1. Introduction
Prostate cancer is the second most commonly diagnosed cancer among men and a significant cause of cancer-related mortality [
1]. Due to its high prevalence, early detection and screening have been widely implemented since the late 1980s to mitigate the disease burden [
2]. One crucial aspect of prostate disease management is the accurate measurement of prostate volume (PV) [
3]. PV estimation is essential for determining prostate-specific antigen density, which is a critical marker for assessing prostate cancer risk [
4]. Additionally, precise PV measurement is vital for planning therapeutic interventions such as brachytherapy, where accurate volume calculations are necessary for effective dose distribution [
5]. Furthermore, PV assessment is important for diagnosing benign prostate conditions like lower urinary tract symptoms and benign prostatic hyperplasia [
6].
In clinical settings, imaging modalities such as computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and ultrasound (US) are used to evaluate prostate malignancy and volume. Each imaging modality has unique characteristics that determine its suitability based on the clinical context. MRI-based PV estimation is considered the gold standard due to its superior signal-to-noise ratio [
7]. However, transrectal ultrasound (TRUS) is more commonly used in clinical practice because it is cost-effective, portable, and allows for rapid PV estimation [
7,
8]. Transabdominal ultrasound (TAUS) is another viable option, often preferred for its non-invasive and more comfortable approach [
9].
Figure 1 illustrates examples of prostate images obtained by TAUS, TRUS, and MRI, highlighting the differences among these imaging modalities.
Estimating PV with US is particularly valuable for early-stage diagnosis. However, accurate PV estimation using US is challenging due to the complexities in interpreting US images. Tasks like prostate segmentation and annotation often lead to significant variability and inaccuracies [
10]. This is primarily due to poor contrast between the prostate and surrounding tissues, along with imaging artifacts such as echoic shadows and calcifications [
11]. Additionally, TAUS faces unique challenges, including difficulties in observing the prostate when shadow artifacts disrupt the prostate boundary due to ultrasonic reflection by the pelvic bone [
12].
To address these challenges, computer-aided methods have been developed to reduce clinician workload, shorten examination times, and improve segmentation and annotation accuracy. There has been a growing interest in automated prostate segmentation methods to derive PV. Traditional methods such as deformable models, edge-based segmentation, and region-based segmentation have been extensively reviewed [
11,
13]. These methods rely heavily on extracting prostate-specific image features, which are often compromised by contrast variations and artifacts in US images [
14].
In recent years, deep learning (DL) architectures have emerged as promising alternatives for automatic prostate assessment. DL models can process entire images and automatically extract multi-level features, capturing both semantic and detailed image information [
15]. Despite these advancements, DL methods still face challenges in accurately delineating prostate boundaries [
16].
This review aims to provide a comprehensive overview of recent advancements in DL architectures for accurate PV estimation in diagnostic US imaging. We present:
A systematic review of developed DL architectures for prostate segmentation and PV estimation on US images.
An overview of proposed methods, including quantitative comparisons of results.
Evaluation of various designs within their respective contexts.
Suggestions for future research directions.
The paper is structured as follows:
Section 2 details the search methodology.
Section 3 presents the results, focusing on DL applications for prostate segmentation. This section discusses key improvements in DL architectures, including US pre-processing methods, multi-directional image data usage, additional shape information integration, attention mechanisms, feature map refinement, and the consistency and robustness of DL models. Finally,
Section 4 concludes with a discussion.
Figure 1.
Cross-section examples of the prostate in different imaging modalities in the transverse (axial) plane, where the prostate is manually delineated in yellow. (a) Magnetic Resonance Imaging (gold-standard for prostate volume evaluation), (b) Transabdominal Ultrasound, (c) Transrectal Ultrasound (Adapted from Karimi et al. (2019) [
16], with permission from Elsevier).
Figure 1.
Cross-section examples of the prostate in different imaging modalities in the transverse (axial) plane, where the prostate is manually delineated in yellow. (a) Magnetic Resonance Imaging (gold-standard for prostate volume evaluation), (b) Transabdominal Ultrasound, (c) Transrectal Ultrasound (Adapted from Karimi et al. (2019) [
16], with permission from Elsevier).
2. Methodology
A review was performed according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines. The core search concepts for this review were deep learning (DL), prostate volume (PV), and ultrasound (US). In October 2023, a comprehensive search was conducted across three scientific databases: PubMed [
17], IEEE Xplore [
18], and Scopus [
19]. Search queries were specifically adapted to each search engine and based on the search criteria seen in Listing 1.
| Listing 1: The search criteria used to construct search queries |
(deep learning OR neural network OR Net) AND
(prostate) AND
(ultrasound OR US OR TRUS OR TAUS) AND
(segmentation OR extraction OR delineation)
|
Inclusion and exclusion criteria were defined prior to the search.
Inclusion Criteria
Studies reporting on PV estimation or prostate segmentation using DL in US, including both transrectal ultrasound (TRUS) and transabdominal ultrasound (TAUS).
Studies involving the registration of US images where segmentation is part of the registration process.
Studies written in English and published from 2016 onwards.
Exclusion Criteria
Articles focusing on organs other than the prostate.
Articles unrelated to US imaging.
Invalid records, review articles, and duplicates.
Articles where proposed registration pipelines did not include an automatic segmentation step or relied on imaging modalities other than ultrasound.
During the title and abstract screening, articles were selected if they met the inclusion criteria. The full-text screening included articles where the proposed segmentation architectures were evaluated on performance. Articles were excluded if they lacked an automatic segmentation step in the proposed registration pipeline or used other imaging modalities.
