Submitted:
03 July 2024
Posted:
03 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Methods
Study Population
Treatment and Follow-Up Examination
Statistical Analysis
Results
Patient Characteristics
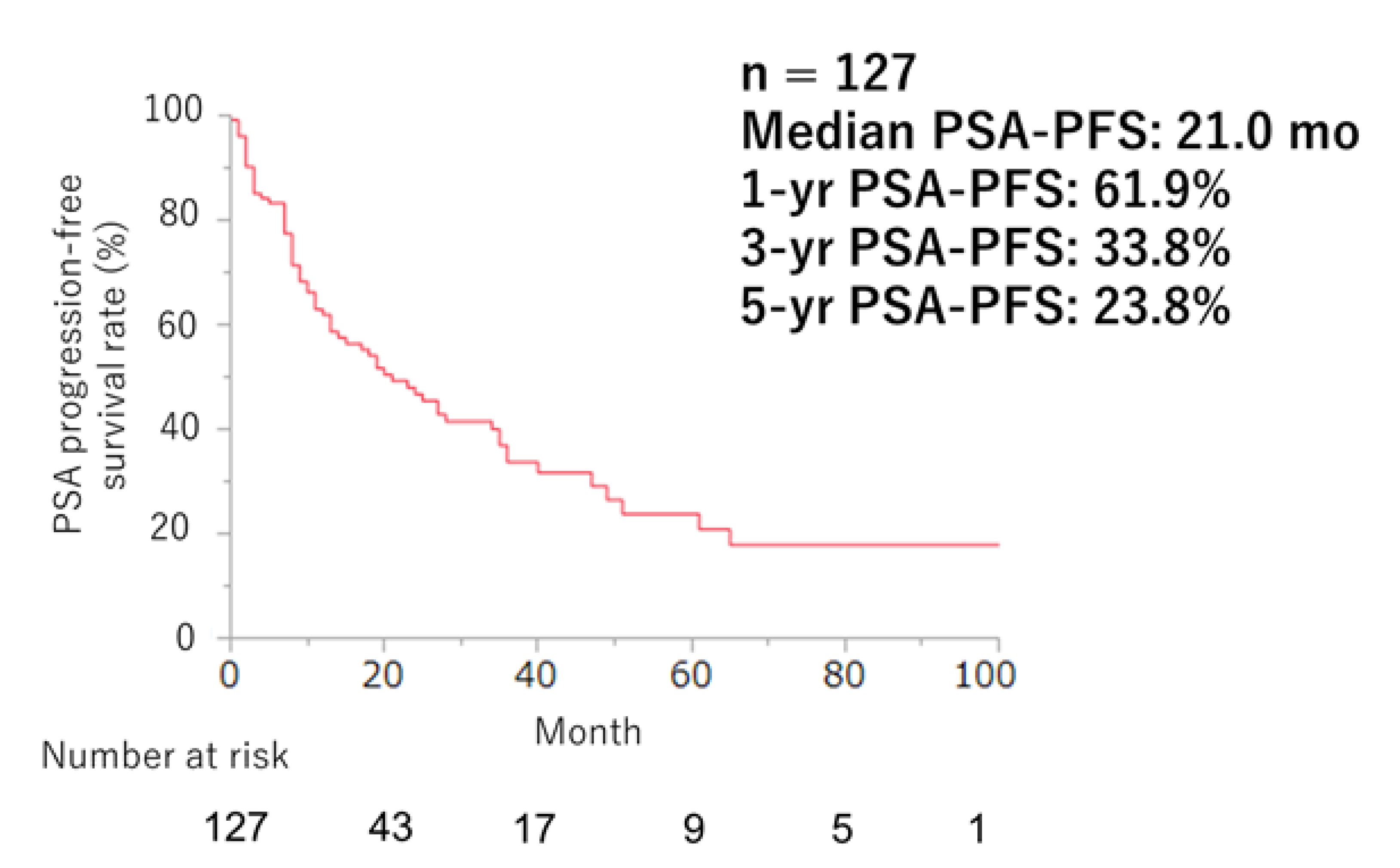
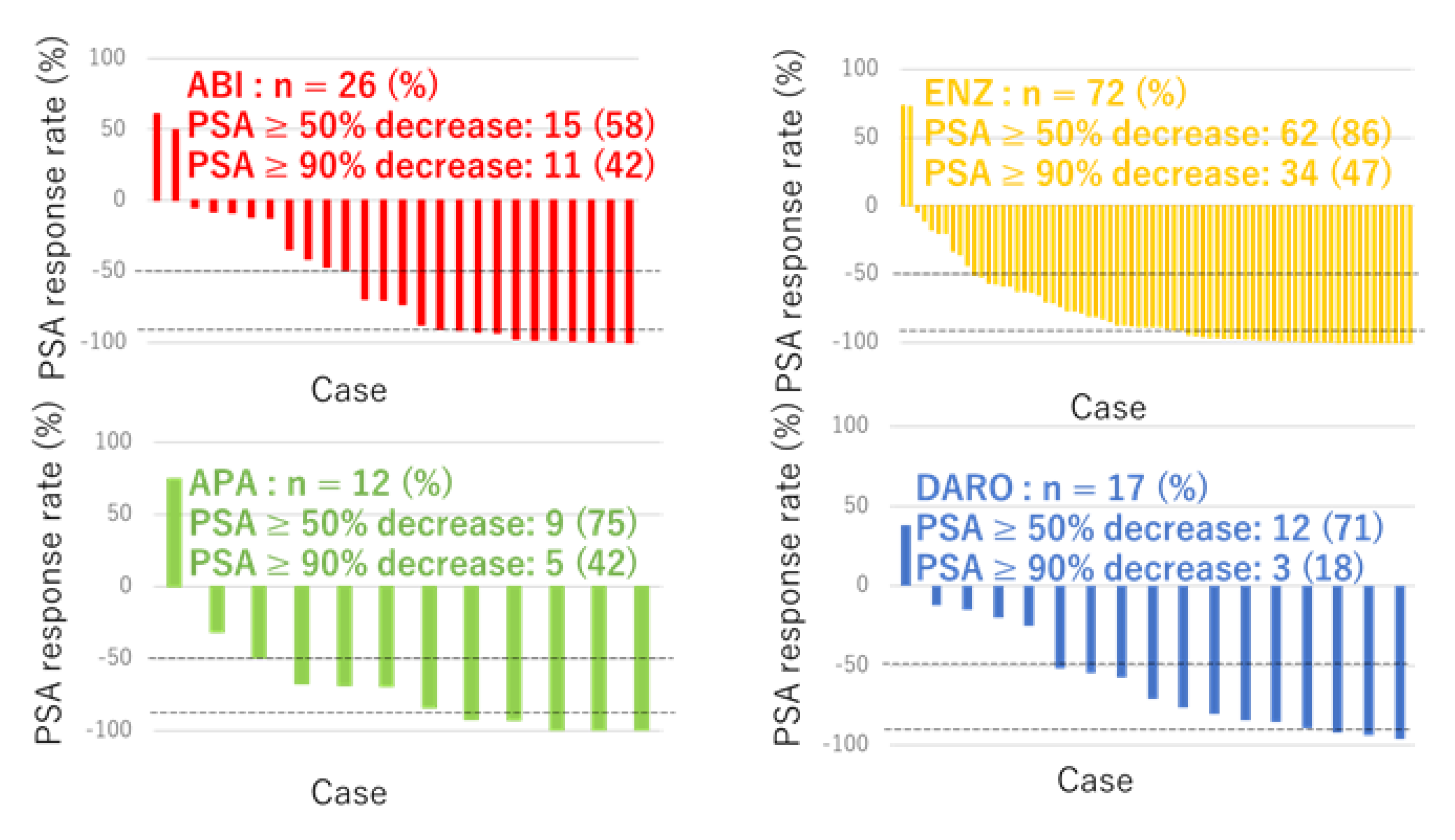
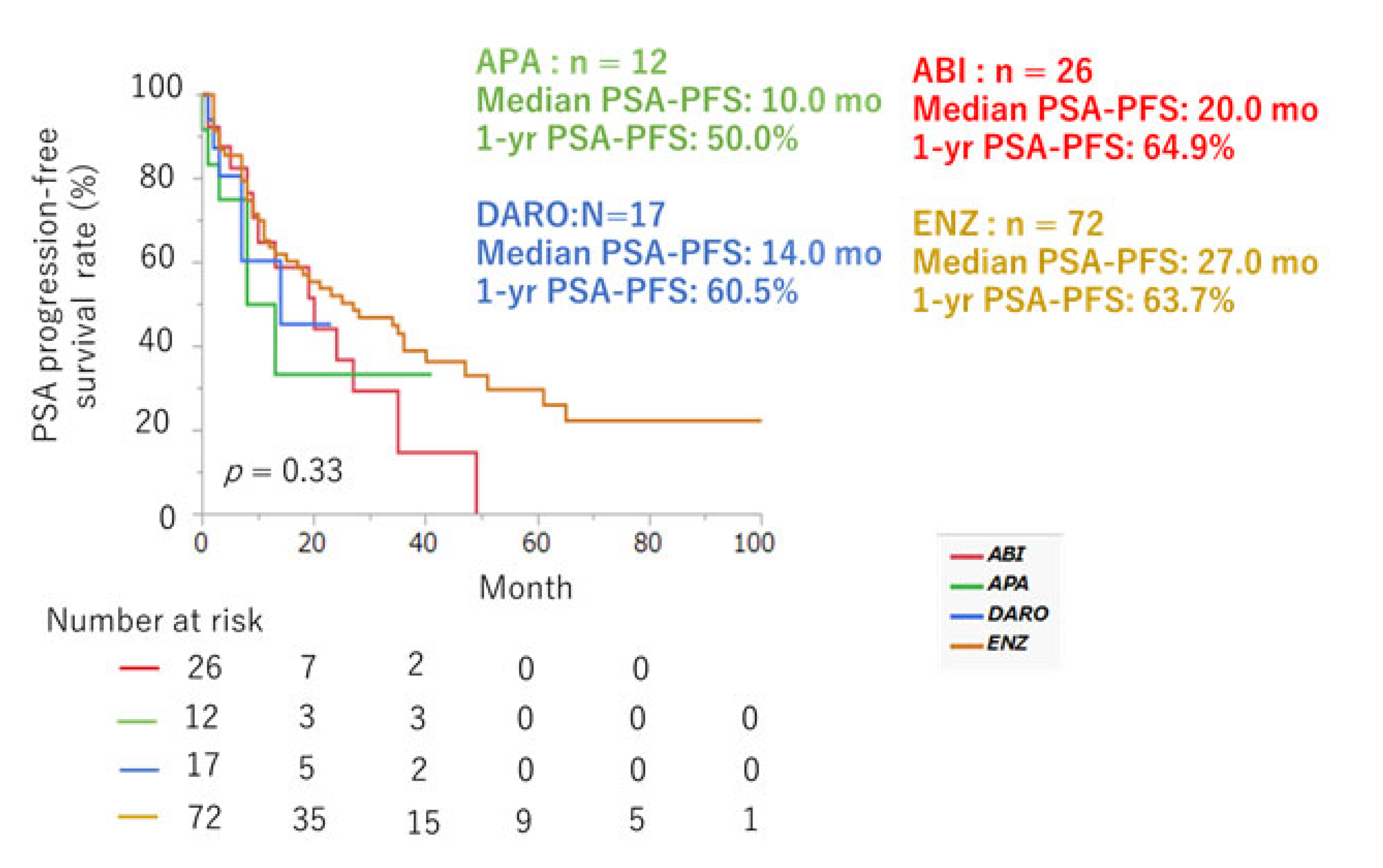
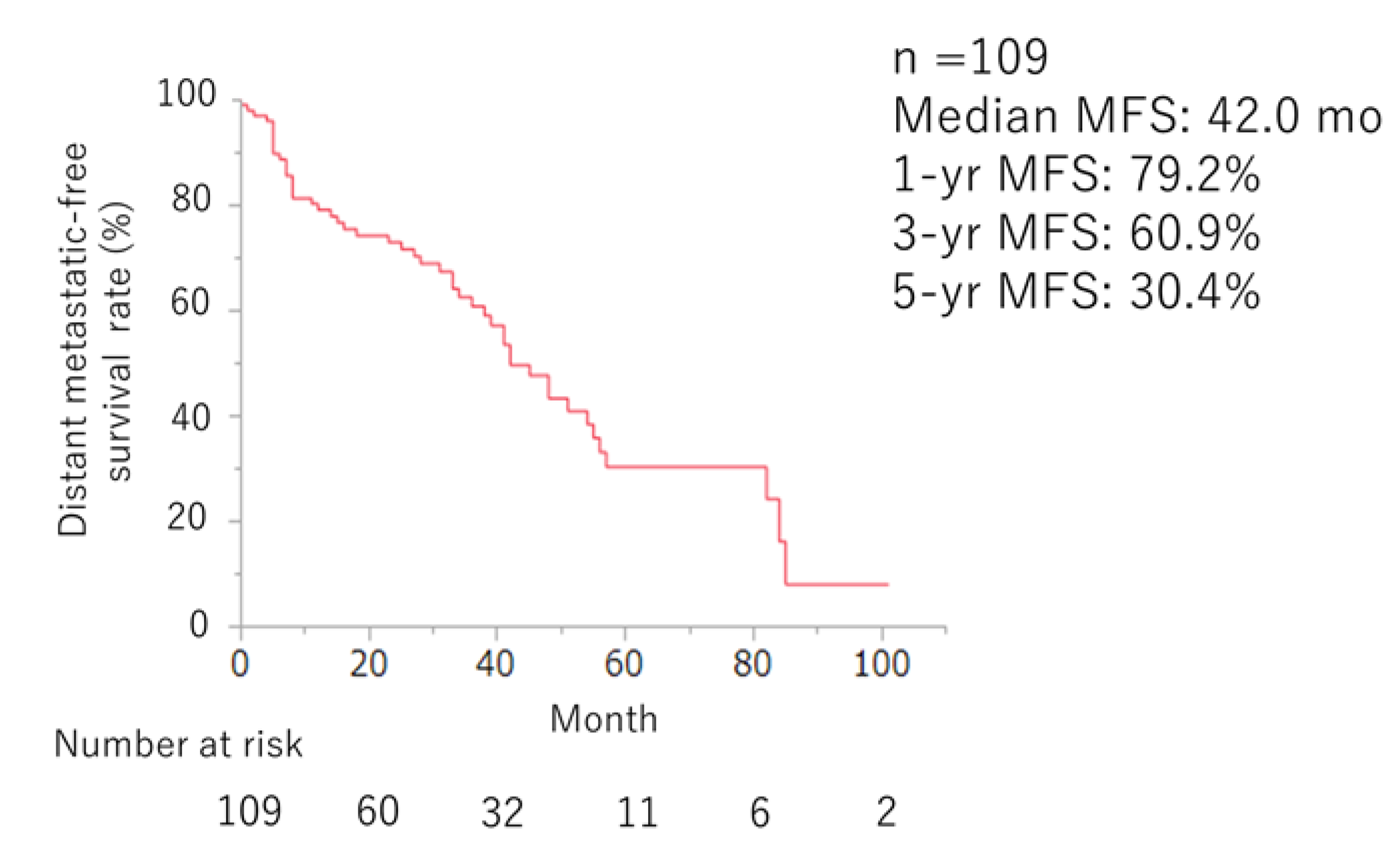
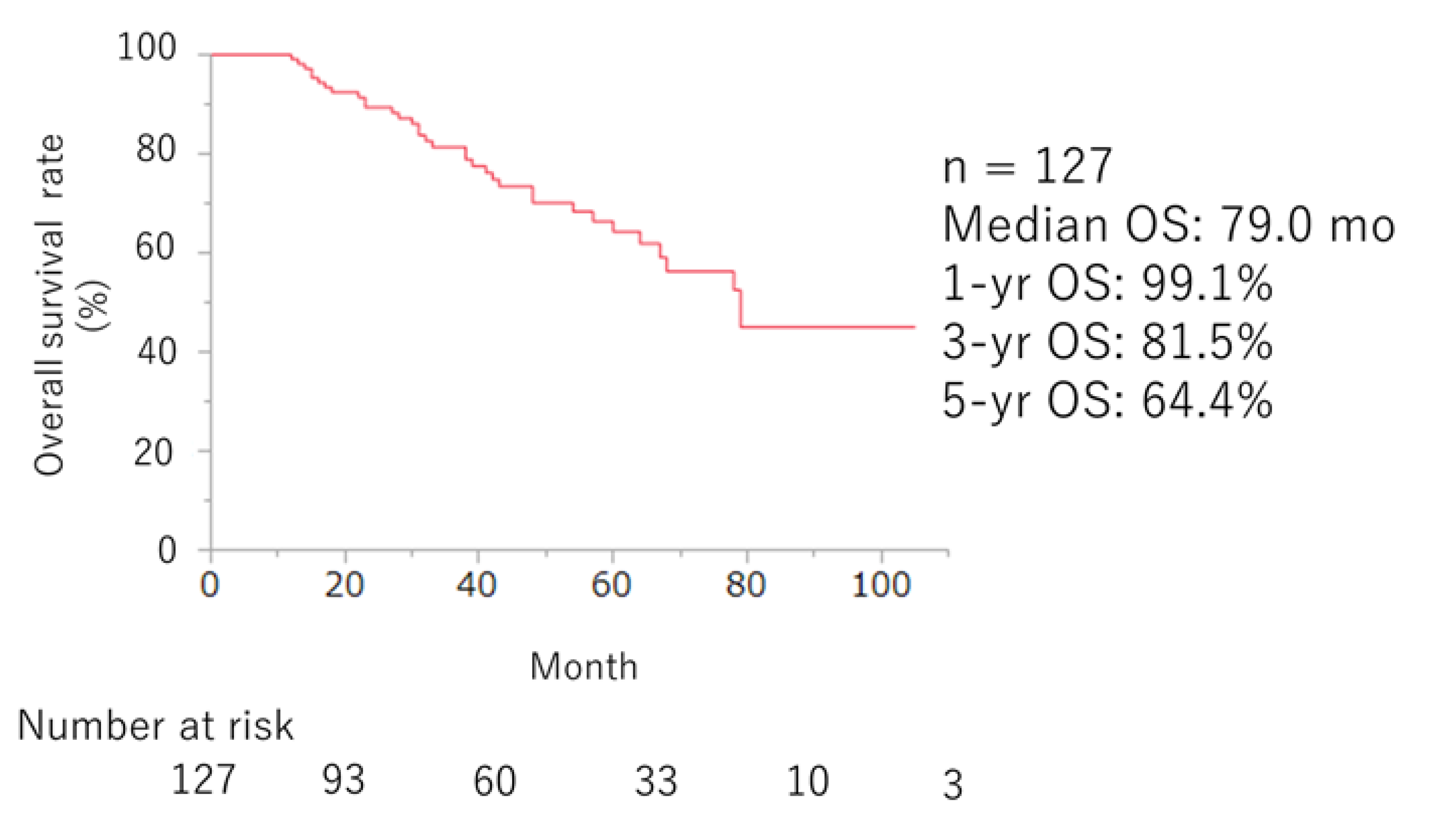
Efficacy of ARSI Therapy
Safety of ARSI Therapy
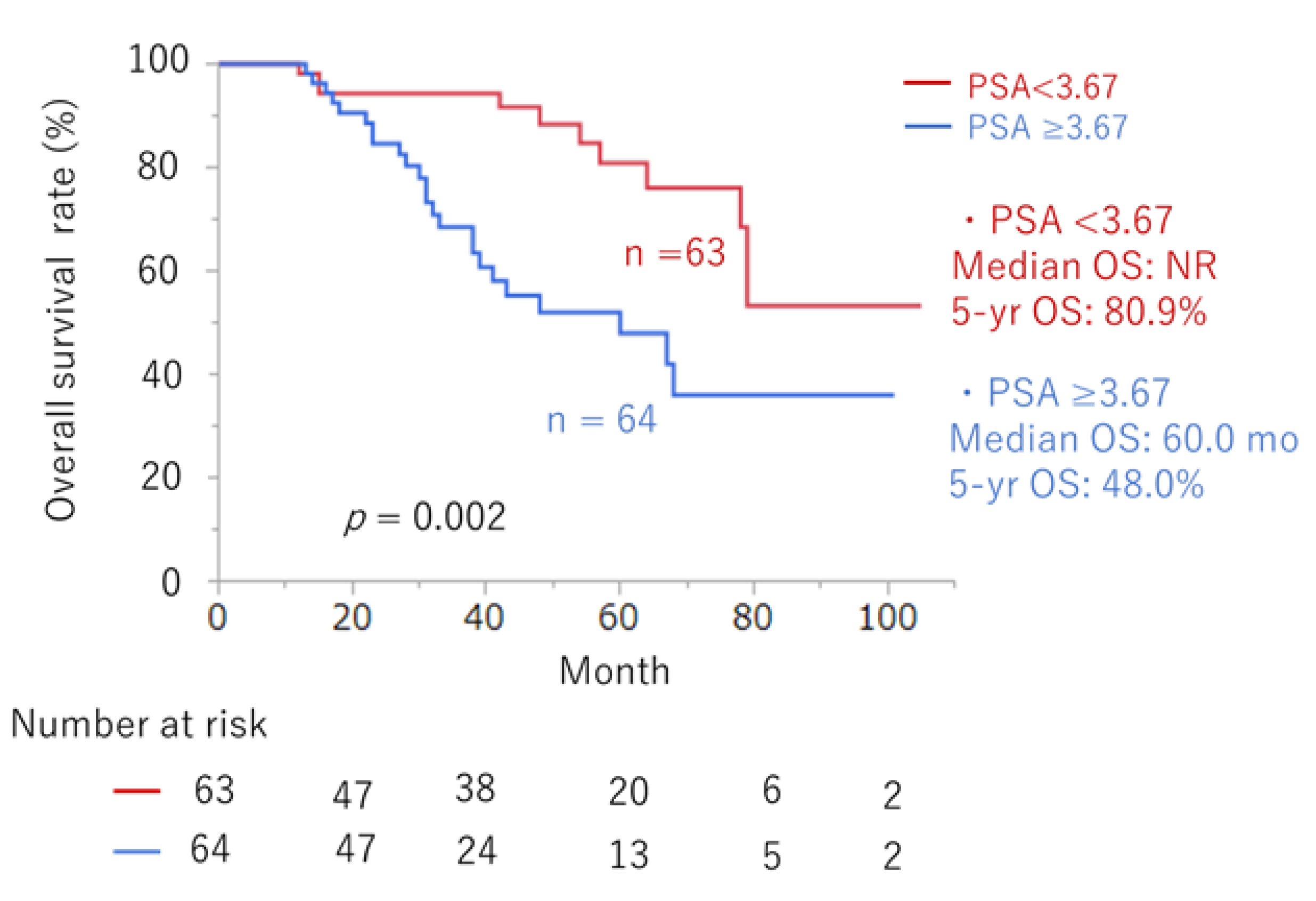
Predictors of Prognosis in ARSI Therapy
Discussion
Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional review board statement
Informed consent statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of interest
References
