Submitted:
06 July 2024
Posted:
08 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
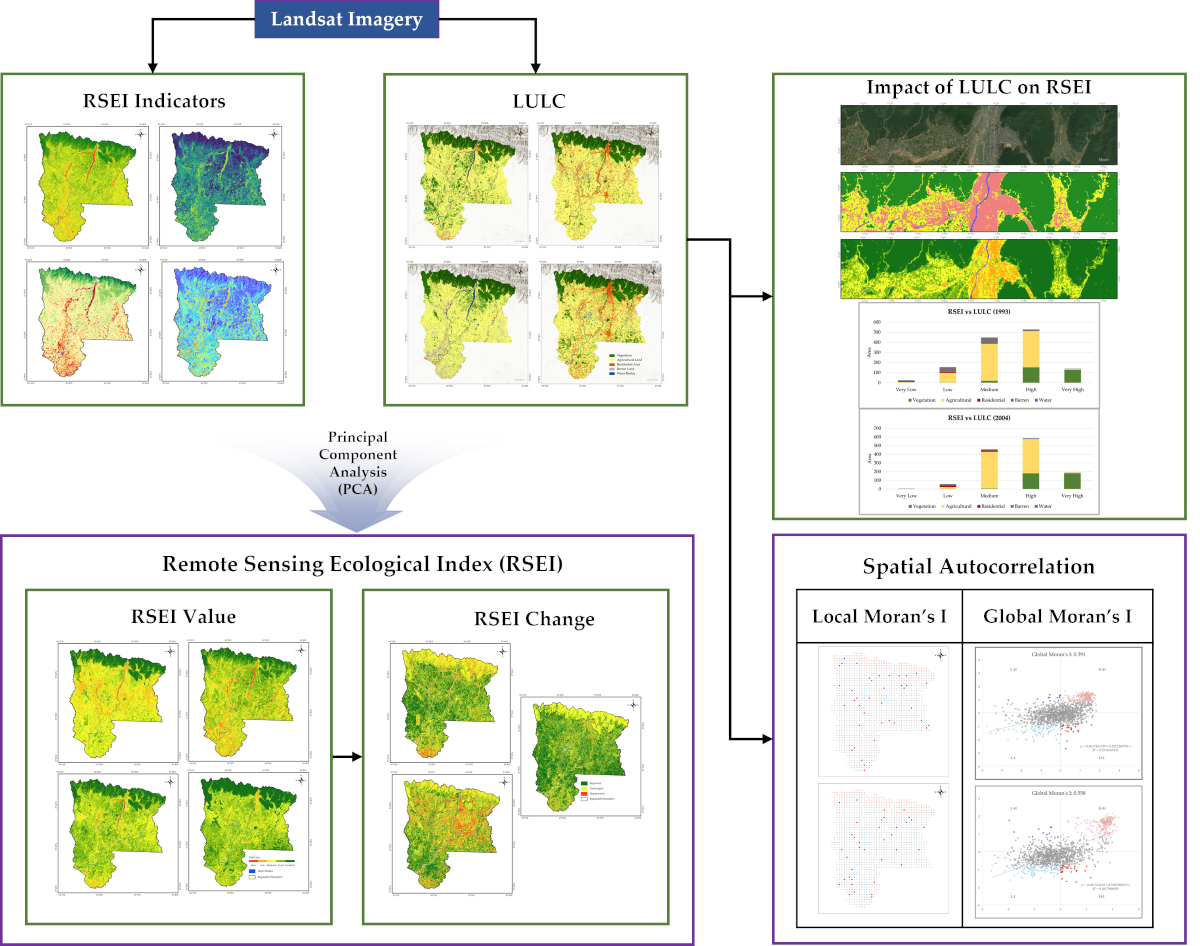
2. Materials and Method
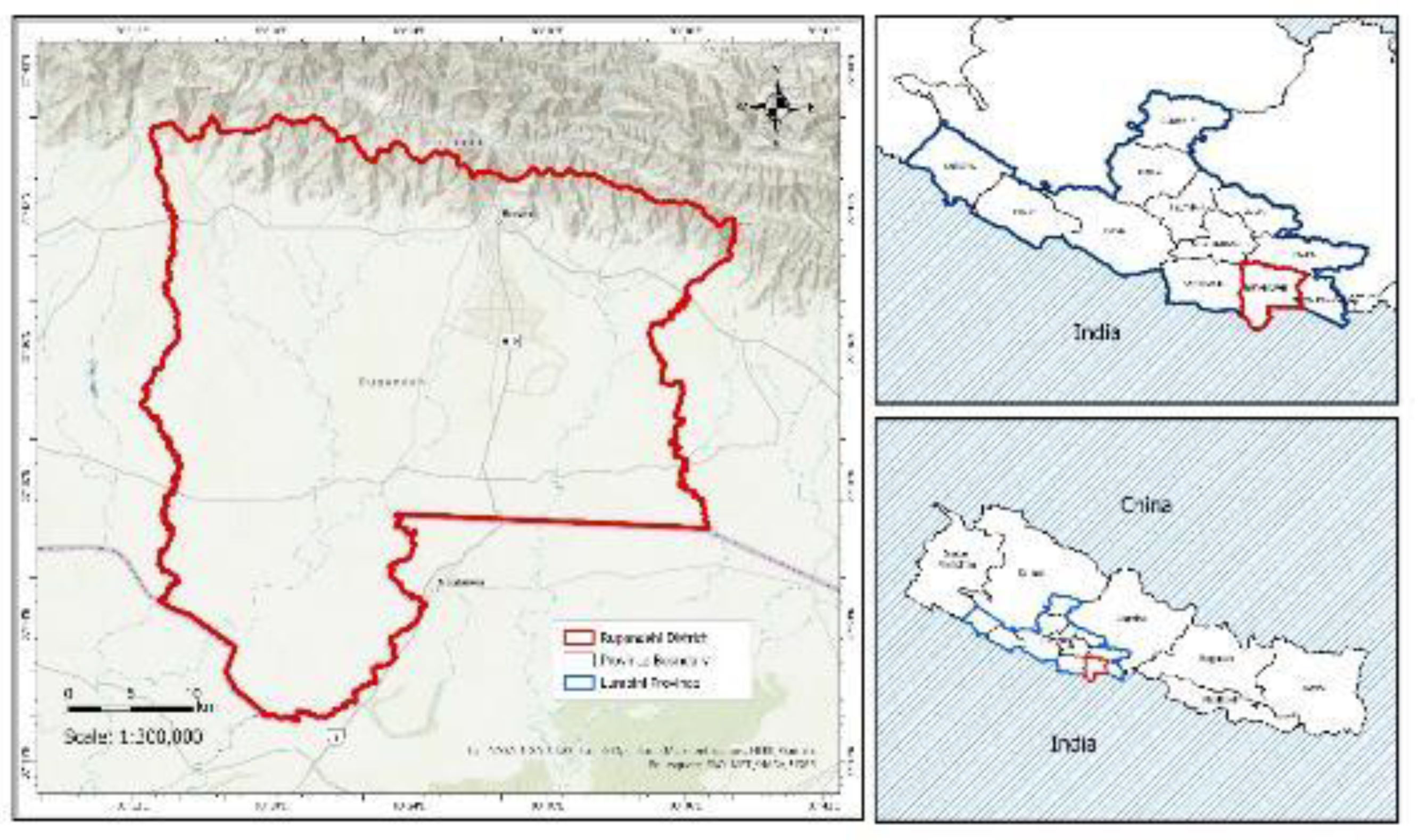
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Datasets
2.3. Construction of RSEI
2.3.1. Greenness Index
2.3.2. Wetness Index
2.3.3. Dryness Index
2.3.4. Heat Index
2.3.5. Normalization of Indicators
2.3.6. Calculation of RSEI
2.4. Spatial Auto-Correlation
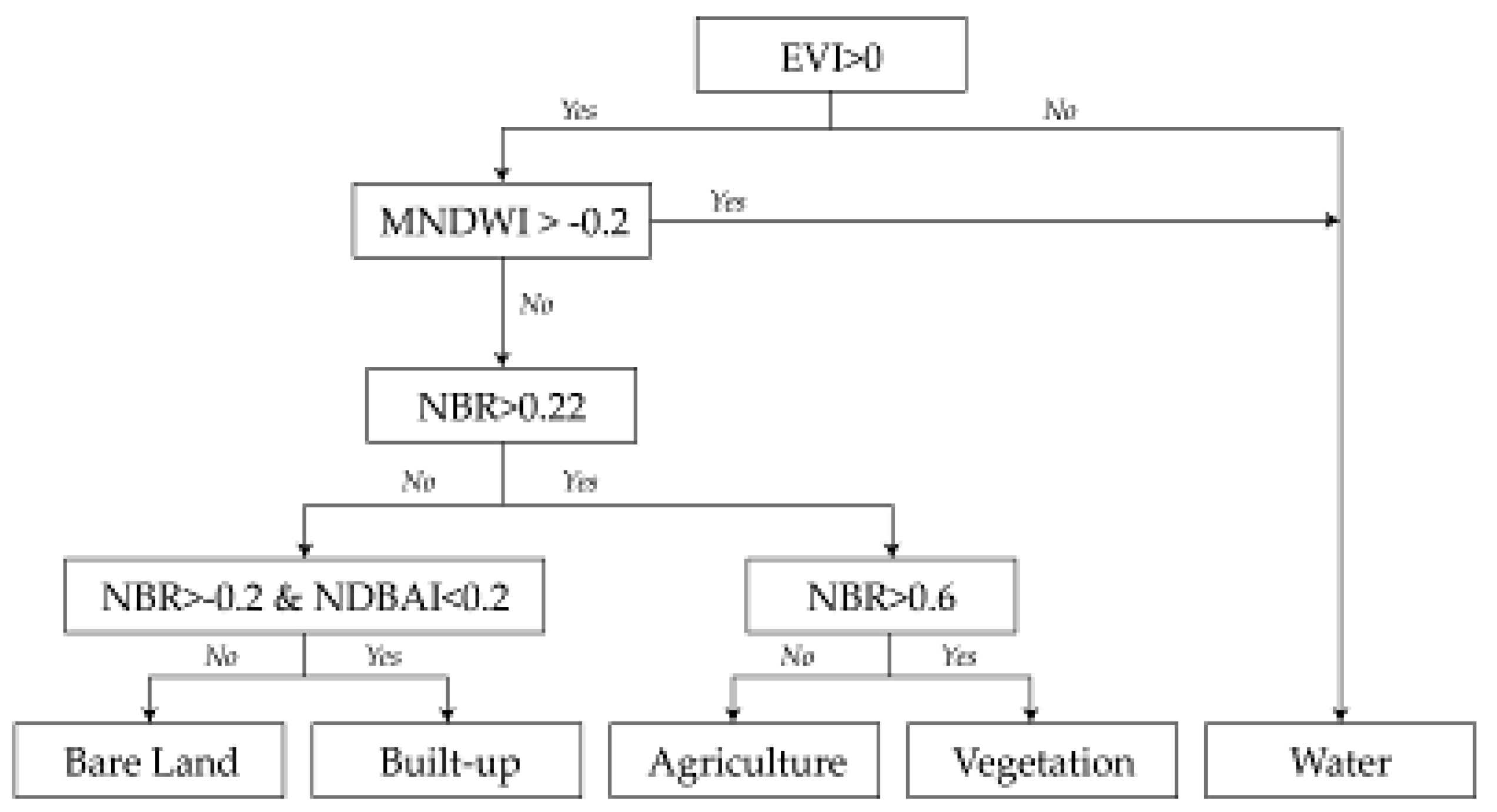
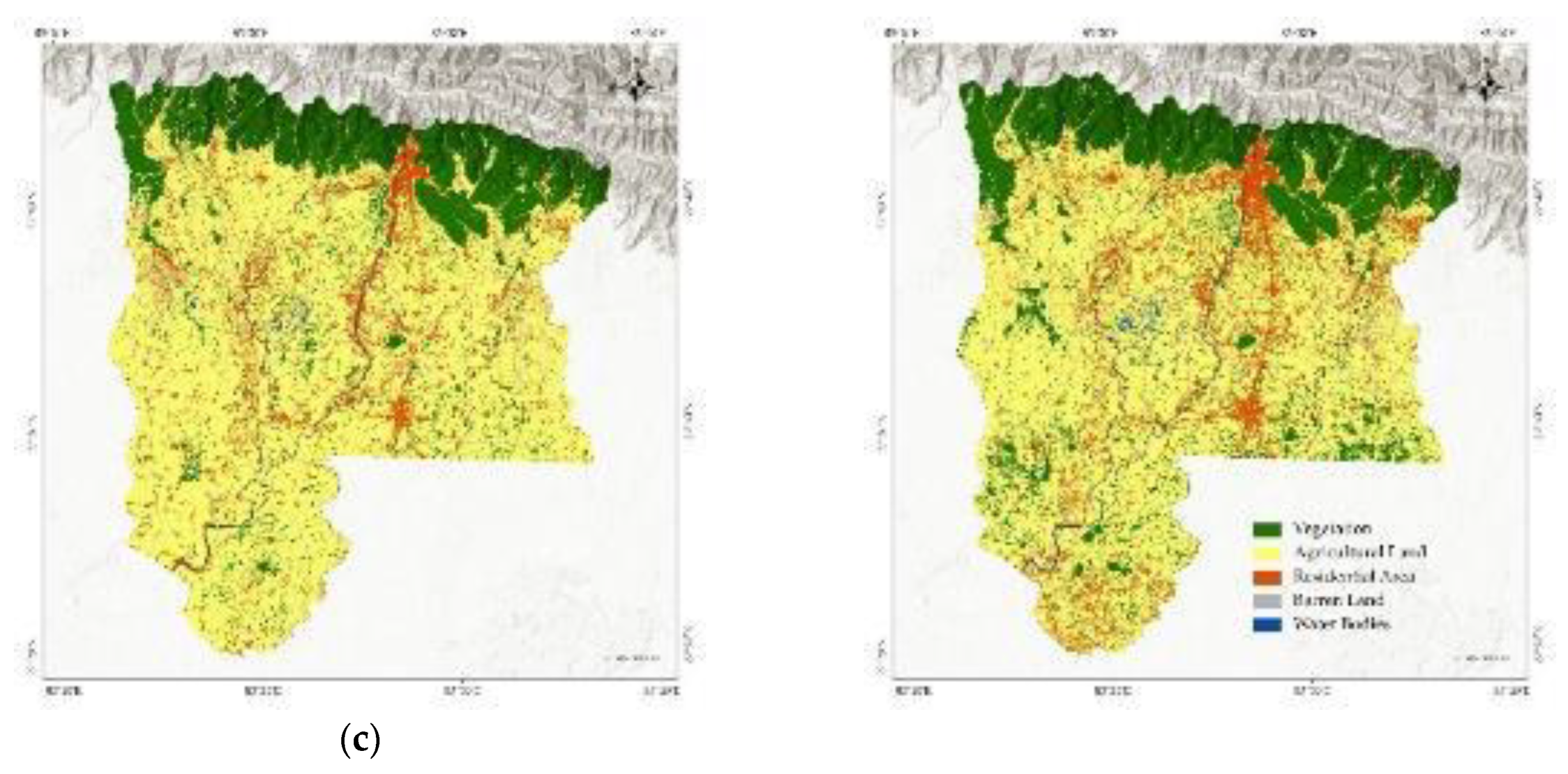
2.4. Land Use/Cover Classification and Accuracy Assessment
3. Results
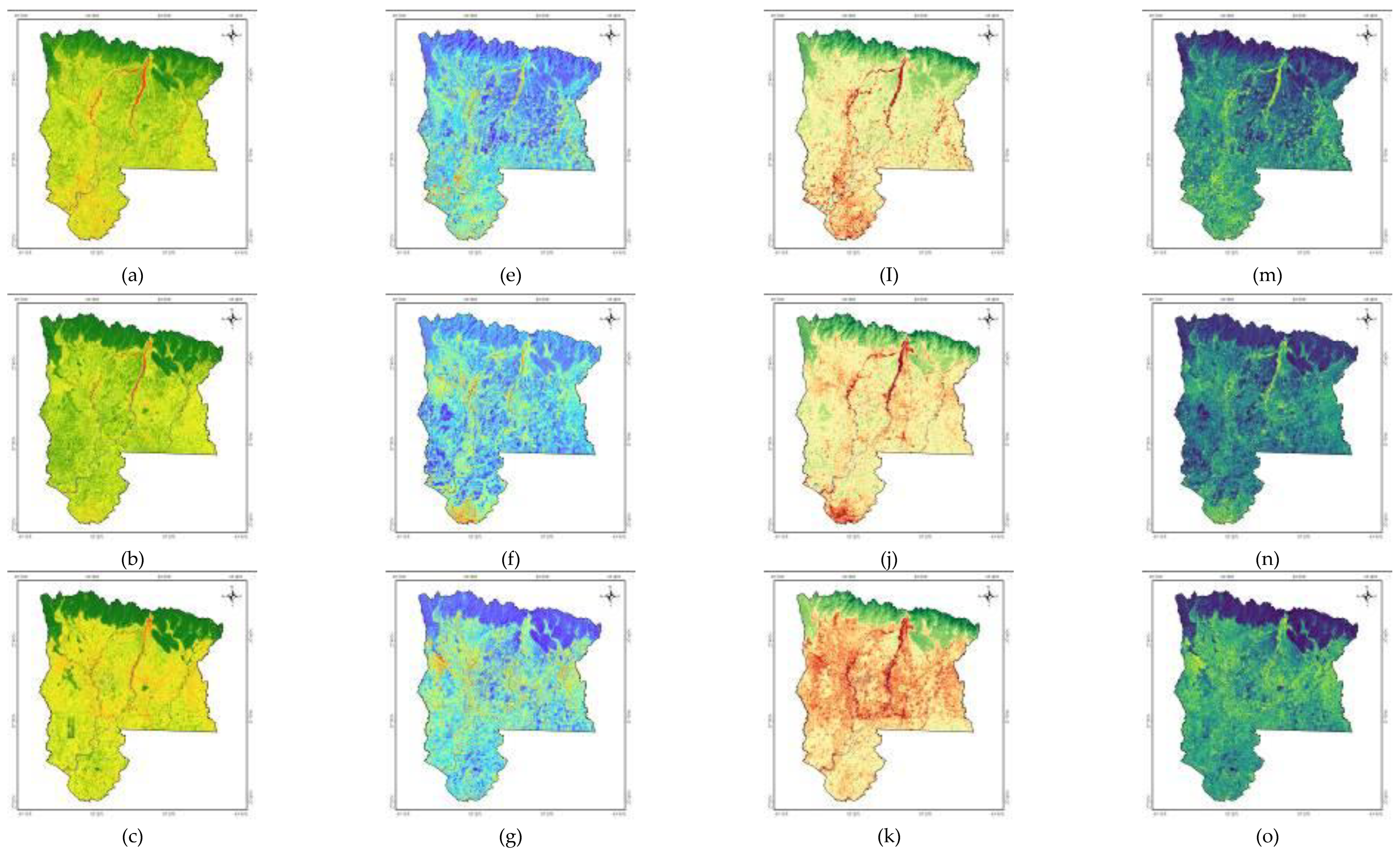
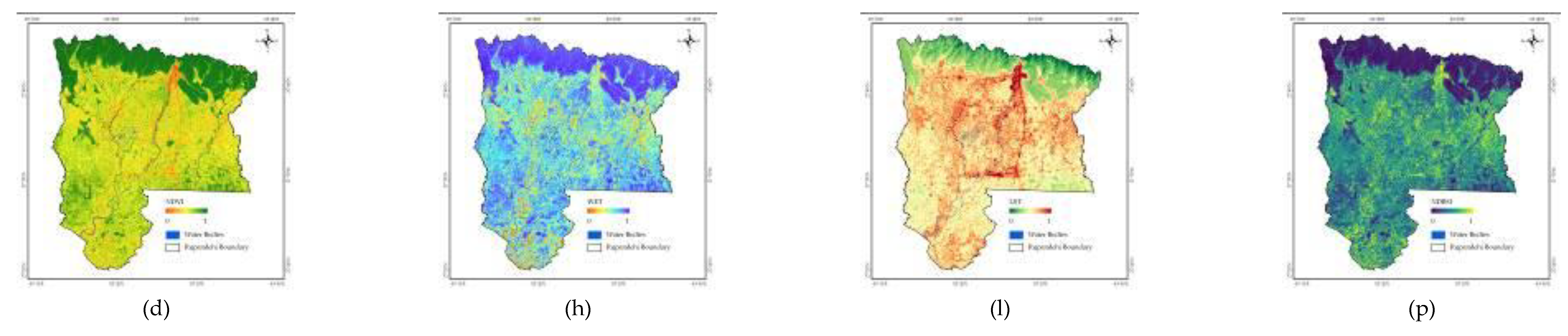
3.1. Principal Component Analysis Results of RSEI Model
| Year | Indicators | Eigen Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | ||
| 1993 | LST | -0.21389 | -0.12906 | 0.94163 | 0.22567 |