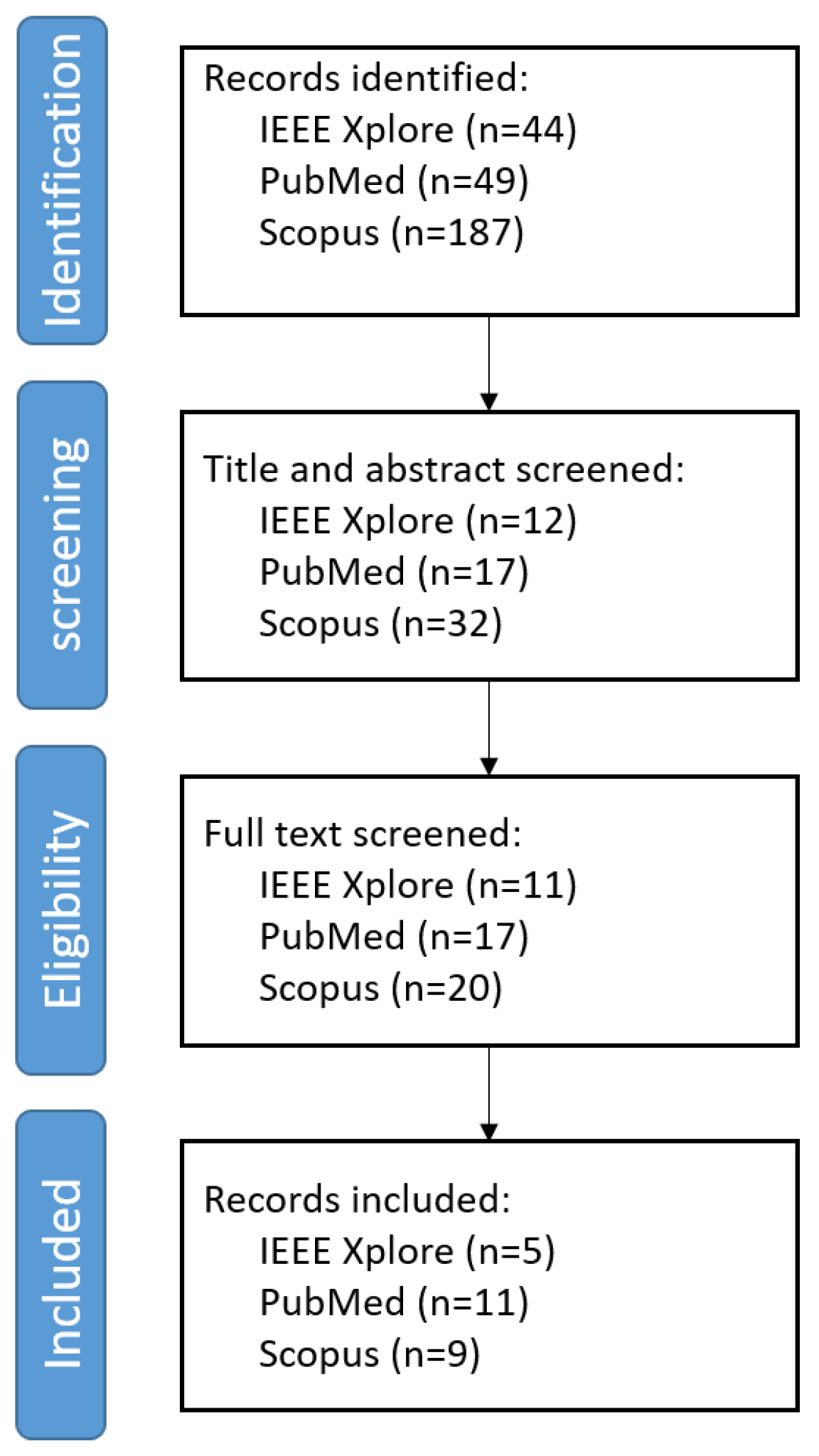
A total of 280 studies were retrieved from PubMed [
17], IEEE Xplore [
18], and Scopus [
19]. After duplicate removal, screening titles, and abstracts, 48 studies met the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Full-text screening resulted in 25 studies being included in this review.
Figure 2 illustrates the flow diagram showing the number of papers identified at each step.
To evaluate the deep learning (DL) architectures reviewed, several parameters were analyzed to provide context for their application:
The purpose of the DL architecture in relation to 2D or 3D prostate segmentation.
The amount of ultrasound (US) data used for training and testing.
The number of patients included in the dataset.
The results concerning the evaluation metrics used.
Additionally, the key innovations in the DL architectures that contributed to performance improvements were explained and compared. All stages of the screening process were conducted by an independent reviewer.
3. Results
Currently, automated prostate volume (PV) estimation primarily relies on segmentation methods based on transrectal ultrasound (TRUS). Our search strategy revealed no available literature on prostate segmentation using transabdominal ultrasound (TAUS). A single research group focused on automating the Ellipsoid formula on TAUS images to obtain the PV. In this section, we explore the significant advancements in deep-learning (DL) methods for prostate segmentation using ultrasound (US) imaging. Generally, the deep learning (DL) architectures reviewed utilize a traditional U-Net as the backbone. Various authors have enhanced the traditional U-Net by implementing residual connections or substituting the encoding path with alternative models. However, the majority of architectural designs incorporate additional modules aimed at improving segmentation accuracy.
Table 1 provides a summary of studies focused on prostate segmentation using TRUS, highlighting the modifications and improvements in different DL architectures. In this table, studies that do not focus on DL methods for prostate segmentation were excluded.
The latter subsections explain various techniques and innovations that enhance segmentation accuracy and robustness. We begin with pre-processing methodologies aimed at improving image quality by mitigating artifacts inherent to US imaging. This is followed by a discussion on the employment of multi-directional image data, which leverages different imaging perspectives to improve segmentation outcomes. We then cover the implementation of additional shape information, which helps in accurately segmenting ambiguous prostate regions by incorporating anatomical landmarks and shape models. Attention mechanisms, both on image and feature levels, are examined for their ability to focus on relevant regions and improve segmentation precision. Further, we discuss feature map refinement techniques that enhance the quality of feature extraction in DL architectures. The consistency and robustness of DL models across diverse datasets are also considered, highlighting strategies to ensure reliable performance. Finally, a quantitative evaluation of various DL architectures is provided, comparing their performance metrics to establish state-of-the-art prostate segmentation in US images.
