1. Introduction
Hepatitis, also known as inflammation of liver, is one of the major health concerns worldwide due to higher rate of morbidity and mortality [
1,
2]. Hepatitis is caused by various factors, such as alcohol consumption, certain medications, autoimmune and genetic disorders, but the five hepatotropic viruses (A to E) are the most common causes [
3]. Among these, hepatitis B virus (HBV) is the most significant and common form of viral infections in humans [
4,
5]. The transmission of HBV infection is 50-100 times faster than human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and it is almost 10 times more communicable than HCV. The abnormalities associated with HBV infection include chronic liver abnormalities, cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma and liver failure [
6].
The chronic HBV infected individuals are almost 300 million worldwide [
7]. Globally, each year, around 1.5 million people suffer from HBV infection [
8]. Among patients of cirrhosis, the HBV infection is more common in Africa and Asia (8–61%) than in Europe, the Americas, and Oceania (UN sub regional prevalence ranges 3–14%) [
9].
The current study is based on age and gender wise prevalence of HBV including their genotypes, and associated risk factors in general population of North Waziristan. The HBV infections were identified by serological means such as ICT and ELISA. However, due to a number of issues with serological testing, such as window time and re-infection with HBV in HBsAg and ELISA based negative individuals, RT-PCR based investigation was also performed. Furthermore, RT-PCR was employed to identify various genotypes of HBV in the study population. Overall, the current study is crucial for planning surveillance, resource allocation, and control programs for prevention of HBV infection.
2. Material and Method
2.1. Study Area
North Waziristan, formally known as EX-FATA (Federal Administrated Tribal Area), is a remote rural district of the Division Bannu, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province, Pakistan. Our study is based on all the three sub divisions including Mir Ali, Miran Shah and Razmak. It is located at altitudes between 32.35° and 33.22° North and at latitudes between 69.22° and 70.38° East, having a total area of 4,707 square KM. The total population of NWTD consists of 543,254 inhabitants and almost 116 people live on one square kilometer in 2023. The average temperature is 19–30 ◦C.
2.2. Study Design and Data Collection
The study was divided into two phases; questionnaire and blood sampling. The questionnaire, filled by each participant, contained information about name, age, gender, level of education, marital status, history of transfusion blood or plasma, surgical and dental procedures, frequent visits to barber shops, history of being pricked by a needle, piercing or tattooing, history of intravenous drug abuse, and living with HBV positive family member.
2.3. Sample Collection
Blood samples were collected on the basis of signs and symptoms from 943 HBV suspected individuals. From each individual, 5 ml of blood was drawn and stored in a gel tube. The sera was separated through centrifugation (at 1100–1300 rpm for 15 minutes), and the separated sera was kept at 20 °C in three aliquots for use in subsequent serological and molecular research.
2.4. Serological Investigation
The initial screening of Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) was done through rapid immunochromatography (ICT) kit (HEALGEN USA) and further verified by ELISA (Enzyme Linked immunosorbent Assay) kit (AUTOBIO) according to the manufacturer protocol.
2.5. DNA Extraction, RT-PCR, and Genotyping
Nucleic acid (DNA) was extracted from all blood samples using a kit (Easy Pure Genomic, China) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. PCR was performed to detect HBV using the following temperature profile: initial activation for duration of 5 minutes at 95°C, which was followed by 40 cycles till 30 seconds each at 94°C, 56°C, and 72°C, and lastly this condition was run for 10 minutes at 72°C. With various reverse primers, semi-nested PCR amplifications were carried out in a manner similar to the first stage. The RT-PCR HBV genotyping was carried out using the same methods, which mark the S-gene of DNA-positive on HBV samples, using forward & reverse primers. Each reaction was conducted again with both positive and negative sample controls available. The projected RT-PCR products was determined by analyzing the migration pattern of 100-bp DNA strands on a 2% agarose gel in order to recognize the RT-PCR end products.
2.6. Data Analysis
All the data was analyzed by SPSS (version 22). The p-value less than 0.05 were considered as significant.
