Submitted:
10 July 2024
Posted:
11 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Instruments
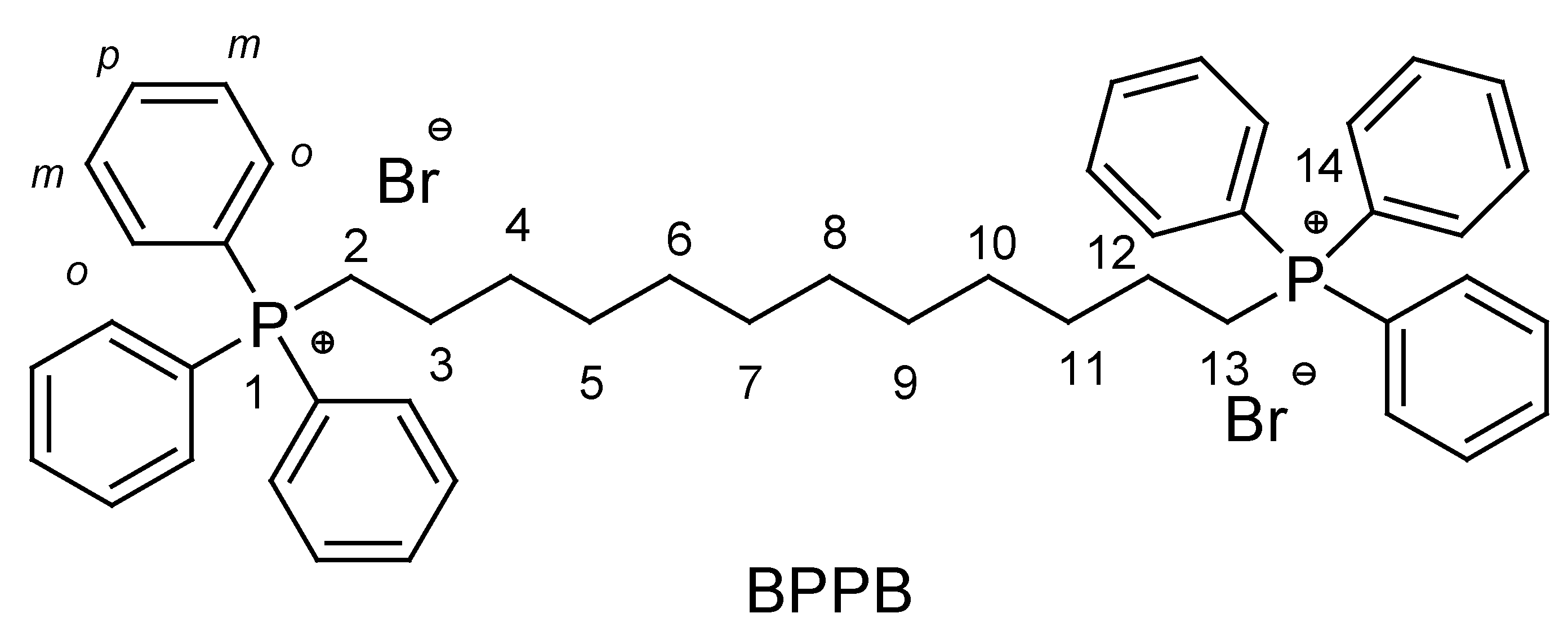
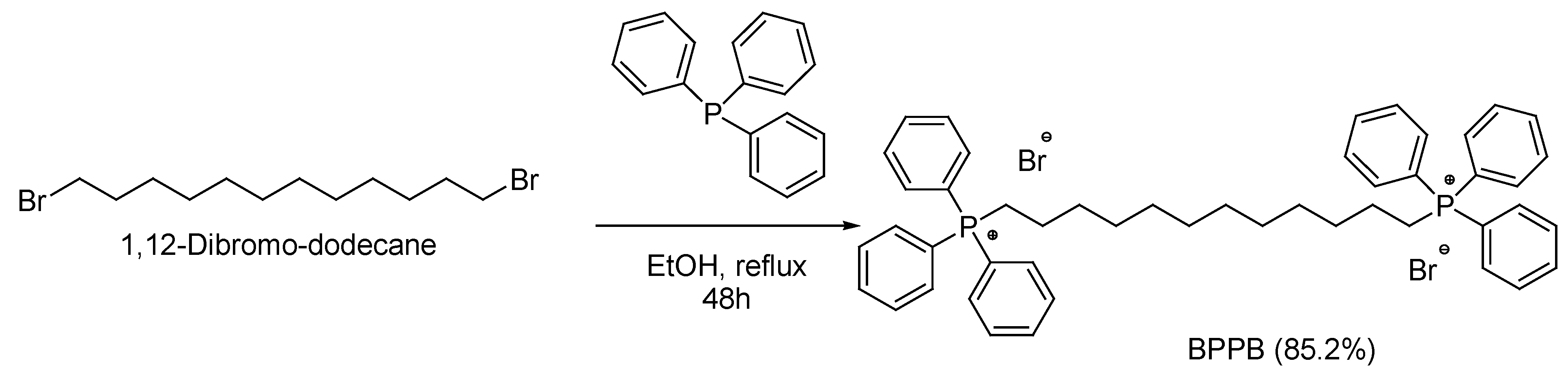
2.2. Synthesis of 1,1-(1,12-dodecanediyl)bis [1,1,1]-triphenylphosphonium di-Bromide (BPPB)
2.3. UV-Vis Analyses
2.4. Potentiometric Titration of BPPB
2.4.1. Preparation of 0.1 M Perchloric Acid Volumetric Solution
2.5. Optical Microscopy Analyses
2.6. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) Analysis
2.7. Microbiology
2.7.1. Microorganisms
2.7.2. Determination of the MICs
2.7.3. Killing Curves
2.8. Concentration-Dependent Cytotoxicity Experiments: MTT and LHD Tests
2.8.1. MTT cytotoxicity assay
2.8.2. LDH cytotoxicity assay
2.8.3. Statistics
3. Results and Discussion
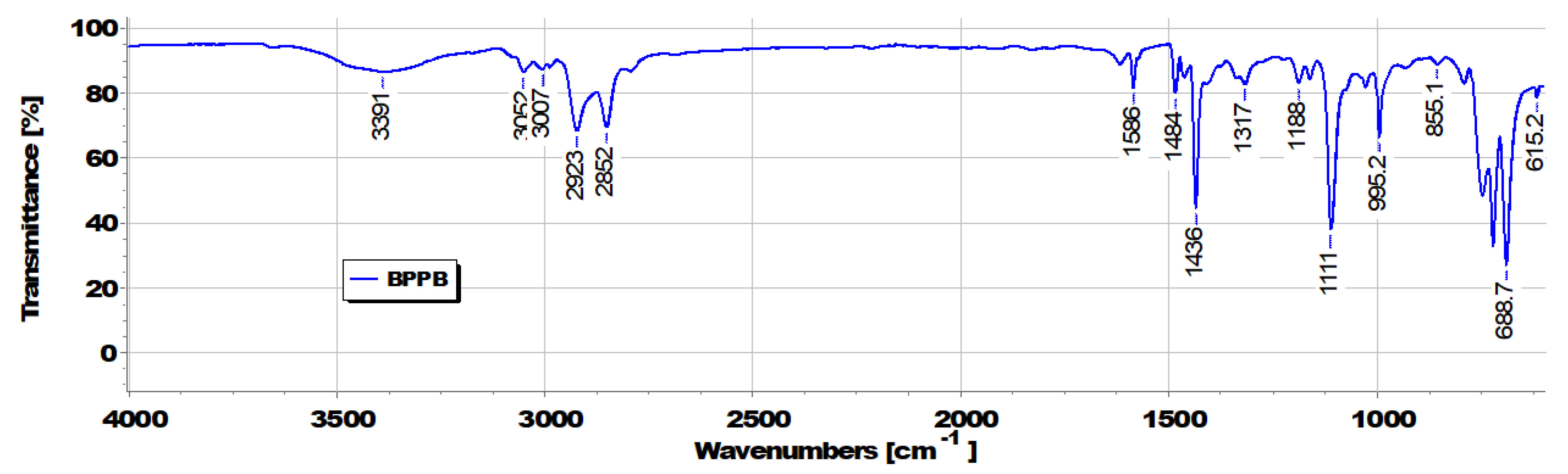
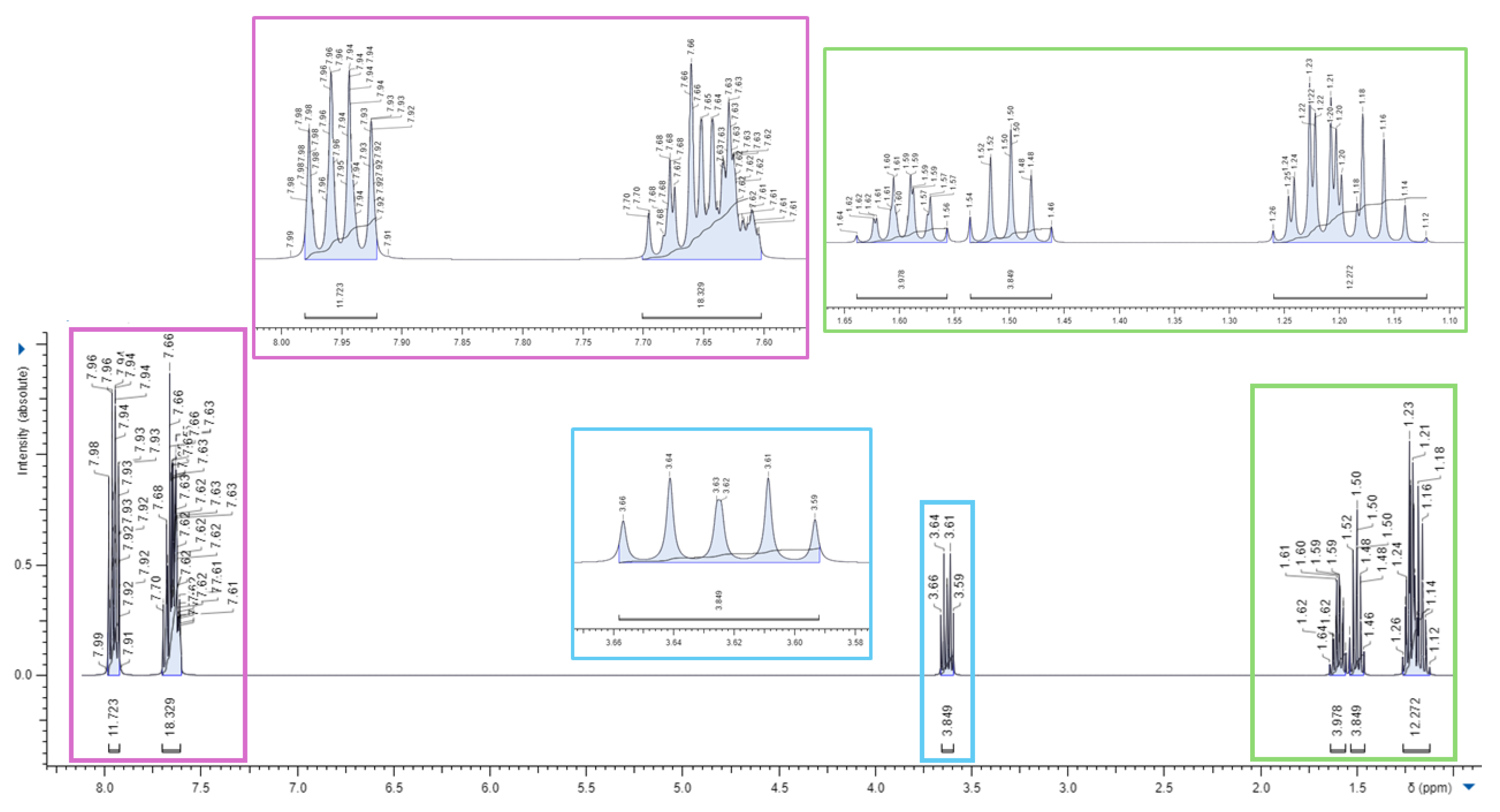
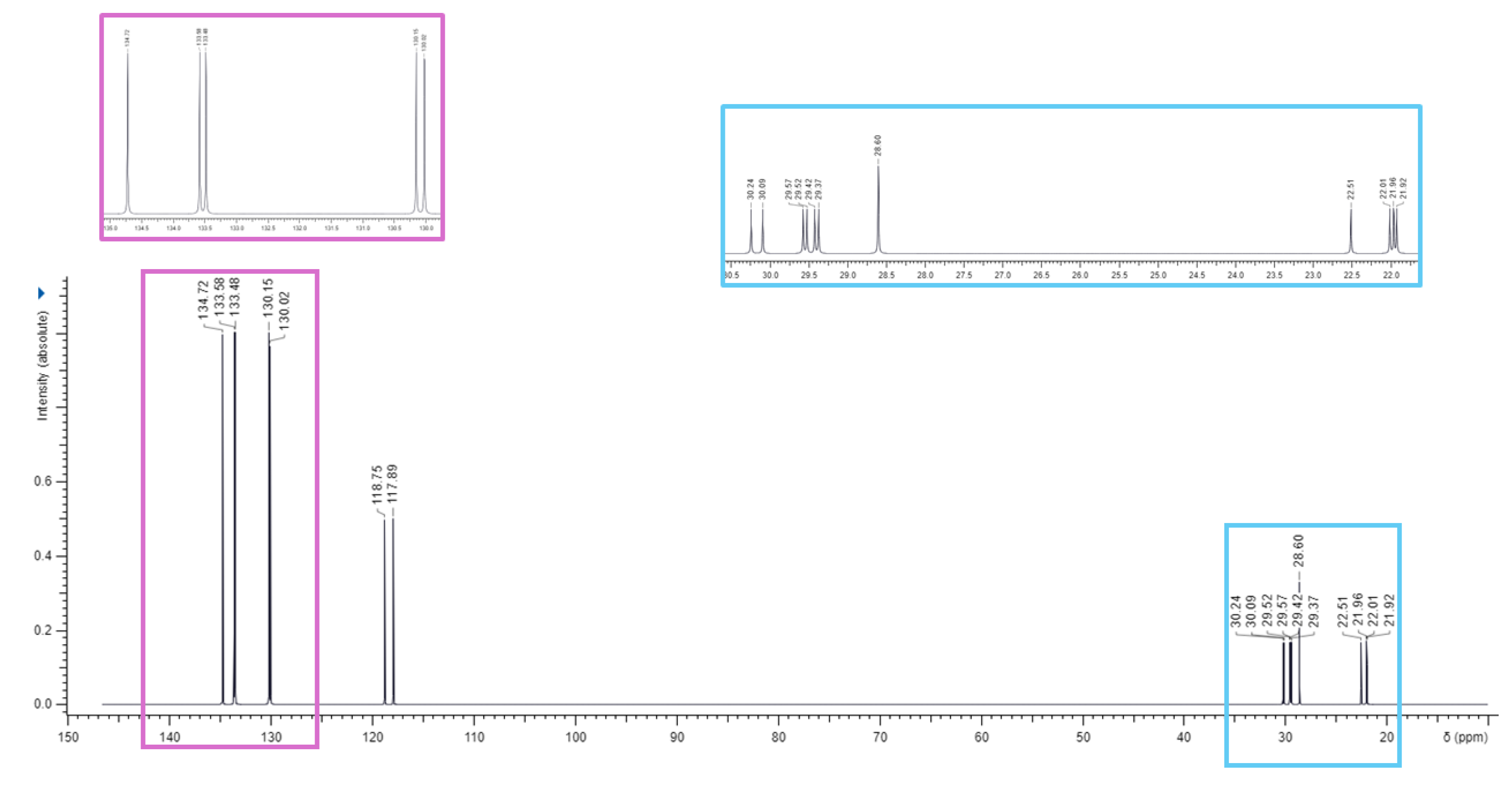
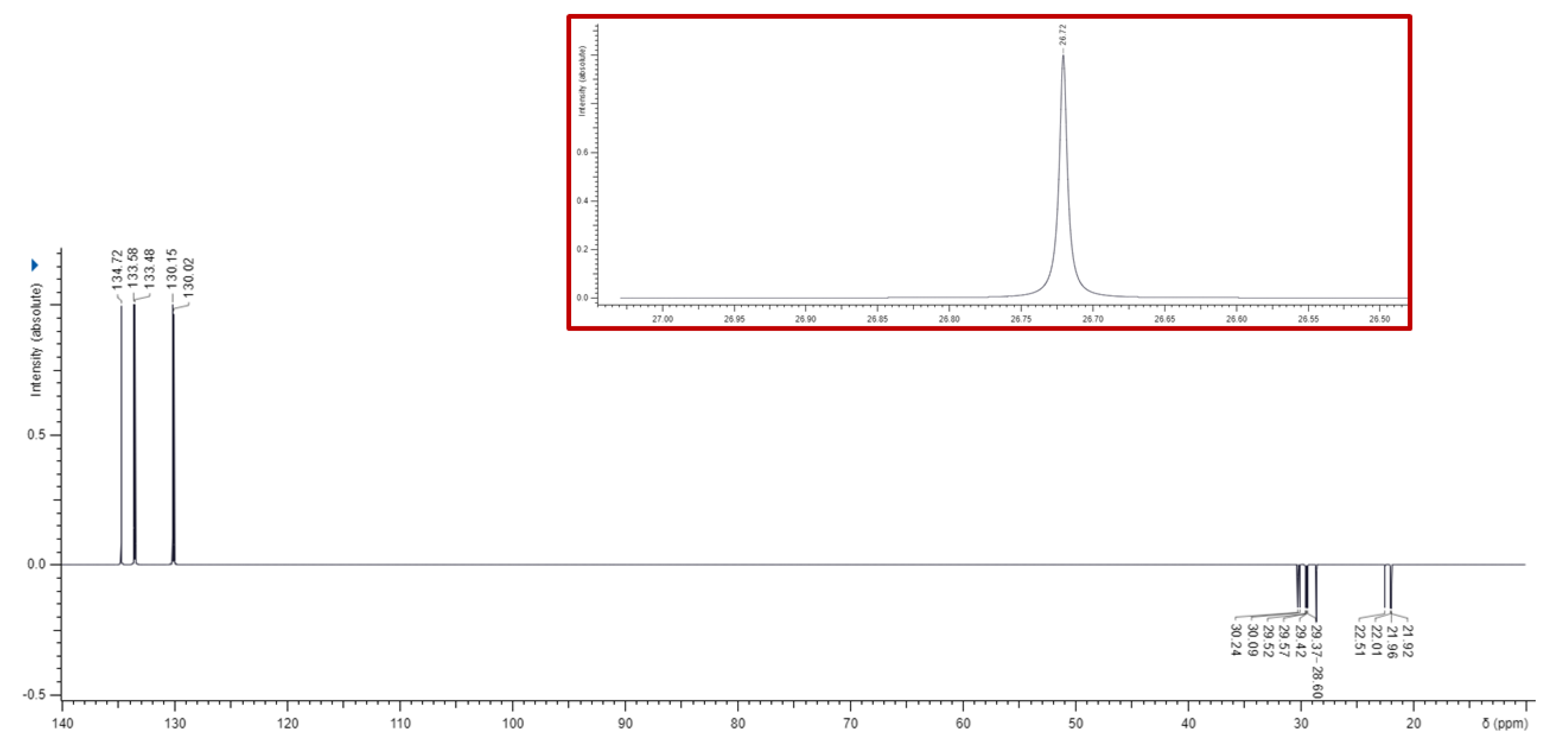
3.1. Synthesis of 1,1-(1,12-dodecanediyl)bis [1,1,1]-triphenylphosphonium di-Bromide (BPPB)
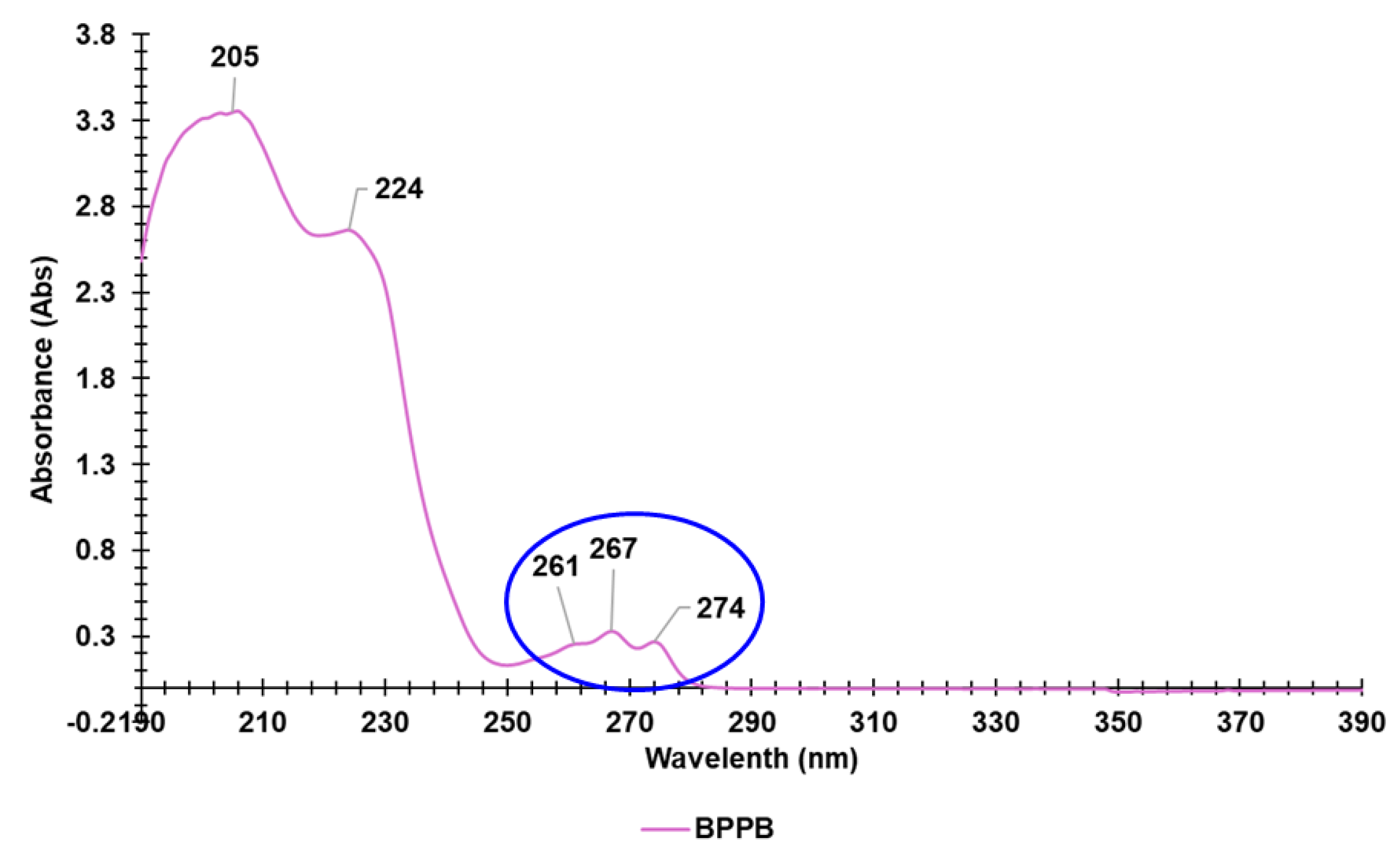
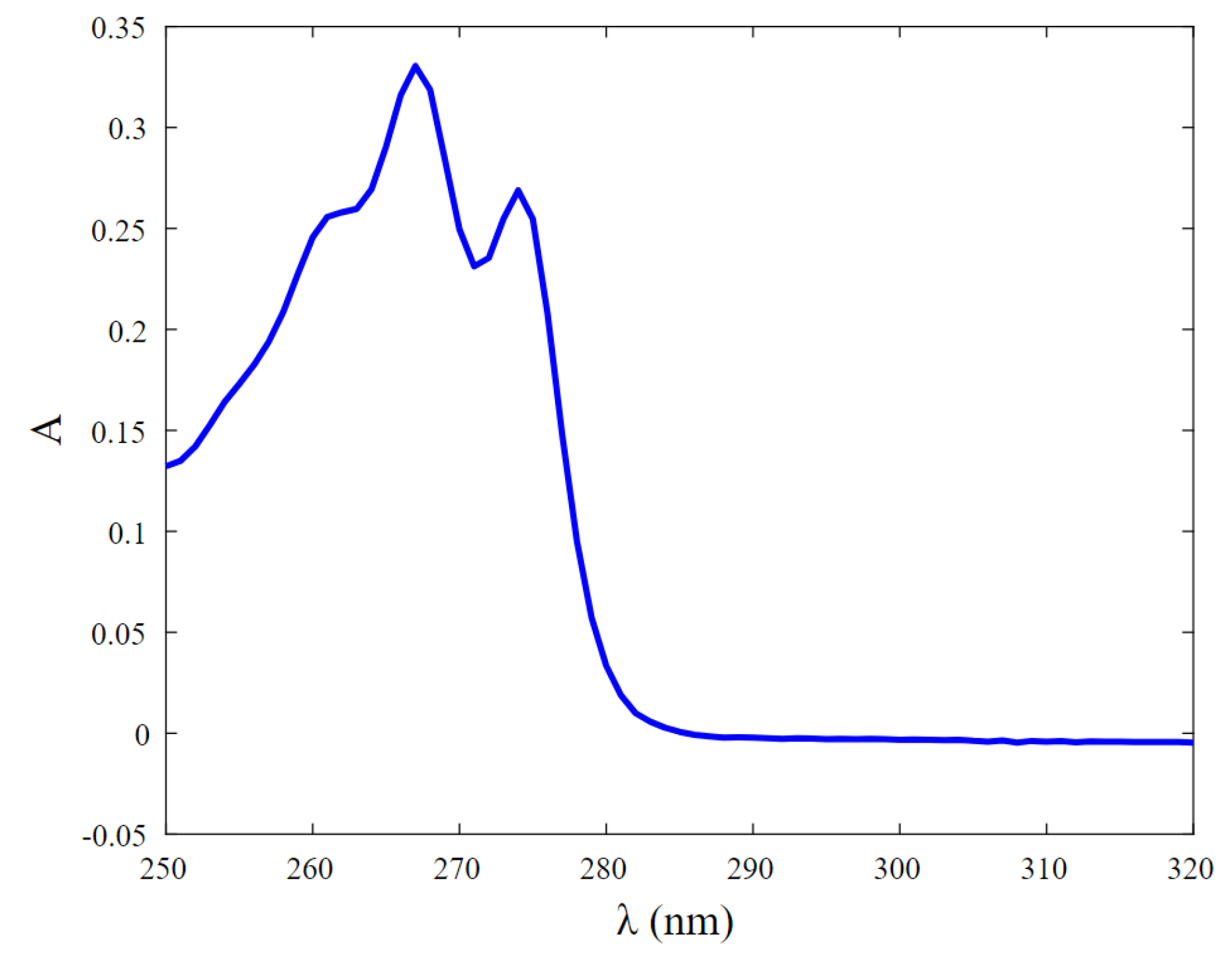
3.2. UV-Vis Analyses
3.3. Potentiometric Titration of BPPB in Non-Aqueous Medium
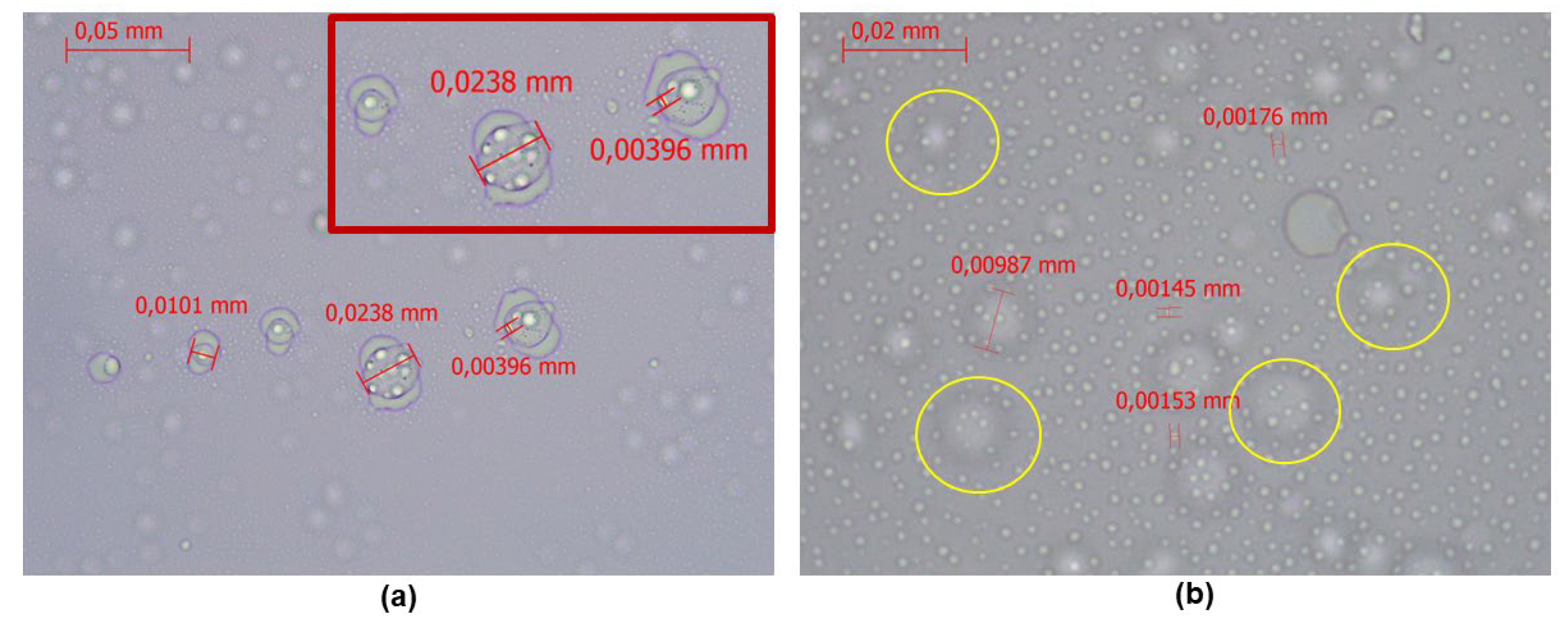
3.4. Optical Microscopy Results
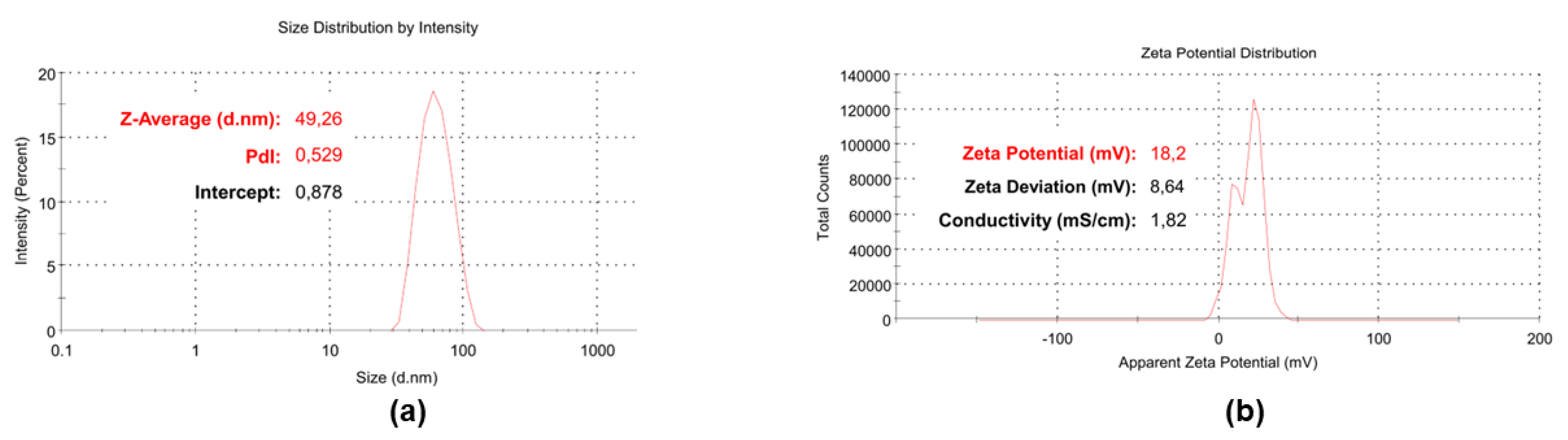
3.5. Particle Size, ζ-p and PDI of BPPB
3.6. Antibacterial Properties
3.6.1. In Vitro Antibacterial Activity of BPPB: Determination of MIC Values (MICs)
- An Overview of Previous Achievements by Using Antibacterial Phosphonium Salts
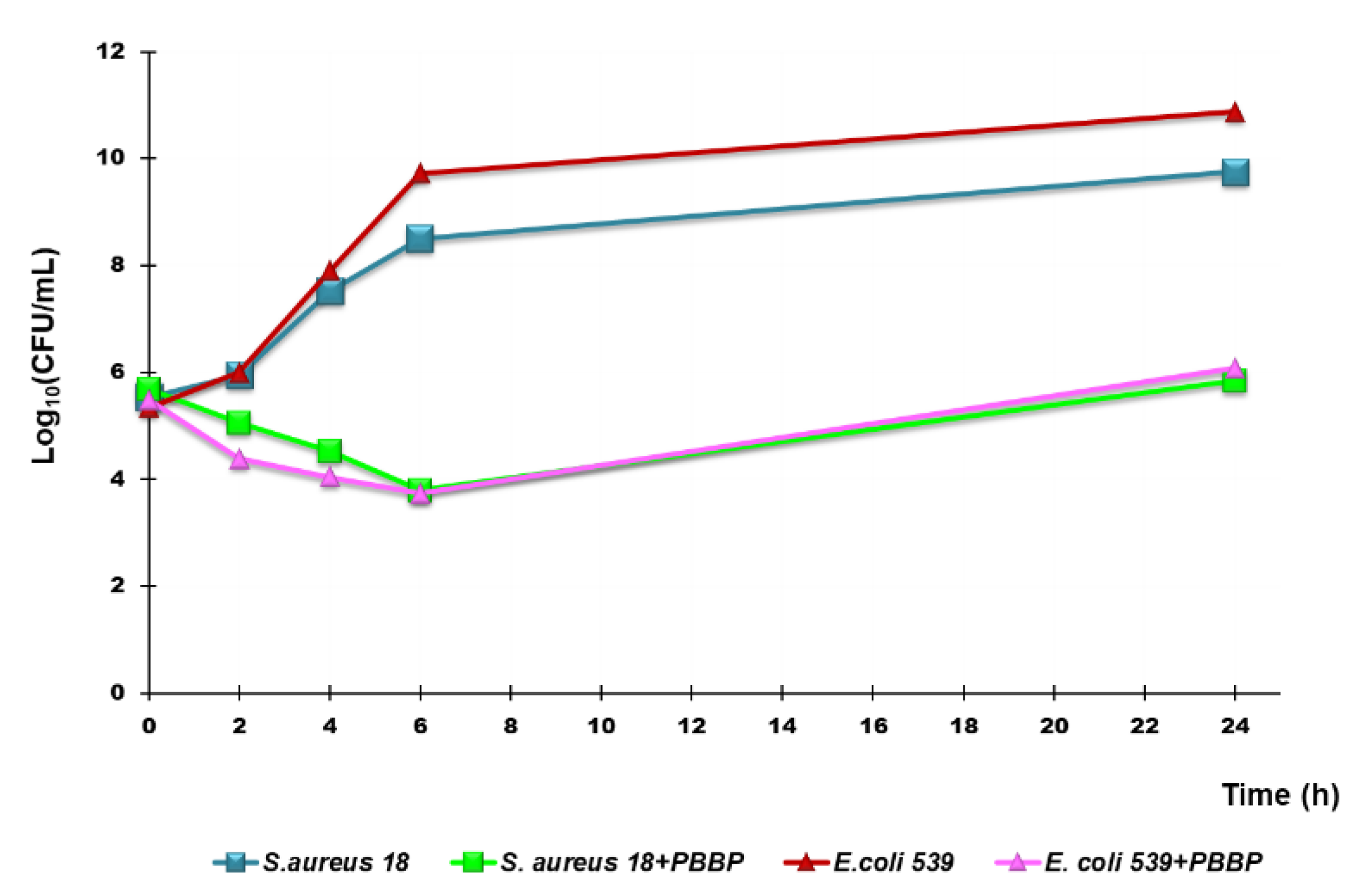
3.6.2. Time-Killing Curves
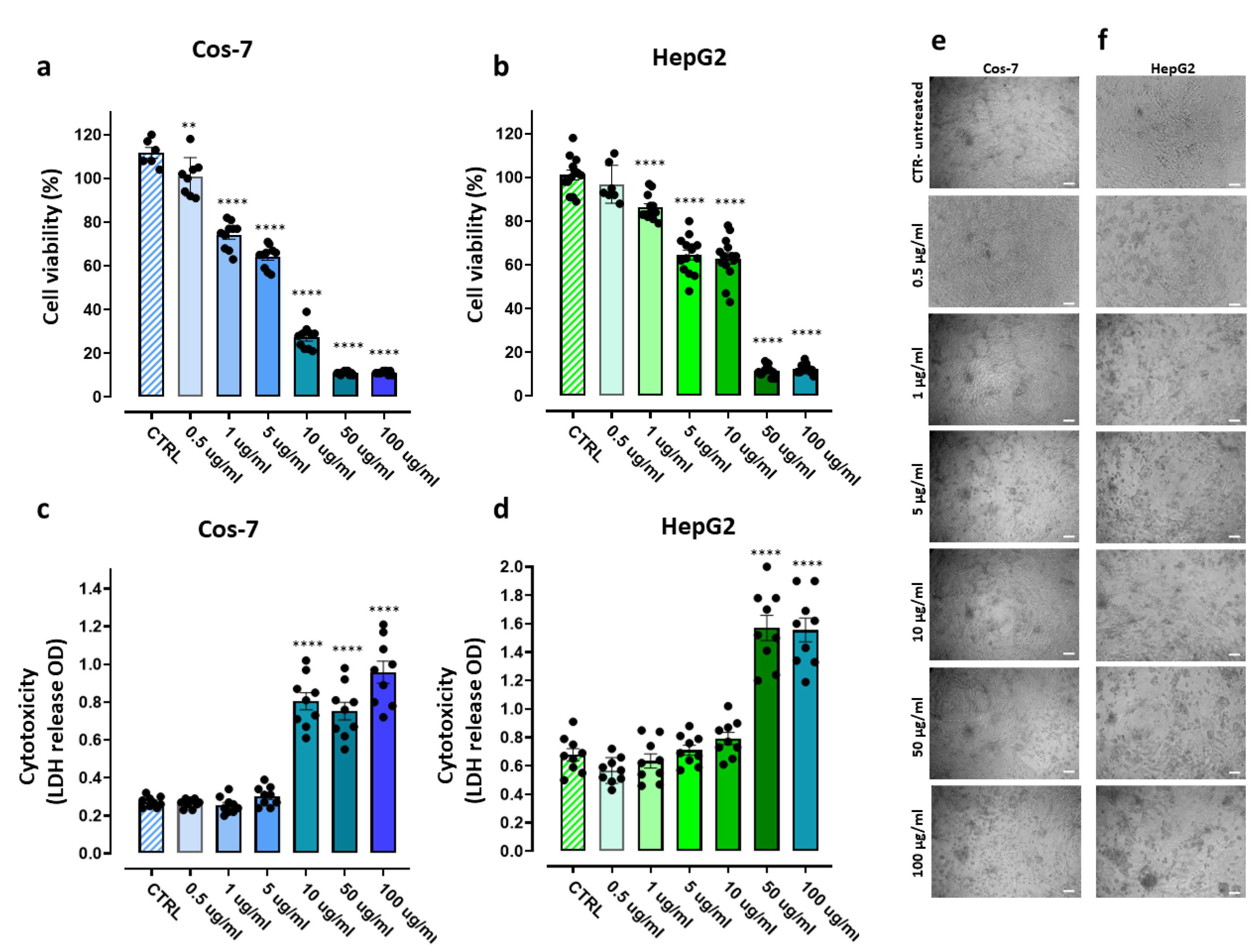
3.7. Cytotoxicity Experiments on Eukaryotic Cells
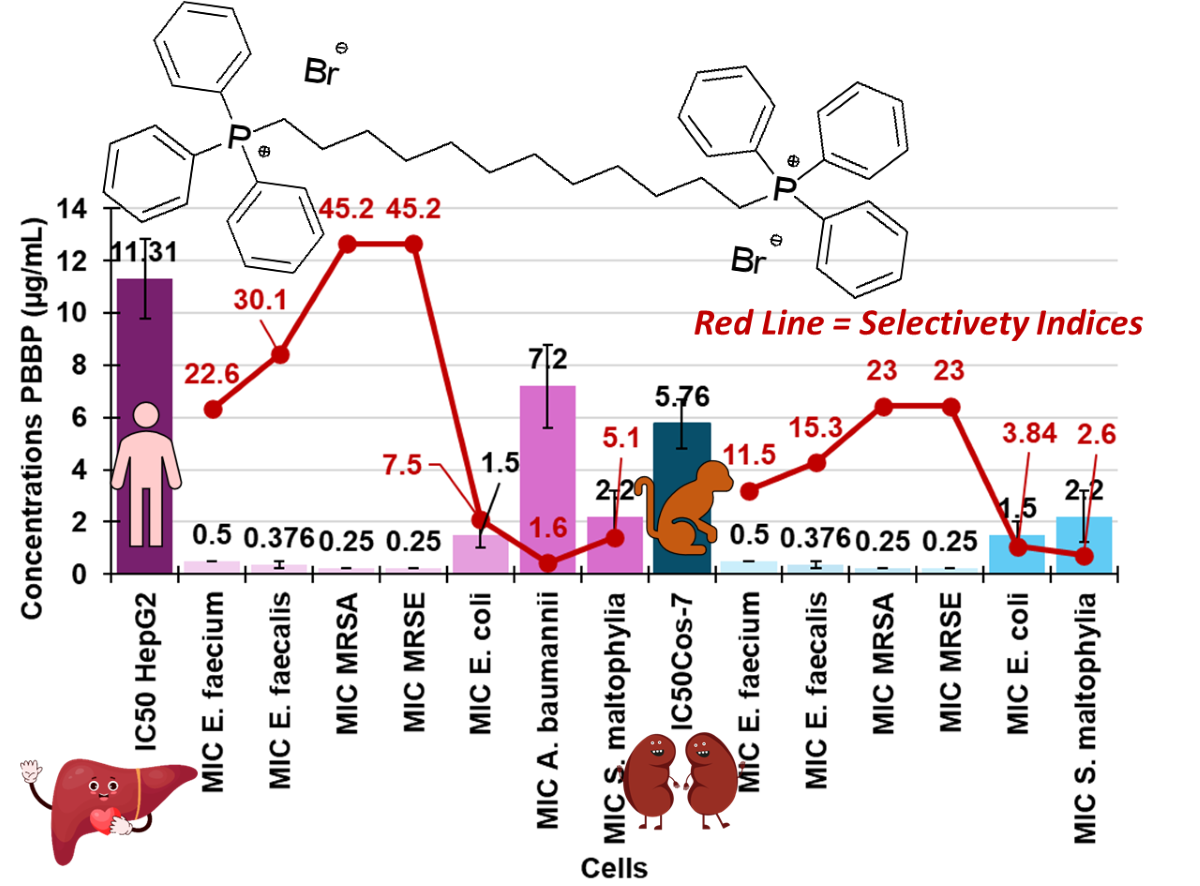
3.7.1. Assessment of the PBBP Concentration-Dependent Effects on Cos-7 and HepG2 Cells by MTT and LDH Essays
3.7.2. IC50 and Selectivity Indices
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ermolaev, V. V.; Arkhipova, D.M.; Miluykov, V.A.; Lyubina, A.P.; Amerhanova, S.K.; Kulik, N. V.; Voloshina, A.D.; Ananikov, V.P. Sterically Hindered Quaternary Phosphonium Salts (QPSs): Antimicrobial Activity and Hemolytic and Cytotoxic Properties. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 23, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saliba, R.; Zahar, J.-R.; Dabar, G.; Riachy, M.; Karam-Sarkis, D.; Husni, R. Limiting the Spread of Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria in Low-to-Middle-Income Countries: One Size Does Not Fit All. Pathogens 2023, 12, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dryden, M. Reactive Oxygen Species: A Novel Antimicrobial. Int J Antimicrob Agents 2018, 51, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, S.C.; Martinez, L.; Kirsner, R. The Diabetic Foot: The Importance of Biofilms and Wound Bed Preparation. Curr Diab Rep 2006, 6, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfei, S.; Caviglia, D. Prevention and Eradication of Biofilm by Dendrimers: A Possibility Still Little Explored. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Chen, X. Current Promising Strategies against Antibiotic-Resistant Bacterial Infections. Antibiotics 2022, 12, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, S.G.; Elli, D.; Kim, H.K.; Hendrickx, A.P.A.; Sorg, J.A.; Schneewind, O.; Missiakas, D. Small Molecule Inhibitor of Lipoteichoic Acid Synthesis Is an Antibiotic for Gram-Positive Bacteria. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2013, 110, 3531–3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfei, S.; Schito, G.C.; Schito, A.M.; Zuccari, G. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)-Mediated Antibacterial Oxidative Therapies: Available Methods to Generate ROS and a Novel Option Proposal. IJMS 2024, 2024051628.
