1.0. Introduction
Freshwater lakes are vital for human sustenance, supporting various economic activities and providing recreational opportunities. However, the presence of cyanobacteria (a.k.a blue-green algae or BGA) is increasingly threatening water quality and public health due to toxins they produce. BGA blooms not only impact drinking water safety but also disrupt the ecosystems. Understanding the factors driving the proliferation of BGAs is crucial for effective freshwater resource management.
The challenges of BGA microorganisms are their potential to pose risks to public health by causing skin irritations, gastrointestinal problems, and even acute liver and neurological disorders due to their toxins. Domestic animals such as cattle, horses, sheep, dogs, and cats are susceptible to cyanobacterial toxins if they drink contaminated water or ingest cyanobacteria while swimming or playing near affected water bodies. Livestock deaths due to cyanobacterial poisoning have been reported worldwide, particularly in areas where Harmful Algal Blooms (HABs) are prevalent. In the US alone, in 2021, a total of 2715 animal illnesses which include 48 domestic pets, 25 Livestock, and 2642 wildlife where 2000 bats died from harmful algal bloom events [
1]. Aquatic species are also affected by cyanobacterial toxicity which can lead to a reduction in aquatic ecosystem biodiversity. Further, certain cyanobacteria species produce compounds that impart unpleasant tastes and odors to water, negatively impacting perceptions of water quality and potentially requiring additional treatment processes including microcystins and saxitoxins. BGA blooms can disrupt nature-based tourism and undermine both the intrinsic and commercial values associated with aquatic environments, with shallow lakes being highly susceptible to human impacts, with cyanobacteria frequently becoming the predominant species in the phytoplankton community of eutrophic shallow lakes, particularly in warmer climates [
2,
3,
4].
BGA, also known as cyanobacteria, thrive in freshwater, saltwater, and brackish environments. They can multiply rapidly in nutrient-rich lakes, especially in warm, calm conditions, forming blooms that turn the water green and may create surface scum. While most BGA species are not harmful, some produce toxins like microcystin, which can be released when cells die or rupture. Exposure to these toxins, typically through contaminated water, can pose risks to human health, leading to HABs. Additionally, some BGA toxins can accumulate in fish, advising caution in consuming fish from areas affected by major blooms.
The increasing prevalence of BGA blooms, linked to excessive eutrophication and global warming, poses a significant challenge in freshwater management worldwide [
5,
6]. Algal blooms disrupt ecological balance, deplete oxygen levels, and endanger aquatic life. Moreover, BGA blooms complicate water treatment processes in drinking water reservoirs, leading to increased costs. Hence, the monitoring of BGA dynamics is essential to safeguard human health, protect the environment, and efficiently manage water resources amid changing environmental conditions [
7].
Nutrients serve as essential factors for the formation of cyanobacteria blooms, with nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) recognized as key drivers influencing the occurrence and longevity of cyanobacteria in freshwater ecosystems [
8,
9]. As a result, the monitoring of nutrient levels and temperatures are crucial for understanding and predicting algal growth, and especially cyanobacterial blooms, for reasons including: a) Nutrient availability as nutrients such as N and P, are primary drivers if N and/or P are in limited quantities. High nutrient levels will trigger rapid cyanobacterial proliferation, leading to HABs which facilitate early detection of eutrophication and opportunities for implementation of management strategies to mitigate its effects; b) Cyanobacteria may produce toxins such as microcystins and, most importantly, nutrient monitoring helps predict toxin production by identifying conditions conducive to cyanobacterial growth and bloom formation; c)Temperature plays a critical role in algal growth rates and bloom dynamics. Warmer temperatures accelerate algal growth providing insights into bloom events; and d) Monitoring nutrient levels and temperature enables authorities to implement timely interventions to diminish or mitigate HABs (thereby protecting public health), provides insights into the complex dynamics of algal growth, including cyanobacterial blooms, and for implementing effective management strategies to safeguard water resources and human well-being.
Predicting the timing, severity, duration, and health implications of these blooms is complex [
10,
11] In Canada, a seasonal Maximum Acceptable Concentration (MAC) of 1.5 µg/L has been established for total microcystins in drinking water [
12]. Toxins produced by freshwater cyanobacteria pose health risks, with Health Canada recommending a maximum concentration of 10 µg/L for total microcystins in waters used for primary contact activities [
10].
Canada, with more than 900,000 lakes [
13], holds the global record for lake abundance in a country. These lakes fulfill essential needs including drinking water, crop irrigation, fishing, swimming, and boating. With more than 246 urban lakes in Canada already experiencing algal blooms [
14] plus many more potentially affected due to anthropogenic inputs and climate change, the full impact of climate change on cyanobacteria growth remains uncertain. Climate change, intensified farming, and urban and industrial expansion will lead to pollutants entering aquatic habitats, further endangering lake health and the crucial ecosystem services they provide [
13]. Nieto et al. [
15] revealed a rising trend in confirmed cyanobacteria-dominated algal blooms, documenting various waterbodies in Ontario from 1994 to 2019. Further, in research described herein, nutrient levels and temperature as monitored in Fairy Lake (a shallow urban lake) are shown to be crucial for understanding and predicting algal growth. As described in the subsections following, the monitored results are described along with a microbial source tracking procedure to assess the presence of human sewage contamination, as well as the entry of human fecal contamination into the Lake from tributaries and storm water outfalls, providing important insights.
(ii) Methodology for Sampling and Consideration of Nutrient Pathways in Lakes
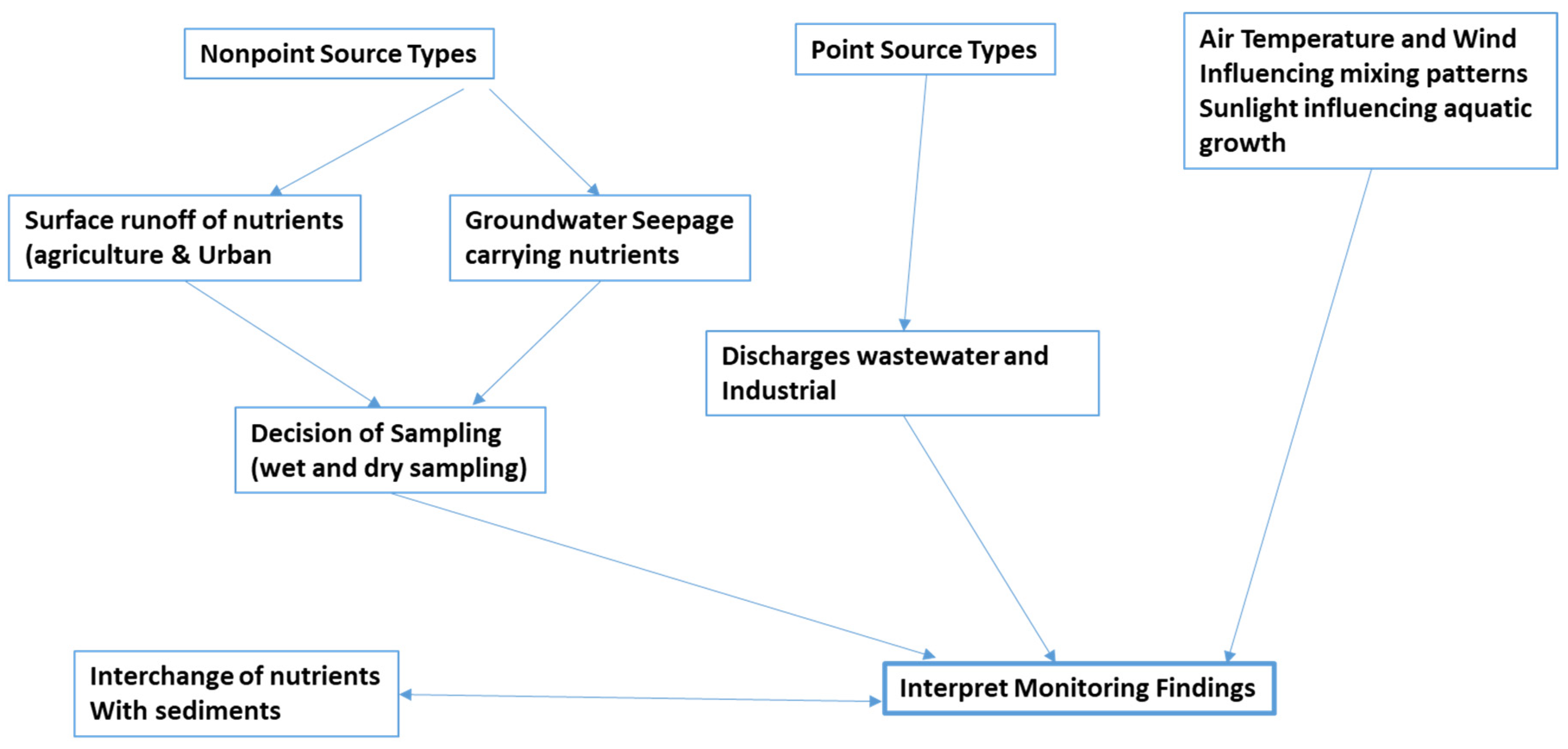
Sampling methodology plays a crucial role in accurately assessing nutrient dynamics within a lake ecosystem. This section outlines a comprehensive approach for sampling, considering both dry and wet sampling techniques, by addressing the pathways through which nutrients are transported within the lake. Sampling methodology encompasses the sampling techniques, consideration of nutrient pathways, source input and influencing processes, and internal processes within a lake. A systematic approach to sampling, considering both dry and wet sampling techniques, coupled with an understanding of nutrient pathways and influencing processes, is essential for assessing and managing cyanobacterial blooms in lakes. By integrating field observations, laboratory analyses, and modeling studies, researchers can gain valuable insights into nutrient dynamics and cyanobacterial ecology, informing evidence-based decision-making for lake conservation and restoration efforts.
