Submitted:
10 July 2024
Posted:
10 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
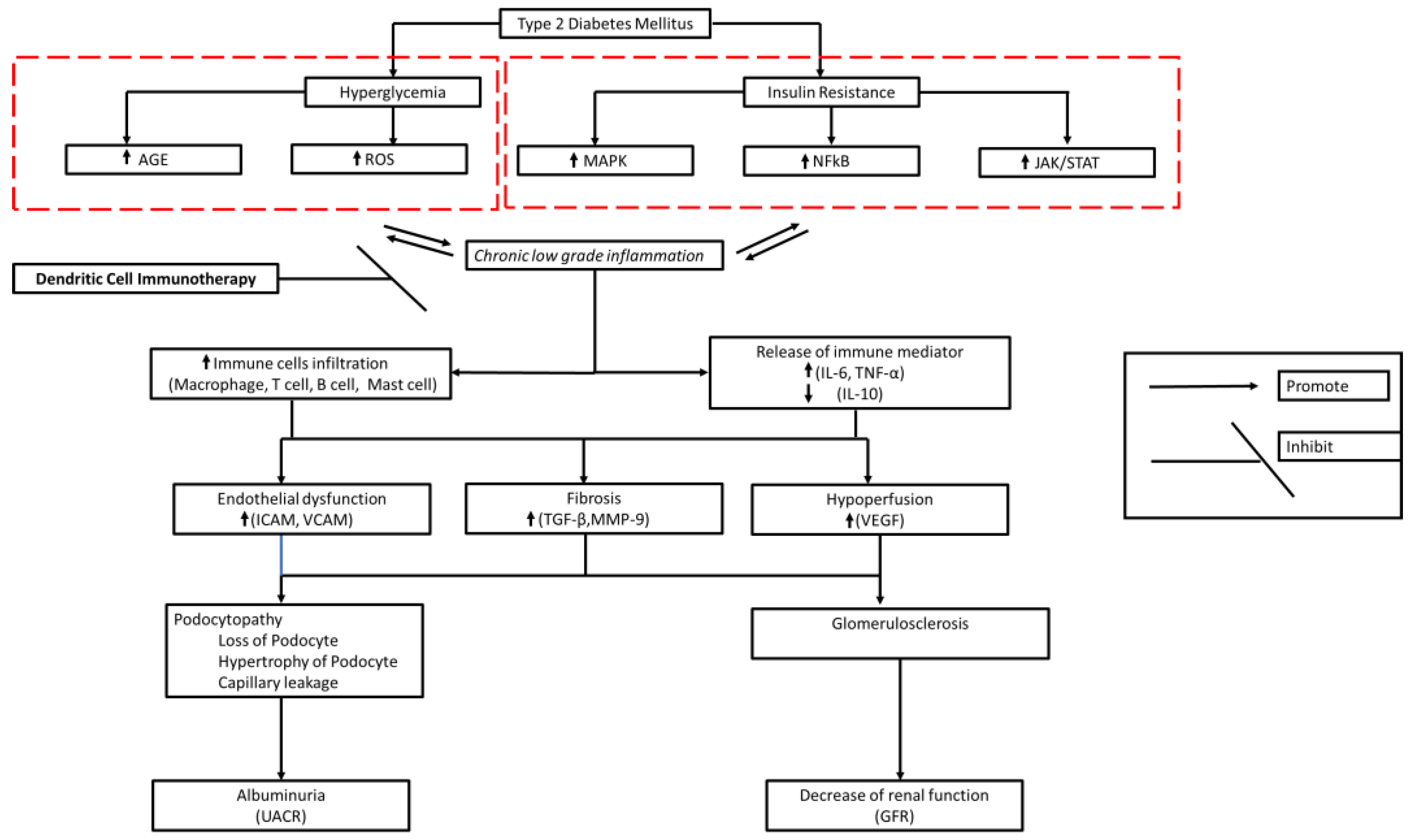
2. Diabetic Kidney Disease Immunopathology
3. The Role of DC in Inducing an Anti-Inflammatory Response
4. Ex Vivo Production of Autologous Dendritic Cells
5. Current State of Cell-Based Therapy for DKD
6. Autologous DC Mechanism of Action in DKD
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Selby, N.M.; Taal, M.W. An updated overview of diabetic nephropathy: Diagnosis, prognosis, treatment goals and latest guidelines. Diabetes, Obes. Metab. 2020, 22, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Li, N.; Wu, Y.; Wang, M.; Yang, S.; Zheng, Y.; Deng, X.; Xiang, D.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, P.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Diabetes-Related Chronic Kidney Disease From 1990 to 2019. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalantar-Zadeh K, Jafar TH, Nitsch D, Neuen BL, Perkovic V. Chronic kidney disease. The Lancet. 2021 Aug;398(10302):786–802. [CrossRef]
- Wada, J.; Makino, H. Inflammation and the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Clin. Sci. 2012, 124, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera-Chimal, J.; Jaisser, F. Pathophysiologic mechanisms in diabetic kidney disease: A focus on current and future therapeutic targets. Diabetes, Obes. Metab. 2020, 22, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikkawa R, Koya D, Haneda M. Progression of diabetic nephropathy. American Journal of Kidney Diseases. 2003 Mar;41(3):S19–21. [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.C.W.; Yiu, W.H. Innate immunity in diabetic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 206–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D'Marco, L.; Guerra-Torres, X.; Viejo, I.; Lopez-Romero, L.; Yugueros, A.; Bermúdez, V.; de Valencia, V.H.G.U.; de Asturias, M.H.U.P.; Bolívar, F.d.C.d.l.S.U.S. Non-albuminuric Diabetic Kidney Disease Phenotype: Beyond Albuminuria. Eur. Endocrinol. 2022, 18, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekinci, E.I.; Jerums, G.; Skene, A.; Crammer, P.; Power, D.; Cheong, K.Y.; Panagiotopoulos, S.; McNeil, K.; Baker, S.T.; Fioretto, P.; et al. Renal Structure in Normoalbuminuric and Albuminuric Patients With Type 2 Diabetes and Impaired Renal Function. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 3620–3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhalla, V.; Zhao, B.; Azar, K.M.; Wang, E.J.; Choi, S.; Wong, E.C.; Fortmann, S.P.; Palaniappan, L.P. Racial/Ethnic Differences in the Prevalence of Proteinuric and Nonproteinuric Diabetic Kidney Disease. