4.1. Identify the Need for a Commitment Monitoring System
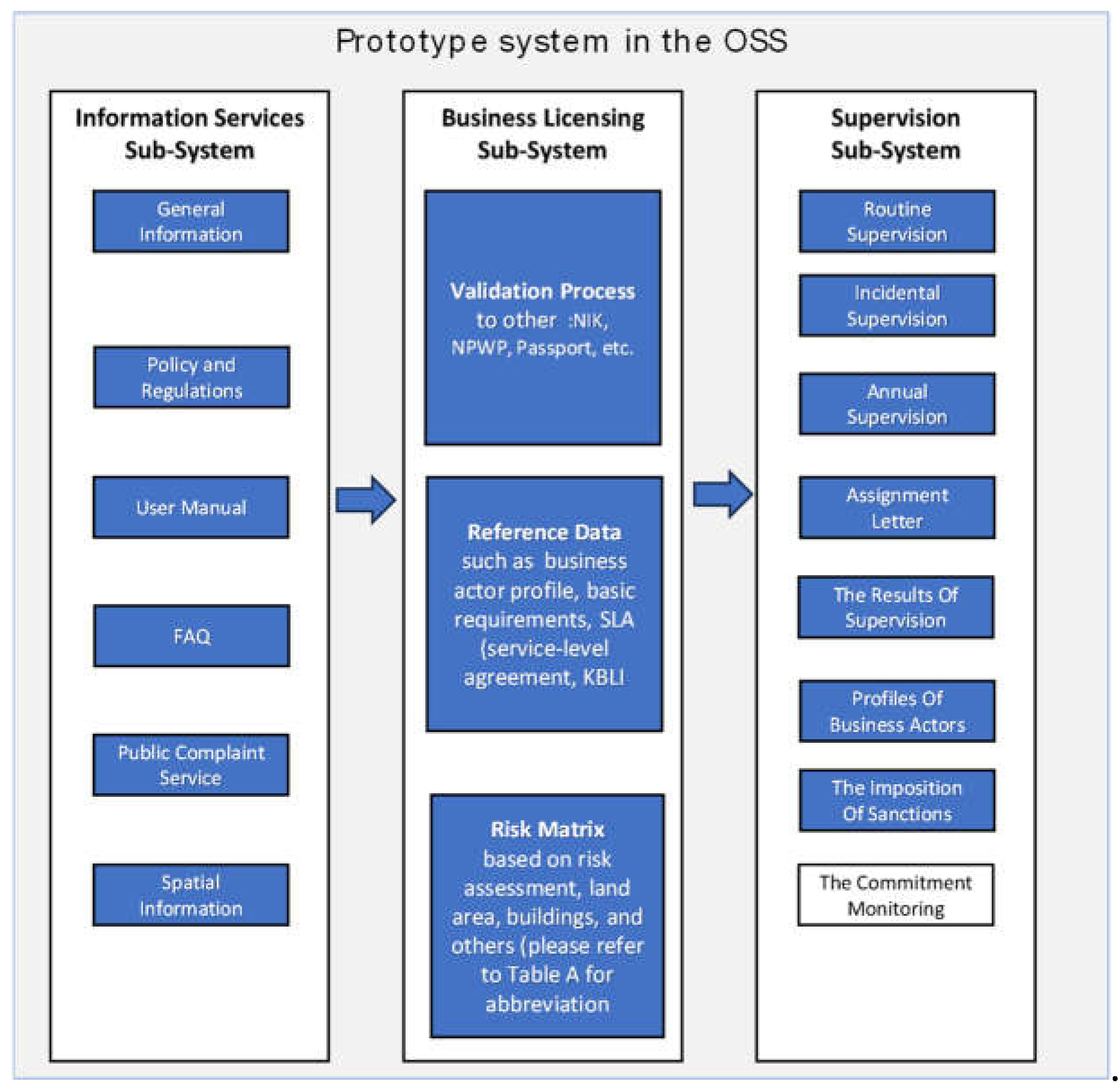
The design of this business commitment's monitoring system as part of the current OSS system (government regulation number 5/2021 concerning the implementation of risk-based business licensing). The OSS system comprises three sub-systems: information services, business licensing, and supervision (see
Figure 3). The information service sub-system is a system that contains a library of information services such as general explanations, guides, regulations, FAQs (frequently asked questions), and others. The business licensing sub-system is where business actors fill out business license applications. In this sub-system, there is a validation process for business actor information such as Identity Number (NIK), Tax Identity Number (NPWP), reference data (such as business actor profile, basic requirements, SLA (service-level agreement), the Indonesian Business Field Standard Classification (KBLI) and a risk matrix based on risk assessment, land area, buildings, and others.
The supervision sub-system, a vital component of the OSS, consists of several activities carried out regularly, such as routine, annual, and incidental supervision. In this sub-system, there is also a supervisory assignment letter, the supervision results, profiles of business actors, and the imposition of sanctions. The proposed commitment monitoring module for business actors will be seamlessly integrated into this sub-system, enabling real-time monitoring of these business actors' commitments and enhancing the overall supervision process.
From the results of the above explanation, OSS has some integration and non-integration processes with systems from other K/L. That is:
Integration using a gateway (via API, file transfer, or others) to validate business actor data.
Integration using a link to the application from the K/L system. Examples: Food and Drug Supervisory Agency (BPOM) distribution license, The Indonesian National Certificate (SNI),
There is no integration, and the Business Identification Number (NIB) is the basis for the commitment process. Halal certificate (currently only an independent statement from MSME actors), SSO licensing, and the National Industrial Information System (SIINas) are examples.
There is no integration because requirements are fulfilled already in OSS. Example: building approvals (PBG).
