Submitted:
04 July 2024
Posted:
05 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
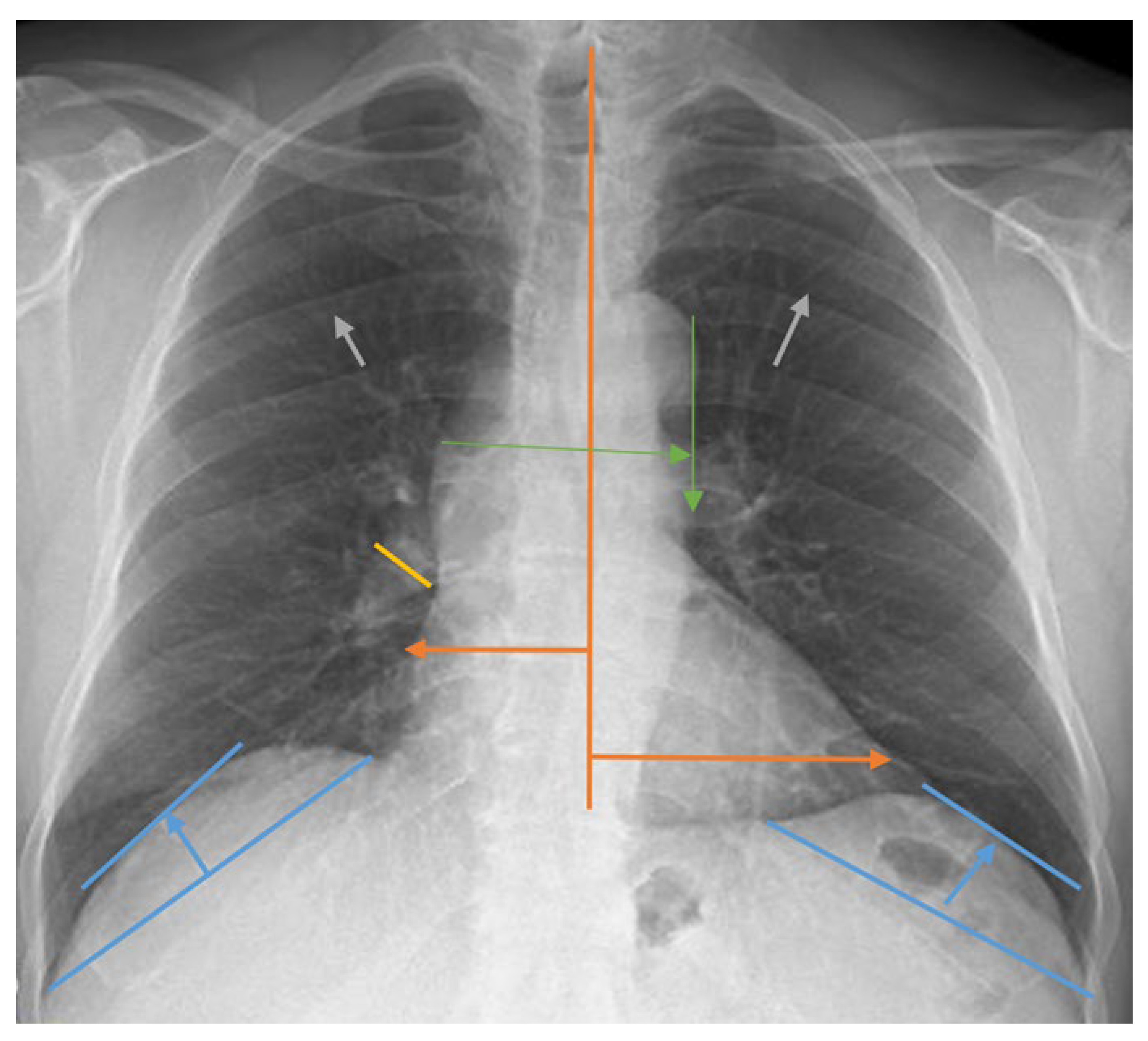
2.2. Lung Radiograph Measurement Calculations
2.3. Ethical Approval
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scott, I.A.; Scuffham, P.; Gupta, D.; Harch, T.M.; Borchi, J.; Richards, B. Going digital: a narrative overview of the effects, quality and utility of mobile apps in chronic disease self-management. Aust. Health Rev. 2018, 44, 62-82. [CrossRef]
- Acosta-Ochoa, I.; Bustamante-Munguira, J.; Mendiluce-Herrero, A.; Bustamante-Bustamante, J.; Coca-Rojo, A. Impact on outcomes across KDIGO-2012 AKI criteria according to baseline renal function. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1323. [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, V.; Khademian, M.H.; Masoumi, S.J.; Morvaridi, M.R.; Ezzatzadegan Jahromi, S. Factors influencing survival time of hemodialysis patients; time to event analysis using parametric models: a cohort study, BMC Nephrol. 2019, 20, 1-9. [CrossRef]
- Thomé, F.S.; Sesso, R.C.; Lopes, A.A.; Lugon, J.R.; Martins, C.T. Brazilian chronic dialysis survey 2017. Braz. J. Nephrol. 2019, 41, 208-214. [CrossRef]
- Liyanage, T.; Ninomiya, T.; Jha, V.; Neal, B.; Patrice, H.M.; Okpechi, I.; Zhao, M.; Lv, J.; Garg, A.X.; Knight, J.; Rodgers, A.; Gallagher, M.; Kotwal, S.; Cass, A.; Perkovic, V. Worldwide access to treatment for end-stage kidney disease: a systematic review. Lancet 2015, 385, 1975-1982. [CrossRef]
- Wetmore, J.B.; Collins, A.J. Global challenges posed by the growth of end-stage renal disease. Ren. Replace. Ther. 2016, 2, 1-7. [CrossRef]
- Kainz, A.; Berner, C.; Ristl, R.; Simon, A.; Stamm, T.; Zitt, E.; Kramar, R.; Antlanger, M.; Kautzky-Willer, A.; Schmaldienst, S.; Schernhammer, E.; Port, F.K.; Carrero, J.J.; Jager, K.J.; Hecking, M. Sex-specific analysis of haemodialysis prevalence, practices and mortality over time: the Austrian Dialysis Registry from 1965 to 2014. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2019, 34, 1026-1035. [CrossRef]
- Naeem, A.; Ahmed, A.R.; Khan, K.; Khan, M.E.; Ali, B.; Banaras, F. Comparison of patient survival between hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis among patients eligible for both modalities. J. Popul. Ther. Clin. Pharmacol. 2023, 30, 1773-1778. [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; Kwan, B.C.; Chow, K.M.; Chung, K.Y.; Leung, C.B.; Li, P.K.; Szeto, C.C. Measurements on the routine chest radiograph as prognostic markers in Chinese peritoneal dialysis patients. Clin. Nephrol. 2011, 76, 16-22. [CrossRef]
- Zandieh, S.; Muin, D.; Bernt, R.; Krenn List, P.; Mirzaei, S.; Haller, J. Radiological diagnosis of dialysis-associated complications. Insights Imaging 2014, 5, 603-617. [CrossRef]