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 1215–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeem, W.; Bakke, R.M.; Appel, S.; Øyan, A.M.; Kalland, K.-H. Dual Pro- and Anti-Inflammatory Features of Monocyte-Derived Dendritic Cells. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo S, Zhou Z. The clinical heterogeneity of diabetes challenges the accuracy of typing diagnosis | 糖尿病的临床异质性对精准分型诊断的挑战. Journal of Chinese Physician. 2022;24(2):179–83.
- Petrelli, A.; Giovenzana, A.; Insalaco, V.; Phillips, B.E.; Pietropaolo, M.; Giannoukakis, N. Autoimmune Inflammation and Insulin Resistance: Hallmarks So Far and Yet So Close to Explain Diabetes Endotypes. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2021, 21, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asfandiyarova, NS. TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS – AN AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE? Russian Journal of Immunology. 2020;23(1):9–18.
- Girard, D.; Vandiedonck, C. How dysregulation of the immune system promotes diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular risk complications. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 991716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lempesis, I.G.; E Georgakopoulou, V. Physiopathological mechanisms related to inflammation in obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus. World J. Exp. Med. 2023, 13, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitrofanova, A.; Fontanella, A.M.; Merscher, S.; Fornoni, A. Lipid deposition and metaflammation in diabetic kidney disease. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2020, 55, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, Y.; Wu, D.; Cai, Z.; Xu, Y.; Ding, X.; Wu, W.; Lan, S.; Chen, L.; Guo, Z.; Balmer, L.; et al. Supra-additive effect of chronic inflammation and atherogenic dyslipidemia on developing type 2 diabetes among young adults: a prospective cohort study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2023, 22, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thimmappa, P.Y.; Vasishta, S.; Ganesh, K.; Nair, A.S.; Joshi, M.B. Neutrophil (dys)function due to altered immuno-metabolic axis in type 2 diabetes: implications in combating infections. Hum. Cell 2023, 36, 1265–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohm TV, Meier DT, Olefsky JM, Donath MY. Inflammation in obesity, diabetes, and related disorders. Immunity. 2022;55(1):31–55.