Therefore, the process of integrating systems in K/L into the OSS system is being carried out gradually, a systematic approach that should reassure the audience. However, not everything has become integrated into the OSS system. As a first step, several systems have used the NIB from the OSS system as unique data for business actors. The second step is to provide application link information for K/Ls that are targets for business actors to fulfill their commitments. These two steps are included in the low-effort steps because the process is easy to do. Meanwhile, the other two steps, namely integration between systems by using a gateway system and adding function modules from the K/L system to the OSS system, are high-effort steps. Because it requires coordination and agreement between the two institutions, including integration costs.
Adding function modules from the K/L system to the OSS system also requires several considerations. The first is related to the costs invested so far in the solution. By the profits obtained (net book value = 0), the risk of the costs should be acceptable. The second is adding complexity to the OSS system, which will be critical. Lastly, there will be additional infrastructure costs if needed for the new module. Therefore, the author proposes a solution with a system that uploads certification documents resulting from related ministries and agencies centrally in the OSS system. It is a form of monitoring the fulfillment of commitments from business actors, especially micro, small and medium enterprises (UMKM) or those with low risk. The advantages (pros) and disadvantages (cons) of the proposed document upload system resulting from this commitment are visible in
Table 2.
With the OSS-RBA system, a testament to its success is the increase in the number of business and investment licenses, as has also happened in the regions. This success story should inspire confidence in the proposed solution. However, there are also problems with its implementation, especially monitoring business licenses [
14]. Other business licensing in other countries, such as the Philippines, where the e-BPLS (Electronic Business Licensing and Licensing System) can speed up service responses that previously used manual processes [
15]. Apart from the system, businesses that do not comply with regulations should have their business licenses rejected, such as the Turkish BRSA (Banking Regulation and Supervision Agency) for fintech that ignore regulations [
16].
4.2. Select Documents as Samples for Fulfilling Business Licensing Documents
The selection of two document criteria as samples in this prototype is not arbitrary; it's because they reflect the very specifics of bio-business licensing (see
Table 3). This is a deliberate choice, a limitation of the system being developed, but one that is crucial in its simplicity and focus. It's only implemented in two documents and only involves two K/Ls, but it's a starting point, a foundation that can later be expanded to document fulfillment in other K/Ls. An example of a business license that is not included in bio-business is a mining business license or a special mining business license (IUP or IUPK).
