1. Introduction
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder affecting motor neurons in the brain and spinal cord, leading to muscle weakness and eventual respiratory failure [
1]. As respiratory failure worsens, non-invasive ventilation (NIV) techniques continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP), bilevel positive airway pressure (BiPAP), volume-assured synchronised intermittent mandatory ventilation(V-SIMV), volume-assured pressure support (V-AC), and pressure-assured synchronised intermittent mandatory ventilation(P-SIMV), pressure-assured pressure support (P-AC) modes are used to manage symptoms [
2]. Respiratory rehabilitation therapies, including the use of cough machines and vests, are also implemented [
3]. When NIV proves insufficient or patient compliance declines, percutaneous dilatational tracheostomy (PDT) may be performed to manage respiratory failure [
4].
Current literature [
5,
6,
7] suggests that PDT combined with adjuvant therapies can play a crucial role in preserving vocal function, a key factor in maintaining quality of life for ALS patients. However, detailed studies evaluating the effectiveness of such combined treatments are limited. This study aims to fill this gap by assessing the impact of PDT and various adjuvant therapies on vocal function preservation in ALS patients. The adjuvant therapies investigated include regenerative injection therapy, low-frequency electrical stimulation, respiratory rehabilitation, and swallowing rehabilitation therapy.
2. Methods
We conducted a retrospective analysis of medical records of 47 ALS patients who underwent Ultrasound-Guided PDT at Rodem Hospital between 2020 and 2023 (
Table 1). Of these patients, 11 were diagnosed with bulbar type ALS, 2 with respiration type, and 34 with limb type ALS. The inclusion criteria were a diagnosis of limb type ALS based on the revised El Escorial criteria and the need for tracheostomy due to worsening respiratory function and low compliance to NIV care. The exclusion criteria included patients with bulbar and respiratory onset who had absolutely lost their voice.
Speech evaluation was based on a retrospective evaluation of the ALSFRS-R rating scale from medical records. The evaluations were conducted by two rehabilitation medicine specialists with expertise in speech and voice disorders. Additionally, second opinion ratings were implemented to improve the reliability of the assessments. This methodological choice acknowledges the practical constraints in rare disease research where double-blind methods are often challenging to implement due to the limited number of patients.
Pulmonary function tests, including forced vital capacity (FVC), were performed before and after the procedure to assess overall respiratory function. These results were analyzed in relation to the ALSFRS-R speech scores to determine any potential correlation between respiratory function and vocal capabilities.
Four of the 34 limb type ALS patients had already lost their speech function before undergoing PDT. To evaluate the respiratory function of the patients, we used the revised Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Functional Rating Scale (ALSFRS-R), which includes a subscore for dyspnea, speech, swallowing3. Pulmonary function tests were performed, and the forced vital capacity (FVC) was recorded. Pre- and post-procedure vocal function were assessed by two rehabilitation medicine doctors with a specialty in speech and voice disorders.
Before undergoing PDT, patients received Non-Invasive Ventilator (NIV) or Invasive Ventilator (IV) support using various modes such as continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP), bilevel positive airway pressure (BiPAP), volume-assured synchronised intermittent mandatory ventilation(V-SIMV), pressure-assured synchronised intermittent mandatory ventilation(P-SIMV), volume-assured control (V-AC), pressure-assured control (P-AC), and average volume pressure support (AVAPS) mode.
Additionally, patients underwent respiratory rehabilitation therapy, including the use of cough assist machines, chest purcussion therapy and High-frequency chest wall oscillation (HFCWO) therapy. [
2,
8]
The PDT procedure was performed in the intensive care unit under local anesthesia and sedation.
After the procedure, patients received low-frequency electrical stimulation to the neck muscles, mesotherapy injections of placental extracts, swallowing rehabilitation therapy, and intensive vocal training for one month(
Table 2).
Low-frequency electrical stimulation was applied using a device that delivers electrical impulses at a frequency of 20-50 Hz. The stimulation targeted the muscles involved in vocalization and swallowing, with sessions conducted three times per week, each lasting 20 minutes.