- Lytrivi M, Igoillo-Esteve M, Cnop M. Inflammatory stress in islet β-cells: therapeutic implications for type 2 diabetes? Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2018;43:40–5.
- Shahid, R.; Chu, L.M.; Arnason, T.; Pahwa, P. Association Between Insulin Resistance and the Inflammatory Marker C-reactive Protein in a Representative Healthy Adult Canadian Population: Results From the Canadian Health Measures Survey. Can. J. Diabetes 2023, 47, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohm TV, Meier DT, Olefsky JM, Donath MY. Inflammation in obesity, diabetes, and related disorders. Immunity. 2022;55(1):31–55.
- Bandawane D, Pujari R, Upaganlawar A. High-fat diets and insulin resistance. Everything You Need to Know About High-Fat Diets. 2023. 213–230 p.
- Li, T.; Wang, P.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Feng, Y.; Wang, Q.; Guo, X.; et al. Inflammation and Insulin Resistance in Diabetic Chronic Coronary Syndrome Patients. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoorzad P, Mousavinasab F, Tofigh P, Kalahroud EM, Aghaei-Zarch SM, Salehi A, et al. Understanding the lncRNA/miRNA-NFκB regulatory network in diabetes mellitus: From function to clinical translation. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2023;202.
- Meyerovich K, Ortis F, Cardozo AK. The non-canonical NF-κB pathway and its contribution to β-cell failure in diabetes. J Mol Endocrinol. 2018;61(2):F1–6.
- Chen X, Liu Z, Liu W, Wang S, Jiang R, Hu K, et al. NF-κB-Inducing Kinase Provokes Insulin Resistance in Skeletal Muscle of Obese Mice. Inflammation. 2023;46(4):1445–57.
- Singh L, Bhatti R. Cellular and molecular mechanisms involved in metabolic disorders. Drug Delivery Systems for Metabolic Disorders. 2022. 21–29 p.
- Lourido, F.; Quenti, D.; Salgado-Canales, D.; Tobar, N. Domeless receptor loss in fat body tissue reverts insulin resistance induced by a high-sugar diet in Drosophila melanogaster. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh L, Bhatti R. Cellular and molecular mechanisms involved in metabolic disorders. Drug Delivery Systems for Metabolic Disorders. 2022. 21–29 p.
- Li, T.; Yang, X.; Zhu, J.; Liu, Y.; Jin, X.; Chen, G.; Ye, L. Current application status and structure–activity relationship of selective and non-selective JAK inhibitors in diseases. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 122, 110660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lourido, F.; Quenti, D.; Salgado-Canales, D.; Tobar, N. Domeless receptor loss in fat body tissue reverts insulin resistance induced by a high-sugar diet in Drosophila melanogaster. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, Q.; He, J.; Li, Y. Immune responses in diabetic nephropathy: Pathogenic mechanisms and therapeutic target. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 958790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Q.; Zhou, J.; Lin, H. The landscape of immune cell infiltration in the glomerulus of diabetic nephropathy: evidence based on bioinformatics. BMC Nephrol. 2022, 23, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, T.; Huang, T.; Lang, Y.; Sheng, Q.; Liu, Y.; Kong, Z.; Gao, Y.; Lu, S.; et al. T cells and their products in diabetic kidney disease. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1084448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rico Fontalvo J, Aroca-Martínez G, Daza-Arnedo R, Raad-Sarabia M, Luis Torres J, Pajaro-Galvis N, et al. Non-proteinuric diabetic kidney disease: State of art | Enfermedad renal diabética no proteinúrica: Estado del arte. Revista de Nefrologia, Dialisis y Trasplante. 2022;42(4):330–9.