- Dryden, M. Reactive Oxygen Therapy: A Novel Therapy in Soft Tissue Infection. Curr Opin Infect Dis 2017, 30, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dryden, M.S.; Cooke, J.; Salib, R.J.; Holding, R.E.; Biggs, T.; Salamat, A.A.; Allan, R.N.; Newby, R.S.; Halstead, F.; Oppenheim, B.; et al. Reactive Oxygen: A Novel Antimicrobial Mechanism for Targeting Biofilm-Associated Infection. J Glob Antimicrob Resist 2017, 8, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunnill, C.; Patton, T.; Brennan, J.; Barrett, J.; Dryden, M.; Cooke, J.; Leaper, D.; Georgopoulos, N.T. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) and Wound Healing: The Functional Role of ROS and Emerging ROS-modulating Technologies for Augmentation of the Healing Process. Int Wound J 2017, 14, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacchetti, F.; Schito, A.M.; Milanese, M.; Castellaro, S.; Alfei, S. Anti Gram-Positive Bacteria Activity of Synthetic Quaternary Ammonium Lipid and Its Precursor Phosphonium Salt. Int J Mol Sci 2024, 25, 2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Y.; Zhou, S.; Dong, C.; Zhang, A.; Lin, Y. PDMS Tri-Block Copolymers Bearing Quaternary Ammonium Salts for Epidermal Antimicrobial Agents: Synthesis, Surface Adsorption and Non-Skin-Penetration. React Funct Polym 2018, 124, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Niu, L.; Ma, S.; Li, J.; Tay, F.R.; Chen, J. Quaternary Ammonium-Based Biomedical Materials: State-of-the-Art, Toxicological Aspects and Antimicrobial Resistance. Prog Polym Sci 2017, 71, 53–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Wang, Y. Structure–Activity Relationship of Cationic Surfactants as Antimicrobial Agents. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 2020, 45, 28–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, S.P.F.; Azevedo, A.M.O.; Pinto, P.C.A.G.; Saraiva, M.L.M.F.S. Environmental Impact of Ionic Liquids: Recent Advances in (Eco)Toxicology and (Bio)Degradability. ChemSusChem 2017, 10, 2321–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfei, S.; Piatti, G.; Caviglia, D.; Schito, A. Synthesis, Characterization, and Bactericidal Activity of a 4-Ammoniumbuthylstyrene-Based Random Copolymer. Polymers (Basel) 2021, 13, 1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, S.; Xu, Y.; Nie, W.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, T.; Chen, P. Quaternary Ammonium Salts: Insights into Synthesis and New Directions in Antibacterial Applications. Bioconjug Chem 2023, 34, 302–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schito, A.M.; Piatti, G.; Caviglia, D.; Zuccari, G.; Alfei, S. Broad-Spectrum Bactericidal Activity of a Synthetic Random Copolymer Based on 2-Methoxy-6-(4-Vinylbenzyloxy)-Benzylammonium Hydrochloride. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22, 5021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfei, S. Shifting from Ammonium to Phosphonium Salts: A Promising Strategy to Develop Next-Generation Weapons against Biofilms. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira, D.M.P.; Forde, B.M.; Kidd, T.J.; Harris, P.N.A.; Schembri, M.A.; Beatson, S.A.; Paterson, D.L.; Walker, M.J. Antimicrobial Resistance in ESKAPE Pathogens. Clin Microbiol Rev 2020, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, Y.; Niu, L.; Ma, S.; Li, J.; Tay, F.R.; Chen, J. Quaternary Ammonium-Based Biomedical Materials: State-of-the-Art, Toxicological Aspects and Antimicrobial Resistance. Prog Polym Sci 2017, 71, 53–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Cui, F.; Zeng, G.; Jiang, M.; Yang, Z.; Yu, Z.; Zhu, M.; Shen, L. Quaternary Ammonium Compounds (QACs): A Review on Occurrence, Fate and Toxicity in the Environment. Science of The Total Environment 2015, 518–519, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Telesiński, A.; Pawłowska, B.; Biczak, R.; Śnieg, M.; Wróbel, J.; Dunikowska, D.; Meller, E. Enzymatic Activity and Its Relationship with Organic Matter Characterization and Ecotoxicity to Aliivibrio Fischeri of Soil Samples Exposed to Tetrabutylphosphonium Bromide. Sensors 2021, 21, 1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmig, J.; Jerchel, D. Die Wirkung von Invertseifen Auf Die Durch Pilze Und Kokken Bedingten Hautkrankheiten. Klin Wochenschr 1950, 28, 429–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanazawa, A.; Ikeda, T.; Endo, T. Synthesis and Antimicrobial Activity of Dimethyl- and Trimethyl-Substituted Phosphonium Salts with Alkyl Chains of Various Lengths. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1994, 38, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfei, S.; Schito, A.M. Positively Charged Polymers as Promising Devices against Multidrug Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria: A Review. Polymers (Basel) 2020, 12, 1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachowska, B.; Kazmierczak-Baranska, J.; Cieslak, M.; Nawrot, B.; Szczęsna, D.; Skalik, J.; Bałczewski, P. High Cytotoxic Activity of Phosphonium Salts and Their Complementary Selectivity towards HeLa and K562 Cancer Cells: Identification of Tri- n -butyl- n -hexadecylphosphonium Bromide as a Highly Potent Anti-HeLa Phosphonium Salt. ChemistryOpen 2012, 1, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfei, S. Cationic Materials for Gene Therapy: A Look Back to the Birth and Development of 2,2-Bis-(Hydroxymethyl)Propanoic Acid-Based Dendrimer Scaffolds. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24, 16006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pugachev, M. V.; Shtyrlin, N. V.; Sysoeva, L.P.; Nikitina, E. V.; Abdullin, T.I.; Iksanova, A.G.; Ilaeva, A.A.; Musin, R.Z.; Berdnikov, E.A.; Shtyrlin, Y.G. Synthesis and Antibacterial Activity of Novel Phosphonium Salts on the Basis of Pyridoxine. Bioorg Med Chem 2013, 21, 4388–4395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieniecka-Rosłonkiewicz, A.; Pernak, J.; Kubis-Feder, J.; Ramani, A.; Robertson, A.J.; Seddon, K.R. Synthesis, Anti-Microbial Activities and Anti-Electrostatic Properties of Phosphonium-Based Ionic Liquids. Green Chemistry 2005, 7, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedard, J.; Caschera, A.; Foucher, D.A. Access to Thermally Robust and Abrasion Resistant Antimicrobial Plastics: Synthesis of UV-Curable Phosphonium Small Molecule Coatings and Extrudable Additives. RSC Adv 2021, 11, 5548–5555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Süer, N.C.; Demir, C.; Ünübol, N.A.; Yalçın, Ö.; Kocagöz, T.; Eren, T. Antimicrobial Activities of Phosphonium Containing Polynorbornenes. RSC Adv 2016, 6, 86151–86157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Hu, W.; Lv, S.; Huang, J.; Huang, K. Synthesis of Aliphatic Symmetric Diphosphonium Salts and Bactericidal Activity of Selected Products. Chemistry Journal of Moldova 2017, 12, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Yuan, B.; Lv, S.; Liao, Q.; Huang, J. Synthesis, Characterization and Performance of a New Type of Alkylene Triphenyl Double Quaternary Phosphonium Salt. Journal of Materials Science and Chemical Engineering 2013, 01, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugachev, M. V.; Shtyrlin, N. V.; Sapozhnikov, S. V.; Sysoeva, L.P.; Iksanova, A.G.; Nikitina, E. V.; Musin, R.Z.; Lodochnikova, O.A.; Berdnikov, E.A.; Shtyrlin, Y.G. Bis-Phosphonium Salts of Pyridoxine: The Relationship between Structure and Antibacterial Activity. Bioorg Med Chem 2013, 21, 7330–7342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Q.; Lai, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, R.; Zhang, W.; Ao, N.; Zhang, H. PEGylated Bis-Quaternary Triphenyl-Phosphonium Tosylate Allows for Balanced Antibacterial Activity and Cytotoxicity. ACS Appl Bio Mater 2020, 3, 6400–6407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceccacci, F.; Sennato, S.; Rossi, E.; Proroga, R.; Sarti, S.; Diociaiuti, M.; Casciardi, S.; Mussi, V.; Ciogli, A.; Bordi, F.; et al. Aggregation Behaviour of Triphenylphosphonium