- Degrassi, F.; Quaia, E.; Martingano, P.; Cavallaro, M.; Cova, M.A. Imaging of haemodialysis: renal and extrarenal findings. Insights Imaging 2015, 6, 309-321. [CrossRef]
- Levin, A.; Ahmed, S.B.; Carrero, J.J.; Foster, B.; Francis, A.; Hall, R.K.; Herrington, W.G.; Hill, G.; Inker, L.A.; Kazancıoğlu, R.; Lamb, E.; Lin, P.; Madero, M.; McIntyre, N.; Morrow, K.; Roberts, G.; Sabanayagam, D.; Schaeffner, E.; Shlipak, M.; Shroff, R.; Tangri, N.; Thanachayanont, T.; Ulasi, I.; Wong, G.; Yang, C.-W.; Zhang, L.; Robinson, K.A.; Wilson, L.; Wilson, R.F.; Kasiske, B.L.; Cheung, M.; Earley, A.; Stevens, P.E. Executive summary of the KDIGO 2024 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease: Known knowns and known unknowns. Kidney Int. 2024, 105, 684-701. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, H.; Diao, Z.; et al. Epidemiological analysis of death among patients on maintenance hemodialysis: results from the Beijing Blood Purification Quality Control and Improvement Center. BMC Nephrol. 2023, 24, 236. [CrossRef]
- Bitar, W.; Helve, J.; Kanerva, M.; Honkanen, E.; Rauta, V.; Haapio, M., et al. Severe infections in peritoneal dialysis and home hemodialysis patients: An inception cohort study. PLoS One. 2023, 18, e0286579. [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Teitelbaum, I. Peritoneal dialysis adequacy: a paradigm shift. Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 41, 150. [CrossRef]
- Daugirdas, J.T.; Depner, T.A.; Inrig, J.; Mehrotra, R.; Rocco, M.V.; Suri, R.S.; Weiner, D.E.; Greer, N.; Ishani, A.; MacDonald, R.; Olson, C.; Rutks, I.; Slinin, Y.; Wilt, T.J.; Rocco, M.; Kramer, H.; Choi, M.J.; Samaniego-Picota, M.; Scheel, P.J.; Willis, K.; Joseph, J.; Brereton, L. KDOQI clinical practice guideline for hemodialysis adequacy: 2015 update. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2015, 66, 884-930. [CrossRef]
- Elasan, S.; Yilmaz, O. Cardiothoracic ratio and left ventricular ejection fraction relationship: A meta-analysis study. Saudi Med. J. 2023, 44, 529. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Shi, R.; Mahler, S.; Gaspard, J.; Gorchynski, J.; D’Etienne, J.; Arnold, T. Vascular pedicle width on chest radiograph as a measure of volume overload: meta-analysis. West. J. Emerg. Med. 2011, 12, 426-432. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, E.T.; Silva, C.I.; Seely, J.M.; Chong, S.; Lee, K.S.; Müller, N.L. Pulmonary artery aneurysms and pseudoaneurysms in adults: findings at CT and radiography. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2007, 188, W126-134. [CrossRef]
- Van Diepen, M.; Ramspek, C.L.; Jager, K.J.; Zoccali, C.; Dekker, F.W. Prediction versus aetiology: common pitfalls and how to avoid them. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2017, 32 (suppl_2), ii1-ii5. [CrossRef]
