1. Introduction
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a prevalent neurodegenerative movement disorder, affecting 1% of people over 65 years of age and rising to 4% of the population by the age of 80 years (Kowal et al., 2013) [
1]. This disease is characterized by degeneration of brainstem nuclei and the accumulation of α−synuclein-containing aggregates (Lewy bodies and neurites) throughout the brain. Increased level of α-synuclein is associated with increased expression of protease activated receptor-2 (PAR2) in the brains of PD patients [
2]. Neuroinflammation is considered a complex defence mechanism leading to neuronal cell death; but the factors involved in the inflammatory process are not completely understood.
The hallmark sign of neuroinflammation in brain is the presence of activated microglia. Microglia in the aged brain shows indeed dystrophic morphology, elevated expression of inflammatory markers, and reduced expression of neuroprotective factors [
3]. Microglial cells mediate communication between the Central Nervous System (CNS) and immune cells. This communication is impaired in the elderly, predisposing them to low-grade chronic inflammation and the onset of neurodegenerative diseases [
4]. Microglial cells survey the local environment and clear cellular and/or bacterial debris by phagocytosis. These activities are both dependent on proteinases and their target receptors [
5]. The involvement of PAR2 and serine proteases is particularly interesting in cases of dyskinesia, given the findings of altered trypsin and serpins expression [
6]. PAR2 belongs to the family of protease activated receptors (PARS) and all the four PARs are widely expressed on neurons and glial cells in the nervous system, regulating diverse cellular functions, including gene transcription, neuronal cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival [
7,
8]. In particular, PAR2 has been shown to have modulatory effects in the peripheral nervous system where the receptor has important roles in inflammation, neuronal signaling, and nociception [
9,
10,
11,
12].
PAR2 has been linked with pro- and anti-inflammatory actions under normal conditions. However, in experimental models of inflammatory brain disease, the receptor determines mainly pro-inflammatory effects [
13,
14,
15]. Similarly, the role of Toll Like Receptor 4 (TLR4) in neurodegenerative diseases is not well understood. Amyloid β activates TLR4, induces neuroinflammation, and thereby drives neuronal apoptosis [
16,
17]. In contrast, it has been reported that the nonpyrogenic LPS-derived monophosphoryl lipid A (MPL) activates TLR4, while reducing the levels of neuroinflammation and improving Alzheimer’s disease-related pathology
in vivo [
18]. These opposite actions may reflect the dual role that microglia has in the innate immune response in different conditions. When in surveillance mode, ramified microglia continuously monitor the environment by sampling the extracellular space via rapid, moving processes. Cellular debris and/or pathogens are detected and then removed by the microglia once it is activated and in phagocytotic mode [
5,
19]. Such activity depends on a complex interaction with proteinases and cellular adhesion molecules. This activity occurs in the immediate environment of the cellular process due to low concentrations of the proteinase and their tight control by irreversibly acting serin protease inhibitors (serpins) [
20], as uncontrolled proteolysis is an undesirable event. Serpins comprise a large superfamily of proteins which control processes that require tight regulation, such as blood coagulation, inflammation, and fibrinolysis [
21]. The role of serpins in brain function is still unknown, although they have been implicated in multiple sclerosis (serpin-A5), Alzheimer’s disease (serpinA3), neuronal plasticity (neuroserpin) [
22,
23,
24], and recently also in Parkinson’s disease (serpinG1) [
25]. It is worth to note that recent data indicate that SerpinB3 is a key molecule for PAR2 synthesis and activation, which in turn determines increased levels of the SerpinB3-transcription factor CCAAT-enhancer-binding protein-β (C/EBP-β) in a positive loop manner [
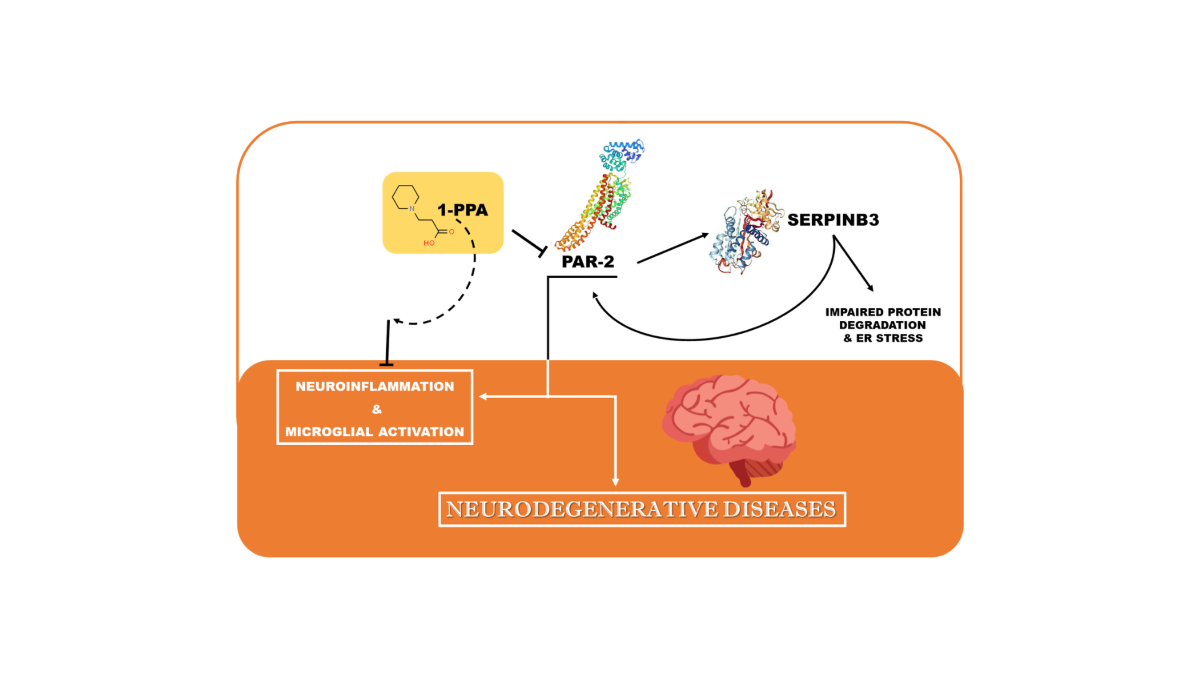
26]. The aim of our study was to evaluate the effect of 1-piperidine propionic acid (1-PPA), a recently identified allosteric inhibitor of PAR2 [
27], in neuroinflammation and microglia activation in Parkinson's disease.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation and culture of primary human fibroblasts
Human fibroblasts were obtained from skin biopsies of patients with Parkinson’s disease, with or without genetic mutations [
28]. Fibroblasts from skin biopsy of two normal subjects were used as control. Cells were grown in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle medium (DMEM) (Gibco) with the addition of 1% penicillin/streptomycin, 1% non-essential amino acids solution, 1 mM l-glutamine and 10% FBS at 37 °C with 5% CO2 atmosphere. Preliminary experiments were conducted on primary human fibroblasts using increasing amounts of 1-PPA over a time frame of 0 to 72 hours to identify the best reagent concentration and the optimal time point. On the basis of the results obtained, all the experiments described below were carried out in fibroblast cultures treated with 1-PPA at the concentration of 10 ng/ml (Merck Sigma-Aldrich St. Louis, MO, USA) for 48 hours.
