1. Introduction
Over the past century, the state of global warming has become more and more obvious, and the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) predicted in its Sixth Assessment Report that global temperatures will rise by more than 1.5℃ by 2030[
1]. The Yili River Valley, located in the interior of northwest China, is a typical arid and semi-arid region with a fragile ecological environment, which is more sensitive to changes in global climate change [
2] Accompanied by global climate change and the impact of human activities, the survival of wild plants is seriously threatened by the biotic or abiotic stress caused by extreme weather, which leads to serious degradation of wild plant habitats[
3], and many species have been severely degraded through migration[
4] or changing their traits[
5] to cope with the changes in the living environment.
Prunus armeniaca L. is a broad-leaved deciduous tree of the genus Apricot in the family Rosaceae, is a dominant species in semi-arid climates[
6], which evolved from the Tertiary relict paleotemperate broadleaf forests and Quaternary boreal forests[
7], and plays an important role in maintaining the prosperity and stability of the Tien Shan ecosystem as well as the domestication and cultivation of apricot worldwide[
8]. However, due to natural factors such as climate change-induced droughts, pest and disease outbreaks[
9], and anthropogenic factors such as agricultural deforestation and reclamation, and excessive tourism development, the distribution area of
Prunus armeniaca L. has been sharply reduced, and the habitat fragmentation is serious, and it is now listed as a second-grade protected plant in China's "List of Nationally Important Wild Plants"[
10]. As the native species of cultivated apricot,
Prunus armeniaca L. is an important biological resource for studying the law of plant evolution, plant economics, and sustainable development of biodiversity[
11], and exploring reasonable protection measures and scientific development pathways for
Prunus armeniaca L. through scientific research is an urgent problem to be solved at present.
Since the end of the 20th century, research on the ecology of
Prunus armeniaca L. has gradually received attention, and in the early stage, it was mainly focused on the conservation measures and basic ecological characteristics of
Prunus armeniaca L., such as morphological and structural characteristics[
12], seed preservation[
13], genetic diversity[
14], etc. In recent years, with the development of remote sensing technology and other information technology, the
Prunus armeniaca L. has become an important biological resource for the sustainable development of the world. In recent years, with the development of remote sensing technology and other information technology to provide new ideas and methods for related research, remote sensing combined with mathematical models, econometric models, and other research has gradually become the mainstream research direction, such as species distribution model[
15], InVEST model[
16], GeoDetector model[
17], MSPA model[
18], etc. Combined with remote sensing technology to provide a method to explore the changes and driving factors of plant habitats. MaxEnt model, as one of the most popular tools to simulate species distribution, has good stability and is a typical method to combine specific species with ecological niche factors[
19].
Prunus armeniaca L. has important ecological and socio-economic values, and it is of practical significance to study its distribution pattern and understand its driving mechanism in the context of the shrinking area of Prunus armeniaca L. due to the superposition of global warming, anthropogenic impacts, and other factors. Based on the Geographic Information System coupled MaxEnt model, the study explores the potential distribution of Prunus armeniaca L.s in the Yili River Valley, calculates and analyzes the shift of its distribution center, reveals the potential geographic distribution of Prunus armeniaca L. and its trend of change in the future, and provides some theoretical references for the future research on Prunus armeniaca L. and its habitat protection and development.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Acquisition and Processing
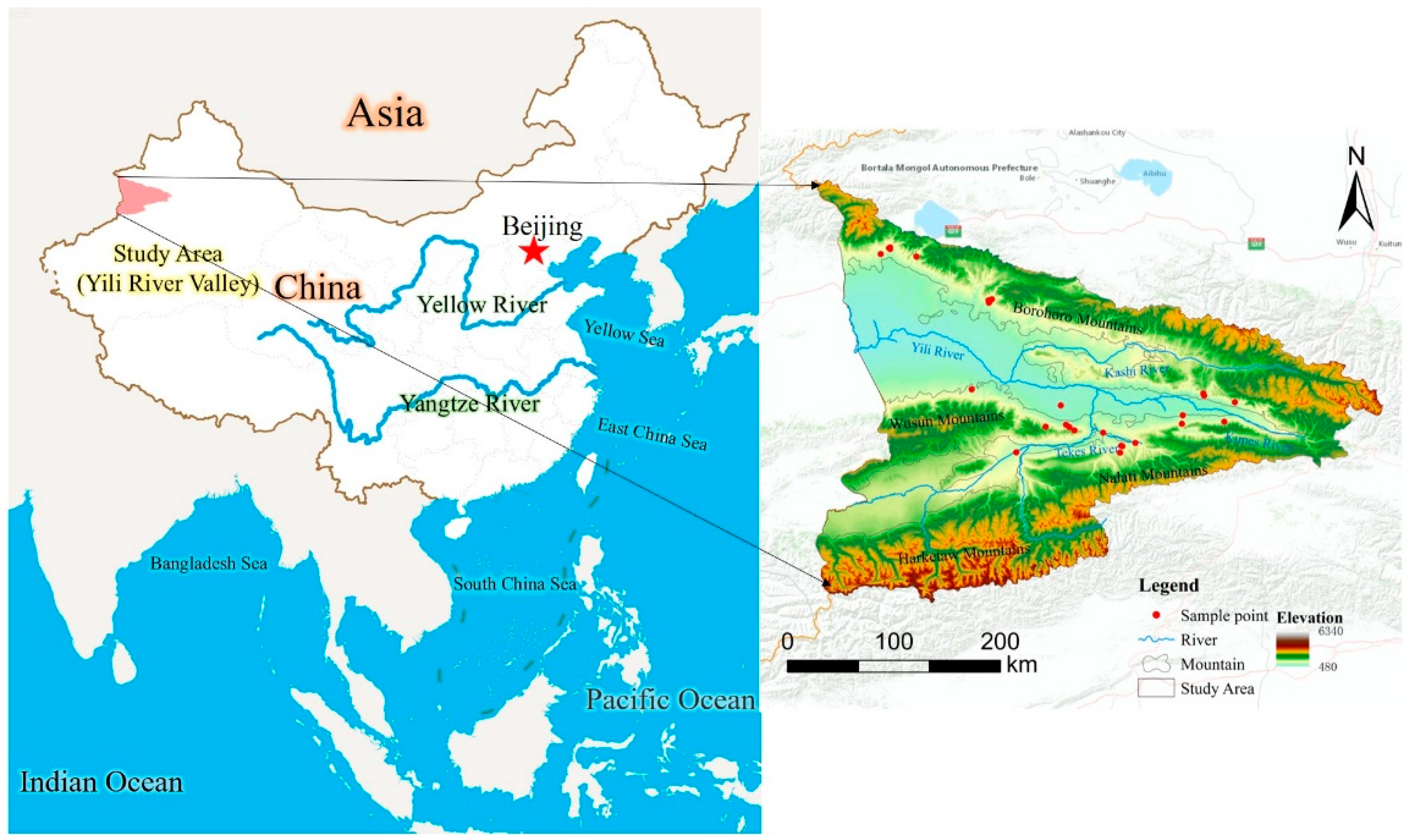
The Yili River Valley is located in the hinterland of the Asia-Europe continent (42°14′16″N-44°50′30″N, 80°9′42″E-84°56′50″E), formed by the erosion and accumulation of the Yili River originating in the Tianshan Mountains, with the climate type of the valley being temperate continental, and the north and south mountainous areas having the characteristics of alpine plateau climate. Due to the mountains in the north, such as the Borokonu Mountains, blocking the southward cold wave, the south side of the Halkhtawu Mountains, blocking the northward heat wave, and to the west the terrain is flat and there are no mountain ranges to block, and the warm and humid airflow from the Atlantic Ocean drives into the valley, creating warm and humid climatic conditions in the Yili River Valley. The average annual temperature ranges from 2.9 to 9.1℃, and the average annual precipitation in the valley is 200 mm, while that in the mountainous areas can be up to 800 mm. The soil type of the valley is mainly composed of black calcium soil, chestnut calcium soil, gray-brown soil, etc. The rich water and heat resources make the river valley a very warm and moist place. The rich water and heat resources in the valley make the valley forested and grassland widespread, known as "Central Asia Wet Island". The east end of the valley is a branch of the Tianshan Mountain, where the Tianshan Mountain is divided into the north and south branches. The complex geological and climatic environment has profoundly influenced the process of plant evolution, and the ancient temperate wild fruit forests left over from the Tertiary Period continue here. However, increasingly intense human activities have brought new ecological and environmental problems, the expansion of traditional agriculture and animal husbandry, and excessive tourism development make the survival of wild fruit forests in the Yili River Valley face new challenges.
