubated overnight at 4 °C with primary antibodies washed with TBS-T and then incubated with horse radish peroxidase-conjugated goat anti-rabbit or goat anti-mouse secondary antibodies (BioRad Hercules, CA, USA #1706515 and #1706516, respectively) washed again and developed with Clarity ECL Substrate (BioRad Hercules, CA, USA). The luminescence signal was captured on X-ray films (AGFA, CP-BU, 0413) and developed by Curix60, 9462 developing machine then quantified using the v.5.2.5. Image Studio software (LI-COR, Lincoln, NE, USA). Experiment’s replicates on separate membranes were normalized calculating the ratio of individual values by the average signal for all samples in the membrane. Primary antibodies used were, from Cell Signaling Technology (Danvers, MA, USA): Phospho-p38 MAPK (Thr180/Tyr182) (#9211), p38 MAPK (#9212), Phospho-SAPK/JNK (Thr183/Tyr185) (#9251), SAPK/JNK (#9252), Phospho-p44/42 MAPK (Erk1/2) (Thr202/Tyr204) (#9101), p44/42 MAPK (Erk1/2) (#9102), Phospho-Stat3 (Tyr705) (D3A7) XP Rabbit mAb (#9145), Stat3 (D3Z2G) Rabbit mAb (#12640), from Abcam (Cambridge, UK): Bcl-xL (#2762), LC3B (#2775) and from BD transduction Laboratories (Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA): Tim23 (#611222). Raw data is included in
Supplementary Figures S2 and S3.
Proteasome activity was determined as previously described [
51], a procedure is based on 7-Methoxycoumarin-4-acetic acid (MCA) fluorescence, which is released following cleavage of the fluorogenic peptide suc-LLVY-MCA in the presence of chymotrypsin-like proteasome activity. The method allows the separate determination of the 20S and the 26S proteasome activities by using its differential requirement for ATP. The 20S subunit does not require ATP, while it is necessary for the proteolytic activity of the fully assembled 26S proteasome. In brief. Following treatments, cell culture plates were washed with 1x PBS and stored at -80 °C. Following thawing, cells were scraped with a rubber spatula in proteasome assay (PA) lysis buffer (250 mM sucrose, 30 mM HEPES, 20 mM MgCl
2, 1.3 mM EDTA, 1.6 mM DTT, pH 7.8), homogenized using a 0.5 mm sonotrode (UP50H, Hielscher, Germany), in sets of three, with 10 0.5 s pulses at 80 % amplitude and then centrifuged. The supernatants were stored at -80 °C. Following thawing, 10 μl of the sample was placed on black 96-well plates along with the reaction mixture corresponding to the proteasome to be analyzed (20S: 1.8 M DTT, 16 mM deoxyglucose, 0.1 mg/mL hexokinase in PA; 26S: 1.8 M DTT 4.5 mM ATP in PA). The reaction was activated by the addition of 180 μM substrate suc-LLVY-MCA and following 1 h incubation at 37 °C the fluorescence was measured in a Victor3 reader, excitation 355 nm, emission 460 nm (PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA, USA). Proteasome activity was estimated as the amount of MCA released per time unit per μg of protein, predetermined with the Pierce 660 nm Protein Assay Reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA).
Statistical analysis was performed with GraphPad Prism 10.1.1 using its inbuilt algorithm to test the equality of variances from medians with the Brown-Forsythe test. One-way ANOVA was used in case of equal variances, followed by the Dunnett’s multiple-comparisons test (when testing multiple experimental groups against a single control group) or Tukey’s multiple-comparison test (when studying a relationship between variables). Unpaired
t test was used when comparing two samples (LC3B data). Two-way ANOVA was used on two sets of data, how two independent variables, in combination, affect a dependent variable. In particular, it was used to test for the interaction of the phosphorylated and non-phosphorylated forms of the proteins JNK and ERK derived from western blot analysis. Data from statistical tests (Brown-Forsythe, One- and Two-way ANOVA, t-test) were compiled and are included in
Supplementary Tables S1–S5. Treated samples were compared to the baseline and untreated controls. All data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD), and the significance level was set at
p<0.05. Statistical parameters, sample sizes (
n) and
p-values, are noted in the figure legends.
3. Results
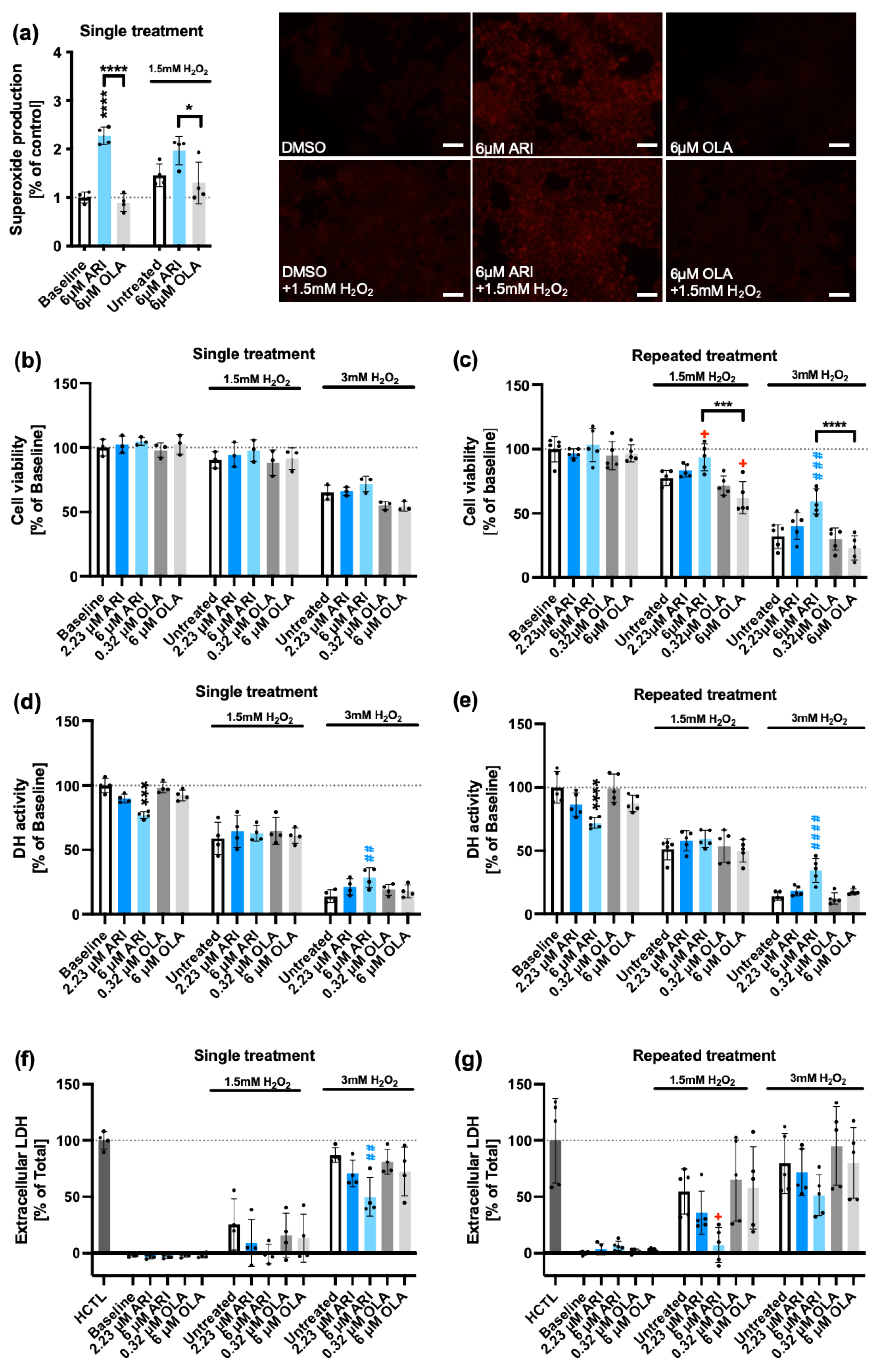
Mitochondrial superoxide (O2∙-). In order to investigate the effects of ARI and OLA interference with mitochondrial function, we first determined mitochondrial O
2∙- production using MitoSOX staining in ARI- and OLA-treated Fao cells and found that at a concentration of 6 M, a single ARI but not OLA treatment, produced a significant increase in mitochondrial O
2∙- (
Figure 1a). This implies that ARI had significant mitochondrial toxicity, a result consistent with the previous observation that ARI at this dosage and timing reduced mitochondrial OCR and increased cellular H
2O
2 levels [
39].