The study protocol received approval by the Ethical Committee for clinical experimentation of Padova Province (Prot. n. 0034435, 08/06/2020). Informed consent for the use of biological samples was obtained from all patients. All procedures on human tissue samples were carried out in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
2.2. Isolation and culture of mouse microglia
Primary mouse microglial cells were derived from mixed gender cultures of C57BL/6J (Charles River, Wilmington, MA) mouse brains (postnatal days P0–P2). Cerebral cortices were stripped of the meninges and mechanically dissociated as previously described [
29]. The cell suspension, obtained from two mouse brains, was plated on poly-l-lysine (0.1 mg/ml, Merck Sigma-Aldrich St. Louis, MO, USA)-coated T-75 flask and cultivated in DMEM, supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum and 1% penicillin/ streptomycin (Gibco, Thermo Fischer Scientific, Waltham, Massachusetts, USA). The next day, the cells were washed three times with DPBS (Gibco, Thermo Fischer Scientific, Waltham, Massachusetts, USA) to remove cellular debris and cultured as previously reported [
30]. After 8–10 days in culture, weakly attached mature microglial cells were detached from the astrocytic monolayer with a repetition of the harvesting procedure every 2–3 days, up to three times.
To induce microglia activation, cells were incubated with 100ng/ml of LPS (Merck Sigma-Aldrich St. Louis, MO, USA) for 24 hours. Cells were then treated with 10 ng/ml of 1-PPA for 24 hours,cell pellets were harvested and used for RNA extraction.
2.3. Thioflavin S staining
To detect amyloid-like structures, Thioflavin S (Th-S) staining was carried out, which leads to an increase of specific fluorescence, when excited under blue light, and can be easily monitored and quantified. The slides of primary human fibroblasts from PD patients were incubated with freshly prepared 0.05% Thioflavin S (Merck Sigma-Aldrich St. Louis, MO, USA) for 8 min and quickly washed twice with 70% non-denatured ethanol, followed by three washes with H2O. Next, slides were incubated with DAPI (1:1,000 in methanol), mounted with Elvanol (Merck Sigma-Aldrich St. Louis, MO, USA) and observed under a fluorescence microscope (Axiovert 200M-Apotome.2, Carl Zeiss MicroImaging GmbH, Göttingen, Germany).
2.4. Immunofluorescence analysis
Human primary skin fibroblasts were seeded on slides (4 *105 cells/slide), the day after they were incubated with 1-PPA (10 ng/ml) or with Medium alone for 48 hours.
Mouse microglial cells (6 *105 cells/slide) were activated using LPS (100ng/ml) for 24 hrs and treated with 10 ng/ml of 1-PPA or saline buffer as control for additional 24 hours.
Cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde, permeabilized with 0.4% Tryton X-100, and blocked with 5% goat serum (Invitrogen Life Technologies, Waltham, MA, USA) in PBS containing 1% BSA. Slides were incubated with monoclonal anti-PAR2 antibody obtained in rabbit and anti-SB3 antibody obtained in mouse for 1 hour at room temperature, followed by incubation with the Alexa-Goat 546 and 488 secondary antibodies, respectively. Cellular nuclei were counterstained with Dapi (Merck Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA). Slides were mounted with ELVANOL (Merck Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) and observed under a fluorescence microscope (Axiovert 200M-Apotome.2, Carl Zeiss MicroImaging GmbH, Göttingen, Germany).
2.5. Quantitative real-time PCR (Q-PCR)
Total RNA was extracted from human fibroblasts and mouse microglial cells using Trizol Reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. After determination of the purity and the integrity of total RNA, complementary DNA synthesis was carried out from 1ug of RNA using LunaScript RT SuperMix (New England BioLabs, Ipswich, Massachusetts, USA). Quantitative real-time PCR reactions (RT-PCR) were performed according to Luna Universal qPCR master Mix (New England Biolabs, Ipswich, Massachusetts, USA) protocol, using the CFX96 Real-Time instrument (Bio-Rad Laboratories Inc, Hercules, CA, USA). The relative gene expression was generated for each sample by calculating 2-Δ Ct [
31].
