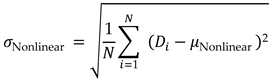2. Methodology
2.1. Data Generation and Parameters
In this study, we generated a synthetic EEG dataset to evaluate the effectiveness of EEG-based parameters for diagnosing bipolar disorder. The dataset included both correctly diagnosed and misdiagnosed cases to simulate realistic clinical conditions. The following EEG parameters were used, as they are the most common and widely recognized in the literature:
Theta-Alpha Mean and Standard Deviation: Captures the average and variability in the voltage of theta and alpha waves.
Frontal Alpha Asymmetry Mean and Standard Deviation: Measures the differences in alpha wave activity between the left and right frontal lobes.
Beta Band Mean and Standard Deviation: Represents the average and variability in beta wave activity.
Event-Related Potentials (ERP) Mean and Standard Deviation: Measures the voltage changes in response to specific stimuli.
Coherence Mean and Standard Deviation: Assesses the synchronization between different brain regions.
Microstates Mean and Standard Deviation: Captures the temporal dynamics of brief, stable states of brain activity.
Nonlinear Dynamics Mean and Standard Deviation: Represents the complexity and variability in brain activity patterns.
These parameters were selected due to their widespread use in EEG research and their relevance in identifying neuropsychiatric conditions. The dataset was generated using a standard EEG configuration with 19 channels, based on the 10-20 system, which is commonly used in clinical practice.
Number of EEGs and Mixing
For this study, we generated a total of 200 synthetic EEG recordings, comprising both non-bipolar and bipolar cases to simulate realistic clinical conditions. The dataset was divided as follows:
Correctly Diagnosed: 90 EEGs generated with parameters typical for non-bipolar individuals.
Misdiagnosed as Bipolar: 10 EEGs generated with parameters typical for bipolar individuals but labeled (at a virtual anamnesis) as non-bipolar to simulate false positives.
- 2.
Bipolar Cases:
Correctly Diagnosed: 90 EEGs generated with parameters typical for bipolar individuals.
Misdiagnosed as Non-Bipolar: 10 EEGs generated with parameters typical for non-bipolar individuals but labeled as bipolar to simulate false negatives.
Data Preparation and Model Training
Dataframe Creation:
Combined the non-bipolar and bipolar EEG recordings into a single dataframe.
Assigned labels: 0 for non-bipolar and 1 for bipolar.