The regenerative injection therapy included placenta extract injection (Rejueve injection drug produced by Huons Pharmaceuticals in Korea), prepared under sterile conditions from human placental tissue. These were administered via intramuscular injections at specified intervals.
Swallowing rehabilitation therapy included exercises designed to strengthen the muscles involved in swallowing. These exercises were tailored to each patient's needs and included maneuvers such as the Mendelsohn maneuver and effortful swallow techniques. Therapy sessions were held twice a week for 30 minutes each.
Intensive vocal training involved structured exercises aimed at improving vocal strength and control. Patients engaged in breathing exercises, phonation drills, and articulation exercises. These sessions were conducted twice a week for 30 minutes each and were supervised by a speech-language pathologist with expertise in voice disorders.
The T-tube was equipped with an adjustable balloon, and a balloon reduction program was implemented to gradually decrease the balloon volume to 2 cc or less, allowing for speech production without compromising the ability to clear secretions.
Data were collected on patient demographics, ALSFRS-R scores, pulmonary function test results, and vocal function. The primary outcome was the preservation of vocal function following PDT in the limb type ALS patients.
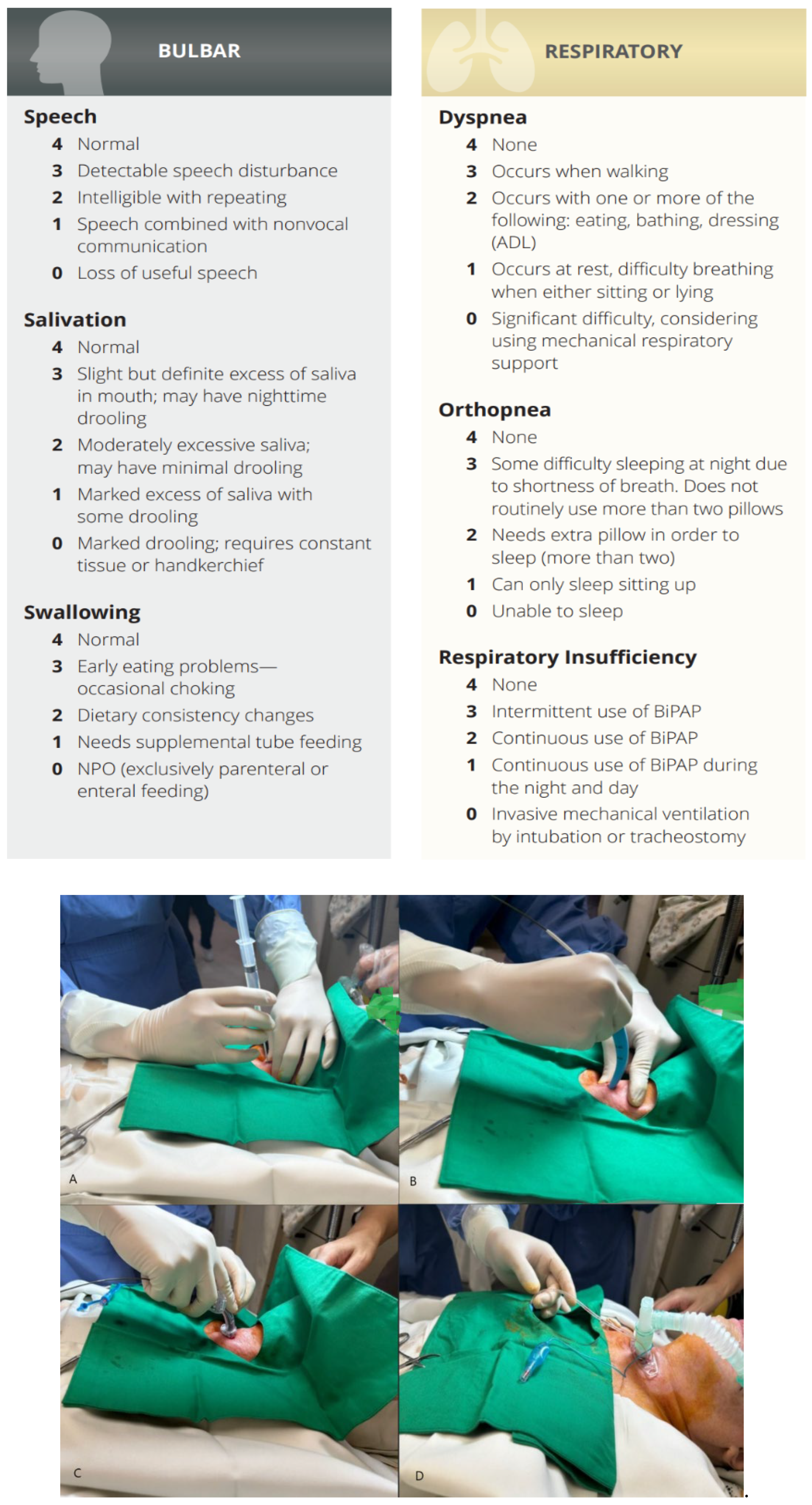
Figure 1.