Section III: Dynamics of Nutrient Levels and Lake Behavior
Understanding the intricate balance of nutrient levels and the behavior of a lake over time is crucial in determining the susceptibility of cyanobacteria growth due to: Nutrient Dynamics, Lake Behavior and Stratification and Processes of Entry into the Lake. Overall, grasping the intricacies of nutrient dynamics, lake behavior, and the processes driving nutrient entry are imperative for comprehensively understanding cyanobacterial dynamics. An understanding of this not only elucidates the mechanisms governing cyanobacterial growth but also informs the development of effective sampling strategies necessary for monitoring and managing waterbodies susceptible to harmful algal blooms as illustrated in
Figure 1, the sequence that will be describing incrementally in the following section of the paper.
3.0. Results
The results are divided into two categories, (i) the monitoring points feeding the water to the Lake (WQ1 WQ2, WQ4, WQ7, WQ8 and WQ10) and (ii) the monitoring points which are in the Lake and at the outlet of Lake (WQ3, WQ5, WQ9, WQ11 and WQ6). Twenty-one (21) monitoring events occurred. The following analyses includes those events, with one-half the detection limit when non-detect.
Detailed monitoring results are presented in supplementary
Tables S1 and S2. Two sets of graphs are presented below for all the monitoring locaction (feeding the Lake, in the Lake and at Lake outlet). The first six graphs show the concentartions for both wet and dry events (orange for wet conditions and green for dry conditions) along with the precipiation to characteruze rain event or dry event impact. They are presented in the
Supplemenry data S3 and box diagrams to view the distribution and magniture of concenrarion.
3.1. Discussion of Each Monitoring Location Parameter-Wise
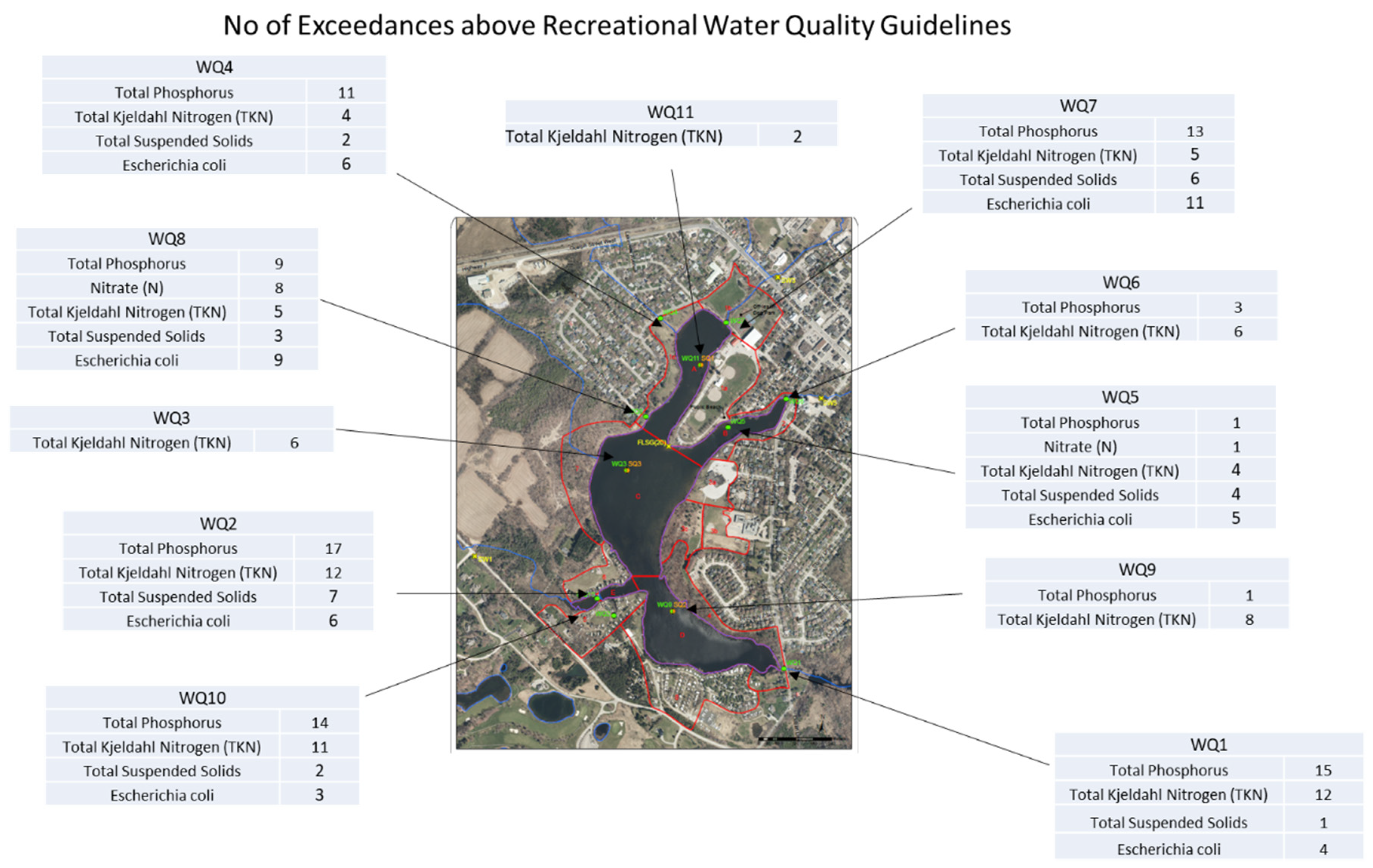
The exceedances of various recreational water quality guidelines are shown in
Figure 3 below and briefly described in the preceding section.
3.1.1. Total Phosphorus
Total phosphorus (P) is recognized as one of the key drivers influencing the occurrence and longevity of cyanobacteria in freshwater ecosystem. The Recreational Water Quality guideline for total phosphors is 0.02 mg/L [
20].
Monitoring Points Feeding Fairy Lake
WQ1 which feeds the southern basin of Fairy Lake, the TP exceedances were observed in sixteen samples, the maximum being 0.19 mg/L in a wet sample. It was observed in five dry samples and in ten wet samples. WQ2, a storm water outlet at the trailer park bring water to Fairy Lake, the TP exceedances were observed in 17 samples, the maximum being 0.22 mg/L in a wet sample. TP was also observed six dry and ten wet samples. WQ4, which is a storm water outlet, had eight (8) exceedances of the TP, the maximum being 0.26 mg/L. WQ7, which is Black Creek inlet, the total phosphorus exceedances were observed in fourteen samples, the maximum being 0.14 mg/L in a wet sample. TP was observed in four dry and ten wet samples. WQ8, another storm water outlet, had eight exceedances of the TP (one dry and seven wet), the maximum being 0.19 mg/L in a wet sample on 2/17/2022. WQ10, which is the west inlet of Fairy Lake, the TP exceedances were observed in 14 samples, the maximum being 0.1 mg/L in a dry sample. TP was observed in five dry samples and in nine wet samples. Overall, there were 81 exceedances of TP from all monitoring locations in all the events.