As mentioned in previous research, bio-business includes biotechnology, human health technology, bioindustry, and agriculture biotechnology [
17]. These are not just abstract concepts, but areas that require specific certificates for fulfilling business commitments. These certificates, issued by relevant ministries and institutions [
18], are not mere formalities, but essential requirements for business licensing obligations in the selected [
19].
In the 2020 KBLI, there are not just a few, but 21 categories, each with its own unique role in the bio-business landscape. Among these, those selected for bio-business are A (agriculture, forestry, and fishing), C (processing industry), and I (providing accommodation and providing food and drink). This diversity is not just a list of numbers, but a testament to the wide range of bio-business opportunities in Indonesia. Of the 21 categories, there are 1349 KBLI, and for example, for the Department of Agriculture, there are 56 KBLI (See
Table 4).
4.4. Design and Development of Monitoring System for Compliance with Business Licensing Documents
The meticulous design and development stages of this monitoring system are a testament to the precision and care we put into our work. It all starts with the design process, which includes a sequence diagram, database design, and document upload design. On the other hand, the development process involves setting up the environment, displaying the login form, registering, checking the status, uploading documents, validating documents, and testing the status (dashboard). The application development process, OCR, and E2E (end-to-end) process checks before testing are a continuation of the process. The testing process consists of scenario design, sample preparation, and test execution. The process of calculating research results and analyzing the results is part of the evaluation process.
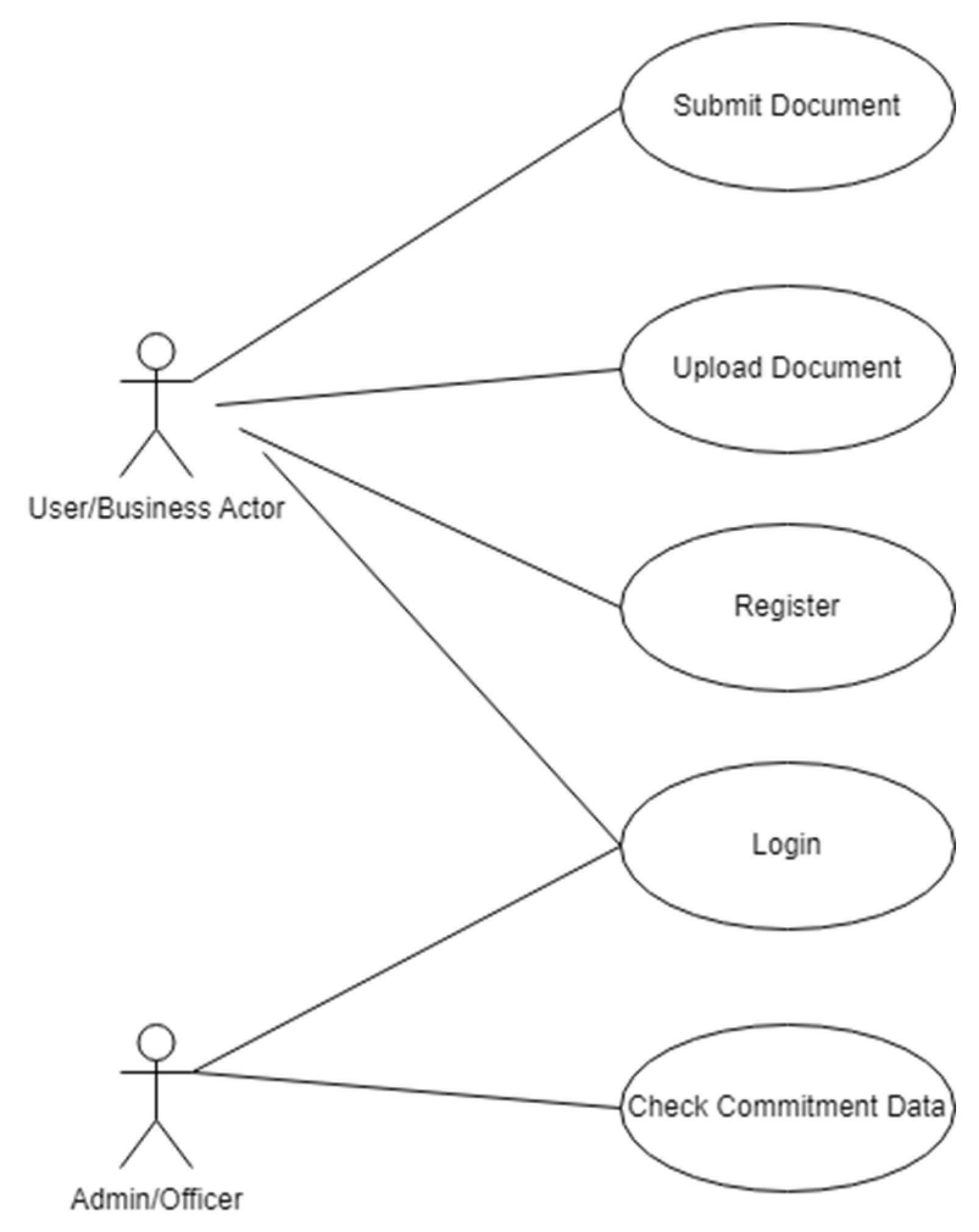
A use case diagram provides an overview of the system's interaction with its environment (see
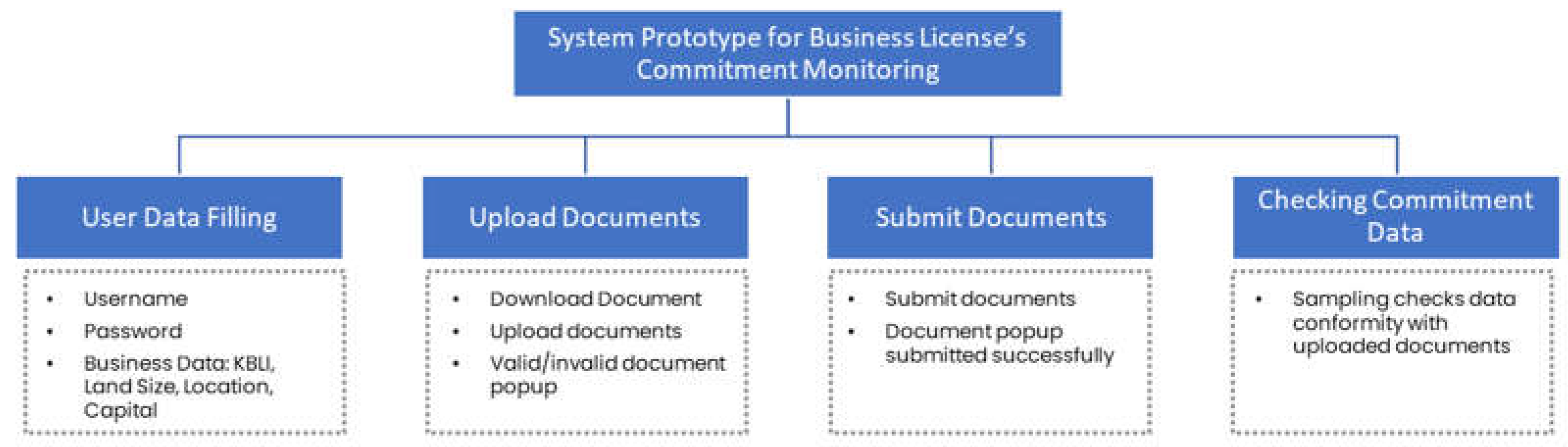
Figure 4). The system has two actors: the user/business actor and the admin/officer. Users or business actors can log in, register, upload documents to check their validity, and submit documents if they are valid. Valid documents will be checked by the administrator or officer using a random method (sampling). In general, the programming structure of the monitoring system consists of four parts: filling in user data, uploading documents, submitting documents, and checking document suitability by the admin (see
Figure 5).
In this research, the expected user journey is: (1) Users can access the business licensing document upload form. (2) Process document uploads according to the type of document required; (3) The system will determine the summary of the uploaded document. (4) The system will record important words previously defined in the document. (5) The system will assess whether the document is valid; if it is not, it will provide a notification or warning to the user. (6) If all documents are complete, the user can submit the document.