2.7. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using Student's t-test for analysis of variance. All reported p-values were two-tailed and considered significant if p ≥ 0.05. The data in the bar charts are presented as mean ± SEM and were obtained from at least three independent experiments. Statistical tests and the concentration-time curves were performed using GraphPad Prism version 6.07 for Windows (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Human primary fibroblasts
To investigate the role of 1-PPA in neurodegenerative diseases, we have used two in vitro models, namely human primary fibroblasts obtained from patients with Parkinson's disease and LPS-activated primary mouse microglial cells.
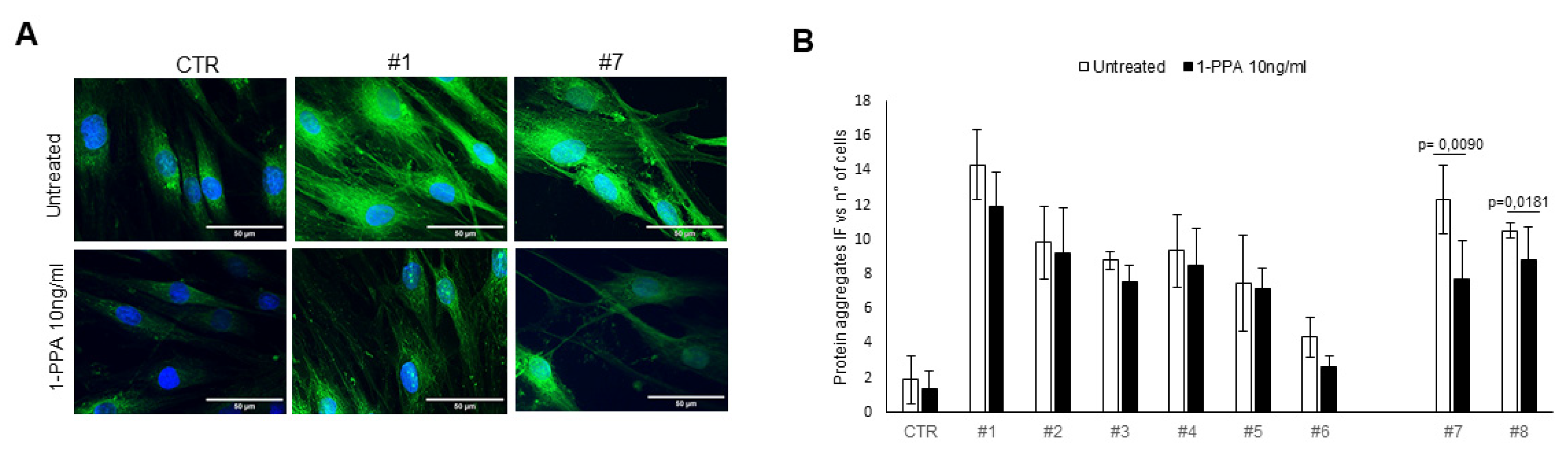
For the first model, it has been widely demonstrated that patient skin fibroblasts can be used as model systems for Parkinson's disease, since amyloid aggregates are also detectable in this compartment and easily obtainable from skin biopsy [