- Van Geloven, N.; Swanson, S.A.; Ramspek, C.L.; Luijken, K.; van Diepen, M.; Morris, T.P.; Groenwold, R.H.H.; van Houwelingen, H.C.; Putter, H.; le Cessie, S. Prediction meets causal inference: the role of treatment in clinical prediction models. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2020, 35, 619-630. [CrossRef]
- Olsen, M.H.; Angell, S.Y.; Asma, S.; Boutouyrie, P.; Burger, D.; Chirinos, J.A.; Damasceno, A.; Delles, C.; Gimenez-Roqueplo, A.-P.; Hering, D.; López-Jaramillo, P.; Martinez, F.; Perkovic, V.; Rietzschel, E.R.; Schillaci, G.; Schutte, A.E.; Scuteri, A.; Sharman, J.E.; Wachtell, K.; Wang, J.G. A call to action and a lifecourse strategy to address the global burden of raised blood pressure on current and future generations: the Lancet Commission on hypertension. Lancet, 2016, 388, 2665-2712. [CrossRef]
- Habas, E.; Habas, E.; Khan, F.Y.; Rayani, A.; Habas, A.; Errayes, M.; Farfar, K.L.; Elzouki, A.N.Y. Blood Pressure and Chronic Kidney Disease Progression: An Updated Review. Cureus, 2022, 14, e24244. [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.Y.; Shao, X.; Qin, H.; Yin, P.; Lin, Y.; Wu, J.; Ren, J.; Zheng, Y. Disease burden and epidemiological trends of chronic kidney disease at the global, regional, national levels from 1990 to 2019. Nephron, 2024, 148, 113-123. [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Lai, J.N.; Haw, Y.; Chiu, L.T.; Huang, S.M.; Cheng, K.L.; Chew, F.Y. Vesicoureteral reflux is associated with increased risk of chronic kidney disease: A nationwide cohort study. Medicine, 2023, 102, e34867. [CrossRef]
- Nardelli, L.; Scalamogna, A.; Ponzano, F.; Sikharulidze, A.; Tripodi, F.; Vettoretti, S.; Alfieri, C.; Castellano, G. Peritoneal dialysis related peritonitis: insights from a long-term analysis of an Italian center. BMC Nephrol. 2024, 25, 163. [CrossRef]
- Thompson, S.; James, M.; Wiebe, N.; Hemmelgarn, B.; Manns, B.; Klarenbach, S.; Tonelli, M. Cause of death in patients with reduced kidney function. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 2504-2511. [CrossRef]
- Andreoli, M.C.C.; Totoli, C. Peritoneal dialysis. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2020, 66, s37-s44. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Auguste, B.L. Five things to know about volume overload in peritoneal dialysis. Can. J. Kidney Health Dis. 2023, 10, 20543581221150590. [CrossRef]
- Almeida, C.P.; Ponce, D.; de Marchi, A.C.; Balbi, A.L. Effect of peritoneal dialysis on respiratory mechanics in acute kidney injury patients. Perit. Dial. Int. 2014, 34, 544-549. [CrossRef]
- Rocco, M.V.; Rigaud, M.; Ertel, C.; Russell, G.; Zemdegs, J.; Vecchio, M. Fluid intake management in maintenance hemodialysis using a smartphone-based application: a pilot study. Kidney Med. 2023, 5, 100703. [CrossRef]
