1. Introduction
Ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP) is a common entity in mechanically ventilated patients with extended use of broad-spectrum antibiotics, prolonged hospitalization and significant morbidity and mortality [
1,
2]. Worldwide, data on VAP incidence associated with pediatric intensive care units (PICUs) report significant variability, which is due to differences in diagnostic criteria, sample collection body sites and diagnostic tests [
3,
4]. Since several conditions and modifiable factors may contribute to clinical worsening, early VAP diagnosis is especially challenging in critically ill patients. The difficulty in applying VAP diagnostic criteria, such as the Clinical Pulmonary Infection Score (CPIS) (fever, leukocytosis, pulmonary secretions, oxygenation and chest X-ray lung infiltrates), is the subjective nature of interpretation of clinical evidence that cannot differentiate the presence of concurrent morbidities in mechanically ventilated patients. Moreover, other underlying conditions could modify clinical parameters, and early VAP diagnosis may be missed. Therefore, clinical criteria, alone, have rather limited value in VAP diagnosis [
5].
In recent years, rapid syndromic molecular testing for identification of pathogens responsible for pneumonia in respiratory samples have shown to benefit targeted antibiotic treatment by providing accurate and much anticipated clinical information to clinicians in “real time” [
6]. The need for rapid and sensitive diagnostic tools able to differentiate a true lung infection from other noninfectious conditions makes the search for valid and quantifiable biomarkers an undisputable demand in clinical practice. Thus, for accurate VAP diagnosis, clinical scoring, molecular diagnostic platforms combined with reproducible biomarkers of infection (host response) using non-invasive methods, need to be investigated to assess their clinical value in early VAP diagnosis in critically ill children. Molecular syndromic panels allow rapid broad range pathogen identification, which is critical to clinicians for prompt treatment. A recent meta-analysis reported sensitivity 94% and specificity 98% for diagnostic PCR panels compared to conventional culture for respiratory infections [
7]. Similar evaluations have been reported from studies using diagnostic respiratory panels for VAP in the pediatric population [
8,
9].
Up to date, universal biomarkers of lung injury and inflammation for targeted antibiotic treatment and prompt coverage of established pathogens for the pediatric population, are lacking. Although several clinical studies have investigated VAP-associated biomarkers, most of them are conducted with adult patients and the findings remain discordant. For example, protein levels of plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 (PAI-1), a protease inhibitor of coagulation/fibrinolysis cascade, were increased only in the lung of adult patients with
P. aeruginosa-induced VAP but did not correlate with other clinical markers of lung injury [
10]. In contrast, increased PAI-1 concentrations were found in the plasma of patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and correlated with increased mortality in these patients [
11]. A retrospective observational study found that plasma levels of soluble receptors for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) had low discriminative power for diagnosing development of ARDS in adult patients with VAP [
12]. A single prospective observational study investigating the ability of the cytokine interleukin 4 (IL-4) to early diagnose VAP in preterm infants showed that it could not differentiate infants with VAP from those without infection [
13].
In this study, we assessed for the first time whether bronchial IL-4, PAI-1 and RAGE levels and their fluctuation in time can be used as biomarkers to improve the accuracy of VAP diagnosis and follow-up in critically ill pediatric patients with suspected VAP.
2. Results
From March 2021 to December 2022 a total of 20 patients (65% males) were enrolled in the study, with median age 7.75 years with IQR 1.7 to 10.2 (
Table 1). These patients had a variety of underlying diseases, such as chronic metabolic diseases, encephalopathies or other chronic diseases (35%), as well as acute severe illnesses, such as encephalitis, near drowning, cardiac arrest, etc. (40%), as described in a previously published report of this project [
14]. At admission in PICU the median PRISM (Pediatric Risk of Mortality) score was 11 (IQR 8-14). All the patients were receiving antibiotics during participation in the study. Of the 20 participants, 65% received at least one new antibiotic for VAP suspicion management, with colistin and vancomycin being the most widely used medicines. The median (IQR) time duration for VAP presentation was 6 (4-12) days of mechanical ventilation. Two deaths were observed during the 30-day follow-up study period, both in patients with underlying chronic disease and with admission PRISM score 8 and 13. The total length of hospitalization for these two patients was 56 and 8 days respectively, and death occurred on 30th and 3rd day after the VAP episode. All the patients exhibited deterioration of respiratory clinical parameters, mechanical ventilator parameters or radiological parameters. Based on mCPIS score, 14 patients were assessed as high suspicion VAP (mCPIS score >6), and 6 patients were assessed as low suspicion VAP (mCPIS score <6). High suspicion group had significantly higher WBC than the low suspicion group (p-value = 0.041;
Table 1).