3. Results
3.1. Overall Prevalence of HBV
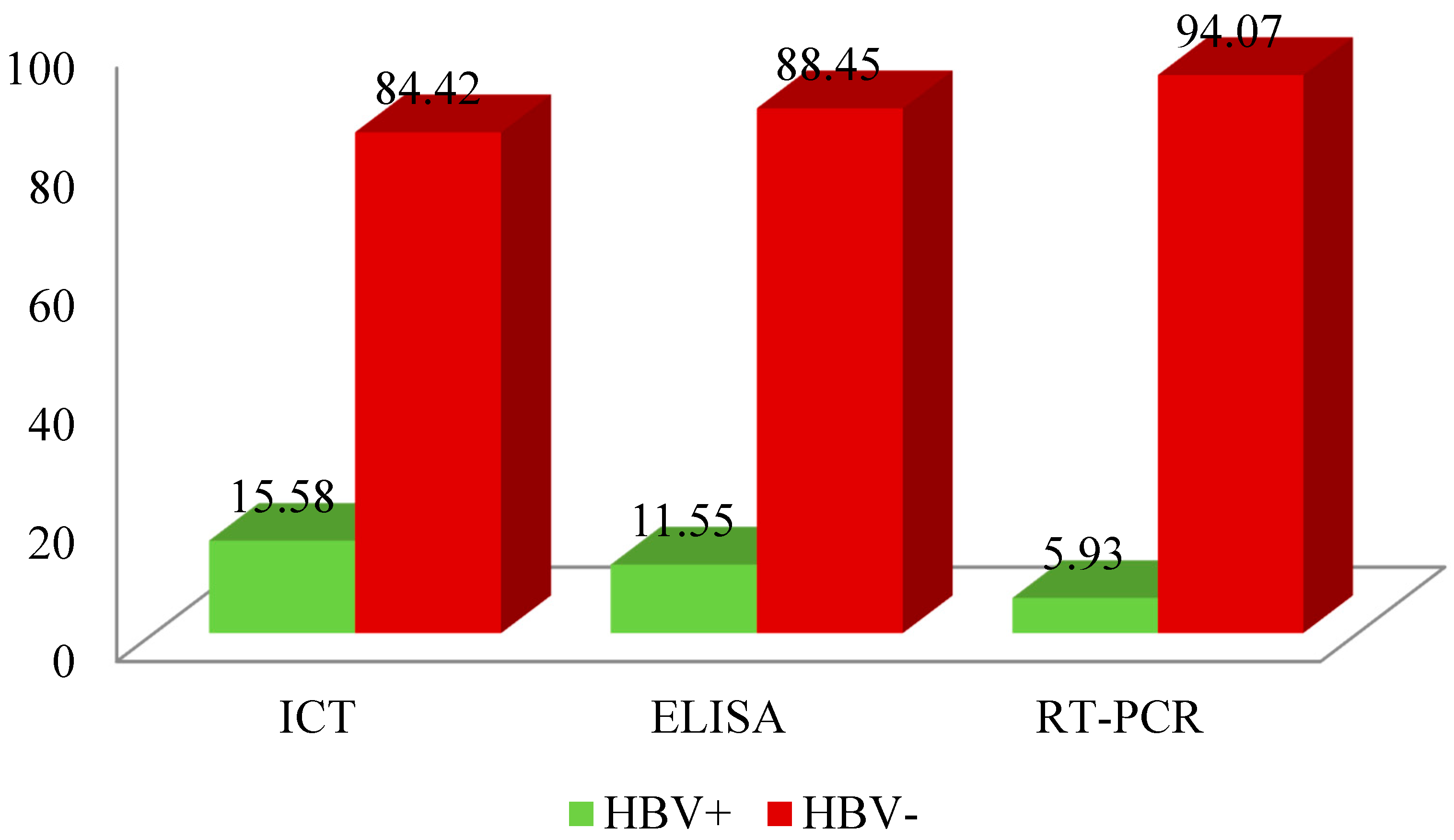
In total, 943 HBV suspected individuals were initially screened serologically through ICT and ELISA, and then verified by RT-PCR. Among the total HBV suspected individuals, 147 (15.58%) were positive on ICT. However, among the ICT positive samples, 109 (11.55% of the total) were positive on the ELISA based screening. Similarly, the RT-PCR based verification of the ELISA based positive sample indicated 54 (5.72% of the total) positive samples. As it observed that RT-PCR based data is more reliable (Anwar
et al., 2021) so according to our results the overall prevalence of HBV is 5.72% in the NWTD.( (
Table 3.1,
Figure 3.1).