Data Splitting:
Split the combined dataset into training (80%) and testing (20%) sets using stratified sampling to maintain the class distribution.
Standardization:
Standardized the features using StandardScaler to ensure each feature had a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1.
Model Architecture:
Constructed a multi-layer perceptron (MLP) model with the following architecture:
Input layer with 128 neurons and ReLU activation.
Hidden layers with 64, 32, 16, 8, and 4 neurons, each using ReLU activation.
Output layer with a single neuron and sigmoid activation for binary classification.
Model Compilation and Training:
Compile the model using the Adam optimizer, binary cross-entropy loss, and accuracy as the metric.
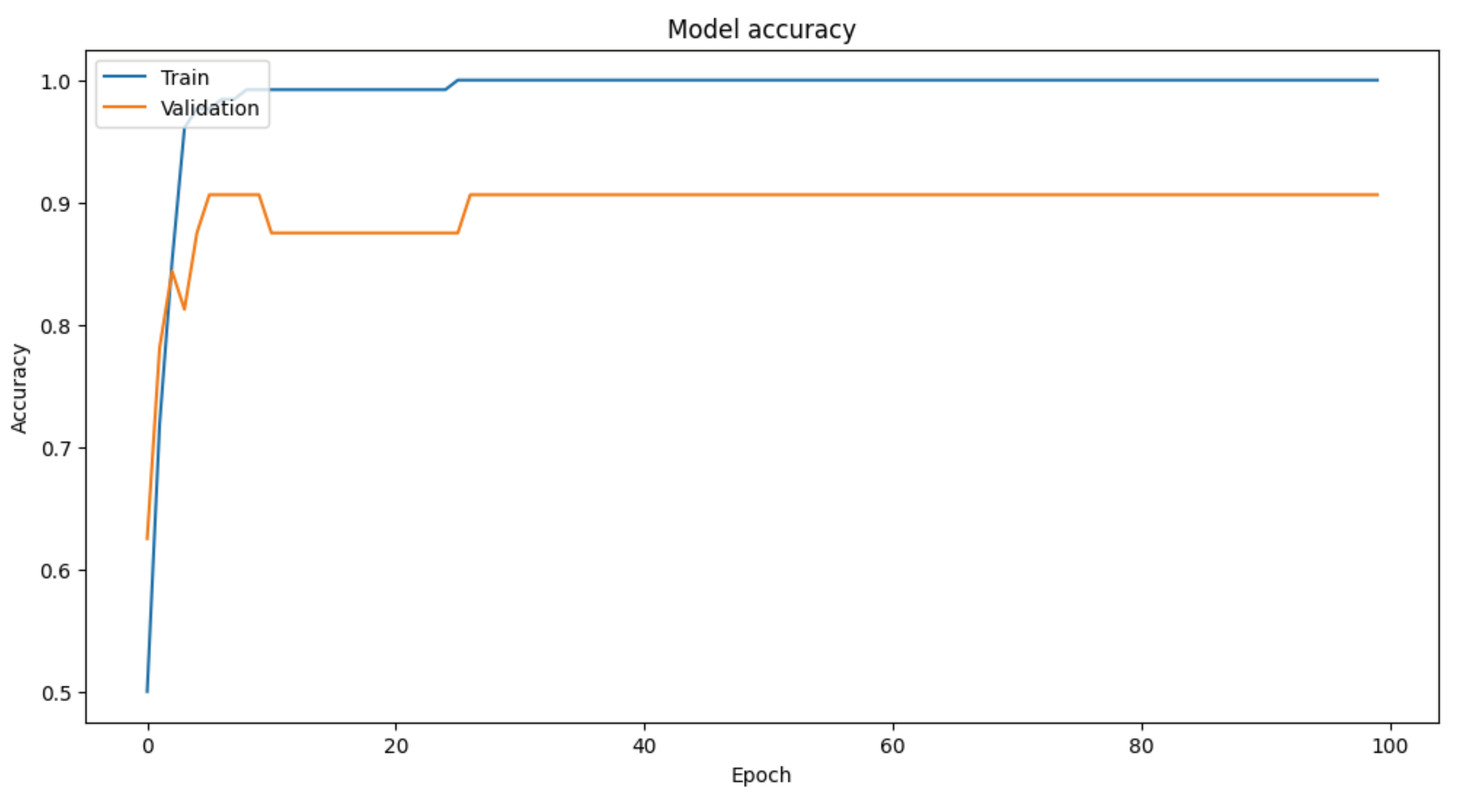
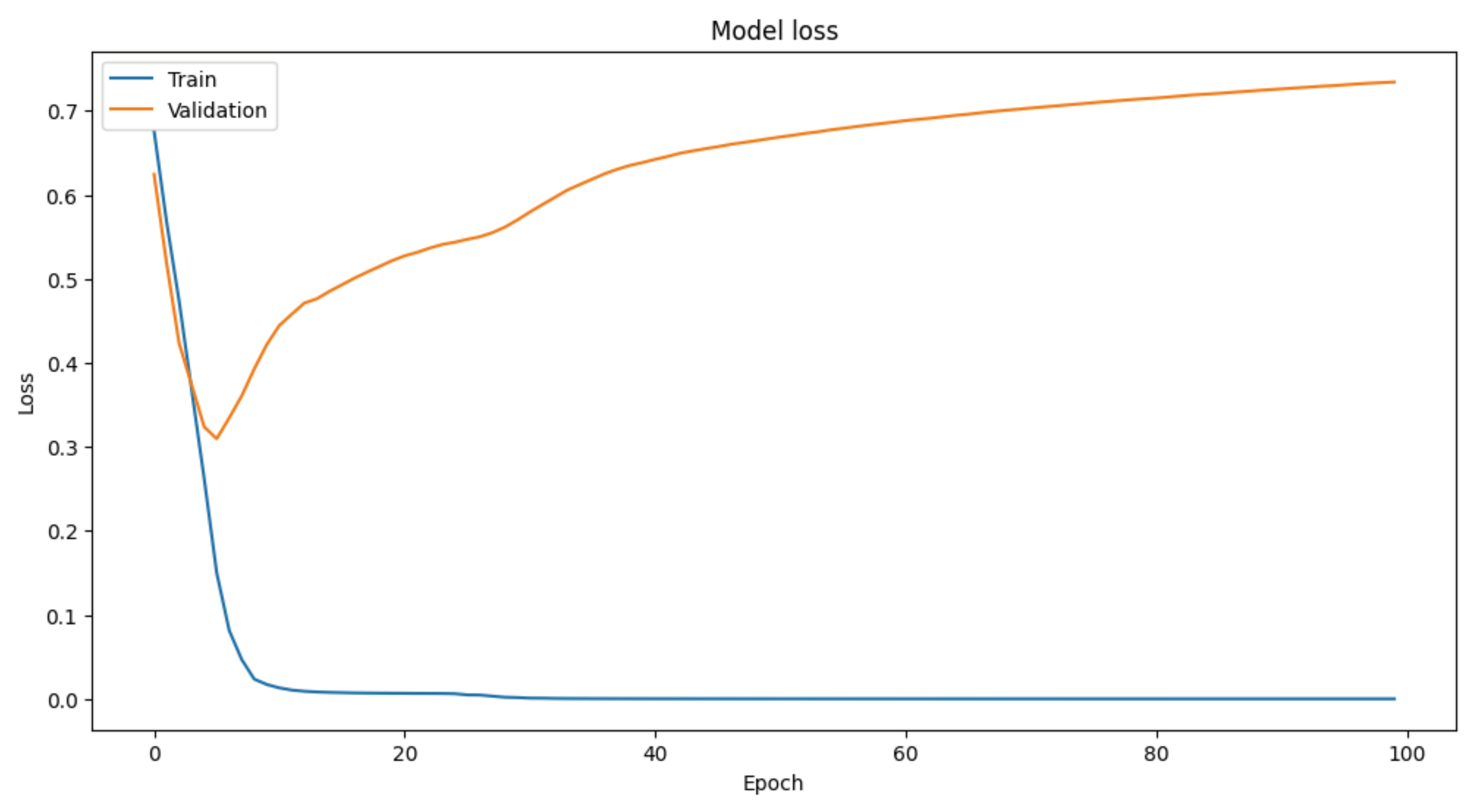
Trained the model for 100 epochs with a batch size of 16 and a validation split of 20%.
2.2. Model Evaluation
Evaluated the model's performance on the test set, achieving a test accuracy of 92%.
This methodology demonstrates the feasibility of using synthetic EEG data to train machine learning models for diagnosing bipolar disorder. The selected EEG parameters, combined with robust data preparation and model training techniques, yielded high diagnostic accuracy, underscoring the potential of EEG-based diagnostics in neuropsychiatry. Of course, and a sine qua non condition, further research with real-world data and diverse clinical settings is needed to validate these findings and enhance their applicability.
2.3. Mathematical Formulas
The mathematical representation of each parameter is as follows:
- 2.
Theta-Alpha Standard Deviation:
- 3.
Frontal Alpha Asymmetry Mean:
- 4.
Frontal Alpha Asymmetry Standard Deviation:
- 6.
Beta Band Standard Deviation:
- 8.
ERP Standard Deviation:
- 10.
Coherence Standard Deviation:
- 12.
Microstates Standard Deviation:
- 13.
Nonlinear Dynamics Mean:
- 14.
Nonlinear Dynamics Standard Deviation:
These parameters and formulas provide a comprehensive representation of EEG signals, enabling the analysis and diagnosis of bipolar disorder using machine learning models.
7. Attachment
Python Code
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import Adam
from tensorflow.keras.losses import BinaryCrossentropy
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Set random seed for reproducibility
np.random.seed(42)
# Create a fictitious dataset
data_size = 200
