1. Introduction
1.1. Geometric Models of SAR Images
The Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) geometric model plays a foundational role in high-precision geolocation processes, encompassing geometric correction, stereo positioning, block adjustment, and three-dimensional reconstruction of SAR imagery [
1,
2,
3,
4]. Geometric models of SAR imagery are generally divided into two categories: rigorous and non-rigorous. Rigorous models rely on the mechanisms of SAR imaging, in which both the sensor’s motion state and imaging parameters are incorporated. Meanwhile, non-rigorous models usually ignore the SAR imaging mechanism and disregard the sensor’s geometric, physical, and imaging parameters, typically fitting the relationship between image and ground coordinates.
A variety of rigorous SAR models have been developed, such as the range-zero Doppler model created by F. Leberl, the three-dimensional model created by Touitin from the Canadian Remote Sensing Center, and the SAR collinear equation model created by You from the Chinese Academy of Sciences [
5,
6]. However, the most prevalent and effective model is the Range–Doppler (R-D) equations introduced by Curlander in 1982 [
7]. From a geometric perspective, the Doppler equation confines the target of observation within an imaging Doppler cone, with the sensor’s position serving as the vertex and the velocity vector as the axis. Meanwhile, the range equation bounds the target within a sphere centered on the sensor, with a radius equivalent to the SAR measurement distance. The intersection curve between the sphere corresponding to the range equation and the cone corresponding to the Doppler equation is a circle, representing the location range of the SAR observation target.
In the course of image correction, the R-D model either takes elevation as a known parameter or as integrated with the Earth’s ellipsoid model, which accounts for the elevation parameter [
8]. The R-D model subsequently calculates the object’s spatial coordinates (X, Y, and Z). In stereo positioning, two or multiple sets of R-D equations, derived from corresponding points in multi-view images, are used jointly to determine the object’s spatial coordinates [
9,
10]. At present, the R-D model is used as the basis for a majority of methods for the precise geometric processing of SAR images. Yuan et al. [
11] developed an airborne SAR target positioning algorithm which refines the R-D model parameters through the use of corresponding points from airborne SAR and reference images, thereby enhancing the positioning accuracy. Pu-Huai Chen [
10] presented a weighted spatial intersection algorithm that predicts algorithm accuracy based on prediction error analysis. Schubert et al. [
12] achieved high-precision geolocation of TerraSAR-X images using the R-D model without ground control points (GCPs) through the use of calibrated sensor parameters and correcting for atmospheric and tidal effects.
Using the R-D and digital elevation models, accurate ground positioning within 2 meters can be achieved for TH2 imagery [
13]. Considering the scale differences between the range and Doppler equations, researchers have normalized the R-D model and improved the positioning accuracy through a weighting strategy [
14]. The model’s efficiency has been validated through experiments conducted on the Gaofen-3 and TerraSAR-X satellite data sets. To address the complexity of traditional geometric models, Liu [
15] introduced a fast algorithm based on local linear approximation to simplify the associated computations. The R-D model is also beneficial in other image-processing tasks; for example, Wang [
9] employed the model to correct geometric distortions in SAR images, resulting in improved accuracy of SAR-SIFT matching.
Non-rigorous models are classified into True Replacement Models and Correspondence Models, as specified by the ISO 19130-1 standard [
16]. The general polynomial transformation is the prevalent Correspondence Model, which creates a functional link between ground and image coordinates, and is usually established by fitting numerous reference points. For the initial positioning of airborne SAR images, Zhang et al. [
17] used a primary affine transformation to approximate the translation between image and geographical coordinates, disregarding the impact of terrain elevation on positioning accuracy. In contrast, Huang et al. [
18] introduced elevation into a general polynomial model for SAR geolocation. The Rational Function Model (RFM)—now the dominant True Replacement model—was originally based on optical satellite imagery [
19] and has become the primary geometric processing model for optical satellite images [
20]. For SAR image positioning, the RFM model has 78 Rational Polynomial Coefficients (RPCs) to be fitted from the R-D model’s virtual positioning results [
21,
22]. Zhang [
22] analyzed factors affecting the RPC fitting accuracy with respect to the R-D model and assessed the impacts of virtual control point grid size, elevation layer number, orbit accuracy, and other aspects on RPC solutions. Their study highlighted the importance of elevation layers in regard to SAR RPC extraction accuracy and suggested that careful adjustment of the terrain conditions should be considered. Typically, the accuracy of RPC fitting with respect to the R-D model exceeds 1% of a pixel. For high-precision sensors such as TerraSAR-X, which have stable motion and excellent imaging capabilities, RPC fitting accuracies better than 10
−3 relative to the R-D model can be achieved [
23].
1.2. Refinement of Geometric Model Parameters
The geometric model describes the relationship between the object’s spatial coordinates and the SAR image coordinates. However, the achievement of high-precision positioning is contingent on calibrating the sensor parameters and refining the model parameters through the use of GCPs.
The positioning accuracy of the R-D model is affected by various factors, such as initial range errors, synchronization discrepancies between the SAR sensor and the Position and Orientation System (POS), sensor motion parameter errors, and errors in the transmission of electromagnetic waves. Several studies have conducted thorough analyses on the effects of parameter errors on the accuracy of SAR image positioning [
24]. Some of these affecting factors, such as initial slant range, slant range rate, and time synchronization, can be calibrated in a laboratory or testing field, while others, such as atmospheric delay and tidal correction, can be obtained through relevant rigorous models. The optimization of sensor system parameters is contingent on the availability of a high-precision calibration field, and the timeliness of calibration is pivotal to ensuring the accuracy of image positioning. However, some sensors may encounter challenges regarding the prompt calibration of parameters, potentially leading to suboptimal geolocation accuracy when only the initial parameters are used. To further enhance the positioning accuracy of SAR images, it is often necessary to employ high-precision reference points for comprehensive optimization of the sensor position, velocity, slant range, time synchronization, and Doppler parameters within the R-D model.
Although conventional methods for enhancing the accuracy of the R-D model are theoretically rigorous, they have several limitations with regard to the practical use of reference points for comprehensive optimization. These limitations include the difficulty of dealing with a large number of model parameters and the necessity of using additional models to express variations throughout an entire image. For example, in terms of additional models, positional and velocity corrections typically require six distinct sets of polynomial parameters [
25,
26]. Strong parameter correlations in the R-D model present challenges related to decorrelation when parameters are solved under conditions of sparse GCPs. These limitations restrict the application of the R-D model in certain scenarios. Analysis has indicated that high-precision positioning using the R-D model is largely dependent on the calibration of sensor parameters and refinement of the R-D model parameters using GCPs. The process of obtaining model parameters through calibration or refining them using GCPs is complex and requires a high level of expertise, significantly hindering advanced users from efficiently performing high-precision SAR image geolocation processing independently. Therefore, it is necessary to develop a simpler and more user-friendly technique for the geometric positioning of SAR images.