28,
32,
33]. In fibroblast of all patients, incuding both genetic and sporadic Parkinson’s disease, amiloid aggregates were visible by the Th-S assay and treatment with 1-PPA for 48 hours determined a decrease of fluorescence signal in all of the cases, reaching a significant difference in fibroblasts of the two sporadic patients (
Figure 1).
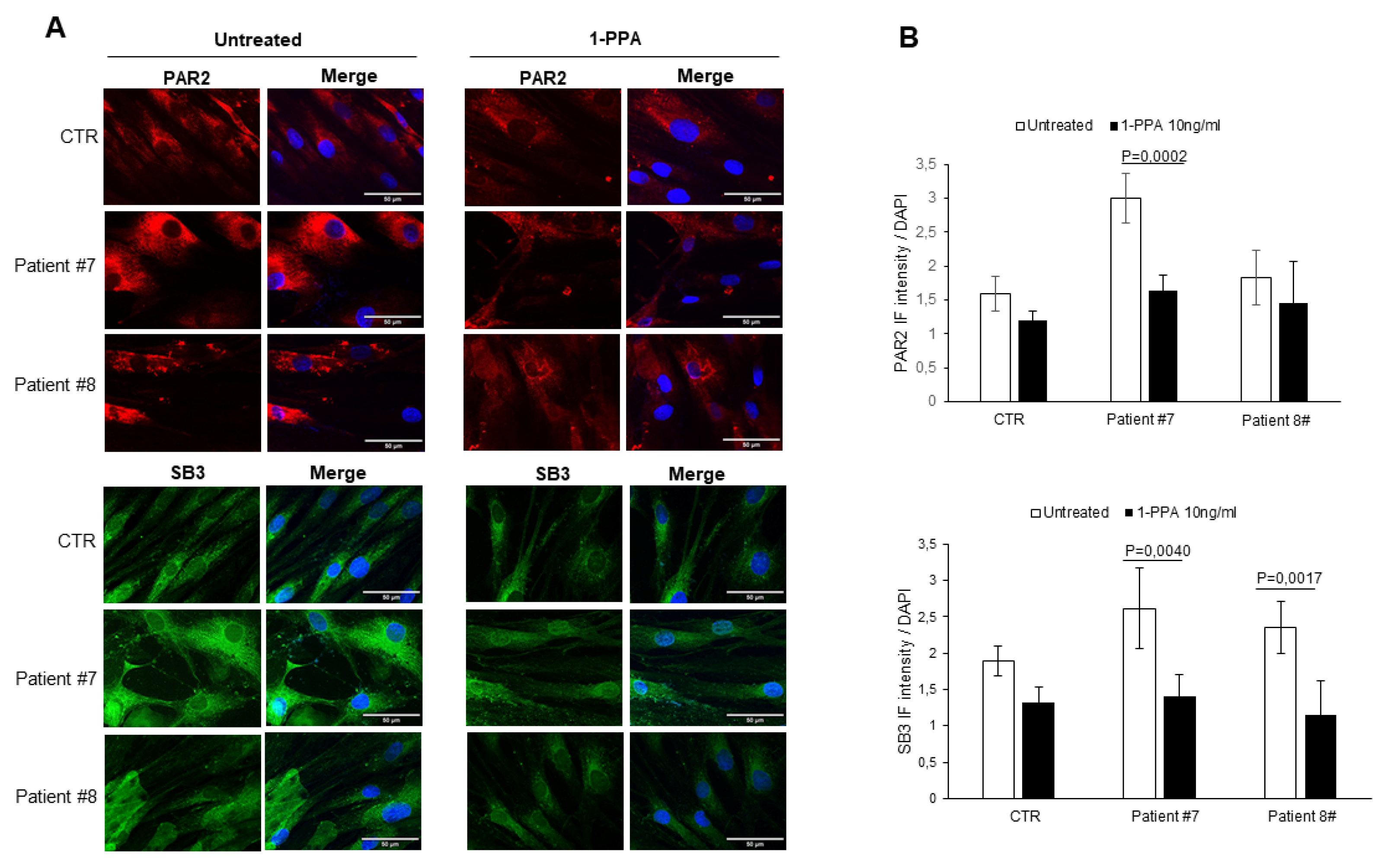
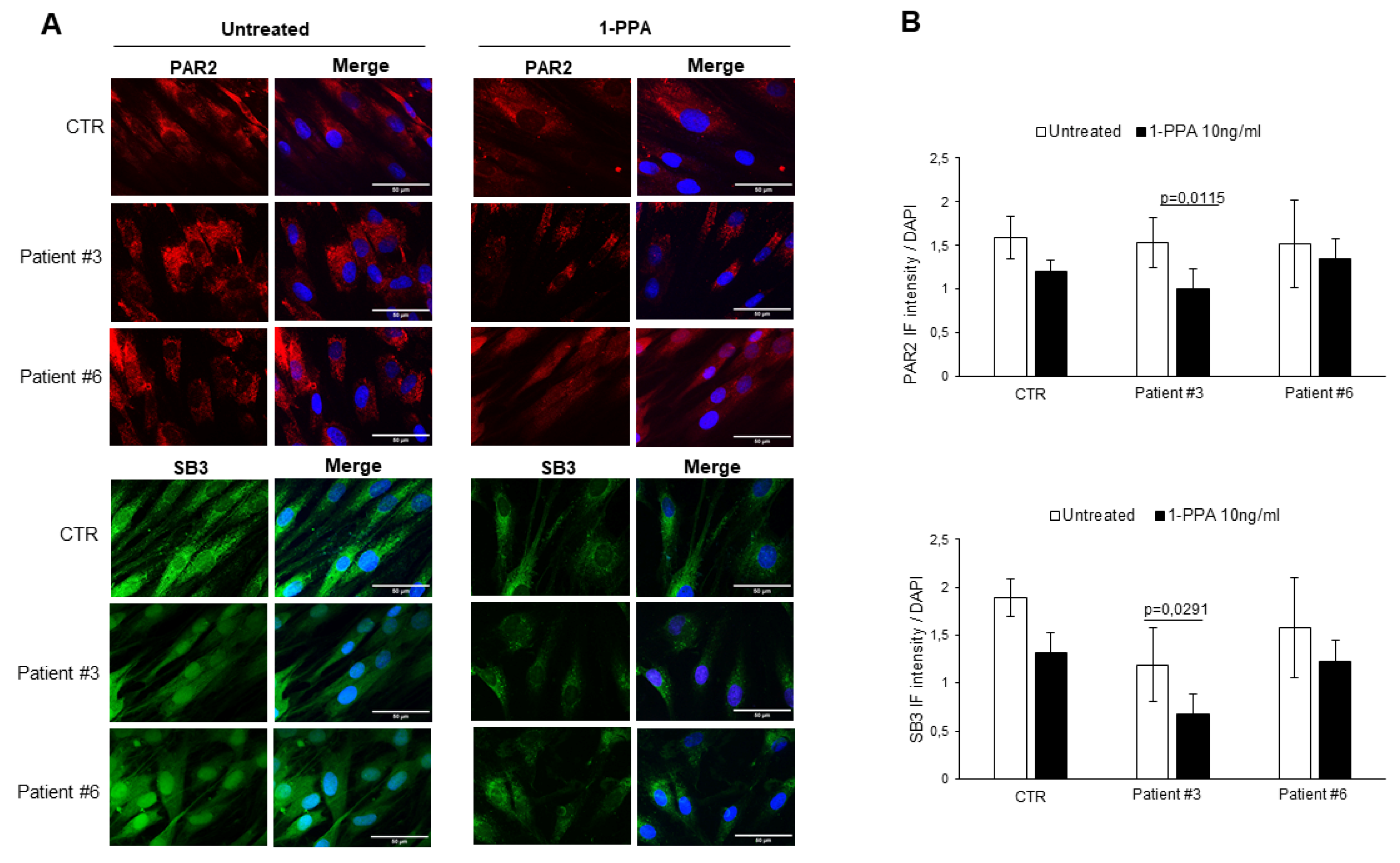
It is worth to know that the same primary fibroblasts from patients with Parkinson's disease, when treated with 1-PPA in the conditions described above, documented a parallel decresase of expression not only of PAR2, but also of SerpinB3, which was previously found to play a relevant role in PAR2 synthesis and expression [
26]. These results were obtained in fibroblast from all patients, both with sporadic (
Figure 2), and genetic Parkinson's disease (
Figure 3).