Based on the above results, it is imperative that sources of the total phosphorus have to be identified and management practices have to be initiated to reduce the TP from the Fairy Lake catchment.
Monitoring Locations in the Lake
In WQ3 and WQ11 there were no exceedances of TP of water quality guidelines. WQ5, which is near the old beach, had only one wet sample above the WQ guideline being 0.026 mg/L. WQ6, which is the outlet of Fairy Lake, had three exceedances of the TP, the maximum being 0.11 mg/L in a wet sample on 3/17/2023. WQ9 which is the south basin of the lake had only one exceedance of the TP in a dry sample being 0.023 mg/L on 1/24/2022.
3.1.2. TSS
Elevated TSS levels can degrade aquatic habitat quality by covering substrates, reducing habitat complexity, and altering the composition of benthic communities. Fine sediments can clog interstitial spaces between substrate particles, affecting the availability of food and shelter for benthic organisms. TSS can serve as carriers for nutrients, organic matter, and contaminants in aquatic environments. Nutrients adsorbed to suspended particles can be transported within the water column and deposited in different areas of the lake, potentially contributing to nutrient enrichment and eutrophication processes.
Monitoring Points Feeding the Fairy Lake
The Recreational Water Quality (RWQ) guideline for TSS is 25.0 mg/L [
20]. In WQ1, only one sample exceeded the RWQ guideline for TSS of 25 mg/L. It was in wet sample at a concentration of 370 mg/L. In WQ2, nine samples (four dry and five wet) exceeded the RWQ guideline for TSS being 250 mg/L in a wet sample. In WQ4, four samples exceeded the RWQ guideline for TSS, the maximum being 69 mg/L in a dry sample. WQ7, seven samples (five wet and two dry) have exceedances of WQ Guideline of TSS, the maximum being, 84 mg/L. WQ8. Only three samples (one dry, two wet) have exceedances of WQ Guideline of TSS, the maximum being, 160 mg/L. WQ10, only two samples (one dry, one wet) have exceedances of WQ Guideline of TSS, the maximum being, 130 mg/L. Among the monitoring points feeding Fairy Lake, there were 30 exceedances of TSS from all monitoring locations in all the events with maximum levels reaching 160 mg/L in WQ10. As high levels of TSS may affect the clearness of water in the Lake and may deposit nutrients in the bed of Lake. Overall, there were 30 exceedances of TSS from all monitoring locations in all the events.
Based on the above results, it is imperative that management practices be initiated to reduce the TSS from the Fairy Lake catchment specially for WQ-7, WQ4 and WQ10 catchments.
Monitoring Locations in the Lake
In WQ3, WQ6, WQ9, and WQ11, there were no exceedances of TSS water quality guidelines. WQ5, four samples (two wet and two dry) have exceedances of WQ Guideline of TSS, the maximum being, 160 mg/L,
3.1.3. E. coli
Exposure to recreational water contaminated with E. coli can increase the risk of gastrointestinal and skin infections. Swallowing or contact with water containing high levels of E. coli can lead to illnesses such as diarrhea, vomiting, and skin rashes. E. coli itself doesn't directly interact with blue-green algae, but their relationship can be indirectly linked through environmental factors. One indirect relationship between E. coli and blue-green algae lies in nutrient pollution. E. coli can be used as an indicator of fecal contamination in water bodies. When there's high fecal contamination, it often means there's also an abundance of nutrients like P and N, which can fuel the growth of cyanobacteria. Therefore, the presence of E. coli in water bodies can be a warning sign of potential HABs caused by cyanobacteria. The RWQ guideline for single maximum concentration for E.coli is ≤ 400 E. coli /100 m [
21].
Monitoring Points Feeding Fairy Lake
In WQ1, four samples exceeded the RWQ guideline for E.coli. All were in wet samples with a maximum of 3,500 E. coli /100 mL. In WQ2, eight samples (two dry and six wet) exceeded the RWQ guideline for E.coli, the maximum being 43,000 E. coli /100 mL on 6/23/2022. WQ4 has six (6) exceedances of RWQ guideline, two in dry samples and four in wet samples with a maximum of 9,700 E. coli /100 mL. WQ7 has eleven (11) exceedances of RWQ guideline, three in dry samples and eight in wet samples with a maximum of 7,800 E. coli /100 mL. WQ8 has nine (9) exceedances of RWQ guideline, two in dry samples and seven in wet samples with a maximum of 8,600 E. coli /100 mL. In WQ10, three wet samples exceeded the RWQ guideline for E.coli, the maximum being 23,000 E. coli /100 mL.
Monitoring Locations in the Lake
In WQ3, WQ6, WQ9, and WQ11, there were no exceedances of E.coli water quality guidelines. In WQ5, three dry samples and two wet samples exceeded the Recreational Water Quality guideline for E.coli, the maximum being 3,000 E. coli /100 mL.
Overall, there were 44 exceedances of E.coli from all monitoring locations in all the events. Based on the above results, it is imperative that sources of the E.coli have to be identified and management practices have to be initiated to reduce the E.coli from the Fairy Lake catchment.
3.1.4. Nitrates
Nitrate (NO3-) is a vital nutrient for the growth of BGA. Cyanobacteria, like other photosynthetic organisms, require nutrients to thrive, and nitrate is essential. Nitrate is involved in the process of photosynthesis, which is how cyanobacteria generate energy. Cyanobacteria require a steady supply of nutrients, including nitrate, for cell division and reproduction. Nitrate availability influences the rate of cell division and overall biomass production in cyanobacterial populations. Managing nitrate levels in water bodies is essential to prevent the proliferation of cyanobacterial blooms while still providing enough nutrients to support healthy aquatic ecosystems.
For Nitrate, the Canadian Water Quality Guideline (CWQG) is 3.0 mg/L [
20]. Only in WQ8, where exceeded eight times (six in wet and two in dry samples), the maximum being 4.86 mg/L on 11/23/2023. One exceedance was in 2022 and all other in 2023. The remainder of the monitoring locations outside or inside the lake have no exceedances.
3.1.5. Total Kjeldahl Nitrogen (TKN)
TKN includes both organic nitrogen and ammonia, which are important sources of nitrogen for cyanobacteria. When levels of TKN are elevated, it can lead to an increase in nitrogen availability for cyanobacteria. This excess nitrogen can fuel the growth of cyanobacterial blooms, leading to HABs. Therefore, the relationship between TKN and cyanobacteria is that elevated TKN levels can contribute to the proliferation of cyanobacterial blooms. No Ontario guideline for TKN is presently available; however, waters not influenced by excessive organic inputs typically range from 0.100 to 0.500 mg/l, Environment Canada [
21], however, Rideau Valley Conservation Authority’s [
22] uses a guideline of 0.500 mg/l to assess TKN within surface waters. In this analysis a TKN value of 0.500 mg/L is used.
Monitoring Points Feeding the Lake
Among the monitoring locations which are on streams or outfalls bringing water to the lake, WQ1 had twelve (12) exceedances of TKN, four in dry events and eight in wet events. In WQ2, there are twelve (12) exceedances of TKN four in dry events and eight in wet events. The maximum concentration of TKN was 2.3 mg/L in a wet event. In WQ4, there are four exceedances of TKN one in dry events and three in wet events. In WQ7, there are five exceedances of TKN one in dry events and four in wet events. The maximum concentration of TKN was 1.17 mg/L in a wet event. In WQ8, there are five (5) exceedances of TKN two in dry events and three in wet events. In WQ10, there are 11 exceedances of TKN three in dry events and eight in wet events. Across various water quality monitoring locations feeding the lake, there were a total of 54 TKN exceedances, with varying distributions between dry and wet events. The highest TKN concentration recorded was 2.3 mg/L in WQ2 during a wet event, while the lowest was 0.83 mg/L in WQ4, also during a wet event.