Species distribution data were mainly obtained through field fieldwork, the Global Biodiversity Information Platform (
http://www.gbif.org), and the National Specimen Platform (
http://www.nsii.org.cn). To reduce the influence of sampling bias, geographic information software was used to further screen the distribution points and delete some over-dense points, and finally, a total of 28
Prunus armeniaca L. distribution points were obtained (
Figure 1).
2.2. Acquisition of the Environmental Data
The environmental variable data used were mainly Digital Elevation Model (DEM), soil type data, and bioclimatic data of the study area, etc. The DEM data were adopted from ASTER GDEM with a spatial resolution of 30 m from Geospatial Data Cloud (
http://www.gscloud.cn); soil type data with a spatial resolution of 1 km from the Resource and Environmental Science and Data Center of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (
https://www.resdc.cn); And bioclimatic data were all from the World Meteorological Database[
20] (
https://www.worldclim.org/data/inde). The BCC-CSM2-MR climate system model selected for the bioclimatic data in the future period (2060-2080) is one of the three BCC models involved in conducting the CMIP6 experiment[
21]. Shared socio-economic pathways (SSPs) are integrated scenarios describing plausible alternative trends in the evolution of social and natural systems in the 21st century at the world and large world-region levels, developed based on RCPs[
22], where the current scenario data have a temporal resolution of 30′ and a spatial resolution of about 1km, and the future scenario data have a temporal resolution of 2.5min and a spatial resolution of about 5km. The data used are widely used in related research fields and have successfully solved many practical problems with high data quality. After data acquisition, the data were pre-processed with the support of Geographic Information System software through resampling, extraction, and other pre-processing means to ensure the uniformity of the spatial scale of the data, and uniformly converted into ASCII format.
Table 1.
Environment variables and their descriptions.
Table 1.
Environment variables and their descriptions.
| Code |
Environment variable |
Code |
Environment variable |
| Bio01 |
Annual Mean Temperature |
Bio13 |
Precipitation of Wettest Month |
| Bio02 |
Mean Diurnal Range |
Bio14 |
Precipitation of Driest Month |
| Bio03 |
Isothermality |
Bio15 |
Precipitation Seasonality |
| Bio04 |
Temperature Seasonality |
Bio16 |
Precipitation of Wettest Quarter |
| Bio05 |
Max Temperature of Warmest Month |
Bio17 |
Precipitation of Driest Quarter |
| Bio06 |
Min Temperature of Coldest Month |
Bio18 |
Precipitation of Warmest Quarter |
| Bio07 |
Temperature Annual Range |
Bio19 |
Precipitation of Coldest Quarter |
| Bio08 |
Mean Temperature of Wettest Quarter |
Ele |
Elevation |
| Bio09 |
Mean Temperature of Driest Quarter |
Slo |
Slope |
| Bio10 |
Mean Temperature of Warmest Quarter |
Asp |
Aspect |
| Bio11 |
Mean Temperature of Coldest Quarter |
Soi |
Soil |
| Bio12 |
Annual Precipitation |
|
|
2.3 Modelling Approach
The Maximum Entropy Model is a species distribution model constructed by the American Museum of Natural History based on the Maximum Entropy Theory proposed by Jaynes in 1957, which is a novel method to predict species distribution. Since the accuracy and stability of the MaxEnt model are affected by the number of environmental variables, too many variables are detrimental to the accuracy of the test results[
23]. The study constructed a model to simulate the potential distribution area of
Prunus armeniaca L. under the current climate, analyzed 23 factors, and selected 10 factors after eliminating those with a contribution rate of less than 1%, imported the screened distribution point data,and bioclimatic data into the MaxEnt model, and randomly selected 75% of the sample points as the model training, and the remaining 25% was used for the model validation The other parameters were set as defaults. The accuracy of the MaxEnt model prediction was expressed by the area under the curve (AUC) of the receiver operating characteristic (ROC curve), the AUC takes the value in the range of [0,1], the closer the value is to 1, the higher the prediction accuracy P[
24,
25]. Based on the MaxEnt model output of the existence probability logic value of
Prunus armeniaca L. (P), P takes values in the range of [0,1]. Geographic Information System software was used to convert the data format of the prediction results and to classify the fitness zones into non-fitness zones (P<0.05), low-fitness zones (0.05≤P<0.25), medium-fitness zones (0.25≤P<0.5), and high-fitness zones (P≥0.5) by reclassification.
3. Result
3.1. Model Results
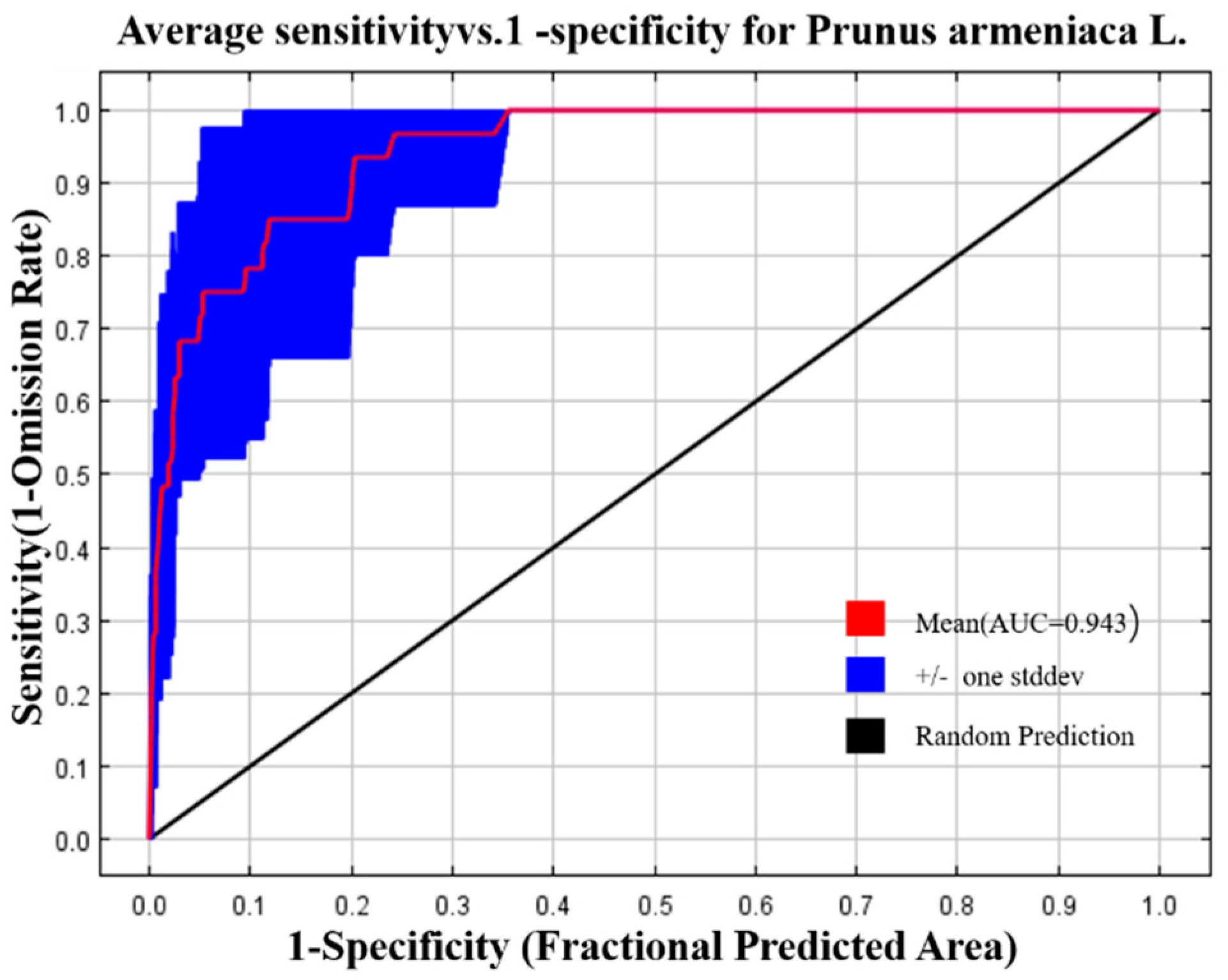
The results of the ROC curve are shown in
Figure 2, and the AUC value for the prediction of the potential distribution of
Prunus armeniaca L.is 0.943. The simulation results show that the MaxEnt model has a high accuracy in the prediction of the potential distribution of
Prunus armeniaca L. in the Yili River Valley.