While in untreated fibroblasts from sporadic PD patients the levels of PAR2 and SerpinB3 were higher than those observed in the controls, in genetic PD patients, the levels of these two molecules was similar to those observed in the controls. These results suggest that the SerpinB3/PAR2 axys is more involved in amyloid aggregates formation in patients with sporadic PD than in patients with genetic PD, although the decrease of these two molecules determined by 1-PPA, which was found indeed also in the controls, favoured the reduction of amyloid deposition in all patients.
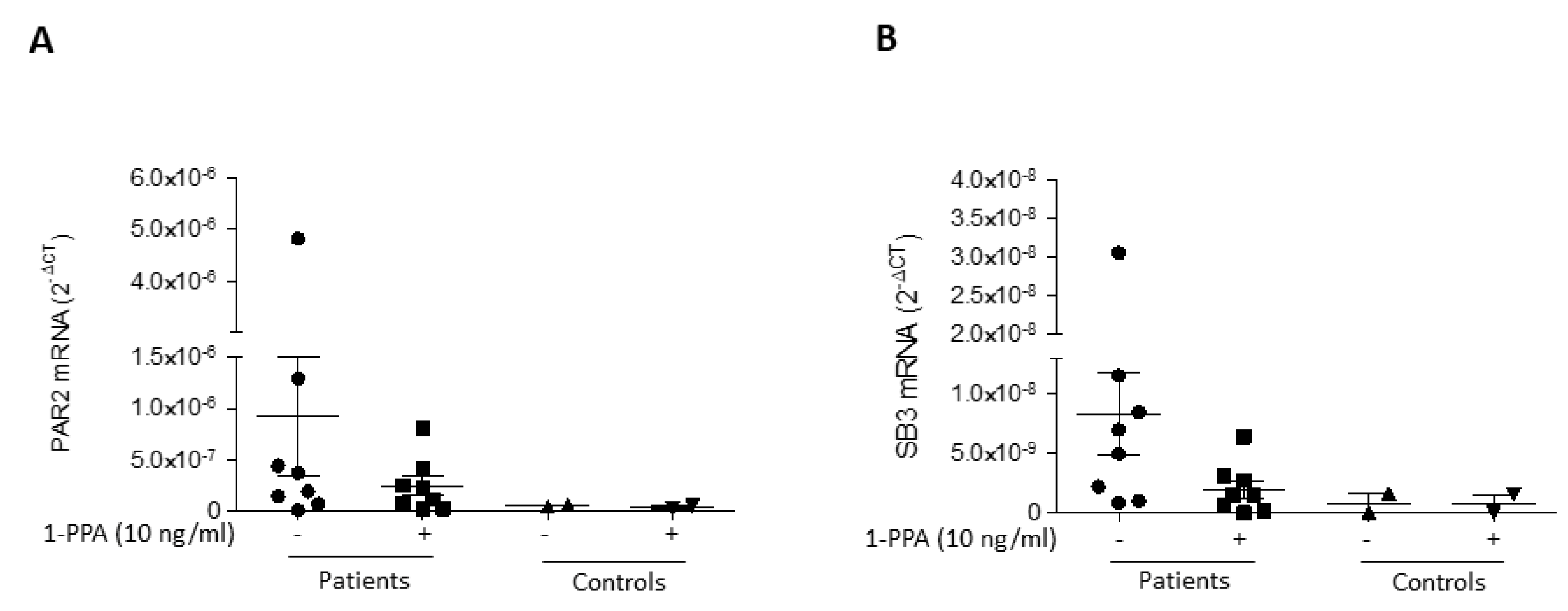
The above described data have also been confirmed at the level of gene expression where a decline of both PAR2 (
Figure 4A) and of SerpinB3 (
Figure 4B) after 1-PPA treatmente was observed in all the patients.
3.2. Primary mouse microglia
To investigate the role of this novel compound in the context of brain microenvironment, focusing on inflammatory response of microglia, primary mouse microglial cells were isolated from C57BL/6J mouse brains, activated with 100ng/ml of LPS and then treated with 10ng/ml of 1-PPA or with medium alone for 24 hours. The expression of the analyzed inflammatory cytokines documented a significant downregulation of IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α in cells treated with increasing amounts of 1-PPA, compared to untreated cells (
Figure 5).
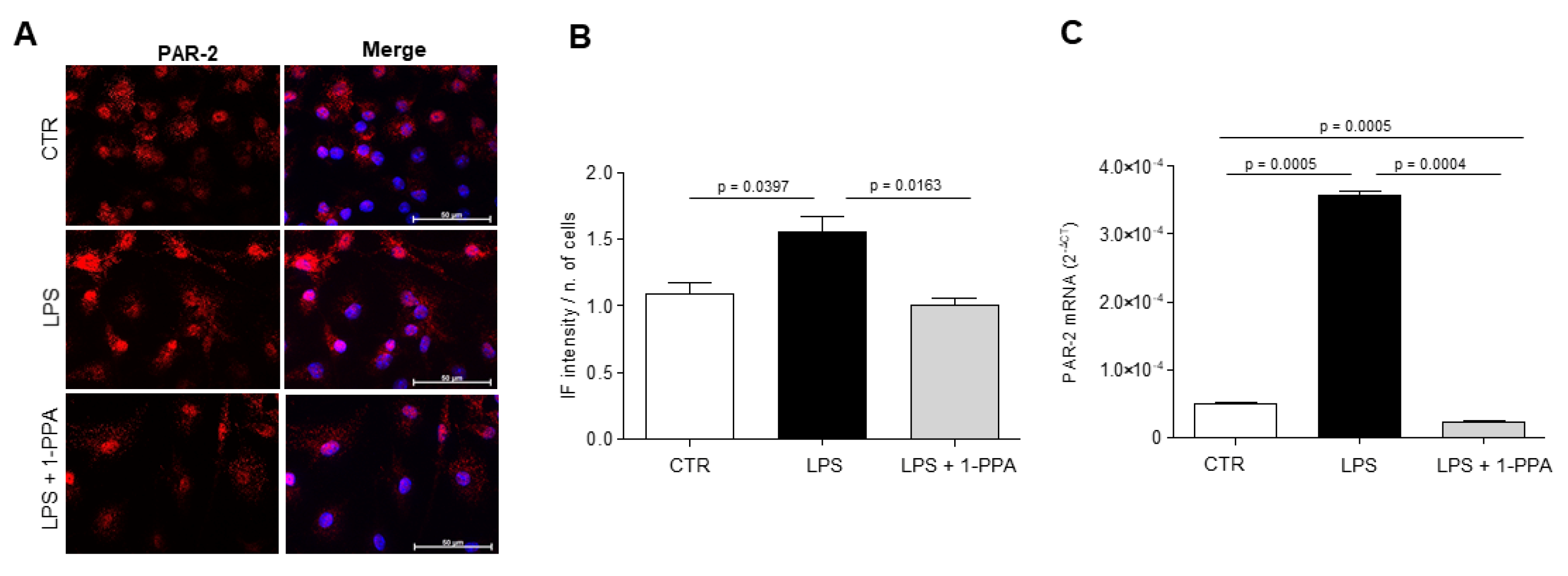
In agreement with the above results, LPS-activated microglial cells treated with 1-PPA showed a significant decrease of PAR2 expression, both at protein and transcription level (
Figure 6).