Monitoring Points in the Lake
At the Lake monitoring locations, several water quality assessments revealed TKN exceedances. In WQ3, there were six exceedances, with four during dry events and two during wet events, peaking at 1.13 mg/L in a wet event. WQ5 recorded four exceedances evenly distributed between dry and wet events, reaching a maximum of 0.62 mg/L in a wet event. Similarly, WQ6 documented six exceedances, with two during dry events and four during wet events, reaching a peak of 0.816 mg/L in a wet event. WQ9 observed eight exceedances, three during dry events and five during wet events, with a maximum of 1.00 mg/L in a dry event. Lastly, WQ11 had two exceedances, all during dry events, reaching a maximum concentration of 0.7 mg/L.
Overall, there has been seventy-five (75) exceedances of TKN above guidelines whereas 49 are from the monitoring points feeding the lake and 26 from monitoring points in the lake. WQ-1 flow is coming through the wetland and that may be causing elevated levels of TKN. WQ-2, WQ-4 and WQ-8 are storm water outlets. Based on the above results, it is imperative that sources of the TKN be identified and management practices initiated to reduce the TKN from the Fairy Lake catchment.
3.2. Statistical Results
All the monitoring results are grouped as a) all wet to the lake, b) all wet
in the lake, c) all dry to the lake and d) all dry in the lake to look for patterns. Results of range and means are presented in
Table 3 and
Table 4.
3.4. Cyanobacteria and Microcystin
Health Canada recommends a maximum microcystin concentration of 10 μg/L for recreational waters to protect against ingestion. Halton Region Public Health visually monitors for BGA at the public beach from late June/early July onward as part of routine beach monitoring. If BGA is seen, staff refrain from entering the water for safety. Daily visual monitoring continues until BGA is no longer observed, then water samples are collected and analyzed for microcystin. Since 2019, HABs have been observed near the boathouse and public beach, prompting the posting of warning signs to alert the public. Blue Green Algae test results are shown in