- Bergengren O; Pekala KR; Matsoukas K; Fainberg J; Mungovan SF; Bratt O; Bray F; Brawley O; Luckenbaugh AN; Mucci L; et al. 2022 update on prostate cancer epidemiology and risk factors-A systematic review. Eur Urol. 2023, Aug;84(2), 191-206. [CrossRef]
- Zumsteg ZS; Spratt DE; Romesser PB; Pei X; Zhang Z; Polkinghorn W; McBride S; Kollmeier M; Yamada Y; Zelefsky MJ. The natural history and predictors of outcome following biochemical relapse in the dose escalation era for prostate cancer patients undergoing definitive external beam radiotherapy. Eur Urol. 2015, Jun;67(6), 1009–1016. [CrossRef]
- Boorjian SA; Thompson RH; Tollefson MK; Rangel LJ; Bergstralh EJ; Blute ML; Karnes RJ. Long-term risk of clinical progression after biochemical recurrence following radical prostatectomy: The impact of time from surgery to recurrence. Eur Urol. 2011, Jun;59(6), 893–899. [CrossRef]
- Kluth LA; Shariat SF; Kratzik C; Tagawa S; Sonpavde G; Rieken M; Scherr DS; Pummer K. The hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis and prostate cancer: Implications for androgen deprivation therapy. World J Urol. 2014, Jun;32(3), 669–676. [CrossRef]
- Aly M; Hashim M; Heeg B; Liwing J; Leval A; Mehra M; Lawson J; Brookman-May SD; Akre O. Time-to-event outcomes in men with nonmetastatic castrate-resistant prostate cancer-A systematic literature review and pooling of individual participant data. Eur Urol Focus. 2019, Sep;5(5), 788–798. [CrossRef]