4. Discussion
In the neurodegenerative disorders truly effective treatments are rare, and the socio-economic costs are expected to increase considerably over the next few decades [
34]. Given the growing demand for central nervous system (CNS) drugs for an aging population, there is an urgent need for effective strategies to improve the success rates in drug discovery and development [
35].
This study aimed to evaluate whether the novel compound 1-PPA, that we have recently demonstrated to inhibit PAR2 activation [
27] and to markedly reduce the inflammatory response [
26], could be an effective compound to reduce neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease. Our findings have shown that 1-PPA is able to reduce the amyloid aggregates, typical finding of neurodegenerative diseases, in primary fibroblast cultures from patients with Parkinson’s disease, independently from the presence of genetic mutations. This effect was corroborated by the analysis of PAR2 expression, which was reduced in fibroblasts of all treated patients. It is interesting to note that in untreated fibroblast of patients with sporadic PD the expression of PAR2 was higher than in controls, at variance with the fibroblasts of patients with genetic PD, although in both groups of patients and also in controls, 1-PPA treatment determined a decrease of expression of this receptor. This behaviour may suggest that PAR2 could play a primary role in amyloid formation in sporadic PD. However, also in genetic PD, the reduced expression of PAR2below the physiological level could favour amyloid regression, being in this case genetic mutation the main driving mechanism. The dual role of PAR2 in Parkinson’s diseases has been widely demonstrated. From one side indeed this molecule can exert neuroprotective effects, especially in ischemic damage. On the other side, the ability to block this molecule during the neuroinflammation process can slow down the neurodegenerative process, typical of these diseases [
13].
Since it has been recently shown that the anti-protease activity of SerpinB3 exerts an important role in PAR2 activation and increased synthesis in metabolic-associated liver disease [
26], we have assessed whether this also occurs in our model of neurodegenerative diseases. The obtained results have demonstrated a parallel behaviour of PAR2 and SerpinB3 molecules in fibroblast cultures of all patients, with a decrease of both molecules after treatment with PAR2. These findings support the role of PAR2/SerpinB3 axis in inflammation and provide evidence of its implication in amyloid deposition. It is worth to note that SerpinB3 also determines a disfunction of the ubiquitin-proteasome system, preventing protein degradation, by selective NEDDylation, since it determines over-expression of the NEDD8-activating enzyme 1 (NAE1) [
36].
In the literature it is well known that in neurological disorders the role of microglia is crucial, as it plays a defense function, however, its persistent activation is one of the most important factors leading to neurodegeneration [
37]. In our experimental conditions, LPS-activated mouse microglia, treatment with 1-PPA determined a significantly downregulation of PAR2 which was associated to a significant decrease of inflammatory cytokines synthesis, providing evidence that this small molecule can control brain inflammation.
These results are of particular relevance, since our preliminary data indicate that 1-PPA is able to cross the blood-brain barrier (manuscript in preparation), and this barrier greatly restricts and controls the movement of substances' entry into the brain, therefore brain drug delivery is one of the main problems for the treatment of neurological disorders [
38].
5. Conclusion
Targeting PAR2, which is involved in many inflammatory diseases as well as in cancer, is an important valuable strategy in neurodegenerative disease, in particular in Parkinson’s disease. In this study we have shown that PAR2 inhibition with the novel compound 1-PPA leads to a reduction of neuroglial inflammation and a decrease of amyloid aggregates, typical features of neurodegenerative processes.
In conclusion, 1-PPA, being part of the very small group of molecules that can reach the brain, provides a concrete new strategy to control neuroinflammation, through pharmacological inhibition of the inflammatory pathway that targets PAR2/SerpinB3 axis.
6. Patents
Italian Patent Application N. 102022000014593 filed by the University of Padova on July 12, 2022; PTC/IB2023/057138 filed on July 12, 2023.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on
Preprints.org, Table S1: List and sequences of murine and human primers used for quantitative real time PCR.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.P., A.A.; methodology, S.Q., M.S.; investigation, M.R., A.B.; resources, M.C., A.E.; data curation, S.Q.; writing—original draft preparation, S.Q.; writing—review and editing, P.P, A.A.; supervision, P.P, A.A.; funding acquisition, P.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded in part by the National Ministry of Health, grant number RF-2019-12369984 (P.P.).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study protocol received approval by the Ethical Committee for clinical experimentation of Padova Province (Prot. n. 0034435, 08/06/2020). All procedures on human tissue samples were carried out in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
Pontisso P, Biasiolo A, Quarta, S, Ruvoletto M. are inventors of the Patent Application of the University of Padova N. 102022000014593. No conflict of interest exists for the other authors.
