Submitted:
01 July 2024
Posted:
02 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
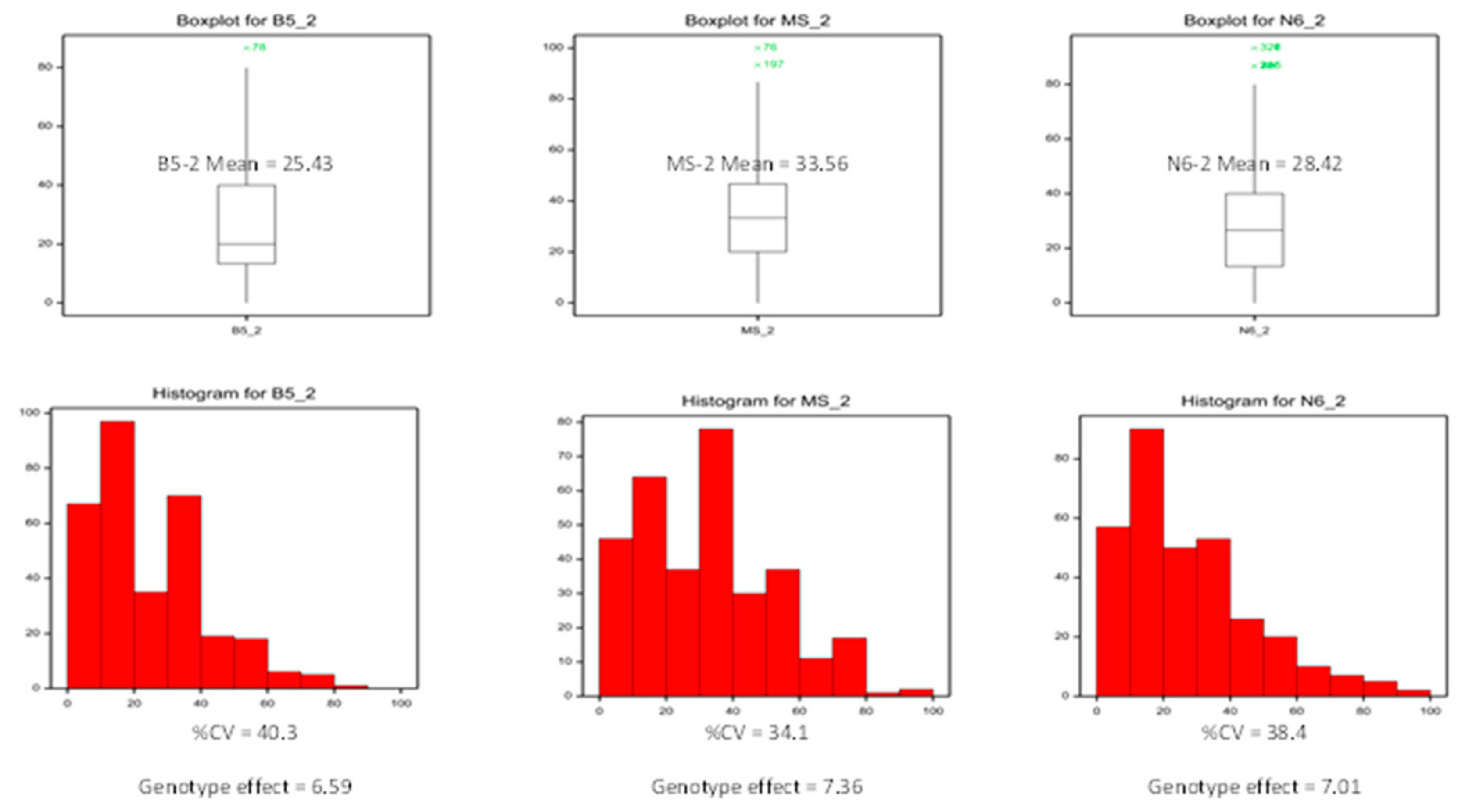
2.1. Callus Induction in the Rice Germplasm Collection
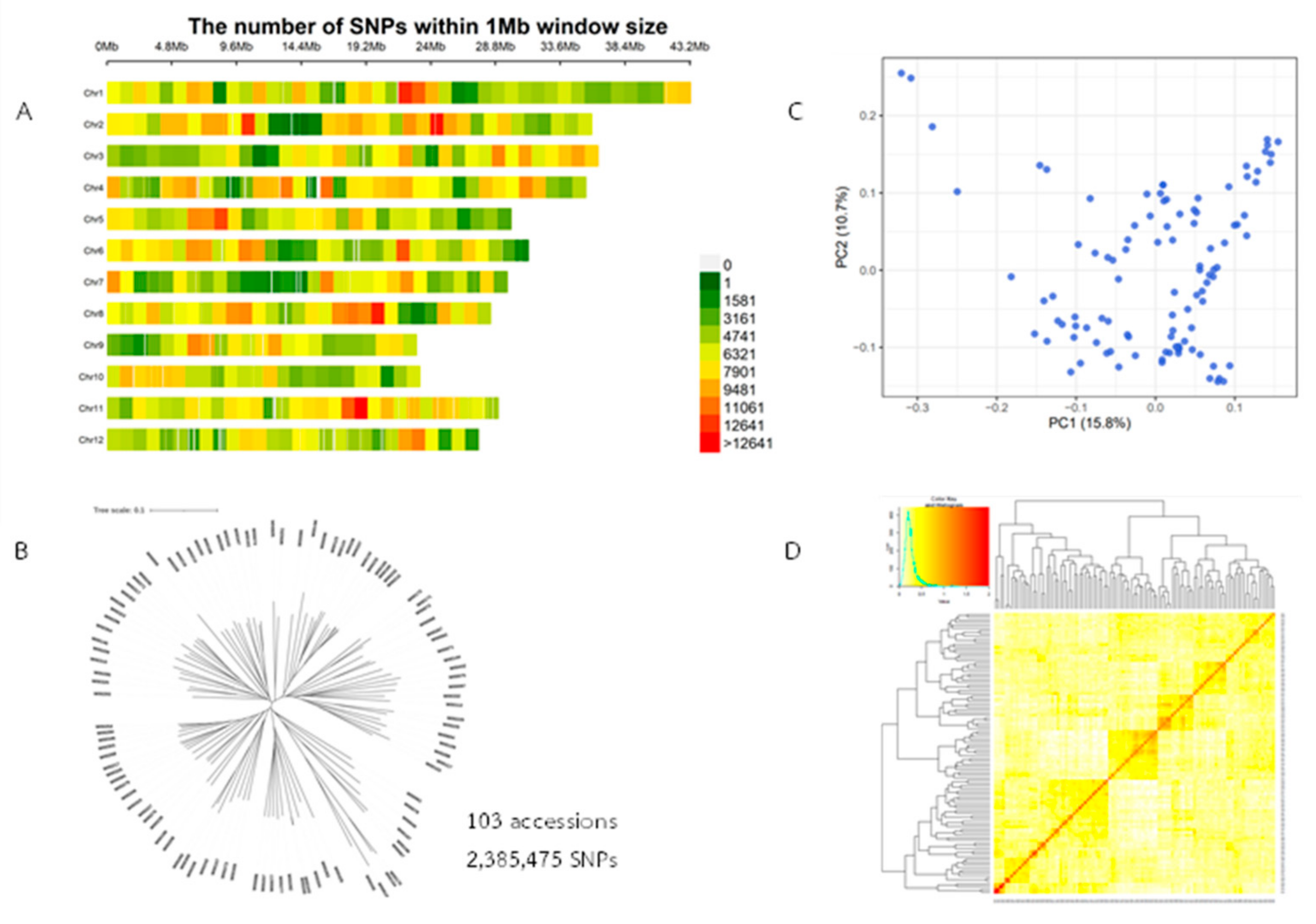
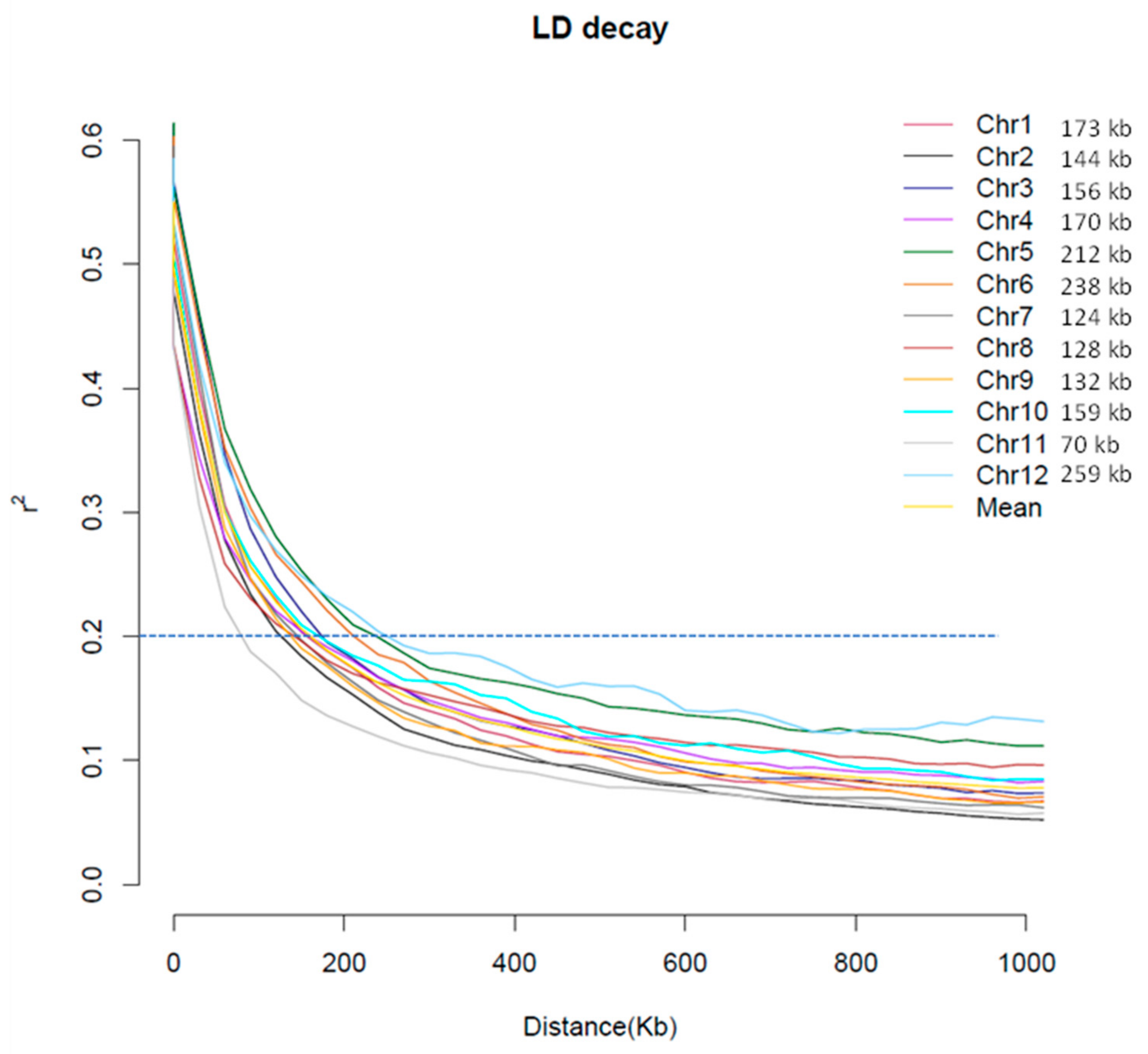
2.2. Genotype Data and Analysis of Population Structure, Relative Kinship, and the Linkage Disequilibrium (LD)
2.3. Identification of the QTLs Associated with Callus Induction by GWAS
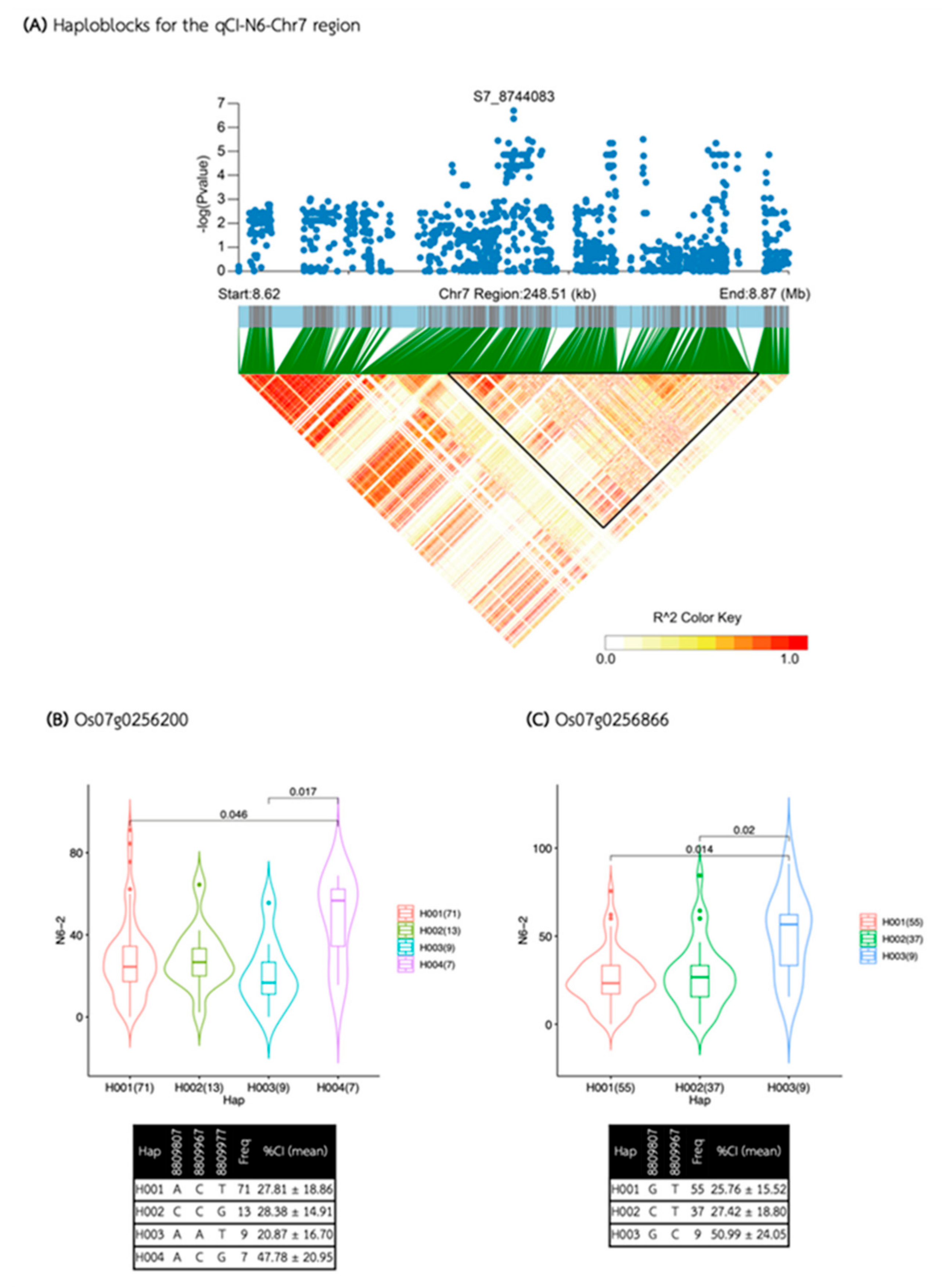
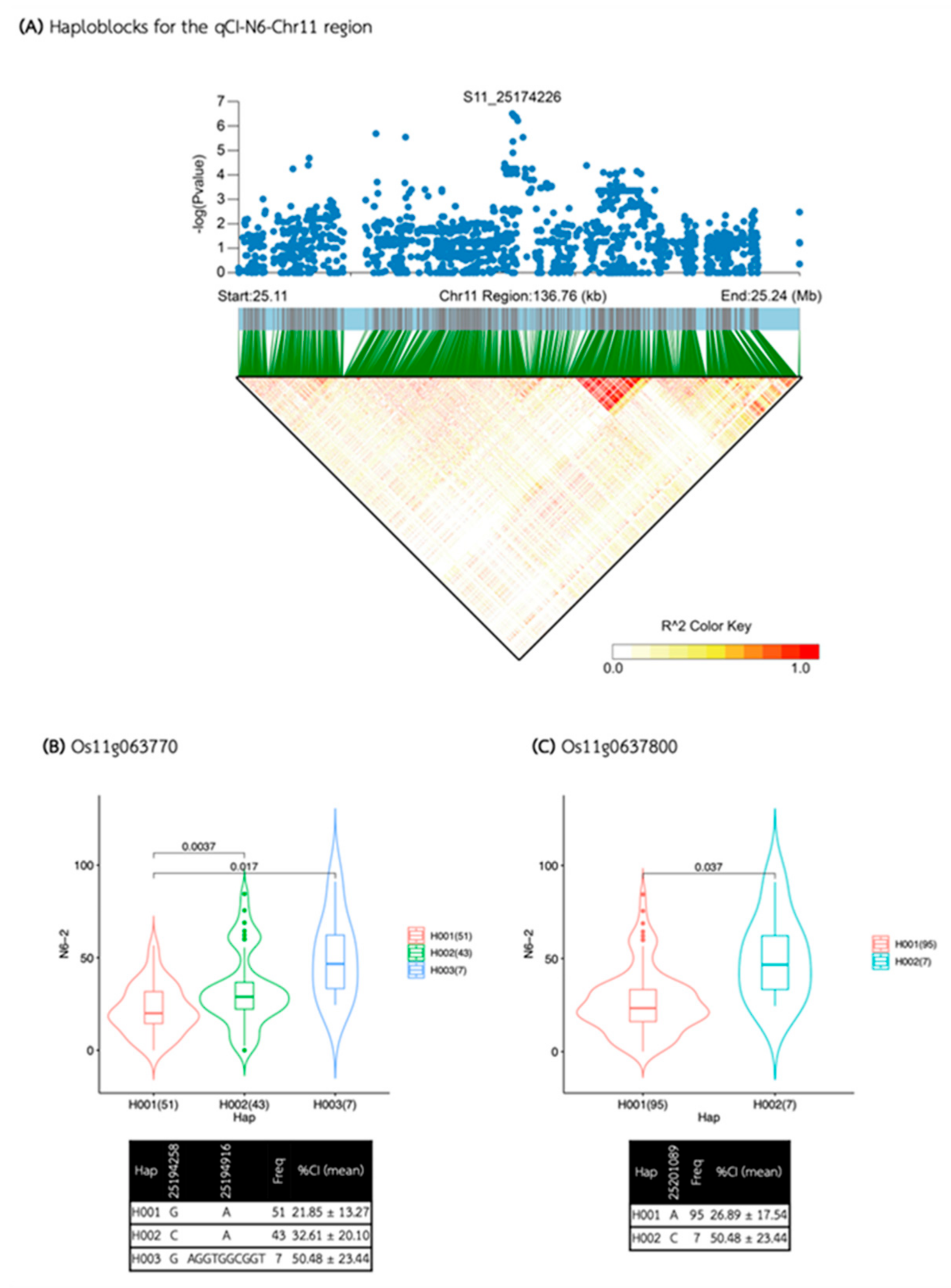
2.4. Haplotype Block Analysis and Candidate Gene Identification
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Association Mapping Panel and Callus Induction Evaluation
4.2. Genome-Wide Association Analysis
