1. Introduction
Culturing edible mushrooms is important worldwide in commercial activity [
1]. The oyster mushrooms of the genus
Pleurotus are the world's third largest commercially cultivated mushroom. They can utilize a wide range of available culture materials due to their great adaptability [
2,
3].
Mushroom cultivation presents an economically important biotechnological industry that has been markedly developed all over the world [
4]. There are about 10,000 known mushroom species, fleshy macrofungi, including some ascomycetes species [
5]. The proficiency of fungi in converting substrate to protein is far superior to that of several plants and even animals [
6]. The mushroom fruit body is low in calories, fat, and cholesterol, while rich in protein, carbohydrates, fibers, vitamins, and minerals. These nutritional properties make mushrooms a very good dietary food [
7]. Pleurotus mushroom cultivation is an economically viable and eco-friendly process for converting various agro wastes into human food. Pleurotus mushrooms are cultivated on a large scale globally, accounting for 27% of its global production [
8,
9]. Africa has successfully developed cultivation methods for sustainable production as a valuable food source to defeat hunger [
10]. In Asia, the Pleurotus mushroom industry has increased rapidly due to low production costs and high-yielding capacity. The cultivation processes include substrate processing, casing, and temperature shocks [
11].
The culture materials called substrates are the most significant factors in the quality and yield of edible fungi and medical mushrooms [
12,
13]. The substrates containing cellulose, hemicelluloses, lignins are the sources of carbon and nitrogen, and other essential minerals. In general, mushrooms can decompose the organic matter and particularly cellulose, hemicellulose, cellulose for which it produces a series of extracellular enzyme activities that were tested enzymes [
14,
15,
16]. The good quality of protein production and flavor formation depends on the different substrates. The substrate offers the nutrition, moisture, and energy that mushrooms require to grow and fruit [
17,
18].
In general, the concentrations of nitrogen and carbohydrate sources are required to achieve a mushroom high yield in terms of dry weight but the high concentration of glucose can affect yield and inhibit the growth of many mushrooms [
19]
. Environmental factors such as humidity, temperature, carbon dioxide, and oxygen, are very essential and affect the growth, and yield production of mushrooms [
20,
21,
22].
Previous research has shown that the Juncao grass,
Miscanthus floridulus, Saccharum arundinaceum, Themeda gigantea, Pennisetum purpureum, and
Sorghum propinquum are high-quality culture materials for
P. ostreatus cultivation [
23].
Pleurotus ostreatus was cultivated in three different juncao grasses, such as
Miscanthus floridulus ju juncao, and Arundo donax grasses after harvesting the spent substrates were utilized as an organic fertilizer for soil remediation [
24,
25]. There is little research that reported active compound, enzymatic activity, nutritional content, and
Pleurotus ostreatus cultivated in three different substrate types of grass.
2. Material and Method
2.1. Spawn Preparation and Mushroom Material
The strain of Pleurotus was obtained from the National Juncao Engineering Research Center of Juncao Technology in Fuzhou City, Fujian Province. The strain was grown on Potato Dextrose Agar (PDA) medium (PSA) at 25℃ for regular subculture. Spawns were prepared in 850-mL polypropylene plastic bags filled with 500g of Dicranopteris Dicholoma supplemented with 20% wheat bran, 1% calcium carbonate,1% lime in terms of dry weight basis, and 60~65% water content, and then sterilized at 121℃ for 2 hr. After cooling to room temperature, 10 cm of mycelium of oyster mushroom were inoculated into each bag of sterilized substrate. The spawn was incubated at 25℃ until the substrate fully colonized.
Figure 1.
Medium culture Preparation of P. ostreatus (p969) PDA.
Figure 1.
Medium culture Preparation of P. ostreatus (p969) PDA.
2.2. Substrate Preparation and Inoculation
Three lignocellulosic substrates Giant grass (JJ), Arundo donax (AL), and Miscanthus (MS) were obtained from the National Juncao Engineering Research Center. The dried chopped culture material of 77% of each juncao grasses(JJ, AL, MS) was supplemented with materials 20% wheat brain,1% coffee grounds, 1% Caco3, and 1% lime were thoroughly mixed with a mixture machine, and water was added to reach moisture content which is approximately 60-65% where you hold it tightly and see the water seems to lick between fingers. The cultivation materials were filled in plastic bags, each bag containing between 800g-1kg, sterilized in an autoclave machine separately at 121oc for 120 minutes then waited for 24 hours to cool down. After cooling to room temperature, 3g of mycelium was inoculated into each plastic bag, and twenty-four culture bags were used for each substrate. The inoculated substrate was incubated at 25℃ for the substrate to be fully colonized and cultivated.
2.3. Incubation and Harvest
The inoculated substrates were kept in an incubation room at 27℃ and 60~70% relative humidity. After total mycelium colonization, the bags were transferred, to a growing room in which temperature was maintained at 24℃ and kept at a related humidity of about 85-90%. For all substrates, three flushes of mushroom were harvested from each of the culture bags when the in-rolled margins of the mushroom caps began to flatten. The time from inoculation to the first harvest and total harvesting time were recorded. At every flush, the harvested fruiting bodies were weighed, and mushroom size was measured. The length and thickness of the stipe, diameter of the cap, and number of effective fruiting bodies per bunch were measured at the first, second, and third flush and the means were also determined [
26,
27]. At the end of the harvest period, the accumulated data were used to calculate the total yield and the BE. The biological efficiency was calculated by the ratio of fresh fruiting body weight (g) per dry weight of substrates (g), expressed as a percentage [
28].