- Alıcı, G.; Waberi, M.M.; Mohamud, M.A.; Bashir, A.M.; Genç, Ö. Pulmonary hypertension among maintenance hemodialysis patients in Somalia: a hospital-based observational study. Egypt. Heart J. 2022, 74, 24. [CrossRef]
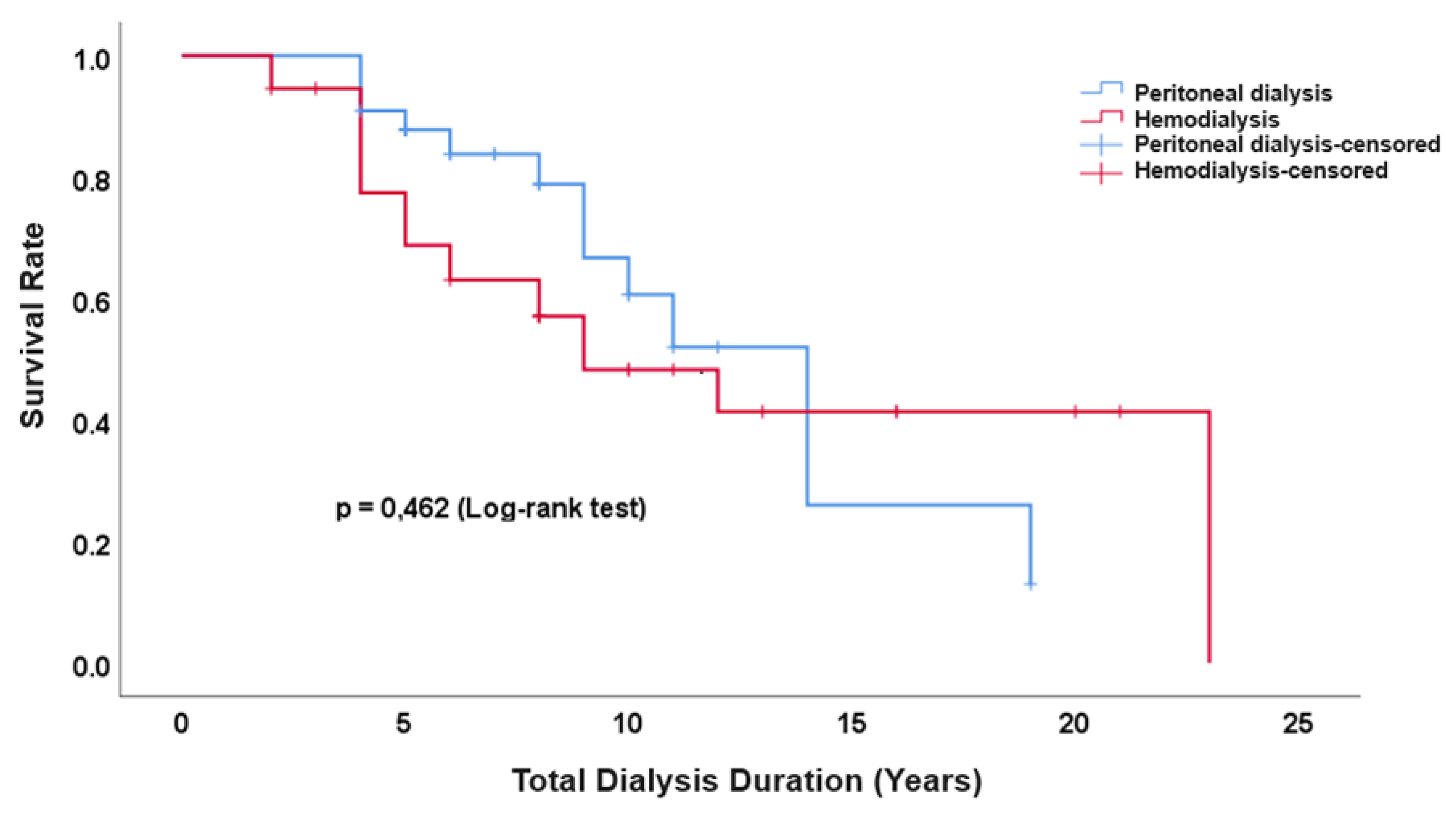
- Miyazaki, M.; Sasaki, K.; Nakashima, A.; Takahashi, A.; Ishiuchi, N.; Tamura, R.; Osaki, Y.; Doi, S.; Masaki, T. Comparison of survival rates between incident hemodialysis patients and peritoneal dialysis patients: a 5-year prospective cohort study with propensity score matching. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2023, 27, 419-426. [CrossRef]
- Moradi, H.; Sica, D.A.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Cardiovascular burden associated with uremic toxins in patients with chronic kidney disease. Am. J. Nephrol. 2013, 38, 136-148. [CrossRef]
- Neves, K.R.; Graciolli, F.G.; dos Reis, L.M.; Graciolli, R.G.; Neves, C.L.; Magalhães, A.O.; Custódio, M.R.; Batista, D.G.; Jorgetti, V.; Moysés, R.M.A. Vascular calcification: contribution of parathyroid hormone in renal failure. Kidney Int. 2007, 71, 1262-1270. [CrossRef]
- Levin, A.; Bakris, G.L.; Molitch, M.; Smulders, M.; Tian, J.; Williams, L.A.; Andress, D.L. Prevalence of abnormal serum vitamin D, PTH, calcium, and phosphorus in patients with chronic kidney disease: results of the study to evaluate early kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2007, 71, 31-38. [CrossRef]
- Kakuta, T.; Ishida, M.; Fukagawa, M. Critical governance issue of parathyroid hormone assays and its selection in the management of chronic kidney disease mineral and bone disorders. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2018, 22, 220-228. [CrossRef]
- Habas, E. S.; Eledrisi, M.; Khan, F.; Elzouki, A.Y. Secondary hyperparathyroidism in chronic kidney disease: pathophysiology and management. Cureus. 2021, 13, e16388. [CrossRef]
- Ben-Dov, I.Z.; Galitzer, H.; Lavi-Moshayoff, V.; Goetz, R.; Kuro-o, M.; Mohammadi, M.; Sirkis, R.; Naveh-Many, T.; Silver, J. The parathyroid is a target organ for FGF23 in rats. J. Clin. Invest. 2007, 117, 4003-4008. [CrossRef]
- Evenepoel, P.; Bover, J.; Torres, P.U. Parathyroid hormone metabolism and signaling in health and chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2016, 90, 1184-1190. [CrossRef]
- Lau, W.L.; Obi, Y.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Parathyroidectomy in the management of secondary hyperparathyroidism. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 13, 952-961. [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, J.; Locatelli, F.; Rodriguez, M. Secondary hyperparathyroidism: pathogenesis, disease progression, and therapeutic options, Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 6, 913-921. [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, D.C.; Winkelmayer, W.C. KDIGO 2017 clinical practice guideline update for the diagnosis, evaluation, prevention, and treatment of chronic kidney disease-mineral and bone disorder (CKD-MBD) foreword. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2017, 7, 1-59. [CrossRef]