- Lis-López L, Bauset C, Seco-Cervera M, Cosín-Roger J. Is the macrophage phenotype determinant for fibrosis development? Biomedicines. 2021;9(12).
- Bell RMB, Conway BR. Macrophages in the kidney in health, injury and repair. Vol. 367, International Review of Cell and Molecular Biology. 2022. 101–147 p.
- Chen, A.; Lee, K.; He, J.C. Treating crescentic glomerulonephritis by targeting macrophages. Kidney Int. 2022, 102, 1212–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, J.-H.; Li, D.-Y.; Liang, S.; Yang, C.; Tang, J.-X.; Liu, H.-F. Macrophage autophagy in macrophage polarization, chronic inflammation and organ fibrosis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 946832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui J, Bai X, Chen X. Autophagy and glomerular diseases. Vol. 1207, Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. 2020. 481–486 p.
- Moon, J.-Y.; Jeong, K.-H.; Lee, T.-W.; Ihm, C.-G.; Lim, S.J.; Lee, S.-H. Aberrant Recruitment and Activation of T Cells in Diabetic Nephropathy. Am. J. Nephrol. 2012, 35, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bending, J.J.; Lobo-Yeo, A.; Vergani, D.; Viberti, G.C. Proteinuria and activated T-lymphocytes in diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes 1988, 37, 507–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriya, R.; Manivel, J.C.; Mauer, M. Juxtaglomerular apparatus T-cell infiltration affects glomerular structure in Type 1 diabetic patients. Diabetologia 2004, 47, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, L.; Andrikopoulos, S.; MacIsaac, R.J.; Mackay, L.K.; Nikolic-Paterson, D.J.; Torkamani, N.; Zafari, N.; Marin, E.C.S.; I Ekinci, E. Role of the adaptive immune system in diabetic kidney disease. J. Diabetes Investig. 2021, 13, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, T.; Huang, T.; Lang, Y.; Sheng, Q.; Liu, Y.; Kong, Z.; Gao, Y.; Lu, S.; et al. T cells and their products in diabetic kidney disease. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1084448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Lei, C.-T.; Zhang, C. Interleukin-6 Signaling Pathway and Its Role in Kidney Disease: An Update. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.E.; O'Keefe, R.A.; Grandis, J.R. Targeting the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signalling axis in cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo HA, Kim JY, Yang SH, Han SS, Joo KW, Kim YS, et al. The role of local IL6/JAK2/STAT3 signaling in high glucose–induced podocyte hypertrophy. Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2016 Dec;35(4):212–8.
- Yin L, Yu L, He JC, Chen A. Controversies in Podocyte Loss: Death or Detachment? Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Nov 22;9.
- Cha, D.R. Interleukin-6 signaling in podocyte hypertrophy. Kidney Res. Clin. Pr. 2016, 35, 195–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, T.; Huang, T.; Lang, Y.; Sheng, Q.; Liu, Y.; Kong, Z.; Gao, Y.; Lu, S.; et al. T cells and their products in diabetic kidney disease. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1084448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coletta I, Soldo L, Polentarutti N, Mancini F, Guglielmotti A, Pinza M, et al. Selective Induction of MCP-1 in Human Mesangial Cells by the IL-6/sIL-6R Complex. Nephron Exp Nephrol. 2000 Jan 14;8(1):37–43.
- Thomas, H.Y.; Versypt, A.N.F. Pathophysiology of mesangial expansion in diabetic nephropathy: mesangial structure, glomerular biomechanics, and biochemical signaling and regulation. J. Biol. Eng. 2022, 16, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barutta, F.; Bruno, G.; Grimaldi, S.; Gruden, G. Inflammation in diabetic nephropathy: moving toward clinical biomarkers and targets for treatment. Endocrine 2014, 48, 730–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idriss HT, Naismith JH. TNF Alpha and the TNF receptor superfamily: Structure-function relationship(s). Microsc Res Tech. 2000 Aug 1;50(3):184–95.