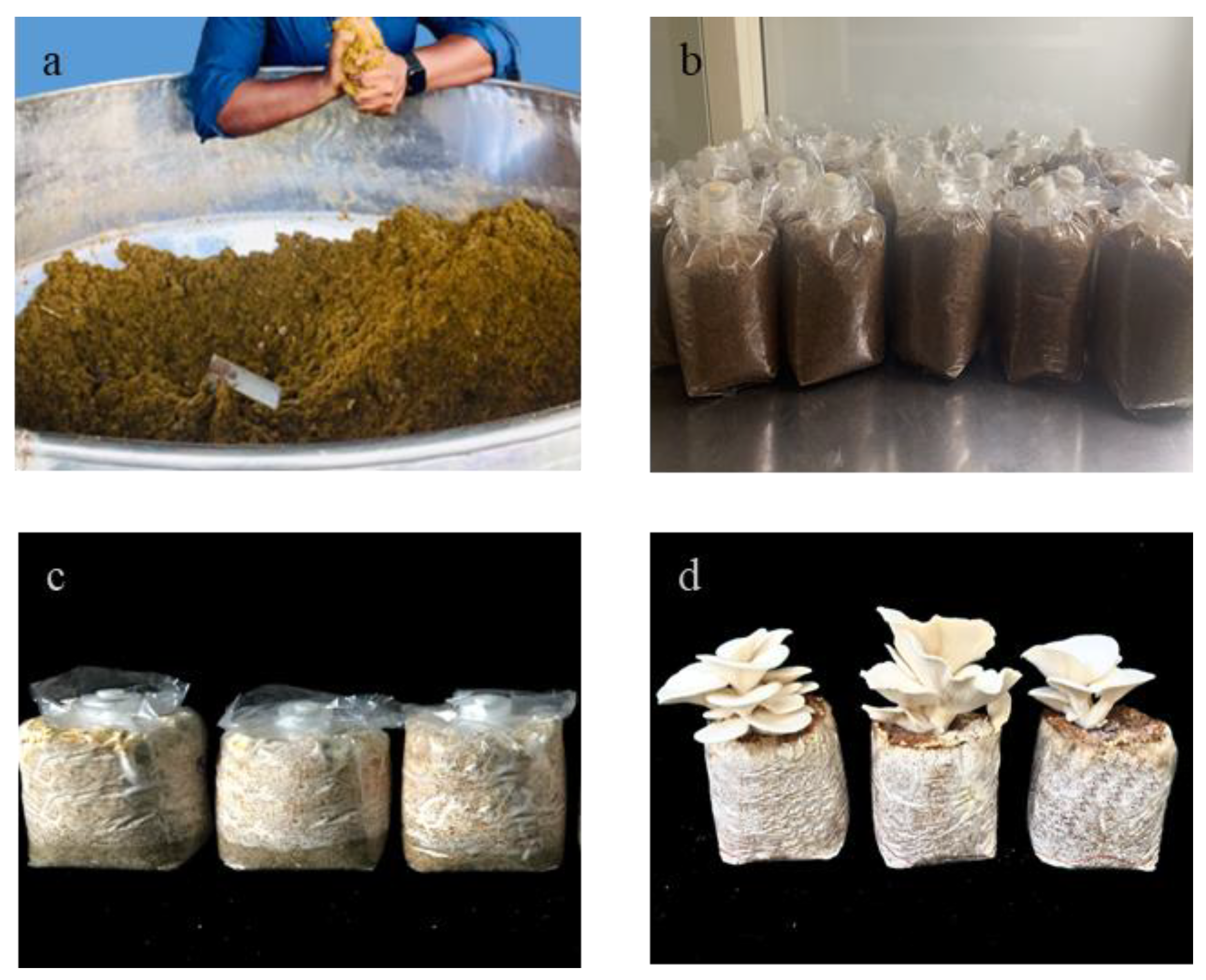
Figure 2.
Different stages of oyster mushroom cultivation (Pleurotus ostreatus) p969, (a) art of substrate preparation (b) sterilized substrate ready for inocuration (c) colonized substrate (d) first flush for three different grass.
Figure 2.
Different stages of oyster mushroom cultivation (Pleurotus ostreatus) p969, (a) art of substrate preparation (b) sterilized substrate ready for inocuration (c) colonized substrate (d) first flush for three different grass.
2.4. Experimental Design and Data Analysis
The following experiments were performed at the National Juncao Engineering Laboratory in Fuzhou. The experiment was laid out in a randomized complete block design with three replications of 24 culture bags each. The data were compared using analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Significant differences between means were determined by honest significant difference (HSD-Tukey test) at the level of p< 0.05. Data were reported as mean values±standard deviation of three independent replicates (p< 0.05, 95%) [
29].
2.5. Analysis of Enzyme Activities
The Elisa method as proposed by A.T. Hoang [
30] was used to assay for the laccase, manganese peroxidase (MnP), lignin peroxidase enzyme activity, xylanases, exoglucanases (FPase), and endoglucanase in the samples from the mycelium and fruiting stage . Add 10 µL of reconstituted standard mixed with 990 µL of incubation buffer in one well as a standard well of the micro-ELISA test strip plate. Add 40 µL of the sample dilution buffer into the well of the testing sample. Then added 10 µL of the testing sample to the wells and mixed gently, except the blank well. 100 µL of HRP-conjugate reagent then added to each well in each plate then closed with an adhesive strip and incubated for 30 minutes at 37 ℃. Then further constant numbers of 1,000 Titer stock of the washing solution was prepared with distilled water and stored until used. Discard the closed plates and dry using a swing to uncover them. Then add washing buffer again and hold for 30 sec then drain. Further incubation was done with 50 µL of HRP-conjugate reagent in all but the blank well in the plates at 37ºC with another washing process using the buffer for a duration of 30 minutes. 50 µL of each chromogenic solution A and chromogenic solution B is added gently to maintain the volume in each well and incubated at 37°C for 15 minutes under light protection. Following the previous report [
31] the reaction was next terminated by the addition of 50 µL of the H2SO4 solution into each well. Once the solution changes color from blue to yellow, the absorbance (optical density – OD) was read within the first 15 minutes of adding the stop solution at a wavelength 450 nm. Based on the standard curve prepared, the sample density was calculated from the OD value. For each enzyme, the actual sample density was the dilution factor multiplied by the sample density on the graph.
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Different Substrates on the Mycelium Running, and Biological Efficiency
The results showed in the (
Table 1) the mycelium running in three different substrate were 28day up do 40days.Substrate named Giant grass (GG) considered as control in this study were very faster 28(day) than Arundo donax (AR) followed by Miscanthus ( 28,32,40days respectively).Previous scientist King T.R. [
32] were reported quite close to the results founded in this research. Substrate namely which showed a high contamination rate (65%) during the incubation period. Therefore There is no significant difference the yield, stipe,cap, and BE of
Pleurotus ostreatus planted in GG(control) and AR. The lowest yield, cap, stipe,mycelium running of
Pleurotus ostreatus were found in the MS.
