1. Introduction
Type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) is a chronic progressive lifelong condition associated with significant morbidity and increased mortality mainly from cardiovascular disease [
1,
2]. A large Swedish National Diabetes Registry showed that excess mortality was significant among patients with T1DM, and this was mainly due to cardiorenal complications thus showing an unmet need in improvement of secondary prevention in this vulnerable patient strata [
3]. Many adults with T1DM experience a low health-related quality of life, are more likely to be unemployed, and have more sickness days compared to the general population [
4]. The morbidity from T1DM is substantial since it starts early in life and thus has a strong propensity for the development of microvascular and macrovascular complications [
5,
6]. Chronic hyperglycemia sustains and promotes oxidative stress, vascular inflammation, monocyte adhesion and perturbations in arterial wall and endothelium that leads to development of overt cardiovascular disease [
7]. A meta-analysis by Cai et al. showed that diagnosis of T1DM was strongly associated with an increased risk of several types of cardiovascular diseases including ischemic heart disease, myocardial infarction, heart failure, atrial fibrillation and stroke [
8]. Independent factors for ischemic stroke among patients with T1DM were duration of diabetes, presence of diabetic nephropathy, higher hemoglobin A1c, higher systolic blood pressure, smoking and degree of insulin resistance [
9]. Interestingly, T1DM carries significantly greater risk of hemorrhagic stroke as well, compared to patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, therefore, highlighting general propensity of T1DM for potential cerebrovascular complications [
10]. In line with this, the life expectancy in someone with T1DM is about 11 years shorter in men and 13 years in women, most of it being driven by a cardiovascular disease [
11].
Taken together, there is a great clinical and public health interest in preventing and managing cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease in patients with T1DM.
The burden and impact of cardiac and cerebrovascular disease (CCD) on patients who are admitted to hospital with T1DM is largely unknown. The underlying pathology in these conditions may be related to diseases of the peripheral vasculature, coronary arteries, myocardium, structural cardiac changes, or cardiac electrical activity, which contributes to inpatient hospital admission. How frequently these conditions account for hospitalizations in patients with T1DM and how they affect outcomes on a large nationwide scale is not known and has not been examined yet. Hence, the need to consider population level data is required to capture the frequency of relevant clinical events, especially those that are less common.
In this comprehensive analysis, we examined a representative, large, nationwide database consisting of hospital records from the United States to evaluate the CCD burden among patients with T1DM and their respective outcomes. In-hospital mortality, length of stay and cost were explored in detail across a range of CCD conditions.
2. Materials and Methods
This manuscript was prepared in accordance with the recommendations of the STROBE checklist [
12]. Ethical approval was not required as we analyzed a non-identifiable public large-scale dataset. We analyzed nationally representative data in the United States from the National Inpatient Sample (NIS). The NIS is a database created by the Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project which is the largest publicly available all-payer inpatient healthcare database in the United States which can be utilized to provide national estimates of inpatient utilization, access, costs, quality, and outcomes [
13].
A retrospective nationwide cohort study was undertaken of all hospital records in the United States with a discharge diagnosis of T1DM between 2016 to 2019. These years were chosen because the hospital admission information was in ICD-9 codes prior to 2016 and excluded years beyond 2019 to avoid possible confounding effect of COVID-19 pandemic. We excluded patients with age <18 years, missing values for death, and sex. From this group of patients, the first ICD-10 diagnostic code was used to define CCD as described in detail in
Supplementary Table S1. CCD included angina pectoris, acute myocardial infarction, pulmonary embolism, acute pericarditis, aortic valve disorder, mitral valve disorder, right sided heart valve disorder, endocarditis, myocarditis, cardiomyopathy, heart failure, atrial fibrillation or flutter, 2° or 3° atrioventricular block, intracranial hemorrhage, subarachnoid hemorrhage and cerebral infarction. The discharge diagnosis codes, which were up to 40, were used to define coexisting illnesses and demographic, hospital information and outcome data (in-hospital mortality, length of stay and costs) were available in the NIS dataset.
