1. Introduction
Geothermal energy is an important non-conventional energy resource in many countries in the world with an installed global power capacity of 17 GW (World GT Power, 2023). Earths internal heat from the mantle (though mantle melting and convection) and core (from accretion heat)contributes to volcanism and geothermal energy (Dincer and Ezzat,2018).Earth’s surface heat flows(internal heat flow per unit area) shows distinct spatial variations from nearly zero to several thousand mWm-2.(IFSC heat flow data,2023). Previous studies has shown that high surface heat flows occur in geothermal provinces and active volcanoes (Ranalli and Rybach, 2005; Lysak, 1992). It will be worthwhile to compare characteristics of volcanism and heat flows in different rocky planetary bodies in our solar system in the context of geothermal power potential.
In this paper we have attempted to answer the following relevant questions related to geothermal energy resources and volcanism (i)what is the critical value of surface heat flow required to maintain a geothermal province or power resource for its efficient operation?(ii)how geothermal energy resources are related to volcanism?(iii) how we can compare current heat flows and volcanism in inner solar system planetary bodies (iv) how the geological time evolution of internal heat affects volcanism and geothermal power resources in earth (iv) probable age of cessation of plate tectonics in earth and related critical heat flows if the mantle cools in the current enhanced rates .The methodology followed is modelling based on analysis of relevant data collected from published literature and international databases.
2. Surface Heat Flows Associated with Geothermal Provinces in Earth
In this section we have studied surface heat flows associated with geothermal provinces in three major geothermal power producing countries viz: USA, Mexico and Iceland.
In
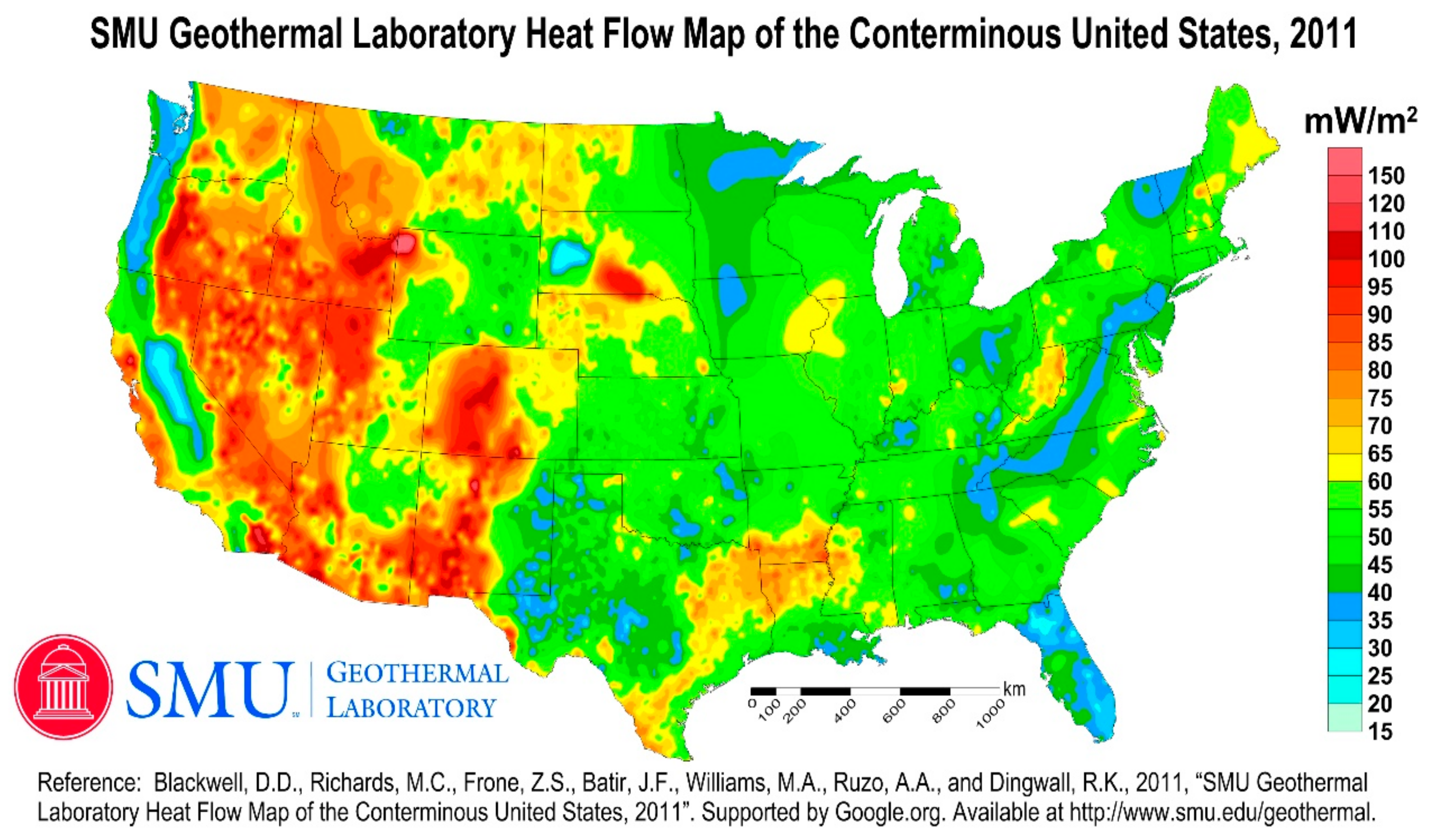
Figure 1 we have shown map of spatial distribution of measured vales of internal heat flow (HF) in USA (Blackwell et al, 2011). In
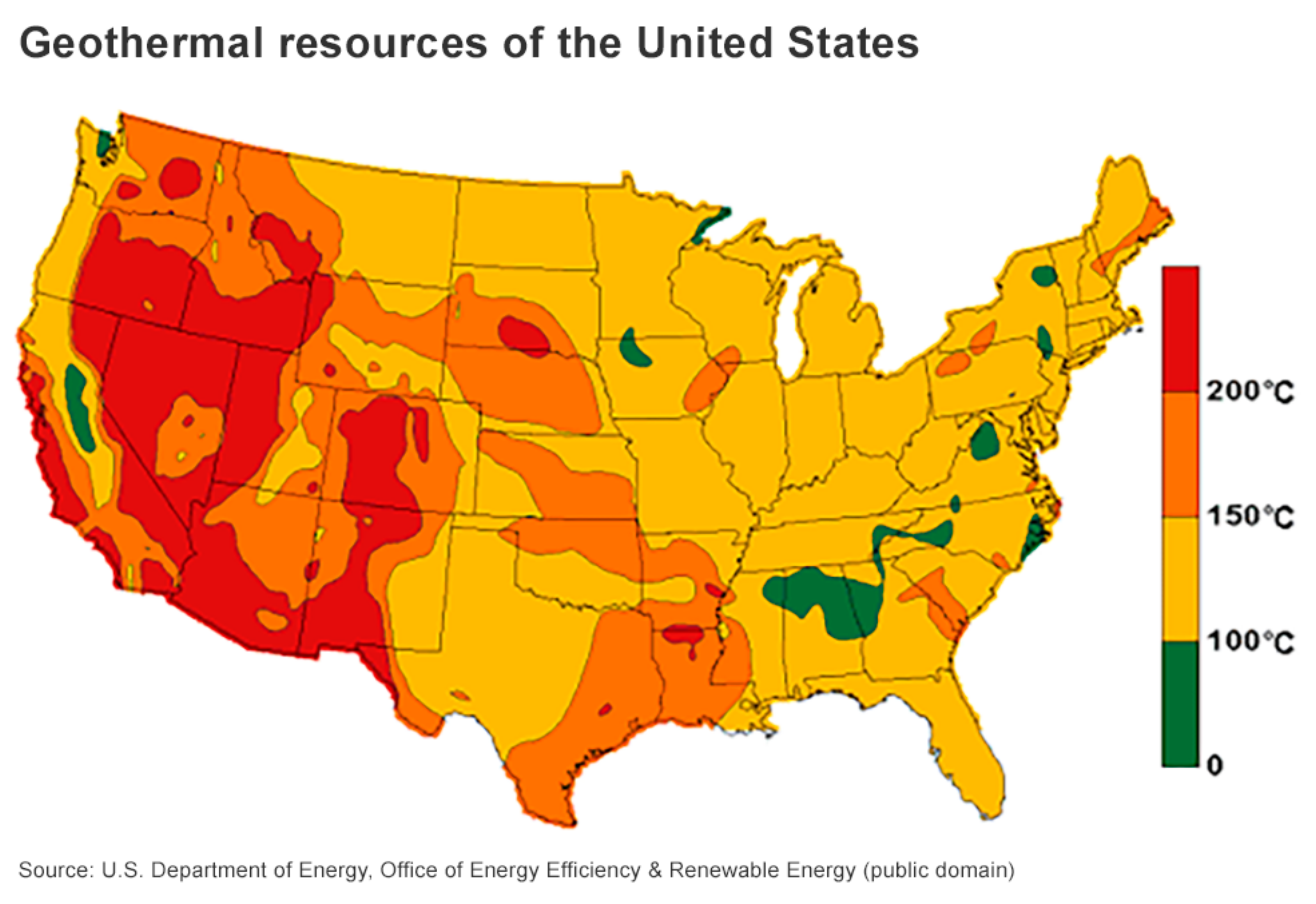
Figure 2 is a geothermal map depicting spatial distribution of sub-surface temperature in USA (GT USA, 2023) .The high heat flow values are found mostly in the western part of USA. The areas marked in red in
Figure 2 with a temperature >150
oCare geothermal provinces in this country which is in match with high heat flow areas marked in red/pink with values ranging from 90-150 mWm
-2.
Geothermal provinces in Mexico (Prol-Ledesmaa and Morán-Zenteno, 2019) are found to be associated with surface heat flows in the range 100-200 mWm-2.In a similar way prominent geothermal power resources in Iceland (Jóhannesson et al, 2020) is found to be associated with surface heat flows in the range 200-350 mWm-2.