3.2. Effect of Different Substrates on the Nutritional Composition of the Fruiting Body
Fundamental food characteristics such as polysaccharides, fiber, protein, and carbohydrate content of oyster mushrooms grown on different substrates were presented in
Table 2. Effect of substrate CK and MS was not significant on polysaccharide content (2.31-2.43%) of cultivated mushrooms, while polysaccharide content (2.77%) in AR substrate has significantly higher than GG, MS. The result was quite similar to the value stated by Wang et al. [
29,
33]. The study indicated that the fruiting bodies of oyster mushrooms PO grown on all substrate formulas are quite rich in fiber, Carbohydrates, protein, Amino acids, and antioxidants making them excellent foods that can be used in low-caloric diets.
The protein of mushrooms was significantly different in all substrates. The highest protein content was found in Giant grass (GG) followed by Arundo (AR) and Miscanthus (MS) at 1.84%,1.48%, and 1.39% respectively. The differences in protein content of mushrooms grown on different substrates could be due to the varying nitrogen content of substrates. The high nitrogen content of JJ, and AR, contributed to the higher protein content of fruiting bodies while MS provided less nitrogen and it could be attributed to the nitrogen utilization efficiency by the species. The fiber content on dry weight basis of oyster mushrooms was not significantly different in all substrates. Where the highest carbohydrates were not significant in MS and JJ at 67.93%, and 64,80% respectively significantly different from AR with 60.63%. Which is recommended for cultivation as a second option. In this study the carbohydrate content is higher than that reported by H.T.Hao et al. and the total carbohydrate content in this study was higher than that reported 40.64~55.92%, growing in different substrates. The free amino acids of Pleurotus ostreatus were significantly different (P≤0.05) in all substrates. The highest free amino acid content was found in Giant grass (JJ) followed by Arundo (AR) and Miscanthus (MS) at 0.39%,0.29%, and 0.27% respectively.
The fruit body of Pleurotus harvested in the substrates JJ and MS showed a high antioxidant activity (16.86%,16,70%)repectevely but non significants difference compared to AR content (13.83%)were significantly different at the level of p< 0.05.The results shown had the similarity to the results reported by P.Diamantopoulou et all [