Bolaamphiphiles. J Colloid Interface Sci 2018, 531, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfei, S.; Caviglia, D.; Piatti, G.; Zuccari, G.; Schito, A.M. Synthesis, Characterization and Broad-Spectrum Bactericidal Effects of Ammonium Methyl and Ammonium Ethyl Styrene-Based Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfei, S.; Castellaro, S.; Taptue, G.B. Synthesis and NMR Characterization of Dendrimers Based on 2, 2-Bis-(Hydroxymethyl)-Propanoic Acid (Bis-HMPA) Containing Peripheral Amino Acid Residues for Gene Transfection. Organic Communications 2017, 10, 144–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfei, S.; Castellaro, S. Synthesis and Characterization of Polyester-Based Dendrimers Containing Peripheral Arginine or Mixed Amino Acids as Potential Vectors for Gene and Drug Delivery. Macromol Res 2017, 25, 1172–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfei, S.; Taptue, G.B.; Catena, S.; Bisio, A. Synthesis of Water-Soluble, Polyester-Based Dendrimer Prodrugs for Exploiting Therapeutic Properties of Two Triterpenoid Acids. Chinese Journal of Polymer Science 2018, 36, 999–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pifer, C.W.; Wollish, E.G. Potentiometric Titration of Salts of Organic Bases in Acetic Acid. Anal Chem 1952, 24, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUCAST. European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Available Online: Https://Www.Eucast.Org/Ast_of_bacteria/ (Accessed on 20 January 2024).
- Schito, A.M.; Piatti, G.; Stauder, M.; Bisio, A.; Giacomelli, E.; Romussi, G.; Pruzzo, C. Effects of Demethylfruticuline A and Fruticuline A from Salvia Corrugata Vahl. on Biofilm Production in Vitro by Multiresistant Strains of Staphylococcus Aureus, Staphylococcus Epidermidis and Enterococcus Faecalis. Int J Antimicrob Agents 2011, 37, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berridge, M. V.; Herst, P.M.; Tan, A.S. Tetrazolium Dyes as Tools in Cell Biology: New Insights into Their Cellular Reduction. In; 2005; pp. 127–152.
- Kumar, P.; Nagarajan, A.; Uchil, P.D. Analysis of Cell Viability by the Lactate Dehydrogenase Assay. Cold Spring Harb Protoc 2018, 2018, pdb–prot095497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AVALOS, F.; ORTIZ, J.; ZITZUMBO, R.; LOPEZMANCHADO, M.; VERDEJO, R.; ARROYO, M. Phosphonium Salt Intercalated Montmorillonites. Appl Clay Sci 2009, 43, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daasch, L.; Smith, D. Infrared Spectra of Phosphorus Compounds. Anal Chem 1951, 23, 853–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkhipova, D.M.; Samigullina, A.I.; Minyaev, M.E.; Lyubina, A.P.; Voloshina, A.D.; Ermolaev, V. V. Synthesis, Crystal Structure, and Biological Activity of Menthol-Based Chiral Quaternary Phosphonium Salts (CQPSs). Struct Chem 2024, 35, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galkina, I. V.; Andriyashin, V. V.; Romanov, S.R.; Egorova, S.N.; Vorob’eva, N. V.; Shulaeva, M.P.; Pozdeev, O.K.; Litvinov, I.A.; Bakhtiyarova, Y. V. Synthesis, Structure and Antimicrobial Activity of Sterically Hindered Bis-Phosphonium Derivatives of 2,6-Di-Tert-Butyl-4-Methylphenol. Mendeleev Communications 2023, 33, 635–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akshay Ravindra, P.; Karpagam, S. Synthesis and Biological Activity of Azine Heterocycle Functionalized Quaternary Phosphonium Salts. IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng 2017, 263, 022017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratochvil, Byron. Titrations in Nonaqueous Solvents. Anal Chem 1982, 54, 105–121. [CrossRef]