ROS generally induce compensatory responses, including enhanced expression of antioxidants. However, previous observations implied that in single treatments Fao cells did not increase antioxidant capacity since at least superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GPx) and catalase activities were not significantly modified in response to ARI, however, the activities of GPx and catalase significantly increased over the control upon continuous exposure to 6 μM ARI for 4-8 weeks [
39]. In sum, increased ROS production was not linked to an overall increase in antioxidant capacity following a single treatment, but may do so following a long-term exposure, suggesting that long-term ARI treatment could be modifying the cellular capacity to respond to oxidative stress.
To evaluate this possibility, the response of Fao cells was tested following repeated exposure to ARI/OLA for 4-8 weeks, to an oxidative 3 h challenge with 1.5-3 mM H
2O
2. It was found that 6 μM treated ARI cells significantly increased the activity of two antioxidants, SOD and catalase, the protein levels of the antioxidant heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), as well as, upregulated the gene expression of sulfiredoxin-1 (
Srxn1), another antioxidant, and
Foxo3a, a transcription factor that controls antioxidant gene expression. In contrast, 6 μM OLA did not induce any of these changes [
48], implying that ARI but not OLA significantly enhanced resistance to oxidative stress upon oxidative challenge. Consistently, repeated exposure to 6 μM ARI was shown to reduce Fao cell death induced by 1.5 mM and 3 mM H
2O
2, while OLA had the opposite effect [
48].
In order to determine if ARI elicited changes in the response to an oxidative challenge required a long-term adaptation (repeated treatment), we tested how and if a single treatment with ARI/OLA modified the response of Fao cells to an oxidative challenge with 1.5-3 mM H
2O
2. Therefore, we evaluated mitochondrial O
2∙- levels, using MitoSOX staining, in Fao cells treated with 6 M ARI/OLA followed by 3 h exposure to 1.5 mM H
2O
2. We found that ARI-treated cells had significantly higher levels of O
2∙- than OLA-treated cells, while O
2∙- production in OLA-treated cells did not differ from controls, a result similar to that obtained in the presence of 1.5 mM H
2O
2 (
Figure 1a).
Cellular viability. Next, we aimed to determine if these differences impacted the cellular viability of ARI-/OLA- pretreated cells challenged with 1.5-3 mM H
2O
2 for the last 3 h. First, we tested the lysosomal uptake of the neutral red (NR) dye, to identify living cells. In single-treated cells, 3 mM H
2O
2 significantly decreased cell viability, but we did not find significant differences among the treatment groups (
Figure 1b). However, we previously observed [
48] that in repeated treatments, at both 1.5 and 3 mM H
2O
2, which decreased cell viability in non-treated cells, 6 μM ARI treated cells had significantly higher NR levels than non-treated controls, while following the 1.5 mM H
2O
2 challenge, 6 μM OLA treated cells survived significantly less than non-treated controls (
Figure 1c). These results imply that ARI-treated cells, although enduring higher ROS levels, are more resistant to oxidative stress-induced cell death. We further tested this concept using an alternative viability test, MTT, which measures cellular NAD(P)H dehydrogenase (DH) activities and is, therefore, also indicative of the cellular metabolic status. In non-treated controls both 1.5 and 3 mM H
2O
2 significantly reduced DH activity. For cells exposed to 1.5 mM H
2O
2 we did not find significant differences among the groups but, in cells challenged with 3 mM H
2O
2 we observed both, for single and repeatedly treated cells, a significantly higher survival rate for cells treated with 6 μM ARI than the basal non-treated cells (
Figure 1d,e), suggesting that ARI enhances survival also following a single treatment (
Figure 1d). Finally, we further tested cell viability using a lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release test, that measures cell rupture by determining the activity of LDH present in the extracellular media. Using this assay, we found that in single-treated cells, following a 3 mM H
2O
2 challenge, which increased LDH levels in non-treated cells, 6 μM ARI-treated cells had significantly lower LDH release than non-treated controls (
Figure 1f) and in repeatedly-treated cells, where both 1.5 and 3 mM H
2O
2 increased LDH release in non-treated cells, following a 1.5 mM H
2O
2 challenge, 6 μM ARI-treated cells also had significantly lower LDH release than non-treated controls (
Figure 1g). Altogether, these data support that ARI enhances cell survival following an H
2O
2 challenge, while OLA if any, has the opposite effect. Of note, as previously reported, at baseline (without H
2O
2) 6 μM ARI, in both single and repeated treatments, significantly reduces MTT activity (
Figure 1d,e). As there is no corresponding decrease in NR or increase in LDH release, this reduction is possibly related to ARI mitotoxicity.
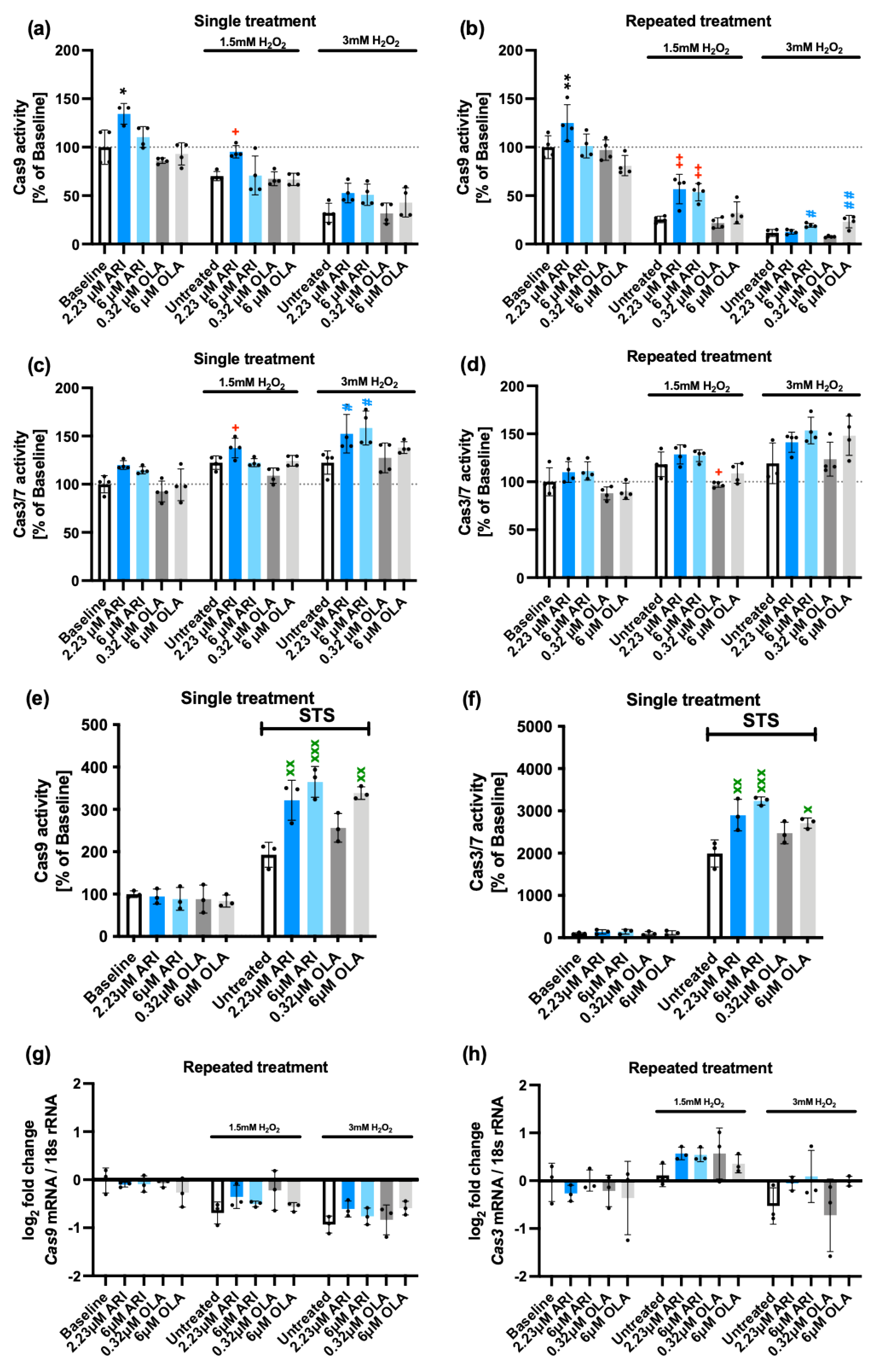
Apoptosis. Since oxidative stress can lead to different types of cell death, including apoptosis, necroptosis, pyroptosis and ferroptosis [
52], we decided to determine if the activation of apoptosis following the H
2O
2 challenge differed with the ARI/OLA pre-treatment. To that end, we evaluated the activity of Caspase 9, mainly involved in the mitochondrial cell death pathway, and the final effectors of apoptosis, Caspase 3/7. As previously reported, Fao cells both single- and repeatedly-treated with 2.23 μM ARI have significantly higher Caspase 9 activity at baseline (without H
2O
2) (
Figure 2a,b). Even though Caspase 9 activity was lower in H
2O
2-treated cells than in baseline samples, we consistently found that both single and repeated treatment with 2.23 μM ARI also significantly maintained higher Caspase 9 activity compared to equally treated controls in 1.5 mM H
2O
2 challenged cells (
Figure 2a,b). Furthermore, 6 μM ARI had the same effect in repeatedly treated cells, while these effects were not observed following treatment with OLA (
Figure 2a,b). Nevertheless, when cells were challenged with 3 mM H
2O
2 both 6 μM ARI and 6 μM OLA in repeated treatment maintained higher Caspase 9 levels than those of untreated cells (
Figure 2a,b). These results imply that the pro-survival activity of ARI is not related to a larger reduction in mitochondria-induced apoptosis. In fact, the observation that ARI-treated cells consistently show more Caspase 9 activity may relate to the higher levels of mitochondrial ROS and lower mitochondrial activity observed following ARI treatment.