3.2. Gender Wise Prevalence
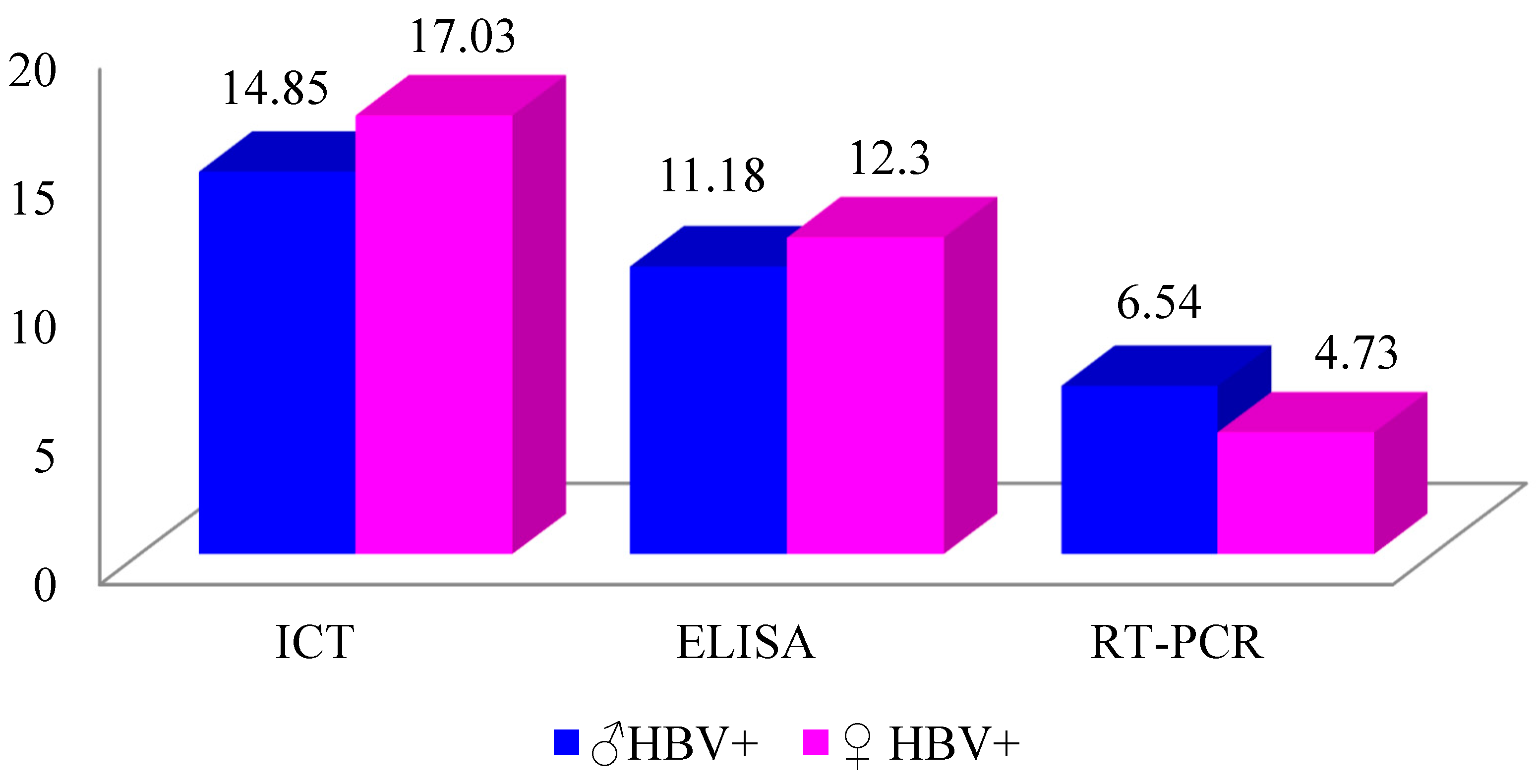
Gender-based analysis, comprising of both males and females, was conducted. The HBV testing participants’ pool comprised a total of 943 Individuals. The total numbers of ICT tested male and female participants were 626 and 317, respectively. Among these 93 (18.9%) males and 54 (17.3%) females were tested positive. According to the ELISA based screening, among the ICT based positive male and female, 70 (11.2% of total male) and 39 (12.3 % of total female) were tested positive, respectively. And according to the RT-PCR based screening, among the ELISA based positive male and female, 41 (6.5 %) and 15 (4.7 %) were tested positive, respectively. In this regard, according to our results HBV is more prevalent in male than female in the NWTD (
Table 3.2,
Figure 3.2).