4.3. Haplotype Block Analysis and Candidate Gene Identification
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zafar SA, Zaidi SS, Gaba Y, Singla-Pareek SL, Dhankher OP, Li X, Mansoor S, Pareek A. Engineering abiotic stress tolerance via CRISPR/ Cas-mediated genome editing. J Exp Bot. 2020 Jan 7;71(2):470-479.
- Sukegawa S, Nureki O, Toki S, Saika H. Genome editing in rice mediated by miniature size Cas nuclease SpCas12f. Front Genome Ed. 2023 Mar 13;5:1138843.
- Fehér A. Callus, Dedifferentiation, Totipotency, Somatic Embryogenesis: What These Terms Mean in the Era of Molecular Plant Biology? Front Plant Sci. 2019 Apr 26;10:536.
- Espinosa-Leal CA, Puente-Garza CA, Garc?a-Lara S. In vitro plant tissue culture: means for production of biological active compounds. Planta. 2018 Jul;248(1):1-18.
- Ikeuchi M, Sugimoto K, Iwase A. Plant callus: mechanisms of induction and repression. Plant Cell. 2013 Sep;25(9):3159-73.
- Lee K.S., Jeon H.S., Kim M.Y. Optimization of a mature embryos-based in vitro culture system for high frequency somatic embryogenic callus induction and plant regeneration form japonica rice cultivar. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2002;71:9-13.
- Main, M., Frame, B., & Wang, K. Rice, japonica (Oryza sativa L.). Agrobacterium Protocols: Volume 1, 2015, 169-180.
- Sah, S. K., Kaur, A., & Sandhu, J. S. High frequency embryogenic callus induction and whole plant regeneration in japonica rice Cv. Kitaake. J. Rice Res. 2014, 2(2), 1-5.