3. Associations between Volcanism and Geothermal Energy Sources in Earth
3.1. Possible Linear Relation between Number of Active Volcanoes and Geothermal Power Potential of Different Countries
In several countries we can find close associations between spatial distribution of active volcanoes and locations of geothermal power resources. This is true for USA, Indonesia, Mexico and Iceland and we will explain this fact in
Section 4. In
Table 1 we have given the number of active volcanoes within the Holocene period present in top ten geothermal power producing counties in the world. Here latest annual power production details (World GT Power, 2023) are also given. In this Table we have given latest estimates of geothermal power potential (Gp) in these countries. We have attempted to find linear regression relations between number of active volcanoes (N
v) and Gp in top geothermal power producing countries given in
Table 1 as an update of a previous study (Stefansson, 2005).The results are given below.
3.2. Heat Flows in Volcanic Regions in Earth
Now we will examine heat flow values associated with volcanic regions in Earth.In
Table 2 we have shown heat flow values in specific volcanic regions in different countries. We can find that the minimum heat flow associated with these volcanic regions is 100 mWm
-2.The country average heat flow values (H
av) for top geothermal power producing countries (Country average heat flow,2024) is given in
Table 1. From this table we can find that for Japan, Indonesia, Mexico and Iceland Hav varies roughly between 95-150 mWm
-2.The diagrams showing spatial distributions of active volcanoes in different counties is available in literature. Spatial distribution active volcanoes in countries with higher mean heat flow like Japan etc.is found to be homogeneous. In contrast with this the distribution of active volcanoes with in USA can be found to be inhomogenous (volcanoes are found mainly in the west coast).Hence in USA the country average heat flow is only 75.6 mWm
-2.
4. Results
4.1. Critical Heat Flows for Geothermal Power Resources
Point observations of surface heat flows are available for more than 70000 locations on Earth (IFSC heat flow data, 2023).To avoid bias in spatial distribution of data points in different parts of Earth, grided average or weighted mean values of heat flows are often used. Following such a methodology Davies and Davies (2010) estimated that the total internal heat in Earth is 47 TW. The global average of surface heat flows in Earth can be found as 92.16 mWm-2 if assume 510 million km2 is the surface area of our planet.
In this context we will pose an important question. Is there is any critical value of heat flow (minimum surface heat flow required for sustaining the feature) is associated with geothermal provinces or power resources in Earth? The heat flow maps of top geothermal power producing counties will help us to find an answer to this question (see
Section 2).A location in Earth can be considered as a geothermal power resource is its sub-surface temperature is >150
o C. In USA (the top geothermal energy producing country in the world) the heat flows associated with geothermal power resources is found between 90-150 mWm
-2.Geothermal provinces in Mexico is found to be associated with heat flows in the range 100-200 mWm
-2 and in Iceland is found to be in the range 200-350 mWm
-2.Higher values of heat flows are found in Mexico and Iceland compared to USA because of the peculiar geological settings of the geothermal provinces in these countries (often related to active volcanoes). The average heat flow(Putra et al, 2016) in the onshore Northwest Java Basin (a well known geothermal province in Indonesia) is found to be 94.05 mWm
-2.These results suggests that critical surface heat flow associated with geothermal power resources in Earth is comparable to the current global average surface heat flows of the Earth (92.16 mWm
-2).
4.2. Critical Heat Flows for Active Volcanoes in Earth
From the results summarized in
Table 2 it can be inferred that the critical heat flow in volcanic regions in Earth is 100 mWm
-2.This implies that the minimum heat flow to sustain an active volcanic region in Earth is around 100 mWm
-2 and this value is at least 8.5 % higher than the global mean heat flow of Earth
4.3. Comparison of Volcanism and Geothermal Power Resources in Earth and Venus
In
Table 3 we have given details of active volcanoes and heat flow characteristics in different rocky planetary objects in the inner solar system. From this Table it can be seen that active volcanoes are observed at present only in our Earth and Venus. For Moon, Mars and Mercuy global surface heat flow values are generally low which suggests absence of active volcanoes or geothermal power resources (Zhang et al, 2020; Parro et al, 2017; Egea Gonzalez and Ruiz, 2014).The current number of active volcanoes and locations where heat flow is above critical (required to maintain an active volcano)is significantly higher in Earth compared to Venus.The mean heat flow in Venus in a recent work is suggested to be 101 mWm
-2 (Smerker et al, 2023) But it must be noted that this is inferred from observations in 89 locations in Venus. Further this is not a weighted mean. The mean heat flow of 73000 plus raw measurements in Earth from a recent compilation (IHSC Heat flow data, 2023) is found to be 227 mWm
-2 which is more than double the above estimate for Venus.We can see that Earth is the only rocky planet in our solar system to have a significant number of geothermal power resources in our solar system.The geothermal power potential of Venus is finite but practical geothermal energy conversion will be difficult in this planet due to its very high surface temperature.
In the entire geological history we can find only 847 volcanoes in Venus with a diameter of 5 km or more (Hahn and Byrne, 2023) In the case of Earth out of 1550 subaerial volcanoes which has erupted during the Holocene period, size data is available for 1287 volcanoes.Majority of them has a size greater than 15 km. Over the geological time in Earth more than 250 volcanoes (mainly Large Igneous Provinces) is observed to have a diameter greater than 100 km. The number of large volcanoes (>100km) in the geological history of Venus is inferred to be 118-168 (Hahn and Byrne, 2023: Varnana et al, 2020).The present surface of Venus is built from intense volcanic activity which occurred between 300-800 Ma in our twin planet. It is estimated that the number of active volcanoes in Venus now is around 37 (Gulcher et al, 2020).So we can infer a significant decline the volcanism in Venus during the past 300 Ma. Heat flow measurements are available for 89 locations in which 33 has half value of 100 MW-2 or more in rough agreement with number of active volcanoes in Venus.