- Braga Gomes K, Fontana Rodrigues K, Fernandes AP. The Role of Transforming Growth Factor-Beta in Diabetic Nephropathy. International Journal of Medical Genetics. 2014 Jan 28;2014(2):1–6.
- Gu, Y.-Y.; Liu, X.-S.; Huang, X.-R.; Yu, X.-Q.; Lan, H.-Y. Diverse Role of TGF-β in Kidney Disease. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, R.; Xu, S.; Quan, X.; Nguyen, T.T.; Kong, I.D.; Chung, C.H.; Lee, E.Y.; Cha, S.-K.; Park, K.-S. Upregulation of mitochondrial Nox4 mediates TGF-β-induced apoptosis in cultured mouse podocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2014, 306, F155–F167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pestka, S.; Krause, C.D.; Sarkar, D.; Walter, M.R.; Shi, Y.; Fisher, P.B. Interleukin-10andRelatedCytokines andReceptors. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 22, 929–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran-Salgado, M.B. Diabetic nephropathy and inflammation. World J. Diabetes 2014, 5, 393–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naz, S.; Shafique, N.; Sharif, S.; Manzoor, F.; Saifi, S.Z.; Firasat, S.; Kaul, H. Association of Interleukin 10 (IL-10) Gene with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus by Single Nucleotide Polymorphism of Its Promotor Region G/A 1082. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 2020, 30, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barry, J.C.; Shakibakho, S.; Durrer, C.; Simtchouk, S.; Jawanda, K.K.; Cheung, S.T.; Mui, A.L.; Little, J.P. Hyporesponsiveness to the anti-inflammatory action of interleukin-10 in type 2 diabetes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samsu, N. Diabetic Nephropathy: Challenges in Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, L.C.; Kim, A.Y.; Curley, S.P.; Chen, X.; Dworkin, L.D.; Cooper, C.J.; Gupta, R. Interleukin-10 attenuates renal injury after myocardial infarction in diabetes. J. Investig. Med. 2022, 70, 1233–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, H.; Shou, S. The role of IL-10 in kidney disease. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 108, 108917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, H.; Shou, S. The role of IL-10 in kidney disease. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 108, 108917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenz, O.; Fornoni, A.; Ijaz, A.; Tejada, T. Role of Inflammation in Diabetic Nephropathy. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2008, 4, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, S.; Shikata, K.; Matsuda, M.; Ogawa, D.; Usui, H.; Kido, Y.; Nagase, R.; Wada, J.; Shikata, Y.; Makino, H. Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1–Deficient Mice Are Resistant Against Renal Injury After Induction of Diabetes. Diabetes 2003, 52, 2586–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, F.Y.; Nikolic-Paterson, D.J.; Ozols, E.; Atkins, R.C.; Tesch, G.H. Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1 Deficiency Is Protective against Nephropathy in Type 2 Diabetic db/db Mice. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 1711–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Ishibashi, M.; Hiasa, K.-I.; Tan, C.; Takeshita, A.; Egashira, K.; S, F.; K, E.; T, K.; T, O.; et al. Essential Role of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Angiotensin II–Induced Vascular Inflammation and Remodeling. Hypertension 2004, 44, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhruddin, S.; Alanazi, W.; Jackson, K.E. Diabetes-Induced Reactive Oxygen Species: Mechanism of Their Generation and Role in Renal Injury. J. Diabetes Res. 2017, 2017, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giri, B.; Dey, S.; Das, T.; Sarkar, M.; Banerjee, J.; Dash, S.K. Chronic hyperglycemia mediated physiological alteration and metabolic distortion leads to organ dysfunction, infection, cancer progression and other pathophysiological consequences: An update on glucose toxicity. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 107, 306–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassén, E.; Daehn, I.S. Molecular Mechanisms in Early Diabetic Kidney Disease: Glomerular Endothelial Cell Dysfunction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinlan, C.; Rheault, M.N. Genetic Basis of Type IV Collagen Disorders of the Kidney. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 16, 1101–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabluchanskiy, A.; Ma, Y.; Iyer, R.P.; Hall, M.E.; Lindsey, M.L. Matrix Metalloproteinase-9: Many Shades of Function in Cardiovascular Disease. Physiology 2013, 28, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Chen, H.; Liu, F.; Ma, Q. Up-regulation of matrix metalloproteinases-9 in the kidneys of diabetic rats and the association with neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin. BMC Nephrol. 2021, 22, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcos-Sacramento VG, Sampieri CL, Sandoval-Lozano VH, Orozco-Ortega RA, Acuña-Hernández MA, Morales-Romero J, et al. Urinary MMP-9/UCr association with albumin concentration and albumin-creatinine-ratio in Mexican patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. PeerJ. 2020 Dec 16;8:e10474.