- Brandenburg, V.; Ketteler, M. Vitamin D and secondary hyperparathyroidism in chronic kidney disease: a critical appraisal of the past, present, and the future. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3009. [CrossRef]
- Cozzolino, M.; Bernard, L.; Csomor, P.A. Active vitamin D increases the risk of hypercalcaemia in non-dialysis chronic kidney disease patients with secondary hyperparathyroidism: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Kidney J. 2021, 14, 2437-2443. [CrossRef]
- Villa-Bellosta, R.; Rodriguez-Osorio, L.; Mas, S.; Abadi, Y.; Rubert, M.; de la Piedra, C.; Gracia-Iguacel, C.; Mahillo, I.; Ortiz, A.; Egido, J.; González-Parra, E. A decrease in intact parathyroid hormone (iPTH) levels is associated with higher mortality in prevalent hemodialysis patients. PLoS One 2017, 12, e0173831. [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Han, P.; Song, P.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Niu, J.; Yu, C.; Ding, W.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, L.; Qi, H.; Shao, X.; Su, H.; Guo, Q. Mediating effects of malnutrition on the relationship between depressive symptoms clusters and muscle function rather than muscle mass in older hemodialysis patients. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2022, 26, 461-468. [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Tocino, M.L.; Miranda-Serrano, B.; López-González, A.; Villoria-González, S.; Pereira-García, M.; Gracia-Iguacel, C.; González-Ibarguren, I.; Ortíz-Arduan, A.; Mas-Fontao, S.; González-Parra, E. Sarcopenia and mortality in older hemodialysis patients. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2354. [CrossRef]
- Natoli, J.L.; Boer, R.; Nathanson, B.H.; Miller, R.M.; Chiroli, S.; Goodman, W.G.; Belozeroff, V. Is there an association between elevated or low serum levels of phosphorus, parathyroid hormone, and calcium and mortality in patients with end stage renal disease? A meta-analysis. BMC Nephrol. 2013, 14, 1-16. [CrossRef]
- Streja, E.; Wang, H.Y.; Lau, W.L.; Molnar, M.Z.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Park, J. Mortality of combined serum phosphorus and parathyroid hormone concentrations and their changes over time in hemodialysis patients. Bone 2014, 61, 201-207. [CrossRef]
- Al Salmi, I.; Bieber, B.; Al Rukhaimi, M.; AlSahow, A.; Shaheen, F.; Al-Ghamdi, S.M.G.; Al Wakeel, J.; Al Ali, F.; Al-Aradi, A.; Hejaili, F.A.; Maimani, Y.A.; Fouly, E.; Robinson, B.M.; Pisoni, R.L. for the GCC-DOPPS Study Group. Parathyroid hormone serum levels and mortality among hemodialysis patients in the Gulf Cooperation Council countries: Results from the DOPPS (2012-2018). Kidney360 2020, 1, 1083-1090. [CrossRef]