In contrast, the RFM can relatively easily achieve high-precision geolocation through introducing an error compensation model for the image space with the support of GCPs. The most common approach involves using a linear affine transformation model to correct image errors caused by various factors. Studies have suggested that, with the support of adequate GCPs, the positioning accuracy of RFMs enhanced with affine transformations is comparable to that of R-D models refined with model parameters [
21,
27,
28]. For instance, Eftekhari et al. [
23] demonstrated that RFMs with affine transformations can achieve sub-pixel accuracy. This methodology has been gradually applied to multi-scene imagery, as demonstrated in the studies conducted by Zhang et al. [
29] and Wang et al. [
30], who employed RFM-based block adjustment techniques to accomplish high-precision positioning for GF-3 and YG-5 multi-scene images.
SAR image positioning is significantly less influenced by sensor construction parameters than optical imagery. Moreover, the SAR imaging process includes motion compensation, which reduces the positioning errors caused by the stability of sensor motions and attitudes. Analyses and applications have demonstrated that, within a single image scene, the consistency of positioning errors is typically greater than that for optical imagery (especially for airborne SAR). Considering the inherent complexities and difficulties of implementation in the classical refinement of the R-D model with GCPs, we raise a question: is it possible to achieve high-precision positioning for the R-D model, in order to allow it to be combined with an image-based compensation function? This idea is similar to the approach used in the RFM. If feasible, it could greatly simplify the refinement process for the R-D model. In addition, the RFM is primarily designed for spaceborne images and has not been effectively applied to airborne images (until now). In contrast, the R-D model with image compensation may be easily extended to airborne SAR images.
To the best of our knowledge, there is still no relevant work on the abovementioned aspects. In this regard, we developed an image compensation-based R-D model for SAR high-precision positioning and conducted a variety of experiments on both spaceborne and airborne SAR images to validate its accuracy.
The outline of this paper is as follows. A short overview of SAR image geometric models and model refinement is provided in
Section 1; some limitations related to model refinement are also discussed in this section. In
Section 2, an image compensation-based R-D model for SAR high-precision positioning is proposed, and image compensation using polynomial functions is detailed. In the next section, we report on the comparative experiments we conducted, and the accuracy of the model is validated. We discuss some important issues associated with the proposed model in
Section 4, and the last section contains our conclusions.
2. The Proposed Image Compensation-based R-D model
The image compensation-based R-D model combines the R-D model with a low-order polynomial image compensation model. This section first introduces the R-D model and the image compensation model, followed by the technique for calculating the parameters of the image compensation functions. Subsequently, the method for image geolocation and image correction using the image compensation-based R-D model is presented.
2.1. R-D Model
For any pixel (
c,
r) in an image, the acquisition time can be determined from the image row coordinate
r. Using this time information, data such as sensor position and speed can be extracted from Position and Orientation System (POS) data. Additionally, the SAR measurement of distance from the target to the sensor can be calculated based on the column coordinate
c. The R-D model utilizes this information to establish geometric and physical relationships between the sensor and the ground target, forming the basis for the R-D equations:
where the parameter
R0 represents the initial slant range corresponding to the first column of an image,
Mr is the slant range resolution of the image, and
represents the wavelength of the electromagnetic wave. The first equation represents the range equation, where the left side denotes the distance extracted from the SAR image, and the right side presents the spatial distance between the sensor coordinates (
XS,
YS,
ZS) and the ground target coordinates (
X,
Y,
Z). The second equation expresses the Doppler equation, with the left side representing the Doppler frequency
fD used in imaging, while the right side is the Doppler shift of the SAR electromagnetic wave obtained based on the sensor velocity [
VXs,
VYs,
VZs]
T and the relative position [
X −
XS,
Y −
YS,
Z −
ZS]
T between the sensor and the ground target.
High-precision positioning in the R-D model is typically achieved through optimizing the model parameters using reference points. In Equation 1, the sensor’s position and velocity, imaging Doppler frequency, and initial slant range correction parameters (serving as their functional parameters) are unknown variables. Under the condition of having reference points for support, error equations can be constructed and correction values for the initial values of the model parameters may be determined.
2.2. The Proposed Image Compensation Model
The image compensation model was developed by adding correction values (
) to the original image coordinates. These values were derived from two-dimensional low-order polynomial functions of the original image row and column coordinates (
c,
r). When a second-order polynomial is used, it can be expressed as follows:
where
ai and
bi (
i = 0,1,…,5) represent the coefficients of polynomial functions for image compensation. According to the minimum number of GCPs required and the application requirements, the polynomial order can also be chosen as 0
th order (with parameters
a0 and
b0) or 1
st order (with parameters
a0,
a1,
a2,
b0,
b1, and
b2). In the case of order 0, the equations only contain constant terms while, in the case of order 1, they represent the affine transformation model.
SAR image row data, obtained by moving the sensor along the azimuth direction, primarily involve parallel projections. Image column data depend on the sensor sampling-reflected electromagnetic waves at equal time intervals, constituting range projections. From the perspective of the R-D model form, the main factors affecting SAR imaging or positioning errors include SAR sensor time and POS time synchronization errors as well as the initial slant range error, which are the main factors influencing SAR imaging errors and are mainly characterized by translation [
31]. These imaging errors can be absorbed through the two parameters
a0 and
b0 in the image compensation model. Within a certain time range, the sensor position and velocity errors measured via GNSS are primarily characterized by translation and drift, which can be expressed by a linear model [
32]. Although there is a non-linear functional relationship between the image column coordinates and sensor position error, the position measurement accuracy of GNSS is easily better than the 1 m level. Imaging errors caused by sensor motion errors, as well as the effects of other low-frequency errors, can be corrected using linear or second-order polynomial models. Considering the parallel projection relationship between image lines, a simplified quadratic polynomial model was constructed:
The above polynomial refinement model was used to correct the comprehensive impact of all parameter errors on image imaging and positioning. For ease of expression, image-compensated R-D models were categorized based on the number of polynomial parameters in the compensation functions. The functions containing only parameters consisting of the constant terms a0 and b0 are referred to as the one-parameter model. Polynomials with parameters a0, a1, a2, b0, b1, and b2 are called the three-parameter model, while those with parameters a0, a1, a2, a3, b0, b1, b2, and b5 are termed the four-parameter model. Similarly, Equation (2) is labeled as the six-parameter model, and the R-D model refined in the classical way is denoted as the classical model. Thus, in this article, a total of five types of R-D refinement methods are used. In theory, different polynomial forms yield varying processing accuracies, a notion that will be experimentally evaluated later.
2.3. Solving Polynomial Coefficients of Image Compensation Functions
The determination of parameters involves two main steps, carried out with the support of GCPs. The first step is to calculate the image coordinates using the ground coordinates of GCPs; in other words, the image coordinates (cci, rci) corresponding to the ground point (Xi, Yi, Zi) are calculated utilizing the original orientation parameters. The second step is to determine the parameters of the image compensation polynomial. The least squares fitting approach is employed to compute the differences between the calculated image coordinates and those from the GCPs.