- Li, Y.; Jin, L.; Yan, J.; Zhang, H.; Hu, C. CD28 Genetic Variants Increase Susceptibility to Diabetic Kidney Disease in Chinese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Case Control Study. Mediat. Inflamm. 2021, 2021, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, P.; Li, X.; Dong, Y.; Wu, S.; Xu, M.; Chen, X.; Wang, S.; Zheng, C.; Zou, C. Combination CTLA-4 immunoglobulin treatment and ultrasound microbubble-mediated exposure improve renal function in a rat model of diabetic nephropathy. Aging 2021, 13, 8524–8540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera, M.; Söderberg, M.; Sabirsh, A.; Valastro, B.; Mölne, J.; Santamaria, B.; Valverde, A.M.; Guionaud, S.; Heasman, S.; Bigley, A.; et al. Inhibition of T-cell activation by the CTLA4-Fc Abatacept is sufficient to ameliorate proteinuric kidney disease. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2017, 312, F748–F759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou CP, Li XY, Wei KN, Yang Y, Zhao YZ, Wang P, et al. Therapeutic effects of CTLA-4-Ig on diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus rats ascribed to protection of CTLA-4-Ig on podocytes. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2018;11(10):10516–25.
- Chen, J.; Liu, Q.; He, J.; Li, Y. Immune responses in diabetic nephropathy: Pathogenic mechanisms and therapeutic target. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 958790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey, F.B.; Martin, F. Role of the Immune System in Diabetic Kidney Disease. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2018, 18, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balan S, Saxena M, Bhardwaj N. Dendritic cell subsets and locations. 1st ed. Vol. 348, International Review of Cell and Molecular Biology. Elsevier Inc.; 2019. 1–68 p.
- Saadeh, D.; Kurban, M.; Abbas, O. Update on the role of plasmacytoid dendritic cells in inflammatory/autoimmune skin diseases. Exp. Dermatol. 2016, 25, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, H.; Arimura, K.; Uto, T.; Fukaya, T.; Nakamura, T.; Choijookhuu, N.; Hishikawa, Y.; Sato, K. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells orchestrate TLR7-mediated innate and adaptive immunity for the initiation of autoimmune inflammation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24477–24477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kisielow, P. How does the immune system learn to distinguish between good and evil? The first definitive studies of T cell central tolerance and positive selection. Immunogenetics 2019, 71, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macri C, Pang ES, Patton T, O’Keeffe M. Dendritic cell subsets. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2018;84:11–21.
- Kim, M.K.; Kim, J. Properties of immature and mature dendritic cells: phenotype, morphology, phagocytosis, and migration. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 11230–11238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ugur, M.; Mueller, S.N. T cell and dendritic cell interactions in lymphoid organs: More than just being in the right place at the right time. Immunol. Rev. 2019, 289, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilligan, K.L.; Ronchese, F. Antigen presentation by dendritic cells and their instruction of CD4+ T helper cell responses. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 17, 587–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roche, P.A.; Cresswell, P. Antigen Processing and Presentation Mechanisms in Myeloid Cells. Microbiol. Spectr. 2016, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golubovskaya V, Wu L. Different Subsets of T Cells, Memory, Effector Functions, and CAR-T Immunotherapy. Cancers (Basel). 2016 Mar 15;8(3):36.