4.4. Enhanced Mantle Cooling in the Recent Geological Past and the Inference of Mean Heat Flow of Earth since 800 Myrs
Internal heat evolution in Earth is related to mantle potential temperature, mantle convection and the thermal cooling of Earth This due to surface heat loss. is illustrated by the following equation:
Heat balance equation (Stacey, 1981) in the Earth’s interior is given by
Here Q (t) is the surface heat loss or heat flow at time t
M is the mass of the Earth
T is the mantle temparature
Cp is the average heat capacity in the core-mantle boundary
MCp(dT/dt) represent the mantle cooling
So enhancements in Cp and mantle cooling will result in decrease in surface heat flows (Q) in Earth assuming H(t) is a constant over the time interval of our interest.
A recent study from measurements of ocean crust inferred that Earth’s mantle cooling rate almost doubled in the last 170 Ma. The average (Van Avendonk et al, 2017) cooling rate was between 6-110C per 100 Ma since the Archean age (2.5Ga) and in the recent geological past it became11-200C per 100 Ma. Another experimental study (Motohiko Murakami et al, 2022) found that the thermal conductivity of bridgmanite found in Earth’s core-mantle boundary (which controls Cp in equation) is found to be 1.5 times higher than previous value. The later result also contributes to higher mantle cooling than expected.
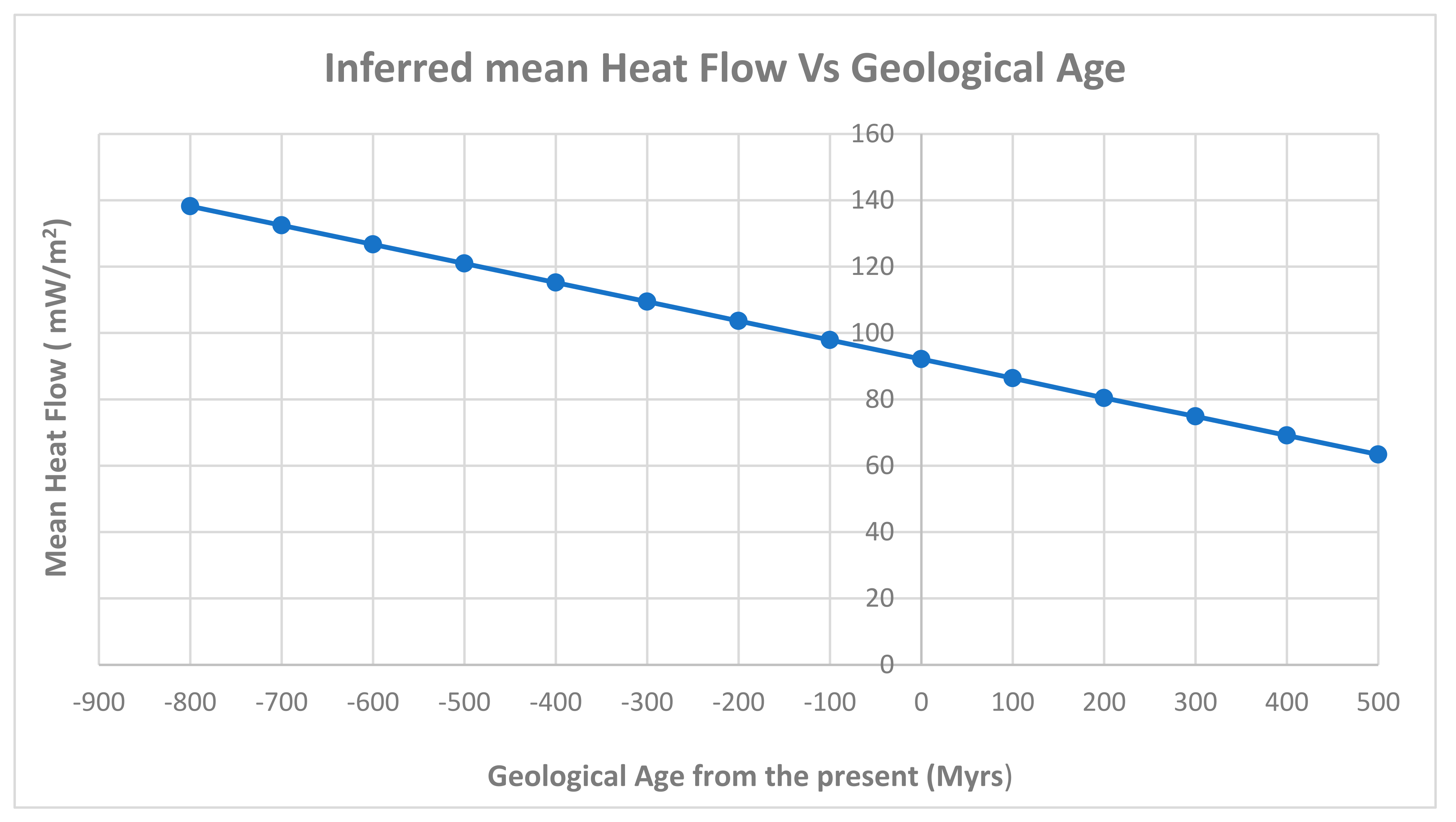
We are interested to infer the future evolution of internal heat in Earth and its possible impact on volcanism and geothermal power resources. Earth is known to be a planet with plate tectonics in contrast with other rocky planetary bodies in the solar system (Moon, Mercury, Venus and Mars).A recent study inferred that the current oceanic heat flux declined by 25% during the past 400 Ma (Karlsen et al, 2021).If we assume that this decrease is reflected in global mean flux of Earth also, then we can infer that Hm is decreasing at a rate of 5.76 mW/m2 in every 100 Myrs. Applying this rate of decrease of Hm since 800 Myrs in the geological past we have shown the variations in Hm up to 500 Myrs from now in
Figure 3.