- Lin YJ, Zhang Q. Optimising the tissue culture conditions for high efficiency transformation of indica rice. Plant Cell Rep. 2005 Jan;23(8):540-7.
- Ge X, Chu Z, Lin Y, Wang S. A tissue culture system for different germplasms of indica rice. Plant Cell Rep. 2006 May;25(5):392-402.
- Ho TL., Te-chato S., Yenchon S. Callus induction and plantlet regeneration systems in indica rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivar Sangyod. Walailak J Sci & Tech 2018; 15(10): 753-763.
- Binte Mostafiz S, Wagiran A. Efficient Callus Induction and Regeneration in Selected Indica Rice. Agronomy. 2018; 8(5):77.
- Wu J, Chang X, Li C, Zhang Z, Zhang J, Yin C, Ma W, Chen H, Zhou F, Lin Y. QTLs Related to Rice Callus Regeneration Ability: Localization and Effect Verification of qPRR3. Cells. 2022 Dec 19;11(24):4125.
- Koo BH, Yoo SC, Park JW, Kwon CT, Lee BD, An G, Zhang Z, Li J, Li Z, Paek NC. Natural variation in OsPRR37 regulates heading date and contributes to rice cultivation at a wide range of latitudes. Mol Plant. 2013 Nov;6(6):1877-88.
- Taguchi-Shiobara F, Yamamoto T, Yano M, Oka S. Mapping QTLs that control the performance of rice tissue culture and evaluation of derived near-isogenic lines. Theor Appl Genet. 2006 Mar;112(5):968-76.
- Wang Y, Yang X, Xu G, Ye X, Ji Y, Lou X, Su J, Sun C, Fu Y, Zhang K. Mapping quantitative trait loci associated with callus browning in Dongxiang common wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.). Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Apr;50(4):3129-3140.
- Huang C, Zhang J, Zhou D, Huang Y, Su L, Yang G, Luo W, Chen Z, Wang H, Guo T. Identification and candidate gene screening of qCIR9.1, a novel QTL associated with anther culturability in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet. 2021 Jul;134(7):2097-2111.
- Guo F, Wang H, Lian G, Cai G, Liu W, Zhang H, Li D, Zhou C, Han N, Zhu M, Su Y, Seo PJ, Xu L, Bian H. Initiation of scutellum-derived callus is regulated by an embryo-like developmental pathway in rice. Commun Biol. 2023 Apr 25;6(1):457.
- Zhang Z, Zhao H, Li W, Wu J, Zhou Z, Zhou F, Chen H, Lin Y. Genome-wide association study of callus induction variation to explore the callus formation mechanism of rice. J Integr Plant Biol. 2019 Nov;61(11):1134-1150.
- Zhang, YC., Zhou, YF., Cheng, Y, Huang JH, Lian JP, Yang L, He RR, Lei MQ, Liu YW, Yuan C, Zhao WL, Xiao S, Chen YQ. Genome-wide analysis and functional annotation of chromatin-enriched noncoding RNAs in rice during somatic cell regeneration. Genome Biol. 2022, 23: 28.
- Oladosu Y, Rafii MY, Samuel C, Fatai A, Magaji U, Kareem I, Kamarudin ZS, Muhammad I, Kolapo K. Drought Resistance in Rice from Conventional to Molecular Breeding: A Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jul 18;20(14):3519.
- Josefina O. Narciso and Kazumi Hattori. Genotypic differences in morphology and ultrastructures of callus derived from selected rice varieties. Philippine Science Letters. 2010, 3:1.
- Chu, C.C., Wang, C.S., Sun, C.C., Hsu, C., Yin, K.C. and Chu, C.Y. Establishment of an efficient medium for anther culture of rice through comparative experiments on the nitrogen sources, Rice research strategies for the future, IRRI. 1975, 610 p.
- Ling, D.H. and Yoshida, S. Study of some factors affecting somatic embryogenesis in I.R. lines of rice (Oryza sativa L.), Acta Bot. Sinica 1987, 29: 1-8.
- Indoliya Y, Tiwari P, Chauhan AS, Goel R, Shri M, Bag SK, Chakrabarty D. Decoding regulatory landscape of somatic embryogenesis reveals differential regulatory networks between japonica and indica rice subspecies. Sci Rep. 2016 Mar 14;6:23050.
- Zhao Y, Hu Y, Dai M, Huang L, Zhou DX. The WUSCHEL-related homeobox gene WOX11 is required to activate shoot-borne crown root development in rice. Plant Cell. 2009 Mar;21(3):736-48.
- Kareem A, Durgaprasad K, Sugimoto K, Du Y, Pulianmackal AJ, Trivedi ZB, Abhayadev PV, Pinon V, Meyerowitz EM, Scheres B, Prasad K. PLETHORA Genes Control Regeneration by a Two-Step Mechanism. Curr Biol. 2015 Apr 20;25(8):1017-30.
- Qiao J, Zhang Y, Han S, Chang S, Gao Z, Qi Y, Qian Q. OsARF4 regulates leaf inclination via auxin and brassinosteroid pathways in rice. Front Plant Sci. 2022 Sep 30;13:979033.
- Kim Y, Chung YS, Lee E, Tripathi P, Heo S, Kim KH. Root Response to Drought Stress in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 22;21(4):1513.
- Nguyen D, Rieu I, Mariani C, van Dam NM. How plants handle multiple stresses: hormonal interactions underlying responses to abiotic stress and insect herbivory. Plant Mol Biol. 2016 Aug;91(6):727-40.
- Suzuki, N. Hormone signaling pathways under stress combinations. Plant Signal Behav. 2016 Nov;11(11):e1247139.
- Dar SA, Nawchoo IA, Tyub S, Kamili AN. Effect of plant growth regulators on in vitro induction and maintenance of callus from leaf and root explants of Atropa acuminata Royal ex Lindl. Biotechnol Rep (Amst). 2021 Nov 14;32:e00688.
- Jin J, Essemine J, Duan JL, Xie QJ, Zhu J, Cai WM. Regeneration of active endogenous IAA in rice calli following acclimation to 2,4-D free medium. Plant Growth Regul. 2021;93:203-220.
- Gamborg OL, Miller RA, Ojima K. Nutrient requirements of suspension cultures of soybean root cells. Exp Cell Res. 1968 Apr;50(1):151-8.
- Shao Q, Liu X, Su T, Ma C, Wang P. New Insights Into the Role of Seed Oil Body Proteins in Metabolism and Plant Development. Front Plant Sci. 2019 Dec 10;10:1568.
- Saadat, F. A computational study on the structure-function relationships of plant caleosins. Sci Rep. 2023; 13, 72.
- Chen DH, Chyan CL, Jiang PL, Chen CS, Tzen JT. The same oleosin isoforms are present in oil bodies of rice embryo and aleurone layer while caleosin exists only in those of the embryo. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2012 Nov;60:18-24.
- Hanano A, Bl?e E, Murphy DJ. Caleosin/peroxygenases: multifunctional proteins in plants. Ann Bot. 2023 Apr 4;131(3):387-409.
- Shang B, Xu C, Zhang X, Cao H, Xin W, Hu Y. Very-long-chain fatty acids restrict regeneration capacity by confining pericycle competence for callus formation in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 May 3;113(18):5101-6.