We next evaluated Caspase 3/7 activities and, consistent with the results found for Caspase 9, we found that following a challenge with 1.5 or 3 mM H
2O
2, Fao cells, exposed to a single treatment with 2.23 μM ARI, maintained higher Caspase 3/7 levels than untreated controls (
Figure 2c). Also, a single treatment with 6 μM ARI significantly showed higher Caspase 3/7 activity than untreated cells, in response to a 3 mM H
2O
2 challenge (
Figure 2c). Similar tendencies were found in repeatedly-treated cells although in this case, differences did not reach statistical significance (
Figure 2d). In contrast, following a challenge with 1.5 mM H
2O
2, cells repeatedly treated with 0.32 μM OLA had significantly lower Caspase 3/7 activity than untreated controls, which may suggest that OLA is somehow preventing apoptosis. In sum, these results suggest that ARI-treated cells are more sensitive to apoptotic cell death through the mitochondrial pathway while OLA at low doses can actually exert a protective effect even though at high doses it can also promote apoptotic cell death in H
2O
2-treated cells. These observations may relate to the higher levels of mitochondrial ROS in ARI-treated cells, and further suggest the concept that ARI pro-survival effects are not likely related to the regulation of apoptosis.
To determine if these apoptotic responses were specific for H
2O
2 exposure or similarly responsive to other pro-apoptotic stimuli, cells were exposed to staurosporine (STS) following a single treatment with ARI/OLA. All treatments were statistically significant compared to the baseline. Furthermore, we found that treatment with both 2.23 and 6 μM ARI, as well as 6 μM OLA increased Caspase 9 as well as Caspase 3/7 activities in response to STS administration (
Figure 2e,f). This result confirms that both ARI and OLA have a general pro-apoptotic effect. Even though differences for the ARI
vs OLA did not reach statistical significance, the observation that, on average, both Caspase 9 and Caspase 3 levels were higher for 6 μM ARI treated cells than for 6 μM OLA following STS administration are consistent with the previous data indicating that ARI is a stronger inducer of cell apoptosis than OLA.
We next determined if the cells were responding to the treatments and the H2O2 challenge modifying the two Caspases’ gene expression. In repeatedly treated cells both at baseline and following 1.5/3 mM H2O2 exposure, we were unable to detect significant changes derived from the treatments. Nevertheless, 1.5/3 mM H2O2 exposure per se resulted in a small, significant, downregulation of Caspase 9 expression (g) and 1.5 mM H2O2 induced a small, non-significant, upregulation of Caspase 3 (h). Therefore, we concluded that ARI/OLA treatments do not affect Caspase’s 9 and 3 gene expression.
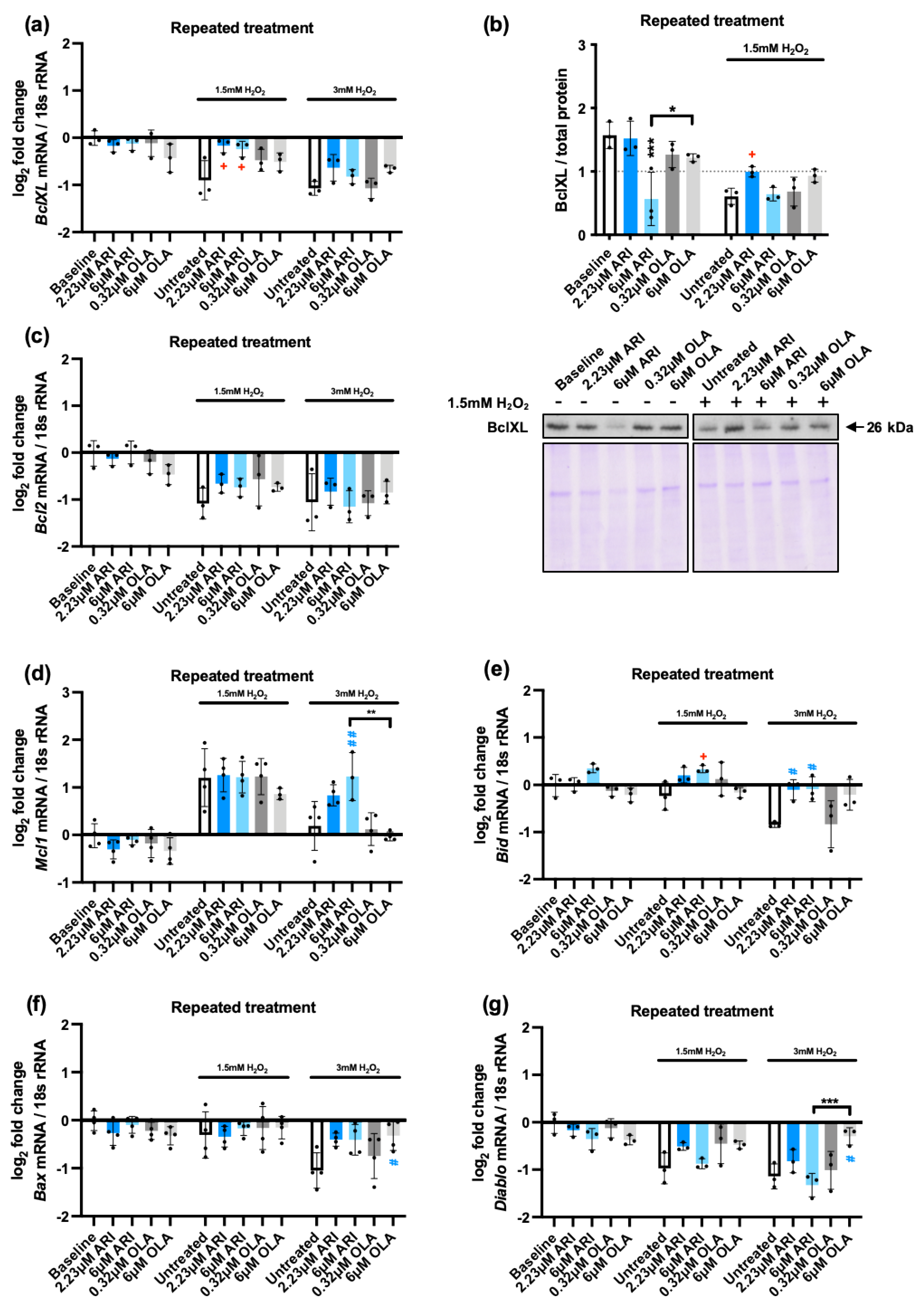
In view of these observations, we decided to evaluate if the observed differences between ARI and OLA regarding their capacity to induce apoptotic cell death may be related to gene expression/protein level changes in other pro- or anti-apoptotic genes/proteins in repeatedly treated cells.