4.5. Occurences of Large Magmatic Events in the Earth during the Past 800 Myrs and Associated Surface Heat Flow Values
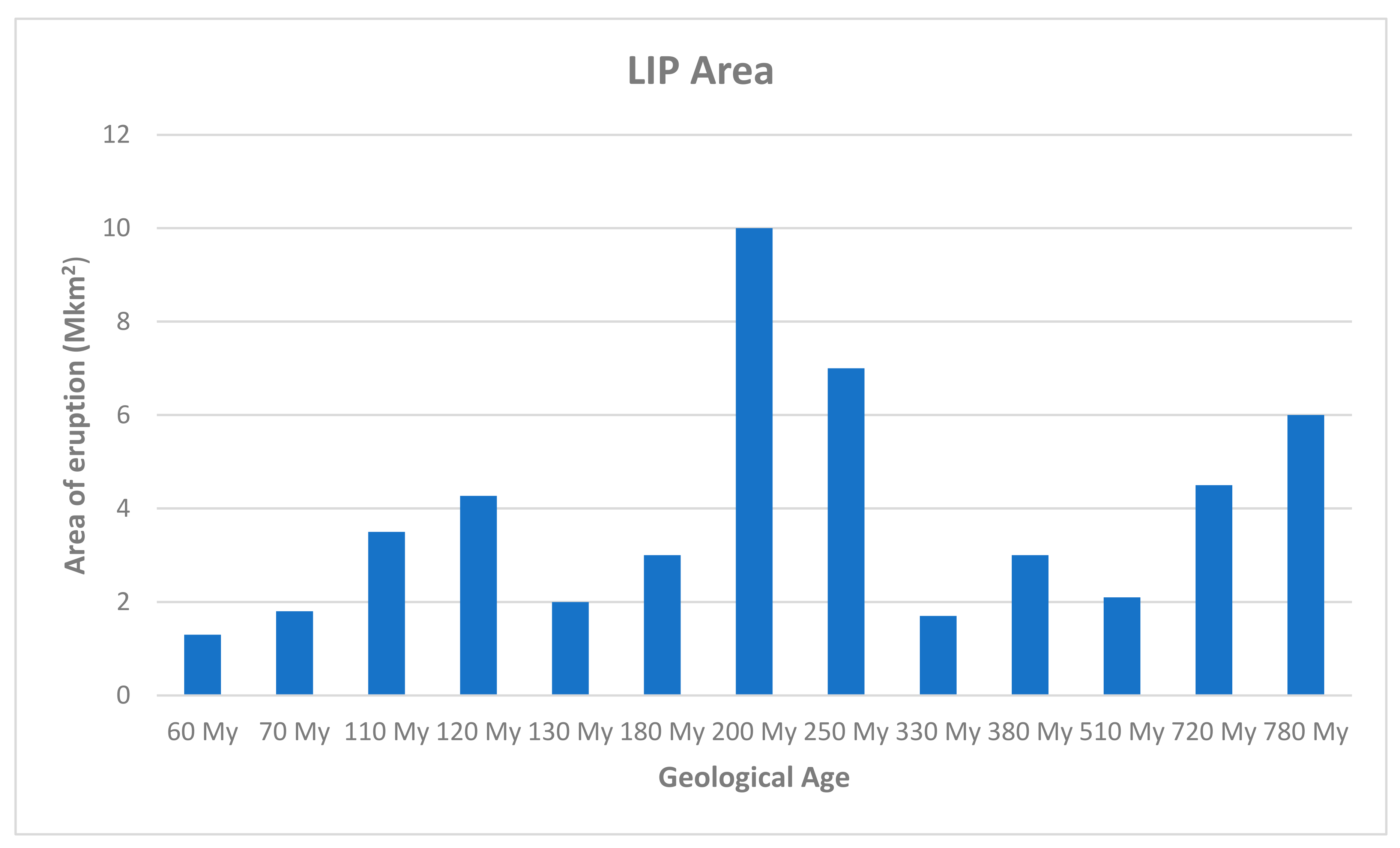
In
Table 4 we have given the characterisitics of super-magmatic events (exceptional large igneous provinces or LIP’s) which occurred since 800 Myrs in Earth. From
Figure 3 we can find that the inferred global mean heat flow of Earth is > 100 mWm
-2 in the since 150 Myrs in the geological past .Five of the six events occurred between 179-780 Myrs when global mean heat flow of Earth is above critical value found for active volcanism.Only one event occurred around 70 Myrs (associated with Deccan traps LIP) when mean heat flow of Earth is sub-ciritical (<100 mWm
-2). In
Figure 4 we have plotted the total area of eruption of all large magmatic events with a value of 1 Mkm
2 or above during the past 780 Myrs.The LIP area values are derived mainly from Large Igneous Provinces Commission Data base (LIPC, 2023)and also from
Table 4 (for selected events).We can find two notable peaks during 200-250 Myrs and 720-780 Myrs respectively. These peaks has occurred when the inferred global mean heat flow of Earth is >100 mW.m
-2 or super critical.