- Seher, A. Dr. I. Gyenes, C. Sc. (Chim.), Titrationen in Nichtwäßrigen Medien, 3. Neubearb. u. Erg. Aufl., 701 S., 206 Abb., 108 Tab., Gln., Ferdinand Enke Verlag, Stuttgart 1970, Preis: 84.—DM. Fette, Seifen, Anstrichmittel 1973, 75, 232–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šafařík, L.; Stránský, Z.; Svehla, G.; Burns, D.T. Titrimetric Analysis in Organic Solvents (Comprehensive Analytical Chemistry, Vol. XXII). Anal Chim Acta 1987, 201, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascellani, Giuseppe.; Casalini, Claudio. Use of Mercuric Acetate in Potentiometric Titrations in a Nonaqueous Medium. Anal Chem 1975, 47, 2468–2470. [CrossRef]
- Kan, P.L.; Papahadjopoulos-Sternberg, B.; Wong, D.; Waigh, R.D.; Watson, D.G.; Gray, A.I.; McCarthy, D.; McAllister, M.; Schätzlein, A.G.; Uchegbu, I.F. Highly Hydrophilic Fused Aggregates (Microsponges) from a C12 Spermine Bolaamphiphile. J Phys Chem B 2004, 108, 8129–8135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschi, S.; Andreu, V.; de Viguerie, N.; Riviere, M.; Lattes, A.; Moisand, A. Synthesis and Aggregation Behaviour of Two-Headed Surfactants Containing the Urocanic Acid Moiety. New Journal of Chemistry 1998, 22, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissig, V.; Torchilin, V.P. Cationic Bolasomes with Delocalized Charge Centers as Mitochondria-Specific DNA Delivery Systems. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2001, 49, 127–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfei, S.; Marengo, B.; Domenicotti, C. Polyester-Based Dendrimer Nanoparticles Combined with Etoposide Have an Improved Cytotoxic and Pro-Oxidant Effect on Human Neuroblastoma Cells. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfei, S.; Zuccari, G.; Caviglia, D.; Brullo, C. Synthesis and Characterization of Pyrazole-Enriched Cationic Nanoparticles as New Promising Antibacterial Agent by Mutual Cooperation. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfei, S.; Caviglia, D.; Piatti, G.; Zuccari, G.; Schito, A.M. Synthesis, Characterization and Broad-Spectrum Bactericidal Effects of Ammonium Methyl and Ammonium Ethyl Styrene-Based Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfei, S.; Brullo, C.; Caviglia, D.; Zuccari, G. Preparation and Physicochemical Characterization of Water-Soluble Pyrazole-Based Nanoparticles by Dendrimer Encapsulation of an Insoluble Bioactive Pyrazole Derivative. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fröhlich, E. The Role of Surface Charge in Cellular Uptake and Cytotoxicity of Medical Nanoparticles. Int J Nanomedicine 2012, 5577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfei, S.; Spallarossa, A.; Lusardi, M.; Zuccari, G. Successful Dendrimer and Liposome-Based Strategies to Solubilize an Antiproliferative Pyrazole Otherwise Not Clinically Applicable. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petri-Fink, A.; Chastellain, M.; Juillerat-Jeanneret, L.; Ferrari, A.; Hofmann, H. Development of Functionalized Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Interaction with Human Cancer Cells. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 2685–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jambhrunkar, S.; Yu, M.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J.; Shrotri, A.; Endo-Munoz, L.; Moreau, J.; Lu, G.; Yu, C. Stepwise Pore Size Reduction of Ordered Nanoporous Silica Materials at Angstrom Precision. J Am Chem Soc 2013, 135, 8444–8447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Mccrate, J.M.; Lee, J.C.-M.; Li, H. The Role of Surface Charge on the Uptake and Biocompatibility of Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles with Osteoblast Cells. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 105708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akinc, A.; Battaglia, G. Exploiting Endocytosis for Nanomedicines. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2013, 5, a016980–a016980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, A.H.; Khare, K.; Saxena, P.; Debnath, P.; Mukhopadhyay, K.; Yadav, D. A Review on Colistin Resistance: An Antibiotic of Last Resort. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, J.T.; López-Medrano, F. Cefiderocol, a New Antibiotic against Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria. Rev Esp Quimioter 2021, 34 Suppl 1, 41–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakonstantis, S.; Rousaki, M.; Kritsotakis, E.I. Cefiderocol: Systematic Review of Mechanisms of Resistance, Heteroresistance and In Vivo Emergence of Resistance. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfei, S.; Schito, A.M. β-Lactam Antibiotics and β-Lactamase Enzymes Inhibitors, Part 2: Our Limited Resources. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfei, S.; Zuccari, G. Recommendations to Synthetize Old and New β-Lactamases Inhibitors: A Review to Encourage Further Production. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schito, A.M.; Piatti, G.; Caviglia, D.; Zuccari, G.; Zorzoli, A.; Marimpietri, D.; Alfei, S. Bactericidal Activity of Non-Cytotoxic Cationic Nanoparticles against Clinically and Environmentally Relevant Pseudomonas Spp. Isolates. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira, D.M.P.; Forde, B.M.; Kidd, T.J.; Harris, P.N.A.; Schembri, M.A.; Beatson, S.A.; Paterson, D.L.; Walker, M.J. Antimicrobial Resistance in ESKAPE Pathogens. Clin Microbiol Rev 2020, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Solache, M.; Rice, L.B. The Enterococcus: A Model of Adaptability to Its Environment. Clin Microbiol Rev 2019, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levitus, M.; Rewane, A.; Perera, T.B. Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococci. 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Chiang, H.-Y.; Perencevich, E.N.; Nair, R.; Nelson, R.E.; Samore, M.; Khader, K.; Chorazy, M.L.; Herwaldt, L.A.; Blevins, A.; Ward, M.A.; et al. Incidence and Outcomes Associated With Infections Caused by Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococci in the United States: Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analysis. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 2017, 38, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, W.R.; Murray, B.E.; Rice, L.B.; Arias, C.A. Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococci. Infect Dis Clin North Am 2016, 30, 415–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Hidalgo, N.; Escolà-Vergé, L. Enterococcus Faecalis Bacteremia. J Am Coll Cardiol 2019, 74, 202–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, T.F.; Coelho, S.S.; Foletto, V.S.; Bottega, A.; Serafin, M.B.; Machado, C. de S.; Franco, L.N.; Paula, B.R.; Hörner, R. Alternatives for the Treatment of Infections Caused by ESKAPE Pathogens. J Clin Pharm Ther 2020, 45, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfei, S.; Brullo, C.; Caviglia, D.; Piatti, G.; Zorzoli, A.; Marimpietri, D.; Zuccari, G.; Schito, A.M. Pyrazole-Based Water-Soluble Dendrimer Nanoparticles as a Potential New Agent against Staphylococci. Biomedicines 2021, 10, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozdogan, B. Antibacterial Susceptibility of a Vancomycin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Strain Isolated at the Hershey Medical Center. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 2003, 52, 864–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsiodras, S.; Gold, H.S.; Sakoulas, G.; Eliopoulos, G.M.; Wennersten, C.; Venkataraman, L.; Moellering, R.C.; Ferraro, M.J. Linezolid Resistance in a Clinical Isolate of Staphylococcus Aureus. The Lancet 2001, 358, 207–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Bayer, A.; Cosgrove, S.E.; Daum, R.S.; Fridkin, S.K.; Gorwitz, R.J.; Kaplan, S.L.; Karchmer, A.W.; Levine, D.P.; Murray, B.E.; et al. Clinical Practice Guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America for the Treatment of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Infections in Adults and Children. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2011, 52, e18–e55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nour El-Din, H.T.; Yassin, A.S.; Ragab, Y.M.; Hashem, A.M. Phenotype-Genotype Characterization and Antibiotic-Resistance Correlations Among Colonizing and Infectious Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Recovered from Intensive Care Units. Infect Drug Resist 2021, Volume 14, 1557–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breijyeh, Z.; Jubeh, B.; Karaman, R. Resistance of Gram-Negative Bacteria to Current Antibacterial Agents and Approaches to Resolve It. Molecules 2020, 25, 1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunes, B.; Cagide, F.; Fernandes, C.; Borges, A.; Borges, F.; Simões, M. Efficacy of Novel Quaternary Ammonium and Phosphonium Salts Differing in Cation Type and Alkyl Chain Length against Antibiotic-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 25, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesevich, A.; Sutton, G.; Ruffin, F.; Park, L.P.; Fouts, D.E.; Fowler, V.G.; Thaden, J.T. Newly Named Klebsiella Aerogenes (Formerly Enterobacter Aerogenes) Is Associated with Poor Clinical Outcomes Relative to Other Enterobacter Species in Patients with Bloodstream Infection. J Clin Microbiol 2020, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahav, D.; Giske, C.G.; Grāmatniece, A.; Abodakpi, H.; Tam, V.H.; Leibovici, L. New β-Lactam–β-Lactamase Inhibitor Combinations. Clin Microbiol Rev 2020, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karaiskos, I.; Galani, I.; Papoutsaki, V.; Galani, L.; Giamarellou, H. Carbapenemase Producing Klebsiella Pneumoniae: Implication on Future Therapeutic Strategies. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 2022, 20, 53–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolston, K.V.I.; Safdar, A. Pseudomonas, Stenotrophomonas, Acinetobacter, and Other Nonfermentative Gram-Negative Bacteria and Medically Important Anaerobic Bacteria in Transplant Recipients. In Principles and Practice of Transplant Infectious Diseases; Springer New York: New York, NY, 2019; pp. 461–472. [Google Scholar]
- Brooke, J.S. Advances in the Microbiology of Stenotrophomonas Maltophilia. Clin Microbiol Rev 2021, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommers, K.J.; Michaud, M.E.; Hogue, C.E.; Scharnow, A.M.; Amoo, L.E.; Petersen, A.A.; Carden, R.G.; Minbiole, K.P.C.; Wuest, W.M. Quaternary Phosphonium Compounds: An Examination of Non-Nitrogenous Cationic Amphiphiles That Evade Disinfectant Resistance. ACS Infect Dis 2022, 8, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zhou, H.; Gai, F.; Chi, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhao (Kent), Z. Synthesis of Quaternary Phosphonium N-Chloramine Biocides for Antimicrobial Applications. RSC Adv 2017, 7, 13244–13249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, J.; Chen, S.; Ning, B.; Tolleson, W.H.; Guo, L. Development of HepG2-Derived Cells Expressing Cytochrome P450s for Assessing Metabolism-Associated Drug-Induced Liver Toxicity. Chem Biol Interact 2016, 255, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donato, M.T.; Tolosa, L.; Gómez-Lechón, M.J. Culture and Functional Characterization of Human Hepatoma HepG2 Cells. Methods Mol Biol 2015, 1250, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolosa, L.; Gómez-Lechón, M.J.; López, S.; Guzmán, C.; Castell, J. V; Donato, M.T.; Jover, R. Human Upcyte Hepatocytes: Characterization of the Hepatic Phenotype and Evaluation for Acute and Long-Term Hepatotoxicity Routine Testing. Toxicol Sci 2016, 152, 214–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Sena, T.; Moro, E.; Moreno-Torres, M.; Quintás, G.; Hengstler, J.; Castell, J. V. Metabolomics-Based Strategy to Assess Drug Hepatotoxicity and Uncover the Mechanisms of Hepatotoxicity Involved. Arch Toxicol 2023, 97, 1723–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donato, M.T.; Tolosa, L.; Gómez-Lechón, M.J. Culture and Functional Characterization of Human Hepatoma HepG2 Cells. In; 2015; pp. 77–93.