A~D. Percutaneous dilatational tracheostomy (PDT).
Figure 1.
A~D. Percutaneous dilatational tracheostomy (PDT).
Figure 2.
A~B. Electrical stimulation therapy for swallowing, vocalization rehabilitation.
Figure 2.
A~B. Electrical stimulation therapy for swallowing, vocalization rehabilitation.
3. Standard Protocol Approvals, Registrations, and Patient Consents
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Public Institutional Bioethics Committee designated by the Ministry of Health and Welfare (P01-202401-01-020). Written informed consent was waived, since this was a retrospective study.
4. Statistical Considerations
We utilized the Shapiro-Wilk test to determine the normality of data distribution. Given the rarity of ALS and the inherent variability in patient responses, it is not unexpected that our data did not follow a normal distribution. Recognizing this, we applied non-parametric methods like the Wilcoxon signed-rank test for paired data analysis. While t-tests were initially performed for supplementary analysis, the primary conclusions are based on non-parametric tests to avoid potential misleading results. This approach ensures a robust and accurate evaluation of the efficacy of PDT and adjuvant therapies in preserving vocal function in ALS patients. For statistical analysis, Jamovi software (version 2.3.28 solid for Windows) was utilized.
In addition to the Wilcoxon signed-rank test, we considered performing a logistic regression analysis to evaluate the impact of different combinations of interventions and patient features on the outcomes. However, given that all 47 patients underwent the same combination of mesotherapy, vocalization therapy, and rehabilitation, it was not feasible to statistically separate the contributions of each individual intervention. This uniformity in treatment prevented us from isolating the effect of each component through regression analysis.
5. Results
The study included a total of 47 ALS patients who underwent PDT, all performed by the lead author, Dr. Jae-Kook Yoo. Anesthesia management and monitoring assistance were provided by Dr. Soon-Hee Kwon and Dr. Sul-Hee Yoon. Given that all procedures were performed by the same surgeon, evaluating the variation in results based on different surgeons was not applicable in this study.
The mean age at the time of PDT was 60.8 ± 9.7 years, and the male-to-female ratio was 1.4:1. The median time from symptom onset to PDT was 26.4 months (interquartile range: 18.5-33.8 months). The mean value of pre-PDT ALSFRS-R speech subscore was 2.63, and the mean post-PDT subscore was 2.28. Overall, 9 patients (75%) maintained their pre-PDT vocal function or experienced only a mild decline (≤1 point) in the ALSFRS-R speech subscore.
The normality of the overall population was assessed using the Shapiro-Wilk test. Due to the data not following a normal distribution, non-parametric statistical methods were applied. Thus, the differences in scores before and after the surgery were evaluated using the Wilcoxon rank test, and statistical significance was set at p < 0.05. The changes in scores were significantly observed. Additionally, considering conventional tracheostomy and usual care patient's speech scores as below 1, the One Sample T-test and Wilcoxon rank test were conducted. This approach yielded superior results compared to the general expectation of less than 1 point.