We first tested the anti-apoptotic BCL-2 family member BclXL [
53] at gene expression (
Figure 3a) and protein levels (
Figure 3b). BclXL protein levels and mRNA levels were reduced in response to H
2O
2 in non-treated cells. In response to the treatments we found that, at baseline conditions 6 μM ARI significantly reduced its protein levels, although it did not alter its gene expression, suggesting this event was post-transcriptional. Following exposure to 1.5 mM H
2O
2 we found that cells treated with 2.23 μM ARI maintained higher mRNA and protein levels of BclXL than untreated controls, implying that these changes were transcriptionally regulated, with untreated cells being susceptible to a downregulation, while ARI-treated cells were more resistant to it. No significant differences were observed in response to OLA. Altogether these results suggest that if BclXL is a relevant factor in the higher capacity of ARI-treated cells to induce Caspase 9 activation, this would be likely related to the lower levels of BclXL in the ARI-treated cells at baseline, prior to H
2O
2 exposure. They also suggest that it is a lack of responsiveness in ARI treated cells that affects
Bclxl transcriptional regulation.
Other anti-apoptotic BCL-2 family members were also evaluated at gene expression level:
Bcl2 and
Mcl1. Regarding
Bcl2, we found no differences in baseline levels among treatments nor following the challenge with 1.5/3 mM H
2O
2. Nevertheless, H
2O
2 induced a downregulation of the gene at the two doses tested, similar to what was observed for BclXL. Regarding
Mcl1, we found no differences in baseline levels among treatments. Following the challenge with 1.5 mM H
2O
2 we found in non-treated cells a significant upregulation that was not modified by the treatments. In contrast,
3 mM H
2O
2 exposure did not result in an upregulation of Mcl1 in non-treated cells over baseline levels (
Figure 3d). Of note, following the challenge with 3 mM H
2O
2, 6 μM ARI-treated cells showed higher
Mcl1 expression than both non-treated controls and 6 μM OLA-treated cells, implying that ARI maintained the cellular responsiveness to Mcl1 induction in this case. Altogether, these results indicate that, following H
2O
2 exposure, ARI-treated cells maintain higher anti-apoptotic gene expression levels than non-treated or OLA-treated cells despite their higher caspase activity.
To understand the significance of these findings, since apoptosis is governed to a large extent through the balance between pro- and anti-apoptotic factors, we analyzed at gene expression level two pro-apoptotic members of the Bcl-2 family,
Bid (
Figure 3e) and
Bax (
Figure 3f) and another pro-apoptotic factor,
Diablo [
54] (
Figure 3g). We found that
Bid expression levels at baseline were similar among treatments, but following exposure to 1.5 mM H
2O
2 we observed that cells treated with 6 μM ARI maintained its higher expression levels. Non-treated cells when exposed to 3 mM H
2O
2 reduced B
id levels and treated with either 2.23 or 6 μM ARI had higher
Bid levels than non-treated controls, while OLA-treated cells did not significantly differ from non-treated controls. When
Bax and
Diablo gene expression were tested, we found that, 3 mM H
2O
2 decreased
Bax levels and both 1.5 and 3 mM H
2O
2 decreased
Diablo in non-treated cells. ARI-treated cells did not significantly alter the response tendency to reduce
Bax and
Diablo expression levels in the presence of H
2O
2, while 6 μM OLA-treated cells maintained significantly higher expression levels of both
Bax and
Diablo in the cells challenged with 3 mM H
2O
2. Furthermore, the higher OLA-dependent expression of
Diablo was statistically significant compared to that of ARI (
Figure 3g). Altogether, these results imply that following H
2O
2 exposure, ARI/OLA treated cells maintain higher expression levels of both pro- and anti-apoptotic genes, possibly making them more sensitive to both pro- and anti-apoptotic stimuli. The impact of ARI and OLA is different, and gene-specific. If the overall pro-/anti- apoptotic balance is globally altered by any of the antipsychotics remains to be established.