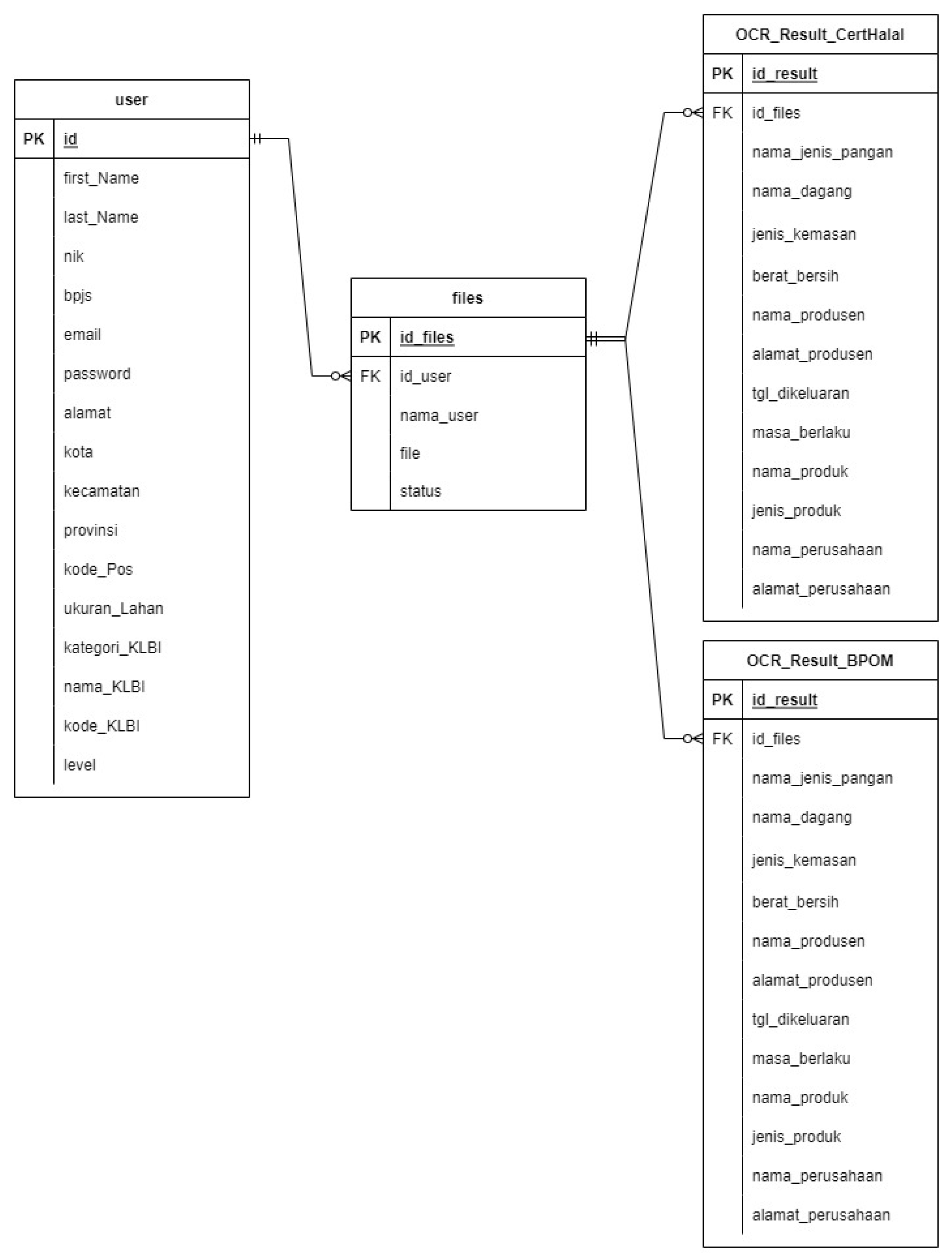
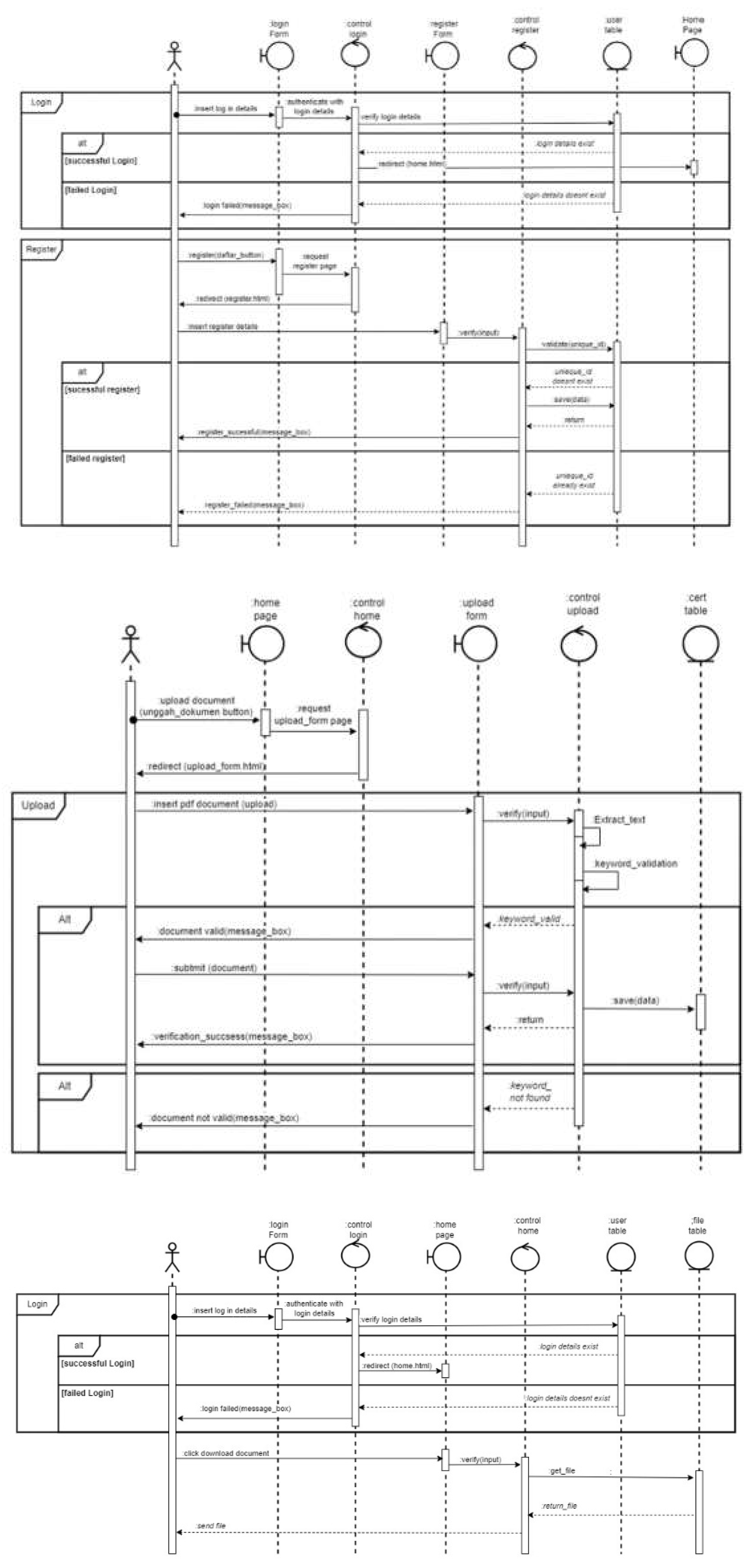
In the prototype for monitoring business actors' commitments, we have implemented stringent security measures in the authentication methods. There are two processes, namely the process of logging in to the monitoring form and the process of downloading commitment documents. The login process can use the login process currently in the OSS application, but a link needs to be added to see the status of fulfilling the commitment document. The login process begins with the user or business actor entering a username and password into the application. Authentication processes can be added to the system, such as 2FA (two-factor authentication) by adding a code in the application other than the username and password, or MFA (multi-factor authentication), which is a login process that not only uses the username and password but also enters a code sent via email, answers secret questions, or uses biometric scans such as fingerprint or face recognition. The next process is the document download process. The document download process will produce a user database and files (see
Figure 6).