In our study, we compared the ALS Functional Rating Scale-Revised (ALSFRS-R) scores of 47 ALS patients before and one month after undergoing Percutaneous Dilatational Tracheostomy (PDT). The pre-operative ALSFRS-R scores, measured between one week and one month prior to the surgery, were compared to those recorded one month post-surgery. Our findings, as presented in
Table 4, demonstrate the impact of PDT and adjunct therapies on various aspects of ALSFRS-R, including speech, salivation, swallowing, dyspnea, orthopnea, and respiratory insufficiency. This comparison provided valuable insights into the efficacy of PDT in managing the symptoms of ALS.
The duration of Percutaneous Dilatational Tracheostomy (PDT) procedures ranged from 10 to 25 minutes. Notably, subcutaneous emphysema was observed in 2 cases, and abdominal distension, presumably related to the establishment of invasive mechanical ventilation, was noted in 3 cases. Apart from these, no significant adverse events were reported. As procedural proficiency increased, the average duration of the surgery decreased from the initial 20 minutes to approximately 10 minutes. Moreover, a notable improvement in patient satisfaction was observed, particularly among the 35 patients who had previously expressed moderate to severe concerns about dyspnea, nocturnal death anxiety, and insomnia post-surgery.
In the area of vocal function, it was observed that among the patients, ALSFRS-R speech scores initially ranging from 1 to 4 points dropped to 0, indicating complete loss of vocalization, in 6 cases on the day following the surgery. However, these patients showed significant improvement after undergoing a two-week intensive program of respiratory rehabilitation, vocal rehabilitation, and regenerative injection therapy. Most patients previously scoring between 2 to 4 points demonstrated a decrease to scores ranging from 1 to 3 points, continuing with consistent training. The vocal rehabilitation training was conducted for 1 to 2 hours daily. The average decrease in score on the following day was 2.2 points, and after two weeks of intensive regenerative treatment, the average decrease was reduced to 0.85 points, indicating substantial preservation of vocal function.
As evident in
Table 5, our data did not conform to a normal distribution, as indicated by the Shapiro-Wilk test results for both pre-operative and post-operative speech values (Shapiro-Wilk p < .001). Consequently, to compare vocal capabilities before and after the surgery, we conducted a non-parametric hypothesis test on the differences in speech abilities. This approach was necessitated due to the non-normality of the speech data, ensuring the accuracy and validity of our comparative analysis.
As
Table 6 demonstrates, a significant change in speech scores was observed pre- and post-operatively, as evidenced by both the Student's t-test and Wilcoxon W test results. This suggests that the surgery had a significant impact on preserving vocal function. However, as shown in
Table 6, when comparing post-operative speech scores against a conventional score of 1 or lower from traditional tracheostomy methods, using the One Sample T-test, our study found superior results. This indicates that patients who underwent PDT with adjuvant therapies exhibited better speech outcomes than those who did not receive such treatments.
The mean ALSFRS-R speech scores pre-PDT were 2.64 ± 1.4, and post-PDT scores were 2.28 ± 1.7. Using the Wilcoxon signed-rank test, we found that the decrease in speech scores post-PDT was statistically significant (p = 0.004). This suggests that while PDT combined with adjuvant therapies may help maintain vocal function in some patients, the overall trend indicates a decrease in speech capability.
Due to the uniformity in the treatment protocols, performing a logistic regression to isolate the effects of individual interventions was not feasible. All patients underwent the same combination of mesotherapy, vocalization therapy, and rehabilitation, making it impossible to statistically differentiate the impact of each therapy.
In our analysis of pulmonary function test results, specifically forced vital capacity (FVC), we did not find a significant positive correlation with ALSFRS-R speech scores (p 0.12) . This indicates that while pulmonary function is an important aspect of ALS management, it was not a decisive factor in the preservation of vocal function post-tracheostomy. Instead, the condition of the vocal cords and related muscles appeared to be more critical, suggesting that targeted therapies to maintain these structures are essential for better vocal outcomes.