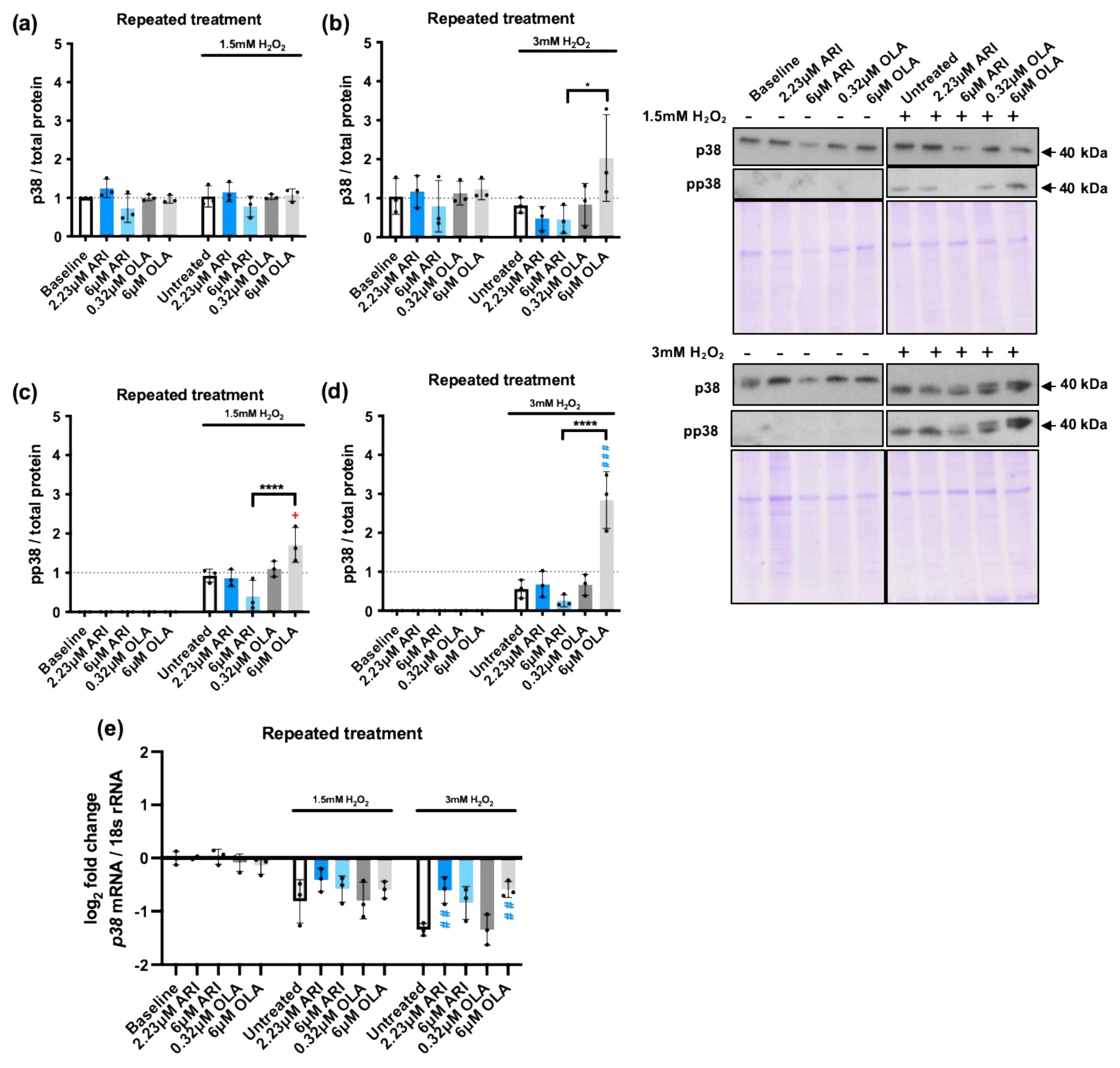
The cellular response to oxidative stress also largely depends on the activation of mitogen activated protein kinases (MAPKs). In fact, their activity determines if the increased ROS levels can drive increased cell proliferation, the activation of other stress response nodes, or cell death [
55]. We, therefore, evaluated the activation of the three main stress kinases: p38, c-Jun amino-terminal kinases (JNKs), and extracellular signal regulated kinase (ERK1/2) (
Figure 4) in response to 1.5 and 3 mM H
2O
2 exposure in cells repeatedly treated with ARI/OLA, testing their phosphorylation status by western blot. As expected, both 1.5 and 3 mM H
2O
2 exposure significantly increased phosphorylation of the three MAPKs. p38 is a multifaceted stress-responsive protein, well known as a ROS and DNA damage-sensitive protein that induces cell cycle arrest and regulates apoptosis [
56]. p38 total protein levels were not modified at baseline by the treatments (
Figure 4a-b) nor, in most cases, in response to H
2O
2 exposure, except for cells treated with 6 μM OLA exposed to 3 mM H
2O
2. Regarding p38 activation, cells treated with 6 μM OLA and 1.5/3 mM H
2O
2 also showed significantly higher p38 phosphorylation levels than non-treated cells (
Figure 4c-d). Furthermore, in cells exposed to both 1.5 and 3 mM H
2O
2, that increased p38 phosphorylation in non-treated cells, there was a significant difference between 6 μM OLA and 6 μM ARI treated cells, with 6 μM OLA inducing higher p38 phosphorylation levels (
Figure 4c-d). We next evaluated
p38 gene expression levels and found that, at baseline (without H
2O
2), the treatments did not modify p38 expression (
Figure 4e). 1.5 and 3 mM H
2O
2 exposure induced a significant downregulation, which was partially prevented by ARI/OLA treatments. The response to 1.5 mM H
2O
2 was not significantly modified by the treatments, but in cells challenged with 3 mM H
2O
2 both, 2.23 μM ARI and 6 μM OLA maintained significantly higher levels of
p38 mRNA than non-treated controls (
Figure 4e). Therefore, the observed hypersensitivity to p38 phosphorylation induced by OLA and its difference with ARI cannot be attributable to gene expression changes, since both treatments seem to promote the maintenance of
p38 levels. Notably, this gene expression pattern is remarkably similar to what was previously observed for pro- and anti-apoptotic factors except
Mcl1.
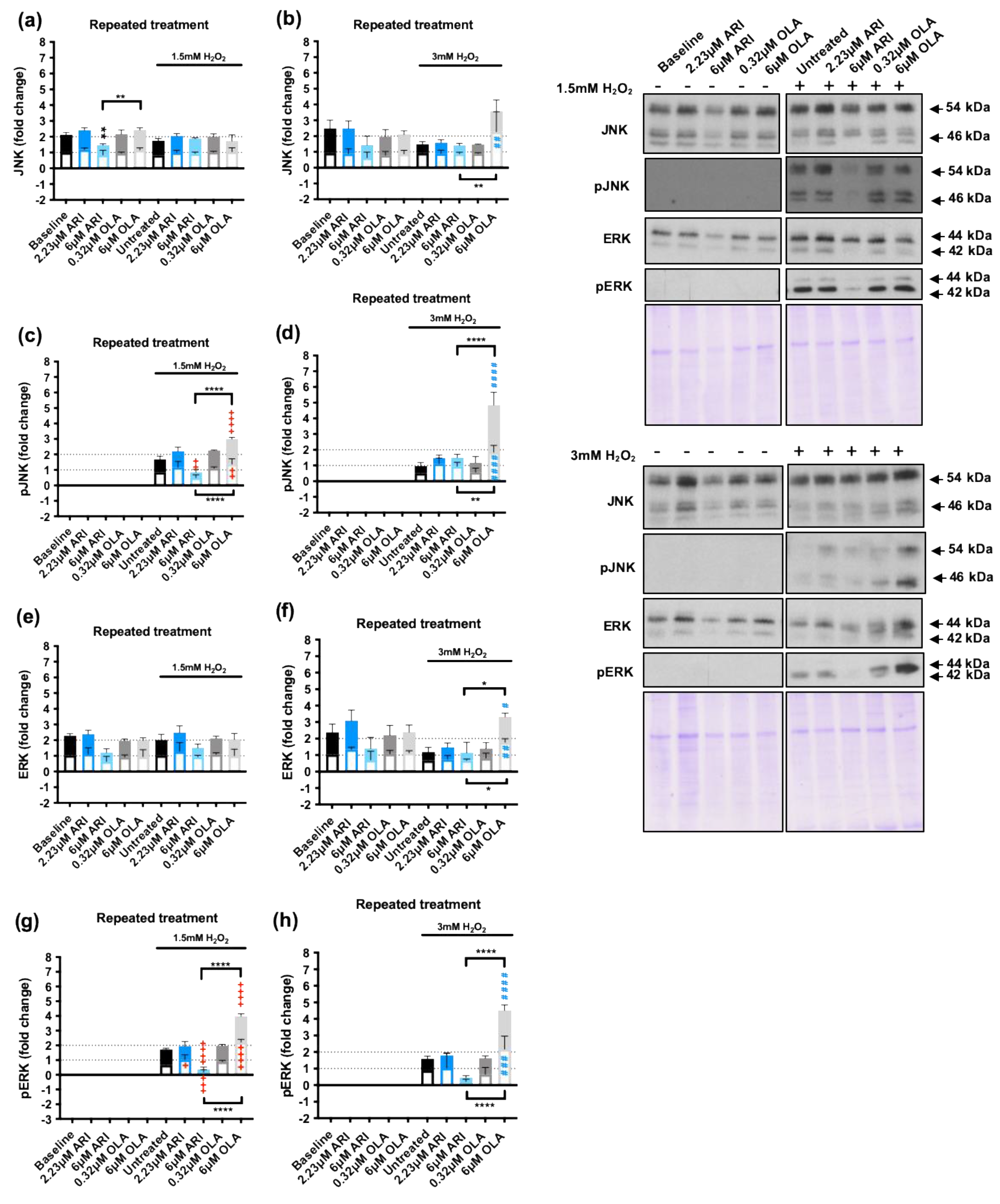
We next evaluated JNK, a MAPK that can promote both cell survival and apoptosis in response to oxidative stress [
57] as well as ERK1/2, a MAPK with well-known proliferative and protective effects on cells exposed to oxidative stress [
58]. We tested JNK protein levels and activation in response to repeated treatments followed by H
2O
2 1.5/3 mM challenge (
Figure 5) and observed that, at baseline conditions, 6 μM ARI significantly reduced JNK levels over those of non-treated cells, and this effect was not observed following 6 μM OLA treatment (
Figure 5a-b). In contrast, JNK levels were increased following the 3 mM H
2O
2 challenge in 6 μM OLA treated cells, and in these conditions the difference between the 6 μM ARI and 6 μM OLA treated cells was significant. Consistently, JNK phosphorylation in response to 1.5 mM H
2O
2 was significantly reduced in cells treated with 6 μM ARI and enhanced in cells treated with 6 μM OLA, with differences among the two being statistically significant (
Figure 5c). Furthermore, JNK phosphorylation in response to 3 mM H
2O
2 was increased in 6 μM OLA treated cells and the difference between 6 μM ARI and 6 μM OLA treated cells was also statistically significant (
Figure 5d). Therefore, the effects of ARI and OLA on p38 and JNK were consistent with ARI reducing and OLA enhancing the response to H
2O
2.