29] where the ntioxidant activity, were influenced by the substrate.
3.3. Concentration of Heavy Metal
The heavy metals (Cadmium, Arsenic, Lead, and, Mercury) were determined in the fruiting body of pleurotus ostreatus. The previous research has indicated that edible fungi accumulate a different concentration level of heavy metal [
34].As is indicated in
Table 3, below the content of four heavy metals were tested from the fruiting body of
Pleurotus ostreatus grown in three different mushroom substrates.
The concentration of plumbum,(pb), mercury (Hg) Arsenic (As) in the fruiting body of pleurotus grown in the substrate GG (Control), MS, AR, were significantly different at the level 0.005, the Cadmium (Cd)concentration in GG (0.032 mg·kg-1 ) control were higher than MS and AR). The concentration level of mercury (Hg) in the fruiting body of Pleurotus ostreatus grown AR (0.079 mg·kg-1) were higher MS followed by GG 0.055;0.047mg.kg-1 repectively.
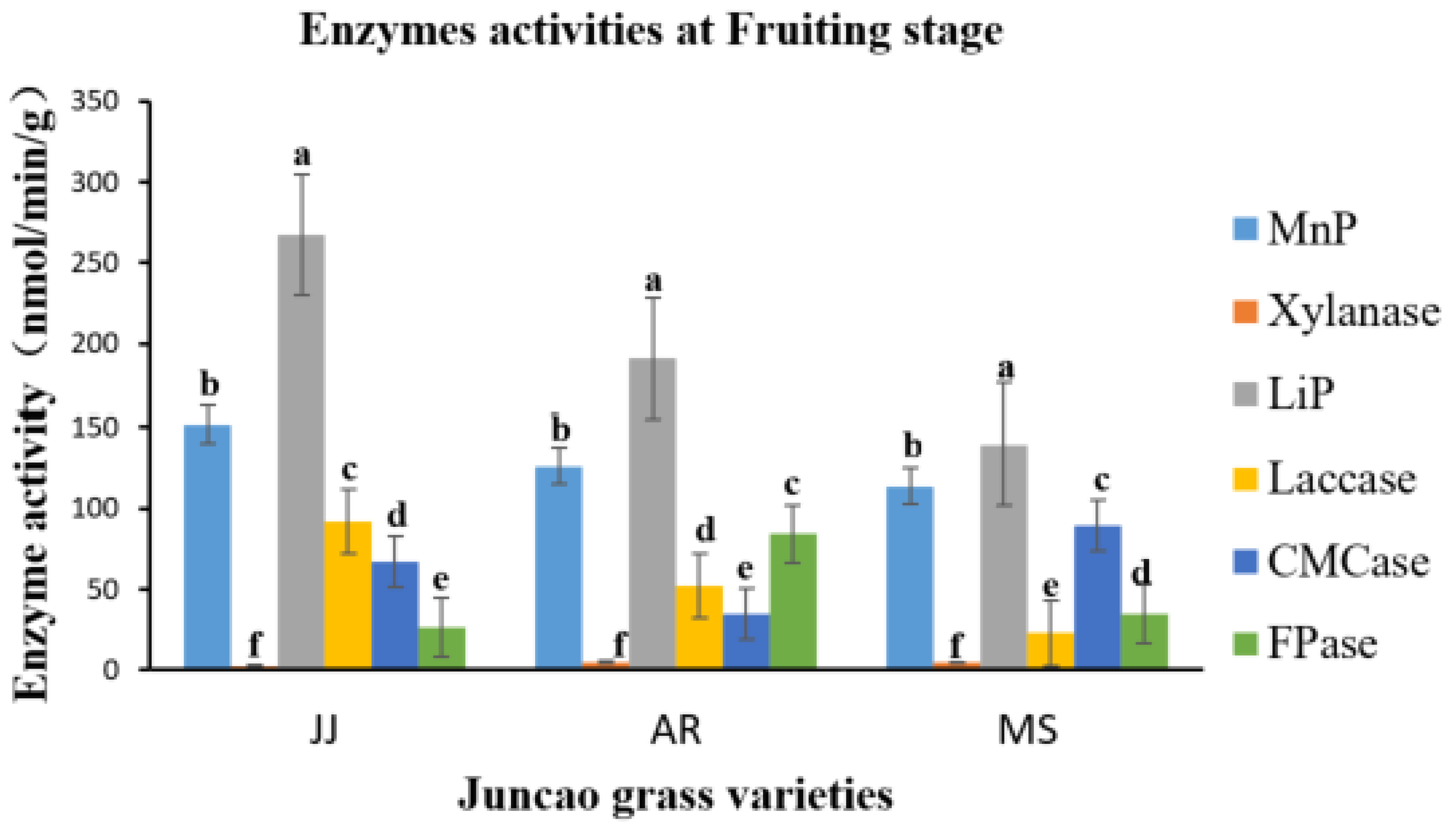
3.4. Effect of Enzyme Activity Assay
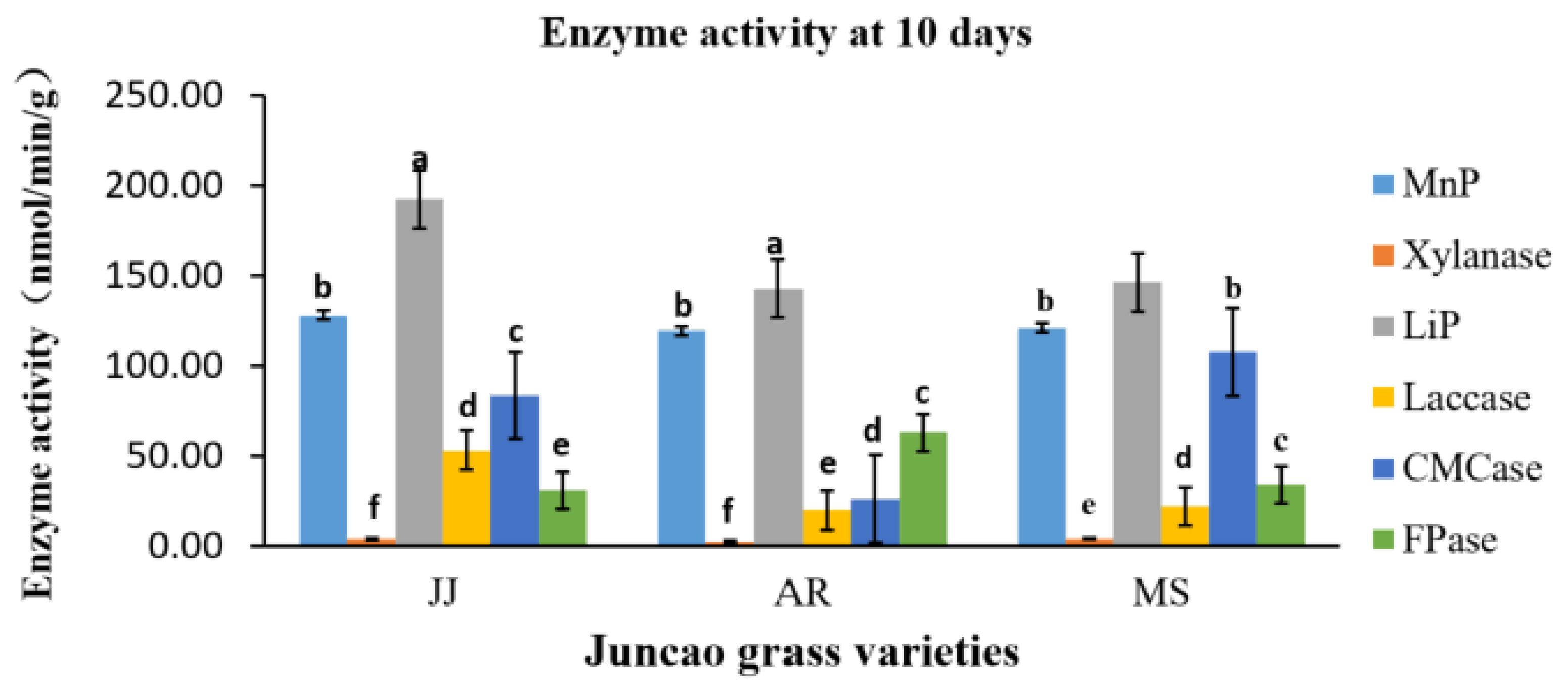
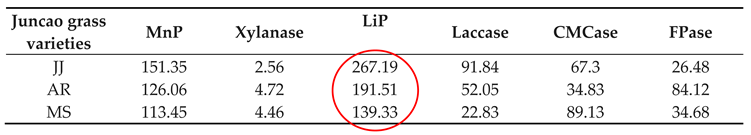
The enzyme activity assays were performed on the tenth day after inoculation of
Pleurotus ostreatus mycelium growth, up to the fruiting stages. The three substrates had a great participation in all enzyme activity, but their activity differed between developmental stages as is demonstrated in
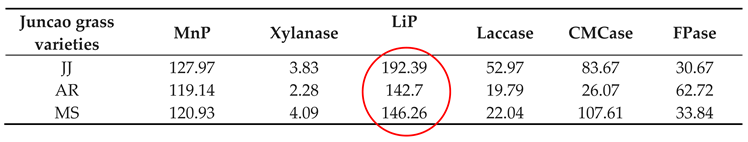
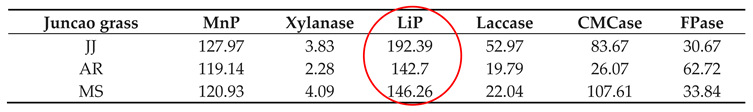
Table 4-1 and
Figure 4-1. Throughout the whole development period, there were significant differences in the activity of lignin peroxidase in
Pleurotus ostreatus grown on three substrates (P≤0.05). From the tenth day up to the fruiting body stage, the lignin peroxidase (LiP) presented the highest activity in all three juncao grasses named JJ, AR, MS (
Table 4-1, table 4-2, and table 4-3). At the fruiting body stage the (LiP) activity in three substrates JJ, AR, and MS was also high, followed by MnP and Laccase. The observation of the high activity of LiP, MnP, and Laccase in the three different substrates studied in this research is quite similar to the earlier findings of Suryadi and Rameshaih [
35,
36] who showed lignin peroxidase the most efficient and best-known ligninolytic enzyme in fungi.