On day 1 of enrollment, bronchial secretions collected from all patients were subjected to pathogen identification using the FilmArray molecular platform of the lower respiratory tract. The following pathogens were detected: Staphylococcus aureus (n=1), Acinetobacter calcoaceticus-baumanii complex (n=3), human rhinovirus/enterovirus (n=2), respiratory syncytial virus (n=1) and parainfluenza virus (n=1). Two of the three patients in the low VAP suspicion group with Acinetobacter present were also positive for NDM and VIM antibiotic resistance genes (
Table 2). Fifty percent of the pathogens recovered were found in the high suspicion VAP group and 50% in the low suspicion VAP group.
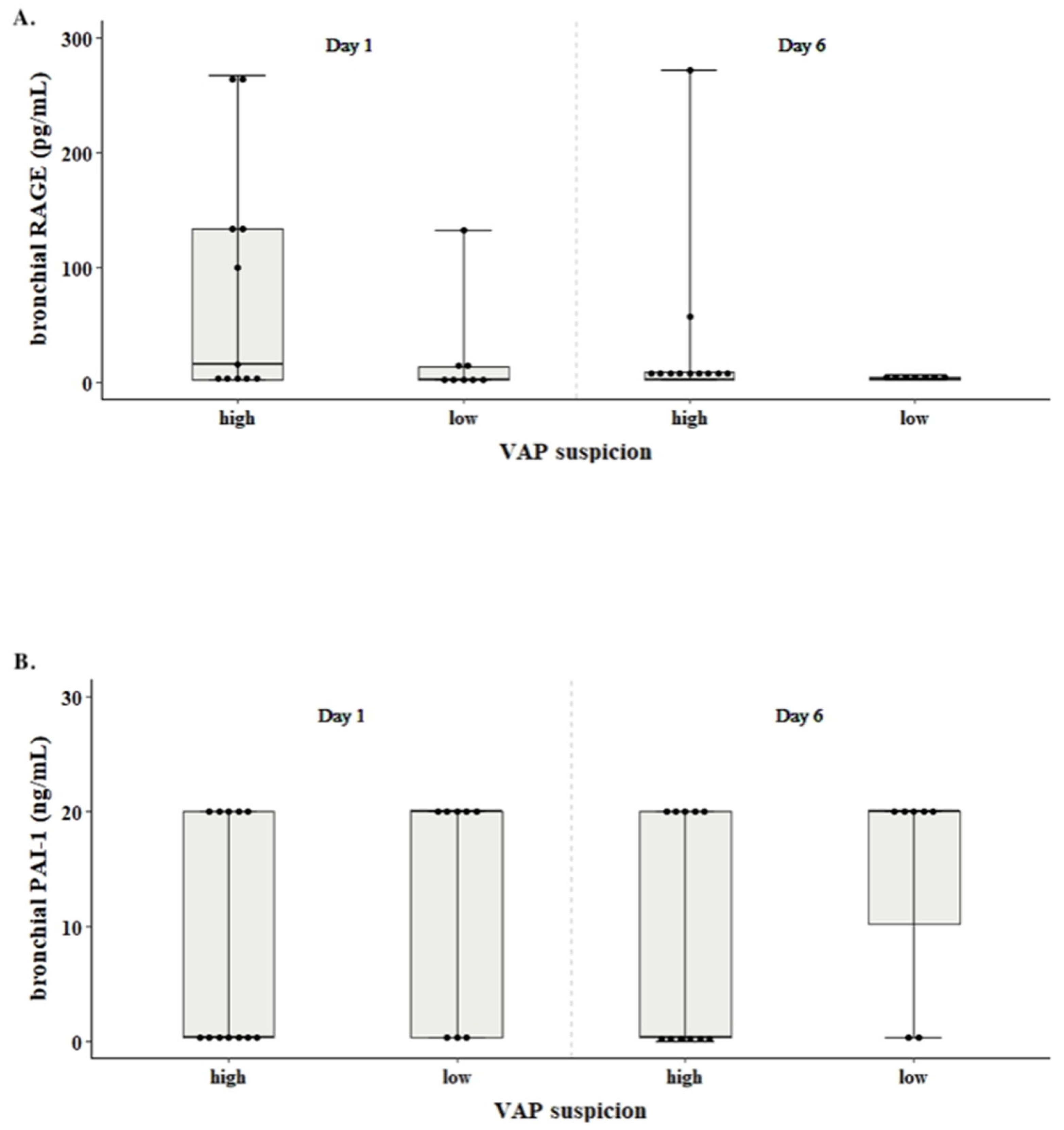
IL-4 was not detected in any of the 2 sample collection time points. The levels of RAGE and PAI-1 did not significantly differ between high and low VAP suspicion groups (p-value = 0.131, p-value = 0.388, respectively;
Figure 1). The levels of RAGE tended to increase with increasing mCPIS (Pearson’s r = -0.159, p-value = 0.504), whereas in the case of PAI-1 levels the opposite trend was observed (Pearson’s r= 0.382, p-value = 0.096,
Figure 1).
PAI-1 and RAGE levels were not significantly correlated with WBC, CRP and temperature in neither VAP suspicion group. Levels of RAGE on day 6 (median 2.06, IQR 2.06 - 6) had a decreasing trend compared to day 1 (median 9.00, ΙQR 2.06 - 133) (p-value=0.118;
Figure 1, panel A). In contrast, levels of PAI-1 were increased from the day 1 (median 10.2, IQR 0.313 – 20) to the day 6 (median 20, IQR 0.313 – 20) (p-value= 0.071;