We also considered other variables such as body mass index (BMI), muscle mass, and phase angle (PA) obtained through bioelectrical impedance analysis BIA(InbodyS10® system, InBody Corp, Seoul, Korea) in relation to the preservation of vocal function. It was found that patients with significantly low BMI and muscle mass showed improvement in vocal function post-tracheostomy after weight gain. However, due to the variability in these factors, it was difficult to isolate their impact as single significant variables. Interestingly, patients who transitioned from NIV to tracheostomy showed an average weight gain of approximately 2.5 kg within one month. This weight gain is believed to result from the reduction in caloric expenditure associated with forced breathing and improved digestive function, as tracheostomy offers more stable breathing compared to NIV, which often causes gastrointestinal discomfort due to air swallowing.
Also particularly noteworthy observation was made with two patients who had ALSFRS-R speech scores of 0 prior to undergoing Percutaneous Dilatational Tracheostomy (PDT). After the surgery and subsequent adjuvant therapies, one patient's score improved to 1, while the other's increased to 2. This significant improvement in their speech scores post-PDT underscores the efficacy of the procedure and adjunctive therapies in enhancing vocal function, even for patients with initially severe impairments.
6. Discussion
In our study, we observed that a significant proportion of ALS patients were able to preserve vocal function following Percutaneous Dilatational Tracheostomy (PDT). This outcome appears to be influenced by using of respiratory, swallowing rehabilitation therapy, mesotherapy, low-frequency electrical stimulation, and a balloon dilation managing program. These aligns with previous findings demonstrating the efficacy of these interventions in preserving vocal function.
The historical development of PDT, which became popular after Ciaglia's introduction 10 in 1985, has revolutionized the approach to tracheostomy, minimizing trauma and potentially preserving vital functions such as speech. The laryngeal muscles, essential for airway maintenance and vocalization, are less likely to be damaged in PDT compared to conventional surgical tracheostomy (ST) [
11]. It is crucial as these muscles [
12,
13,
14], including the infrahyoid and suprahyoid groups, and intrinsic muscles responsible for moving the vocal cords, play a pivotal role in speech and breathing.
Furthermore, while early Non-Invasive Ventilation (NIV) is beneficial in improving survival and quality of life in ALS patients, compliance rates are not as high as expected. Studies [
15,
16] show only about 53.6% of ALS patients comply with NIV within 28 days of initiation, with factors like marital status, income, education, and caregiver availability impacting compliance. However, both compliant and noncompliant participants reported an improvement in quality of life with NIV.
Our study's findings indicate that despite initial reluctance due to fears of voice loss, ALS patients who underwent PDT reported a significant improvement in quality of life. This improvement was particularly notable in those who managed to undergo respiratory rehabilitation during the day without continuous ventilator support. Out of 47 patients who transitioned to PDT, 43 reported an enhancement in their quality of life compared to their experience with NIV. These findings suggest that PDT, especially when it aids in preserving vocal function, is a compelling alternative to NIV, catering to the respiratory needs of ALS patients and addressing their quality-of-life concerns. Therefore, PDT, with its ability to minimize trauma to key muscles and maintain vocal function, combined with its effectiveness in enhancing the quality of life, emerges as a robust alternative for ALS patients, particularly those who struggle with NIV compliance.
The preservation of vocal function following PDT is possible in a significant proportion of ALS patients. Our results suggest that the use of respiration [
17], swallowing rehabilitation therapy [
18], mesotherapy [
19], low-frequency electrical stimulation [
20], and a balloon dilation program [
21] may contribute to this outcome. This is consistent with previous findings that demonstrated the efficacy of these interventions in preserving vocal function. Further research is needed to confirm these findings and optimize the management of speech function in ALS patients undergoing tracheostomy.
