Submitted:
02 July 2024
Posted:
03 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Sickle Cell Disease
2.1. Definition and Diagnostic Criteria
2.2. Epidemiology and Main Clinical Features
2.3. Management Issues and Treatment Options
2.4. Children vs. Adult Patients
3. Neurovascular Manifestations
3.1. Ischemic Stroke
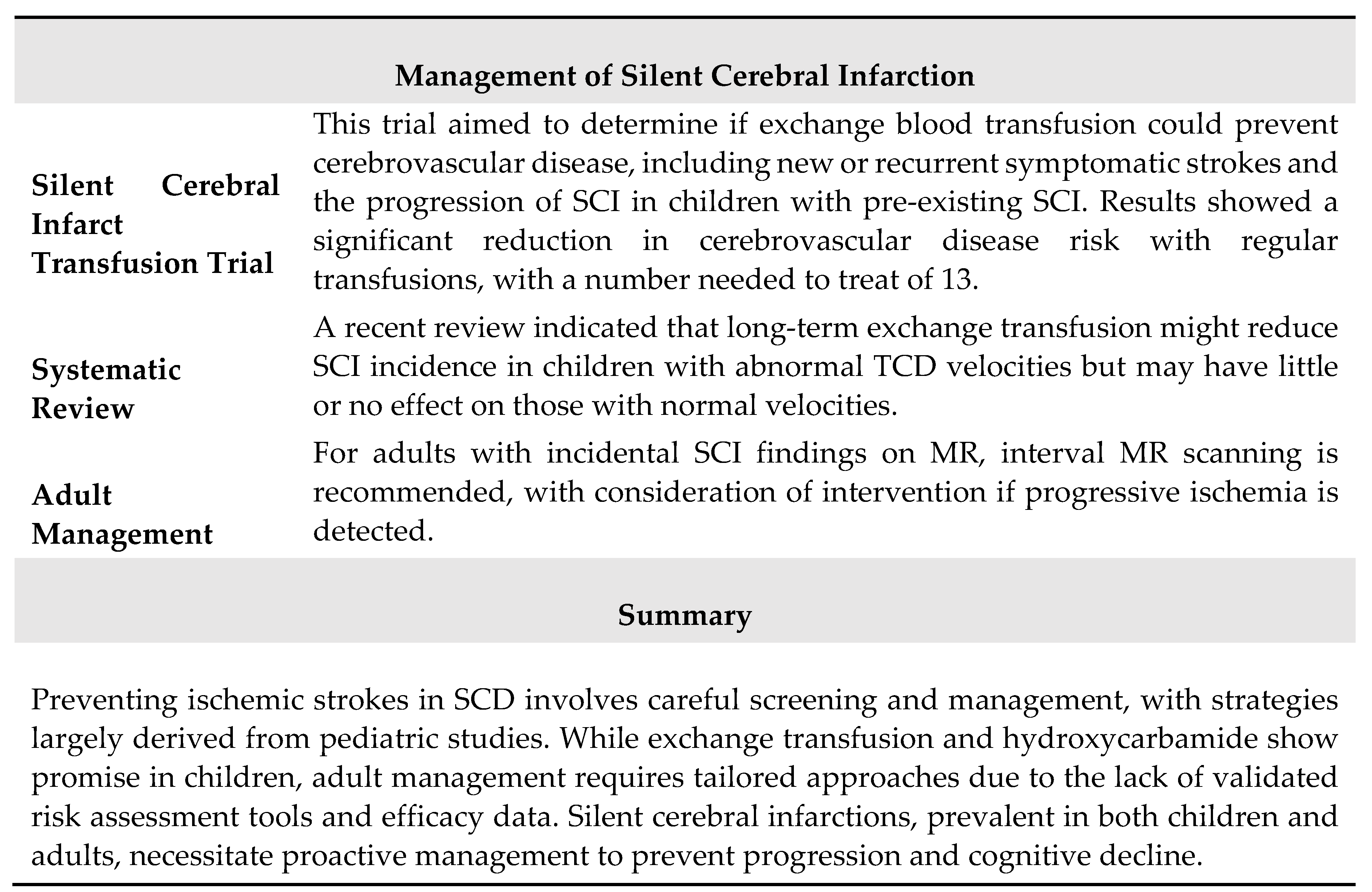
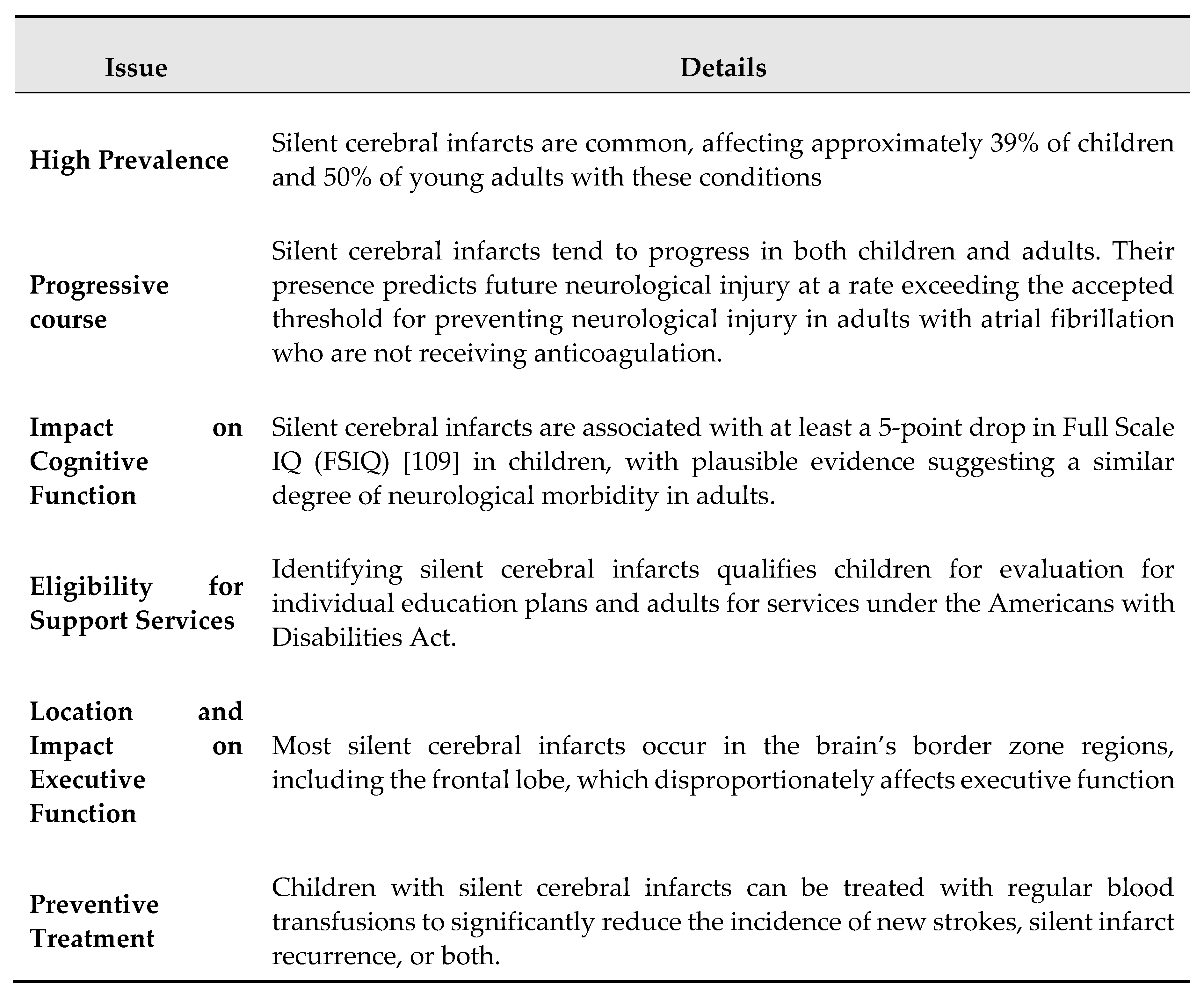
3.2. Silent Cerebral Infarction
3.3. Intracranial Bleeding
3.4. Intracranial Arteriopathy
3.5. Intracranial Aneurysms
4. Main neuroimaging Issues
4.1. Ischemic Stroke
4.2. Silent Brain Infarctions and Small Vessel Disease
4.3. Hemorrhagic Stroke
4.4. Intracranial Arteriopathy
4.5. Cerebral Venous Drainage
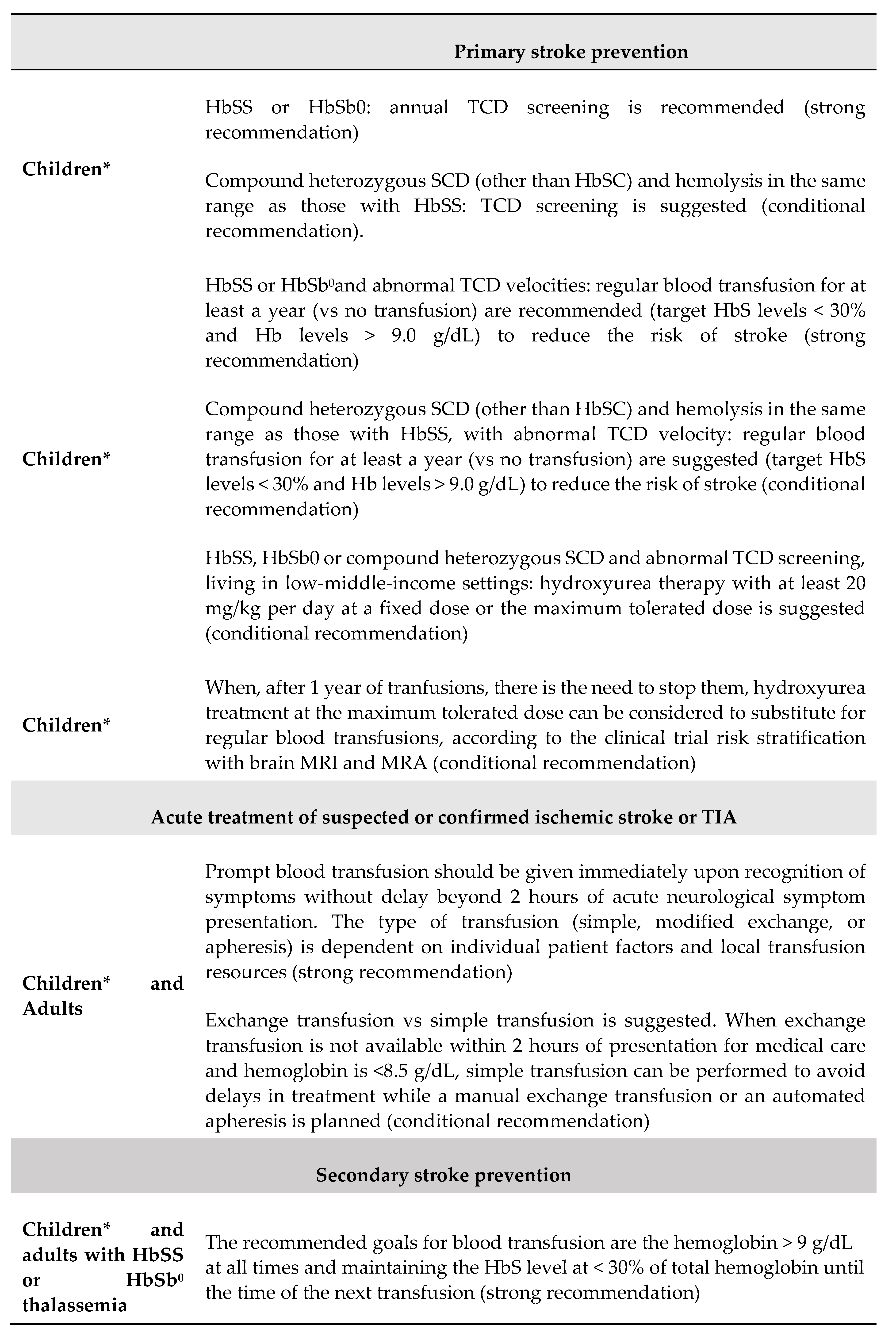
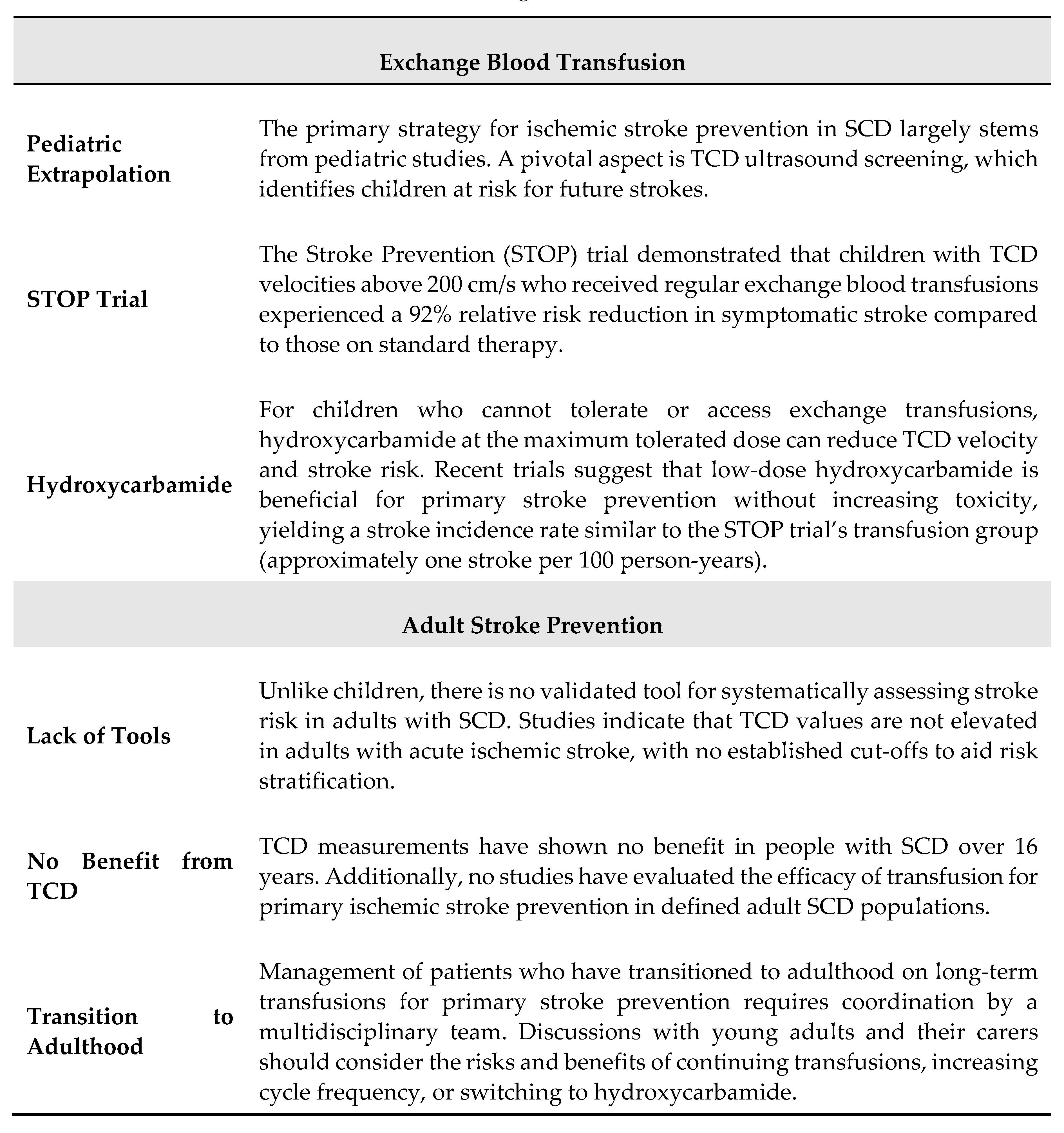
5. Transcranial Doppler and Stroke Prevention Strategie
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rees DC, Williams TN, Gladwin MT. Sickle-cell disease. Lancet. 2010;376:2018–31.
- Thein SL. The molecular basis of β-thalassemia. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2013;3:a011700.
- Bunn HF. Pathogenesis and treatment of sickle cell disease. N Engl J Med. 1997;337:762–9.
- Kato GJ, Gladwin MT, Steinberg MH. Deconstructing sickle cell disease: reappraisal of the role of hemolysis in the development of clinical subphenotypes. Blood Rev. 2007;21:37–47.
- Platt OS, Brambilla DJ, Rosse WF, et al.. Mortality in sickle cell disease. Life expectancy and risk factors for early death. N Engl J Med. 1994;330:1639–44. 10.1056/NEJM199406093302303.
- Ballas SK, Lusardi M: Hospital readmission for adult acute sickle cell painful episodes: frequency, etiology, and prognostic significance. Am J Hematol. 2005, 79:17-25. 10.1002/ajh.20336.
- Platt OS, Thorington BD, Brambilla DJ, Milner PF, Rosse WF, Vichinsky E, Kinney TR: Pain in sickle cell disease. Rates and risk factors. N Engl J Med. 1991, 325:11-16. 10.1056/NEJM199107043250103.
- Ohene-Frempong K, Weiner SJ, Sleeper LA, et al.: Cerebrovascular accidents in sickle cell disease: rates and risk factors. Blood. 1998, 91:288-294.
- Hebbel RP, Osarogiagbon R, Kaul D: The endothelial biology of sickle cell disease: Inflammation and a chronic vasculopathy. Microcirculation. 2004, 11:129-151. 10.1080/10739680490278402.
- Ataga KI, Orringer EP: Hypercoagulability in sickle cell disease: a curious paradox. Am J Med. 2003, 115:721-728. 10.1016/j.amjmed.2003.07.011.