channels = 19 # Number of EEG channels
# Generating random EEG voltage parameters for multiple channels
def generate_eeg_data(size, channels, bipolar=False):
base_mean = 50 if not bipolar else 60 # Adjust mean for bipolar
base_std = 10 if not bipolar else 15 # Adjust standard deviation for bipolar
return {
f'Channel_{i}_Theta_Alpha_Mean': np.random.normal(loc=base_mean, scale=base_std, size=size) for i in range(channels)
} | {
f'Channel_{i}_Theta_Alpha_Std': np.random.normal(loc=5, scale=1 if not bipolar else 2, size=size) for i in range(channels)
} | {
f'Channel_{i}_Frontal_Alpha_Asymmetry_Mean': np.random.normal(loc=40 if not bipolar else 50, scale=10, size=size) for i in range(channels)
} | {
f'Channel_{i}_Frontal_Alpha_Asymmetry_Std': np.random.normal(loc=4, scale=1 if not bipolar else 2, size=size) for i in range(channels)
} | {
f'Channel_{i}_Beta_Band_Mean': np.random.normal(loc=30 if not bipolar else 40, scale=8, size=size) for i in range(channels)
} | {
f'Channel_{i}_Beta_Band_Std': np.random.normal(loc=3, scale=0.8 if not bipolar else 1.5, size=size) for i in range(channels)
} | {
f'Channel_{i}_ERP_Mean': np.random.normal(loc=60, scale=15, size=size) for i in range(channels)
} | {
f'Channel_{i}_ERP_Std': np.random.normal(loc=6, scale=1.5 if not bipolar else 2.5, size=size) for i in range(channels)
} | {
f'Channel_{i}_Coherence_Mean': np.random.normal(loc=55, scale=12 if not bipolar else 18, size=size) for i in range(channels)
} | {
f'Channel_{i}_Coherence_Std': np.random.normal(loc=5.5, scale=1.2 if not bipolar else 2.2, size=size) for i in range(channels)
} | {
f'Channel_{i}_Microstates_Mean': np.random.normal(loc=35 if not bipolar else 45, scale=7, size=size) for i in range(channels)
} | {
f'Channel_{i}_Microstates_Std': np.random.normal(loc=3.5, scale=0.7 if not bipolar else 1.2, size=size) for i in range(channels)
} | {
f'Channel_{i}_Nonlinear_Dynamics_Mean': np.random.normal(loc=45, scale=9, size=size) for i in range(channels)
} | {
f'Channel_{i}_Nonlinear_Dynamics_Std': np.random.normal(loc=4.5, scale=0.9 if not bipolar else 1.5, size=size) for i in range(channels)
}
# Generating data
eeg_data_non_bipolar = generate_eeg_data(90, channels, bipolar=False)
eeg_data_misdiagnosed_bipolar = generate_eeg_data(10, channels, bipolar=True) # 10% misdiagnosed as bipolar in non-bipolar group
eeg_data_bipolar = generate_eeg_data(90, channels, bipolar=True)
eeg_data_misdiagnosed_non_bipolar = generate_eeg_data(10, channels, bipolar=False) # 10% misdiagnosed as non-bipolar in bipolar group