3.2. Key Environments Factors
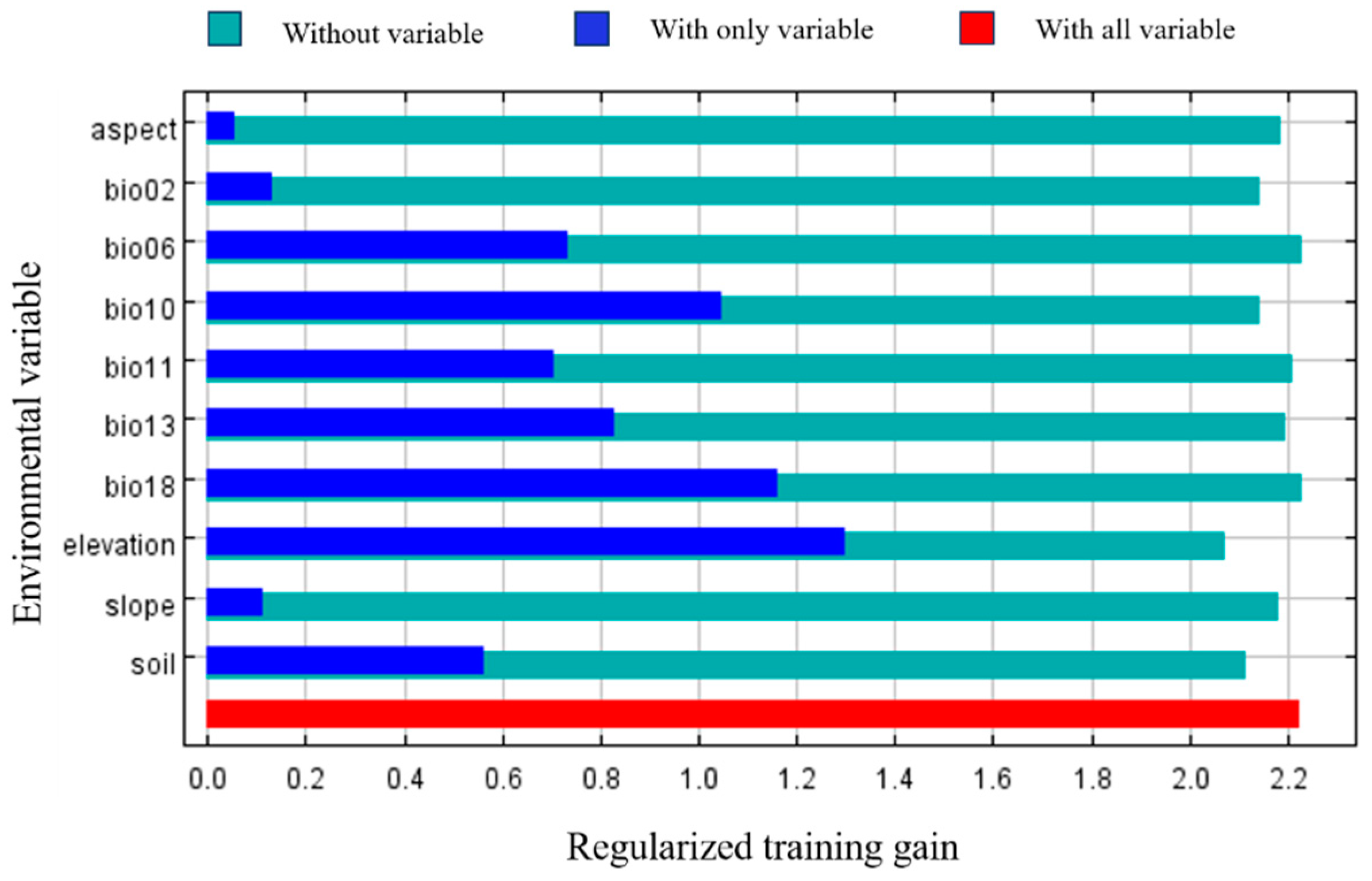
From
Table 2, it was found that the top five environmental factors contributing to the model construction were Bio06 (minimum temperature in the coldest month), Soil (soil type), Bio18 (precipitation in the hottest quarter), Elevation (elevation), and Bio02 (average diurnal range), which contributed 32%, 27.2%, 11.1%, 7.9%, and 7.5%, respectively, with a cumulative contribution was 85.7%, which was significantly higher than other variables. By analyzing the effects of each environmental variable on
Prunus armeniaca L. fitness zones through the knife-cut method (see
Figure 3), it can be seen that Ele (elevation), Bio10 (average temperature in the hottest season), and Bio18 (precipitation in the hottest season) have higher regularization training gains when only this variable is available, suggesting that these items contain information that is not present in other environmental factors. In summary, Bio06 (minimum temperature of the coldest month), Ele (elevation), Bio10 (average temperature of the hottest season), and Bio18 (precipitation of the hottest season) play a key role in the potential geographic distribution of
Prunus armeniaca L.