- Adams RJ, McKie VC, Hsu L, et al.: Prevention of a first stroke by transfusions in children with sickle cell anemia and abnormal results on transcranial Doppler ultrasonography. N Engl J Med. 1998, 339:5-11. 10.1056/NEJM199807023390102.
- DeBaun MR, Kirkham FJ: Central nervous system complications and management in sickle cell disease. Blood. 2016, 127:829-838. 10.1182/blood-2015-09-618579.
- Ware RE, de Montalembert M, Tshilolo L, Abboud MR. Sickle cell disease. Lancet. 2017 Jul 15;390(10091):311-323.
- Perrotta S, Russo G, et al.; Gruppo di Lavoro “Patologia del globulo rosso” Associazione Italiana Ematologia Oncologia Pediatrica. Linee-Guida per la gestione della Malattia Drepanocitica in età pediatrica in Italia-versione 3 (30 gennaio 2018). https://www.aieop.org › web › uploads › 2018/03P3.
- Kutlar A, Kanter J, Liles DK, et al. Effect of crizanlizumab on pain crises in subgroups of patients with sickle cell disease: A SUSTAIN study analysis. Am J Hematol. 2019 Jan;94(1):55-61.
- Matte A, Zorzi F, Mazzi F, et al. New Therapeutic Options for the Treatment of Sickle Cell Disease. Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis. 2019;11(1):e2019002.
- Russo G, De Franceschi L, Colombatti R, et al. Current challenges in the management of patients with sickle cell disease - A report of the Italian experience. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2019 May 30;14(1):120.
- De Franceschi L. La drepanocitosi: un problema emergente di salute pubblica. Prospettive in pediatria. Società Italiana di Pediatria. 2014; 44(174): 88-95.
- De Franceschi L, Graziadei G, Rigano P, et al. Raccomandazioni per la gestione del paziente adulto affetto da anemia falciforme. Società Italiana Talassemie ed Emoglobinopatie-SITE. Collana Scientifica S.I.T.E. n.2 2014.
- Piel FB, Steinberg MH, Rees DC. Sickle Cell Disease. N Engl J Med. 2017 Jul 20;377(3):305.
- World Health Organization (WHO). Report by the Secretariat of the Fifty-ninth World Health Assembly A59/9, 2006.
- Colombatti R, Perrotta S, Samperi P et al. Italian Association of Pediatric Hematology-Oncology (AIEOP) Sickle Cell Disease Working Group. Organizing national responses for rare blood disorders: the Italian experience with sickle cell disease in childhood. Orphanet J Rare Dis 2013;8:169.
- Roberts I, de Montalembert M. Sickle cell disease as a paradigm of immigration hematology: new challenges for hematologists in Europe. Haematologica. 2007 Jul;92(7):865-71.