Figure 1, panel B).
Levels of PAI-1 and RAGE in all enrolled patients at the day 1 of clinical VAP suspicion, regardless of CPIS score, had no significant association to a) length of total PICU stay, b) total length of mechanical ventilation and c) length of mechanical ventilation after day 1 of VAP suspicion (
Table 2).
Levels of PAI and RAGE had no correlation with bacterial or viral identification from lower respiratory tract infections of this cohort of patients (OR= 1.02, 95% CI [0.93, 1.13], and OR= 0.99, 95% CI [0.96, 1] respectively.
Table 2.
Correlation between length of total PICU stay / length of total mechanical ventilation / length of mechanical ventilation after the day 1 of VAP suspicion and RAGE / PAI-1 levels at day 1 and day 6.
Table 2.
Correlation between length of total PICU stay / length of total mechanical ventilation / length of mechanical ventilation after the day 1 of VAP suspicion and RAGE / PAI-1 levels at day 1 and day 6.
| |
Length of total PICU stay |
Length of total MV |
Length of Mechanical Ventilation after day 1 of VAP Suspicion |
RAGE levels
at day 1 |
r= 0.348 (p= 0.133) |
r= 0.259 (p= 0.284) |
r= 0.047 (p= 0.849) |
| at day 6 |
r= -0.194 (p= 0.441) |
r= -0.164 (p= 0.528) |
r= -0.330 (p= 0.195) |
PAI-1 levels
at day 1 |
r= -0.304 (p=0.193) |
r= -0.241 (p= 0.32) |
r= -0.308 (p= 0.199) |
| at day 6 |
r= -0.006 (p= 0.981) |
r= -0.078 (p= 0.767) |
r= 0.018 (p= 0.946) |
Table 3.
Bronchial levels of RAGE (pg/mL) and PAI-1 (ng/mL) on day 1 and day 6, in patients with low and high VAP suspicion.
Table 3.