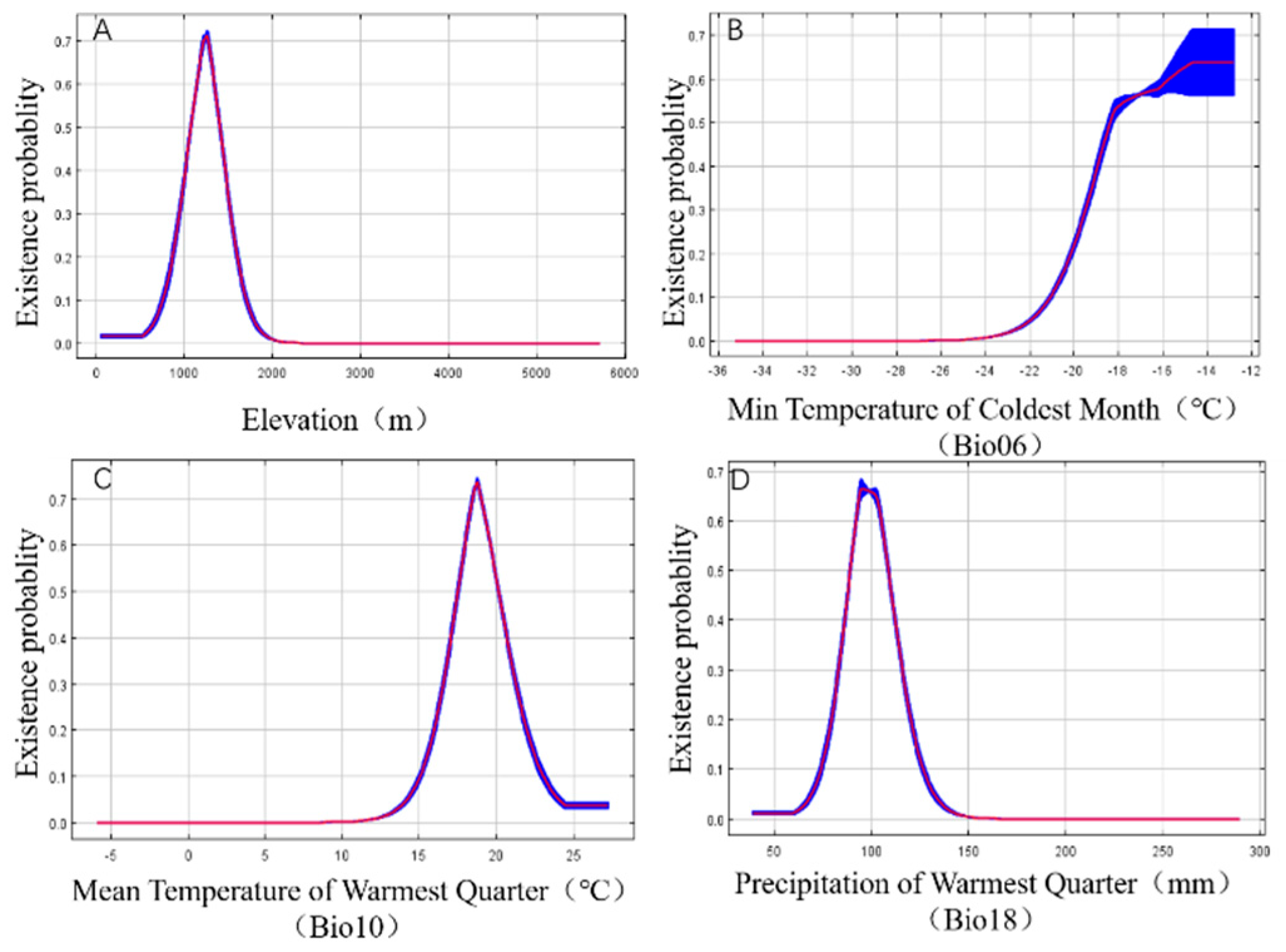
The response curves of the dominant environmental variables (
Figure 4) showed that
Prunus armeniaca L. existed at the optimum altitude in the altitude range of 1000~2000m (
Figure 4-A), and the overall trend was that the probability of existence firstly increased with the increase of altitude, and then decreased with the increase of altitude after reaching the peak value. The probability of the presence of
Prunus armeniaca L. increased with the minimum temperature of the coldest month (
Figure 4-B), with a rapid increase in the probability of presence at -24°C to -18°C, and a flattening of the rate of increase in the probability of presence after -18°C. The average temperature range of
Prunus armeniaca L. in the hottest season was 15°C ~ -20°C at the optimum temperature for presence (
Figure 4-C), and the probability of presence of
Prunus armeniaca L. after the temperature reached its peak gradually decreased with increasing temperature. The optimum precipitation for
Prunus armeniaca L. exists when the precipitation in the hottest season ranges from 75 mm to 100 mm (
Figure 4-D), and the probability of
Prunus armeniaca L. presence decreases with increasing precipitation after the precipitation reaches its peak.
3.3. Predicted Current Potential Distribution Predicted Current Potential Distribution
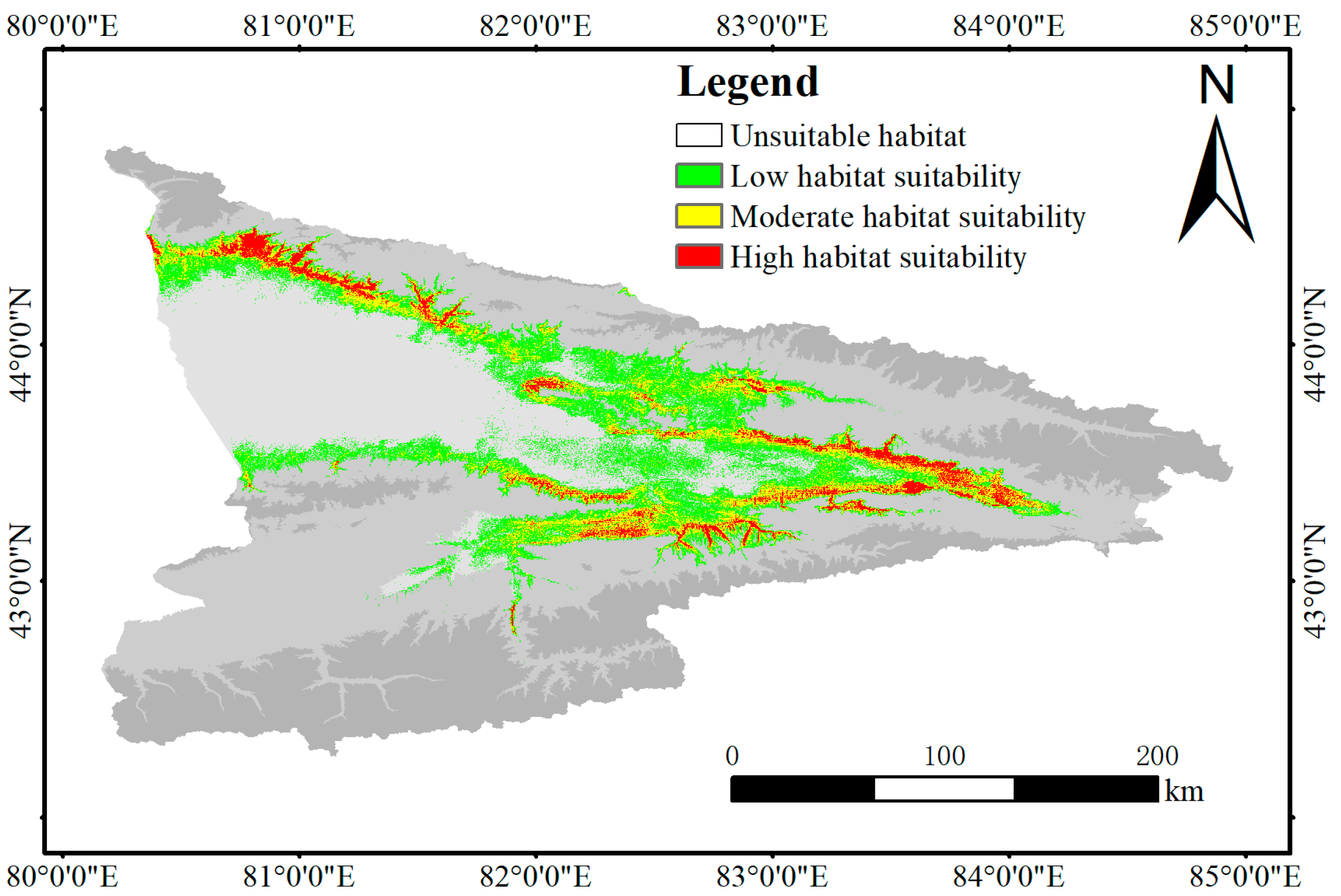
Currently, the Xinjiang Suitable Area in the Yili River Valley is mainly distributed in the eastern part of the valley, with more distribution in the northwestern part of the valley (
Figure 5). The total area of
Prunus armeniaca L. aptitude zone in the Yili River Valley is about 10407.77 km
2, accounting for about 18.45% of the overall land area of the Yili River Valley; the area of the high aptitude zone is about 1380.9 km
2, accounting for about 13.26% of the total aptitude zone, the area of the medium aptitude zone is about 2830.15 km
2, accounting for about 27.19% of the total aptitude zone area, and the area of the low aptitude zone is about 6196.05 km
2, accounting for about 59.53% of the total fertile area. The high and medium-suitable areas are mainly distributed in the foothills and the mid-mountain belt, and the inverse temperature effect of the mountains redistributes heat to create suitable areas in the mid-mountain belt; the non-suitable areas are mainly in the river valley plains and high-altitude areas.