The two steps are detailed below.
(1) Translating Ground Coordinates into Image Calculation Coordinates
The iterative method used to determine the image coordinates (cci, rci) from the ground coordinates (Xi, Yi, Zi) via the R-D model includes the following steps:
1). Begin with temporary values of the image coordinates (c0 and r0);
2). Extract the Doppler value and the SAR range measurement value corresponding to the temporary image coordinates (c0, r0);
3). Determine the image row time and interpolate to determine the sensor’s position and velocity at that time;
4). Calculate the Doppler value and the range distance based on the sensor motion information and the ground target position, then compare these with the values from step 2) to obtain the differences dfD and dR;
5). Calculate the increments of the image coordinates using the formulas dc0 = dfD/Vy and dr0 = dR/Mr;
6). If |dc| < 0.001 and |dr0| < 0.001, terminate the iteration, setting (cci, rci) equal to (c0, r0). Otherwise, update the temporary coordinate values using c0 = c0 + dc0, r0 = r0 + dr0, and return to Step 2).
(2) Determining the Parameters of the Polynomial Coefficients in the Image Compensation Function
For each reference point or GCP (Xi, Yi, Zi, ci, and ri), the calculated values of the image point—denoted as cci and rci—can be determined based on the ground point coordinates (Xi, Yi, Zi) using the R-D model. Meanwhile, the image coordinates of the GCP are denoted as (ci, ri) and the corresponding difference values () for this GCP can be computed. Taking the parameters a0–a5 and b0–b5 in Equation 2 as unknowns, we can establish two error equations for each GCP, resulting in a total of 2n error equations for n GCPs. When one-, three-, four-, and six-parameter models for image refinement are employed, the minimum number of GCPs required are one, three, four, and six, respectively. Once the minimum requirement is met or exceeded, the n parameters can be solved using the least squares method.
Based on Equation 2, error equations for row and column coordinates can be created separately and solved. The error equations for the column coordinate of the GCP, in the form of a vector, can be expressed as follows.
where
is the error vector of image column coordinates,
is the constant vector of image column coordinates, and
n is the number of GCPs.
The coefficient matrix
A for the six-parameter model is shown below:
Xa is the vector of the parameters of the six-parameter model for the image column coordinates:
The unknown parameters in the form of vector
Xa are solved using the least squares method, as follows:
Similarly, the parameters of the image compensation model for row coordinates can be solved:
where
is the constant-term vector for the image row coordinates.
Thus, the original image coordinates and the object space coordinates have the following equations:
2.4. Use of Image Compensation-based R-D model
Applying the R-D model based on image compensation for the geometric processing of images mainly involves the mutual conversion of coordinates between image and object spaces, as well as related processing during image correction.
Assuming that the image coordinates (
c,
r) correspond to a ground elevation
H, the point coordinates
P(
X,
Y,
Z) in the geocentric Cartesian coordinate system with a ground height of
H should satisfy the Earth ellipsoid model:
where
a and
b represent the Earth’s minor and major axes, respectively.
The adjusted values (ca,ra) corresponding to the original image coordinates (c and r) can be determined using the image compensation model. Based on the adjusted values (ca = c + , ra = r + , the corresponding sensor position, velocity, and imaging Doppler parameters for the R-D model can be obtained. Therefore, the R-D model equation and the Earth ellipsoid model together form a system of three equations with three unknowns (X, Y, and Z), which can be solved.
When transforming the coordinates of object point P(
X,
Y,
Z) to the original image coordinates, the method described in
Section 2.3 can be employed first, and the calculated values of the image points (
cc,
rc) corresponding to object points can be obtained. Theoretically, this calculated value should match the adjusted values (
ca,
ra) of the image compensation model from the original image point p(
c,
r); that is,
cc =
ca and
rc =
ra. For the image compensation model based on original image coordinates, these values are unknowns to be determined in this task. There are two solutions:
1) The calculated coordinates of the image points (cc, rc) obtained from object points can be used as the initial values for c and r in the compensation model, and the original image point coordinates and correction values can be refined through step-by-step iteration.
2) Considering that the difference between the calculated image point position (cc, rc) and the real image point position (c, r) corresponding to P is not significant (usually consisting of a few pixels) and the non-constant term coefficients of the compensation model are very small, the original image coordinate in the compensation model can be approximated as (cc − a0, rc − b0). The increment values can be computed and the original image coordinate can be updated without iteration, typically resulting in an error that can be completely ignored.
After obtaining the parameters for the image polynomial compensation function, high-precision ortho-rectification of SAR images can be achieved with the support of a Digital Elevation Model (DEM), a process typically realized through an indirect method. Based on the geolocation coordinates of an image’s four corner points, the corrected mapping image range can be determined. For each corrected image point, the object plane coordinates of the point can be calculated according to the range and the resolution of the corrected image, and the elevation value can be extracted from the DEM; thus, the three-dimensional object coordinates of the point can be obtained. Subsequently, the corresponding position in the original image can be calculated, and the pixel value can be resampled to match the corrected image.
3. Experiments
The purposes of the conducted experiments were to test the precision of the four aforementioned image compensation models under different GCPs, compare the accuracy of the four models with that of the classical R-D refinement model, and evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed method across different satellite and airborne SAR images.
In these experiments, we adopted SAR data sets from three platforms and four sensors; namely, the spaceborne X-band TerraSAR-X, spaceborne C-band GF3-C, manned airborne X-band SAR-X, and low-altitude unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV)-mounted Ku-band miniSAR-Ku image data sets.
The classical R-D refinement model, developed by the Chinese Academy of Surveying and Mapping and integrated into the SARplore software product, was used for comparative studies. The unknowns of the model comprised sensor position, velocity, initial slant range, and Doppler parameters. Sensor position and velocity errors were represented using a linear refinement model, and a combined adjustment approach was employed to solve all unknowns simultaneously.
Under the given conditions of initial orientation parameters, refinement parameters, and ground elevation, there exists a strict transformation between object space coordinates and image coordinates. Accuracy assessment can be conducted using either the ground coordinates of reference points (for assessing geolocation accuracy) or the image coordinates of reference points (for assessing orientation accuracy). In the former method, the image coordinates and elevation of the reference point are treated as known parameters, and the refined model is used to calculate their geolocation plane coordinates, which are then compared with the plane coordinates of the reference point to calculate the accuracy. In the latter method, the refined R-D model and the object coordinates of reference points are used to calculate image coordinates, which are then compared with the image coordinates of the reference points. That means that for the geolocation accuracy values in the following
Table 1-6, we first calculated the planar error for each CP based on the positioning errors
and
using the formula
. Subsequently, the geolocation accuracy was computed with all
n CPs using the formula
(unit: meters). The calculation of image orientation accuracy was similar to that of geolocation accuracy, obtained through calculating the errors in the image coordinates of the reference points and then computing the mean error (unit: pixels). When different models are compared under the same conditions, the same set of GCPs and check points (CPs) is used to prevent their error differences and distribution differences from affecting the accuracy. When some experiments required multiple GCPs but the number of reference points was insufficient, we employed the Leave-One-Out Cross-Validation (LOOCV) method for accuracy validation [
33]; namely, one reference point was selected as a CP in turn, and the remaining reference points were used as GCPs for testing. Through tallying the errors for all the CPs, the accuracy information was obtained. In the following experiments, when the number of CPs was equal to the total number of reference points, LOOCV was applied.