- Colombatti R, Casale M, Russo G. Disease burden and quality of life of in children with sickle cell disease in Italy: time to be considered a priority. Ital J Pediatr. 2021 Jul 29;47(1):163.
- De Franceschi L, Russo G, Sainati L. Raccomandazioni per lo screening neonatale nelle sindromi falciformi. Società Italiana Talassemie ed Emoglobinopatie- SITE. Collana Scientifica S.I.T.E. n. 5 2017.
- Niscola P, Sorrentino F, Scaramucci L, et al. Pain syndromes in sickle cell disease: an update. Pain Med. 2009 Apr;10(3):470-80.
- Dormandy E, James J, Inusa B, et al. How many people have sickle cell disease in the UK? J Public Health 2018;40:e291–5.
- Kassim AA, Pruthi S, Day M, et al. Silent cerebral infarcts and cerebral aneurysms are prevalent in adults with sickle cell anemia. Blood. 2016;127(16):2038-2040.
- Sacco RL, Kasner SE, Broderick JP, et al.; Council on Nutrition, Physical Activity and Metabolism. An updated definition of stroke for the 21st century: a statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2013;44(7):2064-2089.
- Veluswamy S, Shah P, Denton CC, Chalacheva P, Khoo MC, Coates TD. Vaso-occlusion in sickle cell disease: is autonomic dysregulation of the microvasculature the trigger? J Clin Med. 2019;8:1690.
- Hebbel RP, Boogaerts MA, Eaton JW, Steinberg MH. Erythrocyte adherence to endothelium in sickle-cell anemia. A possible determinant of disease severity. N Engl J Med. 1980;302:992–995.
- Kaul DK, Fabry ME, Nagel RL. Vaso-occlusion by sickle cells: evidence for selective trapping of dense red cells. Blood. 1986;68:1162–1166.
- Weigand M, Gomez-Pastora J, Palmer A, Zborowski M, Desai P, Chalmers J. Continuous-flow magnetic fractionation of red blood cells based on hemoglobin content and oxygen saturation— clinical blood supply implications and sickle cell anemia treatment. Processes. 2022;10:927.
- Hirtz D, Kirkham FJ. Sickle cell disease and stroke. Pediatr Neurol. 2019;95:34–41.
- Gladwin MT, Sachdev V. Cardiovascular abnormalities in sickle cell disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;59:1123–1133.
- Chennupati R, Solga I, Wischmann P, et al. Chronic anemia is associated with systemic endothelial dysfunction. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023;10.
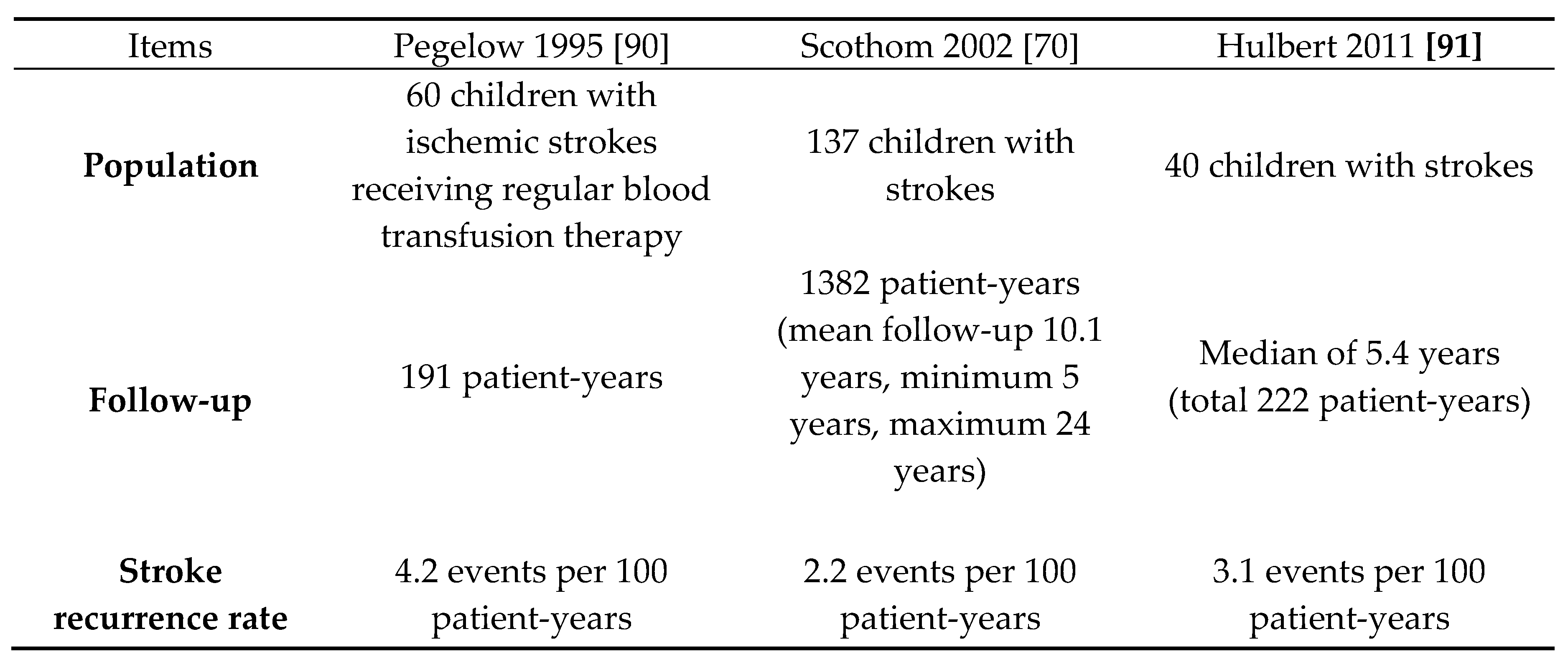
- Ataga KI, Key NS. Hypercoagulability in sickle cell disease: new approaches to an old problem. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2007:91–96.
- Parikh T, Goti A, Yashi K, Ravikumar NPG, Parmar N, Dankhara N, Satodiya V. Pediatric sickle cell disease and stroke: a literature review. Cureus. 2023;15:0.
- Pavlakis SG, Bello J, Prohovnik I, et al. Brain infarction in sickle cell anemia: magnetic resonance imaging correlates. Ann Neurol. 1988;23:125–130.
- Sundd P, Gladwin MT, Novelli EM. Pathophysiology of sickle cell disease. Annu Rev Pathol. 2019;14:263–292.
- Kassim AA, DeBaun MR. Sickle cell disease, vasculopathy, and therapeutics. Annu Rev Med. 2013;64:451–466.
- Elsharawy MA, Moghazy KM, Shawarby MA. Atherosclerosis in sickle cell disease — a review. Int J Angiol. 2009;18:62–66.
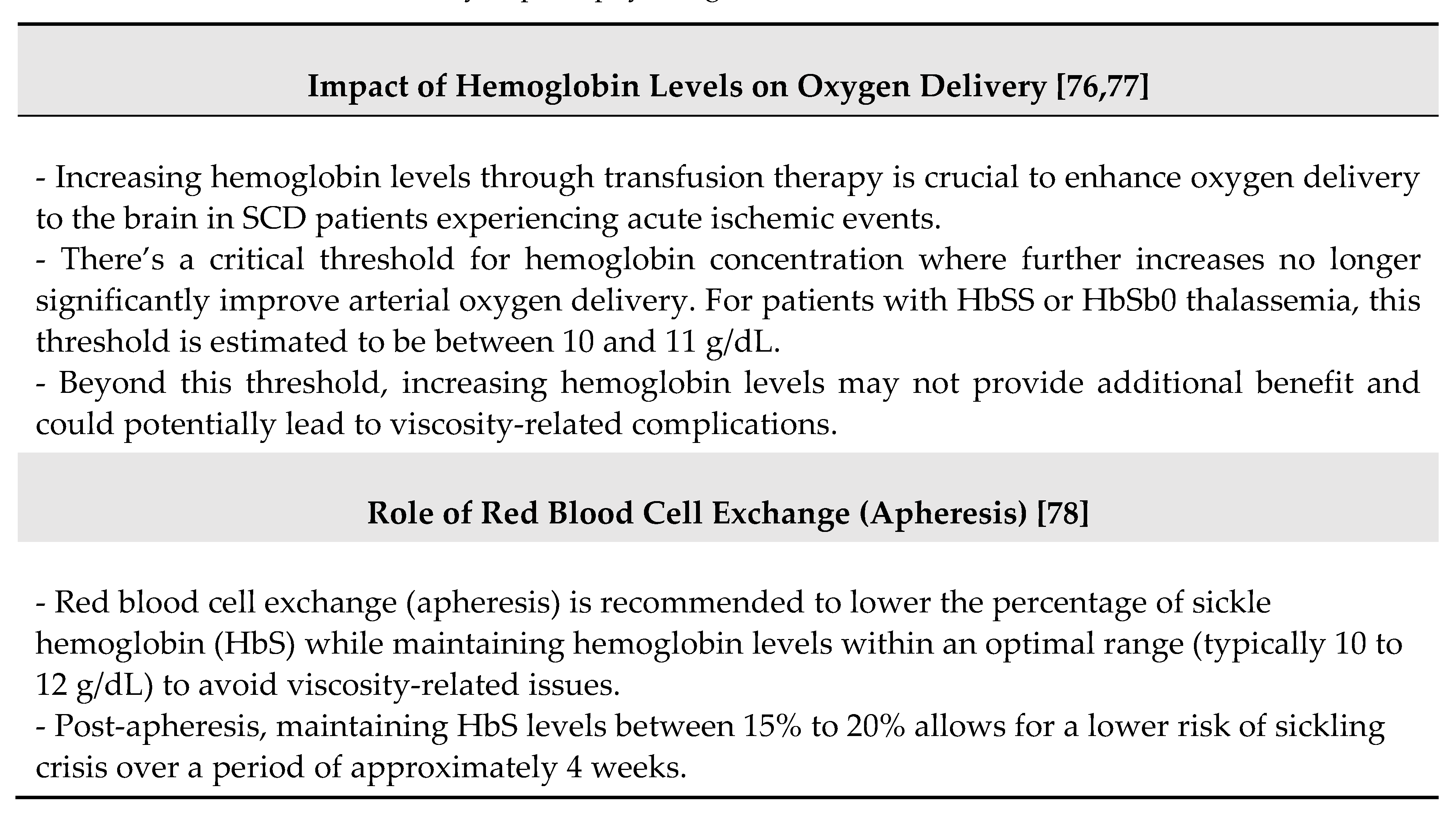
- Prohovnik I, Pavlakis SG, Piomelli S, Bello J, Mohr JP, Hilal S, De Vivo DC. Cerebral hyperemia, stroke, and transfusion in sickle cell disease. Neurology. 1989;39:344–348.