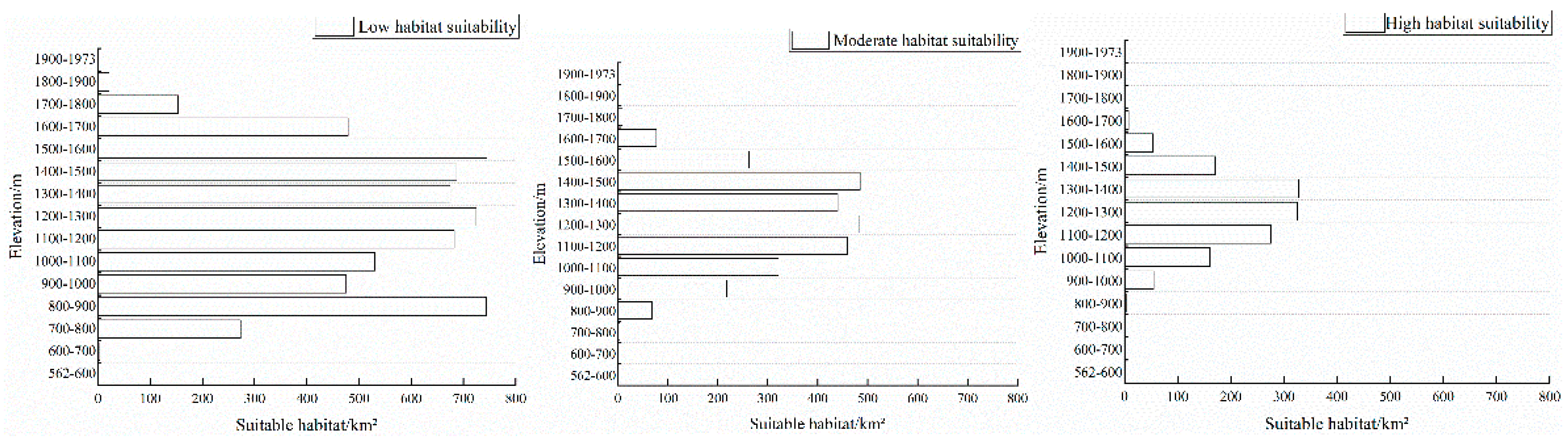
Through the altitude analysis, it was found that the suitable areas for
Prunus armeniaca L. in the Yili River Valley are concentrated at the altitude of 1100~1600m, and the trend of increasing and then decreasing with the increase of the altitude is shown in the overall trend. The low suitable area is mainly concentrated in the area of 1500-1600m above sea level, the medium suitable area reaches its peak at 1400~1500m above sea level, and the high suitable area reaches its peak at 1300~1400m above sea level (
Figure 6). The
Prunus armeniaca L. habitat in the Yili River Valley is mainly concentrated in the cool and humid mid-altitude areas, and is disturbed by human activities at lower altitudes, so the degree of
Prunus armeniaca L. habitability is low; the climate in the mid-altitude and high-altitude areas above the altitude of 1800m is severe and cold, and the habitat is fragile, which is insufficient to satisfy the
Prunus armeniaca L. base survival. The area of the low-fitness zone in the 800~900m altitude zone is second only to the peak of the 1500~1600m altitude zone, which is because the low-fitness zone in one of the altitude zones is distributed in the valleys, which is affected by the closed topography and the surrounding climate, and exhibits a cold climate and is a catchment area, which creates the
Prunus armeniaca L.fitness zone.
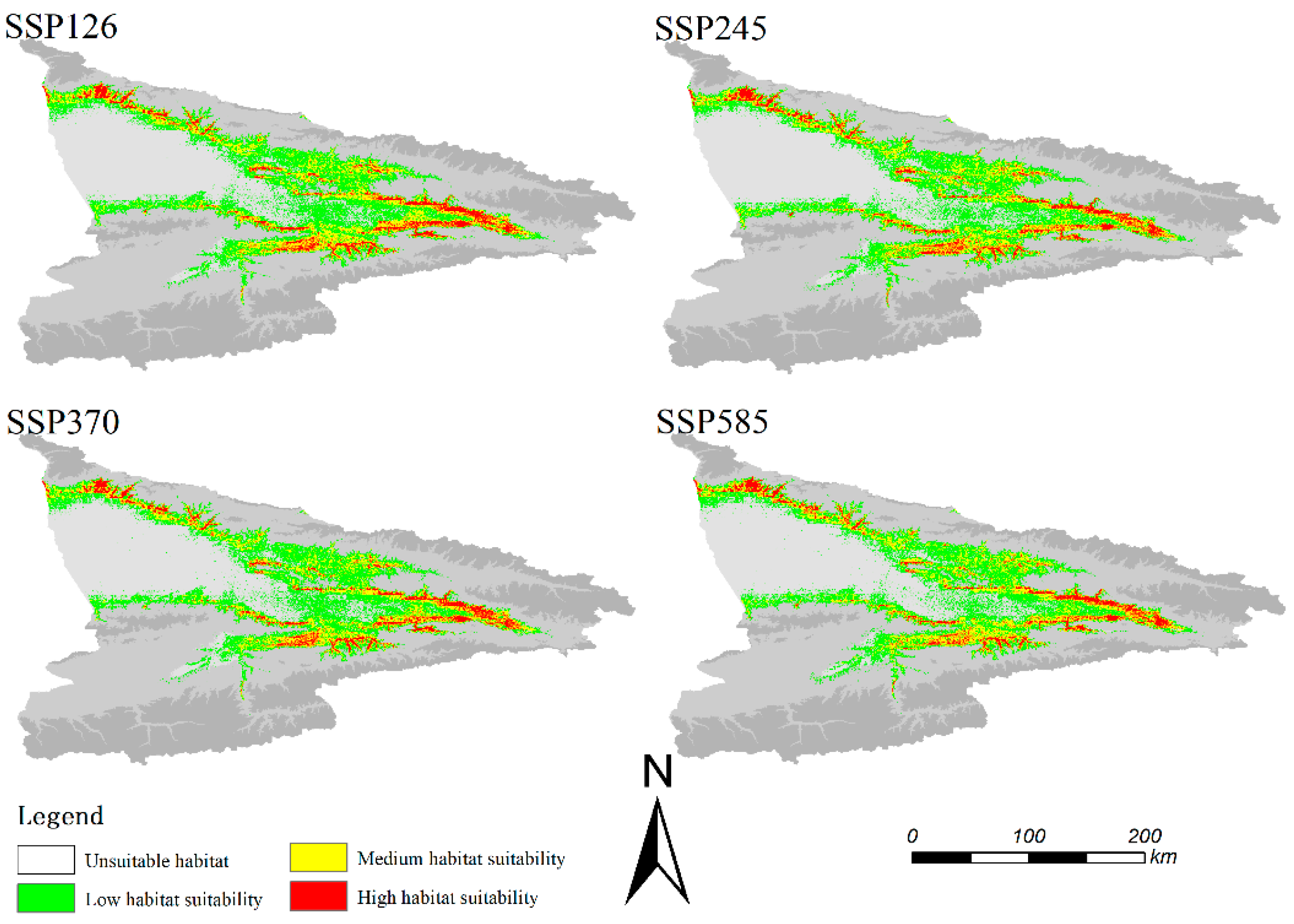
3.4. Predicted Future Potential Distribution
The Maxent model was used to predict the suitable areas for
Prunus armeniaca L. in the Yili Valley under future climate scenarios: SSP126, SSP245, SSP370, and SSP585(
Figure 7).