3.1. Ultrasound Pre-Processing Techniques
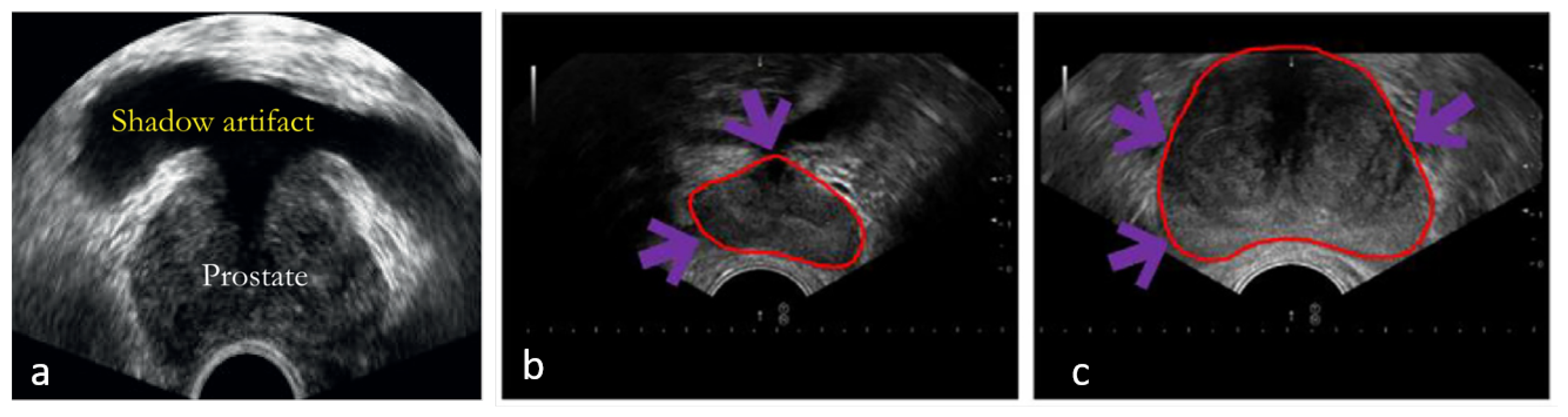
Pre-processing techniques aimed at improving image readability have been extensively explored to address imaging artifacts inherent in US, which often lead to inaccurate prostate segmentations such as shadow (
Figure 3a) and low contrast between the prostate and surrounding structures (
Figure 3b-c). Dark areas, known as acoustic shadows, can arise from structures with high echogenicity, such as bones or calcifications. To tackle this, Xu et al. (2022) [
39] introduced two novel mechanisms to help networks handle shadow regions at both the image and feature levels. Shadow artifacts were artificially added to training images to enhance the diversity of shadows in the dataset, serving as an innovative data augmentation strategy to increase network robustness on prostate images with shadow artifacts. The authors simulated artifacts by extracting shadow regions from other images using soft thresholding and created augmented training data by fusing these shadow artifacts with other images. Furthermore, shadow features were subtracted from the feature maps, creating a feature space that ignores shadow regions, similar to a systematic drop-out layer. This approach encourages the model to learn the prostate boundary using the remaining shadow-free features. When these methods were added to a traditional U-Net architecture, the results showed an increase in Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC) by 1.29% and a reduction in Hausdorff Distance (HD) by 0.33 mm.
Lei et al. (2019) [
29] explored the use of 3D Mean, Median, and Gaussian filters to enhance feature extraction of the prostate boundary in their DL architecture. However, this pre-processing step had no significant effect on DSC, Precision, or Recall, and it slightly degraded HD performance. This indicates that the use of these particular filters is not effective for improving segmentation results in this design.
3.2. Employment of Multi-Directional Image Data
Using multi-directional images can enhance prostate segmentation by addressing visibility variations. For example, the apex and base of the prostate often have ambiguous boundaries on transverse US images but appear clearer in the sagittal and coronal directions. Beitone et al. (2022) [
22] proposed the Multi-eXpert Fusion (MXF) framework, which uses input images from all directions to improve segmentation results. The authors trained three 2D U-Nets on axial, sagittal, and coronal TRUS images, creating view-specific segmentation volumes of the prostate. These volumes served as input for a subsequent fusion network, which generated view-specific confidence maps to create the final segmentation. Similarly, Lei et al. (2019) [
29] trained three view-specific V-Nets and introduced a Multi-Directional Contour Refinement (MDCR) method to post-process the view-specific volumes and estimate the PV. The core concept of MDCR is to define the final boundary contour by averaging boundary intersection coordinates from axial, sagittal, and coronal directions. This approach increased the DSC score from 0.912 to 0.919 (P < 0.001).