3.3. Prevalence of HBV in Different Age Groups Conformed Serologically
The age range of this study was 1-75 years. The study population was sub divided into five age groups consisting of group (I) 1-15 years, group (II) 16-30 years, group (III) 31-45 years, group (IV) 46-60 years and group (V) 61-75 years. In the first age group, out of a total of 73 participant, 6 individuals tested positive (infection rate of 8.2%) on ICT, and 2 individuals were positive (infection rate of 2.7%) on ELISA. In the second age group, among a total of 305 participant, the ICT and ELISA based diagnosis revealed 60 (infection rate of 19.7%), and 52 (infection rate of 17%) infected individuals, respectively. In the third age group, among 340 participants, 65 were positive on ICT and 42 on ELISA with an infection rate of 19.1% and 12.4 %, respectively. Among the total 156 participants of the fourth age group, 10 were positive on ICT with an infection rate of 6.4% whereas 8 were positive on ELISA with an infection rate of 5.1%. In the final fifth age group, 6 individuals were positive on ICT among a total of 69 participants with a positivity rate of 8.7%. On the other hand, 5 individuals were positive on ELISA with a positivity rate of 7.2%. According to this analysis, the II and III age groups showed higher rate of prevalence in respect of the other groups. The prevalence rate was found significant (P<0.05) (Table 3.3, Figure 3.3). 3.4. Prevalence of HBV in Different Age Groups Tested through RT-PCR.
Among the 109 ELISA based positive samples, 56 were tested positive on RT-PCR examination. Real Time PCR results showed different viral loads in different age groups. The viral loads were categorized as mild (2000 IU/mL), moderate (2001 to 10000 IU/mL), elevated (10001 to 80000 IU/mL) and aggressive (80000 through highest IU/mL).
In the first age group, only one patient was detected with mild viral load.
The second age group revealed 3 patients with mild, 9 with moderate and 13 with elevated viral loads.
In the third age group, 2 patients were having mild, 2 moderate, 9 elevated and 11 aggressive viral loads. The fourth age group showed 1 patient with mild, 1 patient with moderate and 2 patients with elevated viral loads. In the fifth age group, 1 patient with elevated and 1 with aggressive viral loads were detected. In total, 7 patients with mild, 12 with moderate, 25 with elevated and 12 with aggressive viral loads in all age groups.
According to these analysis, aggressive viral loads were present in the individuals the age group III and V having 11 case and 1, respectively. In over all, the numbers of patients having mild, moderate and elevated viral loads were higher in the age group II and III. The data is statically significant (P<0.05) (Figure 3.4).