The area of suitable areas for Prunus armeniaca L. in the Yili Valley under future climate scenarios was 11604.31km2, accounting for 20.57% of the total land area of the Yili Valley, which was an increase of 1196.53km2, compared with the total area of suitable areas for Prunus armeniaca L. in the Yili Valley under current climate scenarios. 1196.53km2, an increase of about 11.49%. The increase in the area of the high aptitude zone was about 13.77%, the increase in the area of the medium aptitude zone was about 23.29%, and the increase in the area of the low aptitude zone was about 5.59%. The total suitable area of Prunus armeniaca L. under the SSP245 scenario is 11046.77 km2, accounting for about 19.58% of the total land area of the Yili River Valley, which is an increase of 639 km2 or 6.13% compared with that of Prunus armeniaca L. under the current climatic conditions. The area of high suitable area increased by about 9.22%, the area of medium suitable area increased by about 18.84%, and the area of low suitable area decreased by 21.92km2, or about 0.35%. The total suitable area of Prunus armeniaca L. under the SSP370 scenario is 10921.88 km2, accounting for about 19.36% of the total land area of the Yili River Valley, and the total suitable area of Prunus armeniaca L. under the current climatic conditions has increased by 514.11 km2 or about 4.93%. The increase in the area of the high aptitude zone was about 4.71%, the increase in the area of the medium aptitude zone was about 10.72%, and the increase in the area of the low aptitude zone was about 2.34%. The total suitable area of Prunus armeniaca L. under SSP585 is 11091.17 km2, accounting for 19.66% of the total land area of the Yili River Valley, which is 683.4 km2 more than that of Prunus armeniaca L. under the current climatic conditions, with an increase of about 6.56%. The increase in the area of the high aptitude zone was about 5.58%, the increase in the area of the medium aptitude zone was about 20.5%, and the increase in the area of the low aptitude zone was about 0.41%. The total area of Prunus armeniaca L. suitable area and the area of high suitable area changed most significantly under the SSP126 scenario, and the area of Prunus armeniaca L. in the low suitable area slightly shrunk under the background of SSP245 compared with the current scenario, but the area of medium and high suitable areas showed an expanding trend, and the Prunus armeniaca L. was more suitable for survival in the Yili River Valley under the low radiative forcing scenario.
Table 3.
Suitable areas for Prunus armeniaca L. different climate change scenarios (km2).
Table 3.
Suitable areas for Prunus armeniaca L. different climate change scenarios (km2).
| Classification Level |
Current Climate |
Future Climate Conditions |
| SSP126 |
SSP245 |
SSP370 |
SSP585 |
| Low habitat suitability |
6196.05 |
6543.00 |
6174.13 |
6341.35 |
6221.89 |
| Moderate habitat suitability |
2830.81 |
3490.16 |
3364.32 |
3134.49 |
3411.29 |
| High habitat suitability |
1380.90 |
1571.14 |
1508.32 |
1446.03 |
1457.97 |
| Suitable habitat |
10407.77 |
11604.31 |
11046.77 |
10921.88 |
11091.17 |
3.5. Future Center of Gravity Migration
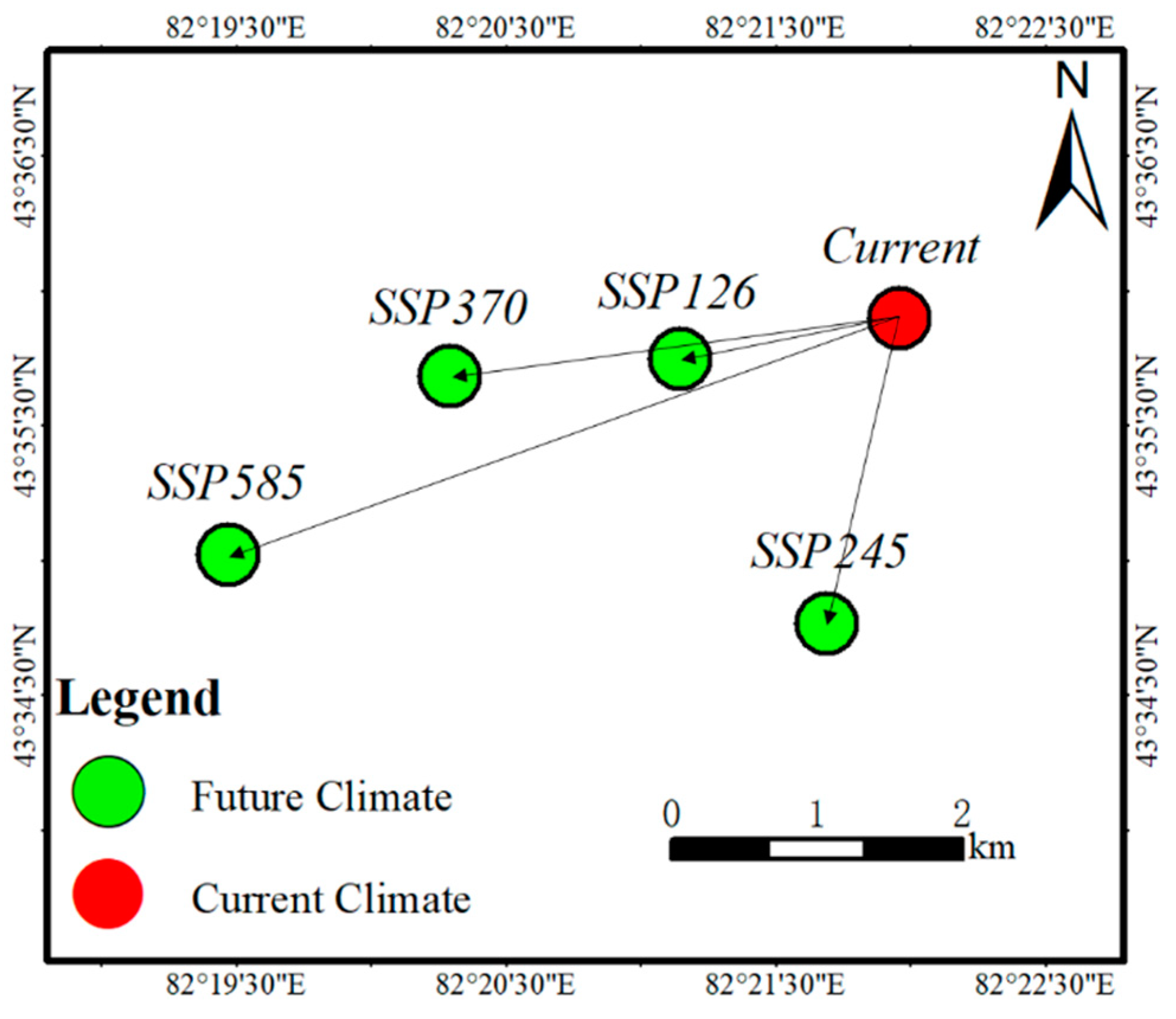
Analyzing the migration of the center of mass of the
Prunus armeniaca L. niche under the current and future climate scenarios with the support of Geographic Information System software, it was found that the distribution center of mass of the
Prunus armeniaca L. niche was 43.59°N, 82.36°E at the current time (
Figure 8). Under the SSP126 climate scenario, the center of mass of the future
Prunus armeniaca L. distribution in the Yili River Valley migrated 13.82 m to the southwest, with the coordinates of 43.59°N, 82.35°E; under the SSP245 climate scenario, the center of mass of the future
Prunus armeniaca L. distribution in the Yili River Valley migrated 19.38 m to the southwest, with the coordinates of 43.57°N, 82.36°E; and under the SSP370 climate scenario, the center of mass of the future
Prunus armeniaca L. distribution in the Yili River Valley migrated 19.38 m to the southwest, with the coordinates of 43.57°N, 82.36°E. In the climate scenario SSP370, the center of mass of the future
Prunus armeniaca L. distribution in the Yili River Valley migrated 28.07m to the southwest, with coordinates 43.59°N, 82.33°E; in the climate scenario SSP585, the center of mass of the future
Prunus armeniaca L. distribution in the Yili River Valley migrated 44.03m to the southwest, with coordinates 43.58°N, 82.32°E. Although there is no overlap in the direction of the geographic distribution center of the mass of
Prunus armeniaca L. in the different climate scenarios, there is no overlap in the overall direction of the geographical distribution center of the
Prunus armeniaca L. in the different climate scenarios. Although the migration directions of the geographic centers of
Prunus armeniaca L. in different climatic scenarios did not overlap, they generally migrated in a southwesterly direction, with the largest migration angle in the SSP245 scenario and the largest migration distance in the SSP585 scenario.