Statistical Methods
Statistical analysis was performed on Stata 13 (College Station, TX). A p value <0.05 was considered as statistically significant. The hospital admissions were stratified by those which had CCD and those without CCD. Descriptive statistics were presented with median and interquartile range (IQR) for continuous variables, and as percent for categorical variables. The non-parametric equality-of-medians test on Stata was used to determine if there were any statistical differences for continuous variables and the Chi2 test was used for categorical variables. The frequency of the different individual diagnoses that composed CCD was determined together with the rate of mortality associated with each diagnosis. Both the median and mean length of stay for the individual diagnoses were presented. The total cost in US$ was derived from the total charge multiplied by the charge-to-cost ratio and the average cost was used together the frequency of the condition to estimate the total cost per year for the hospitalizations associated with CCD.
3. Results
There were a total of 1,442,794 weighted hospital admissions with T1DM included in the analysis (
Supplementary Figure S1, Appendix A). A total of 59,860 patients had a primary diagnosis of CCD and 1,382,934 did not have a primary diagnosis of CCD. The proportion of the different cardiovascular diagnoses that make up the CCD is shown in
Figure 1. Acute myocardial infarction represented 41.7% of CCD followed by cerebral infarction (19.6%), heart failure (13.3%) and atrial fibrillation/atrial flutter (8.5%).
The demographics and comorbidities of included patients according to the presence or absence of a primary diagnosis of cardiovascular disease are shown in
Table 1. The median age of patients with CCD was older compared to those without CCD (median 60 vs. 39 years, p<0.001). There were more female patients in the group without CCD compared to those with CCD (52.4% vs. 47.5%, p<0.001). In terms of race, patients who were white had a greater proportion of patients with CCD compared to those without CCD (74.9% vs. 64.9%). The proportion of patients receiving Medicare was greater among patients who had CCD (55.4% vs. 32.7%) and the proportion of patients self-paying was greater for those without CCD (7.2% vs. 2.7%). The proportions of patients with obesity (18.2% vs 10.1%, p<0.001), hypertension (83.3% vs 54.3%, p<0.001), hyperlipidemia (64.5% vs 31.7%, p<0.001), previous myocardial infarction (16.4% vs 5.8%, p<0.001), previous stroke (16.2% vs 6.7%, p<0.001), previous heart failure (28.6% vs 7.8%) and chronic lung disease (19.1% vs 14.7%, p<0001) were greater in the group of patients with T1DM and primary CCD compared to the group without CCD.
The mean and median length of hospital stay were significantly longer for patients with CCD (5.7 and 4 days vs. 4.6 and 3 days, respectively) compared to no CCD and the healthcare costs were significantly higher (mean US $21,802 and median $13,762 vs. mean US $11,924 and median US $7,113, respectively).
The in-hospital mortality rate was 4.1% for T1DM patients with CCD vs. 1.1% for T1DM patients without CCD (p<0.001).
The length of hospital stay and cost of admissions for different primary diagnosis of CCD in patients with T1DM is shown in
Table 2.
The median length of stay was longest for patients with right sided heart valve disease, endocarditis, subarachnoid hemorrhage, mitral valve disease, and intracranial hemorrhage. The median cost was greatest for patients with right-sided heart valve disease followed by patients with mitral valve disease and those with aortic valve disease and subarachnoid hemorrhage. The estimated cost of hospitalizations for all admissions with primary diagnosis of CCD was approximately US $326 million each year with the admissions for acute myocardial infarction costing US $163 million per year.