- Park C, Choi YS. How do follicular dendritic cells interact intimately with B cells in the germinal centre? Immunology. 2005 Jan 16;114(1):2–10.
- Passeri, L.; Marta, F.; Bassi, V.; Gregori, S. Tolerogenic Dendritic Cell-Based Approaches in Autoimmunity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comi, M.; Avancini, D.; de Sio, F.S.; Villa, M.; Uyeda, M.J.; Floris, M.; Tomasoni, D.; Bulfone, A.; Roncarolo, M.G.; Gregori, S. Coexpression of CD163 and CD141 identifies human circulating IL-10-producing dendritic cells (DC-10). Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 17, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boks MA, Kager-Groenland JR, Haasjes MSP, Zwaginga JJ, van Ham SM, ten Brinke A. IL-10-generated tolerogenic dendritic cells are optimal for functional regulatory T cell induction — A comparative study of human clinical-applicable DC. Clinical Immunology. 2012 Mar;142(3):332–42.
- Bakdash, G.; Vogelpoel, L.T.; van Capel, T.M.; Kapsenberg, M.; de Jong, E. Retinoic acid primes human dendritic cells to induce gut-homing, IL-10-producing regulatory T cells. Mucosal Immunol. 2015, 8, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morante-Palacios, O.; Fondelli, F.; Ballestar, E.; Martínez-Cáceres, E.M. Tolerogenic Dendritic Cells in Autoimmunity and Inflammatory Diseases. Trends Immunol. 2020, 42, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochando, J.; Ordikhani, F.; Jordan, S.; Boros, P.; Thomson, A.W. Tolerogenic dendritic cells in organ transplantation. Transpl. Int. 2019, 33, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manicassamy, S.; Pulendran, B. Dendritic cell control of tolerogenic responses. Immunol. Rev. 2011, 241, 206–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, E.H.; Lee, J.-H.; Park, E.-H.; Park, H.E.; Jung, N.-C.; Kim, T.-H.; Koh, Y.-S.; Kim, E.; Seung, K.-B.; Park, C.; et al. Infarcted Myocardium-Primed Dendritic Cells Improve Remodeling and Cardiac Function After Myocardial Infarction by Modulating the Regulatory T Cell and Macrophage Polarization. Circ. 2017, 135, 1444–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung DJ, Sharma S, Rangesa M, DeWolf S, Elhanati Y, Perica K, et al. Langerhans dendritic cell vaccine bearing mRNA-encoded tumor antigens induces antimyeloma immunity after autotransplant. Blood Adv. 2022 Mar 8;6(5):1547–58.
- Constantino, J.; Gomes, C.; Falcão, A.; Neves, B.M.; Cruz, M.T. Dendritic cell-based immunotherapy: a basic review and recent advances. Immunol. Res. 2017, 65, 798–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino K, Long MD, Kajihara R, Matsueda S, Oba T, Kanehira K, et al. Generation of cDC-like cells from human induced pluripotent stem cells via Notch signaling. J Immunother Cancer. 2022 Jan 31;10(1):e003827.
- Sung SSJ. Monocyte-Derived Dendritic Cells as Antigen-Presenting Cells in T-Cell Proliferation and Cytokine Production. In 2019. p. 131–41. Available from: http://link.springer.com/10. 1007.
- Sung SSJ. Monocyte-Derived Dendritic Cells as Antigen-Presenting Cells in T-Cell Proliferation and Cytokine Production. In 2019. p. 131–41.