- Stotesbury H, Kawadler JM, Hales PW, Saunders DE, Clark CA and Kirkham FJ (2019) Vascular Instability and Neurological Morbidity in Sickle Cell Disease: An Integrative Framework. Front. Neurol. 10:871. [CrossRef]
- Hakami F, Alhazmi E, Busayli WM, Althurwi S, Darraj AM, Alamir MA, Hakami A, Othman RA, Moafa AI, Mahasi HA, Madkhali MA. Overview of the Association Between the Pathophysiology, Types, and Management of Sickle Cell Disease and Stroke. Cureus. 2023 Dec 15;15(12):e50577. [CrossRef]
- Balkaran B, Char G, Morris JS, Thomas PW, Serjeant BE, Serjeant GR. Stroke in a cohort of patients with homozygous sickle cell disease. J Pediatr. 1992;120:360–366.
- DeBaun MR, Armstrong FD, McKinstry RC, Ware RE, Vichinsky E, Kirkham FJ. Silent cerebral infarcts: a review on a prevalent and progressive cause of neurologic injury in sickle cell anemia. Blood. 2012;119:4587–4596.
- Dowling MM, Noetzel MJ, Rodeghier MJ, et al. Headache and migraine in children with sickle cell disease are associated with lower hemoglobin and higher pain event rates but not silent cerebral infarction. J Pedatr. 2014;164:1175–1180.
- Solh Z, Taccone MS, Marin S, et al. Neurological presentations in sickle cell patients are not always stroke: a review of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in sickle cell disease. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2016;63:983–989.
- Vargas A, Testai FD. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in adult sickle-cell patients: case series and literature review. J Clin Neurosci. 2019;70:249–250.
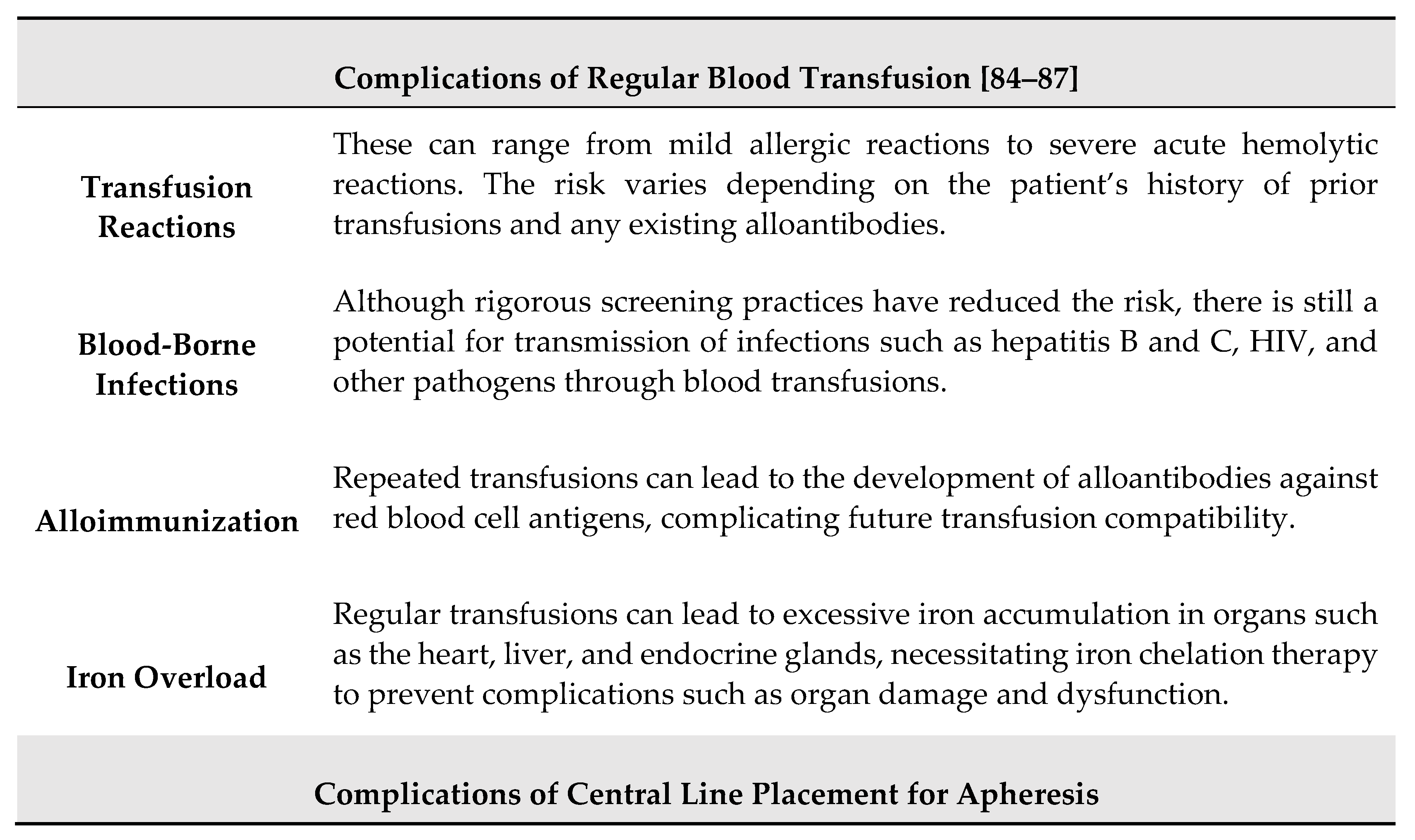
- Adams RJ, McKie VC, Brambilla D, Carl E, Gallagher D, Nichols FT, et al. Stroke prevention trial in sickle cell anemia. Control Clin Trials. (1998) 19:110–29. [CrossRef]
- Hart RG, Kanter MC. Hematologic disorders and ischemic stroke. A selective review. Stroke. (1990) 21:1111–21. [CrossRef]
- Jabbarli R, Dinger TF, Pierscianek D, Oppong MD, Chen B, Dammann P, et al. Intracranial aneurysms in sickle cell disease. Curr Neurovasc Res. (2019) 16:63–76. [CrossRef]
- Strouse JJ, Hulbert ML, DeBaun MR, Jordan LC, Casella JF. Primary hemorrhagic stroke in children with sickle cell disease is associated with recent transfusion and use of corticosteroids. Pediatrics. (2006) 118:1916–24. [CrossRef]
- Switzer JA, Hess DC, Nichols FT, Adams RJ. Pathophysiology and treatment of stroke in sickle-cell disease: present and future. Lancet Neurol. (2006) 5:501–12. [CrossRef]
- de Araujo OMR, Ivo ML, Ferreira Júnior MA, Pontes ERJC, Bispo IMGP, Oliveira, et al. Survival and mortality among users and non-users of hydroxyurea with sickle cell disease. Rev Lat Am Enfermagem. (2015) 23:67– 73. [CrossRef]
- Powars D, Wilson B, Imbus C, Pegelow C, Allen J. The natural history of stroke in sickle cell disease. Am J Med. (1978) 65:461–71. [CrossRef]
- Ataga KI, Gordeuk VR, Agodoa I, Colby JA, Gittings K, Allen IE. Low hemoglobin increases risk for cerebrovascular disease, kidney disease, pulmonary vasculopathy, and mortality in sickle cell disease: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2020;15:0.
- Strouse JJ, Lanzkron S, Urrutia V. The epidemiology, evaluation and treatment of stroke in adults with sickle cell disease. Expert Rev Hematol. 2011;4:597–606.
- Lopez-Vicente M, Ortega-Gutierrez S, Amlie-Lefond C, Torbey MT. Diagnosis and management of pediatric arterial ischemic stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2010;19:175–183.
- Belisário AR, Silva CM, Velloso-Rodrigues C, Viana MB. Genetic, laboratory and clinical risk factors in the development of overt ischemic stroke in children with sickle cell disease. Hematol Transfus Cell Ther. 2018;40:166–181.
- Kirkham FJ, Lagunju IA. Epidemiology of stroke in sickle cell disease. J Clin Med. 2021;10.
- Alakbarzade V, Maduakor C, Khan U, Khandanpour N, Rhodes E, Pereira AC. Cerebrovascular disease in sickle cell disease. Pract Neurol. 2023 Apr;23(2):131-138. [CrossRef]
- Makin SD, Doubal FN, Dennis MS, Wardlaw JM. Clinically confirmed stroke with negative diffusion-weighted imaging magnetic resonance imaging: longitudinal study of clinical outcomes, stroke recurrence, and systematic review. Stroke. 2015;46(11):3142-3148.
- Hulbert ML, Scothorn DJ, Panepinto JA, et al. Exchange blood transfusion compared with simple transfusion for first overt stroke is associated with a lower risk of subsequent stroke: a retrospective cohort study of 137 children with sickle cell anemia. J Pediatr. 2006;149(5):710-712.
- Guilliams KP, Fields ME, Ragan DK, et al. Red cell exchange transfusions lower cerebral blood flow and oxygen extraction fraction in pediatric sickle cell anemia. Blood. 2018;131(9):1012-1021.
- Juttukonda MR, Lee CA, Patel NJ, et al. Differential cerebral hemometabolic responses to blood transfusions in adults and children with sickle cell anemia. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2019;49(2):466-477.
- Prohovnik I, Hurlet-Jensen A, Adams R, De Vivo D, Pavlakis SG. Hemodynamic etiology of elevated flow velocity and stroke in sickle-cell disease. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2009;29(4):803-810.
- Bush AM, Borzage MT, Choi S, et al. Determinants of resting cerebral blood flow in sickle cell disease. Am J Hematol. 2016;91(9):912-917.
- Scothorn DJ, Price C, Schwartz D, et al. Risk of recurrent stroke in children with sickle cell disease receiving blood transfusion therapy for at least five years after initial stroke. J Pediatr. 2002;140(3):348-354.