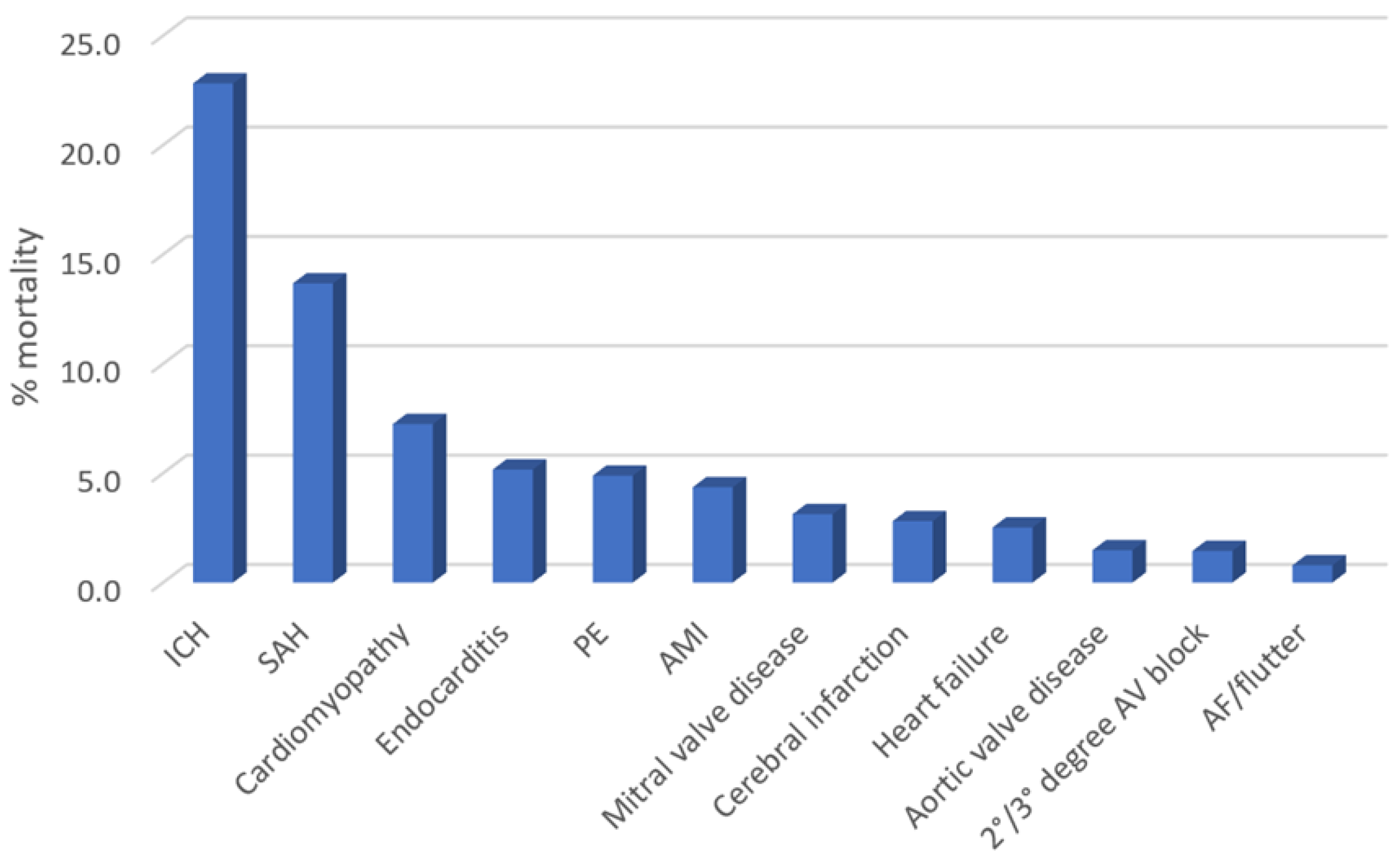
The rates of in-hospital mortality according to the different primary diagnosis of CCD are depicted in
Figure 2. The mortality rate was greatest for patients admitted with intracranial hemorrhage (22.8%), subarachnoid hemorrhage (13.7%), cardiomyopathy (7.3%), endocarditis (5.2%), and pulmonary embolism (4.9%).