Table 5.
As seen in
Table 5, all the Microcystin results were below the Health Canada recommendations of a maximum microcystin concentration of 10 μg/L for recreational waters to protect against ingestion.
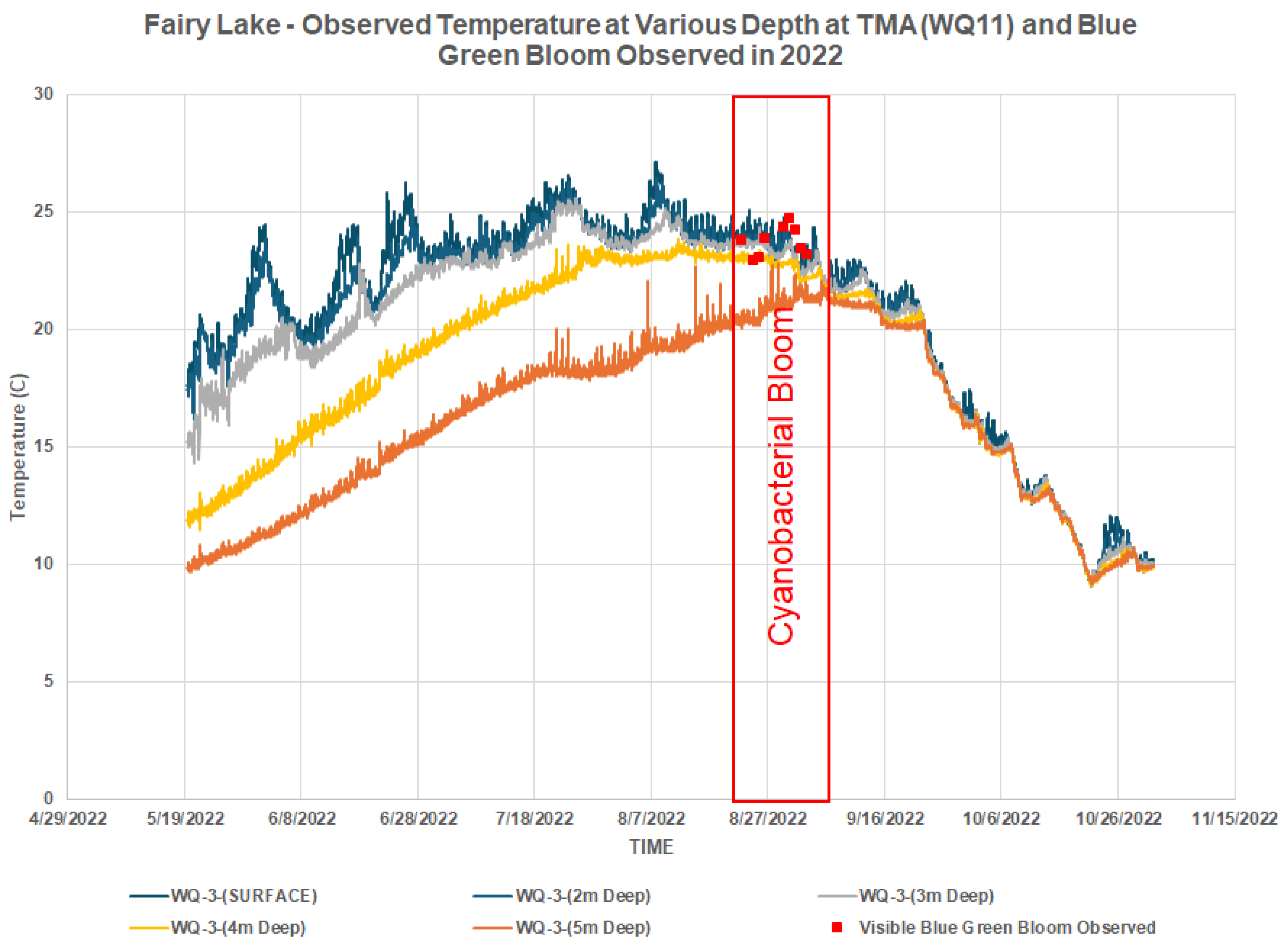
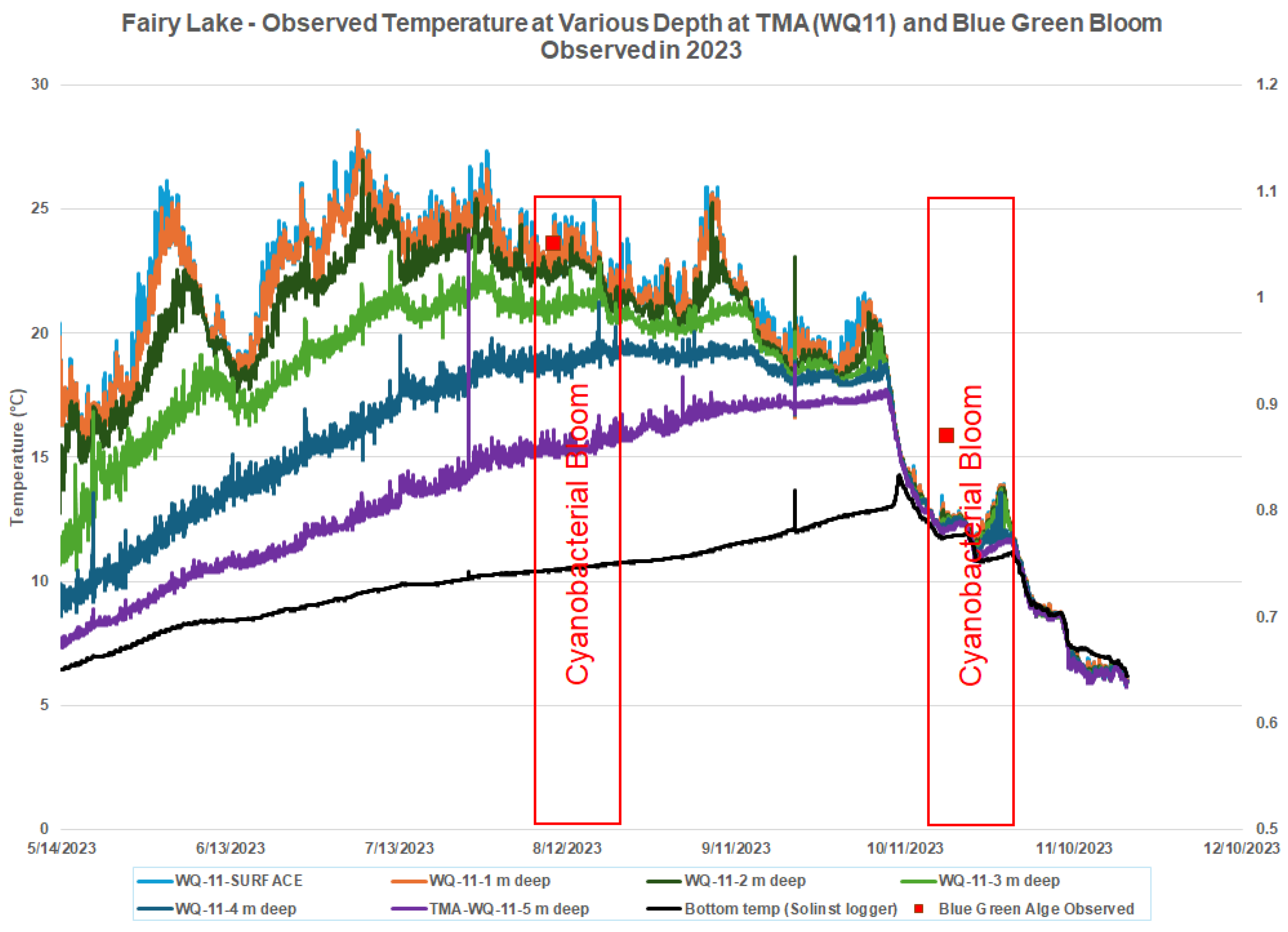
3.5. Temperature
A primary key to estimate the growth of Cyanobacterial is the water temperature. The optimal temperature ranges for Cyanobacterial growth and the occurrence of blooms are typically between 20°C to 30°C (68°F to 86°F) [23, 24, 25, 26]. A minimal optimal temperature of 20°C for Cyanobacterial growth and the occurrence of blooms is selected for this analysis which is based on the review of literature [
24,
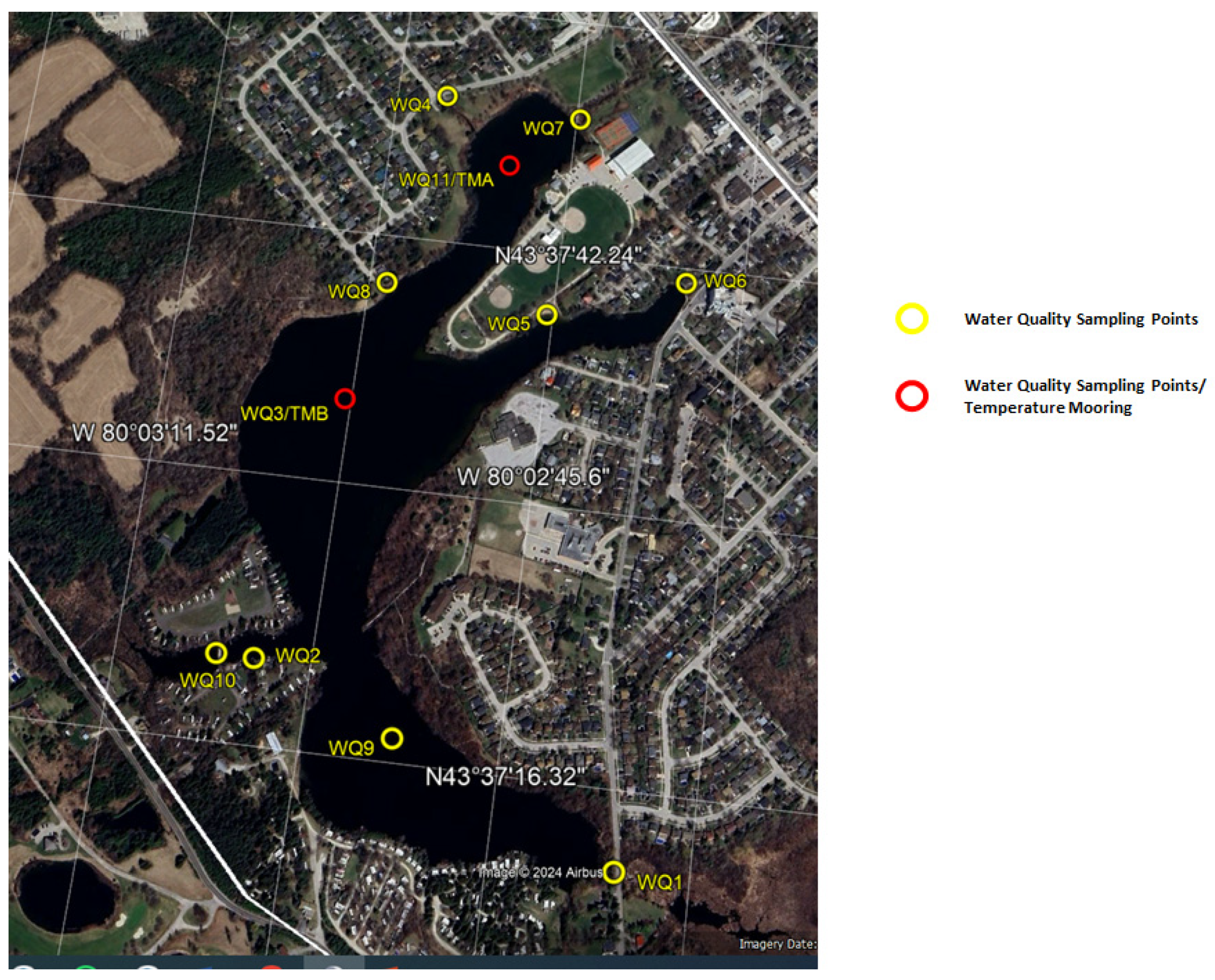
26]. Two Temperature Mooring (TMA and TMB) were installed in Fairy Lake are shown in
Figure 2. Water level data has been barometrically compensated using barometric data from the climate station at Acton Wastewater Treatment Plant. The Town of Halton Hills has recently conducted a bathymetric survey in April 2022 and elevation of water surface in the lake was 345.7m above sea level [
18].
At the surface, 1-m depth and 2-m depth the water temperatures are several degrees oC below and even more so, for 3-m depth. At 4-m and 5- m depth the water temperatures are substantially lower than surface water temperature until October and goes higher than surface water temperature.
In 2023, at depths of 0.5-meter, 1-meter depth and 2-meter, the water temperatures several degrees oC below than surface water temperature. At 4-meter and 5- meter depth they are quite lower up till October and goes higher than 0.5 meter- temperature. This shows overturning of water in the Lake.
Detections of cyanobacteria, on 10/18/2023 when the water temperature was below 15 demands further analysis as 20°C in mostly mentioned as the minimum optimal temperature for cyanobacteria blooms.