- Ghonimi, T.; Hamad, A.; Fouda, T.; AlAli, F.; Ezzat, M.; Awad, M.; Ibrahim, R.; Amin, M.; Alkadi, M.; Al-Malki, H.A. Cardiovascular calcification in hemodialysis patients: A Qatar-based prevalence and risk factors study. Qatar Med. J. 2024, 1,18. [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.H.; Choi, B.S.; Cha, D.R.; Chee, D.H.; Hwang, E.; Kim, H.W.; Chang, J.H.; Kim, J.K.; Noh, J.W.; Joo, K.W.; Lee, S.C.; Han, S.W.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.W.; Shin, S.K.; Park, W.; Kim, W.; Huh, W.; Kwon, Y.J.; Kang, Y.S. Serum calcium and phosphorus levels in patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis: A multicentre study in Korea. Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 2014, 33, 52-57. [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Martín, J.L.; Martínez-Camblor, P.; Dionisi, M.P.; Floege, J.; Ketteler, M.; London, G.; Locatelli, F.; Gorriz, J.L.; Rutkowski, B.; Ferreira, A. Improvement of mineral and bone metabolism markers is associated with better survival in haemodialysis patients: the COSMOS study. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2015, 30, 1542-1551. [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhang, L.; Zuo, L.; Jin, C.G.; Li, W.G.; Chen, J.B. Association of CKD-MBD markers with all-cause mortality in prevalent hemodialysis patients: a cohort study in Beijing. PLoS One 2017, 12, e0168537. [CrossRef]
| Dialysis Etiology | n | n% |
|---|---|---|
| Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus | 1 | 1.4% |
| Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus | 19 | 27.1% |
| Hypertension | 34 | 48.6% |
| Glomerulonephritis | 6 | 8.6% |
| Urogenital Disorders | 8 | 11.4% |
| Pyelonephritis | 1 | 1.4% |
| Amyloid Nephropathy | 1 | 1.4% |
| Total | 70 | 100% |
| Ex Cause | PD (n=33) | HD (n=37) | P* | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | ||
| Pneumonia | 1 | 7.7% | 3 | 15.8% | 0.590 |
| Heart failure | 2 | 15.4% | 1 | 5.3% | 0.567 |
| Aortic dissection | 1 | 7.7% | 0 | 0.0% | 0.410 |
| Dialysis complications | 2 | 15.4% | 2 | 10.5% | 1.000 |
| Peritonitis | 5 | 38.5% | 0 | 0.0% | 0.005 |
| Myocardial Infarction | 1 | 7.7% | 2 | 10.5% | 1.000 |
| Other cardiovascular causes | 1 | 7.7% | 9 | 47.4% | 0.013 |
| Malignancy | 0 | 0.0% | 2 | 10.5% | 0.506 |
| Total | 13 | 100% | 19 | 100% | 0.008 |
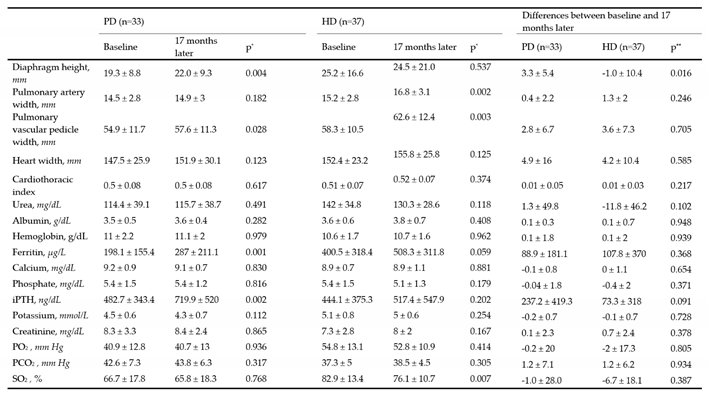
| Baseline | PD (n=33) | HD (n=37) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17 months Later | p* | 17 months Later | p* | |||||
| No | Yes | No | Yes | |||||
| Cardiomegaly | No | 14 | 6 | 0.508 | 11 | 4 | 0.125 | |
| Yes | 3 | 10 | 0 | 20 | ||||
| Redistribution | No | 14 | 1 | 0.219 | 12 | 2 | 1.000 | |
| Yes | 5 | 13 | 1 | 21 | ||||