Bronchial levels of RAGE (pg/mL) and PAI-1 (ng/mL) on day 1 and day 6, in patients with low and high VAP suspicion.
| |
High suspicion VAP |
Low suspicion VAP |
| |
day 1 |
day 6 |
day 1 |
day 6 |
| RAGE |
57.5 (2.06-165)
(2.06-165) |
2.06 (2.06-9)
(2.06-9) |
2.53 (2.06-14)
(2.06-14) |
2.06 (2.06-4.03)
(2.06-4.03) |
| PAI-1 |
0.313 (0.313-20) 20)2200)2000202222222222222222222222222222222222222220020002220) (0.313-2020)
(0.313-20) |
0.313 (0.313-20)
(0.313-20) |
20 (0.313-20)
(0.313-20) |
20 (10.2-20)
(10.2-20) |
3. Discussion
In this study, for the first time, the biomarkers RAGE, PAI-1 and IL-4, previously detected in the lungs of intubated adult patients, were tested for their diagnostic value and clinical monitoring ability in critically ill pediatric patients with VAP suspicion in real-life scenarios and including different levels of clinical uncertainty. At a second step and using the mCPIS score [
15], the study population was categorized into two groups of high and low VAP suspicion. No statistically significant differences were detected in the RAGE and PAI-1 levels between high and low VAP suspicion patients in day 1 or day 6 of sample collection. Pearson’s rank-order correlations performed between each biomarker and other inflammatory indices, such as WBC, CRP levels or temperature did not reveal any associations.
All three biomarkers, namely RAGE, PAI-1 and IL-4 have been investigated in the pathophysiology of respiratory diseases [
16,
17,
18]. RAGE, a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily of cell surface molecules, is highly expressed in lung tissue under normal circumstances. Several in vivo animal studies investigating the role of RAGE in lung injury have shown that the soluble isoform is a promising biomarker of alveolar type I cell injury [
19,
20,
21], which can be utilized as a diagnostic tool to differentiate among multiple lung diseases, the most prevalent of them being the obstructive lung diseases [
22] and acute lung injury/ARDS conditions [
23,
24]. A retrospective observational study on the diagnostic accuracy of RAGE in ARDS adult patients with VAP showed that RAGE plasma levels have limited discriminative power, which is in line with our findings [
12].
The role of PAI-1 as a regulator of fibrinolysis triggered research about its contribution in acute respiratory distress syndrome [
25], pleural effusion [
26] and aspiration pneumonitis [
27]. VAP is suggested to provoke procoagulant changes in the lungs. Many studies have shown an alveolar coagulopathy with hypercoagulative state and fibrinolysis depression, which leads to increased levels of PAI-1 in bronchoalveolar lavage both in vitro [
28,
29] and in clinical studies [
27,
30,
31]. The diagnostic efficacy of PAI-1 has been studied primarily in adult patients with VAP [
10,
11,
31] with controversial results. Scultz et al used CPIS supplemented by other clinical, therapeutic and microbiological data to diagnose VAP in an adult ICU. Levels of PAI-1 in non-direct BAL were significantly increased in patients with VAP [
31]. Another study conducted in adult patients who had positive BAL for Pseudomonas aeruginosa found no difference in BAL PAI-1 levels between those who were diagnosed with VAP and those without VAP. Nonetheless, PAI-1 levels were associated with increased mortality in this cohort of patients which was independent of the presence of VAP or ARDS. In this study VAP diagnosis was based on radiographic results, BAL culture >10
4 CFUs and the presence of fever, leukocytosis/leukopenia or purulent tracheal secretions [
10]. The correlation of increased PAI-1 levels with poor outcomes has also been found in pediatric and adult patients with acute lung injury and collectively these data could indicate that this biomarker is elevated in the late stages of lung inflammation conditions, limiting its use in early VAP diagnosis [
10,
11,
32]. In our study PAI levels in bronchial aspirates had no significant difference between patients with high or low VAP suspicion and could not be associated with patients’ outcome such as length of mechanical ventilation and length of ICU stay. Mortality was too low and precluded the drawing of definitive conclusions.
In the pediatric population, only one study has compared the ability of PAI-1 and RAGE to distinguish VAP pneumonia from respiratory bacterial colonization [
33]. In this study, CDC definition or clinical assessment was used for VAP definition, and BAL culture was needed for diagnosis confirmation. BAL PAI-1 levels differed significantly between children diagnosed with VAP and colonized children during ventilation but without VAP; no difference was detected in RAGE levels between the comparator groups. This heterogeneity observed in the studies conducted, with significant variations in VAP diagnostic criteria, including the reference test employed for diagnostic accuracy evaluation, variations in comparator groups, case and controls definition, the different specimen used, and the very small sample sizes used in the very few published studies cannot safely determine the diagnostic value of PAI-1 and RAGE in VAP, and more research is definitely needed. To our knowledge, monitoring of RAGE and PAI-1 fluctuation in lungs during the pediatric VAP course had not previously been reported.