3.5. Prevalence of HBV Enotypes
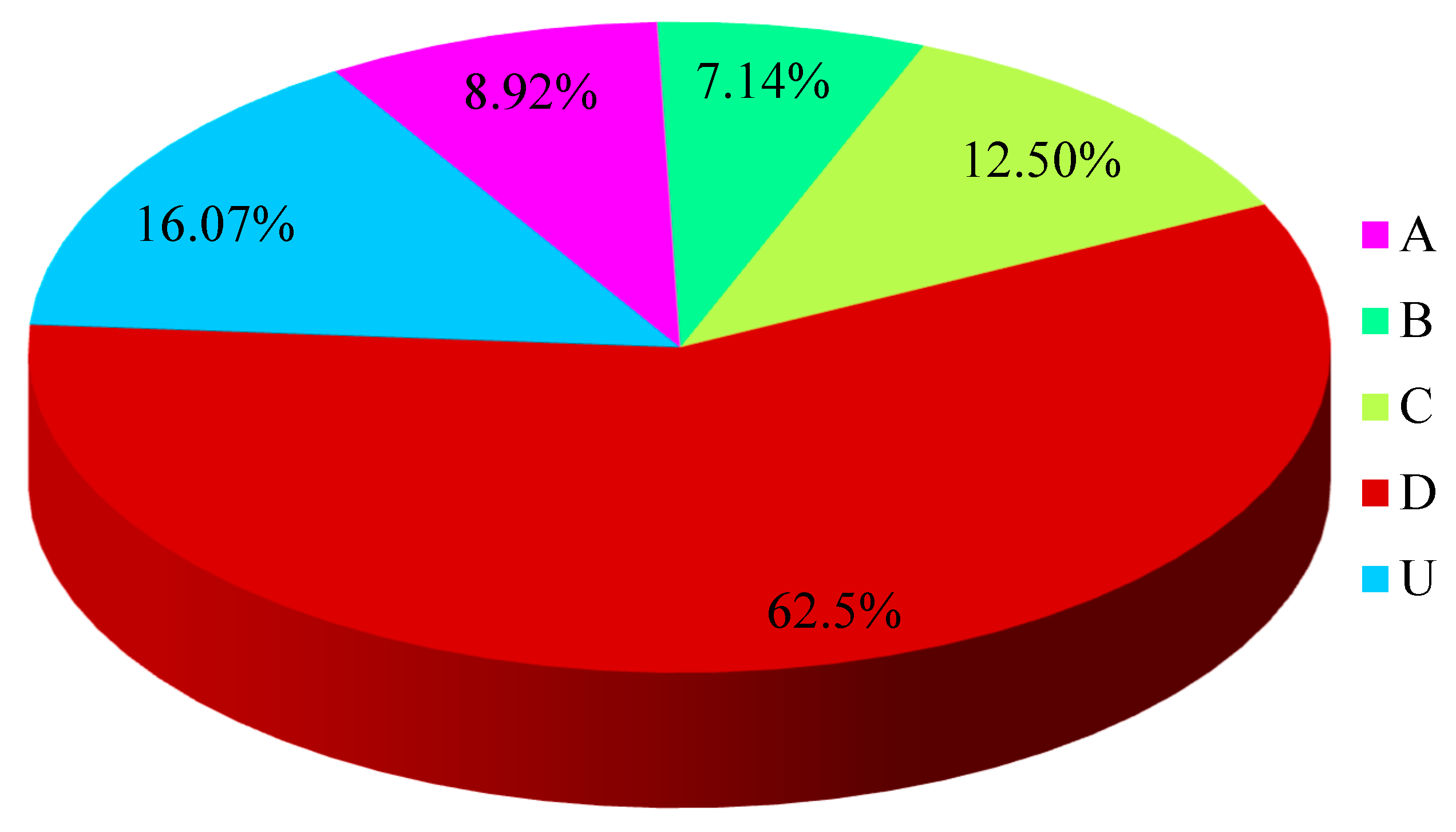
The total RT-PCR positive samples were further subjected to HBV genotype analysis. The genotypes based analysis revealed various genotypes of HBV in different age groups of the study population. The most prevalent genotype, found in 62.5% individuals, was D. There were 16.07% people with genotype U, 12.5% with genotype C, 8.92% with genotype A, and 7.14% with genotype B (
Figure 3.5).