| Interstitial pattern | No | 18 | 2 | 0.453 | 13 | 4 | 1.000 | |
| Yes | 5 | 8 | 5 | 15 | ||||
| Pleural fluid | No | 20 | 5 | 1.000 | 28 | 5 | 0.219 | |
| Yes | 5 | 3 | 1 | 3 | ||||
| Pleural thickness | No | 26 | 1 | 1.000 | 25 | 0 | 1.000 | |
| Yes | 0 | 6 | 0 | 11 | ||||
| Alveolar infiltration | No | 30 | 2 | 0.500 | 33 | 1 | 1.000 | |
| Yes | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | ||||
| Atelectasis | No | 30 | 1 | 1.000 | 37 | 0 | - | |
| Yes | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| Survived (n=38) | Ex (n=32) | p | Hazard Ratio (95% Confidence Interval) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, year | 52.2 ± 12.7 | 63.5 ± 10.8 | 0.016 | 1.034 (1.006 - 1.062) | ||
| Diaphragm height, mm | 21.6 ± 11.4 | 23.5 ± 16.4 | 0.599 | 1.007 (0.980 - 1.036) | ||
| Pulmonary artery diameter, mm | 14.5 ± 2.8 | 15.3 ± 2.8 | 0.302 | 1.070 (0.941 - 1.218) | ||
| Pulmonary Vascular Pedicle Width, mm | 56.5 ± 11.9 | 57 ± 10.2 | 0.140 | 1.024 (0.992 - 1.056) | ||
| Width of the heart, mm | 147.8 ± 23.1 | 152.8 ± 26.1 | 0.156 | 1.011 (0.996 - 1.025) | ||
| CTI | 0.5 ± 0.1 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | 0.478 | 5.169 (0.055 - 484.6) | ||
| Urea, mg/dL | 129.3 ± 43.4 | 128.7 ± 34.1 | 0.831 | 1.001 (0.991 - 1.011) | ||
| Albumin, g/dL | 3.7 ± 0.4 | 3.4 ± 0.6 | 0.005 | 0.339 (0.159 - 0.726) | ||
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | 11.1 ± 2 | 10.4 ± 1.9 | 0.040 | 0.810 (0.662 - 0.990) | ||
| Ferritin, µg/L | 229.7 ± 180.1 | 394.6 ± 334.3 | 0.047 | 1.001 (1.000 - 1.002) | ||
| Calcium, mg/dL | 9.1 ± 0.8 | 9 ± 0.8 | 0.546 | 0.878 (0.575 - 1.340) | ||
| Phosphate, mg/dL | 5.4 ± 1.6 | 5.5 ± 1.4 | 0.650 | 1.059 (0.826 - 1.359) | ||
| iPTH, ng/dL | 524.8 ± 380.1 | 388 ± 321.3 | 0.013 | 0.998 (0.997 - 1.000) | ||
| Potassium, mmol/L | 4.9 ± 0.7 | 4.7 ± 0.8 | 0.035 | 0.630 (0.410 - 0.968) | ||
| Creatinine, mg/dL | 7.4 ± 3.3 | 8.2 ± 2.6 | 0.505 | 0.957 (0.842 - 1.088) | ||
| PO2, mm Hg | 47.3 ± 13.4 | 49.4 ± 16.1 | 0.955 | 0.999 (0.976 - 1.023) | ||
| PCO2 , mm Hg | 39.8 ± 5.7 | 39.8 ± 7.7 | 0.919 | 1.003 (0.949 - 1.060) | ||
| SO %2, | 74.5 ± 16.3 | 76.2 ± 19 | 0.793 | 1.003 (0.982 - 1.024) | ||
| Gender |
Woman | 26 (68.4) | 18 (56.3) | 1 (Reference) | ||
| Male | 12 (31.6) | 14 (43.8) | 0.159 | 1.665 (0.819 - 3.387) | ||
| Dialysis Type |
PD | 20 (52.6) | 13 (40.6) | 1 (Reference) | ||
| HD | 18 (47.4) | 19 (59.4) | 0.481 | 1.293 (0.633 - 2.642) | ||
| Cardiomegaly |
No | 23 (60.5) | 13 (40.6) | 1 (Reference) | ||
| Yes | 15 (39.5) | 19 (59.4) | 0.154 | 1.693 (0.820 - 3.492) | ||
| Aortic calcification |
No | 13 (34.2) | 3 (9.4) | 1 (Reference) | ||
| Yes | 25 (65.8) | 29 (90.6) | 0.252 | 2.010 (0.608 - 6.639) | ||
| Redistribution |
No | 14 (36.8) | 15 (46.9) | 1 (Reference) | ||
| Yes | 24 (63.2) | 17 (53.1) | 0.680 | 1.166 (0.563 - 2.415) | ||