4.0. Trend Analysis
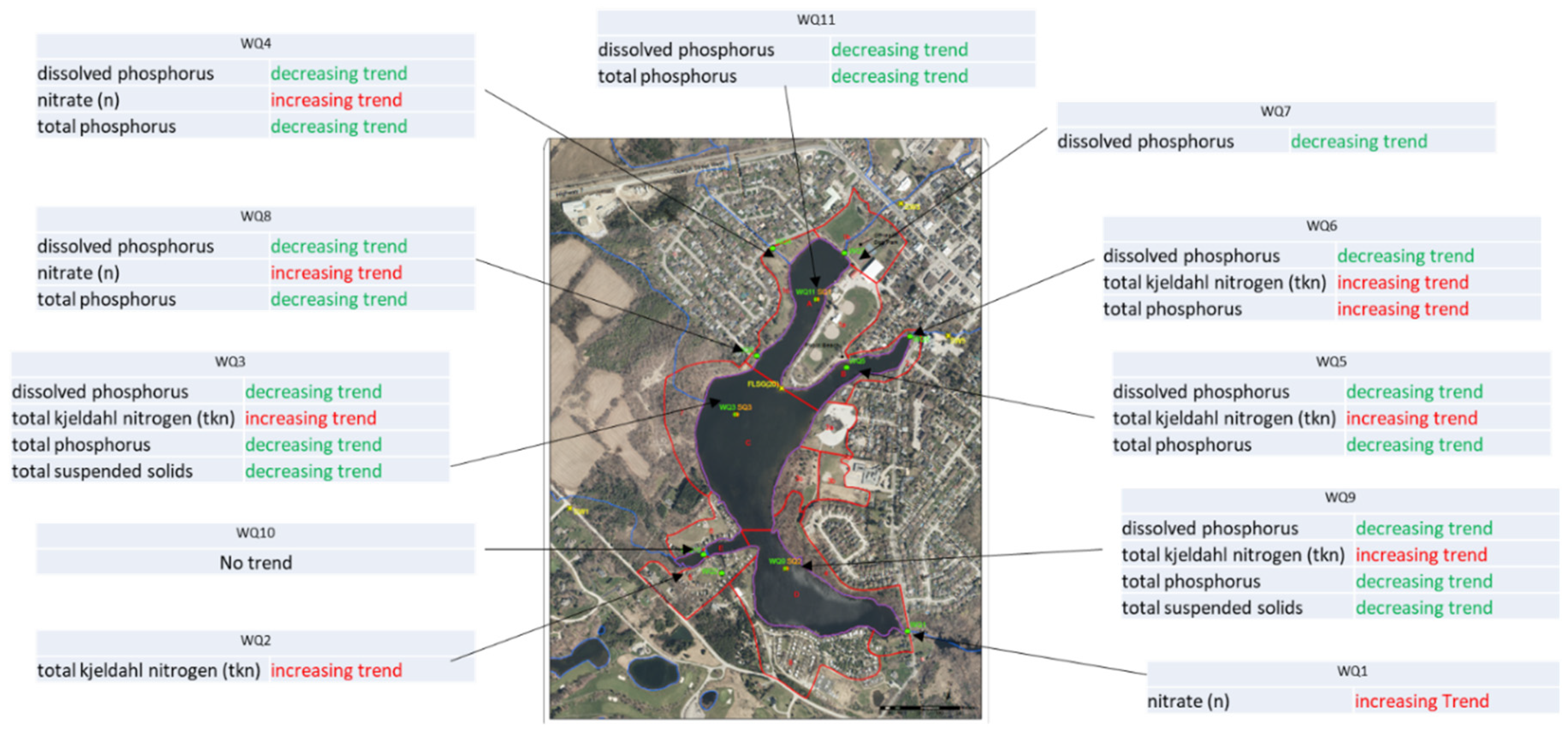
The Mann-Kendall Trend Test (MK Test) used to detect trends in time series data to determine whether there is a systematic upward or downward trend in the monitoring data (without making assumptions about the distribution of the data or the underlying trend shape). Trend analysis is conducted by using USEPA ProUCL 5.1 software and MK Test is used. The results show that the concentrations of dissolved phosphorus and total phosphorus have decreasing trends from the flow contributing locations to the Lake in wet and dry sampling events. However, N and TSS have increasing trends. In the Lake, only N has decreasing trends possibly showing that N is being consumed or being deposited in sediments.
Table 6.
Trend Analysis Results of Various Parameters in each Group.
Table 6.
Trend Analysis Results of Various Parameters in each Group.
| |
All wet sampling events to of lake |
All dry sampling events to the lake |
All Wet sampling events in the lake |
All dry sampling events in the lake |
| NumObs |
88 |
41 |
38 |
29 |
| # Missing |
3 |
15 |
14 |
3 |
| Variable |
Trend |
Trend |
Trend |
Trend |
| dissolved phosphorus |
decreasing trend |
decreasing trend |
Insufficient evidence |
Insufficient evidence |
| E. coli |
increasing Trend |
Insufficient evidence |
Insufficient evidence |
Insufficient evidence |
| nitrate (n) |
increasing Trend |
increasing Trend |
decreasing trend |
decreasing trend |
| total kjeldahl nitrogen (tkn) |
decreasing trend |
Insufficient evidence |
Insufficient evidence |
Insufficient evidence |
| total phosphorus |
decreasing trend |
Insufficient evidence |
Insufficient evidence |
Insufficient evidence |
| total suspended solids) |
increasing Trend |
increasing Trend |
Insufficient evidence |
Insufficient evidence |
An analysis is also carried out for each monitoring location for both in the Lake and outside the Lake and the results are provided in
Table 7 and
Table 8. All the results are shown in
Figure 5.
Monitoring Points Feeding to The Lake
For dissolved phosphorus, there are decreasing trends for WQ4, WQ7 and WQ8. While for Total phosphorus, there are decreasing trends for WQ4 and WQ8..
Monitoring Points in The Lake
For the monitoring locations in the Lake the dissolved phosphorus and TP, there are decreasing trends for WQ3, WQ5, WQ9 and WQ11. While for TKN, there are increasing trends for WQ3, WQ5 and WQ9. TSS are also decreasing in WQ3 and WQ9.
Figure 5.
Trend Analysis of dissolved phosphorus, nitrate and total phosphorus for all monitoring locations.
Figure 5.
Trend Analysis of dissolved phosphorus, nitrate and total phosphorus for all monitoring locations.
4.1. TN/TP Ratio
Regulating nutrients, particularly N and P, are crucial in preventing cyanobacterial HABs. Variations in the significance of different nutrients (e.g. N and P), their forms (e.g., soluble/particulate, oxidized/reduced, bioavailable/refractory), and their ratios (e.g., TN:TP) for the occurrence of CyanoHABs across various locations may be attributed to species-specific physiological adaptations, such as atmospheric N fixation [
27,
28]. A study evaluating future scenarios of nutrient load reduction in Lake Winnipeg, using the PB model WASP [
29], reported that a 10% reduction in TP load would decrease the abundance of total cyanobacteria but increase the total biomass of non N-fixing cyanobacteria. Consequently, the recommended management strategy for this scenario was to reduce TP while maintaining a minimum TN to TP ratio [
30].
Much of the debate revolves around whether low TN:TP ratios contribute to the occurrence of HAB blooms and can serve as predictors for these blooms. Various researchers [
31,
32,
33,
34,
35,
36] have reported values for N-limited and P limited values such as 20-50, 6-16, 8-24 and more. However, Lefler et al. [
4] reported that TN:TP ≥ 23 indicates P-limitation, TN:TP ≤ 9 indicates N-limitation, and 23 > TN:TP > 9 indicates co-nutrient limitation. Smith [
37] reported that a high concentration of P and a low TN:TP ratio tend to favor the development of cyanobacterial blooms.
The probable risk of microcystin concentrations exceeding water quality guidelines was greatest when the ratio of N to P was low and rapidly decreased at higher TN:TP ratios. Maximum concentrations of microcystins occurred in hypereutrophic lakes at mass ratios of TN:TP below 23 [
38]. Li et al. [
39] conducted a study in Lake Vombsjön, located in southern Sweden to assess changes in the risk of cyanobacterial bloom occurrence and enhance understanding of how N and P impact cyanobacteria growth. Their findings indicate that TP exhibits a stronger positive correlation with cyanobacteria biomass compared to dissolved inorganic P (DIP), while dissolved inorganic N(DIN) shows a stronger negative correlation with cyanobacteria biomass than TN. Moreover, the DIN:TP ratio demonstrates a stronger negative correlation with cyanobacteria biomass than the TN:TP ratio. Elevated cyanobacteria biomass, exceeding the WHO Alert Level 2 (10 mm
3/L) for drinking water, corresponds to a DIP/TP ratio below 10.
Li et al. [
39] suggested that to mitigate cyanobacteria growth, emphasis should be placed on controlling TP and DIN, ideally maintaining TP levels below 0.02 mg/L and ensuring the DIN:TP ratio remains above 10, preferably above 50, thus reducing the likelihood of nitrogen limitation favoring cyanobacterial blooms.
4.1.1. TN/TP Analysis of Fairy Lake
All the monitoring results of various locations are grouped locations contributing water to the Lake and other in the Lake. Wet and dry results in both the groups were analyzed separately for calculating the statistics, as presented in
Table 9. The TN/TP ratios for Lake samples are low although the 50%ile numbers are higher than 27 which is slightly above the P limiting number.
The results show that minimum TN/TP ratio in all dry and wet evens went below 10 as this ratio is alarming meaning that water has N-limitation as TN:TP ≤ 9 indicates N-limitation and it may help cyanobacteria to grow.