- Wan X, Wu S, Li Z, An X, Tian Y. Lipid Metabolism: Critical Roles in Male Fertility and Other Aspects of Reproductive Development in Plants. Mol Plant. 2020 Jul 6;13(7):955-983.
- Furuta K, Kubo M, Sano K, Demura T, Fukuda H, Liu YG, Shibata D, Kakimoto T. The CKH2/PKL chromatin remodeling factor negatively regulates cytokinin responses in Arabidopsis calli. Plant Cell Physiol. 2011 Apr;52(4):618-28.
- Xiao J, Jin R, Wagner D. Developmental transitions: integrating environmental cues with hormonal signaling in the chromatin landscape in plants. Genome Biol. 2017 May 10;18(1):88.
- Guo H, Guo H, Zhang L, Fan Y, Wu J, Tang Z, Zhang Y, Fan Y, Zeng F. Dynamic Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Uncharacterized Complex Regulatory Pathway Underlying Genotype-Recalcitrant Somatic Embryogenesis Transdifferentiation in Cotton. Genes (Basel). 2020 May 7;11(5):519.
- Murashige, T. and Skoog, F. A revised method for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiologia Plantarum 1962, 15: 473-479.
- Osabe D, Tanahashi T, Nomura K, Shinohara S, Nakamura N, Yoshikawa T, Shiota H, Keshavarz P, Yamaguchi Y, Kunika K, Moritani M, Inoue H, Itakura M. Evaluation of sample size effect on the identification of haplotype blocks. BMC Bioinformatics. 2007 Jun 14;8:200.
- Sun B, Ding X, Ye J, Dai Y, Cheng C, Zhou J, Niu F, Tu R, Hu Q, Xie K, Qiu Y, Li H, Feng Z, Shao C, Cao L, Zhang A, Chu H. Unveiling the Genetic Basis Underlying Rice Anther Culturability via Segregation Distortion Analysis in Doubled Haploid Population. Genes (Basel). 2023 Nov 17;14(11):2086.
- Chun HJ, Baek D, Jin BJ, Cho HM, Park MS, Lee SH, Lim LH, Cha YJ, Bae DW, Kim ST, Yun DJ, Kim MC. Microtubule Dynamics Plays a Vital Role in Plant Adaptation and Tolerance to Salt Stress. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 31;22(11):5957.
- Park JS, Choi Y, Jeong MG, Jeong YI, Han JH, Choi HK. Uncovering transcriptional reprogramming during callus development in soybean: insights and implications. Front Plant Sci. 2023 Aug 4;14:1239917.
- Wang D, Guo Y, Wu C, Yang G, Li Y, Zheng C. Genome-wide analysis of CCCH zinc finger family in Arabidopsis and rice. BMC Genomics. 2008 Jan 27;9:44.
- Zhang Q, Xie J, Zhu X, Ma X, Yang T, Khan NU, Zhang S, Liu M, Li L, Liang Y, Pan Y, Li D, Li J, Li Z, Zhang H, Zhang Z. Natural variation in Tiller Number 1 affects its interaction with TIF1 to regulate tillering in rice. Plant Biotechnol J. 2023 May;21(5):1044-1057.
- Liu L, Trendel J, Jiang G, Liu Y, Bruckmann A, Küster B, Sprunck S, Dresselhaus T, Bleckmann A. RBPome identification in egg-cell like callus of Arabidopsis. Biol Chem. 2023 Sep 29;404(11-12):1137-1149.
- Shaikh AA, Alamin A, Jia C, Gong W, Deng X, Shen Q, Hong Y. The Examination of the Role of Rice Lysophosphatidic Acid Acyltransferase 2 in Response to Salt and Drought Stresses. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 29;23(17):9796.
- Wang, J. and Zhang, Z. GAPIT Version 3: boosting power and accuracy for genomic association and prediction. Genomics, proteomics & bioinformatics 2021, 19(4), pp.629-640.
- Evanno G, Regnaut S, Goudet J. Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: a simulation study. Mol Ecol. 2005 Jul;14(8):2611-20.
- Lipka AE, Tian F, Wang Q, Peiffer J, Li M, Bradbury PJ, Gore MA, Buckler ES, Zhang Z. GAPIT: genome association and prediction integrated tool. Bioinformatics. 2012 Sep 15;28(18):2397-9.
- Hao Z, Lv D, Ge Y, Shi J, Weijers D, Yu G, Chen J. RIdeogram: drawing SVG graphics to visualize and map genome-wide data on the idiograms. PeerJ Comput Sci. 2020 Jan 20;6:e251.
- Kaler AS, Purcell LC. Estimation of a significance threshold for genome-wide association studies. BMC Genomics. 2019 Jul 29;20(1):618.
- Turner, S.D. qqman: An R package for visualizing GWAS results using QQ and manhattan plots. bioRxiv 2014, 005165. [Google Scholar]
- Dong SS, He WM, Ji JJ, Zhang C, Guo Y, Yang TL. LDBlockShow: a fast and convenient tool for visualizing linkage disequilibrium and haplotype blocks based on variant call format files. Brief Bioinform. 2021 Jul 20;22(4):bbaa227.
- McLaren W, Gil L, Hunt SE, Riat HS, Ritchie GR, Thormann A, Flicek P, Cunningham F. The Ensembl Variant Effect Predictor. Genome Biol. 2016 Jun 6;17(1):122.
- Zhang R, Jia G, Diao X. geneHapR: an R package for gene haplotypic statistics and visualization. BMC Bioinformatics. 2023 May 15;24(1):199.
- Kawahara Y, de la Bastide M, Hamilton JP, Kanamori H, McCombie WR, Ouyang S, Schwartz DC, Tanaka T, Wu J, Zhou S, Childs KL, Davidson RM, Lin H, Quesada-Ocampo L, Vaillancourt B, Sakai H, Lee SS, Kim J, Numa H, Itoh T, Buell CR, Matsumoto T. Improvement of the Oryza sativa Nipponbare reference genome using next generation sequence and optical map data. Rice (N Y). 2013 Feb 6;6(1):4.
- Miklaszewska M, Zienkiewicz K, Klugier-Borowska E, Rygielski M, Feussner I, Zienkiewicz A. CALEOSIN 1 interaction with AUTOPHAGY-RELATED PROTEIN 8 facilitates lipid droplet microautophagy in seedlings. Plant Physiol. 2023 Nov 22;193(4):2361-2380.
- Zeng X, Jiang J, Wang F, Liu W, Zhang S, Du J, Yang C. Rice OsClo5, a caleosin protein, negatively regulates cold tolerance through the jasmonate signalling pathway. Plant Biol (Stuttg). 2022 Jan;24(1):52-61.