After adjustments for demographics and comorbidities, the multivariable-adjusted odds of in-hospital mortality compared to patients with non-CCD admission was greatest for intracranial hemorrhage (OR 17.37, 95%CI 12.68-23.79, p<0.001), pulmonary embolism (OR 4.39, 95%CI 2.70-7.13, p<0.001), endocarditis (OR 3.46, 95%CI 1.22-9.84, p=0.020), acute myocardial infarction (OR 2.31, 95%CI 1.92-2.77, p<0.001) and cerebral infarction (OR 1.47, 95%CI 1.04-2.09, p=0.030) (
Table 3). Finally, most common single primary diagnostic codes for patients that died were sepsis, T1DM with ketoacidosis without coma, non-ST elevation myocardial infarction, acute respiratory failure with hypoxia and cardiac arrest with unspecified cause.
4. Discussion
T1DM influences morbidity, length of stay and mortality in patients with CCD. In a large, nationwide analysis of US data we show that the CCD-related hospitalizations among patients with T1DM impose a great burden for hospital systems. The DCCT study showed good glycemic control can reduce microvascular complications, but the effect on macrovascular complications is not clear [
14]. Nevertheless, better management of cardiovascular risk factors and comorbidities in patients with T1DM which includes adequate blood pressure control, lipid management and lifestyle interventions have reduced the burden of cardiovascular disease, but it is not clear what happens to patients with T1DM and underlying CCD when they are admitted to the hospital and what their outcomes are.
In our study, we analyzed the effect of CCD in patients with T1DM admitted to nationwide array of US hospitals, along with analyzing individual CCD conditions that drive morbidity and mortality.
Many studies consider cardiovascular disease as an outcome which refers primarily to ischemic heart disease and stroke with or without peripheral vascular disease. However, the vascular nature of the term cardiovascular disease precludes important cardiological conditions such as heart valve disease, arrhythmias, infective endocarditis and inflammatory conditions of the heart muscle or pericardium and our study tried to account for these deficiencies in the literature.
There is a strong evidence that T1DM will increase atherosclerotic risk factors which can then independently increase cardiovascular risk but whether either the diabetes itself or the associated risk factors change the risk for CCD is not known [
15]. This is important as patients may develop a CCD condition because of the diabetes and risk factors or they may develop the condition independently, but their outcomes are affected by either the diabetes or risk factors. As Verges previously stated - cardiovascular risk remains high among well-controlled T1DM patients without traditional cardiovascular risk factors thus suggesting other potential factors that drive poor outcomes [
7]. Therefore, in the present analysis, it was important to perform multivariable adjustment for comorbid conditions and other factors which may impact outcomes in a population of patients with T1DM.
The frequency of comorbid conditions and absolute mortality burden of CCD in type 1 diabetes should be considered. We show that mortality rates in patients with intracranial hemorrhage, subarachnoid hemorrhage, cardiomyopathy, and infective endocarditis are high. Several studies have evaluated these conditions in patients with T1DM. A case-control study of 120 patients with intracranial hemorrhage and 135 control patients with low back pain found that diabetes mellitus was more prevalent in the group with intracranial hemorrhage (33.1% vs. 22.2%), but it was not clear if there were any patients with T1DM [
16]. A prospective cohort study of 4,083 patients with T1DM reported that during a median follow up of 9.4 years, 15 patients developed subarachnoid hemorrhage and 4 had died [
17]. For cardiomyopathy, a Swedish cohort study of 20,985 patients with T1DM found that there was a 4-fold increase in risk of development of heart failure for patients with HbA1c ≥10.5% compared to patients with HbA1c <6.5% [
18]. Furthermore, a recent meta-analysis showed that patients with T1DM had 3-fold greater risk of developing heart failure, compared to controls without T1DM, and this was even more pronounced among women (had nearly 5-fold risk in that study) [
19]. Regarding infective endocarditis, in a study of 559 patients with definite infective endocarditis, 13% of patients had T1DM and insulin-dependent diabetes was associated with a 4.7-fold increase in odds of in-hospital mortality [
20].