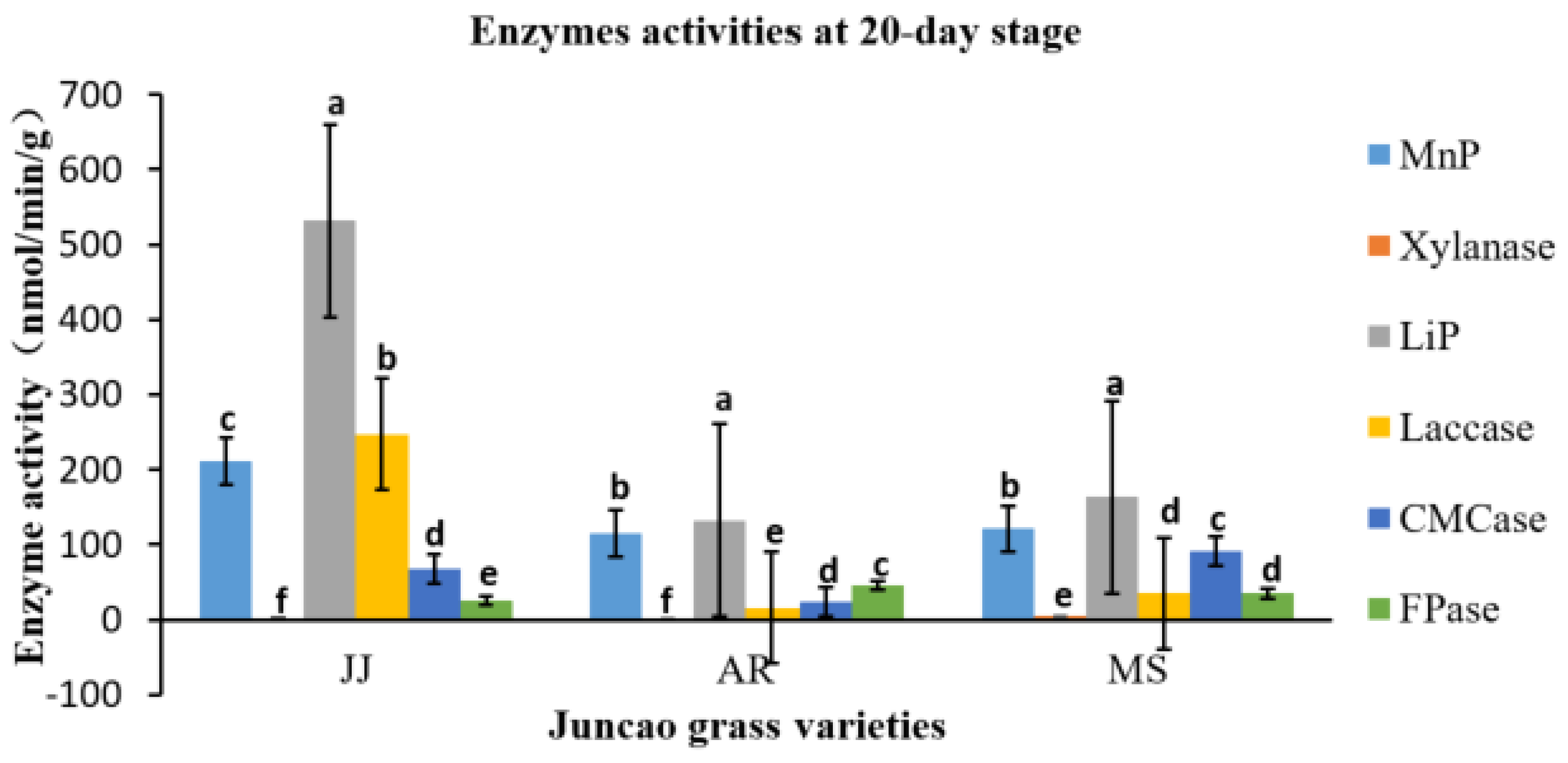
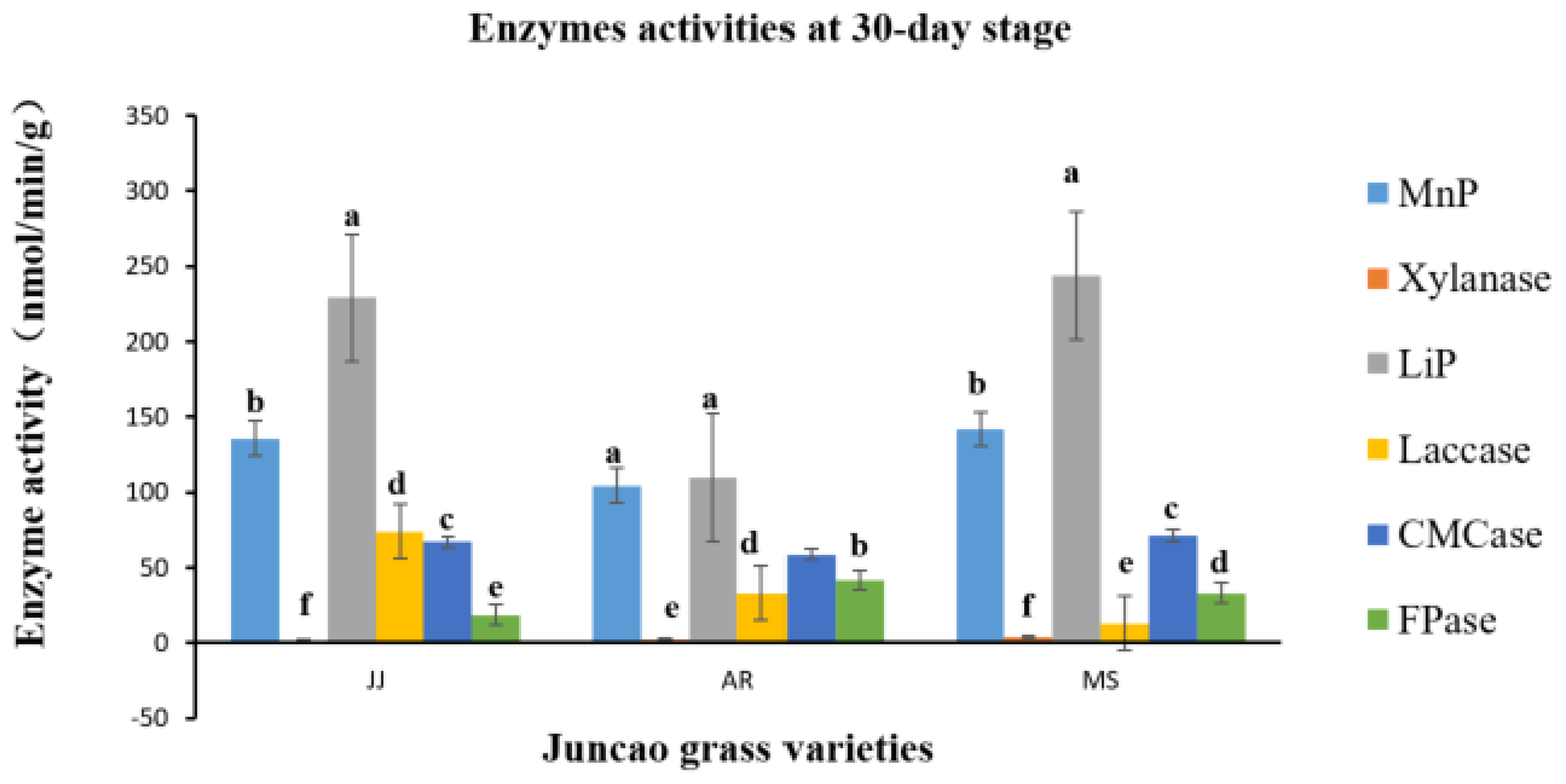
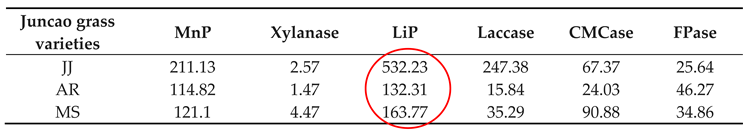
As illustrated in
Table 4-3, on the 30-day stage, there was substantial differences (P≤0.05) in Laccase activity production between the three juncao grass substrates (JJ, AR, and MS). At the fruiting body stage, endo-glucanase and exo-glucanase produced significantly the highest activities in MS substrate, followed by JJ and AR. (figure 4-3) and the quite similar findings was reported by Wang. H et al [
37]. The results showed that xylanase activity consistently decreased during all developmental stages of each juncao grass substrate. The results of changes in activity of six analyzed enzymes in this study, is quite similar to those reported by Sitar et al [
38].
Figure 3.
Effect of different substrates on Pleurotus ostreatus enzyme activity on the tenth day. LiP: Lignin peroxidase; Laccase; MnP: Manganese peroxidase; Xylanase; FPase: Exo- glucanase; CMCase: Endo-glucanase. Substrate JJ: Giant grass; AR: Arundo donax; MS: Miscanthus.
Figure 3.
Effect of different substrates on Pleurotus ostreatus enzyme activity on the tenth day. LiP: Lignin peroxidase; Laccase; MnP: Manganese peroxidase; Xylanase; FPase: Exo- glucanase; CMCase: Endo-glucanase. Substrate JJ: Giant grass; AR: Arundo donax; MS: Miscanthus.
Figure 4.
Effect of different substrates on Pleurotus ostreatus enzyme activity on the twentieth day.MnP: Lignin peroxidase; Laccase; MnP: Manganese peroxidase; Xylanase; FPase: Exo-glucanase; CMCase: Endo-glucanase.Substrate JJ: Giant grass; AR: Arundo donax; MS: Miscanthus.
Figure 4.
Effect of different substrates on Pleurotus ostreatus enzyme activity on the twentieth day.MnP: Lignin peroxidase; Laccase; MnP: Manganese peroxidase; Xylanase; FPase: Exo-glucanase; CMCase: Endo-glucanase.Substrate JJ: Giant grass; AR: Arundo donax; MS: Miscanthus.
Figure 5.
Effect of different substrates on Pleurotus ostreatus enzyme activity on the thirtieth day. LiP: Lignin peroxidase; Laccase; MnP: Manganese peroxidase; Xylanase; FPase: Exo-glucanase; CMCase: Endo-glucanase. Substrate JJ: Giant grass; AR: Arundo donax; MS: Miscanthus.
Figure 5.