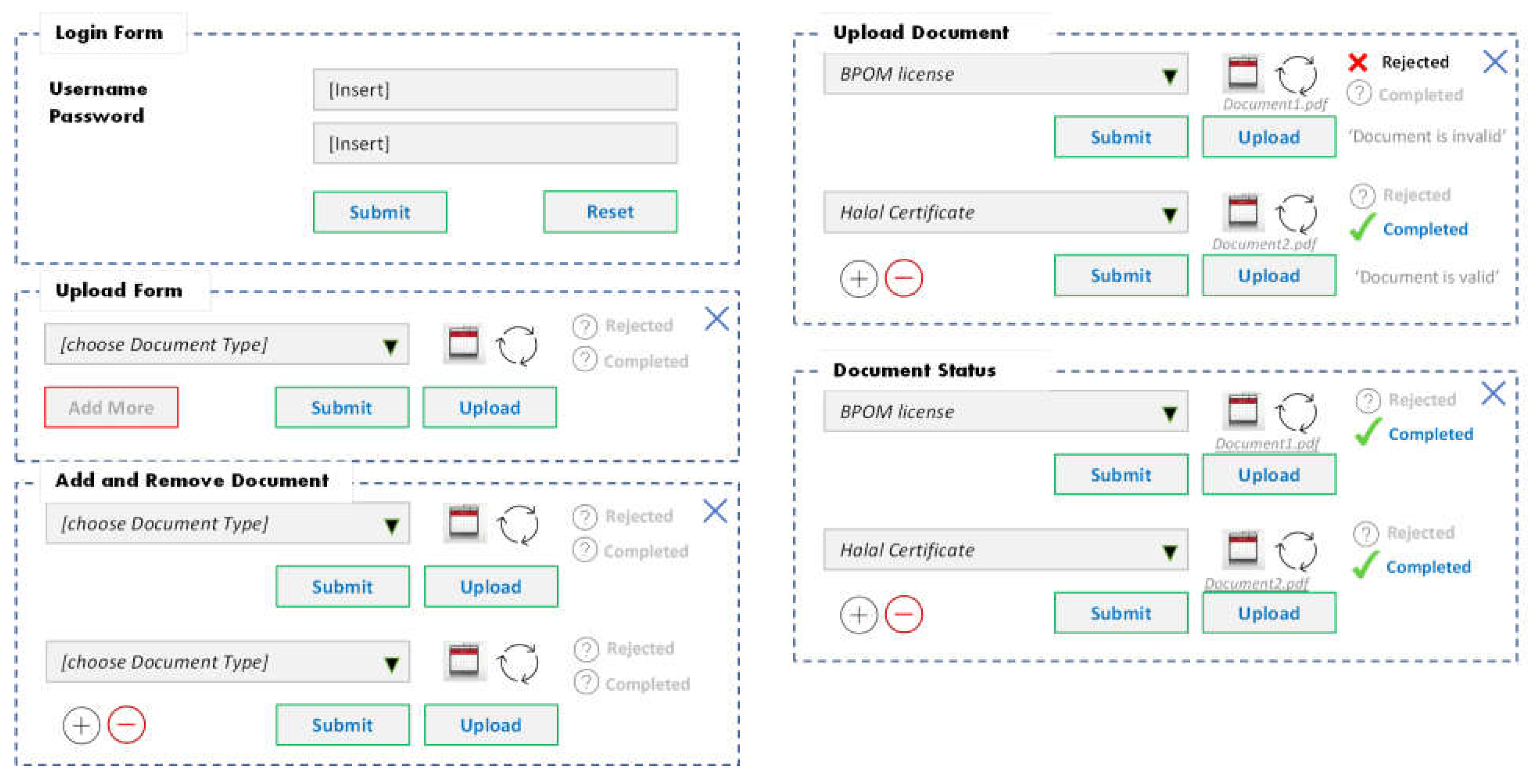
The next process is the document upload process. There are three processes when uploading documents: the process of entering data, the process of checking data, and the process of uploading data into the system. In the process of entering data, users can add more if they want to enter more than one document. Users can also delete or remove documents that are not needed. After confirming the number of documents to be downloaded, the user can select the documents to be uploaded from the files on his computer. Then the user can upload the document until the process is successful. You can refer to the visual guide in
Figure 7 for a better understanding of this process.