References
- S. L. Kowal, T. M. Dall, R. Chakrabarti, M. V. Storm, and A. Jain. The current and projected economic burden of Parkinson’s disease in the United States», Mov Disord, 2013, vol. 28 (3), pp. 311–318. [CrossRef]
- P. Liua, L. Sunb, X.L. Zhaoc, P. Zhangd, X-M Zhaoa, J. Zhang. PAR2-mediated epigenetic upregulation of α-synuclein contributes to the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease. Brain Res 2014, vol. 1565, pp. 82-89. [CrossRef]
- Niraula, J. F. Sheridan, e J. P. Godbout. Microglia Priming with Aging and Stress. Neuropsychopharmacology, 2017, vol. 42 (1), pp. 318–333. [CrossRef]
- N. Zilka et al., Who fans the flames of Alzheimer’s disease brains? Misfolded tau on the crossroad of neurodegenerative and inflammatory pathways. J Neuroinflammation 2012, vol. 9 (1), p. 47. [CrossRef]
- H. Kettenmann, U.-K. Hanisch, M. Noda, and A. Verkhratsky, Physiology of Microglia. Physiol Rev, 2011, vol. 91 (2), pp. 461–553. [CrossRef]
- M.J. Hurley, P. F. Durrenberger, S.M. Gentleman, A. F. Walls, D. T. Dexter. Altered Expression of Brain Proteinase-Activated Receptor-2, Trypsin-2 and Serpin Proteinase Inhibitors in Parkinson's Disease. J Mol Neurosci. 2015, vol 57(1), pp48-62. [CrossRef]
- V. S. Ossovskaya e N. W. Bunnett. Protease-Activated Receptors: Contribution to Physiology and Disease, Physiol Rev 2004, vol. 84 (2), pp. 579–621. [CrossRef]
- S. R. Macfarlane, M. J. Seatter, T. Kanke, G. D. Hunter, e R. Plevin. Proteinase-activated receptors. Pharmacol Rev. 2001, vol. 53 (2), pp. 245–282.
- G. S. Cottrell, S. Amadesi, F. Schmidlin, N. Bunnett. Protease-activated receptor 2: activation, signalling and function. Biochem. Soc. Transact. 2003, vol. 31 (6), pp. 1191–1197. [CrossRef]
- M. Steinhoff, N. Vergnolle, S. H. Young, M. Tognetto, S. Amadesi, H. S. Ennes, M .Trevisani, M. D. Hollenberg, J. L. Wallace, et al. Agonists of proteinase-activated receptor 2 induce inflammation by a neurogenic mechanism. Nat Med 2000, vol. 6 (2), pp. 151–158. [CrossRef]
- N. Vergnolle, J. L. Wallace, N. W. Bunnett, e M. D. Hollenberg. Protease-activated receptors in inflammation, neuronal signaling and pain. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2001, vol. 22 (3), pp. 146–152. [CrossRef]
- N. Vergnolle, M. Ferazzini, M. R. D’Andrea, J. Buddenkotte, M. Steinhoff. Proteinase-activated receptors: novel signals for peripheral nerves. Trends in Neurosci. 2003, vol. 26 (9), pp. 496–500. [CrossRef]
- Afkhami-Goli, F. Noorbakhsh, A.J. Keller, N. Vergnolle, D. Westaway, J. H. Jhamandas, P. Andrade-Gordon, M. D. Hollenberg, H.Arab, R.H. Dyck,et al. Proteinase-Activated Receptor-2 Exerts Protective and Pathogenic Cell Type-Specific Effects in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Immunol. 2007, vol. 179 (8), pp. 5493–5503. [CrossRef]
- G. Jin, T. Hayashi, J.Kawagoe, T. Takizawa, T.Nagata, I. Nagano, M. Syoji, K. Abe et al. Deficiency of PAR-2 Gene Increases Acute Focal Ischemic Brain Injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2005, vol. 25 (3), pp. 302–313. [CrossRef]
- F. Noorbakhsh, , S.Tsutsui, N. Vergnolle, L.A. Boven, N. Shariat, M. Vodjgani, K. G. Warren, P. Andrade-Gordon, M. D. Hollenberg, C.Power . Proteinase-activated receptor 2 modulates neuroinflammation in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and multiple sclerosi. J Exp. Med. 2006, vol. 203 (2), pp. 425–435. [CrossRef]
- S.-C. Tang, J.D. Lathia, P. K. Selvaraj, D. Jo, M.R. Mughal, A. Cheng, D. A. Siler, W.R. Markesbery, T. V. Arumugam, M.P. Mattson. Toll-like receptor-4 mediates neuronal apoptosis induced by amyloid β-peptide and the membrane lipid peroxidation product 4-hydroxynonenal. Exp. Neurol., 2008, vol. 213 (1), pp. 114–121, set.. [CrossRef]
- M. Zeuner, K. Bieback, D. Widera. Controversial Role of Toll-like Receptor 4 in Adult Stem Cell., Stem Cell Rev and Rep. 2015, vol. 11 (4), pp. 621–634, ago.. [CrossRef]
- J.-P. Michaud, M. Hallé, A. Lampron, P.Thériault, P. Préfontaine, M. Filali, P. Tribout-Jover, A. Lanteigne, R. Jodoin, C.r Cluff et al. Toll-like receptor 4 stimulation with the detoxified ligand monophosphoryl lipid A improves Alzheimer’s disease-related pathology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2013, vol. 110 (5), pp. 1941–1946. [CrossRef]
- Nimmerjahn, F. Kirchhoff, e F. Helmchen. Resting Microglial Cells Are Highly Dynamic Surveillants of Brain Parenchyma in Vivo. Science 2005, vol. 308 (5726) pp. 1314–1318. [CrossRef]