3.1. Experiments on Spaceborne SAR images
The X-band TerraSAR-X images and C-band GF3-C images were selected for the spaceborne SAR experiments.
(1) TerraSAR-X Images
The TerraSAR-X images and reference points used in this study have also been used in the literature [
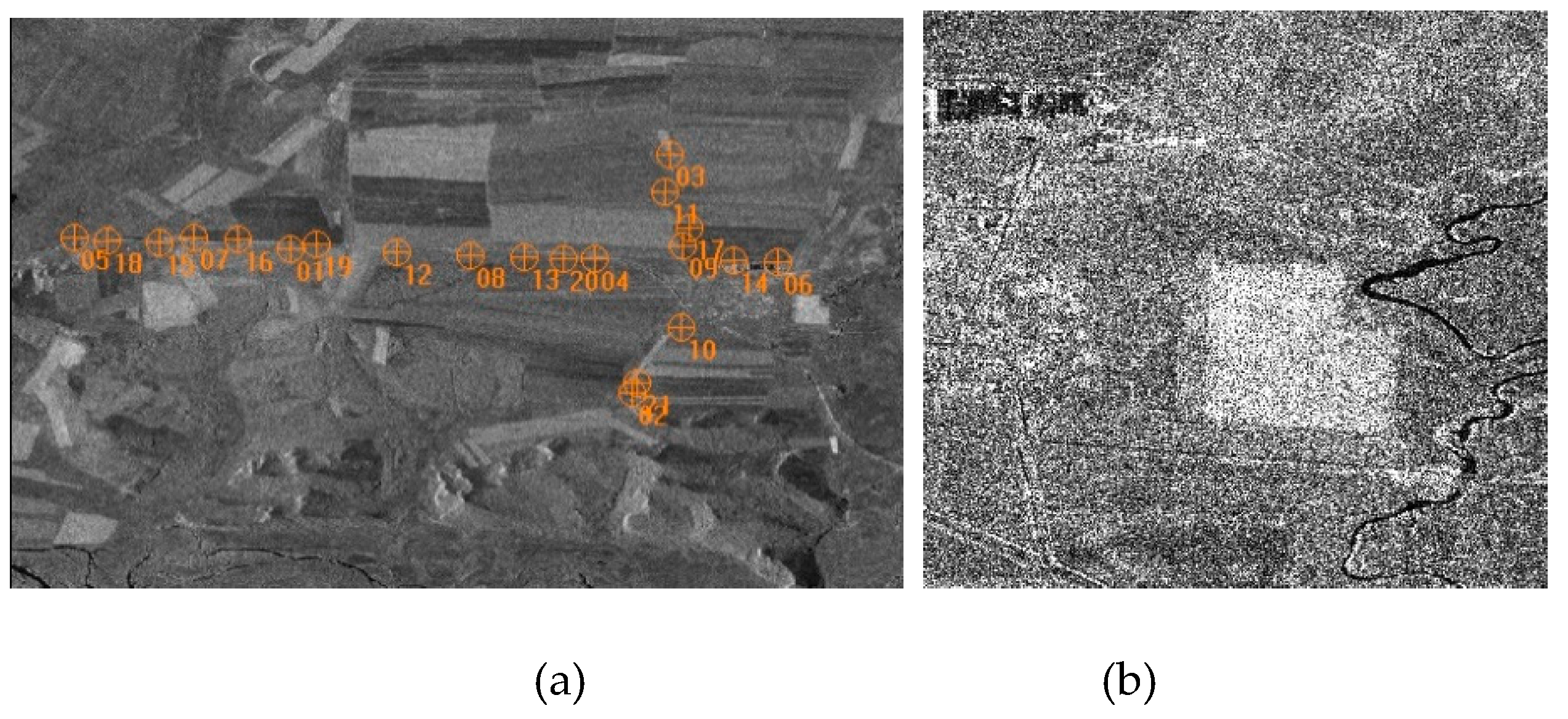
34] as an experimental data set. This image data set was acquired on September 5, 2012, at a center longitude and latitude of E120.78° and N50.37°, respectively. The test area is located near Yigen Farm to the east of Eerguna City in the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China. The average elevation of the study area is 706 meters. This area is characterized by relatively flat terrain consisting of bare soil, farmland, and woodland. The image resolution is 2.614 meters in the azimuth and 0.909 meters in the slant range direction. A total of 21 corner reflectors (numbered 01 to 21) were strategically placed along approximately straight lines in both the range and azimuth directions.
Figure 1 illustrates the image, including the distribution of corner reflectors (a), and a part of the TerraSAR-X Image (b).
Different configurations, wherein different GCPs and CPs from the reference points were selected, were designed for accuracy validation. The GCP numbers selected were 0, 1 (labeled as 01), 3 (from 01 to 03), 6 (from 01 to 06), 9 (from 01 to 09), 14 (from 01 to 14), and 20 (LOOCV). When GCP 0 was used, it means that the original data set was utilized for R-D positioning. In this case, the five models were identical. Positioning tests were performed using image compensation-based R-D models with one, three, four, and six parameters, along with the classical R-D refinement model. The table values represent the image geolocation accuracy in meters. In the table, the “/” signifies that there is no value at that position.
Under the condition of not having any GCPs with which to refine the R-D model, the mean square errors of orientation accuracy in the range/azimuth direction were 0.62/0.39 pixels, and the average error absolute values for all CPs were 0.45/0.37 pixels. For the three-parameter model with six GCPs, the accuracies in the range/azimuth directions were 0.09/0.09 pixels for GCPs and 0.11/0.12 pixels for CPs.
(2) GF3-C Image
GF3 is China’s first C-band multi-polarization synthetic aperture radar imaging satellite, with a maximum resolution of 1 meter. The image selected for the test was acquired on September 27, 2019, with dimensions of 16,886 × 24,878 pixels, which was captured from a descending orbit. The slant range resolution of the image is 1.54 m, and the azimuth resolution is 1.12 m. The test area is located in the northeast corner of Beijing, China, characterized by flat and mountainous terrains with elevations ranging from 10 m to 400 m. In the area covered by the image, 12 uniformly distributed reference points (labeled A01–A12) are shown, as illustrated in
Figure 2(a). A part of the image is shown in
Figure 2(b).