- Silva GS, Vicari P, Figueiredo MS, Carrete H Jr, Idagawa MH, Massaro AR. Brain magnetic resonance imaging abnormalities in adult patients with sickle cell disease: correlation with transcranial Doppler findings. Stroke. 2009;40(7):2408-2412.
- Ford AL, Ragan DK, Fellah S, et al. Silent infarcts in sickle cell disease occur in the border zone region and are associated with low cerebral blood flow. Blood. 2018;132(16):1714-1723.
- Kim HC. Red cell exchange: special focus on sickle cell disease. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2014;2014:450-456.
- Swerdlow PS. Red cell exchange in sickle cell disease. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2006;2006:48-53.
- Faye BF, Sow D, Seck M, et al. Efficacy and safety of manual partial red cell exchange in the management of severe complications of sickle cell disease in a developing country. Adv Hematol. 2017;2017:3518402.
- Schmalzer EA, Lee JO, Brown AK, Usami S, Chien S. Viscosity of mixtures of sickle and normal red cells at varying hematocrit levels. Implications for transfusion. Transfusion. 1987;27(3):228-233.
- Alexy T, Pais E, Armstrong JK, Meiselman HJ, Johnson CS, Fisher TC. Rheologic behavior of sickle and normal red blood cell mixtures in sickle plasma: implications for transfusion therapy. Transfusion. 2006;46(6):912-918.
- Hurlet-Jensen AM, Prohovnik I, Pavlakis SG, Piomelli S. Effects of total hemoglobin and hemoglobin S concentration on cerebral blood flow during transfusion therapy to prevent stroke in sickle cell disease. Stroke. 1994;25(8):1688-1692.
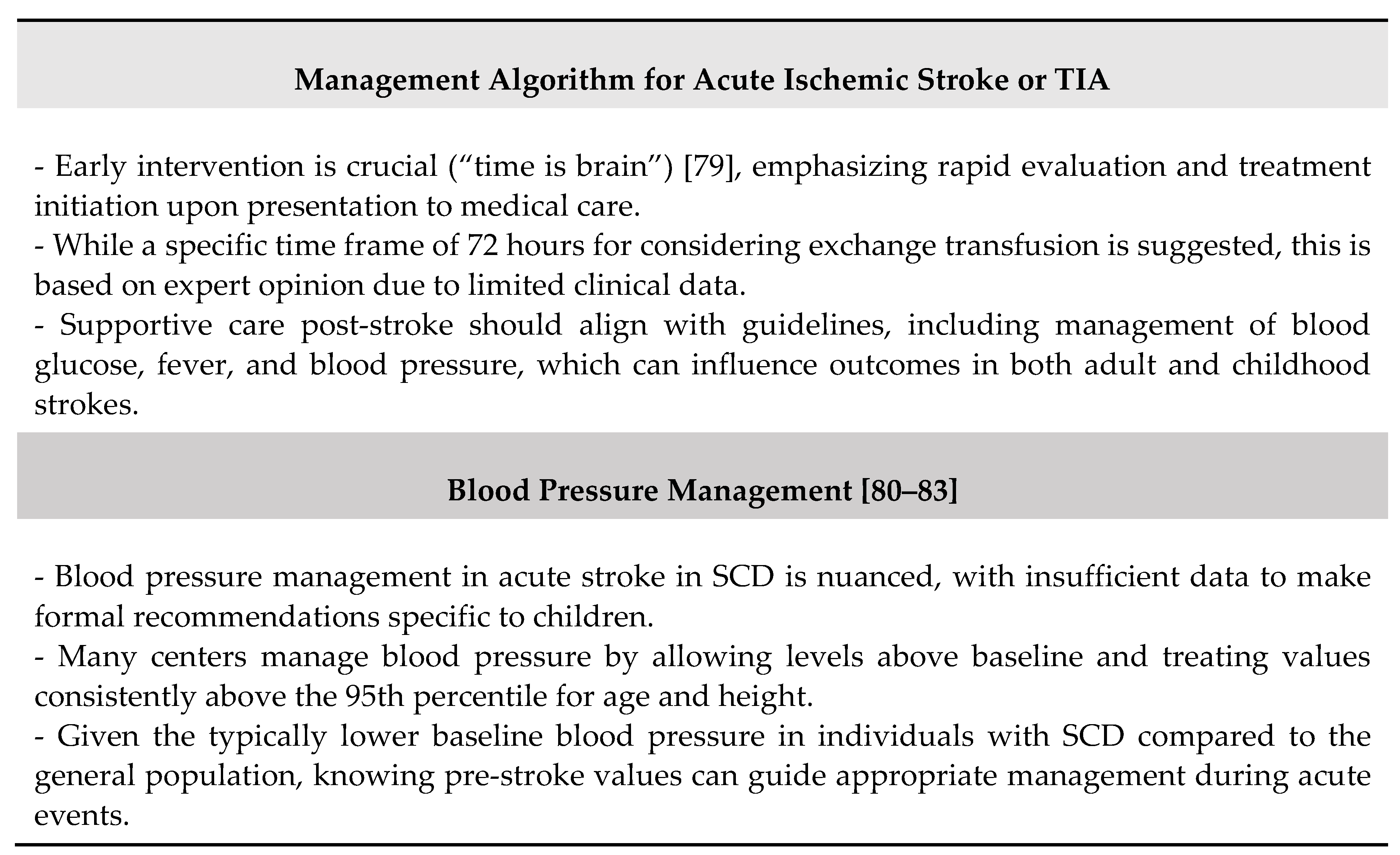
- Saver JL. Time is brain--quantified. Stroke. 2006;37(1):263-266.
- Ferriero DM, Fullerton HJ, Bernard TJ, et al.; American Heart Association Stroke Council and Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing. Management of stroke in neonates and children: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2019;50(3): e51-e96.
- Brush LN, Monagle PT, Mackay MT, Gordon AL. Hypertension at time of diagnosis and long-term outcome after childhood ischemic stroke. Neurology. 2013;80(13):1225-1230.
- Rivkin MJ, Bernard TJ, Dowling MM, Amlie-Lefond C. Guidelines for urgent management of stroke in children [published correction appears in Pediatr Neurol. 2016;64:105]. Pediatr Neurol. 2016;56:8-17.
- Pegelow CH, Colangelo L, Steinberg M, et al. Natural history of blood pressure in sickle cell disease: risks for stroke and death associated with relative hypertension in sickle cell anemia. Am J Med. 1997;102(2):171-177.
- Aygun B, Wruck LM, Schultz WH, et al.; TCD With Transfusions Changing to Hydroxyurea (TWiTCH) Trial Investigators. Chronic transfusion practices for prevention of primary stroke in children with sickle cell anemia and abnormal TCD velocities. Am J Hematol. 2012;87(4):428-430.
- Vichinsky EP, Luban NL, Wright E, et al.; Stroke Prevention Trail in Sickle Cell Anemia. Prospective RBC phenotype matching in a stroke-prevention trial in sickle cell anemia: a multicenter transfusion trial. Transfusion. 2001;41(9):1086-1092.
- Files B, Brambilla D, Kutlar A, et al. Longitudinal changes in ferritin during chronic transfusion: a report from the Stroke Prevention Trial in Sickle Cell Anemia (STOP). J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2002;24(4):284-290.
- Adamkiewicz TV, Abboud MR, Paley C, et al. Serum ferritin level changes in children with sickle cell disease on chronic blood transfusion are nonlinear and are associated with iron load and liver injury. Blood. 2009;114(21):4632-4638.
- DeBaun MR, Jordan LC, King AA, et al. American Society of hematology 2020 guidelines for sickle cell disease: prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of cerebrovascular disease in children and adults. Blood Adv 2020;4:1554–88.
- Adams RJ, Cox M, Ozark SD, et al. Coexistent sickle cell disease has no impact on the safety or outcome of lytic therapy in acute ischemic stroke: findings from Get With The Guidelines-Stroke. Stroke. 2017;48(3):686-691.
- Pegelow CH, Adams RJ, McKie V, et al. Risk of recurrent stroke in patients with sickle cell disease treated with erythrocyte transfusions. J Pediatr. 1995; 126(6):896-899.
- Hulbert ML, McKinstry RC, Lacey JL, et al. Silent cerebral infarcts occur despite regular blood transfusion therapy after first strokes in children with sickle cell disease. Blood. 2011;117(3):772-779.
- Aygun B, Mortier NA, Kesler K, et al.; Stroke With Transfusions Changing to Hydroxyurea (SWiTCH) Trial Investigators. Therapeutic phlebotomy is safe in children with sickle cell anaemia and can be effective treatment for transfusional iron overload. Br J Haematol. 2015;169(2):262-266.
- Ware RE, Helms RW; SWiTCH Investigators. Stroke with transfusions changing to hydroxyurea (SWiTCH). Blood. 2012;119(17):3925-3932.
- Lagunju IA, Brown BJ, Sodeinde OO. Stroke recurrence in Nigerian children with sickle cell disease treated with hydroxyurea. Niger Postgrad Med J. 2013;20(3):181-187.
- Bernaudin F, Dalle JH, Bories D, et al.; Soci ’et ´e Française de Greffe de Moelle et de Therapie Cellulaire. Long-term event-free survival, chimerism and fertility outcomes in 234 patients with sickle-cell anemia younger than 30 years after myeloablative conditioning and matched-sibling transplantation in France. Haematologica. 2020;105(1):91-101.
- de la Fuente J, Dhedin N, Koyama T, et al. Haploidentical bone marrow transplantation with post-transplantation cyclophosphamide plus thiotepa improves donor engraftment in patients with sickle cell anemia: results of an international learning collaborative. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019;25(6):1197-1209.
- Fitzhugh CD, Hsieh MM, Taylor T, et al. Cyclophosphamide improves engraftment in patients with SCD and severe organ damage who undergo haploidentical PBSCT. Blood Adv. 2017;1(11):652-661.
- Jordan LC, Juttukonda MR, Kassim AA, et al. Haploidentical bone marrow transplantation improves cerebral hemodynamics in adults with sickle cell disease. Am J Hematol. 2019;94(6):E155-E158.