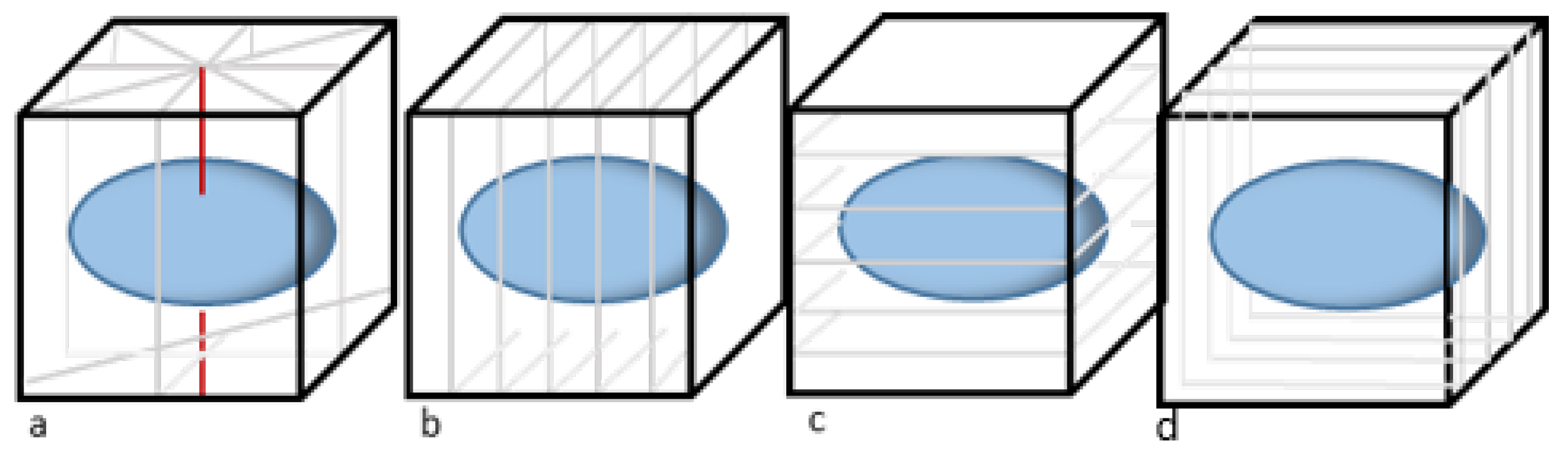
Orlando et al. (2020) [
32] proposed a novel 3D segmentation method by utilizing a modified U-Net to segment twelve 2D radial slices, which were subsequently used for 3D volume reconstruction. The choice to obtain radial prostate segmentations, as opposed to transverse segmentations, was motivated by the observation that the prostate presents more clearly when the center of the gland is in-plane.
Figure 4 illustrates the difference between radial, sagittal, and axial image slices. A modified U-Net was trained on 6773 2D images obtained randomly from axial, coronal, sagittal, and radial planes. The resulting 12 segmentations were placed in the initial 3D space, and the 3D prostate boundary was reconstructed. The resulting 3D segmentation was compared to a traditional V-Net, and the modified U-Net showed improved segmentation performance (DSC = 0.94 vs 0.91). Although the V-Net was not rigorously optimized, this comparison suggests that segmentation based on 3D information can yield better results than less spatially-dense image information.
In clinical practice, adjacent slices in a 2D acquisition are often considered during manual segmentation to distinguish the prostate boundary from surrounding tissue. Ghavami et al. (2018) explored the integration of neighboring slices as input to a traditional U-Net to improve 2D TRUS segmentation. Their evaluation showed that the DSC increased significantly by 1% when two adjacent slices on each side of the input image were added. However, integrating three adjacent slices did not show significant improvement, indicating that adding two adjacent slices is sufficient to enhance segmentation performance.
3.3. Implementation of Additional Shape Information
To accurately segment ambiguous prostate regions, additional shape information can be incorporated into DL architectures. Girum et al. (2020) [
27] explored the use of boundary landmarks to improve segmentation in 2D TRUS images. They employed automatically extracted boundary landmarks to form a mask reconstruction fused with the decoder’s output, aiming to make the final segmentation less prone to low contrast and artifacts across the prostate’s full boundary. The encoder part of a modified U-Net extracted anatomical landmarks from the U-Net’s bottleneck when the prostate was present in the image. This approach decreased HD by an average of 2.04 mm.
Bi et al. (2022) [
23] aimed to improve the training phase of a traditional U-Net by combining boundary information using an active shape model. A boundary map was generated by processing the ground truth segmentation with morphological operations and key point initialization to eliminate boundary irregularities. This boundary map was used to evaluate the intermediate feature maps/segmentations as a deep supervision strategy. The DL architecture was trained with a loss function considering the discrepancy between the boundary map and the intermediate segmentation outcomes, increasing the DSC from 0.90 to 0.93.
Karimi et al. (2019) [
16] explored using an MRI-based statistical shape model (SSM) to improve the segmentation results of a U-Net ensemble trained on TRUS data. By matching an SSM containing MRI information of the expected prostate shape, HD was decreased by approximately 1 mm.
3.4. Implementation of Attention Mechanisms
Since US images of the prostate often contain artifacts, methods to focus attention on the most relevant regions are desired. Hard attention can be achieved at the image level by defining a Region of Interest (ROI), which directs the relevant feature space. Lei et al. (2021) [
29] inherently obtained the ROIs of the prostate using a probability map of the organ’s center of mass, which was then used to form a bounding box corresponding to the ROI. In contrast, PROST-Net, proposed by Palladino et al. (2022) [
33], used a Region Proposal Network to define the ROI. When evaluated, PROST-Net segmented 2D TRUS images with a DSC of 0.87, while Lei et al. [
29] achieved a DSC of 0.93.
Alternatively, soft attention can be achieved by introducing channel/spatial attention modules to the DL architecture. This allows the network to adaptively recalibrate the weights of each channel or region in the feature space. Wang et al. (2019) [
37] were pioneers in introducing soft attention for prostate segmentation on TRUS, integrating an attention module that leverages spatial information to select more discriminative features. Although the proposed DL architecture achieved a DSC of 0.90, the contribution of the attention module was not quantitatively evaluated, nor was the network tested on separate test data. Following this work, Vesal et al. (2022) [
36] retrained their architecture based on 802 training samples and achieved a DSC of 0.92, proving the robustness of their network on unseen data.
Similarly, Vesal et al. (2022) [
36] incorporated Coordinate Attention Blocks (CAM) to increase segmentation performance. CAM aims to perform channel attention while preserving positional information. Ultimately, this method presented similar DSC outcomes compared to Wang et al. (2019) [
37] when evaluated on the same test data.
In the proposed ADC-Net by Liu et al. (2023) [
31], a spatial-based attention module was introduced to enhance the network’s ability to learn useful features, improving the DSC and Jaccard index by 3% and 4%, respectively.