In this experiment, accuracy was assessed using different GCPs and CPs. The quantities of GCPs chosen were 0, 1 (labeled A01), 3 (A01 to A03), 6 (A01 to A06), 9 (A01 to A09), and 11 (LOOCV). Various models, namely, one-, three-, four-, and six-parameter image compensation-based R-D models, along with the classical R-D refinement model, were employed to calculate the positioning accuracy. The results are summarized in
Table 2. Different GCPs and models were utilized to compute positioning errors, and the geolocation accuracy for CPs is presented in
Table 2.
In the absence of GCPs, the orientation accuracies in the range/azimuth directions were recorded as 16.84/2.48 pixels, while the mean error absolute values of all CPs were 16.82/2.26 pixels. Under the refinement of a three-parameter model with six GCPs, the precision values for GCPs in the range/azimuth directions were 0.55/0.68 pixels, while those for CPs were 0.63/0.65 pixels.
3.2. Experiments Conducted on Manned Airborne SAR images
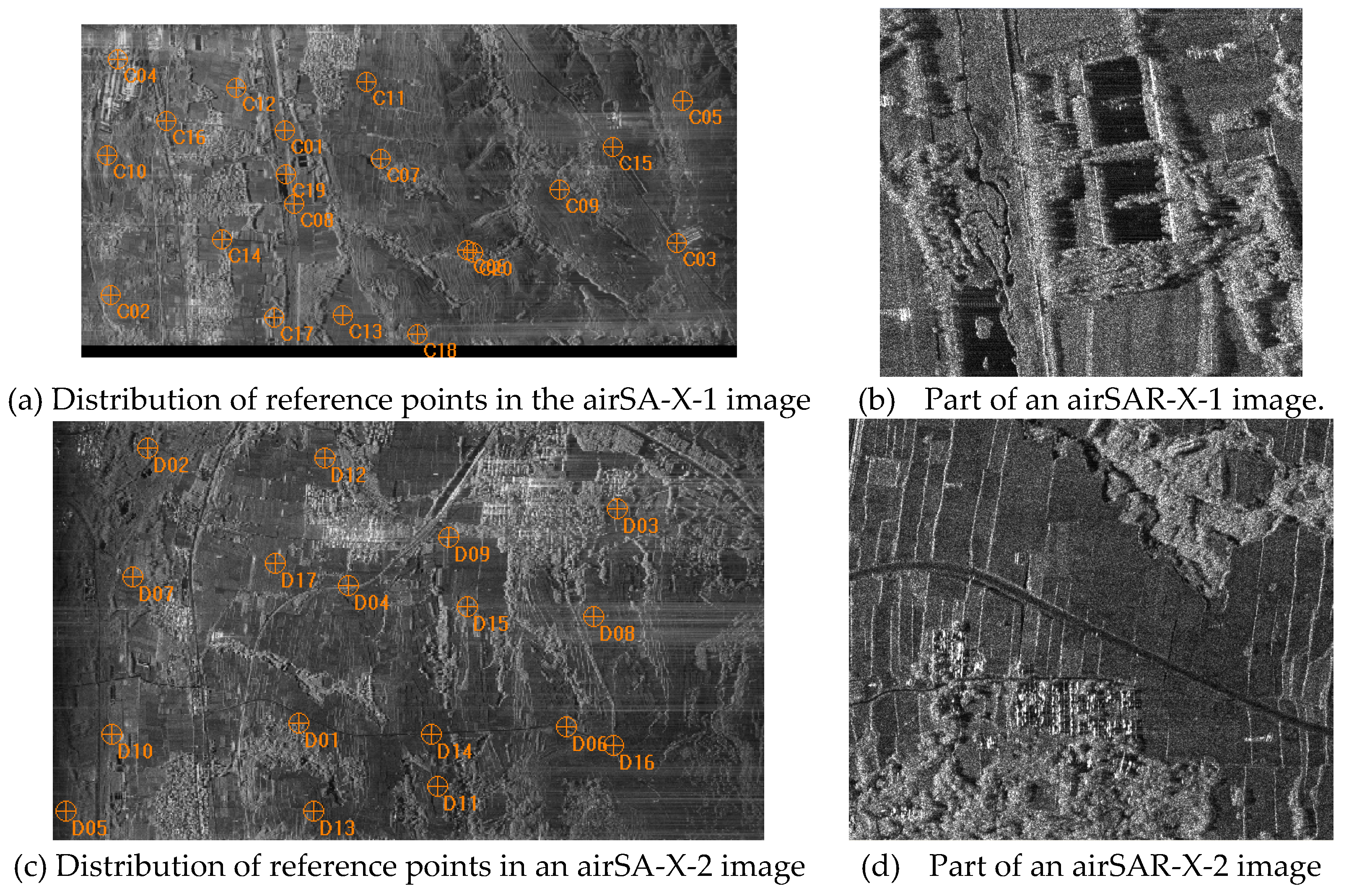
The X-band manned airborne SAR sensor was developed by the Aerospace Information Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. This data set was acquired in 2012 and constitutes early Chinese airborne SAR experimental data. Rigorous indoor and outdoor geometric calibrations before flying and imaging were not undertaken for the sensor. The system was equipped with a high-precision POS(POS510) capable of obtaining highly accurate sensor position and attitude parameters. The test area is located in Gaocheng Town, Dengfeng, Henan Province, China, with an elevation ranging from 230 to 350 meters. It is an area characterized by hilly terrain. Surveying flights were conducted in both east–west and west–east directions. Two scenes of images with a resolution of 0.15 m—namely, the airSAR-X-1 image from the east–west flight and the airSAR-X-2 image from the west–east flight—were selected for geometric positioning experiments. There are 20 and 17 reference points in the two images, respectively. Their distribution and parts of the two images are shown in
Figure 3. Different GCPs were selected to conduct accuracy comparison tests for the above models. For the airSAR-X-1 image, GCPs were chosen in quantities of 0, 1 (labeled C01), 3 (C01 to C03), 6 (C01 to C06), 12 (C01 to C12), and 19 (LOOCV). For the airSAR-X-2 image, GCPs were selected in quantities of 0, 1 (D01), 3 (D01 to D03), 6 (D01 to D06), 12 (D01 to D12), and 16 (LOOCV). The above five types of R-D refinement models were realized using different numbers of GCPs, and the geolocation accuracies of CPs for each model are indicated in
Table 3 and
Table 4.
Wit
For the original, unrefined R-D model, the airSAR-X-1 image orientation accuracies regarding range/azimuth were 514.85/4.83 pixels, and the mean error absolute values for all CPs were 514.85/4.77 pixels. The airSAR-X-2 orientation accuracies were 514.14/4.42 pixels, and the mean absolute values were 514.14/4.39 pixels.