- King AA, McKinstry RC, Wu J, et al. Functional and radiologic assessment of the brain after reduced-intensity unrelated donor transplantation for severe sickle cell disease: Blood and Marrow Transplant Clinical Trials Network Study 0601. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019;25(5):e174-e178.
- Bernaudin F, Verlhac S, Arnaud C, et al. Chronic and acute anemia and extracranial internal carotid stenosis are risk factors for silent cerebral infarcts in sickle cell anemia. Blood 2015;125:1653–61.
- Estcourt LJ, Fortin PM, Hopewell S, et al. Interventions for preventing silent cerebral infarcts in people with sickle cell disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2017;5:CD012389.
- Thangarajh M, Yang G, Fuchs D, et al. Magnetic resonance angiography-defined intracranial vasculopathy is associated with silent cerebral infarcts and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase mutation in children with sickle cell anaemia. Br J Haematol 2012;159:352–9.
- DeBaun MR, Sarnaik SA, Rodeghier MJ, et al. Associated risk factors for silent cerebral infarcts in sickle cell anemia: low baseline hemoglobin, sex, and relative high systolic blood pressure. Blood 2012;119:3684–90.
- Dowling MM, Quinn CT, Plumb P, et al. Acute silent cerebral ischemia and infarction during acute anemia in children with and without sickle cell disease. Blood 2012;120:3891–7.
- Arkuszewski M, Krejza J, Chen R, et al. Sickle cell anemia: intracranial stenosis and silent cerebral infarcts in children with low risk of stroke. Adv Med Sci 2014;59:108–13.
- DeBaun MR, Gordon M, McKinstry RC, et al. Controlled trial of transfusions for silent cerebral infarcts in sickle cell anemia. N Engl J Med Overseas Ed 2014;371:699–710.
- Jordan LC, Kassim AA, Donahue MJ, et al. Silent infarct is a risk factor for infarct recurrence in adults with sickle cell anemia. Neurology 2018;91:e781–4.
- Rigano P, De Franceschi L, Sainati L, et al. Real-Life experience with hydroxyurea in sickle cell disease: a multicenter study in a cohort of patients with heterogeneous descent. Blood Cells Mol Dis 2018;69:82–9.
- DeBaun MR, Armstrong FD, McKinstry RC, Ware RE, Vichinsky E, Kirkham FJ. Silent cerebral infarcts: a review on a prevalent and progressive cause of neurologic injury in sickle cell anemia. Blood. 2012;119(20):4587-4596.
- Akinsheye I, Alsultan A, Solovieff N, et al. Fetal hemoglobin in sickle cell anemia. Blood. 2011;118:19–27.
- Allali S, Taylor M, Brice J, de Montalembert M. Chronic organ injuries in children with sickle cell disease. Haematologica. 2021;106:1535–1544.
- Kamath SD, Pai MG. A case series of hemorrhagic neurological complications of sickle cell disease: multiple faces of an underestimated problem! Asian J Transfus Sci. 2021;15:241–246.
- Hariharan N, Brunson A, Mahajan A, Keegan TH, Wun T. Bleeding in patients with sickle cell disease: a population-based study. Blood Adv. 2020;4:793–802.
- Jordan LC, Hillis AE. Hemorrhagic stroke in children. Pediatr Neurol. 2007;36:73–80.
- An SJ, Kim TJ, Yoon BW. Epidemiology, risk factors, and clinical features of intracerebral hemorrhage: an update. J Stroke. 2017;19:3–10.
- Kato GJ, Steinberg MH, Gladwin MT. Intravascular hemolysis and the pathophysiology of sickle cell disease. J Clin Invest. 2017;127:750–760.
- Preul MC, Cendes F, Just N, et al. Intracranial aneurysms and sickle cell anemia: multiplicity and propensity for the vertebrobasilar Territory. Neurosurgery 1998;42:971–7.
- Nabavizadeh SA, Vossough A, Ichord RN, et al. Intracranial aneurysms in sickle cell anemia: clinical and imaging findings. J Neurointerv Surg 2016;8:434–40.
- Brandow AM, Liem RI. Advances in the diagnosis and treatment of sickle cell disease. J Hematol Oncol. 2022;15:20.
- Steiner T, Salman RA-S, Beer R, et al. European stroke organisation (ESO) guidelines for the management of spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. Int J Stroke 2014;9:840–55.
- Yamashita M, Tanaka K, Matsuo T, et al. Cerebral dissecting aneurysms in patients with moyamoya disease. Report of two cases. J Neurosurg 1983;58:120–5.
- Oka K, Yamashita M, Sadoshima S, et al. Cerebral haemorrhage in moyamoya disease at autopsy. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol 1981;392:247–61.
- Russell MO, Goldberg HI, Hodson A, et al. Effect of transfusion therapy on arteriographic abnormalities and on recurrence of stroke in sickle cell disease. Blood 1984;63:162–9.
- Dobson SR, Holden KR, Nietert PJ, et al. Moyamoya syndrome in childhood sickle cell disease: a predictive factor for recurrent cerebrovascular events. Blood 2002;99:3144–50.
- Dlamini N, Saunders DE, Bynevelt M, et al. Nocturnal oxyhemoglobin desaturation and arteriopathy in a pediatric sickle cell disease cohort. Neurology. 2017;89:2406–2412.
- Jacob M, Saunders DE, Sangeda RZ, et al. Cerebral infarcts and vasculopathy in Tanzanian children with sickle cell anemia. Pediatr Neurol. 2020;107:64–70.
- Kaushal M, Byrnes C, Khademian Z, et al. Examination of reticulocytosis among chronically transfused children with sickle cell anemia. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0153244.
- Griessenauer CJ, Lebensburger JD, Chua MH, et al. Encephaloduroarteriosynangiosis and encephalomyoarteriosynangiosis for treatment of moyamoya syndrome in pediatric patients with sickle cell disease. J Neurosurg Pediatr 2015;16:64–73.
- Smith ER, McClain CD, Heeney M, et al. Pial synangiosis in patients with moyamoya syndrome and sickle cell anemia: perioperative management and surgical outcome. Neurosurg Focus 2009;26:E10.
- Fryer RH, Anderson RC, Chiriboga CA, et al. Sickle cell anemia with moyamoya disease: outcomes after EDAS procedure. Pediatr Neurol 2003;29:124–30.
- Lawrence C, Webb J. Sickle cell disease and stroke: diagnosis and management. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 2016;16:27.
- Hogan AM, Kirkham FJ, Isaacs EB, Wade AM, Vargha-Khadem F. Intellectual decline in children with moyamoya and sickle cell anaemia. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2005;47(12):824-829.
- Alamri A, Hever P, Cheserem J, Gradil C, Bassi S, Tolias CM. Encephaloduroateriosynangiosis (EDAS) in the management of moyamoya syndrome in children with sickle cell disease. Br J Neurosurg. 2019;33(2):161-164;
- Hall EM, Leonard J, Smith JL, et al. Reduction in overt and silent stroke recurrence rate following cerebral revascularization surgery in children with sickle cell disease and severe cerebral vasculopathy. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2016;63(8):1431-1437.
- Ng J, Thompson D, Lumley JP, Saunders DE, Ganesan V. Surgical revascularisation for childhood moyamoya. Childs Nerv Syst. 2012;28(7):1041-1048.
- Smith ER, McClain CD, Heeney M, Scott RM. Pial synangiosis in patients with moyamoya syndrome and sickle cell anemia: perioperative management and surgical outcome. Neurosurg Focus. 2009;26(4):E10.
- Winstead M, Sun PP, Martin K, et al. Encephaloduroarteriosynangiosis (EDAS) in young patients with cerebrovascular complications of sickle cell disease: Single-institution experience. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2017;34(2):100-106.
- Yang W, Xu R, Porras JL, et al. Effectiveness of surgical revascularization for stroke prevention in pediatric patients with sickle cell disease and moyamoya syndrome. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2017;20(3):232-238.
- Hankinson TC, Bohman LE, Heyer G, et al. Surgical treatment of moyamoya syndrome in patients with sickle cell anemia: outcome following encephaloduroarteriosynangiosis. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2008;1(3):211-216.
- Guilliams KP, Fields ME, Dowling MM. Advances in understanding ischemic stroke physiology and the impact of vasculopathy in children with sickle cell disease. Stroke. (2019) 50:266–73. [CrossRef]
- Lyon M, Jeter J, Lottenberg R. Approach to the diagnosis and treatment of acute subarachnoid hemorrhage in a patient with sickle cell disease. Am J Emerg Med. 2015;33:481.e3-481.e4.
- Brandao RA, de Carvalho GT, Reis BL, Bahia E, de Souza AA. Intracranial aneurysms in sickle cell patients: report of 2 cases and review of the literature. Surg Neurol. 2009;72:296-299.
- Yao Z, Li J, He M, You C. Intracranial Aneurysm in Patients with Sickle Cell Disease: A Systematic Review. World Neurosurg. 2017 Sep;105:302-313. [CrossRef]
- Saini S, Speller-Brown B, Wyse E, Meier ER, Carpenter J, Fasano RM, et al. Unruptured intracranial aneurysms in children with sickle cell disease: analysis of 18 aneurysms in 5 patients. Neurosurgery. 2015;76:531-538.
- Kirkham FJ. Therapy insight: stroke risk and its management in patients with sickle cell disease. Nat Clin Pract Neurol. 2007;3:264–278.