- Y. Wang, W. Luo, G. Reiser.Trypsin and trypsin-like proteases in the brain: Proteolysis and cellular functions. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2008, vol. 65 (2), pp. 237–252. [CrossRef]
- J. A. Huntington. Serpin structure, function and dysfunction. J Thromb. and Haemost. 2011, vol. 9, pp. 26–34. [CrossRef]
- M. H. Han, S.-I. Hwang, D. B. Roy, D. H. Lundgren, J. V. Price, S. S. Ousman, G. H. Fernald, B. Gerlitz, W. H. Robinson, et al. Proteomic analysis of active multiple sclerosis lesions reveals therapeutic targets. Nature 2008, vol. 451 (7182), pp. 1076–1081. [CrossRef]
- G. A. Hastings, T. A. Coleman, C. C. Haudenschild, S. Stefansson, E. P. Smith, R. Barthlow, S. Cherry, M. Sandkvist, D. A. Lawrence. Neuroserpin, a Brain-associated Inhibitor of Tissue Plasminogen Activator Is Localized Primarily in Neurons. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, vol. 272 (52), pp. 33062–33067. [CrossRef]
- S. Janciauskiene, H. T. Wright. Inflammation, antichymotrypsin, and lipid metabolism: autogenic etiology of Alzheimer’s disease. Bioessays, 1998, vol. 20 (12), pp. 1039–1046. [CrossRef]
- M.H. Seo, S.H. Kim, S. Yeo. Serping1 associated with alpha-synuclein increase in colonic smooth muscles of MPTP-induced Parkinson's disease mice. Sci Rep. 2024 vol. 14(1), p. 1140. [CrossRef]
- G. Villano, E.Novo, C. Turato, S. Quarta, M.Ruvoletto, A. Biasiolo, F. Protopapa, M. Chinellato, A. Martini, E. Trevellin . The protease activated receptor 2 - CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta - SerpinB3 axis inhibition as a novel strategy for the treatment of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Mol. Met. 2024vol. 81, p. 101889. [CrossRef]
- M. Chinellato, M. Gasparotto, S. Quarta, M. Ruvoletto, A. Biasiolo, F. Filippini, L.Spiezia, L. Cendron, P. Pontisso. 1-Piperidine Propionic Acid as an Allosteric Inhibitor of Protease Activated Receptor-2. Pharmaceuticals, 2023, vol. 16 (10), p. 1486,. [CrossRef]
- G. Auburger, M. Klinkenberg, J. Drost, K. Marcus, B. Morales-Gordo, W. S. Kunz, U. Brandt, V. Broccoli, H. Reichmann et al. Primary Skin Fibroblasts as a Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2012, vol. 46 (1), pp. 20–27. [CrossRef]
- Russo, G. Berti, N. Plotegher, G. Bernardo, R.Filograna, L. Bubacco, E. Greggio., Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 positively regulates inflammation and down-regulates NF-κB p50 signaling in cultured microglia cells., J Neuroinflam. 2015, vol. 12 (1), p. 230. [CrossRef]
- H. Scheiblich, A. Schlütter, D. T. Golenbock, E. Latz, P. Martinez-Martinez, M. T. Heneka. Activation of the NLRP 3 inflammasome in microglia: the role of ceramide. J. Neurochem. 2017, vol. 143 (5), pp. 534–550, dic.. [CrossRef]
- K. J. Livak, T. D. Schmittgen. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, vol. 25 (4), pp. 402–408. [CrossRef]
- G. P. Connolly. Fibroblast models of neurological disorders: fluorescence measurement studies.Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1998, vol. 19(5), pp. 171–177. [CrossRef]
- L. Gasparini, M. Racchi, G. Binetti, M. Trabucchi, S. B. Solerte, D. Alkon, R. Etcheberrigaray, G. Gibson, J. Blass, R. Paoletti, S. Govoni. Peripheral markers in testing pathophysiological hypotheses and diagnosing Alzheimer’s disease. FASEB J. 1998, vol. 12 (1), pp. 17–34. [CrossRef]
- L. Cui, W. Yang, J. Shuai, Y. Ma, Y. Yan. Lifestyle and Socioeconomic Transition and Health Consequences of Alzheimer's Disease and Other Dementias in Global, from 1990 to 2019. J Prev Alzheimers Dis. 2024, Vol 11(1), pp. 88-96. [CrossRef]
- J. Yang, W. Zhi, L. Wang. Role of Tau Protein in Neurodegenerative Diseases and Development of Its Targeted Drugs: A Literature Review. Molecules. Vol 29(12), 2024, p. 2812. [CrossRef]
- S. Cannito, B. Foglia, G. Villano, C. Turato, T. C. Delgado, E. Morello, F. Pin, E. Novo, L. Napione, S. Quarta, et al. SerpinB3 Differently Up-Regulates Hypoxia Inducible Factors -1α and -2α in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Mechanisms Revealing Novel Potential Therapeutic Targets. Cancers 2019, vol 11, p. 1933. [CrossRef]
- Santiago-Balmaseda, A. Aguirre-Orozco, I.E. Valenzuela-Arzeta, M.M. Villegas-Rojas, I. Pérez-Segura, N. Jiménez-Barrios, E. Hurtado-Robles, L.D. Rodríguez-Hernández, E.R. Rivera-German, M. Guerra-Crespo, et al. Neurodegenerative Diseases: Unraveling the Heterogeneity of Astrocytes. Cells, 2024, vol. 13(11), p. 921. [CrossRef]
- D.A. Peterson. Blood–Brain Barrier. In: eLS. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd: Chichester, 2012. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).