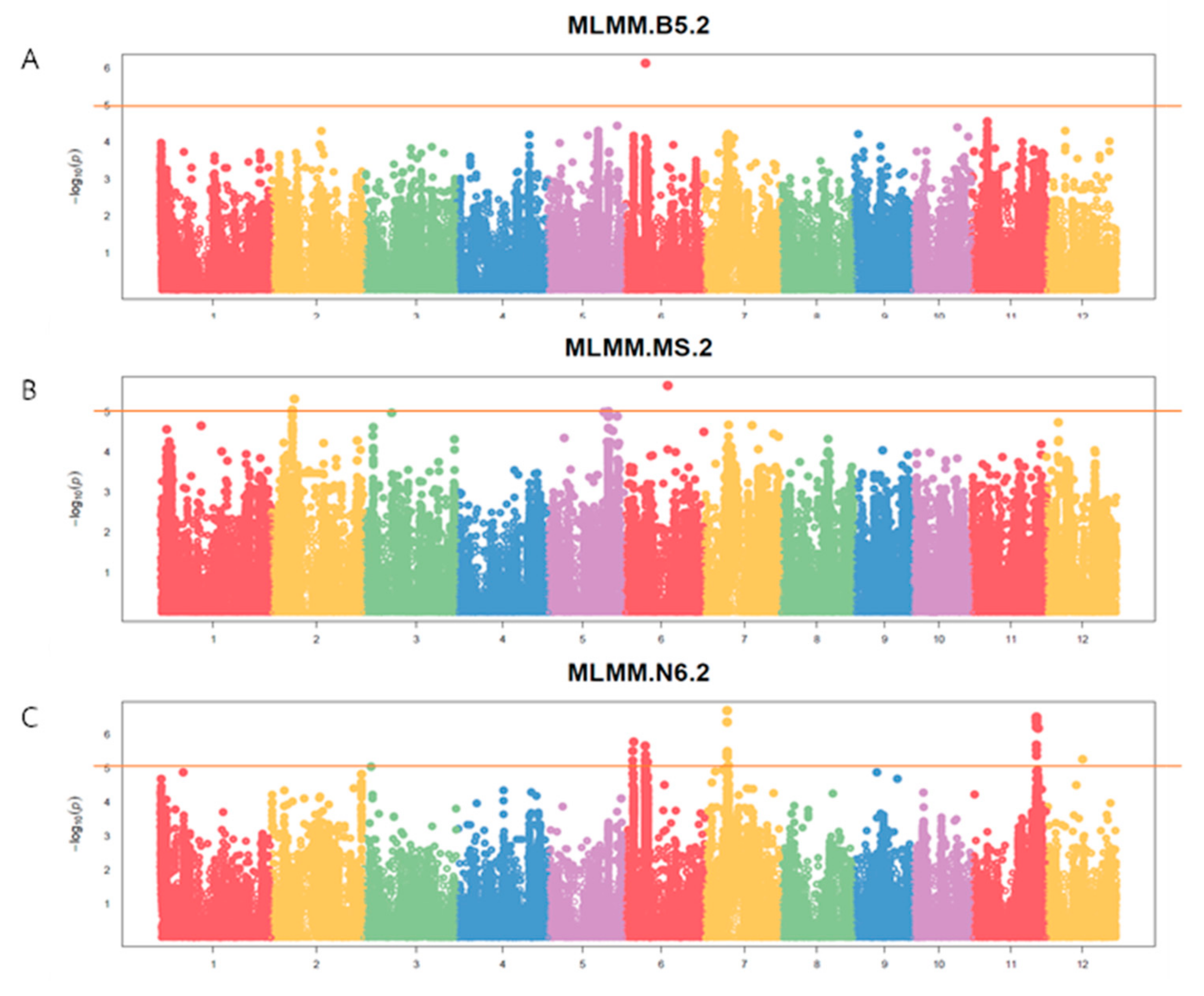
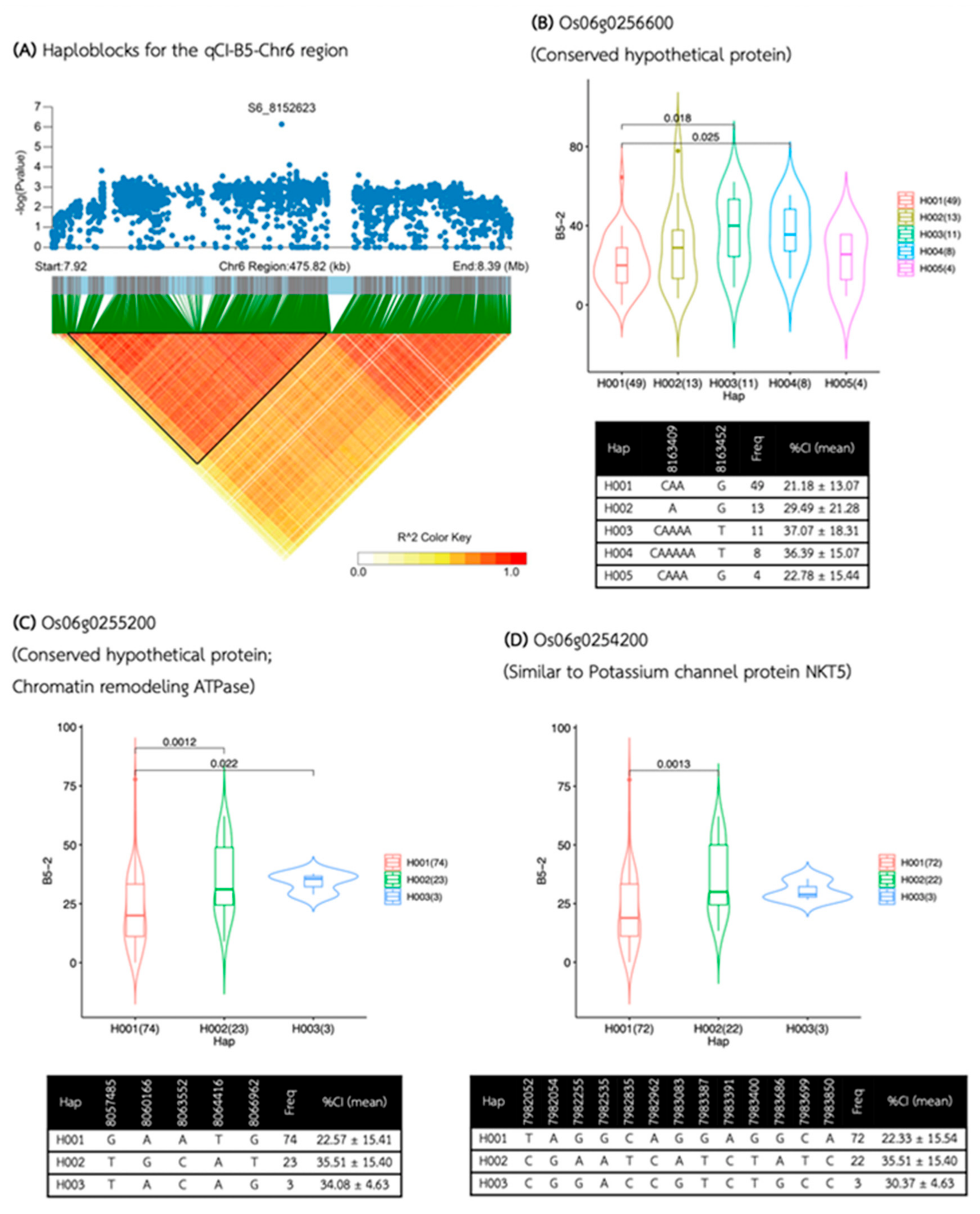
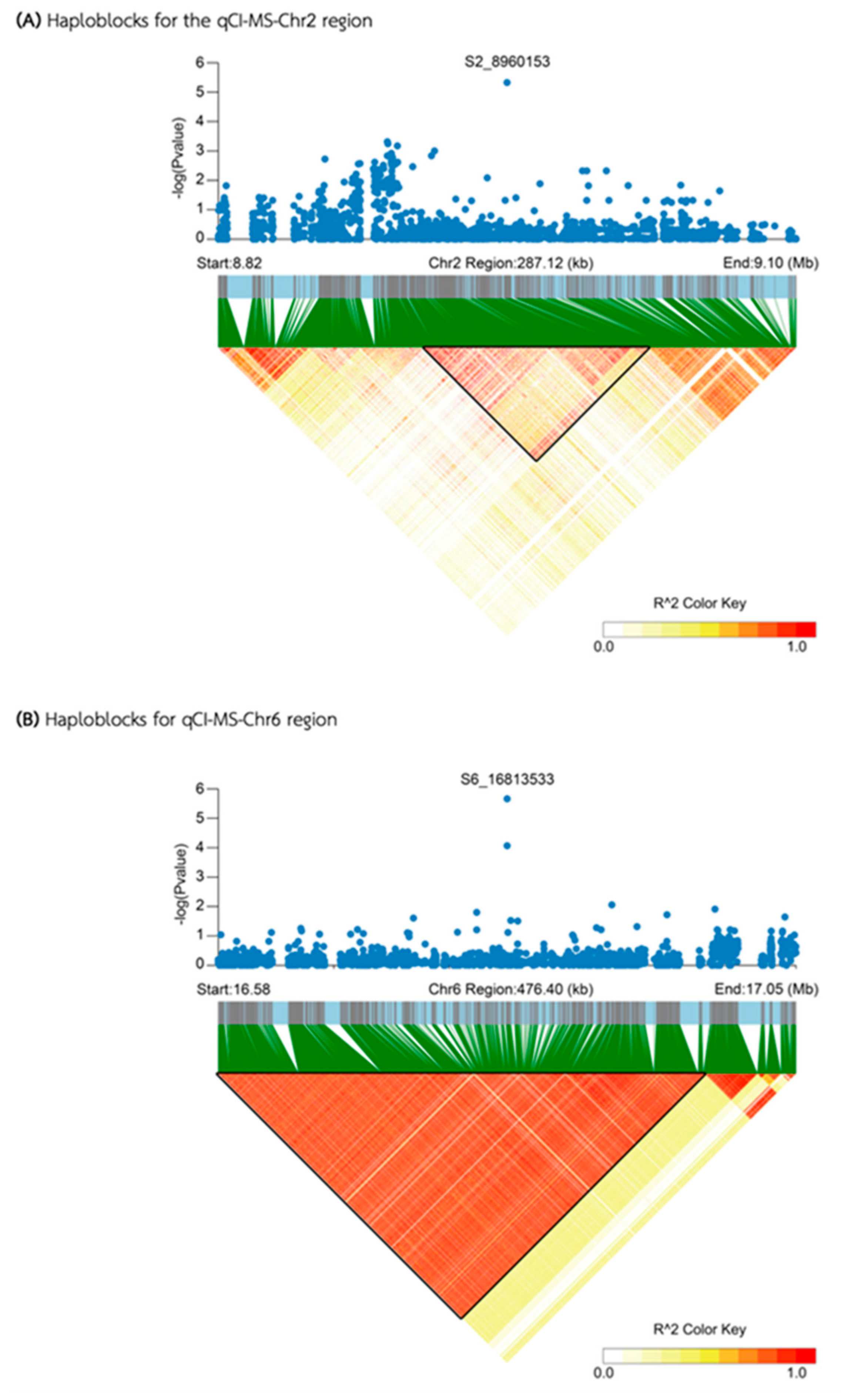
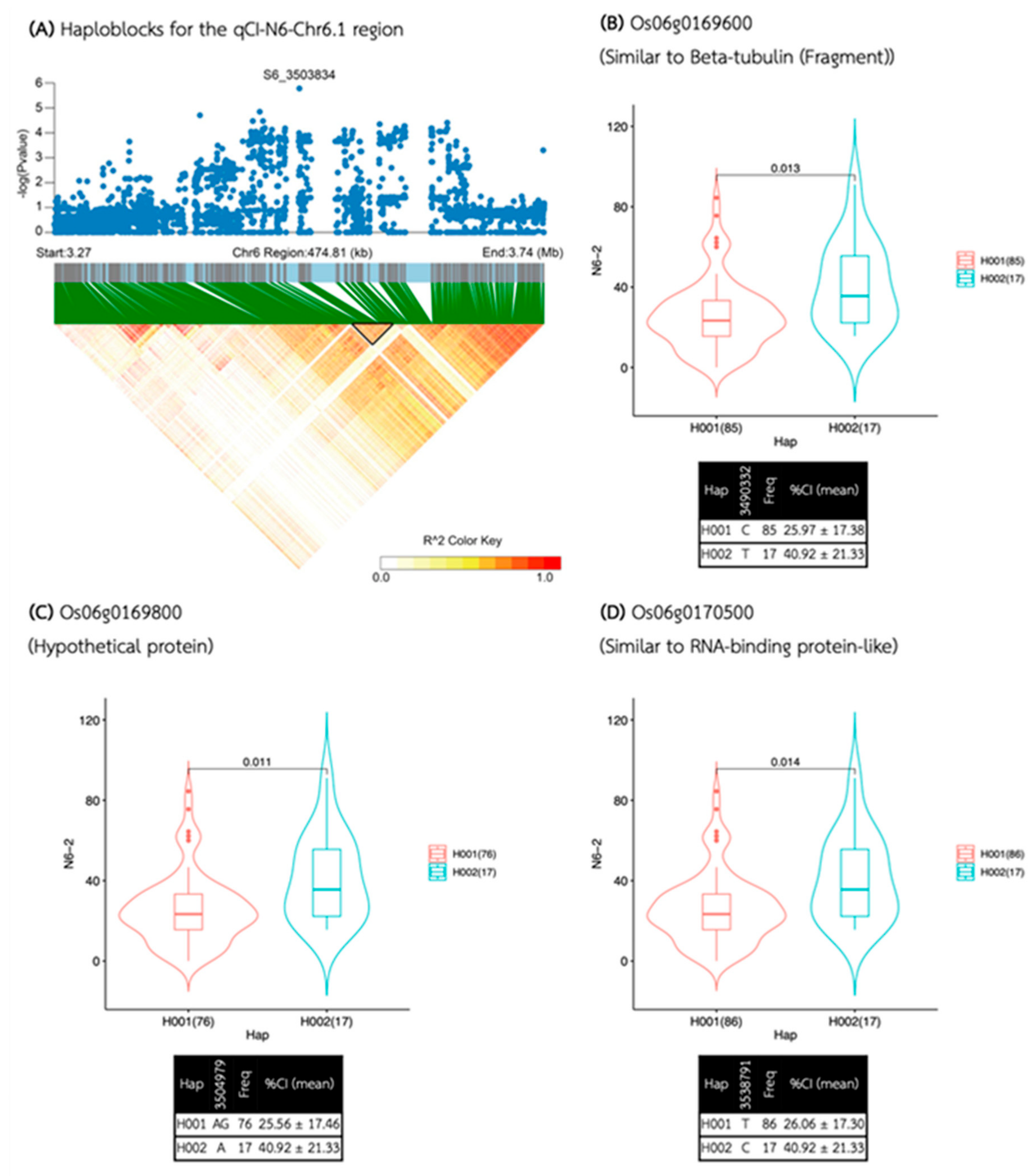
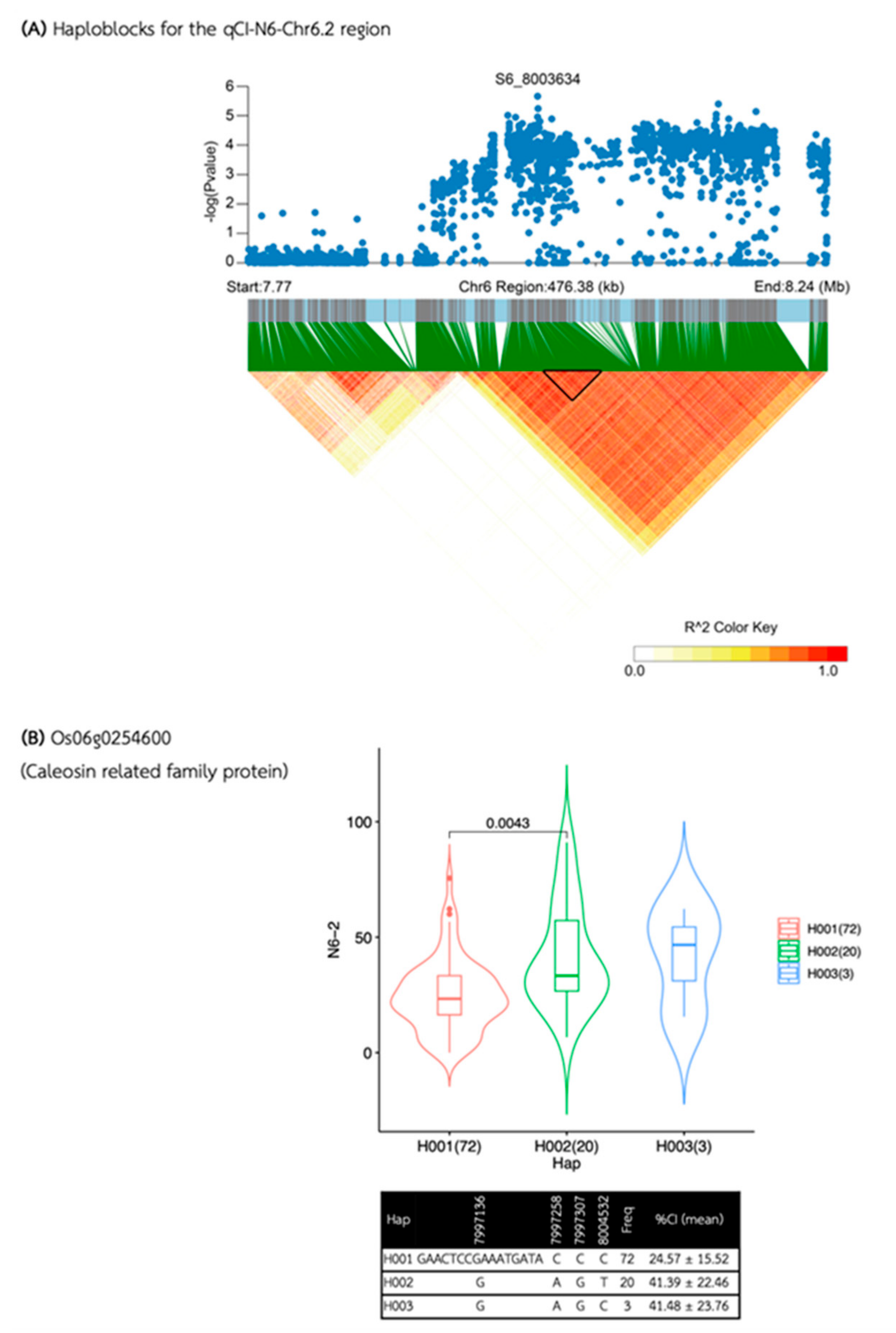
| Media | QTL | SNP id. | Chr | Pos | P.value | MAF | Effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B5 | qCI-B5-Chr6 | S6_8152623 | 6 | 8,152,623 | 1.75E-06 | 0.17 | -13.81 |
| MS | qCI-MS-Chr2 | S2_8960153 | 2 | 8,960,153 | 4.74E-06 | 0.13 | -13.38 |
| qCI-MS-Chr6 | S6_16813533 | 6 | 16,813,533 | 2.19E-06 | 0.06 | 23.91 | |
| N6 | qCI-N6-Chr6.1 | S6_3503834 | 6 | 3,503,834 | 1.67E-06 | 0.17 | 15.15 |
| qCI-N6-Chr6.2 | S6_8003634 | 6 | 8,003,634 | 2.20E-06 | 0.26 | -10.82 | |