Similarly, although in baseline conditions ERK1/2 levels were not significantly modified by any of the treatments (
Figure 5e-f) in cells challenged with 3 mM H
2O
2, 6 μM OLA treated cells had significantly higher levels of ERK1/2 than non-treated controls as well as than 6 μM ARI treated cells. Also, the level of ERK1/2 phosphorylation in response to 1.5 mM H
2O
2 was significantly lower in 6 μM ARI than in non-treated controls, while the levels of ERK1/2 phosphorylation in response to 1.5/3 mM H
2O
2 where significantly higher in 6 μM OLA treated cells than in non-treated controls or than in cells treated with 6 μM ARI (
Figure 5g-h). In sum, while treatment with 6 μM ARI reduced JNK and ERK levels activation in response to an oxidative stress challenge, 6 μM OLA treatment increased p38, JNK, and ERK1/2 activation in response to H
2O
2, indicating that while ARI tends to reduce MAPKs responsiveness to H
2O
2 exposure, OLA treatment has the opposite effect; this result is consistent with the changes observed in pro- and anti-apoptotic factors. These effects may be related to the basal oxidative stress levels that the cells are exposed to since ROS levels can alter the activity of regulatory phosphatases, peroxiredoxins, and tyrosine kinases, reducing the sensibility of signal transduction systems [
59].
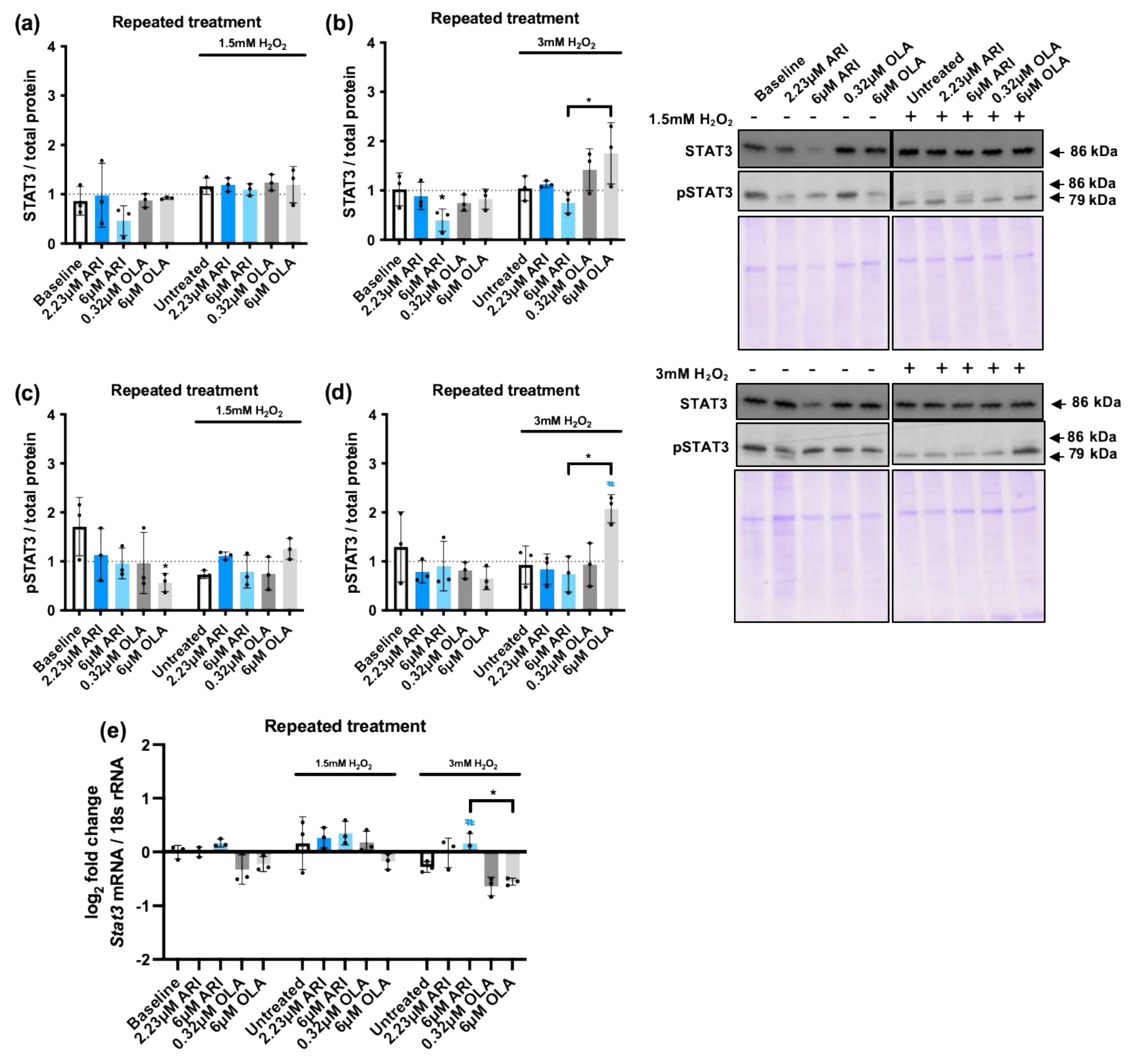
Another key mediator of the cellular response to stress is the transcription factor STAT3 [
60], which generally plays a cytoprotective role preventing cellular apoptosis [
61]. The cross-talk of MAPKs and STAT3 signaling pathways is crucial during the cellular response to oxidative stress [
62]. Therefore, we analyzed STAT3 levels in repeatedly treated cells and we found a possibly relevant reduction at baseline in cells treated with 6 M ARI. In cells challenged with 3 mM H
2O
2 the levels of STAT3 were found to be significantly higher in 6 μM OLA treated cells than in 6 μM ARI treated cells (
Figure 6b). Next, we evaluated STAT3 activity analyzing its phosphorylation. Consistently, we found that STAT3 phosphorylation following the challenge with 3 mM H
2O
2 was higher in 6 μM OLA treated cells than in 6 μM ARI treated cells (
Figure 6d). Finally, we analyzed
Stat3 gene expression that was reduced by H
2O
2 exposure in non-treated cells and, although we did not find differences at baseline among the groups, 3 mM H
2O
2 exposure reduced
Stat3 levels more in cells treated with 6 μM OLA than in cells treated with 6 μM ARI. These results, along with the previously observed changes in MAPK activity and pro- and anti- apoptotic factor regulation, imply that overall ARI reduces while OLA enhances stress sensitivity, and change in responsiveness affects pro-survival and pro-apoptotic pathways. Notably, while ARI-dependent reduced sensitivity could be related to the observed oxidative stress, known to reduce the sensitivity of many signaling pathways, and in particular Tyr-receptor signaling, the mechanism involved in OLA-dependent enhanced sensitivity would need to be clarified.