4. Discussion
Species distribution is mainly influenced by environmental factors, and climatic conditions are important factors affecting the geographical distribution of species[
26]. Studies have shown that the distribution of
Prunus armeniaca L. is mainly influenced by precipitation-related bioclimatic variables (Bio 18: precipitation in the hottest season), three temperature-related bioclimatic variables (Bio02: daily difference in mean temperature Bio06: minimum temperature in the coldest month, Bio10: mean temperature in the hottest season), elevation and soil type. Temperature and precipitation are key environmental elements that influence plant physiological processes[
27,
28], the probability of the presence of
Prunus armeniaca L. increased with the minimum temperature of the coldest month (
Figure 4-B) and leveled off after -18°C;
Prunus armeniaca L. existed at the optimum temperature in the mean temperature range of 15°C to -20°C in the hottest season (
Figure 4-C); and
Prunus armeniaca L. existed at the average temperature in the hottest season when precipitation ranged from 75mm- 100 mm in the hottest season (
Figure 4-D), which corroborates with Zhai Chaoyang's paper[
29] finding that
Prunus armeniaca L. seedling grow and develop better in habitats with higher air temperatures, higher soil temperatures, stronger light conditions, and relatively dry air humidity.
The altitude factor response curve showed that
Prunus armeniaca L. exists at an optimum altitude in the altitude range of 1000m~2000m (
Figure 4-A), and the significant feature of mountain climate is that a smaller altitude gradient can cause a huge climatic difference[
30], and the Yili Valley, as a region with typical vertical zonation characteristics, has a more significant impact of mountain climate on the local ecological environment. The study is consistent with the study of PAPER[
6], emphasizing that altitude is an important environmental factor affecting the distribution of
Prunus armeniaca L.
Soil type is another key variable in determining the distribution of
Prunus armeniaca L. in the study area. Soil can, to some extent, reflect the type of climate in the distribution space of the type of soil or reflect the effect of climate on organisms in its distribution space[
31]. Related studies have shown that plants are very sensitive to changes in soil properties driven by temperature changes[
32,
33], which likewise provides some basis for the vulnerability of
Prunus armeniaca L. to sustained persistent climate change.
In the future climate context, the total area of
Prunus armeniaca L.' suitable area in Xinjiang increased, and the study found that the distribution of
Prunus armeniaca L.'s suitable area generally migrated southward, which was consistent with the conclusions of PAPER[
34] in the study of the relationship between community structure and environment of wild fruit forests on the northern slope of the Yili River Valley. On the one hand, the future global temperature generally shows an upward trend, and some higher altitude areas redistribute the water and heat conditions to develop suitable conditions for the survival of
Prunus armeniaca L.; on the other hand, changes in the intensity of human activities in the future will still affect the survival environment of the
Prunus armeniaca L., and the concentration of the population in the towns and cities is favorable to the recovery of
Prunus armeniaca L. or expansion of the habitat to the lower altitude areas. PAPER[
35] and PAPER[
36], by studying the distribution of suitable zones for other studied the distribution of other tree species in their habitat areas and successfully revealed their distribution patterns in the future climatic context. Due to the different environmental attributes and tree species characteristics in the study area, the results of the present study differ slightly from those of the present study, but the consistent means of attribution once again proved the correctness of the experiment. In the selection of experimental data, the study used CMIP6 future climate prediction data, which can better reflect the multiple possibilities of aerosol influence on recent climate change, and at the same time, the multi-model ensemble prediction reduces the single-model systematic error, and can more accurately predict the change of
Prunus armeniaca L.fitness zone in the Yili Valley under the future climate conditions.
5. Conclusions
The study was based on Geographic Information System software combined with the MaxEnt model to explore the change of Prunus armeniaca L. suitable areas in the Yili River Valley under the future climate background, and analyze the drive of each environmental factor on the suitable area of Prunus armeniaca L. in the Yili River Valley, and get the following conclusions:
(1) The AUC value of the training data for Prunus armeniaca L. potential distribution suitable area prediction is 0.969, and the AUC value of the test data is 0.993, and the MaxEnt model has high accuracy in predicting the potential distribution suitable area of Prunus armeniaca L. in the Yili River Valley.
(2) Currently, the suitable area of Xinjiang in the Yili River Valley is mainly distributed in the eastern part of the valley, and there are also more distributions in the northwestern part. The total area of the Prunus armeniaca L. suitable area in the Yili River Valley is about 10407.77km2, accounting for about 18.45% of the overall land area of the Yili River Valley; the area of the high suitable area is about 1380.9km2, accounting for about 13.26% of the total suitable area, the area of the medium suitable area is about 2830.15km2, accounting for about 27.19% of the total suitable area, and the area of the low suitable area is about 6196.05 km2, accounting for about 59.53% of the total suitable area.
(3) The increase in the total area of the suitable area and the area of the high suitable area under the SSP126 scenario was the largest among the four scenarios, and the Prunus armeniaca L. was more suitable for survival in the Yili River Valley under the background of low radiative forcing. Under the premise of Prunus armeniaca L. fitness area protection, the low radiation forcing scenario is the main direction of future environmental development.
(4) The migration directions of the geographic centers of mass of Prunus armeniaca L. under different climate scenarios did not overlap. Generally, they migrated in a southwesterly direction, in which the migration angle was the largest under the SSP245 scenario and the migration distance was the largest under the SSP585 scenario.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization、methodology、software and investigation, Ang Ning and Wanji Chen; data curation, Ang Ning and Wenbing Cui; writing—original draft preparation,Ang Ning;writing—review and editing, Ang Ning,Wanji Chen,Wenbing Cui,Muyassar·Saydahmat and Erfan·Akberjan; supervision, Yang Zhao and Wanji Chen; project administration, Yang Zhao. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the The Third Xinjiang Comprehensive Scientific Investigation Progarm (2022xjkk0405), the Key Project of Open Subjects of the Institute of Resources and Environment of Yili Normal University (YLNURE202305), Innovation and Entrepreneurship Program Training Project for College Students of Yili Normal University(S2023107640016), and the Innovative Practical Training Program for Undergraduates of Chinese Academy of Science.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Author Introduction
Ang Ning (2003-), Male, Bachelor's Degree, research direction is remote sensing of ecology and environment; Wanji Chen (2001-), Male, Master's degree in progress, Member of Chinese Geographic Society (S110014548A), research interests are oasis geoscape and remote sensing of ecology and environment; Yang Zhao (1988-), Male, Master, Lecturer, research interests include remote sensing of resources and environment; Wenbing Cui (2002-), Male, Bachelor, research interests are remote sensing of ecology and environment; Muyassar·Saydahmat(1999-), Female,Bachelor's degree,with research interests in ecological civilization construction and publicity and education methods; Erfan·Akberjan(1998-),Male,Master's Degree,Forestry Professional Technician,with research interests in Plant Physiology and Ecology.