- Arzumanian, V.A.; Kiseleva, O.I.; Poverennaya, E. V. The Curious Case of the HepG2 Cell Line: 40 Years of Expertise. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22, 13135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cushnie, T.P.T.; Cushnie, B.; Echeverría, J.; Fowsantear, W.; Thammawat, S.; Dodgson, J.L.A.; Law, S.; Clow, S.M. Bioprospecting for Antibacterial Drugs: A Multidisciplinary Perspective on Natural Product Source Material, Bioassay Selection and Avoidable Pitfalls. Pharm Res 2020, 37, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
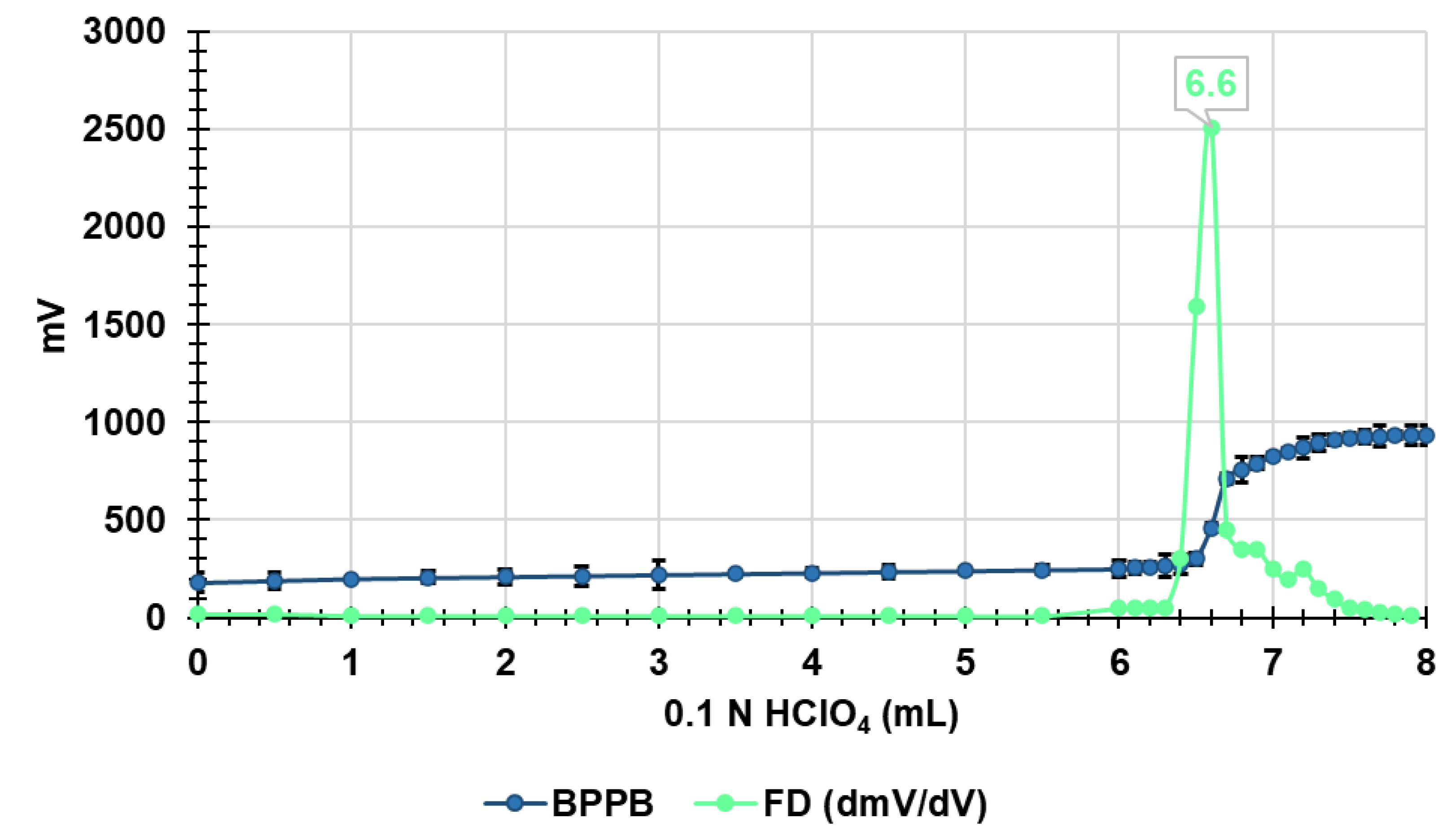
| Sample | Weight (mg) | * MW | * P+ (mmol) |
0.1 N HClO4 (mL) | ** P+ (mmol) |
** MW | *** Residuals | Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BPPB | 280.0 | 852.7 | 0.6567 | 6.60 | 0.6600 | 848.5 | 4.2 | 0.5 |
| Measure | PBBP * NPs |
|---|---|
| Z-Ave (nm) | 45.28 ± 3.99 |
| PDI | 0.557 ± 0.03 |
| ζ-p (mV) | +18.33 ± 0.98 |
| Strains | BPPB (852.7) 1 | Reference antibiotics |
|---|---|---|
| MIC µg/mL |
MIC µg/mL |
|
| E. faecalis 1 VRE | 0.50 | 256 (V); 64 (T) |
| E. faecalis 79 VRE | 0.50 | 256 (V); 128 (T) |
| E. faecalis 365 VRE | 0.50 | 32 (V); 0.5 (T) |
| E. faecalis 425 VRE | 0.50 | 32 (V); 1 (T) |
| E. faecium 152 VRE | 0.25 | 128 (V); 64 (T) |
| E. faecium 182 VRE | 0.25 | 64 (V); 1 (T) |
| E. faecium 364 VRE | 0.50 | 32 (V); 0.5 (T) |
| E. faecium 479 VRE | 0.50 | 64 (V); 1 (T) |
| S. aureus A MRSA | 0.25 | 256 (O) |
| S. aureus B MRSA | 0.25 | 512 (O) |
| S. aureus D MSSA | 0.25 | 1 (O) |
| S. aureus F MSSA | 0.50 | 0.5 (O) |
| S. aureus 17 MRSA | 0.25 | 256 (O) |
| S. aureus 18 MRSA | 0.25 | 512 (O) |
| S. aureus 187 MRSA | 0.50 | 256 (O) |
| S. aureus 195 MRSA | 0.25 | 256 (O) |
| S. epidermidis 195 MRSE | 0.25 | 256 (O) |
| S. epidermidis 2 MRSE | 0.25 | 128 (O) |
| S. epidermidis 22 MRSE | 0.25 | 128 (O) |
| S. epidermidis 171 MRSE * | 0.25 | 256 (O) |
| S. epidermidis 178 MRSE * | 0.25 | 64 (O) |
| S. epidermidis 181 MRSE * | 0.50 | 256 (O) |
| Strains | BPPB (852.7) 1 | Reference antibiotics |
|---|---|---|
| MIC µg/mL |
MIC µg/mL |
|
| P. aeruginosa 1V °,* | 32 | 16 (M) |
| P. aeruginosa 2V °,* | 16 | 16 (M) |
| P. aeruginosa 259 °,*,** | 32 | 4 (M) |
| P. aeruginosa 265 MDR *** | 32 | 16 (M) |
| A. baumannii 257 * | 8 | 16 (M) |
| A. baumannii 279 * | 8 | 16 (M) |
| A. baumannii 283 * | 4 | 8 (M) |
| A. baumannii 236 * | 8 | 16 (M) |
| A. baumannii 406 * | 8 | 8 (M) |
| S. maltophylia 280 | 1 | 0.5 (TMP-SMX) |
| S. maltophylia 384 R TMP-SMX | 4 | 32 (TMP-SMX) |
| S. maltophylia 390 | 2 | 1 (TMP-SMX) |
| S. maltophylia 39 | 2 | 0.5 (TMP-SMX) |
| S. maltophylia 392 | 2 | 0.5 (TMP-SMX) |
| K. pneumoniae 376 *,KPC | 16 | 32 (M) |
| K. pneumoniae 377 *,KPC | 16 | 16 (M) |
| K. pneumoniae 488 *,KPC | 16 | 32 (M) |
| K. pneumoniae 490 *,KPC,*** | 16 | 32 (M) |
| K. pneumoniae 540 *,VIM, RC | 16 | 32 (M) |
| K. aerogenes 500 *,KPC | 16 | 64 (M) |
| E. coli 224 S | 1 | 0. 03 (M) |
| E. coli 462 *,NDM | 2 | 32 (M) |
| E. coli 477 *,KPC | 1 | 16 (M) |
| E. coli 539 *,NDM, RC | 2 | 32 (M) |
| E. coli 525 *,VIM | 16 | 32 (M) |
| E. cloacae 517 *,VIM | 16 | 8 (M) |
| E. cloacae 527 *,VIM | 32 | 32 (M) |
| E. hormaechei 544 *,VIM, RC | 32 | 32 (M) |
| Strains | BPPB (852.7) 1 | Cos-7 | HepG2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| MIC (µg/mL) | SI | SI | |
| E. faecalis | 0.50 | 11 | 23 |
| E. faecium | 0.25-0.50 | 11-22. | 23-46 |
| S. aureus | 0.25 | 22 | 46 |
| S. epidermidis | 0.25 | 22 | 46 |
| Strains | BPPB (852.7) 1 | Cos-7 | HepG2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| MIC (µg/mL) | SI | SI | |
| P. aeruginosa | 32 | 0.2 | 0.4 |
| A. baumannii | 8 | 0.7 | 1.4 |
| S. maltophylia | 2 | 2.8 | 5.6 |
| K. pneumoniae | 16 | 0.4 | 0.7 |
| K. aerogenes | 16 | 0.4 | 0.7 |
| E. coli | 1-2 | 5.5-2.8 | 11.3-5.6 |
| E. cloacae | 16-32 | 0.4-0.2 | 0.7-0.4 |
| E. hormaechei | 32 | 0.2 | 0.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