3.6. Risk Factors Based Analysis
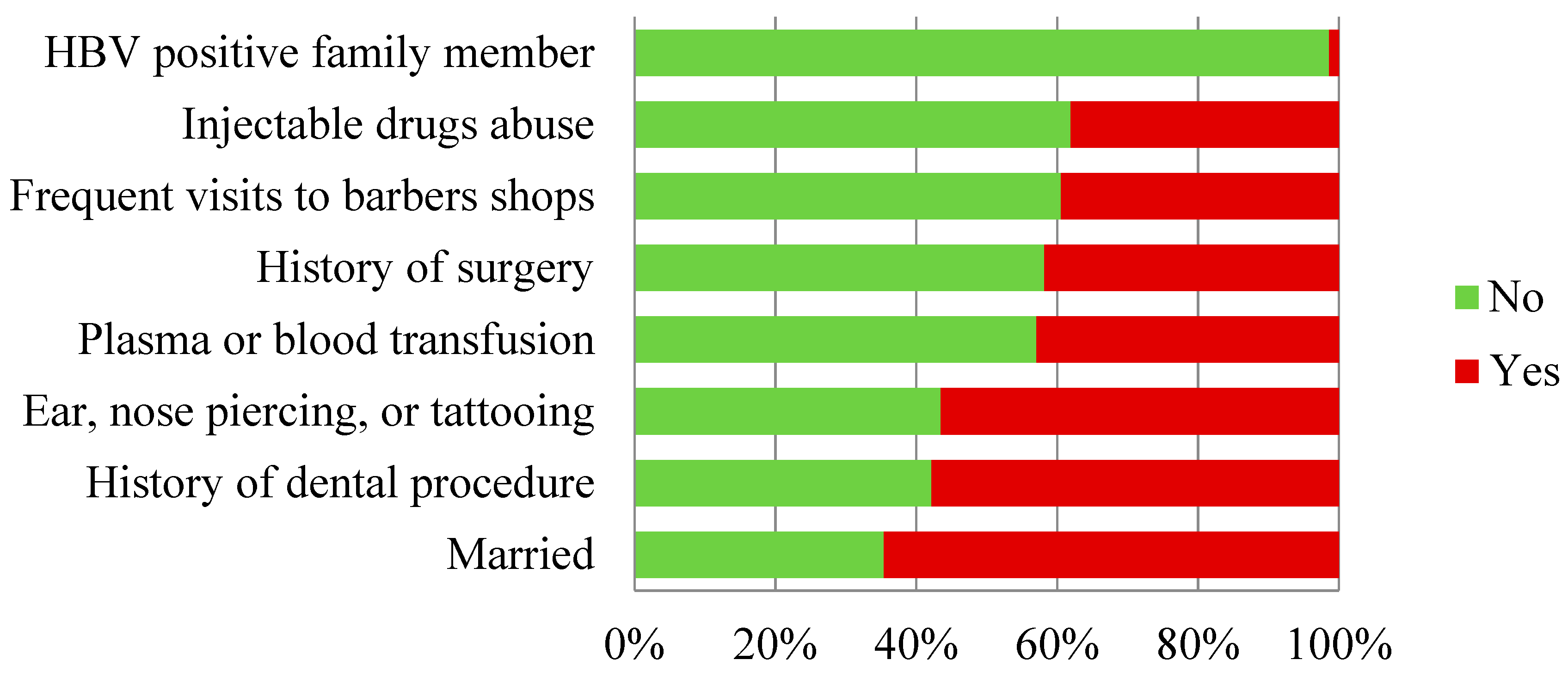
The different factors that contribute to HBV prevalence in population are known as risk factors for HBV infection. A predesigned questionnaire method was adopted to study various risk factors associated with transmission of HBV infection. Among the various risk factors, certain factors stood out as being strongly linked to HBV infection. The possible risk factors related to HBV transmission include a marital status (married life), history of dental procedures, ear or nose piercing or tattooing and uses of un-disposable syringes, history of blood or plasma transfusions, surgery and frequent visits to barber shops, and addiction of injectable drugs. The questionnaire based data was statistically significant for the risk factors associated with HBV infection (p<0.05). The highest prevalence of HBsAg was observed among married individuals (64.6%), whereas the lowest was among individuals with a history of HBV positive family member (1.4 %). The other risk factors contributed were history of dental procedures (57.8%), ear, nose, piercing, or tattooing and uses of un-disposable syringes (56.5%), transfusion of blood or plasma (42.9%), surgery (41.8%), frequent visits to barber shops (39.45%), and addiction of injectable drugs (38.1%) (Tablet 3.4, Fig 3.6).
Table 3.5.
ICT Based Risk Factor of HBV.
Table 3.5.
ICT Based Risk Factor of HBV.
| ICT Based Risk Factor |
Total |
No |
Yes |
% Age |
P Value |
| Family member with Positive |
147 |
145 |
2 |
1.4 |
.0001 |
| History of dental procedure |
147 |
62 |
85 |
57.8 |
| History of surgery |
147 |
86 |
61 |
41.8 |
| History of transfusion plasma or blood |
147 |
84 |
63 |
42.9 |
| History of ear, nose, piercing, or tattooing, syringe |
147 |
64 |
83 |
56.5 |
| Married |
147 |
52 |
95 |
64.6 |
| History of Barbers Shop |
147 |
89 |
58 |
39.45 |
| History of Injection Drugs use |
147 |
91 |
56 |
38.1 |
Figure 3.6.