IL-4 is an interleukin secreted by lymphocytes, associated with many pulmonary diseases, such as allergic asthma, respiratory infections [
34,
35] and community-acquired pneumonia in children [
36]. Animal studies claim that mechanical ventilation leads to IL-4 mediated macrophage dysfunction and subsequent vulnerability to VAP occurrence [
37,
38]. In our study, IL-4 was not detected in any sample for the manufacturer detectable range 15.6-1000 pg/mL. This observation is in accordance with the results of the single published study by Pinilla-Gonzalez et al. conducted in preterm neonates, whose maximum IL-4 value was 0.4 pg/mL in BAL detected by flow cytometry, under our lower detectable limit with ELISA [
13].
The study had some limitations: a) The sample size used for biomarker analysis in this pilot study was relatively small, due to scarce VAP cases in critically ill infants and children. b) As this study was conducted in real circumstances, the antibiotic administration in all patients before and during a possible VAP could probably influence levels of inflammatory biomarkers. c) We did not include controls to reflect the gradual differentiation in biomarker levels between cases and controls, but cases with different levels of clinical uncertainty for VAP diagnosis, which reflect the routine practice in a PICU, were used instead. d) mCPIS score used for categorization of VAP suspicion is not a gold standard diagnostic method for pediatric VAP to the diagnostic accuracy of biomarkers be evaluated [
15]. Also, the absence of prior knowledge about cut-off values of the biomarkers tested and the inconsistency between the very few published studies did not offer the chance of using the appropriate detection range of the kit used.
Nevertheless, our study had several strengths such as a) the test of biomarkers of interest in a large scale of grading VAP suspicion population which reflects the daily practice and the intensivists’ decision making point for starting or not a new antimicrobial agent, b) the use of rigorous inclusion criteria based on clinical, laboratory, microbiological and radiological findings, c) the prospective collection of data, d) the use of non-invasive techniques to evaluate biomarkers in inflammation site, and e) the use of a novel fast-track molecular diagnostic method for pathogen identification.
4. Materials and Methods
We conducted a single-center prospective pilot cohort study from March 2021 to December 2022 on mechanically ventilated critically ill children in an 8-bed multivalent PICU of a tertiary university-affiliated hospital. As this is a continuation study of a previously reported study [
14] we briefly mention some of the study methods below.
Patient enrolment: Children hospitalized in the PICU on mechanical ventilation for ≥48 h with clinical suspicion of VAP were eligible for enrollment. Briefly, inclusion criteria followed a patient-customized approach for VAP suspicion according to local practice: (1) purulent respiratory or positive bronchial aspirate culture and initiation of antibiotics upon suspicion of VAP infection; (2) >20% increase of oxygen requirement together with fever or hypothermia, leukocytosis or leukopenia and initiation of antibiotics; (3) new radiological findings interpreted as lung infiltrates and >2 criteria from the following: temperature >38°C or <36°C, requirement of >20% oxygen, purulent respiratory secretions, blood leucocyte count <4 or >12 × 109 cells/L together with CRP >10 mg/L. The Ethics Committee of our tertiary Hospital approved the study and an informed consent was signed prior to study enrollment. Patients were excluded if informed consent was declined, the patient was expected not to survive >48 h after enrollment, pregnancy had not been excluded for adolescent female subjects, and if body weight was less than 3 kg.
On day 1 of study enrollment and based on the modified CPIS (mCPIS) tool [
15] for VAP diagnosis, the patients were divided in two groups: a group with high suspicion for VAP (mCPIS >6) and a group with low suspicion for VAP (mCPIS <6).