5. Discussion
We have found that critical heat flow required to maintain active volcanoes (Hcv) in Earth is 100 W/m2. (Reading et al.,2022, Supplementary material) reported that mean heat flow in magmatic provinces in Earth is 99. 33 which is close to our estimate for Hcv. .The present estimate of Hcv is higher than the value reported for sustaining major volcanism in rocky planetary bodies by (Varnana et al .,2018). In contrast with this, critical heat flow (Hcg) required for maintaining geothermal provinces (power resources) is found in this study to be 90 Wm-2 which is close to the current global mean heat flow for Earth. Some geothermal provinces are found in non-volcanic regions in Earth. This justifies why Hcg < Hcv in our study.
From Davies and Davies (2010) we can find more than 2000 grided areas (see
Figure 3(a) in their paper) in Earth to have a mean heat flow equal to greater than 100 mWm
-2. The maximum number of active volcanoes in Earth is only 1500. This supports the fact that there are locations in Earth with high heat flow values out side the volcanic regions. Heat flow map of USA (
Figure 1) is a good example in this context. However the number of active volcanoes is still a useful indicator of the geothermal power potential of a country (
Table 1) or a planet (
Table 3).
Venus is the only planet in the inner solar system at present to have active volcanoes apart from Earth. But the volcanism in Venus has declined significantly since the resurfacing period(300 Myrs ago). The recent intensity of volcanism in Venus (Byrne and Krishnamoorthy,2022) is inferred to be low (VEI<4) . According to our previous studies (Varnana et al, 2020;Varnana et al, 2021) peak volcanism in different rocky planetary bodies in the solar system occurred when their global mean heat flows is around 120 mW/m2.Further decline in the global mean heat flows of planetary bodies below a critical value will lead to cessation of major volcanism in these bodies.In this manner major volcanism ceased in Venus, Mercury, Mars and Moon in the geological past.Earth is the only rocky planetary body in the solar system with plate tectonics which will have a control on its surface heat flows and volcanism.Still we need to address the possibility of cessation of volcanism in Earth in the near geological future since Earth’s internal heat engine is not driven by a Perpetuam mobile. Cheng et al.,2018 found that the intensity and duration of large magmatic events in Earth inferred from zircon geochronology (see for eg:Stern, 2018) was decreasing systematically since the Archean period (2.5 to 3 Gyrs) and if it continues so then it implies that plate tectonics in Earth will stop within a period of 1.45 Gyrs from now.
Enhanced mantle cooling in recent geological past has reflected on the oceanic heat flow and perhaps global mean heat flow earth since 400 Myrs.If it continues like this then the global mean heat flow of earth will decline to 74.88 mWm
-2 in the next 300 Myrs and 63.36 mWm
-2 in the next 500 Myrs. It is expected that number of active volcanoes and geothermal power resources will decline significantly in the next 300-500 Myrs. Further if the Earths mantle cools at a rate of 20
o C per 100 Myrs (maximum value inferred in ref) then the current mantle potential temperature (1350
oC) will reduce to mantle solidus temperature (1200
o C) in a time period of 750 million years from now. At that time plate tectonics and allied volcanism in Earth will also cease. The global mean heat flow at this cessation period (750 Myrs) can be estimated to be 49 mWm
-2. It is quite interesting to mention that Williams et al (1997) suggested a value of global mean heat flow between corresponding values (see
Table 3) for Earth and Mars for sustaining plate tectonics in a rocky planet. This can be calculated to be around 55.58 mWm
-2.
6. Conclusions
(i)From analysis of relevant data we have inferred that the critical or minimum heat flow required to sustain geothermal power resources in Earth is at least 90 mWm-2 which is comparable to the current global mean heat flow of Earth. Similar investigations related to current volcanism in Earth suggests that critical heat flow required to sustain active volcanos in Earth is at least 100 mWm-2 which is 8.5 % higher than the current global mean heat flow of Earth (92.16 mWm-2).
(ii)Active volcanism in Venus is found to have declined significantly in the past 300 Ma. There are few geothermal power resources found in this planet however practical energy conversion is not possible due to the very high surface temperature.
(iii)Recent studies suggest that Earth is loosing significant part of its internal heat and is subjected to enhanced mantle cooling in the recent geological past (within 400 Ma).If we assume that global mean heat flow of Earth is decreasing at a rate of at least 5.76 mW per 100 Ma then significant number of active volcanoes and geothermal power resources present now may disappear in the next 300-500 Ma.
(iv) At the current maximum inferred rate of mantle cooling (20oC per 100 Ma) plate tectonics in Earth is likely to cease within the next 750 Ma. The global mean heat flow at this cessation age can be inferred to be 49 mW/m2. The critical heat flow required to maintain plate tectonics in a rocky planet including Earth shall be between 50-55 mW/m2 if consider earlier proposal by Williams (1997) also.