- Stotesbury H, Kawadler JM, Saunders DE, Kirkham FJ. MRI detection of brain abnormality in sickle cell disease. Expert Rev Hematol. 2021 May;14(5):473-491. [CrossRef]
- Adams RJ, Nichols FT, McKie V, McKie K, Milner P, Gammal TE. Cerebral infarction in sickle cell anemia: mechanism based on CT and MRI. Neurology. (1988) 38:1012–7. [CrossRef]
- Pavlakis SG, Bello J, Prohovnik I, Sutton M, Ince C, Mohr JP, et al. Brain infarction in sickle cell anemia: magnetic resonance imaging correlates. Ann Neurol. (1988) 23:125–30. [CrossRef]
- Guilliams KP, Fields ME, Ragan DK, Chen Y, Eldeniz C, Hulbert ML, et al. Large-vessel vasculopathy in children with sickle cell disease: a magnetic resonance imaging study of infarct topography and focal atrophy. Pediatr Neurol. (2017) 69:49–57. [CrossRef]
- Dowling MM, Kirkham FJ. Stroke in sickle cell anaemia is more than stenosis and thrombosis: the role of anaemia and hyperemia in ischaemia. Br J Haematol. (2017) 176:151–3. [CrossRef]
- Cancio MI, Helton KJ, Schreiber JE, Smeltzer MP, Kang G, Wang WC. Silent cerebral infarcts in very young children with sickle cell anaemia are associated with a higher risk of stroke. Br J Haematol. (2015) 171:120–9. [CrossRef]
- Wang WC, Langston JW, Steen RG, Wynn LW, Mulhern RK, Wilimas JA, et al. Abnormalities of the central nervous system in very young children with sickle cell anemia. J Pediatr. (1998) 132:994–8. [CrossRef]
- Kwiatkowski JL, Zimmerman RA, Pollock AN, Seto W, Smith-Whitley K, Shults J, et al. Silent infarcts in young children with sickle cell disease. Br J Haematol. (2009) 146:300–5. [CrossRef]
- Pegelow CH, Macklin EA, Moser FG, Wang WC, Bello JA, Miller ST, et al. Longitudinal changes in brain magnetic resonance imaging findings in children with sickle cell disease. Blood. (2002) 99:3014–8. [CrossRef]
- Wang W, Enos L, Gallagher D, Thompson R, Guarini L, Vichinsky E, et al. Neuropsychologic performance in school-aged children with sickle cell disease: a report from the cooperative study of sickle cell disease. J Pediatr. (2001) 139:391–7. [CrossRef]
- DeBaun MR, Gordon M, McKinstry RC, et al. Controlled trial of transfusions for silent cerebral infarcts in sickle cell anemia. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(8):699-710.
- Choudhury NA, DeBaun MR, Rodeghier M, King AA, Strouse JJ, McKinstry RC. Silent cerebral infarct definitions and full-scale IQ loss in children with sickle cell anemia. Neurology. 2018;90(3):e239-e246.
- Jordan LC, Kassim AA, Donahue MJ, et al. Silent infarct is a risk factor for infarct recurrence in adults with sickle cell anemia. Neurology. 2018;91(8):e781-e784.
- Vichinsky EP, Neumayr LD, Gold JI, et al.; Neuropsychological Dysfunction and Neuroimaging Adult Sickle Cell Anemia Study Group. Neuropsychological dysfunction and neuroimaging abnormalities in neurologically intact adults with sickle cell anemia. JAMA. 2010;303(18):1823-1831.
- Kawadler JM, Clayden JD, Kirkham FJ, Cox TC, Saunders DE, Clark CA. Subcortical and cerebellar volumetric deficits in paediatric sickle cell anaemia. Br J Haematol. (2013) 163:373–6. [CrossRef]
- Kim JA, Leung J, Lerch JP, Kassner A. Reduced cerebrovascular reserve is regionally associated with cortical thickness reductions in children with sickle cell disease. Brain Res. (2016) 1642:263–9. [CrossRef]
- Kirk GR, Haynes MR, Palasis S, Brown C, Burns TG, McCormick M, et al. Regionally specific cortical thinning in children with sickle cell disease. Cereb Cortex. (2009) 19:1549–56. [CrossRef]
- Mackin RS, Insel P, Truran D, Vichinsky EP, Neumayr LD, Armstrong FD, et al. Neuroimaging abnormalities in adults with sickle cell anemia: associations with cognition. Neurology. (2014) 82:835–41. [CrossRef]
- Baldeweg T, Hogan AM, Saunders DE, Telfer P, Gadian DG, Vargha-Khadem F, et al. Detecting white matter injury in sickle cell disease using voxel-based morphometry. Ann Neurol. (2006) 59:662–72. [CrossRef]
- Choi S, Bush AM, Borzage MT, Joshi AA, Mack WJ, Coates TD, et al. Hemoglobin and mean platelet volume predicts diffuse T1-MRI white matter volume decrease in sickle cell disease patients. NeuroImage Clin. (2017) 15:239–46. [CrossRef]
- Schatz J, Buzan R. Decreased corpus callosum size in sickle cell disease: relationship with cerebral infarcts and cognitive functioning. J Int Neuropsychol Soc. (2006) 12:24–33. [CrossRef]
- Chen R, Arkuszewski M, Krejza J, Zimmerman RA, Herskovits EH, Melhem ER. A prospective longitudinal brain morphometry study of children with sickle cell disease. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. (2015) 36:403–10. [CrossRef]
- Darbari DS, Eigbire-Molen O, Ponisio MR, Milchenko MV, Rodeghier MJ, Casella JF, et al. Progressive loss of brain volume in children with sickle cell anemia and silent cerebral infarct: a report from the silent cerebral infarct transfusion trial. Am J Hematol. (2018) 93:E406–8. [CrossRef]
- Kawadler JM, Clark CA, McKinstry RC, Kirkham FJ. Brain atrophy in paediatric sickle cell anaemia: findings from the silent infarct transfusion (SIT) trial. Br J Haematol. (2017) 177:151–3. [CrossRef]
- Balci A, Karazincir S, Beyoglu Y, Cingiz C, Davran R, Gali E, et al. Quantitative brain diffusion-tensor MRI findings in patients with sickle cell disease. AJR Am J Roentgenol. (2012) 198:1167–74. [CrossRef]
- Chai Y, Coloigner J, Qu X, Choi S, Bush A, Borzage M, et al. Tract specific analysis in patients with sickle cell disease. Proc SPIE Int Soc Opt Eng. (2015) 9681:968108. [CrossRef]
- Choi S, Bush AM, Borzage M, Joshi A, Coates TD, Leahy R, et al. Regional susceptibility to chronic anemia in WM microstructure using diffusion tensor imaging. Blood. (2016) 128:3640.
- Kawadler JM, Kirkham FJ, Clayden JD, Hollocks MJ, Seymour EL, Edey R, et al. White matter damage relates to oxygen saturation in children with sickle cell anemia without silent cerebral infarcts. Stroke. (2015) 46:1793–9. [CrossRef]
- Sun B, Brown RC, Hayes L, Burns TG, Huamani J, Bearden DJ, et al. White matter damage in asymptomatic patients with sickle cell anemia: screening with diffusion tensor imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. (2012) 33:2043–9. [CrossRef]
- Stotesbury H, Kirkham FJ, Kölbel M, Balfour P, Clayden JD, Sahota S, et al. White matter integrity and processing speed in sickle cell anemia. Neurology. (2018) 90:e2042–50. [CrossRef]
- Birkeland P, Gardner K, Kesse-Adu R, et al. Intracranial aneurysms in sickle-cell disease are associated with the hemoglobin SS genotype but not with moyamoya syndrome. Stroke. 2016;47:1710–1713.
- Hamm J, Rathore N, Lee P, et al. Cranial epidural hematomas: a case series and literature review of this rare complication associated with sickle cell disease. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2017;64:64.
- Saha B, Saha A. spontaneous epidural hemorrhage in sickle cell disease, Are they all the same? A case report and comprehensive review of the literature. Case Rep Hematol. 2019:8974580.
- Mitchell P, Wilkinson I, Hoggard N, et al. Detection of subarachnoid haemorrhage with magnetic resonance imaging. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2001;70:205-11.
- Chalela JA, Kidwell CS, Nentwich LM, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography in emergency assessment of patients with suspected acute stroke: a prospective comparison. Lancet (London, England) 2007;369:293-8.
- Verma RK, Kottke R, Andereggen L, et al. Detecting subarachnoid hemorrhage: comparison of combined FLAIR/SWI versus CT. Eur J Radiol 2013;82:1539-45.
- Kidwell CS, Chalela JA, Saver JL, et al. Comparison of MRI and CT for detection of acute intracerebral hemorrhage. JAMA 2004;292:1823-30.
- Kang BK, Na DG, Ryoo JW, et al. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of intracerebral hemorrhage. Korean J Radiol 2001:2;183-91.
- Kija EN, Saunders DE, Munubhi E, et al. Transcranial Doppler and magnetic resonance in Tanzanian children with sickle cell disease. Stroke 2019;50:1719-26.
- Novelli EM, Elizabeth Sarles C, Jay Aizenstein H, et al. Brain venular pattern by 7T MRI correlates with memory and haemoglobin in sickle cell anaemia. Psychiatry Res 2015;233:18-22.
- Guilliams KP, Fields ME, Dowling MM. Advances in understanding ischemic stroke physiology and the impact of vasculopathy in children with sickle cell disease. Stroke. (2019) 50:266–73. [CrossRef]
- Seeler RA, Royal JE, Powe L, Goldberg HR. Moyamoya in children with sickle cell anemia and cerebrovascular occlusion. J Pediatr. (1978) 93:808–10. [CrossRef]
- Powars D, Adams RJ, Nichols FT, Milner P, Charache S, Sarnaik S. Delayed intracranial hemorrhage following cerebral infarction in sickle cell anemia. J Assoc Acad Minor Phys. (1990) 1:79–82.
- Kassim AA, Galadanci NA, Pruthi S, DeBaun MR. How I treat and manage strokes in sickle cell disease. Blood. (2015) 125:3401–10. [CrossRef]
- Buch K, Arya R, Shah B, Nadgir RN, Saito N, Qureshi MM, et al. Quantitative analysis of extracranial arterial tortuosity in patients with sickle cell disease. J Neuroimaging. (2017) 27:421–27. [CrossRef]
- Hyacinth HI, Sugihara CL, Spencer TL, Archer DR, Shih AY. Higher prevalence of spontaneous cerebral vasculopathy and cerebral infarcts in a mouse model of sickle cell disease. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. (2019) 39:342–51. [CrossRef]
- Steen RG, Langston JW, Ogg RJ, Manci E, Mulhern RK, Wang W. Ectasia of the basilar artery in children with sickle cell disease: relationship to hematocrit and psychometric measures. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. (1998) 7:32–43. [CrossRef]
- Steen RG, Reddick WE, Glass JO, Wang WC. Evidence of cranial artery ectasia in sickle cell disease patients with ectasia of the basilar artery. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. (1998) 7:330–8. [CrossRef]
- Kossorotoff M, Brousse V, Grevent D, Naggara O, Brunelle F, Blauwblomme T, et al. Cerebral haemorrhagic risk in children with sickle-cell disease. Dev Med Child Neurol. (2015) 57:187–93. [CrossRef]
- Koshy M, Thomas C, Goodwin J. Vascular lesions in the central nervous system in sickle cell disease (neuropathology). J Assoc Acad Minor Phys. (1990) 1:71–8. 50.