3.3. Experiments Conducted on UAV-mounted miniSAR-Ku Strip Images
The Ku-band UAV SAR data set (with a wavelength of 0.0205 m) utilized in this study was developed by the Aerospace Information Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. An octocopter UAV was employed as the payload platform for the sensor. The miniSAR-Ku system was used to acquire the experimental data set in June 2021 over Anyang, Henan Province, China. The UAV flew at a relative altitude of 350 m. Two strip images, miniKu-1 and miniKu-2, from two flight lines were selected for experiments. The azimuth resolution is 0.080 m and the slant range resolution is 0.125 m. Both images have a column width of 3536 pixels, while the miniKu-1 image has a row height of 28,800 pixels and the miniKu-2 image has a row height of 26,752 pixels. These sizes indicate that the two data sets include long-strip images. Both strip images have uniformly distributed reference points, with 28 in miniKu-1 and 38 in miniKu-2. The distribution of some reference points used as GCPs in the following experiments and parts of the two images are shown in
Figure 4. In these experiments, we used different numbers of GCPs and CPs to validate the accuracy of the five models. In particular, 0, 1 (labeled G01/F01), 3 (G01/F01 to G03/F03), 6 (G01/F01 to G06/F06), and 20 (G01/F01 to G20/F20) GCPs were selected, and the accuracies of the five types of refinement models are summarized in
Table 5 and
Table 6.
I In the absence of GCPs, the image orientation accuracies for the miniKu-1 image were 8.45/2.76 pixels in the distance/azimuth direction, and the mean absolute values for all CPs were 7.97/2.45 pixels. For the three-parameter model with 12 GCPs, the accuracies were 0.86/1.02 pixels for the GCPs and 0.95/0.91 pixels for the CPs. Similarly, in the absence of GCPs, the orientation accuracies for the miniKu-2 image were 7.29/1.81 pixels, with mean absolute values of 7.22/1.42 pixels. For the three-parameter model with 12 GCPs, the GCP accuracies were 0.89/0.77 pixels and the CP accuracies Were 1.01/0.89 pixels.
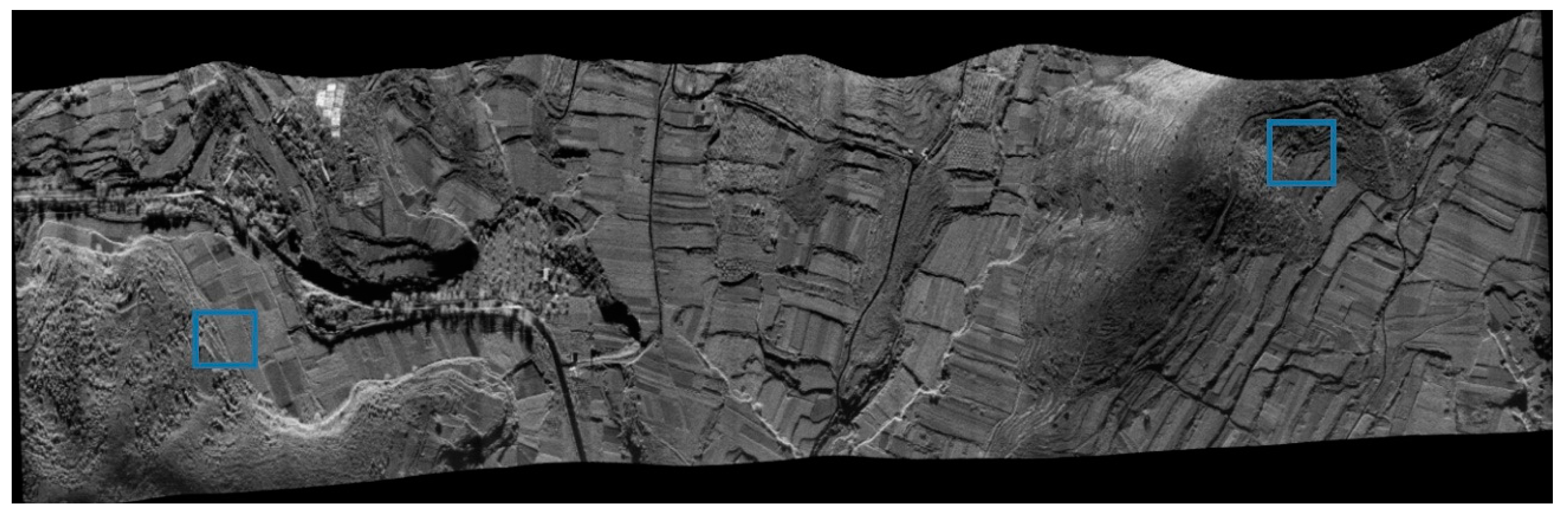
For the miniKu-2 image, 20 GCPs were utilized to refine the three-parameter model and the classical model, and the refined parameters were subsequently employed to ortho-rectify the image. The DOM attained using the three-parameter model is shown in
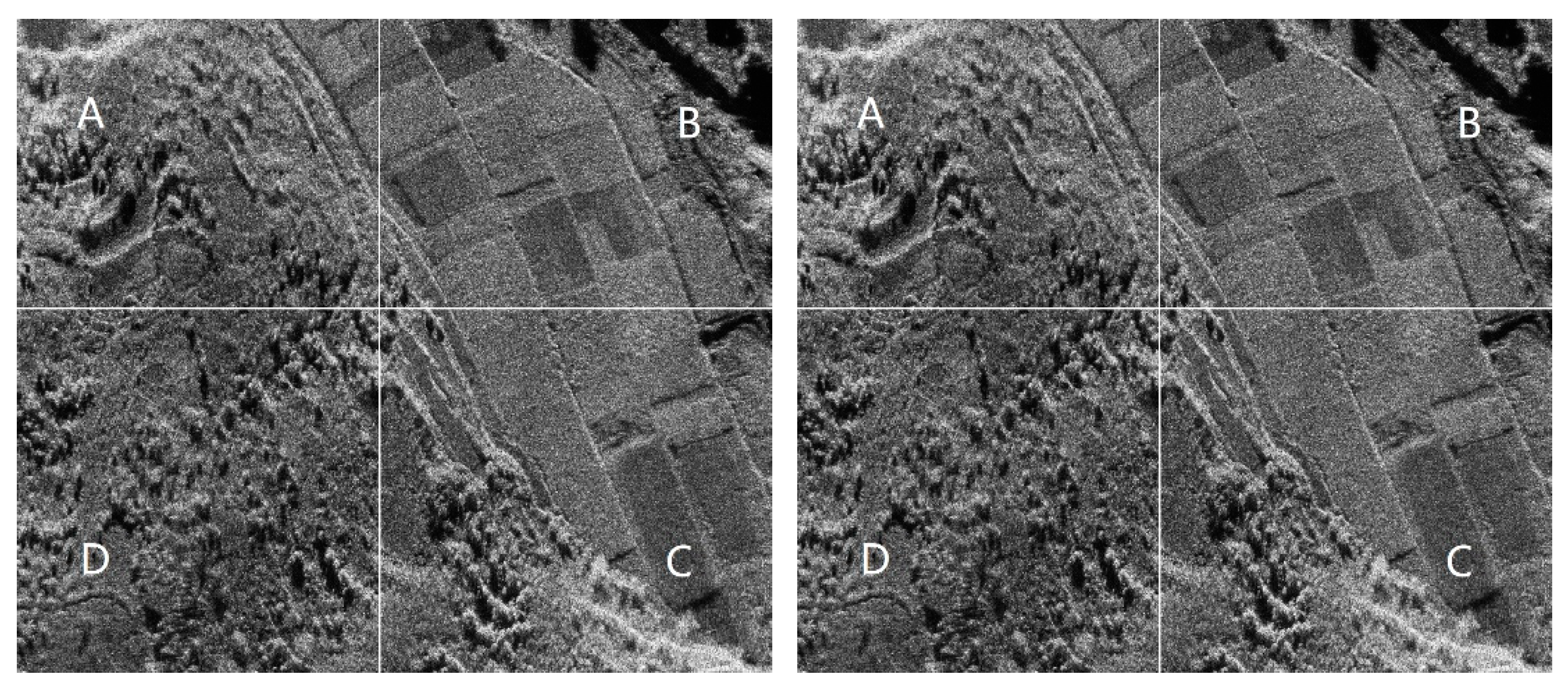
Figure 5, and the stitched images in two local regions (indicated by the boxes in
Figure 5) for both models are displayed in
Figure 6. In the stitched images of the local areas, part A and part C (top-left and bottom-right) represent the corrected results achieved using the three-parameter model, while part B and part D (bottom-left and top-right) show the corrected results obtained using the classical model.