Effect of different substrates on Pleurotus ostreatus enzyme activity on the thirtieth day. LiP: Lignin peroxidase; Laccase; MnP: Manganese peroxidase; Xylanase; FPase: Exo-glucanase; CMCase: Endo-glucanase. Substrate JJ: Giant grass; AR: Arundo donax; MS: Miscanthus.
Figure 6.
Effect of different substrates on Pleurotus ostreatus enzyme activity at the fruiting body stage. LiP: Lignin peroxidase; Laccase; MnP: Manganese peroxidase; Xylanase; FPase: Exo-glucanase; CMCase: Endo-glucanase.Substrate JJ: Giant grass; AR: Arundo donax; MS: Miscanthus .
Figure 6.
Effect of different substrates on Pleurotus ostreatus enzyme activity at the fruiting body stage. LiP: Lignin peroxidase; Laccase; MnP: Manganese peroxidase; Xylanase; FPase: Exo-glucanase; CMCase: Endo-glucanase.Substrate JJ: Giant grass; AR: Arundo donax; MS: Miscanthus .
Table 4.
Enzyme activities (nmol/min/g) at 10 days in three different juncao grass varieties.
Table 4.
Enzyme activities (nmol/min/g) at 10 days in three different juncao grass varieties.
Table 5.
Enzyme activities (nmol/min/g) at a 20-day stage in three different juncao grass varieties.
Table 5.
Enzyme activities (nmol/min/g) at a 20-day stage in three different juncao grass varieties.
Table 6.
Enzyme activities (nmol/min/g) at a 30-day stage in three different juncao grass varieties.
Table 6.
Enzyme activities (nmol/min/g) at a 30-day stage in three different juncao grass varieties.
Table 7.
Enzyme activities (nmol/min/g) at the fruiting body stage in three different juncao grass varieties.
Table 7.
Enzyme activities (nmol/min/g) at the fruiting body stage in three different juncao grass varieties.
4. Discussion
Pleurotus ostreatus, representing oyster mushrooms, is the most wanted, expansively grown, and consumed macromycetes throughout the whole world. It is also commonly known as common Indian or commercial oyster mushrooms [
39].
This study was assessed the physiological and biochemical responses of Pleurotus ostreatus cultivated on various substrates. Numerous studies have demonstrated that the yield, biological characteristics, nutritional content, and enzyme activities of PO are heavily influenced by the choice of cultivation materials.