- Oyesiku NM, Barrow DL, Eckman JR, Tindall SC, Colohan AR. Intracranial aneurysms in sickle-cell anemia: clinical features and pathogenesis. J Neurosurg. (1991) 75:356–63. [CrossRef]
- Connes P, Verlhac S, Bernaudin F. Advances in understanding the pathogenesis of cerebrovascular vasculopathy in sickle cell anaemia. Br J Haematol. (2013) 161:484–98. [CrossRef]
- Russell MO, Goldberg HI, Hodson A, et al. Effect of transfusion therapy on arteriographic abnormalities and on recurrence of stroke in sickle cell disease. Blood. 1984;63:162–169.
- Helton KJ, Adams RJ, Kesler KL, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging/angiography and transcranial Doppler velocities in sickle cell anemia: results from the SWiTCH trial. Blood. 2014;124:891–898.
- Dlamini N, Saunders DE, Bynevelt M, et al. Nocturnal oxyhemoglobin desaturation and arteriopathy in a pediatric sickle cell disease cohort. Neurology. 2017;89:2406–2412.
- Guilliams KP, Fields ME, Ragan DK, et al. Large-vessel vasculopathy in children with sickle cell disease: a magnetic resonance imaging study of infarct topography and focal atrophy. Pediatric Neurology. 2017;69:49–57.
- Montanaro M, Colombatti R, Pugliese M, et al. Intellectual function evaluation of first generation immigrant children with sickle cell disease: the role of language and sociodemographic factors. Ital J Pediatr. 2013;39:36.
- Nottage KA, Ware RE, Aygun B, et al. Hydroxycarbamide treatment and brain MRI/MRA findings in children with sickle cell anaemia. Br J Haematol. 2016;175:331–338.
- Green NS, Munube D, Bangirana P, et al. Burden of neurological and neurocognitive impairment in pediatric sickle cell anemia in Uganda (BRAIN SAFE): a cross-sectional study. BMC Pediatr. 2019;19:381.
- Kija EN, Saunders DE, Munubhi E, et al. Transcranial doppler and magnetic resonance in Tanzanian children with sickle cell disease. Stroke. 2019;50:1719–1726.
- Husson B, Rodesch G, Lasjaunias P, et al. Magnetic resonance angiography in childhood arterial brain infarcts: a comparative study with contrast angiography. Stroke. 2002;33:1280–1285.
- Kandeei AY, Zimmerman RA, Ohcnc-Frempong K, et al. Comparison of magnetic resonance angiography and conventional angiography in sickle cell disease: clinical significance and reliability. Diagnostic Neuroradiol. 199638:409-16.
- Husson B, Lasjaunias P. Radiological approach to disorders of arterial brain vessels associated with childhood arterial stroke - A comparison between MRA and contrast angiography. Pediatr Radiol. 2004;34:10–15.
- Mori N, Mugikura S, Higano S, et al. The leptomeningeal “ivy sign” on fluid-attenuated inversion recovery MR imaging in moyamoya disease: a sign of decreased cerebral vascular reserve? Am J Neuroradiol 2009;30:930-5.
- Maeda M, Tsuchida C. “Ivy sign” on fluid-attenuated inversion recovery images in childhood moyamoya disease. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1999;20:1836-8.
- Telfer PT, Evanson J, Butler P, et al. Cervical carotid artery disease in sickle cell anemia: clinical and radiological features. Blood. 2011;118:6192–6199.
- Rinne J, Hernesniemi J, Puranen M, et al. Multiple intracranial aneurysms in a defined population: prospective angiographic and clinical study. Neurosurgery 1994;35:803-8.
- Sailer AMH, Wagemans BAJM, Nelemans PJ, et al. Diagnosing intracranial aneurysms with MR angiography: systematic review and meta-analysis. Stroke 2014;45:119-26.
- Buonanno FS, Schmahmann JD, Romero JM, et al. Case records of the Massachusetts General Hospital. Case 10–2016. A 22-year-old man with sickle cell disease, headache, and difficulty speaking. N Engl J Med 2016;374:1265-7.
- Gallas S, Tuilier T, Ebrahiminia V, et al. Intracranial aneurysms in sickle cell disease: aneurysms characteristics and modalities of endovascular approach to treat these patients. J Neuroradiol 2019;47:221-6.
- Winchell AM, Taylor BA, Song R, et al. Evaluation of SWI in children with sickle cell disease. Am J Neuroradiol. 2014;39:1016–1021.
- Novelli EM, Sarles C, Aizenstein J, et al. Brain venular pattern by 7T MRI correlates with memory and haemoglobin in sickle cell anaemia. Psychiatry Res – Neuroimaging. 2015;233:18–22.
- Adler K, Reghunathan A, Hutchison LH, et al. Dural venous sinus diameters in children with sickle cell disease: correlation with history of stroke in a case-control study. South Med J. 2016;109:511–515.
- Ciurea SO, Thulborn KR, Gowhari M. Dural venous sinus thrombosis in a patient with sickle cell disease: case report and literature review. Am J Hematol 2006;81:290–293.
- Sidani CA, Ballourah W, El Dassouki M, et al. Venous sinus thrombosis leading to stroke in a patient with sickle cell disease on hydroxyurea and high hemoglobin levels: treatment with thrombolysis. Am J Hematol. 2008;83:818–820.
- Wang MK, Shergill R, Jefkins M, et al. A sickle cell disease patient with dural venous sinus thrombosis: a case report and literature review. Hemoglobin. 2019;43:193–197.
- Sébire G, Tabarki B, Saunders DE, et al. Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis in children: risk factors, presentation, diagnosis and outcome. Brain. 2005;128:477–489.
- Adams RJ, Brambilla D. Optimizing primary stroke prevention in sickle cell anemia trial I. discontinuing prophylactic transfusions used to prevent stroke in sickle cell disease. N Engl J Med 2005;353:2769–78.
- Abboud MR, Yim E, Musallam KM, et al. Discontinuing prophylactic transfusions increases the risk of silent brain infarction in children with sickle cell disease: data from stop II. Blood 2011;118:894–8.
- Rankine-Mullings A, Reid M, Soares D, et al. Hydroxycarbamide treatment reduces transcranial Doppler velocity in the absence of transfusion support in children with sickle cell anaemia, elevated transcranial Doppler velocity, and cerebral vasculopathy: the EXTEND trial. Br J Haematol 2021;195:612–20.
- Abdullahi SU, Jibir BW, Bello-Manga H, et al. Hydroxyurea for primary stroke prevention in children with sickle cell anaemia in Nigeria (spring): a double-blind, multicentre, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Haematol 2022;9:e26–37.
- Valadi N, Silva GS, Bowman LS, et al. Transcranial Doppler ultrasonography in adults with sickle cell disease. Neurology 2006;67:572–4.
- Haematology GBSf. An audit of compliance with the British Society for haematology (BSH) guideline on red cell transfusion in sickle cell disease (SCD). Part II: indications for transfusion; 2016.
- Lawrence C, Webb J. Sickle cell disease and stroke: diagnosis and management. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 2016;16:27.
- Mack AK, Thompson AA. Primary and secondary stroke prevention in children with sickle cell disease. J Pediatr Health Care 2017;31:145–54.
- Chou ST, Fasano RM. Management of patients with sickle cell disease using transfusion therapy: guidelines and complications. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am 2016;30:591–608.
- Ware RE, Davis BR, Schultz WH, et al. Hydroxycarbamide versus chronic transfusion for maintenance of transcranial Doppler flow velocities in children with sickle cell anaemia—TCD with transfusions changing to hydroxyurea (twitch): a multicentre, open-label, phase 3, non-inferiority trial. The Lancet 2016;387:661–70.
- Galadanci NA, Umar Abdullahi S, Vance LD, et al. Feasibility trial for primary stroke prevention in children with sickle cell anemia in Nigeria (SPIN trial). Am J Hematol. 2017;92(8):780-788.
- Brambilla DJ, Miller ST, Adams RJ. Intra-individual variation in blood flow velocities in cerebral arteries of children with sickle cell disease. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2007;49(3):318-322.
- Day ME, Rodeghier M, Driggers J, Bean CJ, Volanakis EJ, DeBaun MR. A significant proportion of children of African descent with HbSb0 thalassaemia are inaccurately diagnosed based on phenotypic analyses alone. Br J Haematol. 2019;185(1):153-156.
- Venketasubramanian N, Prohovnik I, Hurlet A, Mohr JP, Piomelli S. Middle cerebral artery velocity changes during transfusion in sickle cell anemia. Stroke. 1994;25(11):2153-2158.
- Enninful-Eghan H, Moore RH, Ichord R, Smith-Whitley K, Kwiatkowski JL. Transcranial Doppler ultrasonography and prophylactic transfusion program is effective in preventing overt stroke in children with sickle cell disease. J Pediatr. 2010;157(3):479-484.
- Gage BF, Waterman AD, Shannon W, Boechler M, Rich MW, Radford MJ. Validation of clinical classification schemes for predicting stroke: results from the National Registry of Atrial Fibrillation. JAMA. 2001;285(22):2864-2870.
- Kilonzi, M.; Mlyuka, H.J.; Felician, F.F.; Mwakawanga, D.L.; Chirande, L.; Myemba, D.T.; Sambayi, G.; Mutagonda, R.F.; Mikomangwa, W.P.; Ndunguru, J.; et al. Barriers and Facilitators of Use of Hydroxyurea among Children with Sickle Cell Disease: Experiences of Stakeholders in Tanzania. Hemato 2021, 2, 713–726. [CrossRef]
- Fome, A.D.; Sangeda, R.Z.; Balandya, E.; Mgaya, J.; Soka, D.; Tluway, F.; Masamu, U.; Nkya, S.; Makani, J.; Mmbando, B.P. Hematological and Biochemical Reference Ranges for the Population with Sickle Cell Disease at Steady State in Tanzania. Hemato 2022, 3, 82-97. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Dahiya, A.; Alavi, A.; Woldie, I.; Sharma, A.; Karson, J.; Singh, V. Patterns of Blood Transfusion in Sickle Cell Disease Hospitalizations. Hemato 2024, 5, 26-34. [CrossRef]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).