Sample collection and processing: Bronchial samples were collected by standard clinical practices, liquefied in a sterile 0.9% saline solution and were divided into three aliquots. The two aliquots were processed immediately for microbiology (cultured 30 min after collection on blood and MacConkey agar) and molecular diagnostics; the third aliquot was frozen at −75°C for biomarker measurements. The diagnostic threshold for infection was specified as bacterial growth present at ≥104CFU/mL. Species identification and susceptibility testing were determined using the VITEK-2 automated system (bioMérieux, Marcy l’ Étoile, France). Bronchial aliquots were analyzed using the Biofire Filmarray pneumonia plus platform (BioFire Diagnostics, LLC, Salt Lake City, UT). The cutoff value for colonization or infection was set at 104 copies/mL.
Βronchial samples obtained at day 1 and day 6 were stored at -70oC until processing by a sandwich ELISA assay according to the manufacturer’s recommendations (ELISA PAI-1 and IL-4 kits from Proteintech Group, Manchester, UK; ELISA RAGE kit from Millipore, Sigma Aldrich, Saint Louis, MO, USA). Reagent preparations were performed as recommended prior to assay commencement. The samples were diluted (two-fold for RAGE detection, eighty-fold for PAI-1 and two-fold for IL-4 measurements) and run in duplicate on a 96-well format. Final protein concentrations were obtained by being multiplied by the respective dilution factors. The highest and lowest limits of each protein standard were used as sample values for the samples read as outliers by the assay. The range of detection for sRAGE was 2-1500 pg/mL, for IL-4 was 15.6-1000 pg/mL and for PAI-1 was 0.312-20 ng/mL. Protein concentrations for each biomarker and experimental condition were obtained using a four-parameter logistic regression curve fit.
Statistical analysis: Continuous variables were presented as mean with standard deviations (SD) or medians and interquartile ranges (IQR), whenever not normally distributed. Respectively, comparisons between two groups were tested using an unpaired Student’s t or a Mann–Whitney U test. Categorical values were expressed as frequencies with percentages and comparisons were made using chi square or Fisher’s exact tests, whenever the expected counts were less than 5. The correlation between continuous variables was assessed with Spearman’s correlation, and the association between a dichotomous variable and a continuous variable was estimated with logistic regression and was expressed with odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI). All data analysis was performed using the IBM SPSS v28 software. A two-tailed p value <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
5. Conclusions
The role of soluble RAGE, PAI-1 and IL-4 in lung for the early diagnosis and monitoring of pediatric VAP seems to be limited. Fluid biomarkers obtained with non-invasive techniques, and with immediately available results, can constitute the future in VAP diagnosis and clinical decision making. Data on biomarkers in early pediatric VAP diagnosis are extremely limited, with small sample sizes. However, suspicion of VAP remains the main reason for high antimicrobial consumption in pediatric critically ill children and the use of multiple relevant biomarkers used concurrently may be the way to increase diagnostic specificity for VAP diagnosis.
Author Contributions
A.F. (Argyro Ftergioti) was involved in data curation, statistical analysis and writing the original draft of the manuscript. M.S. (Maria Simitsopoulou) was involved in experimental design and result acquisition, statistical analysis, writing the original draft of the manuscript, final editing and formatting. M.S. (Maria Sdougka) was involved in sample and medical record data collection. S.A.K. (Styliani Antonia Kallou) was involved in medical record data collection. A-B. H. (Anna-Bettina Haidich) was involved in the design of the study and the statistical analysis. C.V. (Christina Virgiliou) reviewed the manuscript. G.T. (Georgios Theodoridis) was involved in reviewing the manuscript and supervising. E.R. (Emmanuel Roilides) was involved in funding acquisition and reviewing the manuscript. E.I. (Elias Iosifidis) was involved in funding acquisition, project administration, supervision, statistical analysis, final editing and formatting of the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research project was supported by the Hellenic Foundation for Research and Innovation (H.F.R.I.) under the “2nd Call for H.F.R.I. Research Projects to support Post-Doctoral Researchers” (Project Number: 1047).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of Hippokration General Hospital of Thessaloniki, protocol code:58291/7.12.2020, date of approval: 14 April 2021.
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects enrolled in the study. It was presented in part at the European Society for Pediatric Infectious Diseases, Copenhagen, Denmark, May 2024.