The following process is the data-checking process. If the file entered is incorrect, there will be a message or notification that the file is wrong. If the document is appropriate, a message will be successfully uploaded. Users can upload other documents, and if succeed, then users can submit the appropriate documents. The final process is uploading data into the system. If the data has finished uploading, there will be a message indicating whether it was successful (completed) or not (rejected) (see
Figure 8).
From the above process, there are several characteristics of a smart system
Keywords from each required document represent embedded knowledge in the system.
There is a response if the document is valid or by the stored knowledge.
Communication between the user and the system is subject to the information received about whether the uploaded document is valid.
In conducting this research, it is necessary to first delve into several concepts of text recognition. In document classification processes such as text mining, determining important words in documents is very necessary. Examples include determining plant genetic resources [
29]. But beyond this, the complexity of the task is further revealed in the need to summarize the document [
30]. Text summarization, a process that can use soft computing methods (subject, predicate, and object rules) and fuzzy logic [
31], or a word embedding approach [
32], such as SummCoder or autoencoder, and sentence embedding [
33], is a multifaceted challenge that requires careful consideration and understanding.
Another important thing is the text classification process, which determines whether the text falls into a predetermined category [
34]. Text classification can be knowledge-based, corpus-based, or learning-based [
35]. Text classification can also use feature selection methods like Hebb rules [
36]. Other methods of text classification with a semantic approach are role labeling and explicit semantic analysis [
37], taxonomy [
38], the hidden Markov model (HMM) for opinion mining [
39], a new term weighting approach using Least Information Theory (LIT) is adopted for hierarchical classification [
40]; and the standard inverse moment of gravity formula [
41]. To improve computational efficiency, another approach to document categorization is a feature projection method that selects the very first layer of fusion information [
42] and a very deep Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) [
43].
The development of this solution is initial and enhance its capabilities, namely supporting sustainable development. There is a close relationship between artificial intelligence (AI) and sustainable development targets, especially with the cultural shift towards digital [
44]. The existence of AI is not just a trend but can also change business models and the global economy [
45].
One use of AI in recognizing text is with OCR (optical character recognition). Text recognition using the OCR flask and Tesseract has an average accuracy above 90% [
46]. Therefore, it is widely used in record-management systems [
47]. To increase accuracy, document classification using OCR can also be combined with the Naïve Bayes Classifier [
48] or other methods to obtain document classification automatically [
49].
The system development process begins with setup, development, and testing environments. The specifications are as follows:
- a.
OS: MS Windows Server
- b.
- 1)
CPU: 2 cores
- 2)
Memory: 8 GB;
- 3)
Storage: 20 GB
- c.
- d.
Application:
- 1)
Frontend template: Bootstrap 5
- 2)
Apps: Python 3.12.2
- 3)
Framework: Flask
- 4)
API: Rest API
- 5)
Database: MySQL
The results of the frontend and backend development are a login form (see
Figure 9), a registration form (see
Figure 10), a homepage (see
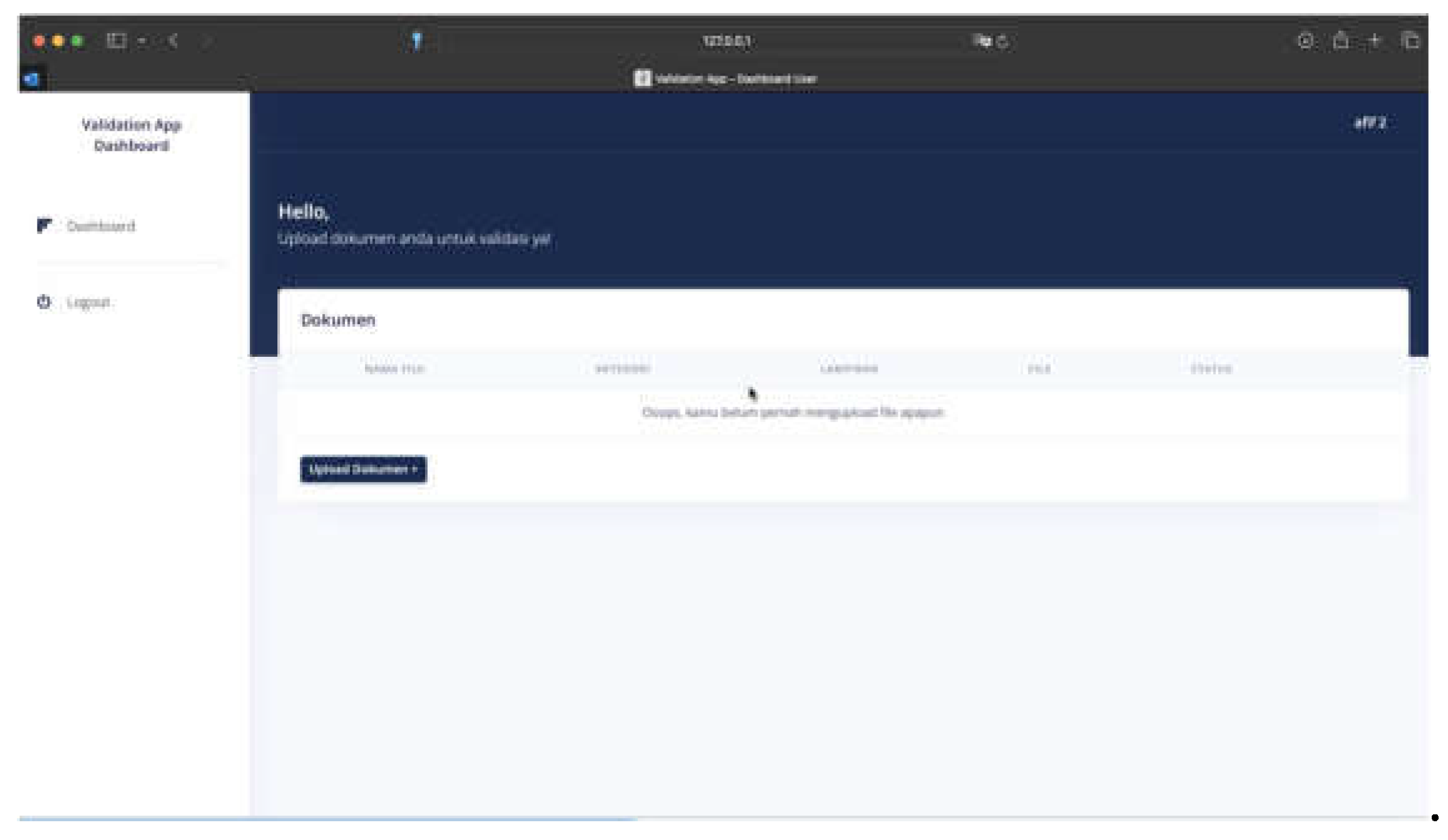
Figure 11), and a dashboard page for uploading and sending documents (see
Figure 12).