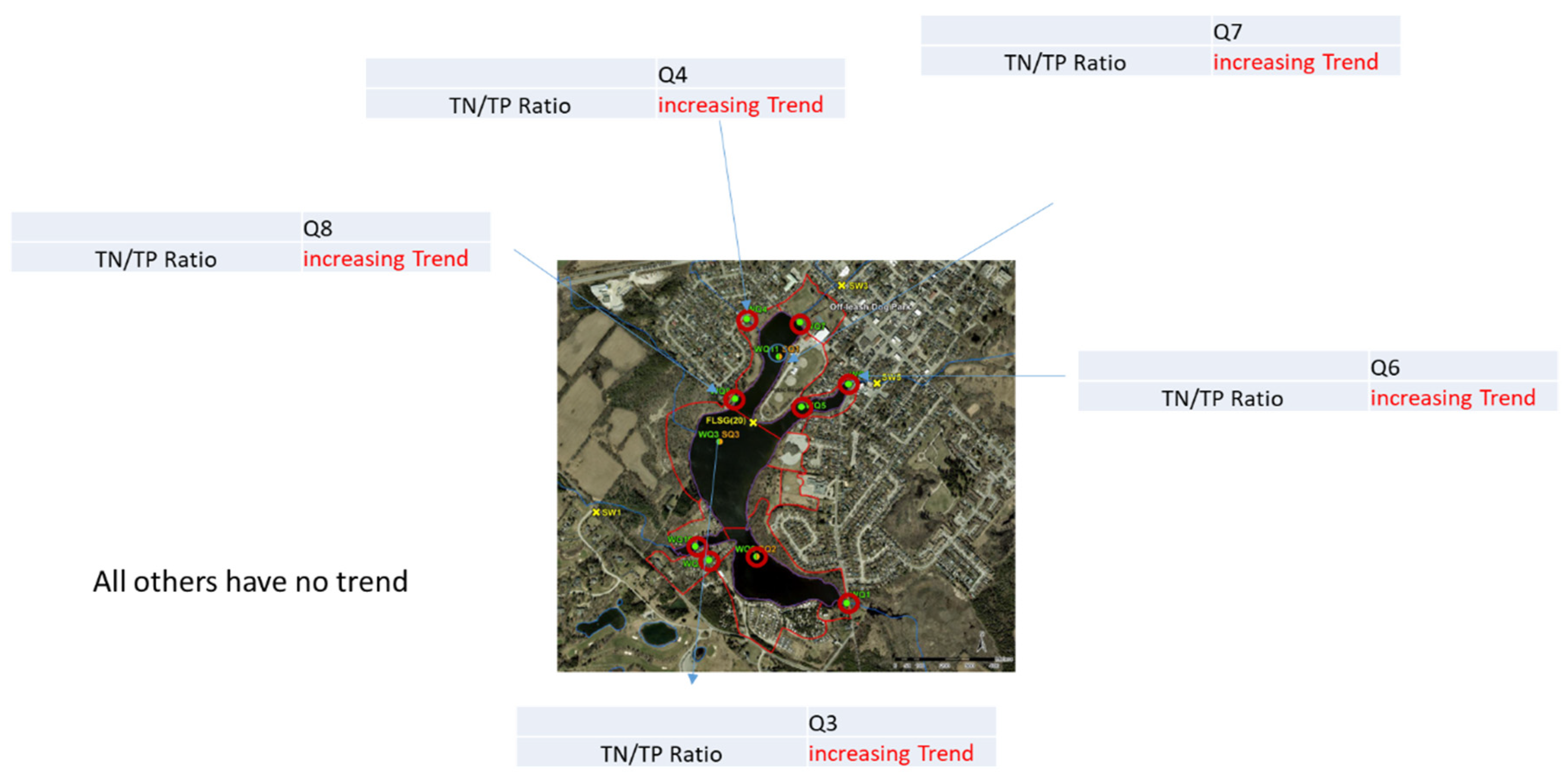
4.1.2. Trend Analysis of TN/TP Ratio
Trend analyses of these samples show increasing trends for the samples wet and dry to the Lake and wet in the Lake. However, there was insufficient evidence of any trend for dry in the Lake.
Table 10.
Statistics of TN/TP ratio in Wet and Dry Events to the lake and in the Lake.
Table 10.
Statistics of TN/TP ratio in Wet and Dry Events to the lake and in the Lake.
| |
NumObs |
# Missing |
Variable |
TN/TP |
| Wet events to the lake |
88 |
3 |
Trend |
increasing Trend |
| dry evens to the lake |
41 |
15 |
Trend |
increasing Trend |
| wet events in the lake |
38 |
14 |
Trend |
increasing Trend |
| dry evens in the lake |
29 |
3 |
Trend |
Insufficient evidence |
TN/TP Trend analysis was conducted for all the monitoring locations individually and results where there were trends are shown in
Figure 6. TN/TP Trend analyses of all the monitoring locations feeding the Lake and in the Lake are shown in
Figure 7.
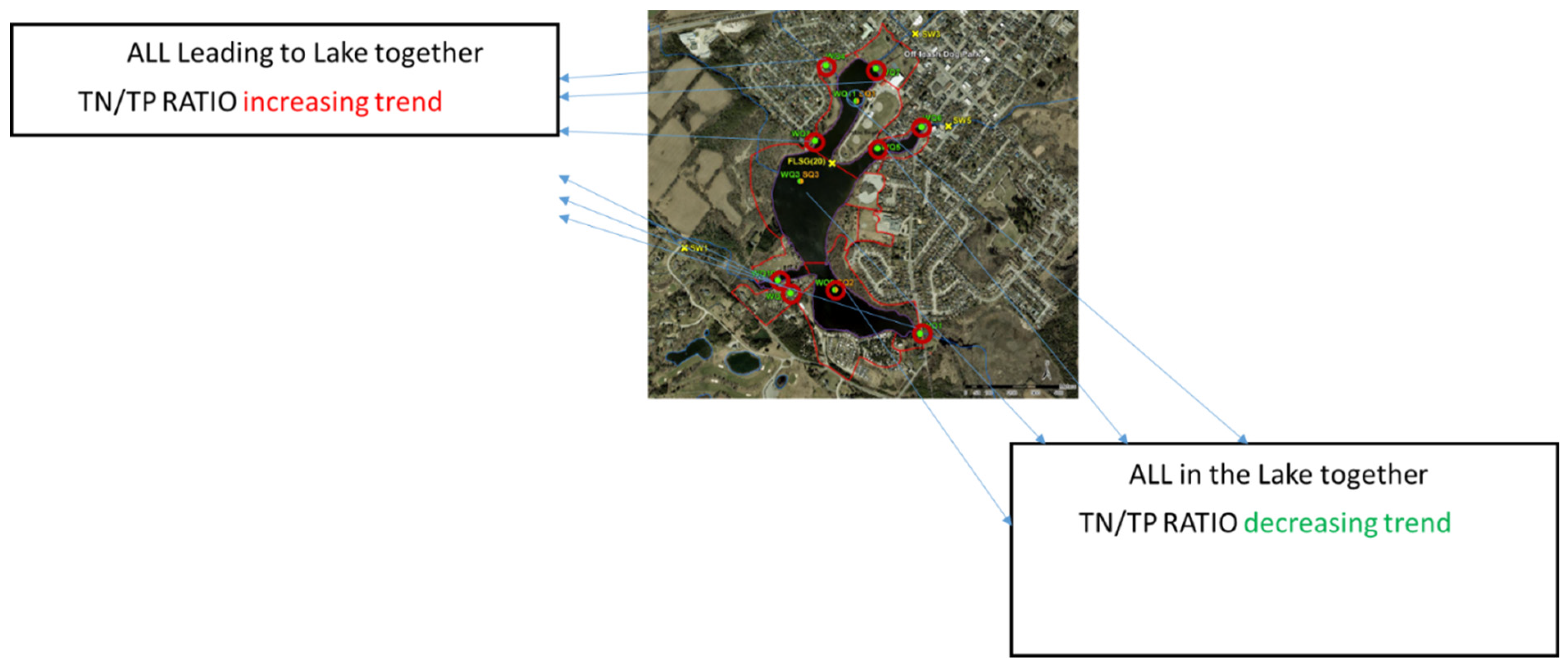
Although TN/TP ratio trend from contributing flows is increasing but in the Lake itself is decreasing; this finding is considered indicative that the total N is being consumed or there is an internal loading of TP from the sediments similar to that reported by Swann et al. [
40]. Swann et al. [
40] reported that during summer, phosphorus (P) entering a lake can undergo cycling within food webs or become retained in sediment. Under oxidizing conditions, P is adsorbed onto ferric oxy-hydroxides and deposited in sediment. Thermal stratification in summer prevents the vertical exchange of dissolved oxygen (DO), leading to anoxic sediments releasing chemically bound P into pore water. This P is eventually internally loaded into the overlying water column via advection and diffusion. Additionally, aerobic decomposition of organic matter can further release both inorganic and dissolved organic P into the water column [
41,
42].