The preservation of the infrahyoid muscles [
18,
22,
23] is crucial as they play a vital role in phonation and swallowing. As such, PDT increases the likelihood of preserving vocalization and swallowing functions in ALS patients, making it a more favorable option for tracheostomy in this patient population. Comparatively, PDT is associated with shorter operation times and lower complication rates, making it a safer and more efficient alternative to ST [
11,
24]. This reduced trauma approach is particularly beneficial for ALS patients, who often face respiratory and vocal challenges as their condition progresses.
Compared to traditional surgical tracheostomy [
10,
11,
24], PDT offers several advantages in terms of muscle damage and preservation of vocalization [
25]. In conventional tracheostomy, there is a higher likelihood of damage to neck muscles, including the sternocleidomastoid, strap muscles, and infrahyoid muscles. Among these muscles, the infrahyoid muscles are particularly crucial for phonation and swallowing. As a result, vocalization is rarely possible following traditional tracheostomy. On the other hand, PDT is a less invasive procedure with a shorter operation time, resulting in less muscle damage. Importantly, PDT reduces the risk of injury to muscles involved in vocalization and swallowing, thereby increasing the likelihood of preserving these functions. This advantage makes PDT a more favorable option for tracheostomy in ALS patients.
We believe that the application of low-frequency stimulation to the neck, swallowing rehabilitation therapy [
18,
26], and regenerative injection therapy for wound healing19 have contributed to the recovery of vocalization in our patients, irrespective of their swallowing function. These combined therapies have likely enhanced the overall recovery process and facilitated the restoration of important functions such as phonation. The comprehensive and multidisciplinary approach to the management of ALS patients following PDT may play a crucial role in improving their quality of life and maintaining their ability to communicate effectively
In addition to the preservation of vocal function, we also observed improvements in the patients' overall quality of life after PDT. Following tracheostomy and connection to a home ventilator, patients were able to practice breathing without the ventilator, enhancing their respiratory function and overall preparedness for potential safety incidents. Furthermore, patients were able to spend time with their families without the ventilator, even going on wheelchair-assisted walks together. These improvements highlight the positive impact of PDT on patients' daily lives and underscore the importance of comprehensive post-PDT management strategies.
Furthermore, the T-tube's adjustable balloon and the balloon reduction program were essential in enabling patients to produce speech while maintaining the ability to clear secretions. By gradually reducing the balloon volume to 2 cc or less, patients could produce sound without compromising their airway clearance. In the T-tube, it is initially necessary to inject an appropriate amount of air for proper fixation within the trachea and to prevent the surgical opening from enlarging. However, indiscriminately filling the balloon with air due to the patient's sputum production can cause the balloon size to increase, leading to tracheal expansion and, in severe cases, the development of tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF) [
27]. Therefore, it is not always ideal to fill the balloon completely with air.
Therefore the key to successful phonation lies in inducing the T-tube to be secured through appropriate training of the neck muscles and the smooth muscle of the trachea [
28]. This training helps ensure that the T-tube is stabilized, allowing for better voice production while minimizing the risk of complications such as TEF.
Another important aspect to consider in ALS patients is the increased caloric expenditure due to respiratory insufficiency, even after the initiation of Non-Invasive Ventilation (NIV). Desport et al. [
29] reported that nutritional status is a prognostic factor for survival in ALS patients, and respiratory insufficiency could contribute to increased energy expenditure. In our study, we observed that following tracheostomy, the caloric expenditure of patients appeared to decrease, leading to weight gain in 29 cases. This finding suggests that tracheostomy may have a positive impact on the overall nutritional status and quality of life for ALS patients by reducing the energy expenditure associated with respiratory insufficiency.
Furthermore, the observed weight gain might also be attributed to improved digestion and bowel movements, as tracheostomy reduces abdominal pressure compared to NIV. This reduction in abdominal pressure [
30] could facilitate better digestive processes and more efficient bowel movements, contributing to the overall increase in weight and nutritional status.