3.5. Feature Map Refinement
Feng et al. (2023) [
24] explored the enhancement of feature maps by employing a Multi-Stage U-Net. Their proposed architecture consists of three U-Nets, with the encoding paths replaced by a VGG16 model. The first network is trained on 2D TRUS data to obtain a preliminary segmentation. The encoded feature maps then serve as input for a second network, which produces a second segmentation. This step is repeated for a third network. The interim segmentations are fused by element-wise multiplication to generate the final segmentation outcome. Compared to a single U-Net with VGG16 integration, the DSC scores improved by 3.7%. Interestingly, model performance decreased when interim segmentation outcomes were not included in the final segmentation, indicating that different networks learn specific aspects of the prostate boundary.
In the Adaptive Detail Compensation Network (ADC-Net) proposed by Liu et al. (2023) [
31], the feature space is refined with a Detail Compensation Module (DCM). The primary aim was to estimate PV with a 3D U-Net. To reduce the complexity of 3D convolution, the authors decreased the feature channel dimensions. Although this reduces network complexity, it also results in the loss of detailed image information. The DCM enriches the remaining feature maps by embedding a pre-trained ResNet-34 model, which encodes detailed feature maps merged with the feature maps of the 3D U-Net. The effect of the DCM was evaluated in an ablation study, showing improvements of 3%, 4%, 3%, and 3% in DSC, JC, Precision, and Recall, respectively.
3.6. Consistency and Robustness of Deep-Learning Models
A common challenge in implementing DL architectures is achieving robust and consistent results across data from multiple institutions due to the diversity in US images. This diversity arises from variations in imaging manufacturers and patient characteristics. For example, abdominal fat can limit the US signal, resulting in poorer image resolution. Additionally, US acquisitions may vary according to the clinician’s technique. To improve generalizability, large amounts of heterogeneous data are usually required. However, many studies suffer from a scarcity of available data. Therefore, van Sloun et al. (2021) [
35] and Vesal et al. (2022) [
36] aimed to improve the generalization of segmentation models on new data using supervised Domain Adaptation (sDA). The proposed networks were pre-trained on one TRUS dataset in a supervised manner and then retrained on a small number of TRUS images from another dataset to improve performance on unseen data.
Van Sloun et al. (2021) [
35] implemented sDA in a traditional U-Net architecture fine-tuned using three different datasets. However, model performance did not significantly improve, likely due to the homogeneous data used for training and fine-tuning. Vesal et al. (2022) [
36] explored sDA using a multi-class loss function and incorporated a Knowledge Distillation loss to reduce the effect of weight changes in encoded features when updating the model with new data. The implementation of knowledge distillation was quantitatively compared on two other datasets, showing increased model performance on the transferred datasets, indicating the architecture performs well on multi-institutional data. Given that segmentation performance surpassed with a network solely trained on the transferred datasets, knowledge distillation combined with a DSC loss appears to be a promising strategy for handling the diversity in US acquisitions.
3.7. Quantitative Evaluation
Various evaluation metrics are used to assess the segmentation performance of DL architectures. Most commonly, the Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC) and Jaccard index (JC) are used to quantify the performance of the predicted segmentation area with the ground truth area. Additionally, Hausdorff Distance (HD) and Average Surface Distance (ASD) are used to quantify boundary similarity. Desirable segmentation results are associated with higher DSC and JC scores and lower HD and MSD. The described metrics are defined as the following
where
A and
B represent the ground truth segmentation area and the predicted segmentation area, respectively.
and
are the number of pixels in the intersection and union of
A and
B, respectively while
is the number of pixels in
A, and
is the number of elements in
B.
denotes the distance between points
a and
b, sup represents the supremum (or the least upper bound), and inf represents the infimum (or the greatest lower bound).
Table 2 provides a comprehensive comparison of various deep learning (DL) architectures used for prostate segmentation. It includes details about the type of data (2D or 3D), the number of patients involved, the number of images used for training and testing, and key performance metrics.
The DSC values in the table range from 0.87 to 0.95, indicating a generally high level of accuracy across different methods. Anas et al. [
20,
21] reported consistently high DSC scores of 0.93, while Feng et al. [
24] achieved the highest DSC of 0.95, suggesting superior segmentation accuracy with their method. These high DSC values reflect the effectiveness of the various DL architectures in accurately segmenting the prostate.
The JC, which measures the similarity between the predicted and ground truth segmentations, was not reported by several studies. For those that did report JC values, the scores range from 0.82 to 0.93. Palladino et al. (2022) [
33] and Peng et al.(2024) [
34] reported the highest JC score of 0.93, indicating strong agreement between their predicted and actual segmentations.
Average Surface Distance values were provided by fewer studies, but the reported values generally remained below 1 mm, indicating precise boundary predictions. Girum et al.(2020) [
27] reported the lowest ASD of 0.10 mm, reflecting highly accurate boundary delineation. However, Vesal et al.(2022) [
36] reported a higher ASD of 3.41 mm, suggesting a possible improvement in boundary accuracy.
Hausdorff Distance values varied widely, ranging from 1.12 mm to 8.37 mm. Beitone et al. (2022) [
22] reported a relatively high HD of 5.48 mm, while Wang et al.(2019) [
37] and Xu et al. (2022) [
39] reported even higher HD values of 8.37 mm and 5.89 mm, respectively. These results highlight the challenges in achieving precise boundary segmentation, specifically in the case of more complex or less clear imaging data.
Comparing 2D and 3D methods, most 2D methods demonstrated high DSC scores, with notable performance by Anas et al. [
20] and Lei et al. [
28]. 2D methods tend to be less computationally intensive compared to 3D methods, making them suitable for real-time clinical applications. However, 3D methods, such as those by Beitone et al. [
22] and Liu et al. (2022) [
31], generally reported high DSC scores but showed variation in HD values. The advantage of 3D methods lies in their ability to capture volumetric information, which can enhance the accuracy of PV estimation, although they require more computational resources.