The utilization of juncao three cultural materials as experimental material for cultivating
Pleurotus ostreatus. Previous research by Hu.Y.et al. (2019) reported that using Juncao grass (
M. floridulus) and cotton seed waste materials can increase the yield and biological efficiency (BE) of PO. In this study, the results demonstrated that the substrate with the Giant Juncao (JJ) had the fastest mycelia running rate of
Pleurotus ostreatus (28 days), the highest yield (159g/bag), and the highest biological efficiency of 75%. This was followed by
Arundo donax (AR) grass with 32 days, 132g/bag, and 65% BE. These findings were similar to those reported by Hu Yingping et al. [
40].
The six enzyme activity assays were performed on the tenth day after inoculation of PO mycelium growth until the fruiting stages. All three substrates had a significant impact on enzyme activity, but the activity varied between different developmental stages.
Pleurotus ostreatus showed notable differences in lignin peroxidase activity amongst the three substrates during the culture process, indicating substantial differences in results (P≤0.05), with
arundo donax (AR) and miscanthus (MS) showing comparable outcomes. These findings were consistent with the research conducted by Fernández-Fueyo et al. [
41], which highlighted the ability of mycelium growth to decompose lignocellulosic materials.
The nutrient content of polysaccharides, fiber, protein, carbohydrates, antioxidants, and amino acids in oyster mushrooms grown on different substrates. The results indicated that substrate JJ and MS did not significantly affect the polysaccharide content (2.31-2.43%) of the cultivated mushrooms. However, the polysaccharide content (2.77%) in the AR substrate was significantly higher than that in JJ and MS. This finding was consistent with the research conducted by Diamantopoulou P. et al. [
29], which focused on the nutrient compositions of edible mushrooms. Additionally, the protein content of the fruiting body of
Pleurotus ostreatus cultivated using JJ had the highest protein content of 1.80%. Following that, AR and MS had protein contents of 1.48% and 1.39% respectively. The crude fiber content of P.O in all substrates was 0.49%, 0.50%, and 0.50%, showing no significant differences. In terms of polysaccharide content, PO grown in AR had a 2.77% higher content compared to JJ and MS. The mean difference was significant at the 0.05 interval in JJ and AR substrates. Nagulwar, M. [
42] reported that mushrooms are considered low-calorie food with high nutritional value, containing good quality proteins and vitamins, particularly vitamin B complex. Mushrooms have low levels of fat, which mainly consist of healthy unsaturated fat. The concentration of heavy metals (
Cadmium, Arsenic, Lead, and Mercury) was determined in the fruiting body of
Pleurotus ostreatus cultivated in different substrates named JJ, AR, and MS. Therefore the results demonstred that the concentrations of heavy metals found in the fruiting bodies of Pleurotus grown in different substrates were below the minimum allowable levels for vegetable food, as reported in international food regulations which is similar to the findings of research Wang et al [
43].
In conclusion taking into account our research as well as all of the previously listed studies, it can be said that Juncao grasses have a high enzymatic activity, nutrient content, yield, and biological efficiency, making them suitable for producing Pleurotus ostreatus fruiting bodies. However, the Arundo donax in the cultivation of Pleurotus ostreatus has been applied with little or no attention at all through research. Therefore, based on our findings, we suggest more studies on the Arundo donax fungi as an alternative substrate in mushroom cultivation.
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Author Contributions
IC , NA,HM: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Visualization, Writing ,original draft, Writing – review & editing, Software; HZ, PL Conceptualization, Data curation, Software, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.,DL and LZ: Project administration, Supervision, Funding acquisition .Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the Fujian Government , Academy of Juncao Science and Technology, Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University for funding this work.
Conflicts of interest
No conflicts of interest.
Funding
This study was supported by the Special Project for the Protection and Utilization of Agricultural Resources of the Department of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of Fujian Province, "Research and Application of Key Technologies for Innovation and Industrialized Utilization of Juncao Grass and Juncao Mushroom" (22001XA).
References
- Gupta S, Summuna B, Gupta M, et al. Edible mushrooms: cultivation, bioactive molecules, and health benefits. Bioactive molecules in food, 2018, 1(1-33.
- Rathod M G, Gadade R B, Thakur G M, et al. Oyster mushroom: cultivation, bioactive significance and commercial status. Frontiers in Life Science, 2021, 2(21.
- De Mastro, F.; Traversa, A.; Matarrese, F.; Cocozza, C.; Brunetti, G. Influence of Growing Substrate Preparation on the Biological Efficiency of Pleurotus ostreatus. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S. Mushroom production. Biotechnology-Volume VII: Fundamentals in Biotechnology, 2009, 7(74.
- Patel, J.M.; Patel, D.D. Study of Ascomycetes and Basidiomycetes Fungi ( Macro ) : A Review. Int. J. Sci. Res. Sci. Technol. 2022, 9, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kour D, Rana K L, Yadav N, et al. Agriculturally and industrially important fungi: current developments and potential biotechnological applications. Recent advancement in white biotechnology through fungi: Volume 2: Perspective for value-added products and environments, 2019, 1-64.
- Alzand K I, Bofaris M S M, Ugis A. Chemical composition and nutritional value of edible wild growing mushrooms: a review. World J Pharm Res, 2019, 8(3): 31-46.
- Barh, A.; Sharma, V.P.; Annepu, S.K.; Kamal, S.; Sharma, S.; Bhatt, P. Genetic improvement in Pleurotus (oyster mushroom): a review. 3 Biotech 2019, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juárez-Hernández, E.O.; Pérez-Zavala, M.d.L.; Román-Reyes, M.; Barboza-Corona, J.E.; Macías-Sánchez, K.L. Overview of Pleurotus spp., edible fungi with various functional properties. Int. Food Res. J. 2023, 30, 1074–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendiro D, Wacoo A P, Wise G. Identifying indigenous practices for cultivation of wild saprophytic mushroom s: responding to the need for sustainable utilization of natural resources. Journal of Ethnobiology and Ethnomedicine, 2019, 15(1-15.
- Mahari W a W, Peng W, Nam W L, et al. A review on valorization of oyster mushroom and waste generated in the mushroom cultivation industry. Journal of hazardous materials, 2020, 400(123156.
- Balan, V.; Zhu, W.; Krishnamoorthy, H.; Benhaddou, D.; Mowrer, J.; Husain, H.; Eskandari, A. Challenges and opportunities in producing high-quality edible mushrooms from lignocellulosic biomass in a small scale. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 1355–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin X, Lin Z, Lin D, et al. Effects of planting Pennisetum sp.(Giant Juncao) on soil microbial functional diversity and fertility in the barren hillside. Acta Ecol Sin, 2014, 34(15): 4304-12.