Risk Factor based analysis.
Figure 3.6.
Risk Factor based analysis.
4. Discussion:
Hepatitis is one of the major health concerns worldwide [
10]. The prevalence rate of HBV depends upon the socio-economic status, health education, horizontal mobility, and history of visiting health care center, or any other blood, plasma or body liquid related transfusion history [
11].
Our study is aimed to investigate the prevalence of HBV and its genotypes, baseline epidemiology, and the associated risk factors in the general population of the district North Waziristan, Pakistan. Based on signs and symptoms, we selected 943 individuals for HBV screening. These individuals were screened for HbsAg by ICT technique which was further verified by ELISA and PCR. In addition, PCR based screening was employed to identify various kind of genotypes in study population. As the PCR based result are more reliable than ICT and ELISA [
12] so we can conclude that the prevalence of HBV is more males than female in the district North Waziristan. This data is consistent with the results obtained by [
13]. The possible explanation of higher incidence of the HBV in males than females may be the fact that males are more susceptible to the risk factors because males are socially more active in the rural areas of Pakistan.
In the next step, the HBV patients were categorized on the basis their age. The highest prevalence was observed in age group (16-30 years), and age group (31-45 years) which coincide with the work of many researchers in different regions of the country [
13,
14]. On the other hand, it was least prevalent in age group (1-15 years), is consistent with [
15], and age group (61-75years). Many other researchers also found that hepatitis B infection is least frequent in age group above 60 years [
13]. The possible explanation of greater incidence in age group (16-30 years), and age group (31-45 years) may be due to reason that they are more prone to the risk factors.
The questionnaire based study of the risk factors involved in the transmission of HBV infection indicated that the highest prevalence of HBsAg was among married individuals (64.6%) indicating the involvement of sexual intercourse a major contributing factor in the transmission of HBV [
14,
15,
16] , whereas the lowest was among individuals with a history of HBV positive family member (1.4 %). The other risk factors included history of dental procedure 57.8%, history of surgery 41.8%, history of transfusion or plasma 42.9%, history ear, nose, piercing, tattooing or syringe 56.5 % history of frequent visiting a barber shop 39.5 %, history of injection drugs use 38.1% Which follow the similar sort of pattern as previously discussed by [
14,
15,
16,
17,
18].
The information regarding genotype is of primarily necessary for both clinical and epidemiological aspects. The type of infecting genotype tells us about the infection pattern and how it deals with the interferon treatment. In this study, the highest prevalent DNA of HBV was genotype D and the same genotype was reported more prevalent among peoples of DNW by previous researchers [
17,
18,
19]. The possible reason of higher prevalence of genotype D may be due to the fact that it is more common throughout the country [
20]. After genotype D, the second most prevalent is genotype untypable U, then genotype C followed by A and B genotypes which is consistent with the results obtained by [
19,
20,
21]. Our study sheds light on the alarming situation of HBV infection in the region, particularly among young people, and highlights the need for more effective strategies and policies.
5. Conclusion
Our study is focus on the prevalence, risk factors, and genotypes of hepatitis B (HBV) in North Waziristan, Pakistan. The HBV is more prevalent in males than females, with the highest rates observed in the 16-30 and 31-45 age groups. Risk factors for HBV transmission included marital status, dental procedures, surgery, and injection drug use. HBV genotype D was the most prevalent and other genotypes found include A, B, C and U. These findings are important for understanding and addressing these diseases in the region.
References
- Mieli-Vergani, G., Vergani, D., Czaja, A. J., Manns, M. P., Krawitt, E. L., Vierling, J. M., . . . Montano-Loza, A. J. (2018). Autoimmune hepatitis. Nature Reviews Disease Primers, 4(1), 1-21.
- Raviglione, M. C., Snider, D. E., & Kochi, A. (1995). Global epidemiology of tuberculosis: morbidity and mortality of a worldwide epidemic. Jama, 273(3), 220-226.