| Interstitial pattern |
No | 20 (52.6) | 17 (53.1) | 1 (Reference) | ||
| Yes | 18 (47.4) | 15 (46.9) | 0.714 | 1.143 (0.559 - 2.338) | ||
| Pleural fluid |
No | 29 (76.3) | 29 (90.6) | 1 (Reference) | ||
| Yes | 9 (23.7) | 3 (9.4) | 0.362 | 0.572 (0.173 - 1.898) | ||
| Pleural thickness |
No | 30 (78.9) | 22 (71) | 1 (Reference) | ||
| Yes | 8 (21.1) | 9 (29) | 0.624 | 0.812 (0.354 - 1.865) | ||
| Alveolar infiltration |
No | 36 (94.7) | 30 (93.8) | 1 (Reference) | ||
| Yes | 2 (5.3) | 2 (6.3) | 0.530 | 1.587 (0.376 - 6.709) | ||
| Atelectasis |
No | 37 (97.4) | 31 (96.9) | 1 (Reference) | ||
| Yes | 1 (2.6) | 1 (3.1) | 0.910 | 1.123 (0.152 - 8.321) | ||
| Radiological Status |
Deterioration | 7 (18.4) | 17 (53.1) | 1 (Reference) | ||
| Stable or İmproved |
31 (81.6) | 15 (46.9) | 0.055 | 0.500 (0.246 - 1.015) | ||
| Family history |
No | 28 (73.7) | 24 (75) | 1 (Reference) | ||
| Yes | 10 (26.3) | 8 (25) | 0.730 | 0.866 (0.382 - 1.961) | ||
| Clinical Status | Deterioration | 7 (18.4) | 17 (53.1) | 1 (Reference) | ||
| Stable or İmproved | 31 (81.6) | 15 (46.9) | 0.003 | 0.118 (0.028-0.495) | ||
| Beta | p | Hazard Ratio (95% Confidence Interval) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, year | 0.044 | 0.007 | 1.045 (1.012 - 1.078) | |
| Albumin, g/dL | -0.501 | 0.213 | 0.606 (0.275 - 1.334) | |
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | -0.166 | 0.129 | 0.847 (0.683 - 1.050) | |
| Ferritin, µg/L | 0.001 | 0.255 | 1.001 (1.000 - 1.001) | |
| iPTH, ng/dL | -0.002 | 0.040 | 0.998 (0.997 - 1.000) | |
| Potassium, mmol/L | -0.455 | 0.071 | 0.635 (0.387 - 1.040) | |
| Clinical status | -1.933 | 0.009 | 0.145 (0.034 - 0.621) |
| Diaphragm Height | Pulmonary Artery Diameter | Pulmonary Vascular Pedicle Width | CTI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| iPTH | r | 0.112 | -0.156 | -0.272 | -0.070 |
| p | 0.360 | 0.201 | 0.024 | 0.567 | |
| Clinical Status | Phi | p | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deterioration | Stable or İmproved | |||||
| PD and HD | Radiological Status | Deterioration | 20 | 4 | 0.287 | 0.016 |
| Stable or İmproved | 25 | 21 | ||||
| Beta | p | Hazard Ratio (95% Confidence Interval) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, year | 0.040 | 0.016 | 1.040 (1.008 - 1.074) | |
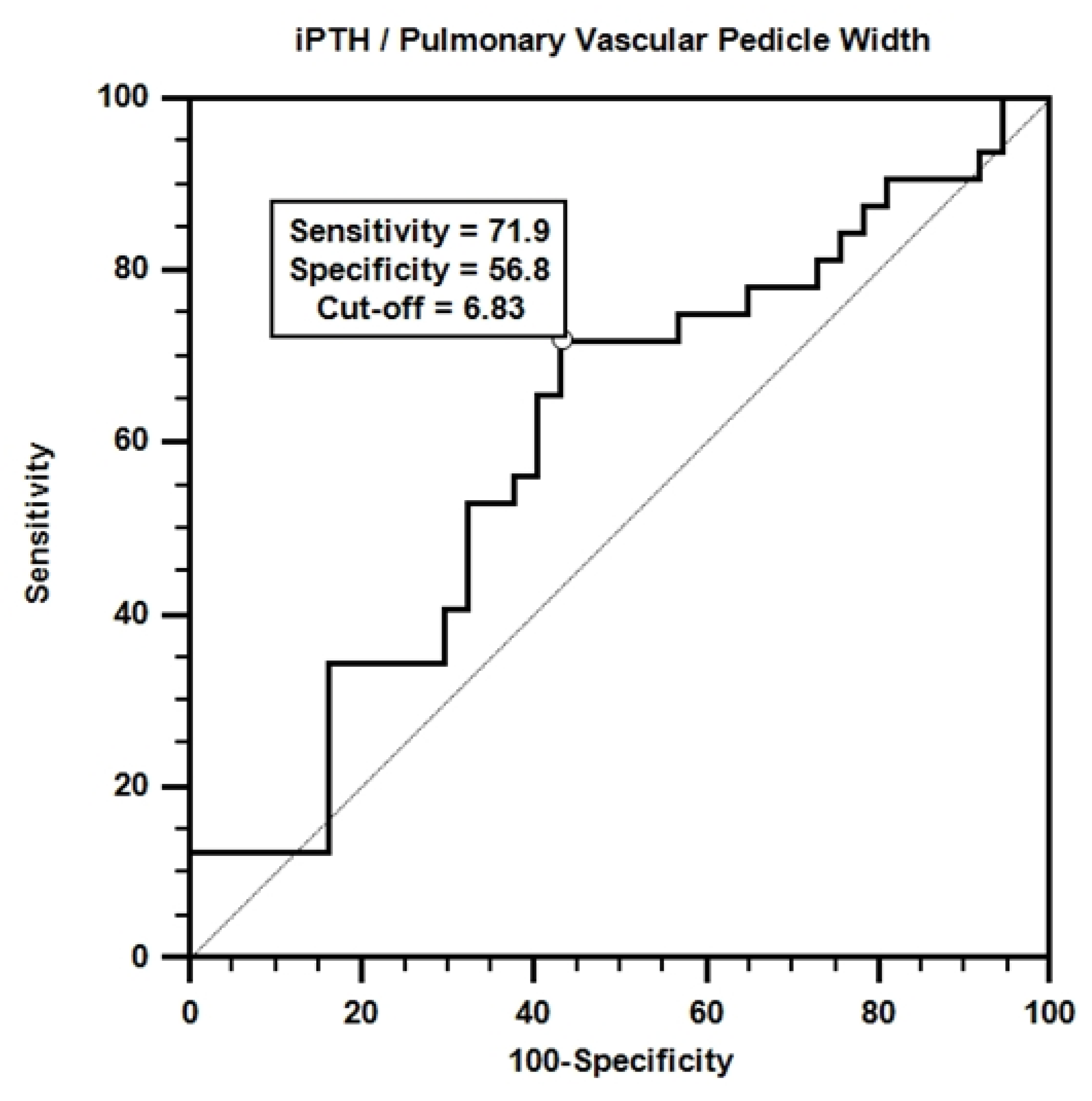
| iPTH/ PVPW | -0.073 | 0.035 | 0.930 (0.869 - 0.995) | |
| Albumin, g/dL | -0.500 | 0.214 | 0.606 (0.275 - 1.335) | |
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | -0.160 | 0.141 | 0.852 (0.689 - 1.054) | |
| Ferritin, µg/L | 0.000 | 0.354 | 1.000 (1.000 - 1.001) | |
| Potassium, mmol/L | -0.440 | 0.083 | 0.644 (0.391 - 1.059) | |
| Clinical Status | -1.985 | 0.008 | 0.137 (0.032 - 0.589) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