Weight gain in ALS patients has been shown to improve their quality of life and reduce pain [
31]. A study highlighted that ALS patients consuming high-calorie diets experienced fewer adverse events and showed improvement in their nutritional status, which is linked to better survival rates and slower disease progression [
32]. This is supported by evidence indicating that improved nutrition can lead to better management of ALS symptoms, including pain and muscle function [
33].
Weight gain in ALS patients has been shown to improve their quality of life and reduce pain. Studies have indicated that maintaining or gaining weight can significantly enhance the overall well-being and functional status of ALS patients. For instance, research published in Brain Sciences [
31] highlights that early and symptom-specific clinical management, including nutritional support, can substantially improve the health-related quality of life (HRQoL) for ALS patients. This study found that ALS patients who were tracheostomized or used mobility aids reported better QoL compared to those who did not use these aids, emphasizing the role of comprehensive care strategies that include weight management.
In our studies, as respiratory function improved, there were notable reductions in pain and sensory symptoms associated with weight gain. Among eight patients who previously reported muscle pain and joint pain, seven experienced significant pain relief, with their VAS (Visual Analog Scale) scores decreasing from 7/10 or higher to 3/10 or lower. Moreover, of the three patients who reported sensory symptoms such as numbness, one showed improvement.
Regarding sleep disorders [
34], the improvement in respiratory function led to a decreased reliance on sleep medications. Out of 20 patients who had sleep disturbances, 18 reported improvements in their sleep quality following tracheostomy. This suggests that the enhancements in breathing not only reduced the need for sleep aids but also contributed to better overall sleep quality.
These findings indicate that tracheostomy can have a multifaceted positive impact on ALS patients, improving not just nutritional status and quality of life, but also alleviating pain [
35], sensory symptoms, and sleep disturbances [
34]. By addressing these various symptoms, tracheostomy emerges as a comprehensive intervention that benefits ALS patients in multiple dimensions, making it a compelling alternative to other respiratory support methods.
An intriguing finding in our study was that three patients were able to maintain normal eating habits without significant dysphagia following the Percutaneous Dilatational Tracheostomy (PDT) procedure. This suggests that PDT might have a positive impact on swallowing function in some ALS patients, in addition to preserving vocalization. Supporting this, a pilot study on Pharyngeal Electrical Stimulation (PES) in ALS patients [
36] demonstrated a significant improvement in swallowing function. In this study, 20 ALS patients with severe dysphagia were randomized to receive PES in addition to Standard Logopaedic Therapy (SLT) or SLT alone. The results showed a significant improvement in swallowing function, as evidenced by a reduction in the Penetration Aspiration Scale (PAS) scores from 3.6 at baseline to 2.3 one day after treatment. These improvements in swallowing function were maintained below baseline levels during subsequent visits, indicating the potential efficacy of such interventions in ALS patients.
Another interesting challenge was the rehabilitation method aimed at increasing the time patients could breathe without using a ventilator. This involved daily training to breathe without the ventilator, combined with various respiratory rehabilitation therapies. The duration was gradually increased from 10 minutes to 20 minutes, and then from 20 minutes to 30 minutes. Not all 47 patients participated in this program, and the results varied among individuals. However, 7 patients were able to breathe for more than 2 hours without the ventilator, and 2 patients were even able to breathe without invasive ventilatory support except during sleep. This aspect also helps to dispel the stigma associated with tracheostomy.
Therefore, the observation of maintained eating habits and reduced dysphagia in our study aligns with existing research, suggesting the potential of PDT to positively impact swallowing function in ALS patients. Further investigation is needed to explore the factors contributing to this outcome and to ascertain the broader applicability of PDT in improving swallowing function in a larger patient population. And it is necessary to confirm these findings and optimize speech function management in ALS patients undergoing tracheostomy.
In the past, many ALS patients faced the prospect of tracheostomy with the fear of losing their voice completely, envisioning a future where they could only blink their eyes while being completely paralyzed. The inability to control non-invasive ventilation often led them to choose end-of-life options. However, with more precise explanations and updated medical information, it is crucial to inform patients that, although full vocal recovery might not be possible, simple communication can still be achieved. Explaining that tracheostomy and various therapies can improve various ALS-related symptoms and provide better quality of life can empower patients to make informed decisions. This approach respects their right to choose and ensures they understand all potential benefits and options available to them.