# Creating DataFrame
df_non_bipolar = pd.DataFrame(eeg_data_non_bipolar)
df_non_bipolar['Label'] = 0 # Non-bipolar label
df_misdiagnosed_bipolar = pd.DataFrame(eeg_data_misdiagnosed_bipolar)
df_misdiagnosed_bipolar['Label'] = 0 # Misdiagnosed as non-bipolar
df_bipolar = pd.DataFrame(eeg_data_bipolar)
df_bipolar['Label'] = 1 # Bipolar label
df_misdiagnosed_non_bipolar = pd.DataFrame(eeg_data_misdiagnosed_non_bipolar)
df_misdiagnosed_non_bipolar['Label'] = 1 # Misdiagnosed as bipolar
# Combining both datasets
df = pd.concat([df_non_bipolar, df_misdiagnosed_bipolar, df_bipolar, df_misdiagnosed_non_bipolar], ignore_index=True)
# Check label distribution
print("Combined Dataset Label Distribution:")
print(df['Label'].value_counts())
# Splitting the data into features and labels
X = df.drop('Label', axis=1)
y = df['Label']
# Split the data into training and testing sets
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42, stratify=y)
# Standardize the features
scaler = StandardScaler()
X_train = scaler.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test = scaler.transform(X_test)
# Define the model
model = Sequential([
Dense(128, input_dim=X_train.shape(1), activation='relu'),
Dense(64, activation='relu'),
Dense(32, activation='relu'),
Dense(16, activation='relu'),
Dense(8, activation='relu'),
Dense(4, activation='relu'),
Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')
])
# Compile the model
model.compile(optimizer=Adam(learning_rate=0.001),
loss=BinaryCrossentropy(),
metrics=['accuracy'])
# Train the model
history = model.fit(X_train, y_train, epochs=100, batch_size=16, validation_split=0.2)
# Evaluate the model on the test set
loss, accuracy = model.evaluate(X_test, y_test)
print(f'Test Accuracy: {accuracy * 100:.2f}%')
# Plot training & validation accuracy values
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
plt.plot(history.history['accuracy'])
plt.plot(history.history['val_accuracy'])
plt.title('Model accuracy')
plt.ylabel('Accuracy')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.legend(['Train', 'Validation'], loc='upper left')
plt.show()
# Plot training & validation loss values
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
plt.plot(history.history['loss'])
plt.plot(history.history['val_loss'])
plt.title('Model loss')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.legend(['Train', 'Validation'], loc='upper left')
plt.show()