The number of patients and images used for training and testing varied significantly across the studies. Larger datasets, such as the one used by Vesal et al. [
36] with 954 patients, contribute to better generalizability of the models. On the other hand, studies with fewer patients, like Anas et al. [
20] with only 18 patients, still achieved high DSC scores, suggesting that effective model design and training strategies can compensate for smaller datasets to some extent.
The comparison in
Table 2 highlights that while most DL architectures achieve high segmentation accuracy, there are variations in performance metrics influenced by dataset size, image quality, and specific architectural modifications.
Figure 5 demonstrates some examples of prostate segmentation using different models.
4. Discussion
Accurate determination of prostate volume is crucial for the effective management of prostate diseases, and ultrasound is commonly used due to its cost-effectiveness and rapid assessment capabilities. Prostate volume can be estimated through US image segmentation and using the Ellipsoid formula. However, clinicians often face challenges in accurately estimating PV due to imaging artifacts that obscure prostate boundaries. To address these issues, automatic methods have been developed to enhance PV determination and reduce patient examination time. This paper reviews recent advancements in applying deep learning (DL) to automatically segment prostate in US images.
Our review of DL architectures for prostate segmentation reveals that the presented methods show comparable performances. However, evaluating these architectures solely based on performance metrics is insufficient, as various factors influence the results. The design of the architecture and characteristics of the dataset, including homogeneity, US image quality, and quantity, play significant roles. Experts should consider dataset quality and its clinical applicability, particularly given the prevalence of low-quality US acquisitions in practice. Public datasets are needed for fair comparisons of DL architectures in prostate segmentation on US. Additionally, standard deviation values should be reported to provide transparency regarding the consistency of results.
In most studies, the performance of DL architectures is highlighted by presenting both the best and worst segmentation outcomes. Inaccurate predictions often occur in the apex and base regions due to poor visibility. Consequently, multi-directional image information has been explored, involving view-specific architectures that generate final segmentation outcomes using axial, coronal, and sagittal prostate information. Future research should examine the extent to which multi-directional image input contributes to segmentation performance, considering the increased training workload. For instance, when a 3D reconstruction is based on a certain number of 2D segmentations, it is essential to determine if adding more slices significantly improves model performance to balance input size and accuracy.
Post-processing strategies like Multi-Directional Contour Refinement (MDCR) should be carefully evaluated, as they depend on set distance parameters that may yield inconsistent results with diverse image data. While incorporating multi-directional information appears to enhance segmentation performance, it is unclear if Beitone et al.’s (2022) [
22] design can be applied in clinical practice, as the authors manually cropped each acquisition to a Region of Interest (ROI), potentially excluding image artifacts that typically degrade model performance.
Several studies have employed additional shape information to enhance segmentation outcomes, using statistical shape models and boundary reconstructions. These implementations generally improved segmentation results. When integrating attention mechanisms, soft attention strategies proposed by Wang et al. (2019) [
37], Feng et al. (2023) [
24], Vesal et al. (2022) [
36], and Liu et al. (2022) [
30] improved segmentation outcomes, with DSC scores above 0.92, likely due to the high number of included patients. A low number of patients often results in poor segmentation generalizability, as the network cannot capture the prostate’s diversity across different patients. This issue is evident in Palladino et al.’s (2022) [
33] performance. However, Anas et al. (2018) [
20] achieved a DSC score of 0.93 with an architecture trained on just 18 patients, contradicting this hypothesis.
Vesal et al. (2022) [
36] and van Sloun et al. (2021) [
35] emphasized the importance of patient heterogeneity in datasets. Supervised Domain Adaptation (sDA) has proven valuable for improving DL architectures’ generalizability when trained on a small number of patients. Inaccurate segmentations due to shadow artifacts may be mitigated with pre-processing strategies proposed by Xu et al. (2020) [
39], particularly for TAUS images, where shadow artifacts frequently disrupt prostate boundaries. Conversely, pre-processing training data with 3D Mean, Median, and Gaussian filters appears less effective for improving segmentation outcomes.
It is recommended to conduct ablation studies when additional models or ensemble networks are implemented. For instance, Lei et al. (2021) [
28] designed a DL architecture with multiple systems to enhance segmentation outcomes, but the contribution of each implementation was not explored. Other experiments clearly report which components of proposed DL architectures improve segmentation outcomes. Understanding how added complexity contributes to model performance is essential, especially since efficient DL models are usually required for real-time application.
Further exploration of DL for prostate segmentation is warranted, as it allows for volume estimation based on the entire prostate region, which is beneficial for patients suspected of prostate cancer due to the variability in prostate shape across individuals. Additionally, prostate segmentation architectures can be utilized in image registration.
In this review, only one study by Albayrak et al. (2022) focused on an automated PV measurement using TAUS images[
43]. While prostate segmentation methods are typically proposed when the PV is estimated on TRUS, the authors automated the workflow of the Ellipsoid formula to obtain the PV by establishing a classification method that predicts the prostate’s transverse, anterior-posterior, and longitudinal diameter on TAUS images. In their work, two DL networks were trained separately for the axial and sagittal imaging planes. One network focused on the 2D axial TAUS images to predict outer landmarks related to the transverse and anterior-posterior diameter, and another network was trained on sagittal TAUS images to identify the landmarks of the longitudinal diameter. The plane-specific networks comprised an ensemble of four ResNet-18 CNNs individually trained on image patches containing the prostate in four image scales. Then, the predicted landmarks served as input to utilize the Ellipsoid formula to infer the PV.
The proposed method was validated by comparing the Mean Absolute Value Difference (MAVD) between the predicted PV and reference PV measurements manually estimated on TAUS. An average MAVD value of 4.95 ml was obtained, which was smaller than the average inter-expert MAVD value of 5.09 ml.