Permissions
Formal request for permission to reproduce a map included in
Figure 1 in this paper is sent to SMU Geothermal Lab, USA even though it is included in National Geothermal Database of USA.
Figure 2 is published by US Department of Energy and does not normally require a permission.
References
- Afandi.A, Nuraini Lusi, IGNB Catrawedarma, Badarus Zaman.M, Subono (2021) Identification of Gradient temperature and heat flow area of Geothermal Ijen Volcano Indonesia. IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 1034, 012072.
- Batir, J.F and Blackwell, D.D (2019): Thermal evolution of the Northern Cordillera Volcanic Province: implication for heat flow in remnant back-arc regions, International Geology Review. [CrossRef]
- Blackburn, T.J et al.(2013) Zircon U-Pb Geochronology Links the End-Triassic Extinction with the Central Atlantic Magmatic Province Science 340, 941. [CrossRef]
- Blackwell, D. D., Bowen, R. G., Hull, D. A., Riccio, J., & Steele, J. L. (1982). Heat flow, arc volcanism, and subduction in northern Oregon. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 87(B10), 8735-8754. [CrossRef]
- Blackwell, D.D., Richards, M., Frone, Z., Batir, J., Dingwall, R., Ruzo, A., Williams, M. (2011). 2011 Geothermal Heat Flow Map of the U.S., Southern Methodist University Geothermal Lab. Available online: https://www.smu.edu›geothermallab›datamaps.
- Byrne, P. K., and Krishnamoorthy, S.(2022). Estimates on the frequency of volcanic eruptions on Venus. Journalof Geophysical Research: Planets, 127, e2021JE007040. [CrossRef]
- Cheng,Q (2018) Extrapolations of secular trends in magmatic intensity and mantle cooling: Implications for future evolution of plate tectonics,Gondwana Research, 63, 268-273. [CrossRef]
- Country average heat flow (2024). Available online: http://heatflow.org/country/.
- Davies, J.H and Davies, D.R (2010) Earth’s surface heat flux, Solid Earth, 1, 5–24.
- Dincer,I and Ezzat,M.F (2018) Geothermal Energy Production, in: Comprehensive Energy Systems,Volume 3, Elsavier Publication, pp 252-303.
- Duncan LA, Hooper, PR, Rehacek, J, Marsh, JS and Duncan, AR (1997) The timing and duration of the Karoo igneous event, southern Gondwana JGR, 102, 18127-18138.
- Egea-González, I and Ruiz, J (2014) Influence of an insulating megaregolith on heat flow and crustal temperature structure of Mercury, Icarus, 232, 220-225. [CrossRef]
- Ehora.S (1992) Thermal structure beneath Kuju volcano, central Kyushu,Japan, Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research,54,107-115.
- Goddéris,Y, Y. Donnadieu, A. Nédélec, B. Dupré, C. Dessert, A. Grard, G. Ramstein, L.M. François (2003) The Sturtian ‘snowball’ glaciation: fire and ice,Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 211, 1-12. [CrossRef]
- GT Potential Iceland (2008) available at:Steingrímsson.B,Björnsson.S, and Adalsteinsson.H, Master plan for Geothermal and Hydropower development in Iceland. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/228473661.
- GT potential Indonesia (2018). Available online: https://www.adb.org/news/features/developing-indonesia-s-geothermal-power-potential#.
- GT potential Italy (2019) available at: Adele Manzella, Davide Serra, Gabriele Cesari, Eleonora Bargiacchi, Maurizio Cei, Paolo Cerutti, Paolo Conti, Geoffrey Giudetti, Mirco Lupi and Maurizio Vaccaro, Geothermal Energy Use, Country Update for Italy, in: Proc. European Geothermal Congress 2019. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/333995413.
- GT potential Japan (2018). Available online: https://www.irena.org/news/articles/2009/Apr/Unlocking-geothermal-potential-in-Japan-through-small-scale-generation.
- GT potential Kenya (2010) available at: Simiyu.S.M, Status of Geothermal Exploration in Kenya and Future Plans for Its Development, in: Proceedings World Geothermal Congress 2010,Bali, Indonesia.
- GT potential Mexico (2023). Available online: https://mexicobusiness.news/energy/news/mexico-has-great-geothermal-potential-unam.
- GT potential Newzeland (2021). Available online: https://www.globaldata.com/data-insights/power-and-utilities/power-generation-and-cumulative-capacity-of-geothermal-power-plants-in-new-zealand-2017-2021/#.
- GT potential Phillipines (2020). Available online: https://www.irena.org.
- GT potential Turkey (2022). Available online: https://www.aydemenerji.com.tr/blog/157/geothermal-energy-potential-of-turkey-and-its-sustainability?hl=en.
- GT potential USA (2021). Available online: https://www.energy.gov/eere/geothermal/articles/now-available-iea-2020-us-geothermal-report#.
- GT USA (2023), Geothermal temperature map of USA, US Department of Energy. Available online: https://www.eia.gov/energyexplained/geothermal/where-geothermal-energy-is-found.php.