4. Discussion
From the comparative experiments using various images, GCPs, and models, it is evident that the image compensation-based R-D model enables high-precision geometric processing of SAR images, albeit with varying accuracy performance under different conditions.
The one-parameter model is capable of geometric positioning across various GCP configurations. Even for images whose original parameters are inadequately accurate, such as airborne SAR data, a single GCP could significantly enhance the performance. The positioning results—both with sparse and sufficient GCPs—demonstrated that the one-parameter model enhances the accuracy of spaceborne SAR images more significantly than it does for the airSAR-X and miniSAR-Ku images, enabling it to readily achieve near-pixel precision, meaning that the errors of satellite images exhibit more regularity compared to those of airborne images.
The three-parameter model consistently yielded optimal performance for all tested SAR image types. Its accuracy was comparable to that of the classical refinement model, regardless of GCP density. Compared to those caused by image resolution, the differences in geolocation accuracy were negligible. Moreover, when there were enough GCPs, the three-parameter linear model was superior to the one-parameter model.
Comparing the four- and six-parameter models with the three-parameter model, when there were enough GCPs, the four- and six-parameter models outperformed the three-parameter model. However, the distinction in accuracy between the four- and six-parameter models was minimal when compared to the image resolution. When there were sparse GCPs, the accuracy of both for CPs was lower than that of the three-parameter model, where the accuracy of the six-parameter model was lower than that of the four-parameter model. This means that sparse GCPs render muti-parameter models prone to over-fitting.
From the experimental results, it is evident that the three-parameter model reaches accuracy comparable to that of the classical refinement model for satellite images. Under the condition of sufficient GCPs, the four-parameter model slightly outperforms the three-parameter model and the classical model with regard to the positioning of large-width or long-strip images. Furthermore, in scenarios with sparse GCPs, the one-parameter model can achieve accuracy approximately comparable to that of the classical model. The experimental results demonstrate that, through selecting the appropriate compensation model based on the number and distribution of control points, it is possible to achieve—or even slightly exceed—the precision of the classical model.
In the airSAR-X image experiments, it was observed that the two uncalibrated images exhibited geolocation accuracies of 174.5 and 183.7 meters, constituting a difference of nearly 10 meters. When considering the orientation accuracy, the two image orientation accuracies in the range/azimuth direction were 514.85/4.83 pixels and 514.14/4.42 pixels, respectively, with the difference being less than 1 pixel. Within the same scene imagery or among images acquired with the same sensor in close temporal proximity, the image orientation residual errors demonstrated greater consistency, compared to the errors for geolocation coordinates. The tests for airborne miniSAR-Ku and spaceborne SAR images exhibited a similar trend. This consistency provides further experimental support for the application of compensation functions in imagery as an alternative approach to achieving high-precision SAR image positioning. The airSAR-X tests indicated that, even though internal and external geometric calibrations were not carried out for the sensors and the original parameters of the image revealed poor accuracy, satisfactory accuracy can still be achieved using the compensation model and sparse GCPs, suggesting that low-order polynomials can effectively absorb the significant image errors derived from coarse sensor parameters.
5. Conclusions
Due to the complexity and the empirical nature of precision assignment in SAR rigorous model refinement, among other shortcomings, the number of commercial remote sensing software packages capable of supporting SAR image high-precision positioning with rigorous models is significantly fewer compared to those for optical images. In this study, we presented an image compensation-based R-D model that can achieve high-precision geometric positioning and be used for the geometric correction of spaceborne and airborne SAR images. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed model can achieve the same accuracy as the classical R-D refinement model, and can also be applied to the same range of scenarios as the classical model. However, when compared to the classical refinement models, the proposed image compensation-based R-D model is much simpler and easier to implement. As the number of parameters to be solved is small, the solution of our model is more robust under the condition of sparse GCPs. Furthermore, our model can be applied not only to spaceborne SAR images but also to airborne SAR images, whereas the RFM-based approach is usually applied to spaceborne SAR images.
Under the conditions of different GCPs, the four types of image compensation models presented distinct characteristics. In practical applications, the four types can be constructed for selection. Based on the type and characteristics of images, the quantity of GCPs, accuracy, and distribution information, a program can be designed to automatically or manually select the most suitable compensation model. Alternatively, according to the method in [
35], a program can utilize the four-parameter model and treat the refinement model parameters as weighted virtual observations within the adjustment model, enabling the image compensation model to meet the requirements of various scenarios and conditions.