| qCI-N6-Chr7 | S7_8744083 | 7 | 8,744,083 | 2.00E-07 | 0.21 | 16.03 | |
| qCI-N6-Chr11 | S11_25174226 | 11 | 25,174,226 | 3.13E-07 | 0.47 | 9.94 |
| QTLs | block start (bp) | block end (bp) | block size (bp) | #SNPs | #genes | #candidate genes | Annotation of the candidate genes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qCI-B5-Chr6 | 7,934,342 | 8,198,412 | 264,070 | 56 | 21 | 16 | Os06g0252800, Os06g0253100, Os06g0253350, Os06g0253600, Os06g0254200, Os06g0254300, Os06g0254600, Os06g0255200, Os06g0255700, Os06g0255900, Os06g0256000, Os06g0256500, Os06g0256600, Os06g0256800, Os06g0257050, Os06g0257200 |
| qCI-MS-Chr2 | 8,906,794 | 8,968,876 | 62,082 | 12 | 4 | 0 | |
| qCI-MS-Chr6 | 16,575,366 | 16,981,445 | 406,079 | 31 | 13 | 0 | |
| qCI-N6-Chr6.1 | 3,483,450 | 3,555,107 | 71,657 | 7 | 4 | 3 | Os06g0169600, Os06g0169800, Os06g0170500 |
| qCI-N6-Chr6.2 | 7,995,999 | 8,014,002 | 18,003 | 4 | 1 | 1 | Os06g0254600 |
| qCI-N6-Chr7 | 8,734,157 | 8,858,375 | 124,218 | 11 | 5 | 2 | Os07g0256200, Os07g0256866 |
| qCI-N6-Chr11 | 25,104,139 | 25,244,312 | 140,173 | 56 | 13 | 10 | Os11g0636900, Os11g0637050, Os11g0637000, Os11g0637100, Os11g0637200, Os11g0637600, Os11g0637700, Os11g0637800, Os11g0637900, Os11g0638200 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