- Smith MR; Saad F; Chowdhury S; Oudard S; Hadaschik BA; Graff JN; Olmos D; Mainwaring PN; Lee JY; Uemura H; et al. Apalutamide and overall survival in prostate cancer. Eur Urol. 2021, Jan;79(1), 150–158.
- Fizazi K; Shore N; Tammela TL; Ulys A; Vjaters E; Polyakov S; Jievaltas M; Luz M; Alekseev B; Kuss I; et al. ARAMIS Investigators. Nonmetastatic, castration-resistant prostate cancer and survival with darolutamide. N Engl J Med. 2020, Sep 10, 383(11), 1040–1049.
- Sternberg CN; Fizazi K; Saad F; Shore ND; De Giorgi U; Penson DF; Ferreira U; Efstathiou E; Madziarska K; Kolinsky MP; et al. Enzalutamide and survival in nonmetastatic, castration-resistant prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2020, Jun 4, 382(23), 2197–2206.
- Schaeffer EM; Srinivas S; Adra N; An Y; Barocas D; Bitting R; Bryce A; Chapin B; Cheng HH; D’Amico AV; et al. Prostate Cancer, Version 4.2023, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2023, Oct;21(10), 1067–1096.
- Miyake H; Matsushita Y; Watanabe H; Tamura K; Motoyama D; Ito T; Sugiyama T; Otsuka A. Comparative assessment of prognostic outcomes between first-generation antiandrogens and novel androgen-receptor-axis-targeted agents in patients with non-metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Int J Clin Oncol. 2019, Jul;24(7), 842–847.
- Fujita N; Hatakeyama S; Tabata R; Okita K; Kido K; Hamano I; Tanaka T; Noro D; Tokui N; Suzuki Y; et al. Real-world effects of novel androgen receptor axis-targeted agents on oncological outcomes in non-metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: A multi-institutional retrospective study. Prostate Int. 2024, Mar;12(1), 46–51.
- Howard LE; Moreira DM; De Hoedt A; Aronson WJ; Kane CJ; Amling CL; Cooperberg MR; Terris MK; Freedland SJ. Thresholds for PSA doubling time in men with non-metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. BJU Int. 2017, Nov;120(5B), E80–E86.
- Scher HI; Morris MJ; Stadler WM; Higano C; Basch E; Fizazi K; Antonarakis ES; Beer TM; Carducci MA; Chi KN; et al. Prostate Cancer Clinical Trials Working Group 3. Trial design and objectives for castration-resistant prostate cancer: Updated recommendations from the Prostate Cancer Clinical Trials Working Group 3. J Clin Oncol. 2016, Apr 20, 34(12), 1402–18.