- Gülcher, A.J.P., Gerya, T.V., Montési, L.G.J. et al. Corona structures driven by plume–lithosphere interactions and evidence for ongoing plume activity on Venus. Nat. Geosci. 13, 547–554 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Hahn, R. M., & Byrne, P. K. (2023).A morphological and spatial analysis of volcanoes on Venus. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 128, e2023JE007753. [CrossRef]
- Holocene Volcano (2024b), Global Volcanism Program, Smithsonian Institution. Available online: https://volcano.si.edu/volcanolist_holocene.cfm.
- Holocene volcanoes (2024a), Number for each country, Countries with Holocene Volcanoes, Smithsonian Institution, Global Volcanism Program. Available online: https://volcano.si.edu/volcanolist_countries.cfm.
- IFSC heat flow data (2023), The IHFC Global Heat Flow Database, The Global Heat Flow Database-Update 2023. Available online: http://ihfc-iugg.org/products/global-heat-flow-database/data.
- Jóhannesson T, Pálmason B,Hjartarson Á, Jarosch AH, Magnússon E, Belart JMC, Gudmundsson MT (2020). Non-surface mass balance of glaciers in Iceland. Journal of Glaciology, 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Jourdan, F, G. Féraud, H. Bertrand, M.K Watkeys and, P.R. Renne (2007) Distinct brief major events in the Karoo large igneous province clarified by new 40Ar/39Ar ages on the Lesotho basalts, Lithos, 98, 195–209.
- Karlsen, K.S, Clinton P. Conrad, Mathew Domeier, and Reidar G. Trønnes (2021) Spatiotemporal Variations in Surface Heat Loss Imply a Heterogeneous Mantle Cooling, GRL, 4, e2020GL092119.
- LIPC (2023) Global list of LIP’s. Available online: http://www.largeigneousprovinces.org/downloads.
- Lysak.S.V (1992) Heat flow variations in continental rifts Technophysics, 208, 309-323.
- Macdonald, F.A and Hysell, N.L.S (2023) The Franklin Large Igneous Province and Snowball Earth Initiation. Elements 2023;; 19 (5): 296–301. [CrossRef]
- Marzen, R.E., Shillington, D.J., Lizarralde, D. et al (2020). Limited and localized magmatism in the Central Atlantic Magmatic Province. Nat Commun 11, 3397. [CrossRef]
- Marzoli, A. et al. (2018). The Central Atlantic Magmatic Province (CAMP): A Review. In: Tanner, L. (eds) The Late Triassic World. Topics in Geobiology, vol 46. Springer, Cham. [CrossRef]
- Motohiko Murakami, Alexander F. Goncharov, Nobuyoshi Miyajima, Daisuke Yamazaki, Nicholas Holtgrewe (2022) Radiative thermal conductivity of single-crystal bridgmanite at the core-mantle boundary with implications for thermal evolution of the Earth,Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 578, 117329. [CrossRef]
- Nagao.T and Uyeda.S (1995) Heat-flow distribution in Southeast Asia with consideration of volcanic heat, Tectonophysics, 251, 153-159.
- Pande K (2002) Age and duration of Deccan traps, India: Review of radiometric and paleomagnetic constraints Proc Ind. Acad.Sci. (Earth Planet Sci), 111, 115-123.
- Parro, L., Jiménez-Díaz, A., Mansilla, F. et al. Present-day heat flow model of Mars. Sci Rep 7, 45629 (2017). [CrossRef]
- Prol-Ledesmaa, R.M and Morán-Zenteno, D.J (2019) Heat flow and geothermal provinces in Mexico,, Geothermics, 78, 183–20.
- Putra, S.D.H. Putra, S.D.H., Suryantini & Srigutomo, W (2016) Thermal modeling and heat flow density interpretation of the onshore Northwest Java Basin, Indonesia.
- Ranalli, G and Rybach, L (2005) Heat flow, heat transfer and lithosphere rheology ingeothermal areas: Features and examples. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 148, 3-19.
- Smrekar, S.E., Ostberg, C. & O’Rourke, J.G. Earth-like lithospheric thickness and heat flow on Venus consistent with active rifting. Nat. Geosci. 16, 13–18 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Stacey, F.P (1981) Cooling of the Earth-A constraint on the Paleotectonic hypothesis, in: Evolution of Earth, Geodynamics series-Vol 5, AGU, USA.
- Stefansson,V (2005), World Geothermal Assessment, in: Proceedings World Geothermal Congress 2005, Turkey, pp 1-16.
- Stern RJ. 2018 The evolution of plate tectonics. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 376: 20170406. [CrossRef]
- Van Avendonk, H., Davis, J., Harding, J. et al. (2017) Decrease in oceanic crustal thickness since the breakup of Pangaea. Nature Geosci 10, 58–61 (2017). [CrossRef]
- Williams, D., Kasting, J. & Wade, R. Habitable moons around extrasolar giant planets (1997) Nature 385, 234–236. [CrossRef]
- World GT Power (2023) Thinkgeoenergy’s top 10 geothermal countries 2022. Available online: https://www.keyfactsenergy.com/news/20375/view/.
- Zhang H et al (2021) Felsic volcanism as a factor driving the end-Permian mass extinction Sci. Adv. 7, eabh1390.
- Zhang,W, Ben Zhao and Xinyu Lou (2020) Moon’s subsurface heat flow mapping, Acta Geophysica. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).