| NDBSI | -0.63029 | 0.13879 | -0.29319 | 0.70535 | |
| NDVI | 0.53844 | 0.73551 | 0.12958 | 0.39028 | |
| WET | 0.51679 | -0.65047 | -0.10286 | 0.54703 | |
| Percent of Eigen Values (%) | 90.3268 | 6.8639 | 1.7145 | 1.0948 | |
| 2004 | LST | -0.24808 | 0.00072 | 0.93768 | 0.24334 |
| NDBSI | -0.67904 | 0.31503 | -0.32925 | 0.57554 | |
| NDVI | 0.61093 | 0.69297 | 0.06311 | 0.37760 | |
| WET | 0.32268 | -0.64850 | -0.09147 | 0.68334 | |
| Percent of Eigen Values (%) | 86.0878 | 9.5212 | 3.4507 | 0.9403 | |
| 2013 | LST | -0.39460 | 0.91818 | -0.03278 | 0.01250 |
| NDBSI | -0.61529 | -0.25373 | 0.50821 | 0.54659 | |
| NDVI | 0.64861 | 0.29824 | 0.64757 | 0.26648 | |
| WET | 0.21216 | 0.06014 | -0.56684 | 0.79377 | |
| Percent of Eigen Values (%) | 91.0715 | 5.1642 | 3.4978 | 0.2665 | |
| 2023 | LST | -0.32008 | 0.90064 | 0.29393 | 0.00072 |
| NDBSI | -0.64211 | -0.31398 | 0.26124 | 0.64874 | |
| NDVI | 0.62795 | -0.00621 | 0.70204 | 0.33582 | |