Even though the presented results appear rewarding, there are considerable aspects of the system that warrant discussion. First, the Ellipsoid formula can only be utilized on the mid-axial and mid-sagittal images, where the cross-section of the prostate is at maximum. Currently, the networks are trained on TAUS images satisfying this criterion, and user interaction and expertise are still required. Hence, the identification of the most suitable prostate slice in the acquisition is necessary. Methods proposed by Beitone et al. (2022) [
22] and Palladino et al. [
33] may be modified to classify the prostate region by its cross-section before the diameters are computed.
Secondly, the system is evaluated based on the Mean Absolute Value Difference (MAVD) of the entire PV, while the outcome relies on the prediction of six landmarks. It remains unclear whether the accuracy of the predicted landmarks contributes equally to the predicted MAVD. In future research, it is recommended to evaluate all components contributing to the final prediction to understand which factors possibly result in inaccuracies.
The employment of TAUS for PV estimation is promising, offering greater patient comfort and reducing clinical practitioners’ workload. Currently, prostate segmentation techniques have only been studied on CT, TRUS, and MRI. Yet, prostate segmentation on TAUS is worth exploring, as a delineation of the prostate can be used to extract the prostate dimensions to enable automatic PV calculations.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.K., T.N., M.F. and B.D.; methodology, L.K., T.N.; validation, L.K., T.N., M.F., B.D.; formal analysis, L.K., T.N., M.F., B.D.; investigation, L.K., T.N., M.F., B.D.; writing—original draft preparation, L.K.; writing—review and editing, T.N., M.F., B.D.; visualization, L.K.; supervision, T.N., M.F., B.D.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
Research at the Netherlands Cancer Institute is supported by institutional grants of the Dutch Cancer Society and of the Dutch Ministry of Health, Welfare and Sport.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Wei, J.T.; Barocas, D.; Carlsson, S.; Coakley, F.; Eggener, S.; Etzioni, R.; Fine, S.W.; Han, M.; Kim, S.K.; Kirkby, E.; Konety, B.R.; Miner, M.; Moses, K.; Nissenberg, M.G.; Pinto, P.A.; Salami, S.S.; Souter, L.; Thompson, I.M.; Lin, D.W. Early Detection of Prostate Cancer: AUA/SUO Guideline Part I: Prostate Cancer Screening. Journal of Urology 2023, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, K.; Oki, R.; Sekine, Y.; Arai, S.; Miyazawa, Y.; Shibata, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Kurosawa, I. Screening for prostate cancer: History, evidence, controversies and future perspectives toward individualized screening, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Tewari, A.; Indudhara, R.; Shinohara, K.; Schalow, E.; Woods, M.; Lee, R.; Anderson, C.; Narayan, P. Comparison of transrectal ultrasound prostatic volume estimation with magnetic resonance imaging volume estimation and surgical specimen weight in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Journal of Clinical Ultrasound 1996, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jue, J.S.; Barboza, M.P.; Prakash, N.S.; Venkatramani, V.; Sinha, V.R.; Pavan, N.; Nahar, B.; Kanabur, P.; Ahdoot, M.; Dong, Y.; Satyanarayana, R.; Parekh, D.J.; Punnen, S. Re-examining Prostate-specific Antigen (PSA) Density: Defining the Optimal PSA Range and Patients for Using PSA Density to Predict Prostate Cancer Using Extended Template Biopsy. Urology 2017, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, J.M.; Swanson, D.A.; Pugh, T.J.; Zhang, M.; Bruno, T.L.; Kudchadker, R.J.; Frank, S.J. Magnetic resonance imaging-based treatment planning for prostate brachytherapy. Brachytherapy 2013, 12, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickel, J.C. NEW PERSPECTIVES ON BPH Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Does Prostate Size Matter? REVIEWS IN UROLOGY 2003, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Hricak, H.; Choyke, P.L.; Eberhardt, S.C.; Leibel, S.A.; Scardino, P.T. Imaging prostate cancer: a multidisciplinary perspective. Radiology 2007, 243, 28–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, S.Y.; Choi, M.H.; Lee, Y.J.; Grimm, R.; von Busch, H.; Han, D.; Son, Y.; Lou, B.; Kamen, A. Prostate gland volume estimation: anteroposterior diameters measured on axial versus sagittal ultrasonography and magnetic resonance images. Ultrasonography 2023, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pate, W.R.; Garg, N.; Wang, L.B.; Wason, S.E.; Barbosa, P.V. Comparison of Transabdominal and Transrectal Ultrasound for Sizing of the Prostate. Urology 2020, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Chung, B.H. Transrectal ultrasound versus magnetic resonance imaging in the estimation of prostate volume as compared with radical prostatectomy specimens. Urologia Internationalis 2007, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghose, S.; Oliver, A.; Martí, R.; Lladó, X.; Vilanova, J.C.; Freixenet, J.; Mitra, J.; Sidibé, D.; Meriaudeau, F. A survey of prostate segmentation methodologies in ultrasound, magnetic resonance and computed tomography images. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine 2012, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betrouni, N.; Vermandel, M.; Pasquier, D.; Maouche, S.; Rousseau, J. Segmentation of abdominal ultrasound images of the prostate using a priori information and an adapted noise filter. Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics 2005, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Guo, Y.; Bi, Z.; Huang, Z.; Yu, G.; Wang, J. Segmentation of prostate ultrasound images: the state of the art and the future directions of segmentation algorithms. Artificial Intelligence Review 2023, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, J.A.; Boukerroui, D. Ultrasound image segmentation: a survey. IEEE Transactions on medical imaging 2006, 25, 987–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litjens, G.; Kooi, T.; Bejnordi, B.E.; Setio, A.A.A.; Ciompi, F.; Ghafoorian, M.; Van Der Laak, J.A.; Van Ginneken, B.; Sánchez, C.I. A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Medical image analysis 2017, 42, 60–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi, D.; Zeng, Q.; Mathur, P.; Avinash, A.; Mahdavi, S.; Spadinger, I.; Abolmaesumi, P.; Salcudean, S.E. Accurate and robust deep learning-based segmentation of the prostate clinical target volume in ultrasound images. Medical Image Analysis 2019, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- “PubMed”, PubMed. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/.