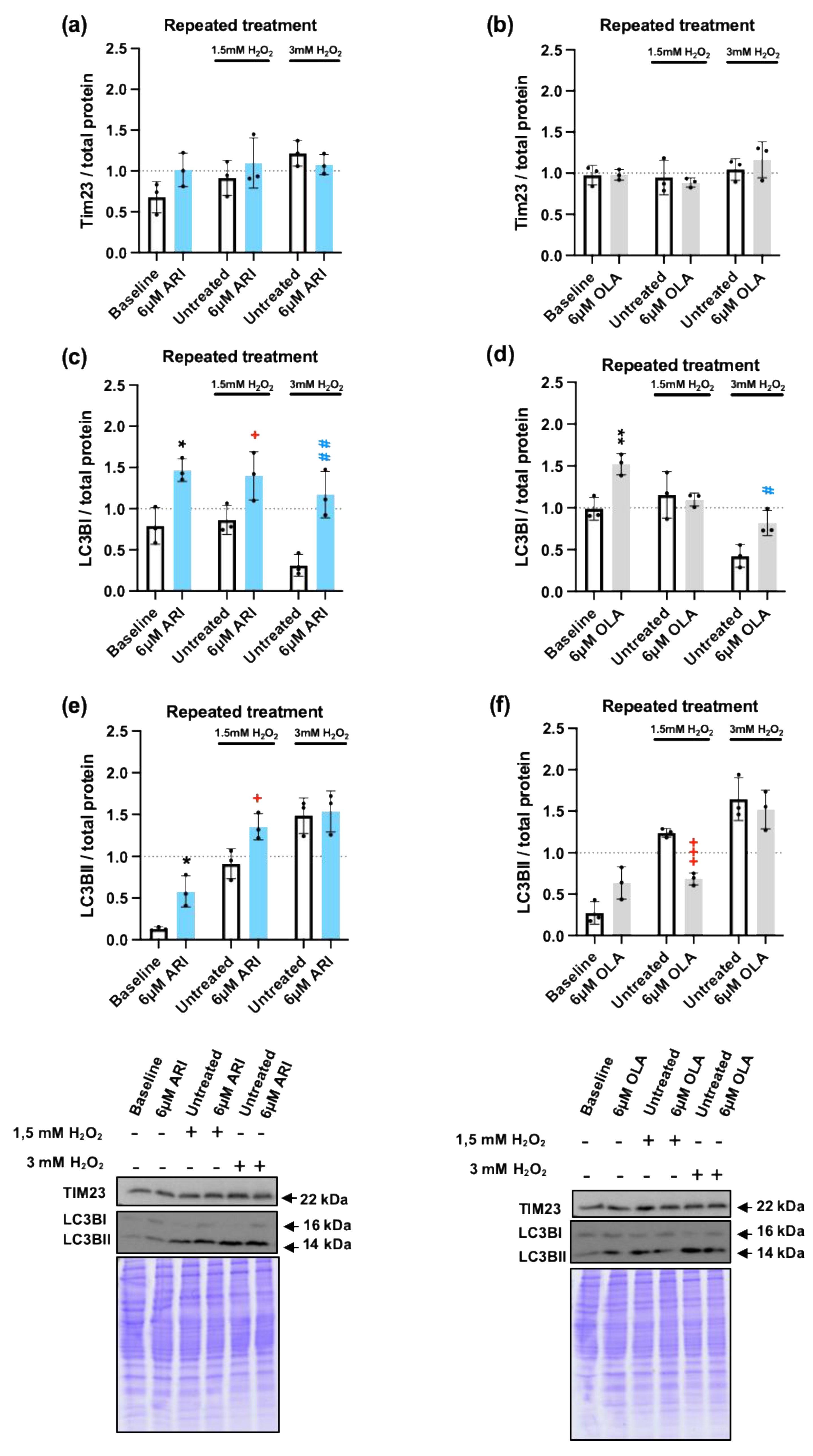
Since alteration of mitochondrial function seemed to be the primary driver in the differential response to H
2O
2, we next decided to determine if the mitochondrial load or the mitochondrial turnover were modified by repeated ARI or OLA treatments, since oxidative-stress damaged mitochondria should be targeted to mitophagy, a specialized form of autophagy, and mitochondrial biogenesis should be activated to compensate for the loss [
24] to maintain the cellular energy balance. Total mitochondrial content was determined by WB with antibodies directed against the mitochondrial protein Tim23, part of the TIM23 complex, localized in the inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM), that drives mitochondrial protein import into the IMM and the mitochondrial matrix [
63]. We did not find any differences among the groups either at baseline or in response to 1.5/3 mM H
2O
2 (
Figure 7a-b). Detection of mitophagy by this method was confirmed in conditions of starvation-induced mitophagy (Supplementary
Figure 3a). We next evaluated autophagy by WB analysis of microtubule-associated protein 1A/1B-light chain 3 (LC3B). The cytosolic form of LC3B (LC3BI) is recruited to the phagosome membranes following conjugation with phosphatidylethanolamine, forming LC3BII. Therefore, the LC3BI/II ratio is commonly used as an indicator of autophagy flux. We found that cells treated with 6 μM OLA both at baseline and following a challenge with 3 mM H
2O
2, maintained significantly higher levels of LC3BI than corresponding non-treated controls, while ARI significantly modified LC3BI levels in all of the conditions tested (
Figure 7c-d). In cells challenged with 1.5 mM H
2O
2, 6 μM ARI treatment significantly increased the levels of LC3BII, while 6 μM OLA treated cells had significantly lower LC3BII levels than non-treated controls (
Figure 7e-f). These results suggest that ARI treated cells may have an enhanced autophagy flux, likely to remove damaged mitochondria exposed to high levels of O
2∙- while OLA treatment leads to a reduction in the levels of autophagy.
Elevated ROS levels increase the cellular load of oxidized/damaged proteins that should be targeted for degradation by the proteasome, however, both ROS themselves and the reduction of mitochondrial oxidative capacity can negatively impact the proteasome activity, leading to the accumulation of damaged proteins and eventually drive the limitation of cellular functionality and even cell death [
64,
65]. There are two main proteasome complexes, the 26S complex activity, which requires ATP and targets ubiquitinated proteins, and is responsible for ≥80% of the total proteasome activity [
66]. The remaining 20% is degraded by the 20S proteasome complex that is both ubiquitin and ATP-independent [
67]. Both 26S and 20S proteasome complexes can degrade oxidatively damaged proteins but the 20S complex is the main protease responsible for degrading oxidized proteins, likely because it is more resistant to ROS than the 26S complex [
68]. Therefore, we decided to evaluate how ARI and OLA repeated treatment modified the proteasomal response to cells exposed to 1.5/3 mM H
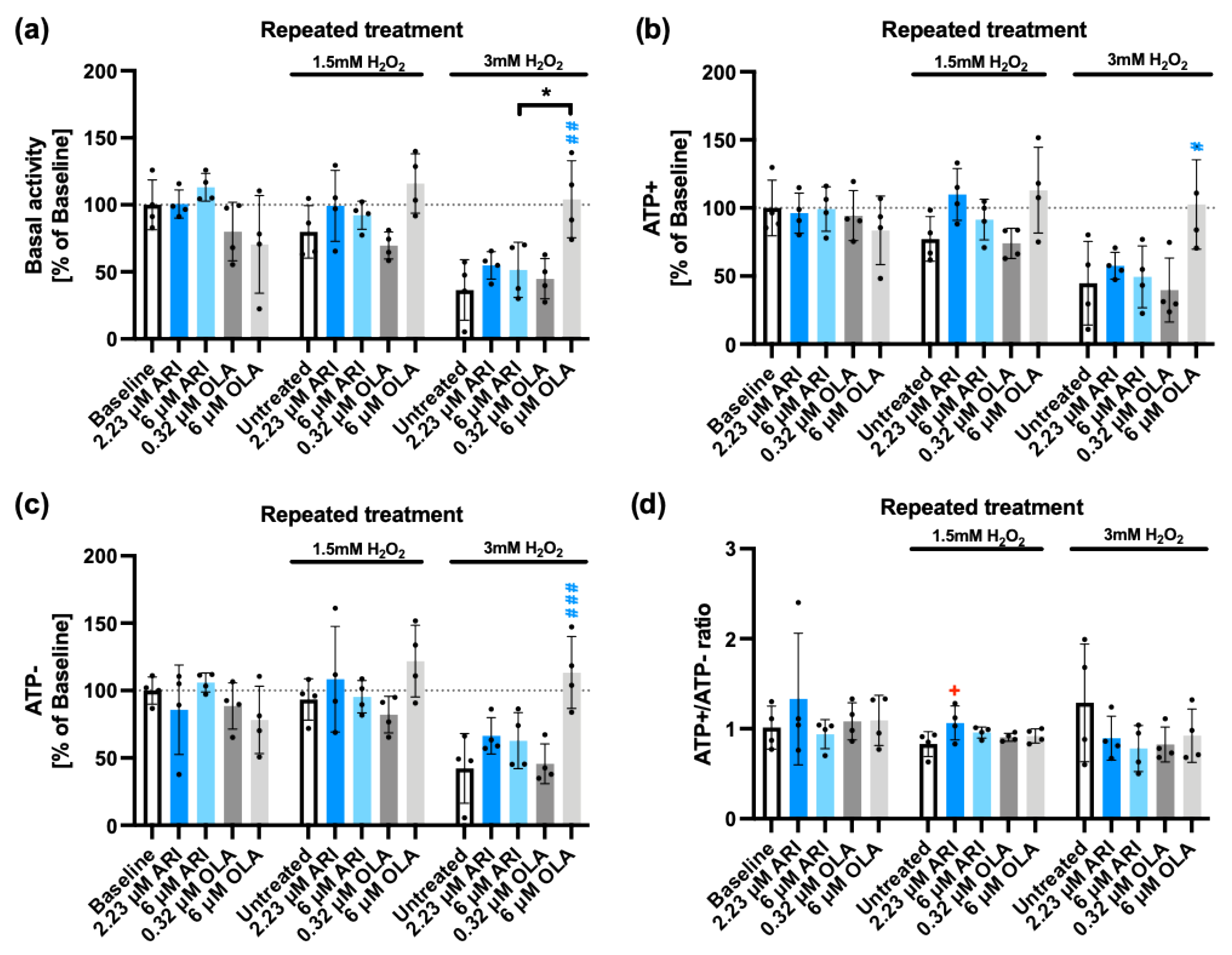
2O
2. Basal proteasomal activity, following ATP addition (ATP+) and ATP depletion (ATP-) were determined as well as the ATP+/ATP- activity ratio. As previously reported [
69], 3 mM H
2O
2 reduced both 26S (ATP-dependent) and 20S (ATP-independent) proteasome activity (
Figure 8). Of note, neither depletion nor addition of ATP did significantly modify the inhibition rate, although 3 mM H
2O
2 produced a non-significant higher inhibition of the ATP dependent activity, with a lower ATP+/ATP- activity ratio (
Figure 8d). ARI treatment did not significantly alter the ATP-dependent (26S) (
Figure 8b) nor ATP-independent (20S) (
Figure 8c) proteasome activities compared to baseline. However, 2.23 μM ARI significantly increased the ATP+/ATP- activity ratio (
Figure 8d), suggesting a better maintenance of the 26S activity than of the 20S complex in this case. Importantly, 6 μM OLA treatment at 3mM H
2O
2 significantly increased proteasomal activity over that of the untreated cells, recovering the proteasomal activity levels observed in the absence of H
2O
2 (
Figure 8b, c). These observations, suggest that OLA treatment has an important general protective role on the ROS-dependent inactivation of the proteasome by H
2O
2, while ARI treatment can have a small but significant effect on the maintenance of the 26S, that could be related to the higher levels of antioxidants over baseline. The protection elicited by OLA is likely more related to the lower load of damaged mitochondria [
70] than to the higher sensitivity to MAPK activation, since p38 has been shown to inhibit proteasome activity [
71].