| WET | 0.30152 | 0.30038 | -0.59371 | 0.68291 | |
| Percent of Eigen Values (%) | 91.8492 | 4.5203 | 3.3144 | 0.3161 | |
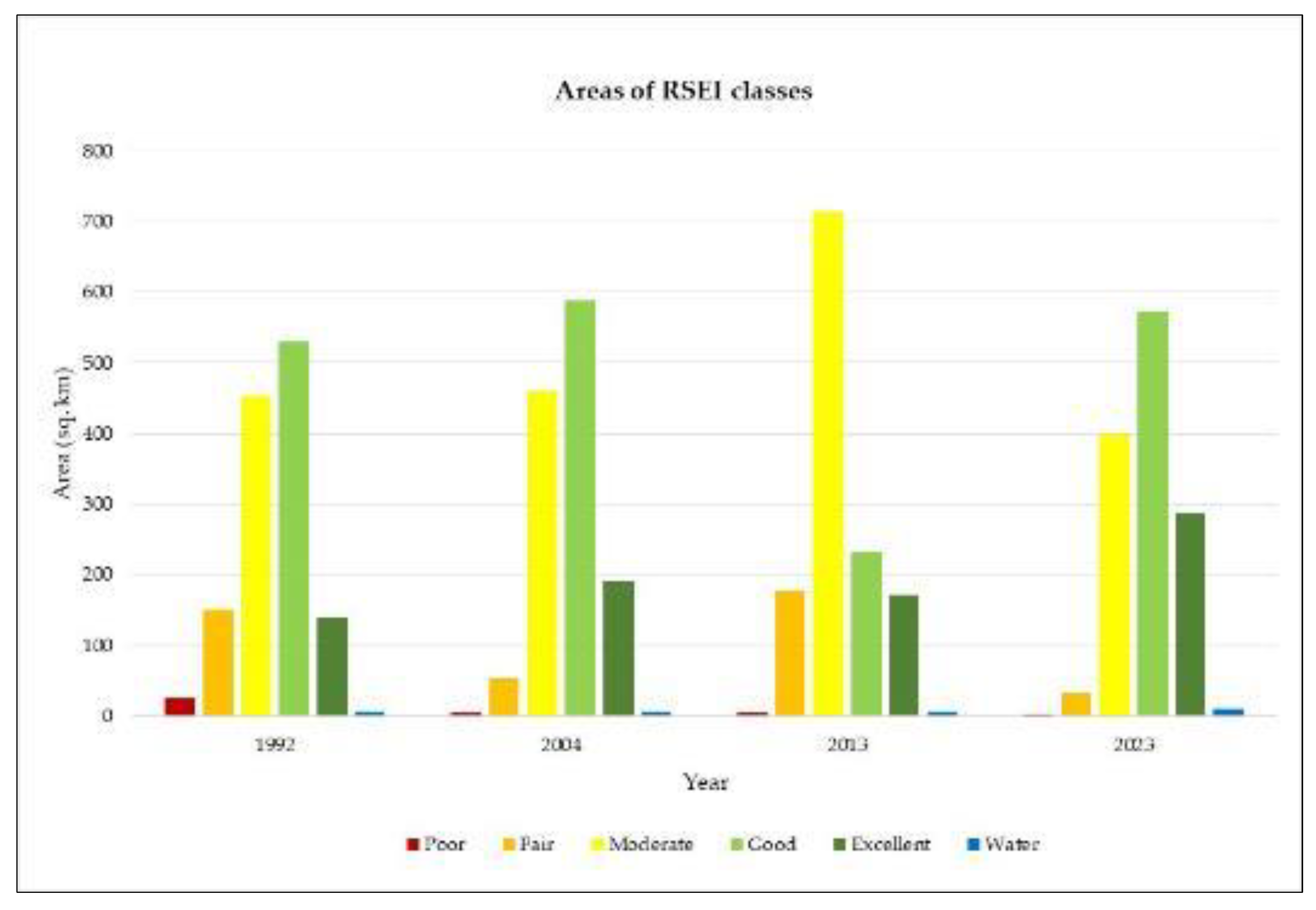
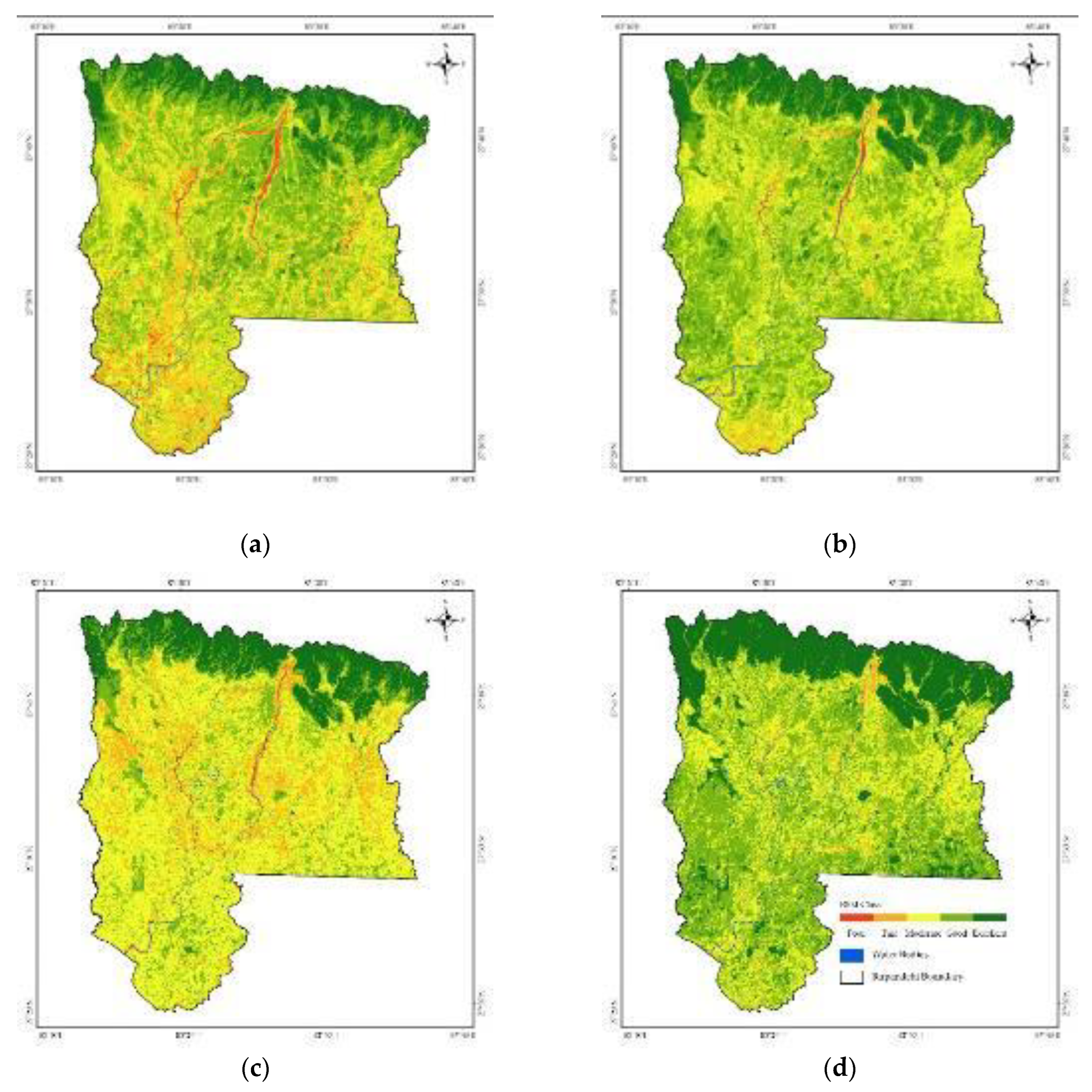
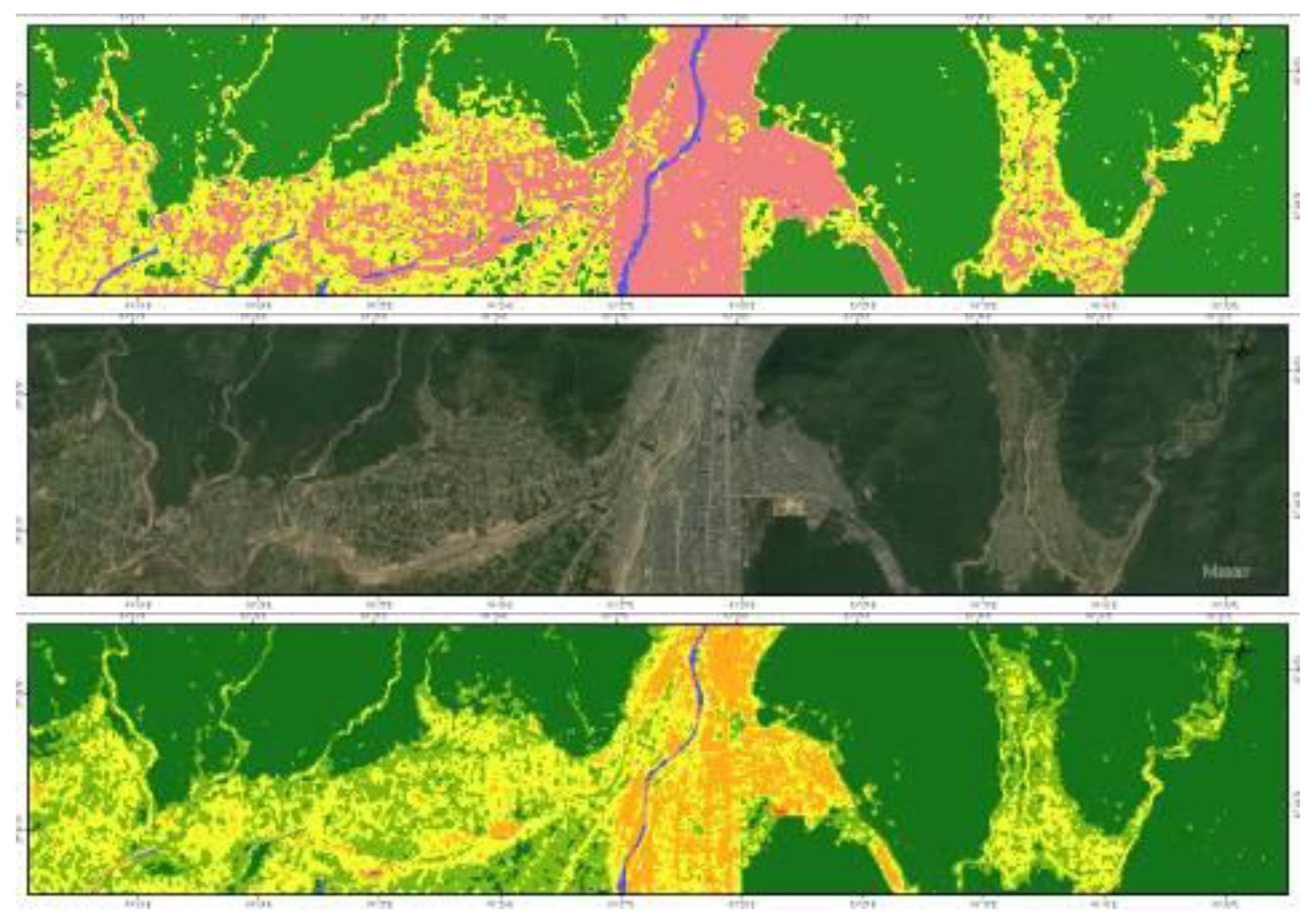
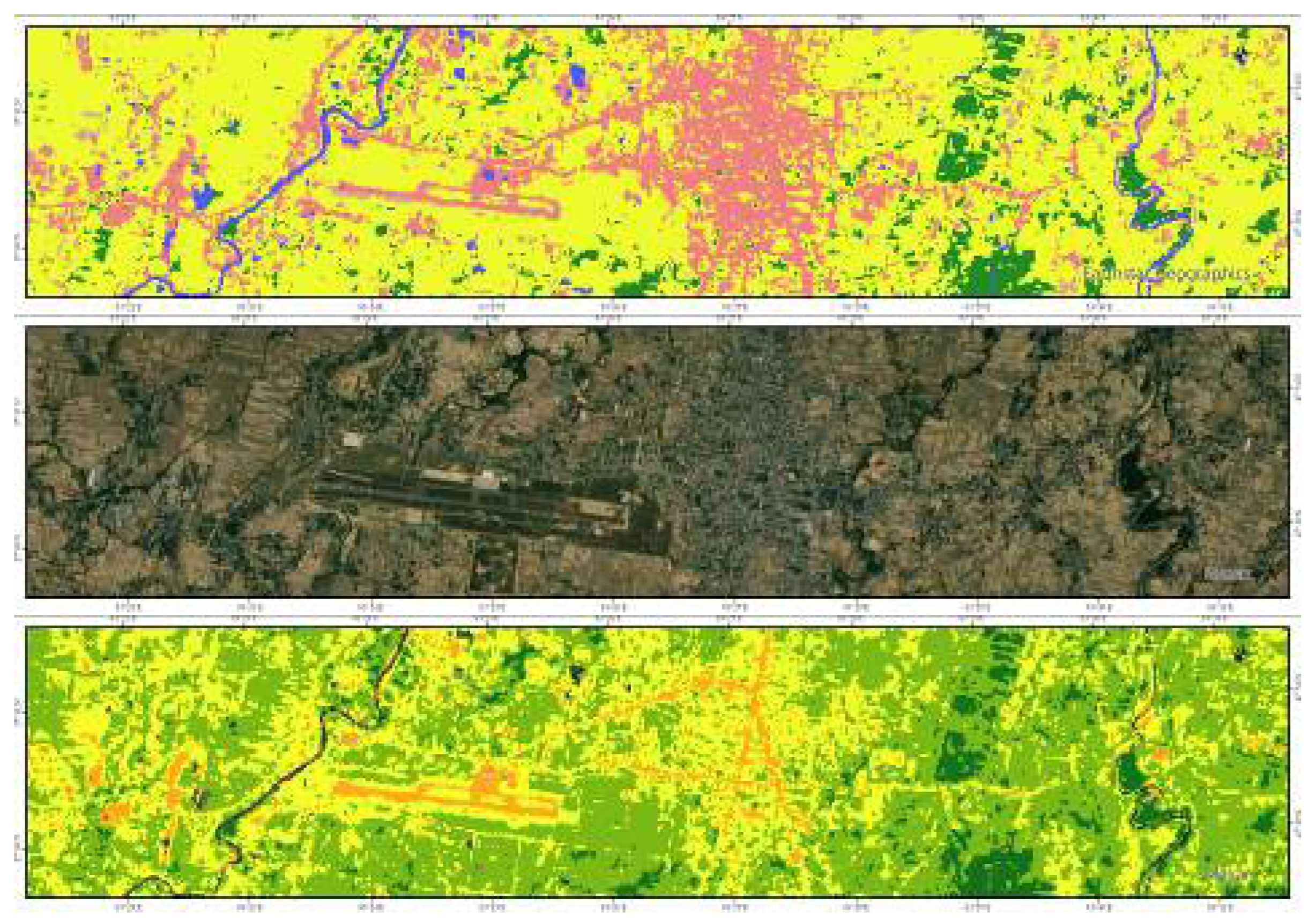
3.2. Spatial Changes in RSEI of Rupandehi
3.3. Temporal Changes in RSEI of Rupandehi
| Year | Index | Mean | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1993 | LST | 0.25 | 0.063 |
| NDBSI | 0.50 | 0.160 | |
| NDVI | 0.64 | 0.145 | |
| WET | 0.71 | 0.138 | |
| RSEI | 0.59 | 0.167 | |
| 2004 | LST | 0.28 | 0.061 |
| NDBSI | 0.45 | 0.136 | |
| NDVI | 0.71 | 0.130 | |
| WET | 0.818 | 0.078 | |
| RSEI | 0.635 | 0.138 | |
| 2013 | LST | 0.39 | 0.103 |
| NDBSI | 0.52 | 0.143 | |
| NDVI | 0.67 | 0.152 | |
| WET | 0.851 | 0.055 | |
| RSEI | 0.55 | 0.156 | |
| 2023 | LST | 0.46 | 0.086 |