- Pound CR; Partin AW; Eisenberger MA; Chan DW; Pearson JD; Walsh PC. Natural history of progression after PSA elevation following radical prostatectomy. JAMA. 1999, May 5, 281(17), 1591–7.
- Ryan CJ; Crawford ED; Shore ND; Underwood W 3rd; Taplin ME; Londhe A; Francis PSJ; Phillips J; McGowan T; Kantoff PW. The IMAAGEN Study: Effect of abiraterone acetate and prednisone on prostate specific antigen and radiographic disease progression in patients with nonmetastatic castration resistant prostate cancer. J Urol. 2018, Aug;200(2), 344–352.
- Yokomizo A; Yonese J; Egawa S; Fukuhara H; Uemura H; Nishimura K; Nagata M; Saito A; Lee T; Yamaguchi S; et al. Correction to: Real-world use of enzalutamide in men with nonmetastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer in Japan. Int J Clin Oncol. 2022, Mar;27(3), 633–634.
- Lowentritt B; Brown G; Pilon D; Ellis L; Germain G; Rossi C; Lefebvre P; Kernen K; Sieber P; Shore N. Real-world prostate-specific antigen response and treatment adherence of apalutamide in patients with non-metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Urology. 2022, Aug;166, 182–188.
- Wenzel M; Nocera L; Collà Ruvolo C; Würnschimmel C; Tian Z; Shariat SF; Saad F; Tilki D; Graefen M; Kluth LA; et al. Overall survival and adverse events after treatment with darolutamide vs. apalutamide vs. enzalutamide for high-risk non-metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2022, Feb;25(2), 139–148.
- Cao B; Kim M; Reizine NM; Moreira DM. Adverse events and androgen receptor signaling inhibitors in the treatment of prostate cancer: A systematic review and multivariate network meta-analysis. Eur Urol Oncol. 2023, Jun;6(3), 237–250.
- Moreira DM; Howard LE; Sourbeer KN; Amarasekara HS; Chow LC; Cockrell DC; Hanyok BT; Aronson WJ; Kane CJ; Terris MK; et al. Predictors of time to metastasis in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Urology. 2016, Oct;96, 171–176.
- Metwalli AR; Rosner IL; Cullen J; Chen Y; Brand T; Brassell SA; Lesperance J; Porter C; Sterbis J; McLeod DG. Elevated alkaline phosphatase velocity strongly predicts overall survival and the risk of bone metastases in castrate-resistant prostate cancer. Urol Oncol. 2014, Aug;32(6), 761–768.
- Smith MR; Saad F; Oudard S; Shore N; Fizazi K; Sieber P; Tombal B; Damiao R; Marx G; Miller K; et al. Denosumab and bone metastasis-free survival in men with nonmetastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: Exploratory analyses by baseline prostate-specific antigen doubling time. J Clin Oncol. 2013, Oct 20, 31(30), 3800–3806.
- Mori K; Kimura T; Fukuokaya W; Iwatani K; Sakanaka K; Kurokawa G; Yanagisawa T; Sasaki H; Miki J; Shimomura T; et al. Values of alkaline phosphatase at the diagnosis of castration resistance and response to primary androgen deprivation therapy as predictors of subsequent metastasis in non-metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Int J Clin Oncol. 2020, Mar;25(3), 479–485.
- Madan RA; Gulley JL; Schlom J; Steinberg SM; Liewehr DJ; Dahut WL; Arlen PM. Analysis of overall survival in patients with nonmetastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer treated with vaccine, nilutamide, and combination therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2008, Jul 15, 14(14), 4526–4531.
- Smith MR; Cook R; Lee KA; Nelson JB. Disease and host characteristics as predictors of time to first bone metastasis and death in men with progressive castration-resistant nonmetastatic prostate cancer. Cancer. 2011, May 15, 117(10), 2077–2085.
- Smith MR; Kabbinavar F; Saad F; Hussain A; Gittelman MC; Bilhartz DL; Wynne C; Murray R; Zinner NR; Schulman C; et al. Natural history of rising serum prostate-specific antigen in men with castrate nonmetastatic prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005, May 1, 23(13), 2918–2925.
- Nørgaard M; Jensen AØ; Jacobsen JB; Cetin K; Fryzek JP; Sørensen HT. Skeletal related events, bone metastasis and survival of prostate cancer: A population based cohort study in Denmark (1999 to 2007). J Urol. 2010, Jul;184(1), 162–167.