In summary, ARI treated cells produce higher levels of mitochondrial ROS, and induce more strongly mitophagy and mitochondria dependent apoptosis in responses to H2O2 exposure. However, these cells die less than controls, possibly because the stress signaling pathways are blunted, as suggested by the reduced activation of the MAPKs and STAT3 in stress conditions, as well as blunted gene expression changes in pro- and anti-apoptotic factors in response to ROS. In contrast, OLA treatment, reduces the mitophagy flux, hyper-sensitizes cells to stress signaling, and protects proteasomal activity in cells exposed to high ROS levels, suggesting it has a sensitizing effect driving effectively cell death in stress conditions despite of the reduced cellular damage.
4. Discussion
The potential hazards derived from the mitochondrial toxicity of pharmacological drugs are a rising concern, especially when the patient is under a lifelong treatment regime [
72]. The nature of neuropharmacology is specially demanding in terms of penetrability, since neuropharmacological drugs have to cross the hemato-encephalic barrier (HEB). Also, circulating drug concentrations need to be relatively high to ensure they cross the HEB at therapeutic levels [
73]. All these likely contribute to the observed increased incidence of metabolic diseases that can be attributable to the pharmacological treatments in patients [
74]. Under terms such as
mitochondrial toxicity or
mitochondrial dysfunction lies a highly complex variety of possible biological effects derived from the incorporation of pharmacological drugs and the disruption of normal mitochondrial physiology. The variety of mitochondrial related pathological outcomes is well illustrated by the often puzzling phenotypical variety of mitochondrial genetic diseases [
75]. Most importantly, up to date there are no implemented protocols that can accurately evaluate these nor provide an effective risk assessment for disease development [
76].
In this study we aimed to understand how two widely used AAPs, ARI and OLA that have been shown to inhibit mitochondria oxidative phosphorylation, alter cellular physiology in terms of changing their capacity to respond to stress. This notion is based on previous studies demonstrating that mitochondrial oxidative function is closely related to the control of the cellular capacity to respond to various types of stressors and thus provide an effective mechanism against disease in general [
26,
77].
Our study shows that ARI but not OLA treatment results in a higher level of mitochondrial oxidative stress, which is likely the driver of an enhanced mitophagy flux in ARI treated cells and is associated with a consistently higher sensitivity to mitochondria-driven apoptosis activation than non-treated controls. Oxidative stress has been shown to induce apoptosis in a wide variety, if not all, of cell types. However, ARI treated cells are actually less sensitive to changes normally induced in stress conditions. This lack of sensitivity includes the loss of transcriptional regulation of genes related to apoptosis control and a reduced activation of both MAPKs and STAT3, while OLA has the opposite effect. These observations are consistent with the known effect of persistent cellular oxidative stress, that can oxidatively inactivate key signaling mediators, including membrane receptors and regulatory phosphatases. Therefore, this lack of responsiveness in ARI treated cells is likely behind the observed reduced cell death rates.
In stark contrast, OLA treatment induces hypersensitivity to stress responses at all tested levels (gene expression of apoptosis regulators, MAPK and STAT3 activation, proteasome activity) that cannot be attributable to detectable differences in mitochondrial oxidative stress, as detected by MitoSOX labeling of O
2∙-, to global changes in oxidative stress that would affect the 26S/20S activity ratio, nor to changes in mitochondrial levels, evaluated through the determination of Tim23 protein levels. Of note, OLA seemed to reduce autophagy in H
2O
2 treated cells or maybe more accurately, the induction of autophagy by H
2O
2 is reduced in OLA treated cells. This result may seem surprising since, in this conditions, OLA does not seem to have a higher antioxidant capacity than control cells [
39], but it could be attributable to the increased activity of the proteasome detectable in challenged OLA treated cells, predictably increasing the cellular capacity to remove oxidatively damaged proteins.
The observed high proteasome activity can also be relevant for the observed hypersensitivity to MAPK activation in OLA treated cells. The connection between MAPK activation and proteasome activity is particularly well characterized in the case of ERK. ERK activation in response to oxidative stress has been shown to be dependent on the activity of the proteasome [
78]. Proteosome inactivation blocks the activation of the ERK upstream kinase MEK [
79].
Oxidative stress is a well-defined activator of the proteasome, however, chronic exposure to ROS and mitochondrial dysfunction tend to reduce the proteasome activity. The critical role of proteasome in ROS dependent effects is highlighted by its role in the activation of the inflammasome, a process that is also dependent on MAPK activation [
80].
The observed higher proteasome activity in OLA treated cells exposed to H2O2 was not associated with any detectable differences in proteasome baseline levels nor in any significant changes in baseline MAPK levels or activity. Therefore, the origin of this conditioning effect remains to be established. Nevertheless, there is one detectable baseline difference in OLA treated cells, a significant increase in LC3BI levels that was not associated with a reduction in LCBII, and therefore, does not seem to be related to an inhibition of the autophagy flux, but may be rather indicative of an increased capacity of the cells to induce it and by extension to the degradation of damaged proteins/structures. Although highly speculative this may hold a connection with the high sensitivity of the proteasome activation in response to OLA. Furthermore, given the differential effects of ARI and OLA, it is tempting to speculate that mitochondrial function may play a role.
Total LC3 levels are regulated by acetylation, which prevents its degradation by the proteasome [
81]. High LC3 levels have been shown in tumor tissues and are associated with advanced tumor stages and poor prognosis [
82]. In fasting conditions, increased NAD
+/NADH ratios activate the deacetylase SIRT1 [
83], rendering the protein more sensitive to proteasomal degradation but also activating the mitophagy flux since it facilitates its phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) conjugation to pre-autophagic membranes [
84]. Therefore, high LC3B levels can be indicative of a good cellular nutritional and redox status. All these possibilities would need to be further investigated.
In sum, our observations highlight the divergent impacts that drug-induced mitochondrial toxicity can have on the physiological responses to stress, evidence the critical role played by chronic mitochondrial oxidative stress exposure in the cellular de-sensitization to stressors and raise a note of caution on the potential pathological outcomes of long-term ARI treatment.