| NDBSI | 0.37 | 0.148 | |
| NDVI | 0.63 | 0.147 | |
| WET | 0.82 | 0.075 | |
| RSEI | 0.67 | 0.14 |
3.4. Trend Analysis of Ecological Environmental Quality in Rupandehi
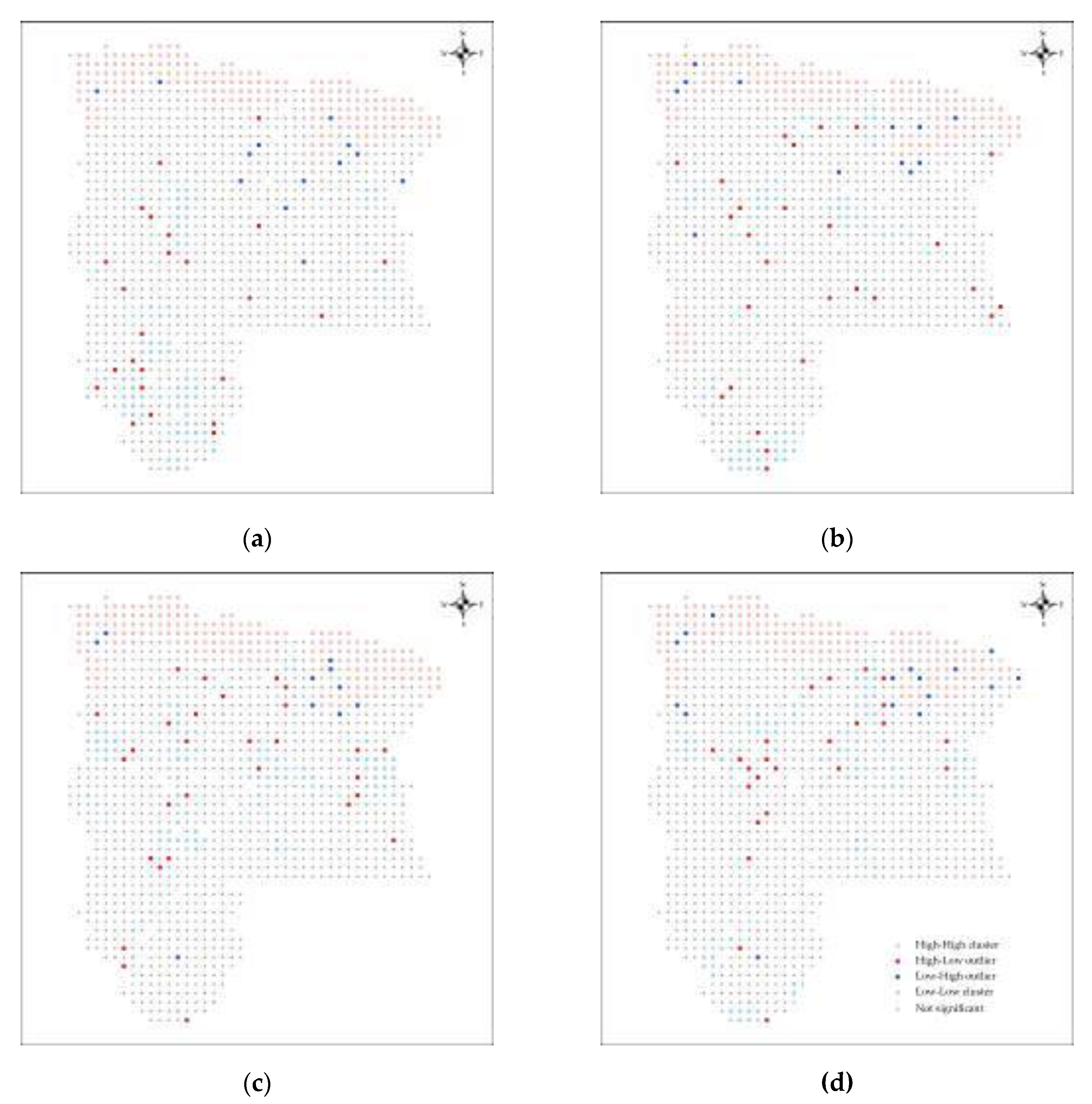
3.5. Spatial Autocorrelation of RSEI
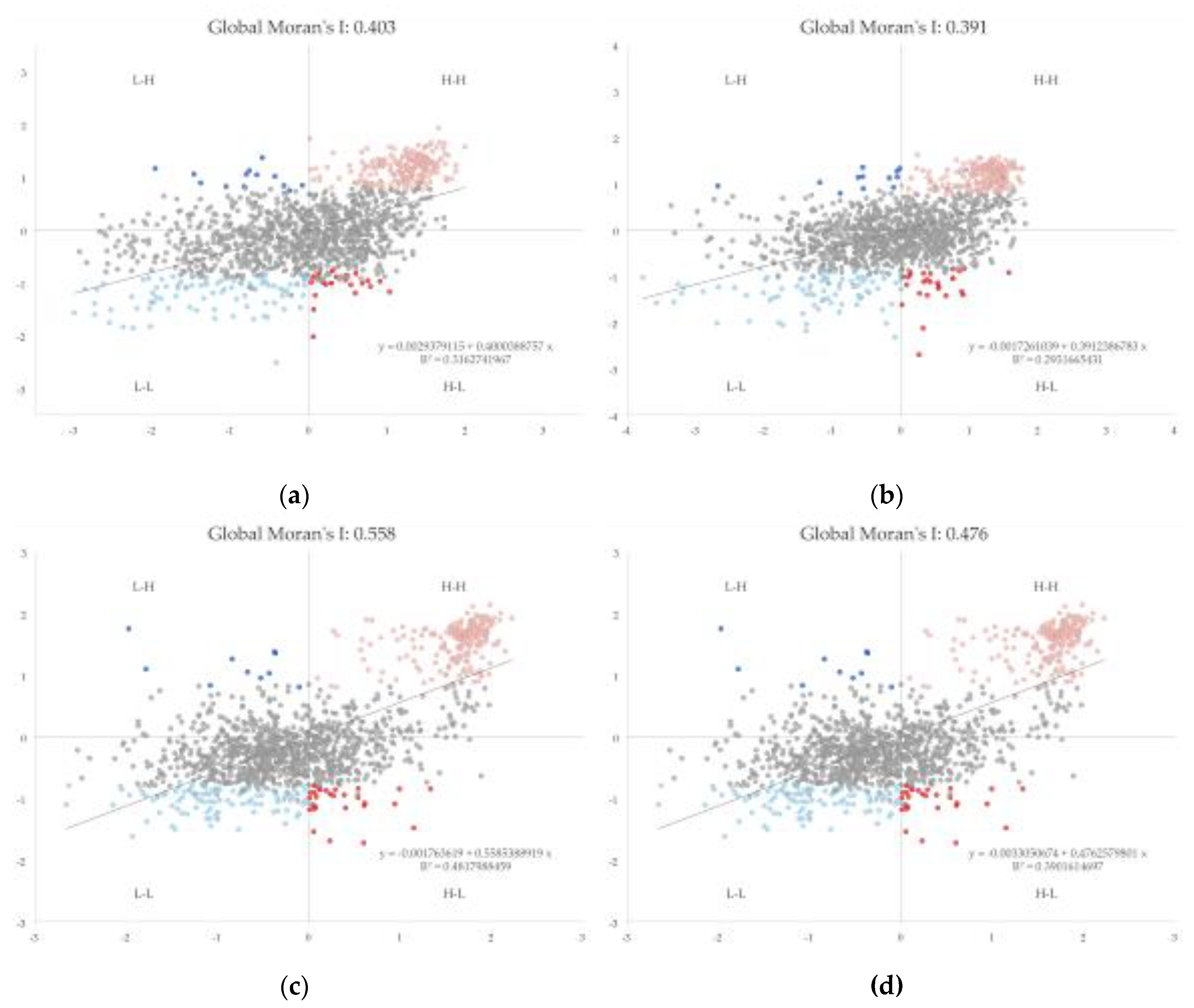
3.6. Local Indicator of Spatial Autocorrelation of RSEI
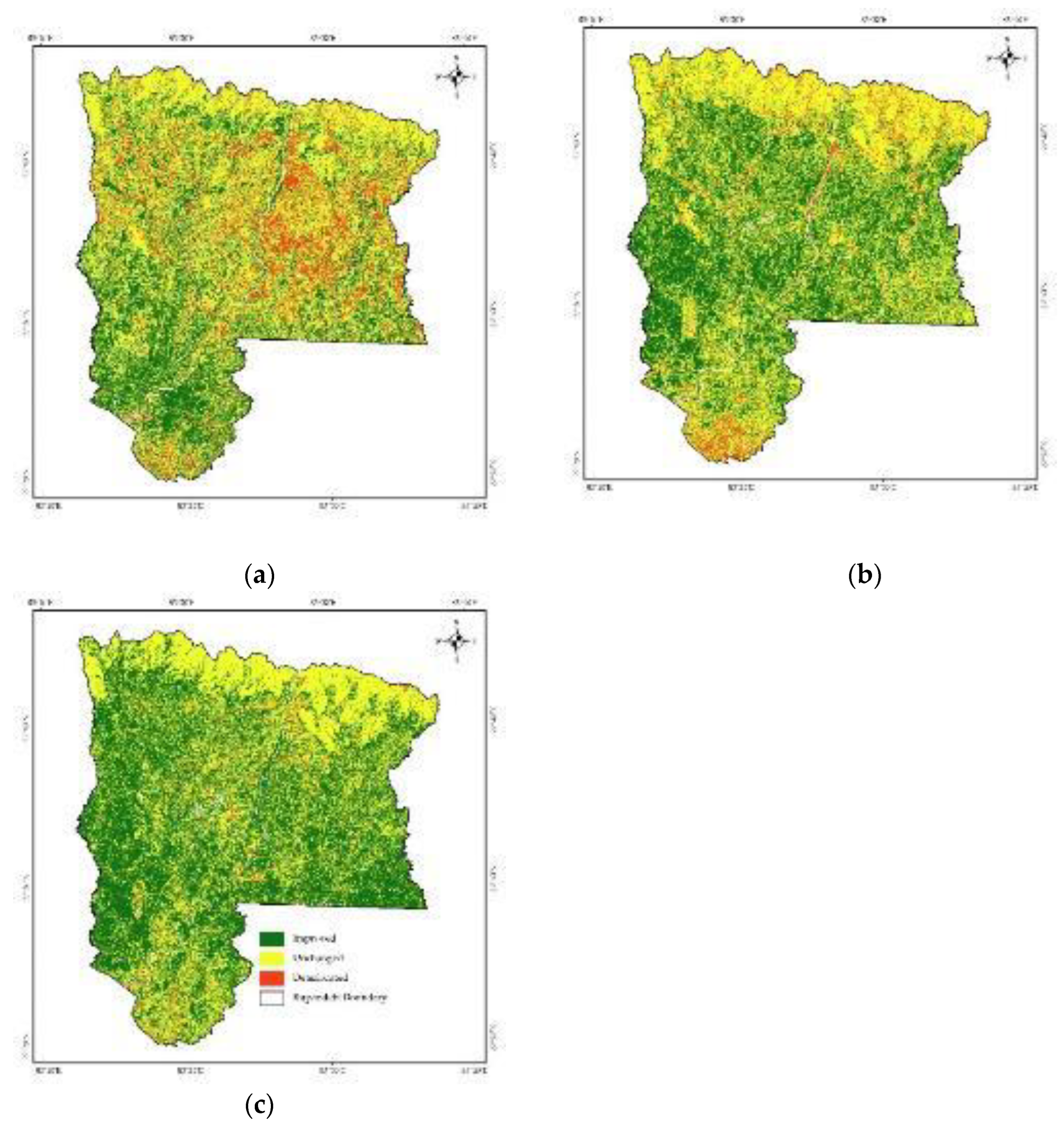
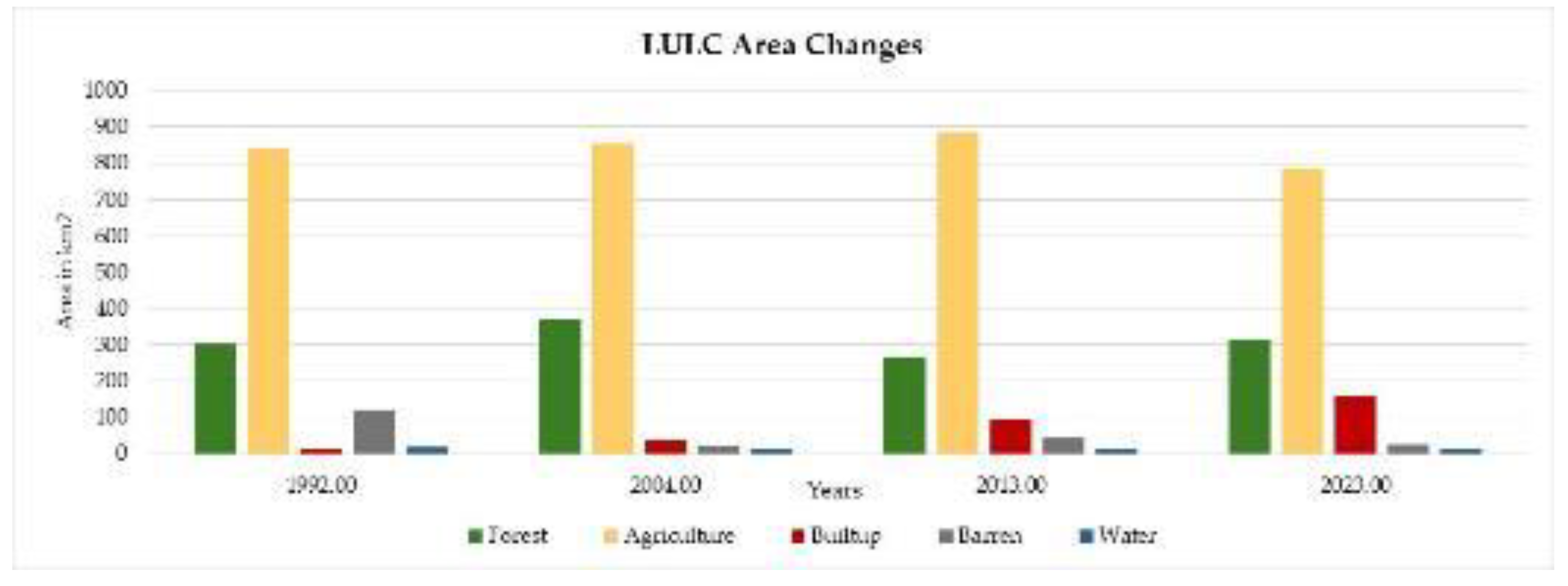
3.7. Spatio-Temporal Change of Land Use Types in Rupandehi
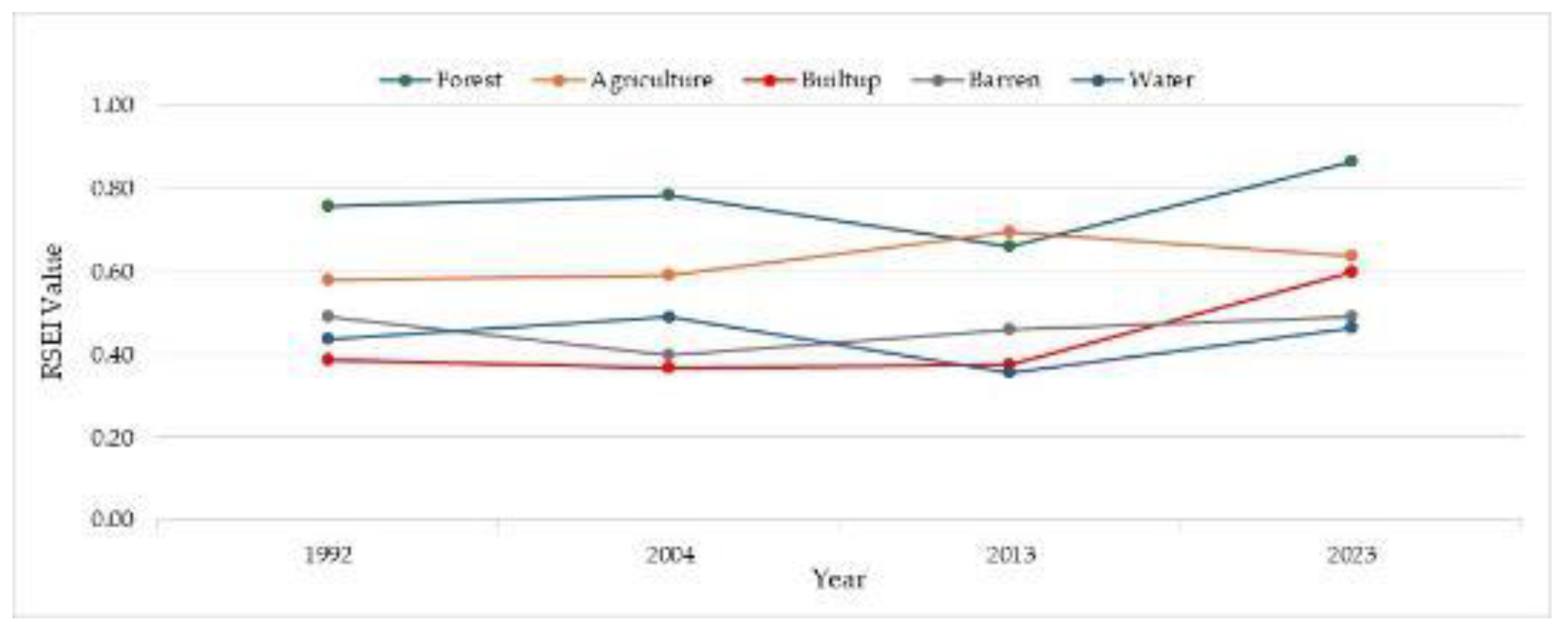
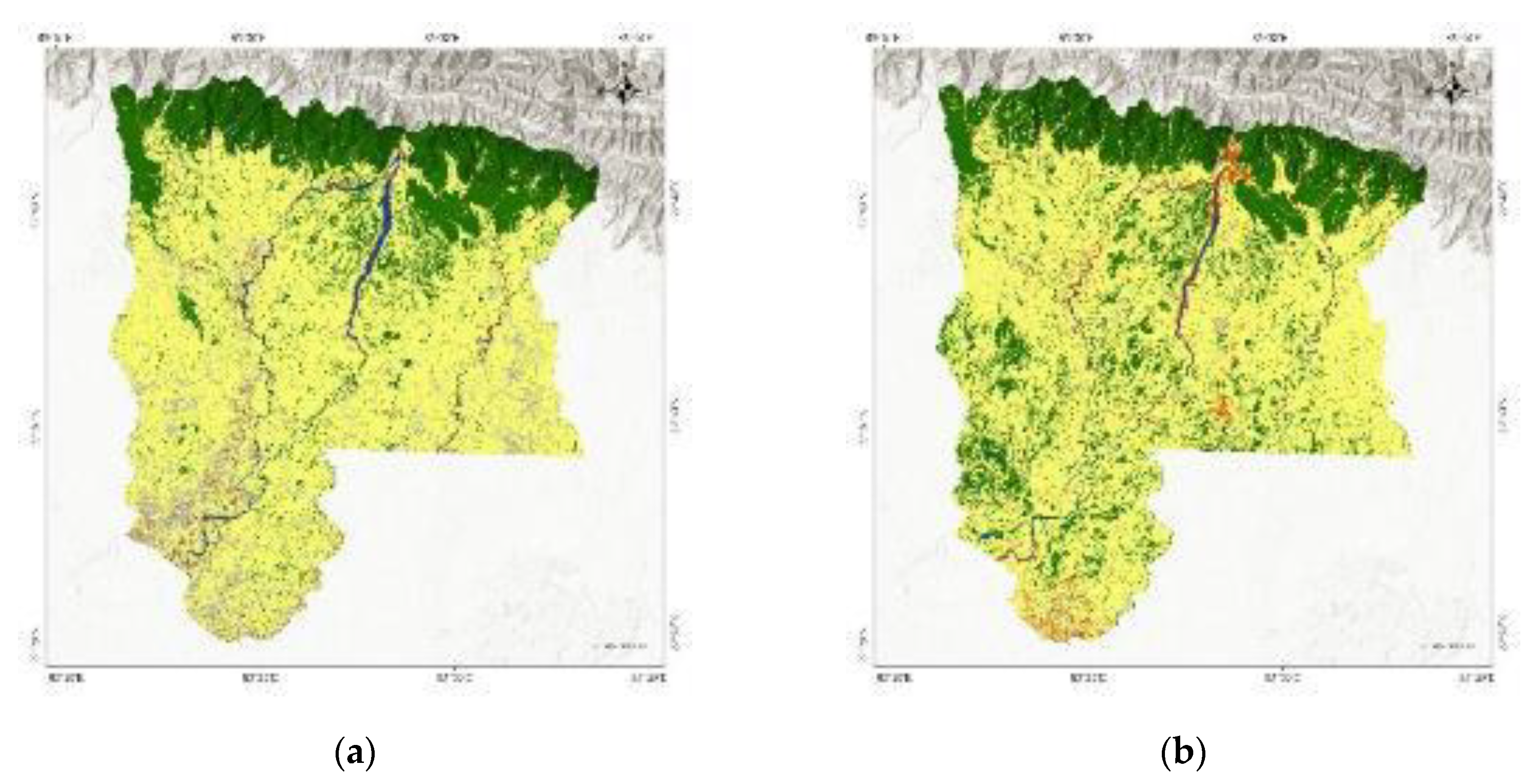
3.8. Effect of Land Use Change on Eco-Environmental Quality of Rupandehi

4. Discussion
4.1. Potential Reasons for Ecological Quality Change
4.2. Challenge/Limitations and Future Work
- The spatial resolution of a Landsat image is only 30m which is comparatively low and will limit the exploration of each of the indices within a minute level. Therefore, future studies can explore the combination of Sentinel-2 images which have comparatively high resolution to that of Landsat.
- We used just 4 indicators based on different literature review, that plays an immense role in affecting the ecological quality. More exploration of multiple indicators is required to optimize the monitoring and evaluation of the EEQ in future.
- We used LULC changes as a driving factor for the EEQ, but there are many other factors like changes in GDP, population, temperature, precipitation, etc. that have an equal impact on the EEQ. Therefore, further study can explore more driving factors to achieve a more accurate EEQ and support policymakers in controlling it.
- Since forest and agricultural land play vital roles in maintaining the eco-environmental quality in the region and it is obvious that in the coming days, there will be less land available for afforestation as well as the agricultural land will decrease due to urbanization, the local government should look after effective measure to balance between urbanization and ecological protection by controlling the massive and haphazard urbanization ongoing on the region and bring proper land use planning and land management system.
- Also, the government should discourage deforestation and land degradation while encouraging people to bring greenery around their surroundings by planting more trees promoting a low-carbon economy by reducing greenhouse gas emissions[18] and making sure that their agricultural land does not go barren by planting any crops available.
5. Conclusion
- The overall quality of the Rupandehi district has remained within the range of medium and high throughout time showing an overall rising trend in 30 years, having the maximum value (0.67) of RSEI in 2023 and a minimum value (0.554) in 2013.