According to results that we report, these conditions were not frequent population-wide and the estimated population deaths over the study years were 485 for intracranial hemorrhage and fewer than 100 deaths for the other three conditions. These low event rates even on a population level reflect the importance of national evaluations and large nationwide analysis that can capture these nuances. While the mortality rate is lower, the estimated absolute number of deaths is greater for acute myocardial infarction (n=1,090). Overall, there were 17,420 deaths in the cohort and 14.1% (n=2,460) were due to CCD. The major non-CCD causes of mortality was sepsis which caused over 4000 deaths and ketoacidosis without coma, acute respiratory failure with hypoxia and cardiac arrest which was more than 500 deaths for each condition.
In our study, we show that patients with T1DM and CCD are different in terms of age and comorbidities compared to their counterparts without CCD. The comorbidities may be relevant because they may require management which contributes to prolonged hospital stay and cost. In addition, an important consideration is whether these factors impact clinical decision making as the elderly and presences of coexisting illness can affect risk of undertaking procedures. The broad nature of the conditions captured in CCD is important there may be interventional and surgical options for management in some of the conditions such as infective endocarditis, valvular heart disease and coronary artery disease. While attempts were made with adjustments in our analysis, the likely reality is that we are not able to account for the entire effect of these factors.
Finally, all patients should also be under the care of diabetes specialist team and there should be locally established care pathways with shared care where appropriate. These pathways may help reduce any missed opportunities to prevent progression of diabetes and complications and enable early detection problems when they develop.
Limitations
This analysis has several limitations. First, we used the primary ICD-10 codes as the method of determining the primary reason for admission. It is possible that there may be more than one key condition that resulted in the condition. Second, the NIS does not contain patient level identifiers so patients who survive admission may be readmitted and considered within a given year and across different years. Third, we do not have information about the management of patients which influences mortality, length of stay, and cost.
5. Conclusions
The burden of CCD in patients with T1DM is large and it is significantly associated with increased in-hospital mortality. The latter ranges from 17-fold increase in odds for intracranial hemorrhage to 1.5-fold increase in odds for cerebral infarction. Likewise, the length of stay and the hospitalization costs associated with CCD are substantial and impose heavy strain on healthcare systems. These findings raise awareness of the importance of taking measure to prevent onset of CCD and manage patients with CCD among patients hospitalized with T1DM.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org, Supplementary Table S1; Supplementary Figure S1;
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Chun Shing Kwok and Gregory Lip; Data curation, Adnan Qureshi; Formal analysis, Chun Shing Kwok, Adnan Qureshi, Anne Phillips, Gregory Lip, Wasim Hanif and Josip Andelo Borovac; Funding acquisition, Josip Andelo Borovac; Investigation, Chun Shing Kwok, Adnan Qureshi, Anne Phillips, Gregory Lip, Wasim Hanif and Josip Andelo Borovac; Methodology, Chun Shing Kwok and Anne Phillips; Project administration, Josip Andelo Borovac; Resources, Josip Andelo Borovac; Supervision, Josip Andelo Borovac; Validation, Wasim Hanif; Writing – original draft, Chun Shing Kwok; Writing – review & editing, Chun Shing Kwok, Adnan Qureshi, Anne Phillips, Gregory Lip, Wasim Hanif and Josip Andelo Borovac.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The National Inpatient Sample (NIS) is a dataset where use and publication for research purposes does not require institutional review board approval or statement.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data used in this analysis may be purchased from the Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP) website. The authors do not have permission to share the data used for the analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Atkinson, M.A.; Eisenbarth, G.S.; Michels, A.W. Type 1 diabetes. Lancet 2014, 383, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawshani, A.; Rawshani, A.; Franzén, S.; Eliasson, B.; Svensson, A.M.; Miftaraj, M.; McGuire, D.K.; Sattar, N.; Rosengren, A.; Gudbjörnsdottir, S. Mortality and Cardiovascular Disease in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1407–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallström, S.; Wijkman, M.O.; Ludvigsson, J.; Ekman, P.; Pfeffer, M.A.; Wedel, H.; Rosengren, A.; Lind, M. Risk factors, mortality trends and cardiovascular diseases in people with Type 1 diabetes and controls: A Swedish observational cohort study. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 2022, 21, 100469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, H.B.; Ovesen, L.L.; Mortensen, L.H.; Lau, C.J.; Joensen, L.E. Type 1 diabetes, quality of life, occupational status and education level - A comparative population-based study. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2016, 121, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daneman, D. Type 1 diabetes. Lancet 2006, 367, 847–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalakova, T.; Yotov, Y.; Tzotchev, K.; Galcheva, S.; Balev, B.; Bocheva, Y.; Usheva, N.; Iotova, V. Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus - Risk Factor for Cardiovascular Disease Morbidity and Mortality. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2021, 17, 37–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergès, B. Cardiovascular disease in type 1 diabetes, an underestimated danger: Epidemiological and pathophysiological data. Atherosclerosis 2024, 394, 117158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.; Li, J.; Cai, W.; Chen, C.; Ma, J.; Xie, Z.; Dong, Y.; Liu, C.; Xue, R.; Zhao, J. Meta-analysis of type 1 diabetes mellitus and risk of cardiovascular disease. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2021, 35, 107833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hägg, S.; Thorn, L.M.; Forsblom, C.M.; Gordin, D.; Saraheimo, M.; Tolonen, N.; Wadén, J.; Liebkind, R.; Putaala, J.; Tatlisumak, T.; Groop, P.H.; FinnDiane Study Group. Different risk factor profiles for ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Stroke 2014, 45, 2558–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janghorbani, M.; Hu, F.B.; Willett, W.C.; Li, T.Y.; Manson, J.E.; Logroscino, G.; Rexrode, K.M. Prospective study of type 1 and type 2 diabetes and risk of stroke subtypes: the Nurses’ Health Study. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 1730–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livingstone, S.J.; Levin, D.; Looker, H.C.; Lindsay, R.S.; Wild, S.H.; Joss, N.; Leese, G.; Leslie, P.; McCrimmon, R.J.; Metcalfe, W.; McKnight, J.A.; Morris, A.D.; Pearson, D.W.M.; Petrie, J.R.; Philips, S.; Sattar, N.A.; Traynor, J.P.; Colhoun, H.M. Estimated life expectancy in a Scottish cohort with type 1 diabetes, 2008-2010. JAMA 2015, 313, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P.; STROBE Initiative. Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: guidelines for reporting observational studies. BMJ 2007, 335, 806–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Healthcare Cost & Utilization Project. Overview of the National (Nationwide) Inpatient Sample (NIS). Available online: https://www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/nisoverview.jsp (accessed on 2 July 2022).
- Nathan, D.M. The diabetes control and complication trial/epidemiology of diabetes interventions and complication study at 30 years: Overview. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colom, C.; Rull, A.; Sanchez-Quesada, J.L.; Pérez, A. Cardiovascular Disease in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: Epidemiology and Management of Cardiovascular Risk. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hesemi, O.; Kasmaei, H.D.; Matani, F.; Assarzadegan, F.; Mansouri, B.; Jabbehdari, S. Relationship between intracerebral hemorrhage and diabetes mellitus: A case-control study. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2015, 9, 8–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korja, M.; Thorn, L.M.; Hägg, S.; Putaala, J.; Liebkind, R.; Harjutsalo, V.; Forsblom, C.M.; Gordin, D.; Tatlisumak, T.; Groop, P.H. Subarachnoid hemorrhage in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 3754–3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lind, M.; Bounias, I.; Olsson, M.; Gudbjörnsdottir, S.; Svensson, A.M.; Rosengren, A. Glycaemic control and incidence of heart failure in 20,985 patients with type 1 diabetes: an observational study. Lancet 2011, 378, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haji, M.; Erqou, S.; Fonarow, G.C.; Echouffo-Tcheugui, J.B. Type 1 diabetes and risk of heart failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2023, 202, 110805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duval, X.; Alla, F.; Doco-Lecompte, T.; Le Moing, V.; Delahaye, F.; Mainardi, J.L.; Plesiat, P.; Celard, M.; Hoen, B.; Leport, C. Diabetes mellitus and infective endocarditis: the insulin factor in patient morbidity and mortality. Eur. Heart J. 2007, 28, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).