- Vieira, F.R.; de Andrade, M.C.N. Optimization of substrate preparation for oyster mushroom (Pleurotus ostreatus) cultivation by studying different raw materials and substrate preparation conditions (composting: phases I and II). World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 32, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miles P G, Chang S-T. Mushrooms: cultivation, nutritional value, medicinal effect, and environmental impact [M]. CRC press, 2004.
- Chang S-T, Miles P G. Edible mushrooms and their cultivation. Edible mushrooms and their cultivation. 1989.
- Assan N, Mpofu T. The influence of substrate on mushroom productivity. Scientific Journal of Crop Science, 2014, 3(7): 86-91.
- Salami, A.O.; Bankole, F.A.; Olawole, O.I. Effect of different substrates on the growth and protein content of oyster mushroom (Pleurotus florida). Int. J. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2016, 10, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Pang, Y.; Zhang, R. Compositional changes of cottonseed hull substrate during P. ostreatus growth and the effects on the feeding value of the spent substrate. Bioresour. Technol. 2001, 80, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mensah O, E. Comparative studies on growth and yield of Pleurotus ostreatus on different types of substrates [D], 2015.
- Chang S T, Wasser S P. The cultivation and environmental impact of mushrooms [M]. Oxford research encyclopedia of environmental science. 2017.
- Bellettini, M.B.; Fiorda, F.A.; Maieves, H.A.; Teixeira, G.L.; Ávila, S.; Hornung, P.S.; Júnior, A.M.; Ribani, R.H. Factors affecting mushroom Pleurotus spp. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 26, 633–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z. Oyster Mushroom Cultivation. Mushroom Grower’s Handbook, 2004, 1(107-13.
- Isikhuemhen, O.S.; Mikiashvili, N.A.; Kelkar, V. Application of solid waste from anaerobic digestion of poultry litter in Agrocybe aegerita cultivation: mushroom production, lignocellulolytic enzymes activity and substrate utilization. Biodegradation 2008, 20, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, C. Modern aspects of mushroom culture technology. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2004, 64, 756–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maheswari S, Rajarajan P, Pandian P M, et al. Influence of different substrates on growth and yield of Pleurotus ostreatus. Journal of Applied Horticulture, 2020, 22(3): 215-9.
- Maheswari S, Rajarajan P, Pandian P M, et al. Yield performance of mushroom (Pleurotus Ostreatus) on different treatment of sugarcane bagasse and saw dust and its nutrient analysis. Plant Cell Biotechnol Mol Biol, 2021, 22(7-13.
- Girmay, Z.; Gorems, W.; Birhanu, G.; Zewdie, S. Growth and yield performance of Pleurotus ostreatus (Jacq. Fr.) Kumm (oyster mushroom) on different substrates. AMB Express 2016, 6, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamantopoulou, P.; Fourtaka, K.; Melanouri, E.M.; Dedousi, M.; Diamantis, I.; Gardeli, C.; Papanikolaou, S. Examining the Impact of Substrate Composition on the Biochemical Properties and Antioxidant Activity of Pleurotus and Agaricus Mushrooms. Fermentation 2023, 9, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang A T, Ong H C, Fattah I R, et al. Progress on the lignocellulosic biomass pyrolysis for biofuel production toward environmental sustainability. Fuel Processing Technology, 2021, 223(106997.
- Sánchez-Ruiz, M.I.; Ayuso-Fernández, I.; Rencoret, J.; González-Ramírez, A.M.; Linde, D.; Davó-Siguero, I.; Romero, A.; Gutiérrez, A.; Martínez, A.T.; Ruiz-Dueñas, F.J. Agaricales Mushroom Lignin Peroxidase: From Structure–Function to Degradative Capabilities. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinge, T.R.; Adi, E.M.; Mih, A.M.; A Ache, N.; Nji, T.M. Effect of substrate on the growth, nutritional and bioactive components of Pleurotus ostreatus and Pleurotus florida. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2016, 15, 1476–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Han, J. Yield, polysaccharides content and antioxidant properties of the mushroom Agaricus subrufescens produced on different substrates based on selected agricultural wastes. Sci. Hortic. 2013, 157, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Jia, Y.; Wan, Y.; Li, H.; Jiang, R. Market Survey and Risk Assessment for Trace Metals in Edible Fungi and the Substrate Role in Accumulation of Heavy Metals. J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, H1612–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suryadi, H.; Judono, J.J.; Putri, M.R.; Eclessia, A.D.; Ulhaq, J.M.; Agustina, D.N.; Sumiati, T. Biodelignification of lignocellulose using ligninolytic enzymes from white-rot fungi. Heliyon 2022, 8, e08865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rameshaiah G, Jagadish Reddy M. Applications of ligninolytic enzymes from a white-rot fungus Trametes versicolor. Universal Journal of Environmental Research & Technology, 2015, 5(1).
- Wang, H.; Lu, Z.; Keyhani, N.O.; Deng, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, S.; Luo, Z.; Jin, K.; Zhang, Y. Insect fungal pathogens secrete a cell wall-associated glucanase that acts to help avoid recognition by the host immune system. PLOS Pathog. 2023, 19, e1011578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sitarz A, K. Laccase Enzymology in Relation to Lignocellulose Processing. 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Marren, P. Mushrooms: the natural and human world of British fungi [M]. Bloomsbury Publishing, 2018.
- Hu Yingping H Y, Lin Xingsheng L X, Lai Youyun L Y, et al. Effects analysis on cultivation of Pleurotus ostreatus with Juncao and lotus seed waste. 2019.
- Fernández-Fueyo, E.; Castanera, R.; Ruiz-Dueñas, F.J.; López-Lucendo, M.F.; Ramírez, L.; Pisabarro, A.G.; Martínez, A.T. Ligninolytic peroxidase gene expression by Pleurotus ostreatus : Differential regulation in lignocellulose medium and effect of temperature and pH. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2014, 72, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagulwar M, More D, Mandhare L. Nutritional properties and value addition of mushroom: a review. Pharma Innov J, 2020, 9(395-8.
- Wang, X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, T.; Wang, Y. Evaluation of heavy metal concentrations of edible wild-grown mushrooms from China. J. Environ. Sci. Heal. Part B 2017, 52, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).