- The spatial distribution of the higher RSEI is concentrated in the Forest area in the northern hilly regions, while low RSEI is concentrated in two major cities: Butwal and Bhairahawa as shown in Figure 10 which are densely populated areas with more impervious surfaces and are subjected to urban heat island effect.
- The different land use land cover types and their changes to each other throughout the time of 30 years have a direct impact on the eco-environmental quality of the district. The conversion of barren land and built-up land to forest and agricultural have a positive impact on the quality. Meanwhile, forest and agricultural land were mostly converted to built-up areas which had a negative impact on the quality and was the main reason for the deterioration of the eco-environmental quality.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Helili, P.; Zan, M. Coupling Coordination Development of Urbanization and Ecological Environment in the Urban Agglomeration on the Northern Slope of the Tianshan Mountains, China. Sustainability (Switzerland) 2023, 15. [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Fang, J.; Xie, R.; Ji, X.; Li, D.; Yuan, J. Impact of Land Cover Change on a Typical Mining Region and Its Ecological Environment Quality Evaluation Using Remote Sensing Based Ecological Index (RSEI). Sustainability 2022, 14, 12694. [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Zhang, X.; Peng, H. Evaluation of Temporal and Spatial Changes in Ecological Environmental Quality on Jianghan Plain From 1990 to 2021. Front Environ Sci 2022, 10, 1–14. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Li, W.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Z. The Assessment of the Spatiotemporal Characteristics of the Eco-Environmental Quality in the Chishui River Basin from 2000 to 2020. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3695. [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, G.; Dong, L.; Lu, F.; Lv, Z.; Miao, X. Evaluation of the Ecological Quality of the Taishan Region Based on Landsat Series of Satellite Images. Tehnicki vjesnik - Technical Gazette 2023, 30, 1308–1314. [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, Q.; Liu, N.; Zhang, H.; Tan, Y.; Zhang, Z. The Impact of Land Use / Cover Changes on the Ecological Envi- Ronment Quality in Suburban Open-Pit Mine Concentration Areas. 2022, 1–25.
- United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, P.D. World Population Prospects 2022: Summary of Results; 2022;
- Liu, P.; Ren, C.; Yu, W.; Ren, H.; Xia, C. Exploring the Ecological Quality and Its Drivers Based on Annual Remote Sensing Ecological Index and Multisource Data in Northeast China. Ecol Indic 2023, 154, 110589. [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Huang, Q.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Q. Analysis and Dynamic Evaluation of Eco-Environmental Quality in the Yellow River Delta from 2000 to 2020. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7835. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, X.; Shi, S.; Xu, L. Exploring the Relationship between the Eco-Environmental Quality and Urbanization by Utilizing Sentinel and Landsat Data: A Case Study of the Yellow River Basin. Remote Sens (Basel) 2023, 15, 743. [CrossRef]
- Gou, R.; Zhao, J. Eco-Environmental Quality Monitoring in Beijing, China, Using an RSEI-Based Approach Combined with Random Forest Algorithms. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 196657–196666. [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wang, Y.; Guan, H.; Shi, T.; Hu, X. Detecting Ecological Changes with a Remote Sensing Based Ecological Index (RSEI) Produced Time Series and Change Vector Analysis. Remote Sens (Basel) 2019, 11, 2345. [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Jiang, W. Evaluation of the Spatiotemporal Variations in the Eco-Environmental Quality in China Based on the Remote Sensing Ecological Index. Remote Sens (Basel) 2020, 12. [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Yu, K.; Xie, Z.; Zhao, G.; Ai, J.; Yang, L.; Yang, H.; Liu, J. Analysis of Spatiotemporal Variation and Drivers of Ecological Quality in Fuzhou Based on RSEI. Remote Sens (Basel) 2022, 14, 4900. [CrossRef]
- Eckert, S.; Hüsler, F.; Liniger, H.; Hodel, E. Trend Analysis of MODIS NDVI Time Series for Detecting Land Degradation and Regeneration in Mongolia. J Arid Environ 2015, 113, 16–28. [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Kuang, T.; Tao, S. Quantifying Influences of Natural Factors on Vegetation NDVI Changes Based on Geographical Detector in Sichuan, Western China. J Clean Prod 2019, 233, 353–367. [CrossRef]
- Pettorelli, N.; Vik, J.O.; Mysterud, A.; Gaillard, J.M.; Tucker, C.J.; Stenseth, N.C. Using the Satellite-Derived NDVI to Assess Ecological Responses to Environmental Change. Trends Ecol Evol 2005, 20, 503–510. [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Jing, H.; Yan, G.; Guo, H.; Luan, W. Long-Term Ecological Environment Quality Evaluation and Its Driving Mechanism in Luoyang City. Sustainability (Switzerland) 2023, 15. [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Huang, T.; DI, L.; Geng, D.; Yan, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Li, L.; Chen, B.; Kang, J. Influence of Different Bandwidths on LAI Estimation Using Vegetation Indices. IEEE J Sel Top Appl Earth Obs Remote Sens 2020, 13, 1494–1502. [CrossRef]
- Asner, G.P.; Scurlock, J.M.O.; Hicke, J.A. Global Synthesis of Leaf Area Index Observations: Implications for Ecological and Remote Sensing Studies. Global Ecology and Biogeography 2003, 12, 191–205. [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Kikon, N.; Verma, P. Impact of Land Use Change and Urbanization on Urban Heat Island in Lucknow City, Central India. A Remote Sensing Based Estimate. Sustain Cities Soc 2017, 32, 100–114. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Tian, G. Analysis of the Impact of Land Use/Land Cover Change on Land Surface Temperature with Remote Sensing. Procedia Environ Sci 2010, 2, 571–575. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Estoque, R.C.; Murayama, Y. An Urban Heat Island Study in Nanchang City, China Based on Land Surface Temperature and Social-Ecological Variables. Sustain Cities Soc 2017, 32, 557–568. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.D.; Zhong, X.H.; Liu, S.Z.; Liu, J.G.; Wang, Z.Y.; Li, M.H. Regional Assessment of Environmental Vulnerability in the Tibetan Plateau: Development and Application of a New Method. J Arid Environ 2008, 72, 1929–1939. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Yang, R.; Yang, Y.; Li, L.; Chen, L. Assessing the Urban Eco-Environmental Quality by the Remote-Sensing Ecological Index: Application to Tianjin, North China. ISPRS Int J Geoinf 2021, 10, 475. [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.; Halike, A.; Chen, L.; Wei, Q. Spatiotemporal Changes of Eco-Environmental Quality Based on Remote Sensing-Based Ecological Index in the Hotan Oasis, Xinjiang. J Arid Land 2022, 14, 262–283. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; She, J.; Long, X.; Zhang, M. Spatio-Temporal Evolution and Driving Factors of Eco-Environmental Quality Based on RSEI in Chang-Zhu-Tan Metropolitan Circle, Central China. Ecol Indic 2022, 144, 109436. [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.Q. A Remote Sensing Urban Ecological Index and Its Application. Shengtai Xuebao/ Acta Ecologica Sinica 2013, 33, 7853–7862. [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Pablo, R.D.A.; Zhang, Y. Eco-Environmental Quality Assessment Using the Remote Sensing Ecological Index in Suzhou City, China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13158. [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Zhu, M.; Mi, H.; Liu, Y. Evaluation of Eco-Environmental Quality and Analysis on Spatio-Temporal Variation in Jinan, China. Pol J Environ Stud 2022, 31, 1061–1072. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, Q.; Cao, M.; Liu, H. Spatiotemporal Change of Eco-Environmental Quality in the Oasis City and Its Correlation with Urbanization Based on RSEI: A Case Study of Urumqi, China. Sustainability (Switzerland) 2022, 14. [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Song, M.; Zhang, A. Dynamics of the Eco-Environmental Quality in Response to Land Use Changes in Rapidly Urbanizing Areas: A Case Study of Wuhan, China from 2000 to 2018. Journal of Geographical Sciences 2023, 33, 245–265. [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wang, M.; Shi, T.; Guan, H.; Fang, C.; Lin, Z. Prediction of Ecological Effects of Potential Population and Impervious Surface Increases Using a Remote Sensing Based Ecological Index (RSEI). Ecol Indic 2018, 93, 730–740. [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Zhang, S.; Rao, X.; Lin, X.; Li, R. Landsat TM/OLI-Based Ecological and Environmental Quality Survey of Yellow River Basin, Inner Mongolia Section. Remote Sens (Basel) 2021, 13. [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Xu, W.; Lu, N.; Huang, S.; Wu, C.; Wang, L.; Dai, F.; Kou, W. Assessment of Spatial–Temporal Changes of Ecological Environment Quality Based on RSEI and GEE: A Case Study in Erhai Lake Basin, Yunnan Province, China. Ecol Indic 2021, 125, 107518. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, H. Spatiotemporal Dynamic Decoupling States of Eco-Environmental Quality and Land-Use Carbon Emissions: A Case Study of Qingdao City, China. Ecol Inform 2023, 75, 101992. [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.; Meng, S.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, R.; Yin, C.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, Y. Analysis of Eco-Environmental Quality and Driving Forces in Opencast Coal Mining Area Based on GWANN Model: A Case Study in Shengli Coalfield, China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10656. [CrossRef]
- KC, A.; Wagle, N.; Acharya, T.D. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Land Cover and the Effects on Ecosystem Service Values in Rupandehi, Nepal from 2005 to 2020. ISPRS Int J Geoinf 2021, 10, 635. [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Liu, T.; Wang, Q.; Li, T.; Li, X.; Song, G.; Feng, Y. Impact of Land Use/Land Cover Change on Ecological Quality during Urbanization in the Lower Yellow River Basin: A Case Study of Jinan City. Remote Sens (Basel) 2022, 14, 6273. [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Luo, Y. Dynamical Changes of Land Use/Land Cover and Their Impacts on Ecological Quality during China’s Reform Periods: A Case Study of Quanzhou City, China. PLoS One 2022, 17, e0278667. [CrossRef]
- Conference, United Nations Development, on T. and UN List of Least Developed Countries Available online: https://unctad.org/topic/least-developed-countries/list.