4.5. System Testing and Evaluation
Testing uses the black box method with several variables for developing business license prototypes. The test data consists of several halal certificates and BPOM licenses taken from the internet, with two samples of valid halal certificates, seven samples of valid BPOM certificates, and two samples of invalid certificates (see Figures A1, A2, and A3 in Appendix). This test data has yet to be available online and is still a hardcopy document. (see
Table 6).
A proposed solution for uploading documents to fulfill business license commitments has the following system assumptions:
- a)
The prototype is built more advanced, from low fidelity (a mock-up) to high-fidelity (a web prototype). An example of a high-fidelity prototype for online attendance during the pandemic is much needed [
50]. Low- and high-fidelity prototypes both reveal usability problems well[
51].
- b)
Using the Tesseract OCR (Optical et al.) package or library to get text summaries from documents (images).
- c)
The text summary extraction results match the previously defined keywords.
- d)
Keywords are defined early, so the system has no modules or functions to add, subtract, or change them.
While System Limitations are:
- a)
The system built stands alone (a stand-alone application); there is no integration process with the current system (OSS).
- b)
These do not include email, SMS, or otherwise notifications to users.
- c)
There has been no feedback from the officer (admin) if there is an incorrect document.
The evaluation compares the number of successful scenarios with the total number of scenarios in Equation 1.