- Scher HI; Solo K; Valant J; Todd MB; Mehra M. Prevalence of prostate cancer clinical states and mortality in the United States: Estimates using a dynamic progression model. PLoS One. 2015, Oct 13, 10(10), e0139440.
- Lecouvet FE; El Mouedden J; Collette L; Coche E; Danse E; Jamar F; Machiels JP; Vande Berg B; Omoumi P; Tombal B. Can whole-body magnetic resonance imaging with diffusion-weighted imaging replace Tc 99m bone scanning and computed tomography for single-step detection of metastases in patients with high-risk prostate cancer? Eur Urol. 2012, Jul;62(1), 68–75.
- Fendler WP; Weber M; Iravani A; Hofman MS; Calais J; Czernin J; Ilhan H; Saad F; Small EJ; Smith MR; et al. Prostate-specific membrane antigen ligand positron emission tomography in men with nonmetastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2019, Dec 15, 25(24), 7448–7454.
| Clinical factors | Number | |
| Median age at the time of CRPC, years (IQR) | 76 (70–81) | |
| Median initial PSA, ng/mL (IQR) | 17 (10-59) | |
| Gleason Score (%) | <8 | 40 (31) |
| ≥8 | 87 (69) | |
| Clinical T Stage | 1-2 | 44 (35) |
| 3-4 | 82 (65) | |
| Unknown | 1 (1) | |
| Clinical N Stage | 0 | 103 (81) |
| 1 | 24 (19) | |
| Local therapy (%) | Surgery | 57 (45) |
| Radiation | 46 (36) | |
| No local treatment | 24 (19) | |
| Previous docetaxel therapy (%) | Yes | 6 (5) |
| No | 121 (95) | |
| PSA doubling time, month (%) | <6 | 99 (78) |
| ≥6 | 27 (21) | |
| Unknown | 1 (1) | |
| First-line ARAT agent (%) | Darolutamide | 17 (13) |
| Apalutamide | 12 (10) | |
| Abiraterone | 26 (20) | |
| Enzalutamide | 72 (57) |
| ENZ (n = 72) | ABI (n = 26) | APA (n = 12) | DARO (n = 17) | |||||
| Any grade (%) | ≥ Grade 3 (%) | Any grade (%) | ≥ Grade 3 (%) | Any grade (%) | ≥ Grade 3 (%) | Any grade (%) | ≥ Grade 3 (%) | |
| Rash | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 (50) | 1 (4) | 0 | 0 |
| Neuropathy | 2 (3) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Fatigue | 11 (15) | 1 (2) | 2 (8) | 2 (17) | 0 | 2 (12) | 1 (6) | |
| Decreased appetite | 4 (6) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Nausea | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 1 (8) | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Dysesthesia | 2 (3) | 0 | 0 | 1 (8) | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Dysgeusia | 1 (1) | 1 (4) | 1 (8) | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Edema | 1 (1) | 1 (4) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Dizziness | 2 (3) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Neutropenia | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Hepatic dysfunction | 0 | 0 | 2 (8) | 0 | 0 | 1 (6) | 0 | |
| Hypokalemia | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Hypertension | 0 | 0 | 1 (4) | 1 (4) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Variables | Univariate | Multivariate | |||
| HR (95% CI) | p value | HR (95% CI) | p value | ||
| Gleason pattern 5 at biopsy | Yes vs. No | 1.75 (0.89, 3.56) | 0.107 | ||
| LDH (U/l) at first-line ARSI | ≥192 vs. <192 | 1.58 (0.79, 3.31) | 0.200 | ||
| ALP (U/l) at first-line ARSI | ≥271 vs. <271 | 1.87 (0.89, 3.75) | 0.097 | NS | |
| Time to CRPC (months) | ≤54 vs. >54 | 1.78 (0.82, 4.43) | 0.172 | ||
| PSA (ng/mL) at initiation of ARSI | >3.67 vs. ≤3.67 | 2.93 (1.46, 6.26) | 0.002 | 2.93 (1.46, 6.26) | 0.002 |
| Previous Docetaxel chemotherapy | Yes vs. No | 1.15 (0.28, 3.24) | 0.817 | ||
| Presence of regional lymph node | Yes vs. No | 2.31 (0.59, 8.15) | 0.215 | ||
| Treatment | 0.084 | NS | |||
| Surgery vs. CAB | 0.47 (0.19, 1.22) | 0.118 | |||
| Radiation vs. CAB | 1.04 (0.46, 2.59) | 0.914 | |||
| Surgery vs. Radiation | 2.22 (1.04, 4.92) | 0.040 | |||
| PSA-DT | ≤6 mo vs. >6 mo | 1.64 (0.59, 6.82) | 0.383 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