- Rimal, B.; Sloan, S.; Keshtkar, H.; Sharma, R.; Rijal, S.; Shrestha, U.B. Patterns of Historical and Future Urban Expansion in Nepal. Remote Sensing 2020, Vol. 12, Page 628 2020, 12, 628. [CrossRef]
- Rijal, S.; Rimal, B.; Stork, N.; Sharma, H.P. Quantifying the Drivers of Urban Expansion in Nepal. Environ Monit Assess 2020, 192. [CrossRef]
- Ning, C.; Subedi, R.; Hao, L. Land Use/Cover Change, Fragmentation, and Driving Factors in Nepal in the Last 25 Years. Sustainability (Switzerland) 2023, 15, 1–19. [CrossRef]
- Gartaula, H.N.; Niehof, A. Migration to and from the Nepal Terai: Shifting Movements and Motives. The South Asianist 2013, 2, 29–51.
- National Statistics Office National Population and Housing Census 2021 Available online: https://censusnepal.cbs.gov.np/results.
- Office, N.S. National Population and Housing Census 2021; 2023;
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, W.; Ji, J.; Chen, C. Urban Ecological Quality Assessment Based on Google Earth Engine and Driving Factors Analysis: A Case Study of Wuhan City, China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 3598. [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wang, Y.; Guan, H.; Shi, T.; Hu, X. Detecting Ecological Changes with a Remote Sensing Based Ecological Index (RSEI) Produced Time Series and Change Vector Analysis. Remote Sens (Basel) 2019, 11, 2345. [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wang, M.; Shi, T.; Guan, H.; Fang, C.; Lin, Z. Prediction of Ecological Effects of Potential Population and Impervious Surface Increases Using a Remote Sensing Based Ecological Index (RSEI). Ecol Indic 2018, 93, 730–740. [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Tang, L.; Hupy, J.P.; Wang, Y.; Shao, G. A Commentary Review on the Use of Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) in the Era of Popular Remote Sensing. J For Res (Harbin) 2021, 32, 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Crist, E.P. A TM Tasseled Cap Equivalent Transformation for Reflectance Factor Data. Remote Sens Environ 1985, 17, 301–306. [CrossRef]
- Baig, M.H.A.; Zhang, L.; Shuai, T.; Tong, Q. Derivation of a Tasselled Cap Transformation Based on Landsat 8 At-Satellite Reflectance. Remote Sensing Letters 2014, 5, 423–431. [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Pablo, R.D.A.; Zhang, Y. Eco-Environmental Quality Assessment Using the Remote Sensing Ecological Index in Suzhou City, China. Sustainability (Switzerland) 2023, 15. [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Xu, H. A New Remote Sensing Index for Assessing the Spatial Heterogeneity in Urban Ecological Quality: A Case from Fuzhou City, China. Ecol Indic 2018, 89, 11–21. [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Xie, X.; Bagan, H.; Chen, C.; Wang, Q.; Yoshida, T. Exploring Spatiotemporal Variations in Land Surface Temperature Based on Local Climate Zones in Shanghai from 2008 to 2020. Remote Sens (Basel) 2023, 15, 3106. [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Munoz, J.C.; Sobrino, J.A.; Skokovic, D.; Mattar, C.; Cristobal, J. Land Surface Temperature Retrieval Methods From Landsat-8 Thermal Infrared Sensor Data. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters 2014, 11, 1840–1843. [CrossRef]
- Estoque, R.C.; Murayama, Y.; Myint, S.W. Effects of Landscape Composition and Pattern on Land Surface Temperature: An Urban Heat Island Study in the Megacities of Southeast Asia. Science of The Total Environment 2017, 577, 349–359. [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.Q. A Remote Sensing Index for Assessment of Regional Ecological Changes. Zhongguo Huanjing Kexue/China Environmental Science 2013, 33, 889–897.
- Szabó, S.; Gácsi, Z.; Balázs, B. Specific Features of NDVI, NDWI and MNDWI as Reflected in Land Cover Categories. Landscape & Environment 2016, 10, 194–202. [CrossRef]
- Faridatul, M.I.; Wu, B. Automatic Classification of Major Urban Land Covers Based on Novel Spectral Indices. ISPRS Int J Geoinf 2018, 7, 453. [CrossRef]
- Li, E.; Du, P.; Samat, A.; Xia, J.; Che, M. An Automatic Approach for Urban Land-Cover Classification from Landsat-8 OLI Data. Int J Remote Sens 2015, 36, 5983–6007. [CrossRef]
- Wardlow, B.D.; Egbert, S.L. A Comparison of MODIS 250-m EVI and NDVI Data for Crop Mapping: A Case Study for Southwest Kansas. Int J Remote Sens 2010, 31, 805–830. [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. Modification of Normalised Difference Water Index (NDWI) to Enhance Open Water Features in Remotely Sensed Imagery. Int J Remote Sens 2006, 27, 3025–3033. [CrossRef]
- Kebede, T.A.; Hailu, B.T.; Suryabhagavan, K.V. Evaluation of Spectral Built-up Indices for Impervious Surface Extraction Using Sentinel-2A MSI Imageries: A Case of Addis Ababa City, Ethiopia. Environmental Challenges 2022, 8, 100568. [CrossRef]
- Alcaras, E.; Costantino, D.; Guastaferro, F.; Parente, C.; Pepe, M. Normalized Burn Ratio Plus (NBR+): A New Index for Sentinel-2 Imagery. Remote Sens (Basel) 2022, 14, 1–19. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Han, J.; Li, P.; Li, H.; Feng, Y.; Hu, B.; Zhang, G.; Li, J. Evidence for Urbanization Effects on Eco-Environmental Quality: A Case Study of Guyuan City, China. Sustainability (Switzerland) 2023, 15. [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wang, M.; Shi, T.; Guan, H.; Fang, C.; Lin, Z. Prediction of Ecological Effects of Potential Population and Impervious Surface Increases Using a Remote Sensing Based Ecological Index (RSEI). Ecol Indic 2018, 93, 730–740. [CrossRef]


| Year | Sensor | Path | WRow | Date | Cloud Cover (Percentage) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1993 | Landsat 5 TM | 142 | 41 | 2004-10-04 | 3 |
| 2004 | 2008-10-15 | 0 | |||
| 2013 | Landsat 8 OLI/TIRS | 2013-10-24 | 0.12 | ||
| 2023 | 2023-10-20 | 2.41 |
| Year | 2023 | 2013 | 2004 | 1993 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall Accuracy | 0.938 | 0.871 | 0.912 | 0.88 | ||||
| Kappa coefficient | 0.923 | 0.798 | 0.891 | 0.854 | ||||
| Accuracy (Producer’s and User’s) | PA | UA | PA | UA | PA | UA | PA | UA |
| Forest | 0.932 | 0.96 | 0.947 | 0.90 | 0.911 | 0.93 | 0.9 | 0.9 |
| Agriculture Land | 0.873 | 0.905 | 0.967 | 0.88 | 0.853 | 0.877 | 0.841 | 0.849 |
| Built-up Area | 0.971 | 0.942 | 0.778 | 0.77 | 0.924 | 0.933 | 0.870 | 0.895 |
| Dry Breland | 0.933 | 0.933 | 0.50 | 0.80 | 0.905 | 0.914 | 0.846 | 0.895 |
| Water | 0.989 | 0.950 | 0.90 | 0.90 | 0.978 | 0.910 | 0.978 | 0.883 |
| Year | Grading | Area | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1993 | Poor | 23.9013 | 1.83 |
| Fair | 151.051 | 11.59 | |
| Moderate | 453.619 | 34.81 | |
| Good | 529.054 | 40.60 | |
| Excellent | 140.188 | 10.76 | |
| Water Body | 5.3767 | 0.41 | |
| 2004 | Poor | 4.69631 | 0.36 |
| Fair | 53.6893 | 4.12 | |
| Moderate | 460.436 | 35.33 | |
| Good | 588.392 | 45.15 | |
| Excellent | 189.278 | 14.52 | |
| Water Body | 6.69839 | 0.51 | |
| 2013 | Poor | 4.49065 | 0.34 |
| Fair | 176.478 | 13.54 | |
| Moderate | 714.06 | 54.79 | |
| Good | 231.279 | 17.75 | |
| Excellent | 170.697 | 13.10 | |
| Water Body | 6.18535 | 0.47 | |
| 2023 | Poor | 0.072406 | 0.01 |
| Fair | 32.61161 | 2.50 | |
| Moderate | 398.9699 | 30.61 | |
| Good | 574.0175 | 44.05 | |
| Excellent | 288.5381 | 22.14 | |
| Water Body | 8.980484 | 0.69 |
| From | To | Area (1993-2004) | Area (2004-2013) | Area (2013-2023) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1.28 | 0.93 | 0.01 |
| 1 | 2 | 3.26 | 1.29 | 1.41 |
| 1 | 3 | 4.92 | 1.23 | 0.94 |
| 1 | 4 | 5.84 | 1.39 | 1.02 |
| 1 | 5 | 7.62 | 1.79 | 1.46 |
| 2 | 1 | 10.79 | 3.31 | 2.10 |
| 2 | 2 | 18.79 | 8.36 | 15.01 |
| 2 | 3 | 30.25 | 10.51 | 38.67 |
| 2 | 4 | 38.89 | 14.60 | 46.71 |
| 2 | 5 | 47.86 | 22.59 | 60.70 |
| 3 | 1 | 60.81 | 38.03 | 81.88 |
| 3 | 2 | 79.34 | 109.62 | 124.84 |
| 3 | 3 | 129.06 | 137.72 | 248.69 |
| 3 | 4 | 114.32 | 120.15 | 193.95 |
| 3 | 5 | 94.83 | 116.03 | 82.84 |
| 4 | 1 | 91.67 | 122.49 | 56.95 |
| 4 | 2 | 100.17 | 126.73 | 45.68 |
| 4 | 3 | 132.67 | 169.98 | 34.94 |
| 4 | 4 | 138.20 | 69.00 | 42.75 |
| 4 | 5 | 36.89 | 31.94 | 35.28 |
| 5 | 1 | 25.61 | 26.38 | 17.23 |
| 5 | 2 | 23.40 | 25.54 | 17.75 |
| 5 | 3 | 27.47 | 35.48 | 25.09 |
| 5 | 4 | 40.13 | 43.26 | 22.16 |
| 5 | 5 | 50.76 | 76.23 | 116.55 |
| Year | Agriculture | Built-up | Water bodies | Forest | Barren | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1993 | 838.91 | 13.32 | 18.02 | 303.87 | 122.45 | |
| 2004 | 852.02 | 36.69 | 15.42 | 368.99 | 22.36 | |
| 2013 | 885.35 | 94.05 | 9.76 | 265.21 | 41.43 | |
| 2023 | 787.00 | 156.16 | 11.80 | 311.44 | 26.47 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