References
- Kikstra, J.S.; Nicholls, Z.R.J.; Smith, C.J.; Lewis, J.; Lamboll, R.D.; Byers, E.; Sandstad, M.; Meinshausen, M.; Gidden, M.J.; Rogelj, J.; et al. The IPCC Sixth Assessment Report WGIII climate assessment of mitigation pathways: from emissions to global temperatures. Geosci. Model Dev. 2022, 15, 9075–9109. [CrossRef]
- Huang, J., et al., An overview of arid and semi-arid climate change. Adv. Climate Change Res, 2013. 9: p. 9-14.
- Kumar, D.; Rawat, S.; Joshi, R. Predicting the current and future suitable habitat distribution of the medicinal tree Oroxylum indicum (L.) Kurz in India. J. Appl. Res. Med. Aromat. Plants 2021, 23. [CrossRef]
- Forister, M.L.; McCall, A.C.; Sanders, N.J.; Fordyce, J.A.; Thorne, J.H.; O’brien, J.; Waetjen, D.P.; Shapiro, A.M. Compounded effects of climate change and habitat alteration shift patterns of butterfly diversity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2010, 107, 2088–2092. [CrossRef]
- Kiat, Y.; Vortman, Y.; Sapir, N. Feather moult and bird appearance are correlated with global warming over the last 200 years. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Tong, G.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, L.; Sang, Z.; Li, Y. A Study on the Suitable Areas for Growing Apricot Kernels in China Based on the MaxEnt Model. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9635. [CrossRef]
- Chiang, H., On the eco-geographical characters and the problems of classification of the wild fruit-tree forest in the Yili Valley of Sinkiang. 1973.
- Zhebentyayeva, T.; Reighard, G.; Gorina, V.; Abbott, A. Simple sequence repeat (SSR) analysis for assessment of genetic variability in apricot germplasm. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2003, 106, 435–444. [CrossRef]
- Linghu, W.; Lu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Gao, G. The Effects of Globose Scale (Sphaerolecanium prunastri) Infestation on the Growth of Wild Apricot (Prunus armeniaca) Trees. Forests 2023, 14, 2032. [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Chen, X.; Liu, G.; Liang, Q.; He, T.; Feng, J. Interspecific hybridization of Prunus persica with P. armeniaca and P. salicina using embryo rescue. Plant Cell, Tissue Organ Cult. (PCTOC) 2007, 88, 289–299. [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Fan, G.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Liao, K. Genetic diversity, population structure, and relationships of apricot (Prunus) based on restriction site-associated DNA sequencing. Hortic. Res. 2020, 7, 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Viti, R.; Bartolini, S.; Minnocci, A. Morphological structure of the stigma and style of several genotypes ofPrunus armeniacaL.. Plant Biosyst. - Int. J. Deal. all Asp. Plant Biol. 2000, 134, 45–51. [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.; Chaudhury, R. Cryopreservation of seeds and embryonic axes of wild apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.). Seed Sci. Technol. 2010, 38, 231–235. [CrossRef]
- Li, M., et al., Genetic variability of wild apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.) populations in the Yili Valley as revealed by ISSR markers. Genetic resources and crop evolution, 2013. 60: p. 2293-2302.
- Al-Khalaf, A.A. Modeling the potential distribution of the predator of honey bees, Palarus latifrons, in the Arabian deserts using Maxent and GIS. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 5667–5673. [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q., et al., Temporal and spatial variation analysis of habitat quality on the PLUS-InVEST model for Ebinur Lake Basin, China. Ecological Indicators, 2022. 145: p. 109632.
- Peng, C.; Du, L.; Ren, H.; Li, X.; Li, X. Spatial Heterogeneity of Combined Factors Affecting Vegetation Greenness Change in the Yangtze River Economic Belt from 2000 to 2020. Remote. Sens. 2023, 15, 5693. [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.-Z.; Dai, J.-P.; Li, S.-H.; Zhang, J.-Z.; Peng, J.-S. Construction of ecological network in Qujing city based on MSPA and MCR models. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1–11. [CrossRef]
- Norberg, A.; Abrego, N.; Blanchet, F.G.; Adler, F.R.; Anderson, B.J.; Anttila, J.; Araújo, M.B.; Dallas, T.; Dunson, D.; Elith, J.; et al. A comprehensive evaluation of predictive performance of 33 species distribution models at species and community levels. Ecol. Monogr. 2019, 89. [CrossRef]
- Hijmans, R.J., et al., Very high resolution interpolated climate surfaces for global land areas. International Journal of Climatology: A Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 2005. 25(15): p. 1965-1978.
- Wu, T.; Lu, Y.; Fang, Y.; Xin, X.; Li, L.; Li, W.; Jie, W.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; et al. The Beijing Climate Center Climate System Model (BCC-CSM): the main progress from CMIP5 to CMIP6. Geosci. Model Dev. 2019, 12, 1573–1600. [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, B.C.; Kriegler, E.; Riahi, K.; Ebi, K.L.; Hallegatte, S.; Carter, T.R.; Mathur, R.; van Vuuren, D.P. A new scenario framework for climate change research: the concept of shared socioeconomic pathways. Clim. Chang. 2014, 122, 387–400. [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Liu, Y. Unveiling the Conservation Biogeography of a Data-Deficient Endangered Bird Species under Climate Change. PLOS ONE 2014, 9, e84529. [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Fan, G.; He, Y. Predicting the current and future distribution of three Coptis herbs in China under climate change conditions, using the MaxEnt model and chemical analysis. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 698, 134141. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, P.; Zou, H.; Ji, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Z. Adaptive Distribution and Vulnerability Assessment of Endangered Maple Species on the Tibetan Plateau. Forests 2024, 15, 491. [CrossRef]
- Wilfried, T., Biodiversity: Climate change and the ecologist. Nature, 2007. 448(7153).
- Barker, D.H.; Vanier, C.; Naumburg, E.; Charlet, T.N.; Nielsen, K.M.; Newingham, B.A.; Smith, S.D. Enhanced monsoon precipitation and nitrogen deposition affect leaf traits and photosynthesis differently in spring and summer in the desert shrub Larrea tridentata. New Phytol. 2006, 169, 799–808. [CrossRef]
- Walther, G.R., et al., Trends in the upward shift of alpine plants. Journal of Vegetation Science, 2005. 16(5): p. 541-548.
- Zhai Z Y, et al.. Effects of microtopography on germination layer soil factors in Armeniaca vulgaris Lam. in Daxigou.Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(6):.
- Zu, K.; Wang, Z. Research progress on the elevational distribution of mountain species in response to climate change. Biodivers. Sci. 2022, 30, 21451. [CrossRef]
- CAI Zucong. The Role of Soil in the Formation of Plant Biodiversity and Its Research Significance[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica,2022,59(1):1-9.
- Sullivan, P.F. Evidence of soil nutrient availability as the proximate constraint on growth of treeline trees in northwest Alaska: reply. Ecology 2016, 97, 803–808. [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Chang, R. Temperature drive the altitudinal change in soil carbon and nitrogen of montane forests: Implication for global warming. CATENA 2019, 182, 104126. [CrossRef]
- TIAN Zhongping, et al.,Relationship Between Community Structure of Wild Fruit Forests and Their Environment on North-facing Slopes of the Iri Valley[J].Chinese Journal of Applied & Environmental Biology,2011,17(01):39-45.
- Wei, L.; Wang, G.; Xie, C.; Gao, Z.; Huang, Q.; Jim, C.Y. Predicting suitable habitat for the endangered tree Ormosia microphylla in China. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1–11. [CrossRef]
- Gao, X., et al., The impact of climate change on the distribution of rare and endangered tree Firmiana.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).