Data Availability Statement
We confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available on reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors extend their appreciation to all PICU staff as well as to Maria Kitsou and Zoe Kravari for their overall assistance in this study. Elena Volakli, Asimina Violaki and Vivian Georgopoulou for sample and medical record data collection and x-ray evaluation.
Conflicts of Interest
Emmanuel Roilides reports fees to his institution from Amplyx, Astellas, Gilead, MSD, Pfizer, Scynexis, GSK and Shionogi, outside the submitted work. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Antalová, N.; Klučka, J.; Říhová, M.; Poláčková, S.; Pokorná, A.; Štourač, P. Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia Prevention in Pediatric Patients: Narrative Review. Children (Basel) 2022, 9, 1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modi, A.R.; Kovacs, C.S. Hospital-Acquired and Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia: Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention. Cleve Clin J Med 2020, 87, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangelova, V.; Kevorkyan, A.; Raycheva, R.; Krasteva, M. Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit—Incidence and Strategies for Prevention. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iosifidis, E.; Pitsava, G.; Roilides, E. Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia in Neonates and Children: A Systematic Analysis of Diagnostic Methods and Prevention. Future Microbiol 2018, 13, 1431–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalamitsou, S.; Violaki, A.; Iosifidis, E.; Avramidou, V.; Mantzafleri, P.-E.; Karaiskou, E.; Karantaglis, N.; Sdougka, M. Ventilator Associated Pneumonia (VAP) in Children: A Diagnostic Challenge. Signa Vitae-Journal of Anesthesiology, Intensive Care Journal, Emergency Medical Journal 2023, 19, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapid Syndromic Molecular Testing in Pneumonia: The Current Landscape and Future Potential - PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31809764/ (accessed on 29 June 2024).
- Performance Evaluation of a PCR Panel (FilmArray® Pneumonia Plus) for Detection of Respiratory Bacterial Pathogens in Respiratory Specimens: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis - PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37709201/ (accessed on 29 June 2024).
- Evaluation PCR Panel of the FilmArray® Pneumonia plus for Pathogen Detection of Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia in Children and Its Impact on Therapeutic Management - PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37069910/ (accessed on 29 June 2024).
- Microorganisms | Free Full-Text | Supporting Clinical Decisions with Rapid Molecular Diagnostic Pneumonia Panel in Pediatric Intensive Care Unit: Single Center Experience in Turkiye. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2076-2607/11/10/2391 (accessed on 29 June 2024).
- Increased Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 Concentrations in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluids Are Associated with Increased Mortality in a Cohort of Patients with Pseudomonas Aeruginosa - PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17264718/ (accessed on 29 June 2024).
- Elevated Levels of Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 in Pulmonary Edema Fluid Are Associated with Mortality in Acute Lung Injury - PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12730079/ (accessed on 29 June 2024).
- Determann, R.M.; Millo, J.L.; Waddy, S.; Lutter, R.; Garrard, C.S.; Schultz, M.J. Plasma CC16 Levels Are Associated with Development of ALI/ARDS in Patients with Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia: A Retrospective Observational Study. BMC Pulmonary Medicine 2009, 9, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinilla-Gonzalez, A.; Lara-Cantón, I.; Torrejón-Rodríguez, L.; Parra-Llorca, A.; Aguar, M.; Kuligowski, J.; Piñeiro-Ramos, J.D.; Sánchez-Illana, Á.; Navarro, A.G.; Vento, M.; et al. Early Molecular Markers of Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia in Bronchoalveolar Lavage in Preterm Infants. Pediatr Res 2023, 93, 1559–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antibiotics | Free Full-Text | Evaluation of Five Host Inflammatory Biomarkers in Early Diagnosis of Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia in Critically Ill Children: A Prospective Single Center Cohort Study. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2079-6382/12/5/921 (accessed on 29 June 2024).
- Value of Clinical Pulmonary Infection Score in Critically Ill Children as a Surrogate for Diagnosis of Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia - PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24581947/ (accessed on 29 June 2024).
- Advances in Biomarkers for Diagnosis and Treatment of ARDS - PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37958192/ (accessed on 29 June 2024).
- Plasma sRAGE Enables Prediction of Acute Lung Injury after Cardiac Surgery in Children - PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22616947/ (accessed on 29 June 2024).