Although the image refinement model proposed in this article has the advantages of simple computation, high accuracy, robust solutions, and broad applicability, this study mainly focused on the application of single-scene SAR images, confirmation of the feasibility of the models, and the provision of a basis for further applications. Stereo positioning and block adjustment of multi-view SAR images are important aspects in SAR geometric processing. In light of the characteristics and advantages of the proposed methods, extension of the image compensation-based R-D model for stereo positioning of multi-view SAR images, block adjustment, and other related applications under the conditions of few or no GCPs are worth further in-depth study.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.D.; data curation, K.C.; investigation, K.C.; methodology, Y.D. and K.C.; supervision, Y.D.; validation, K.C.; writing—original draft preparation, K.C.; writing—review and editing, Y.D. and K.C.; funding acquisition, Y.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China under grants 42171444 and 42301516, the Beijing Natural Science Foundation Project—Municipal Education Commission Joint Fund Project (No. KZ202110016021), the Beijing Municipal Education Commission Scientific Research Project—Science and Technology Plan General project (No. KM202110016005), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Beijing University of Civil Engineering and Architecture (No. X20043).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Aerospace Information Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the Chinese Academy of Surveying and Mapping for providing airborne SAR data and SARplore software. They are also deeply appreciative of Peking University for providing spaceborne SAR data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Jiang, B.; Dong, X.; Deng, M.; Wan, F.; Wang, T.; Li, X.; Zhang, G.; Cheng, Q.; Lv, S. Geolocation Accuracy Validation of High-Resolution SAR Satellite Images Based on the Xianning Validation Field. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei,Y.; Zhao,R.; Fan,Q.; Dai,J.; Zhang,B. Improvement of the spaceborne synthetic aperture radar stereo positioning accuracy without ground control points. Photogramm Record. 2024.39(185):118-140. [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J. A framework for high-precision DEM reconstruction based on the radargrammetry technique. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 10, 1123–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Xu, Q.; Xiong, X.; Jin, G.; Hou, H.; Cui, R. A Robust Method for Block Adjustment of UAV SAR Images. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 43975–43984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leberal, F. Radargrammetric Image Processing. Artech House Inc.1990. Norwood, MA.USA.
- You, H.; Ding, C.; Fu, K. SAR image localization using rigorous SAR collinearity equation model. Acta Geod. CARTO Graphica Sin. 2007, 2, 158–162. [Google Scholar]
- Curlander, J. Location of spaceborne SAR imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1982, 20, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, J.; Deng, K.; Hua, F. Combining optimized SAR-SIFT features and R-D model for multisource SAR image registration. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansosti, E. A simple and exact solution for the interferometric and stereo SAR geolocation problem. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 1625–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Dowman, I. A weighted least squares solution for space intersection of spaceborne stereo SAR data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu,Y. An airborne SAR image target location algorithm based on parameter refining. J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 2019, 41, 1063–1068. [Google Scholar]
- Schubert, A.; Jehle, M.; Small, D.; Meier, E. Mitigation of atmospheric perturbations and solid earth movements in a TerraSAR-X time-series. J. Geod. 2012, 86, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Meng, X.; Lou, L.; Fang, M.; LIU, Z. Target location performance evaluation of single SAR image of TH-2 satellite system[J]. Acta Geodaeticaet Cartographica Sinica, 2501. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y; Qiu, X.; Dong, Q.; Fu, K. A Robust Stereo Positioning Solution for Multiview Spaceborne SAR Images Based on the Range-Doppler Model. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022.19,1-5.
- Liu, X.; Teng, X.; Li, Z.; Yu, Q.; Bian, Y. A fast algorithm for high accuracy airborne SAR geolocation based on local linear approximation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 19130-1: Geographic information Imagery sensor models for geopositioning Part 1: Fundamentals. First edition, 2018. Geneva, Switzerland. 2018. http://www.iso.org.
- Zhang, B.; Yu, A.; Chen, X.; Tang, F.; Zhang, Y. An image planar positioning method base on fusion of dual-view airborne SAR data. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Yue, X.; Zhao, Z. Block adjustment with airborne SAR images based on polynomial ortho-rectification. Geom. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2008, 6, 569–572. [Google Scholar]
- Grodecki, J.; Dial, G. Block adjustment of high-resolution satellite images described by rational polynomials. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2003, 69, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.; Choi, Y.; Bae, J.; Sohn, H. Estimation and improvement in the geolocation accuracy of rational polynomial coefficients with minimum Gcps using KOMPSAT-3A. Remote Sens. 2020, 57, 719–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Fei, W.; Li, Z.; Zhu, X.; Tang, X. Analysis and Test of the Substitutability of the RPC Model for the Rigorous Sensor Model of Spaceborne SAR Imagery.Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica,2010,39(3):264-270.
- Zhang, L.; He, X.; Balz, T. ; Wei, X; Liao, M. Rational function modeling for spaceborne SAR datasets[J]. ISPRS journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2011, 66(1): 133-145.
- Eftekhari, A.; Saadatseresht, M.; Motagh, M. A study on rational function model generation for TerraSAR-X imagery. Sensors (Basel) 2013, 13, 12030–12043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Huang, Q. Influence of the motion error to airborne SAR geolocation accuracy. Electronic Measurement Technology.2007(30)1:63-67.
- Ma, J.; You, H.; Hu, D. Block adjustment of InSAR images based on the combination of F.Leberl and interferometric models. J. Infrared Millim. 2012, 31, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Zhang, J.; Huang, G.; Zhang, L. Range-Cocone equation with Doppler parameter for SAR imagery positioning.J. Remote Sens. 2013, 7, 1444–1458. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Fei, W.; Li, Z.; Zhu, X.; Li, D. Evaluation of the RPC model for spaceborne SAR imagery. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2010, 76, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Zhang, L.; He, X.; Liao, M. Spaceborne SAR image geocoding with RFM model. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 16, 1089–1099. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Wu, Q.; Wang, T.; Zhao, R.; Deng, M.; Jiang, B.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Li, F. Block adjustment without GCPs for Chinese spaceborne SAR GF-3 imagery. Sensors (Basel) 2018, 18, 4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, G.; Li, D.; Zhao, R.; Deng, M.; Zhu, T.; Yu, L. Planar block adjustment and orthorectification of Chinese spaceborne SAR YG-5 imagery based on RPC. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 640–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Jin, G.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, H. Block adjustment with airbrone SAR very high-resolution images using trajectory constraints. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 2383–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X. POS-supported bundle block adjustment. Act Geod. Cart OGRAPHICA Sin. 2008, 3, 342–348. [Google Scholar]
- Brovelli, M.; Crespi, M.; Fratarcangeli, F.; Giannone, F.; Realini, E. Accuracy Assessment of High Resolution Satellite Imagery by Leave-one-out method[A]. Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Spatial Accuracy Assessment in Natural Resources and Environmental Sciences, July,Lisbon, Portugal. 2006. 5–7: 533-542.
- Zhou, X.; Zeng, Q.; Jiao, J. Analysis of TerraSAR-X sensor calibration accuracy and its application. Remote Sens. Inf. 2014, 29, 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, C.; Zhang, J.; Huang, G.; Zhang, L. Combined Positioning of TeraSAR-X and SPOT-5 HRS Images with RFM Considering Accuracy Information of Orientation Parmeters[J]. Acta Geodaeticaet Cartographica Sinica, 2017,46(2):179-187.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).