N = Number of successful scenarios ÷ Number of total scenarios × 100% (1)
There is a note from the process that has been executed. The file size determines the length of the extraction process by OCR. A BPOM-valid marketing authorization file with a size of 2.6 MB can be processed by OCR within 35 seconds (see
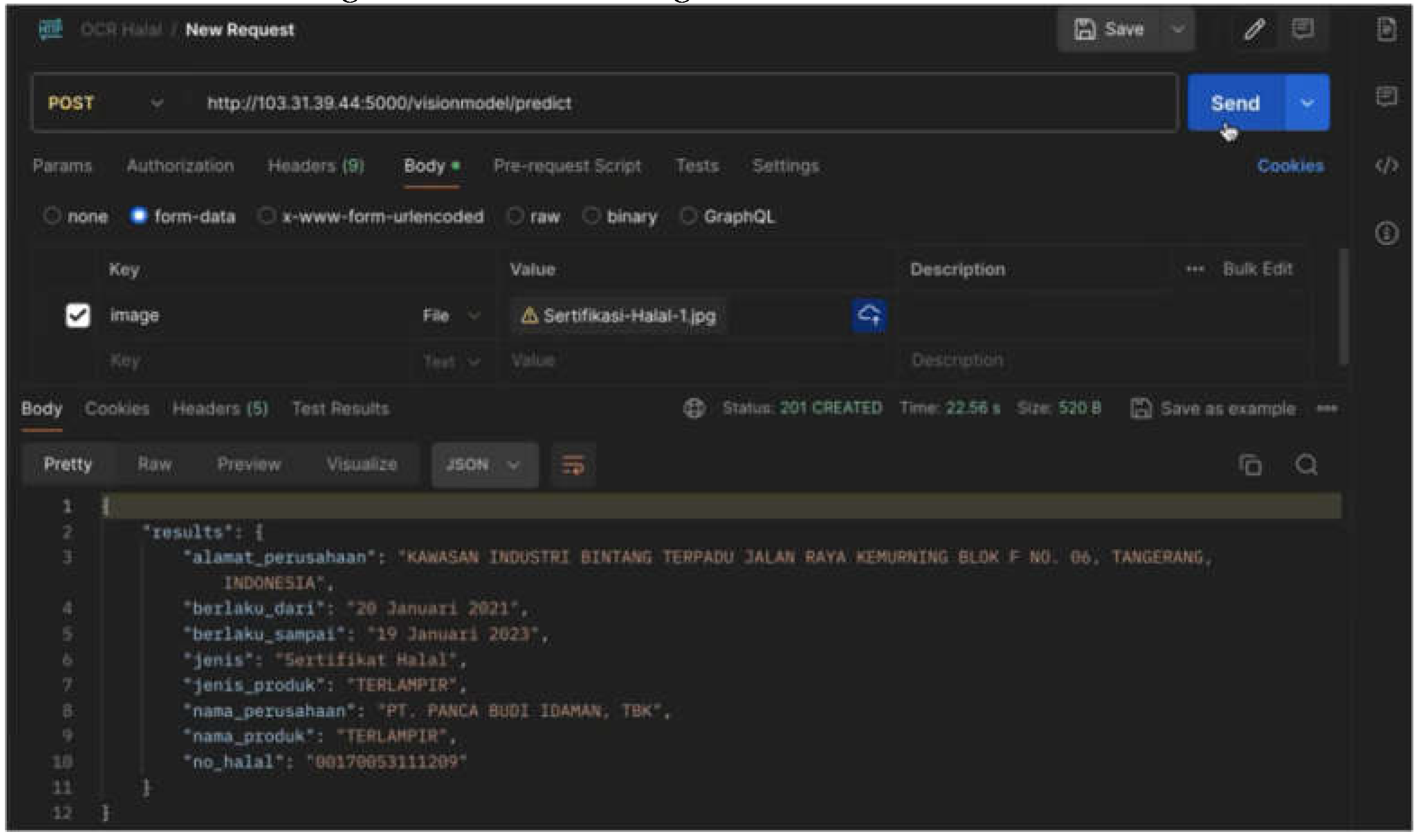
Figure 13). A halal-valid certificate file with a size of 382 kB can be processed by OCR within 25 seconds (see
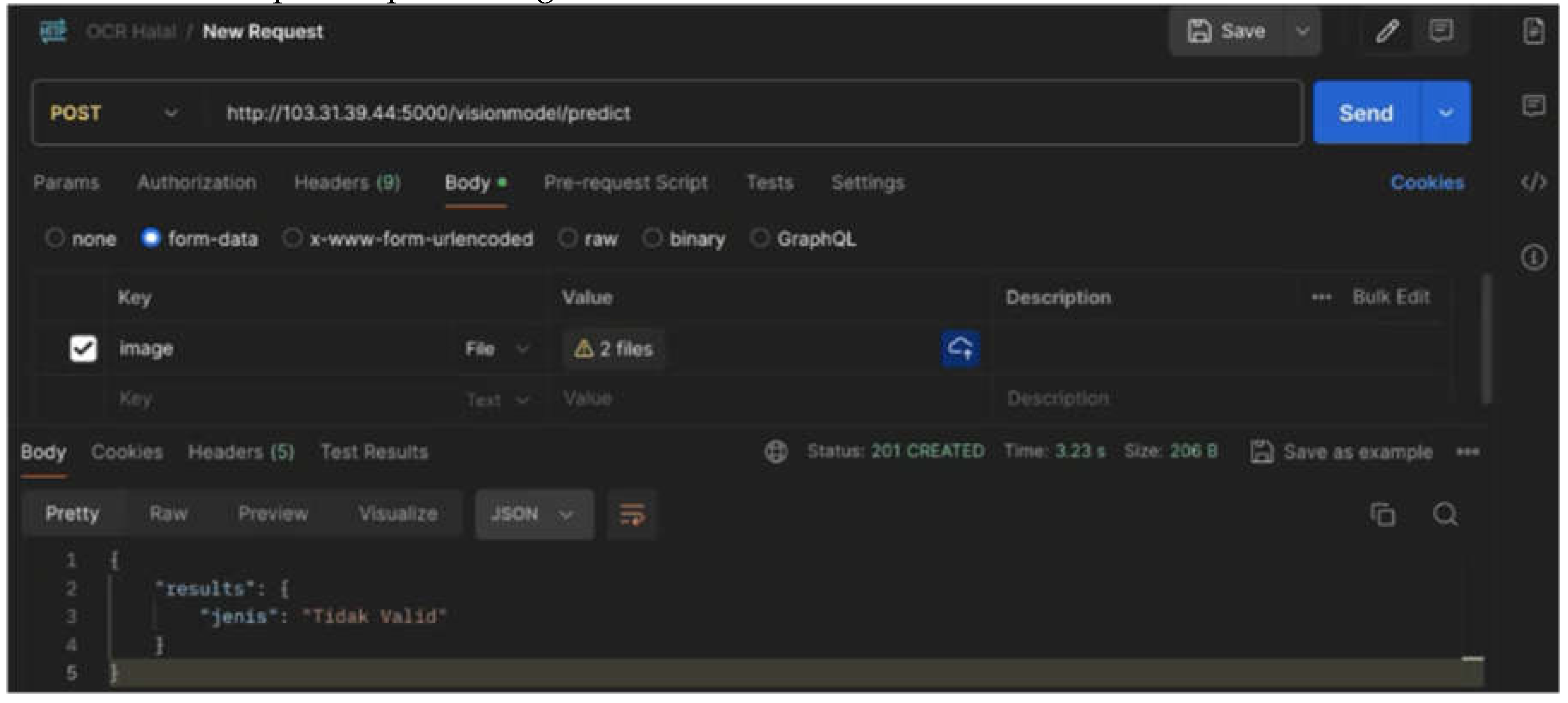
Figure 14), and an invalid document file with a size of 63 kB can be processed by OCR within 5 seconds (see
Figure 15). The machine learning (ML) algorithm runs on a cloud's virtual private server (VPS).
Therefore, an additional Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) is needed so that the processing of this ML algorithm can be faster. GPUs are different from high-performance computing (high-performance computing, or HPC for short), which can process large data sets quickly with parallel computing processes. The combination of GPU and HPC will likely quickly increase the processing capabilities of ML and AI algorithms that use big data.
Another solution is to use better ML algorithms. The easyOCR algorithm can be changed using the GPT4 OCR/image recognition algorithm developed by OpenAI. Of course, further research is required to confirm this, especially the implementation of OCR on the documents used in this research. If the expected time for document processing with OCR is within a specific time limit, limiting the maximum file size is necessary. For example, the maximum limit for the processed file is 100 kB with an expected processing time of 10 seconds.