T/N ratio vs Nutrient Limitation at Various Monitoring Locations.
An analysis was carried out to compare TN/TP ratio with Lefler et al., [
4] who reported that TN:TP ≥ 23 indicates P-limitation, TN:TP ≤ 9 indicates N-limitation, and 23 > TN:TP > 9 indicates co-nutrient limitation. The results are presented below in
Table 11.
Among the monitoring points feeding the Lake, WQ-1, WQ-2, WQ-10 and WQ-3 had N-limitations four, five, three and two times, respectively. The catchment of WQ-1 and WQ-2 needs TN limitation and co-nutrient limitations in total are 11 and 16 out of 18 respectively. A low TN:TP ratio favors the development of cyanobacterial blooms; however, the monitoring points in the Lake had no TN limitations. The above analysis indicates that strong managerial efforts are required to reduce the TP in the catchment to increase the TN/TP ratio.
5.0. Microbial Source Tracking
This study applied a microbial source tracking approach to assess the presence of human sewage contamination at the beach and nearby areas, as well as the entry of human fecal contamination and fecal contamination from birds (gulls) and ruminants (cattle) into the Lake from tributaries or stormwater outfalls. Edge-Water DNA Inc. [
43] helped to conduct this analysis.
Microbial source tracking methods offer new insights into interpreting elevated levels of fecal pollution and E. coli bacteria in water samples, aiding in the identification of pollution sources [
44,
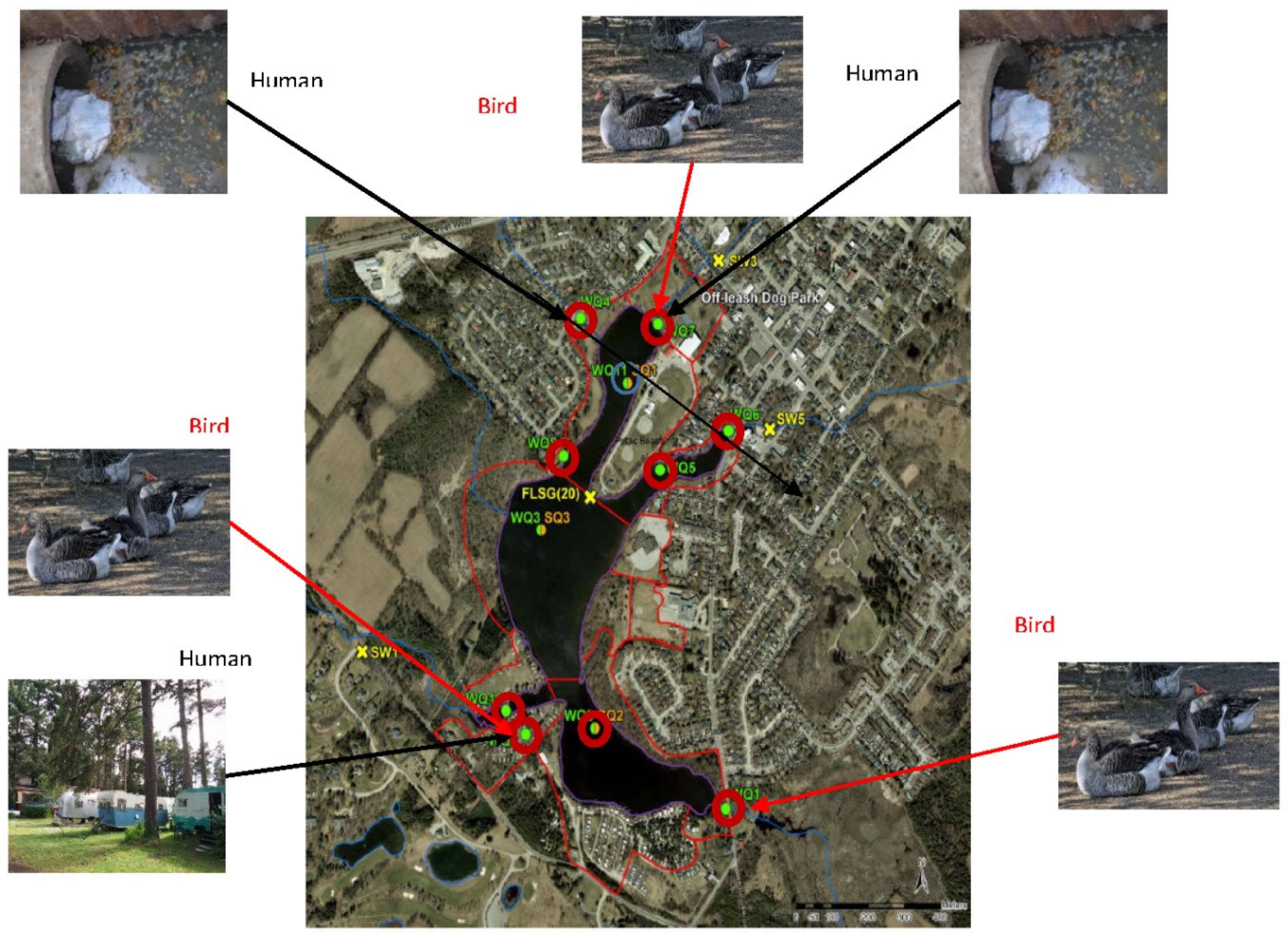
45]. In these methods, a water sample is filtered to collect microorganisms such as bacteria. The DNA from these microorganisms is then extracted and analyzed using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assays. These assays measure the number of copies of specific DNA sequences (DNA markers) present in the water sample. These DNA markers are known to be associated with bacteria found exclusively in the feces of humans or certain animals. For example, detecting high numbers of a DNA marker from a bacterium found only in the human gut indicates human fecal contamination in the water sample. This information aids in interpreting high E. coli counts in water samples and inferring their source as human fecal pollution. Water samples were gathered at 8 designated sites along the shoreline of the Lake, chosen based on assessments by CVC and ongoing water quality surveillance studies for the locations which are WQ1, WQ2, WQ4, WQ5, WQ6, WQ7, WQ8 and WQ10. The human HF183 DNA marker and the Gull4 DNA marker were used to trace human fecal contamination and bird fecal contamination at these locations. Human fecal contamination makers showed presence in WQ2 (trailer park), WQ7 (creek inflow) and the stormwater outfall site WQ4. Bird fecal contamination was detected WQ1, WQ7 and WQ10. These results are shown in
Figure 8.
The Site and its characteristics are discussed. The water quality monitoring stations and various sampling events which encompasses over two years are presented. The dissolved phosphorous, Nitrates(N), Total Kjeldahl Nitrogen (TKN), Total phosphorous, TSS, and Escherichia coli concentrations both in wet and dry conditions are analyzed in lab. Water temperature at the two Temperature Mooring (TMA and TMB) stations are collected. A microbial source tracking approach to assess the presence of human sewage contamination at the beach and nearby areas, as well as the entry of human fecal contamination into the lake from tributaries or stormwater outfalls. The Site and its characteristics are discussed. The water quality monitoring stations and various sampling events which encompasses over two years are presented. The dissolved phosphorous, Nitrates(N), Total Kjeldahl Nitrogen (TKN), Total phosphorous, TSS, and Escherichia coli concentrations both in wet and dry conditions are analyzed in lab. Water temperature at the two Temperature Mooring (TMA and TMB) stations are collected. A microbial source tracking approach to assess the presence of human sewage contamination at the beach and nearby areas, as well as the entry of human fecal contamination into the lake from tributaries or stormwater outfalls.In summary, while repeated sampling and higher sample numbers can provide more confidence in understanding water quality variability and fecal pollution sources, the results in this report identify low levels of human fecal waste sources and bird fecal droppings impacting water quality (and likely nutrient levels) at sites on Fairy Lake
In summary, while repeated sampling and higher sample numbers can provide more confidence in understanding water quality variability and fecal pollution sources, the results show low levels of human fecal waste sources and bird fecal droppings impacting water quality (and likely nutrient levels) at sites on Fairy Lake.