- Biomarker-Based Clustering of Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease - PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36755966/ (accessed on 29 June 2024).
- Receptor for Advanced Glycation End-Products Is a Marker of Type I Cell Injury in Acute Lung Injury - PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16456142/ (accessed on 29 June 2024).
- Receptor for Advanced Glycation End-Products (RAGE) Is an Indicator of Direct Lung Injury in Models of Experimental Lung Injury | American Journal of Physiology-Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology. Available online: https://journals.physiology.org/doi/full/10.1152/ajplung.90546.2008 (accessed on 29 June 2024).
- Receptor for Advanced Glycation End-products Is a Marker of Type I Lung Alveolar Cells - Shirasawa - 2004 - Genes to Cells - Wiley Online Library. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/j.1356-9597.2004.00712.x (accessed on 29 June 2024).
- Receptor for Advanced Glycation End-Products and Environmental Exposure Related Obstructive Airways Disease: A Systematic Review - PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30918021/ (accessed on 29 June 2024).
- Lung Fluid Biomarkers for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis - PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30755248/ (accessed on 29 June 2024).
- Systematic Review of Diagnostic Methods for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome - PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33532455/ (accessed on 29 June 2024).
- Local Abnormalities in Coagulation and Fibrinolytic Pathways Predispose to Alveolar Fibrin Deposition in the Adult Respiratory Distress Syndrome. - PMC. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC548934/ (accessed on 29 June 2024).
- Diagnosis and Management of Pleural Infection - PMC. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10790177/ (accessed on 29 June 2024).
- El Solh, A.A.; Bhora, M.; Pineda, L.; Aquilina, A.; Abbetessa, L.; Berbary, E. Alveolar Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 Predicts ARDS in Aspiration Pneumonitis. Intensive Care Med 2006, 32, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mechanical Ventilation Affects Alveolar Fibrinolysis in LPS-Induced Lung Injury | European Respiratory Society. Available online: https://erj.ersjournals.com/content/28/5/992 (accessed on 29 June 2024).
- Dahlem, P.; Bos, A.P.; Haitsma, J.J.; Schultz, M.J.; Meijers, J.C.M.; Lachmann, B. Alveolar Fibrinolytic Capacity Suppressed by Injurious Mechanical Ventilation. Intensive Care Med 2005, 31, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Disturbed Alveolar Fibrin Turnover during Pneumonia Is Restricted to the Site of Infection | European Respiratory Society. Available online: https://erj.ersjournals.com/content/24/5/786 (accessed on 29 June 2024).
- Local Activation of Coagulation and Inhibition of Fibrinolysis in the Lung during Ventilator Associated Pneumonia | Thorax. Available online: https://thorax.bmj.com/content/59/2/130 (accessed on 29 June 2024).
- Elevated PAI-1 Is Associated with Poor Clinical Outcomes in Pediatric Patients with Acute Lung Injury - PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19855955/ (accessed on 29 June 2024).
- Plasminogen Activation Inhibitor Concentrations in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid Distinguishes Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia from Colonization in Mechanically Ventilated Pediatric Patients - PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20473240/ (accessed on 29 June 2024).
- Soluble Interleukin-4 Receptor in Atopic Children - PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7549506/ (accessed on 29 June 2024).
- Immunological Responses to Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection in Infancy - PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9135260/ (accessed on 29 June 2024).
- Cytokine Concentrations in Plasma from Children with Severe and Non-Severe Community Acquired Pneumonia - PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26407163/ (accessed on 29 June 2024).
- Mechanical Ventilation Induces Interleukin 4 Secretion in Lungs and Reduces the Phagocytic Capacity of Lung Macrophages | The Journal of Infectious Diseases | Oxford Academic. Available online: https://academic.oup.com/jid/article/217/10/1645/4624748 (accessed on 29 June 2024).
- Appraisal of Systemic Inflammation and Diagnostic Markers in a Porcine Model of VAP: Secondary Analysis from a Study on Novel Preventive Strategies | Intensive Care Medicine Experimental | Full Text. Available online: https://icm-experimental.springeropen.com/articles/10.1186/s40635-018-0206-1 (accessed on 29 June 2024).
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).