- Torre, P., Aglitti, A., Masarone, M., & Persico, M. (2021). Viral hepatitis: Milestones, unresolved issues, and future goals. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 27(28), 4603.
- Eke, A. C., Eke, U. A., Okafor, C. I., Ezebialu, I. U., & Ogbuagu, C. (2011). Prevalence, correlates and pattern of hepatitis B surface antigen in a low resource setting. Virology journal, 8(1), 1-8. [CrossRef]
- El-Serag, H. B. (2012). Epidemiology of viral hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology, 142(6), 1264-1273. e1261. [CrossRef]
- Nazeer, A., Ali, S., & Tipu, I. (2019). Age-wise and Gender-wise Prevalence of Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Infection in Lahore, Pakistan. BioScientific Review, 1(4), 20-28. [CrossRef]
- Jindal, A., & Sarin, S. K. (2023). Hepatitis B:“Treat all” or “Treat select”. Hepatology International, 17(1), 38-41.
- Hsu, Y.-C., Huang, D. Q., & Nguyen, M. H. (2023). Global burden of hepatitis B virus: current status, missed opportunities and a call for action. Nature reviews Gastroenterology & hepatology, 1-14. [CrossRef]
- Alberts, C. J., Clifford, G. M., Georges, D., Negro, F., Lesi, O. A., Hutin, Y. J., & de Martel, C. (2022). Worldwide prevalence of hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus among patients with cirrhosis at country, region, and global levels: a systematic review. The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology. [CrossRef]
- Schweitzer, A., Horn, J., Mikolajczyk, R. T., Krause, G., & Ott, J. J. (2015). Estimations of worldwide prevalence of chronic hepatitis B virus infection: a systematic review of data published between 1965 and 2013. The Lancet, 386(10003), 1546-1555. [CrossRef]
- Hwang, E. W., & Cheung, R. (2011). Global epidemiology of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. North American Journal of Medicine and Science, 4(1). [CrossRef]
- Anwar, F., Khan, M., Salman, M., Ahmad, S., Ullah, F., Khan, J., . . . Abbas, M. (2021). Seroprevalence of hepatitis B virus in human population of district Buner Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Pakistan. Clinical Epidemiology and Global Health, 10, 100688. [CrossRef]
- Shah, M. I., & Awan, Z. U. R. (2020). 30. Sero prevalence of Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) in general population of Lakki Marwat, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa-Pakistan. Pure and Applied Biology (PAB), 9(4), 2511-2520.
- Akoth, A. J. (2021). Prevalence and factors associated with hepatitis B and human immunodeficiency virus co-infection among blood donors in Kenyan Coastal Region. JKUAT-COHES.
- Butt, T., & Amin, M. (2008). Seroprevalence of hepatitis B and C infections among young adult males in Pakistan. EMHJ-Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal, 14 (4), 791-797, 2008.
- Zali, M. R. (1996). Epidemiology of hepatitis B in the Islamic Republic of Iran. EMHJ-Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal, 2 (2), 290-298, 1996. [CrossRef]
- Ali, A., Nisar, M., Idrees, M., Ahmad, H., Hussain, A., Rafique, S., . . . Wazir, S. (2012). Prevalence of HBV infection in suspected population of conflict-affected area of war against terrorism in North Waziristan FATA Pakistan. Infection, Genetics and Evolution, 12(8), 1865-1869. [CrossRef]
- Hauri, A. M., Armstrong, G. L., & Hutin, Y. J. (2004). The global burden of disease attributable to contaminated injections given in health care settings. International journal of STD & AIDS, 15(1), 7-16. [CrossRef]
- Khan, A., & Qazi, J. (2018). Risk factors and molecular epidemiology of HBV and HCV in internally displaced persons (IDPs) of North Waziristan Agency, Pakistan. JPMA J Pak Med Assoc, 68(2), 165-169.
- Ozaras, R., Balkan, I. I., Yemisen, M., & Tabak, F. (2015). Epidemiology of HBV subgenotypes D. Clinics and Research in Hepatology and Gastroenterology, 39(1), 28-37.
- Saleha, S., Kamal, A., Ullah, F., Khan, N., Mahmood, A., & Khan, S. (2014). Prevalence of hepatitis C virus genotypes in district Bannu, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. Hepatitis Research and Treatment, 2014. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).