- Bhattacharya, P.; Thiruppathi, M.; Elshabrawy, H.A.; Alharshawi, K.; Kumar, P.; Prabhakar, B.S. GM-CSF: An immune modulatory cytokine that can suppress autoimmunity. Cytokine 2015, 75, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cechim, G.; Chies, J.A. In vitro generation of human monocyte-derived dendritic cells methodological aspects in a comprehensive review. An. da Acad. Bras. de Cienc. 2019, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.J.; Lo, Y.; Luk, D.; Lau, C.S.; Lu, L.; Mok, M.Y. Alternatively activated dendritic cells derived from systemic lupus erythematosus patients have tolerogenic phenotype and function. Clin. Immunol. 2015, 156, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmaeili, S.; Mahmoudi, M.; Rezaieyazdi, Z.; Sahebari, M.; Tabasi, N.; Sahebkar, A.; Rastin, M. Generation of tolerogenic dendritic cells using Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Lactobacillus delbrueckii as tolerogenic probiotics. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 7865–7872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li CH, Zhang J, Baylink DJ, Wang X, Goparaju NB, Xu Y, et al. Dendritic cells, engineered to overexpress 25-hydroxyvitamin D 1α-hydroxylase and pulsed with a myelin antigen, provide myelin-specific suppression of ongoing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. FASEB Journal. 2017;31(7):2996–3006.
- Lo, J.; Xia, C.-Q.; Peng, R.; Clare-Salzler, M.J. Immature Dendritic Cell Therapy Confers Durable Immune Modulation in an Antigen-Dependent and Antigen-Independent Manner in Nonobese Diabetic Mice. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonny, J.; Putranto, T.A.; Sitepu, E.C.; Irfon, R. Dendritic cell vaccine as a potential strategy to end the COVID-19 pandemic. Why should it be Ex Vivo? Expert Rev. Vaccines 2022, 21, 1111–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubský, M.; Jirkovská, A.; Bem, R.; Němcová, A.; Fejfarová, V.; Hazdrová, J.; Sutoris, K.; Chlupáč, J.; Skibová, J.; Jude, E.B. Impact of severe diabetic kidney disease on the clinical outcome of autologous cell therapy in people with diabetes and critical limb ischaemia. Diabet. Med. 2019, 36, 1133–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, A.F.; Tang, T.Y.; Jin, A.; Chong, T.T.; Hausenloy, D.J.; Koh, W.-P. Diabetes and other vascular risk factors in association with the risk of lower extremity amputation in chronic limb-threatening ischemia: a prospective cohort study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2022, 21, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Gao, M.; Wang, W.; Chen, K.; Huang, L.; Liu, Y. Diabetic vascular diseases: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, N.; Scholtemeijer, M.; Shah, K. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Immunomodulation: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 41, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickson, L.J.; Abedalqader, T.; Ben-Bernard, G.; Mondy, J.M.; Bian, X.; Conley, S.M.; Zhu, X.; Herrmann, S.M.; Kukla, A.; Lorenz, E.C.; et al. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Cell-Based Interventions in Experimental Diabetic Kidney Disease. STEM CELLS Transl. Med. 2021, 10, 1304–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packham, D.K.; Fraser, I.R.; Kerr, P.G.; Segal, K.R. Allogeneic Mesenchymal Precursor Cells (MPC) in Diabetic Nephropathy: A Randomized, Placebo-controlled, Dose Escalation Study. EBioMedicine 2016, 12, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sávio-Silva, C.; Beyerstedt, S.; Soinski-Sousa, P.E.; Casaro, E.B.; Balby-Rocha, M.T.A.; Simplício-Filho, A.; Alves-Silva, J.; Rangel. B. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy for Diabetic Kidney Disease: A Review of the Studies Using Syngeneic, Autologous, Allogeneic, and Xenogeneic Cells. Stem Cells Int. 2020, 2020, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waisman, A.; Lukas, D.; Clausen, B.E.; Yogev, N. Dendritic cells as gatekeepers of tolerance. Semin. Immunopathol. 2016, 39, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Coillie S, Wiernicki B, Xu J. Molecular and Cellular Functions of CTLA-4. In 2020. p. 7–32.
- Thomas MC, Brownlee M, Susztak K, Sharma K, Jandeleit-Dahm KAM, Zoungas S. Diabetic kidney disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 30;1(1):15018.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