- “IEEE Xplore”. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/Xplore/home.jsp.
- “Scopus Preview - Scopus - Welcome to Scopus”. https://www.scopus.com/home.uri.
- Anas, E.M.A.; Mousavi, P.; Abolmaesumi, P. A deep learning approach for real time prostate segmentation in freehand ultrasound guided biopsy. Medical Image Analysis 2018, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anas, E.M.A.; Nouranian, S.; Mahdavi, S.S.; Spadinger, I.; Morris, W.J.; Salcudean, S.E.; Mousavi, P.; Abolmaesumi, P. Clinical target-volume delineation in prostate brachytherapy using residual neural networks. 2017, Vol. 10435 LNCS. [CrossRef]
- Beitone, C.; Troccaz, J. Multi-eXpert fusion: An ensemble learning framework to segment 3D TRUS prostate images. Medical Physics 2022, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, H.; Sun, J.; Jiang, Y.; Ni, X.; Shu, H. Structure boundary-preserving U-Net for prostate ultrasound image segmentation. Frontiers in Oncology 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Atabansi, C.C.; Nie, J.; Liu, H.; Zhou, H.; Zhao, H.; Hong, R.; Li, F.; Zhou, X. Multi-stage fully convolutional network for precise prostate segmentation in ultrasound images. Biocybernetics and Biomedical Engineering 2023, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghavami, N.; Hu, Y.; Bonmati, E.; Rodell, R.; Gibson, E.; Moore, C.; Barratt, D. Integration of spatial information in convolutional neural networks for automatic segmentation of intraoperative transrectal ultrasound images. Journal of Medical Imaging 2018, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghavami, N.; Hu, Y.; Bonmati, E.; Rodell, R.; Gibson, E.D.; Moore, C.M.; Barratt, D.C. Automatic slice segmentation of intraoperative transrectal ultrasound images using convolutional neural networks. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Girum, K.B.; Lalande, A.; Hussain, R.; Créhange, G. A deep learning method for real-time intraoperative US image segmentation in prostate brachytherapy. International Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery 2020, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Y.; Wang, T.; Roper, J.; Jani, A.B.; Patel, S.A.; Curran, W.J.; Patel, P.; Liu, T.; Yang, X. Male pelvic multi-organ segmentation on transrectal ultrasound using anchor-free mask CNN. Medical Physics 2021, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Y.; Tian, S.; He, X.; Wang, T.; Wang, B.; Patel, P.; Jani, A.B.; Mao, H.; Curran, W.J.; Liu, T.; Yang, X. Ultrasound prostate segmentation based on multidirectional deeply supervised V-Net. Medical Physics 2019, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Wang, L.; Du, Y.; Cong, M.; Li, Y. 3-D Prostate MR and TRUS Images Detection and Segmentation for Puncture Biopsy. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement 2022, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wu, K.; Jiang, L. ADC-Net: adaptive detail compensation network for prostate segmentation in 3D transrectal ultrasound images. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Orlando, N.; Gillies, D.J.; Gyacskov, I.; Romagnoli, C.; D’Souza, D.; Fenster, A. Automatic prostate segmentation using deep learning on clinically diverse 3D transrectal ultrasound images. Medical Physics 2020, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palladino, L.; Maris, B.; Antonelli, A.; Fiorini, P. PROST-Net: A Deep Learning Approach to Support Real-Time Fusion in Prostate Biopsy. IEEE Transactions on Medical Robotics and Bionics 2022, 4, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; Wang, C.; Tang, C.; Gu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Li, Q.; Cai, J. A multi-center study of ultrasound images using a fully automated segmentation architecture. Pattern Recognition 2024, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Sloun, R.J.; Wildeboer, R.R.; Mannaerts, C.K.; Postema, A.W.; Gayet, M.; Beerlage, H.P.; Salomon, G.; Wijkstra, H.; Mischi, M. Deep Learning for Real-time, Automatic, and Scanner-adapted Prostate (Zone) Segmentation of Transrectal Ultrasound, for Example, Magnetic Resonance Imaging–transrectal Ultrasound Fusion Prostate Biopsy. European Urology Focus 2021, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesal, S.; Gayo, I.; Bhattacharya, I.; Natarajan, S.; Marks, L.S.; Barratt, D.C.; Fan, R.E.; Hu, Y.; Sonn, G.A.; Rusu, M. Domain generalization for prostate segmentation in transrectal ultrasound images: A multi-center study. Medical Image Analysis 2022, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ni, D.; Dou, H.; Hu, X.; Zhu, L.; Yang, X.; Xu, M.; Qin, J.; Heng, P.A.; Wang, T. Deep Attentive Features for Prostate Segmentation in 3D Transrectal Ultrasound. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging 2019, 38, 2768–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Chen, Y.; Huang, B.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, Y. Contour-based medical image fusion for biopsy. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Sanford, T.; Turkbey, B.; Xu, S.; Wood, B.J.; Yan, P. Shadow-Consistent Semi-Supervised Learning for Prostate Ultrasound Segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging 2022, 41, 1331–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, T.; Zhao, J.; Gu, Y.; Wang, C.; Wu, Y.; Cheng, X.; Cai, J. H-ProMed: Ultrasound image segmentation based on the evolutionary neural network and an improved principal curve. Pattern Recognition 2022, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Xu, S.; Turkbey, B.; Kruecker, J. Adaptively learning local shape statistics for prostate segmentation in ultrasound. IEEE transactions on biomedical engineering 2010, 58, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. 2015, Vol. 9351. [CrossRef]
- Albayrak, N.B.; Akgul, Y.S. Estimation of the Prostate Volume from Abdominal Ultrasound Images by Image-Patch Voting. Applied Sciences 2022, 12, 1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).