While the sample size of 47 patients is relatively small, it is representative of the ALS population within our institution. The consistency in procedural performance, with all surgeries conducted by Dr. Jae-Kook Yoo, ensures that the variability due to different surgical techniques is minimized. However, further studies with larger sample sizes and involving multiple surgeons are necessary to generalize these findings more broadly.
In our study, we observed that a significant proportion of ALS patients were able to preserve vocal function following PDT. Despite the non-normal distribution of the data, the application of both parametric and non-parametric statistical methods provided a rigorous evaluation of the outcomes. The absence of double-blind evaluation is a recognized limitation; however, the assessments were conducted by experienced rehabilitation medicine specialists, ensuring a high level of professional scrutiny and reliability in the evaluations.
This study holds significant clinical value, particularly in the context of ALS, a rare and progressive neurodegenerative disease. The findings contribute valuable insights into the management of vocal function in ALS patients, highlighting the potential benefits of PDT combined with adjuvant therapies. Such insights are crucial for improving patient care and guiding future research in this challenging field.
In conclusion, while recognizing the methodological limitations, this study provides meaningful evidence on the effectiveness of PDT and adjuvant therapies in preserving vocal function in ALS patients. Further research with larger sample sizes and more rigorous controls is necessary to build on these findings and optimize treatment strategies for ALS patients.
7. Conclusions
In conclusion, our findings suggest that PDT combined with mesotherapy, low-frequency electrical stimulation, and swallowing rehabilitation therapy may help maintain vocal function in limb type ALS patients. Despite the overall decrease in speech scores, some patients showed improvement, highlighting the potential benefits of this combined approach.
Additionally, the observed weight gain in patients transitioning from NIV to tracheostomy underscores the importance of stable respiratory support in overall patient health. Future studies with larger sample sizes and diverse patient populations are necessary to validate these findings and to explore the long-term benefits of these therapies in ALS management. Furthermore, investigating the specific contributions of individual treatments within the combined approach will be crucial for optimizing therapeutic strategies.
Until more perfect treatments are developed, maintaining vocalization and achieving a near-normal body mass index (BMI) of 23(kg/m²), while being able to sit in a wheelchair and go for walks with family, is now a realistic goal for ALS patients following PDT with adjuvant therapies. This approach respects their right to choose and ensures they understand all potential benefits and options available to them, providing a higher quality of life and better daily experiences. Further research is warranted to confirm these findings and explore the broader implications of tracheostomy in ALS care.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
No conflict of interest.
References
- Brown, R.H.; Al-Chalabi, A. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Longo DL, editor. N Engl J Med [online serial]. N Engl J Med; 2017;377:162–172. Accessed at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28700839/. Accessed April 8, 2023.
- O’Brien, D.; Stavroulakis, T.; Baxter, S., et al. The optimisation of noninvasive ventilation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a systematic review. Eur Respir J [online serial]. Eur Respir J; 2019;54. Accessed at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31273038/. Accessed April 8, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Cedarbaum, J.M.; Stambler, N.; Malta, E., et al. The ALSFRS-R: A revised ALS functional rating scale that incorporates assessments of respiratory function. J Neurol Sci [online serial]. J Neurol Sci; 1999;169:13–21. Accessed at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10540002/. Accessed April 8, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Ciaglia, P.; Firsching, R.; Syniec, C. Elective percutaneous dilatational tracheostomy. A new simple bedside procedure; preliminary report. Chest [online serial]. Chest; 1985;87:715–719. Accessed at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3996056/. Accessed April 8, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Noy R, Macsi F, Shkedy Y, Simchon O, Gvozdev N, Epstein D. Safety of Percutaneous Dilatational Tracheostomy in Critically Ill Patients with Liver Cirrhosis. European Surgical Research [online serial]. S. Karger AG; 2024;65:69–73. Accessed at: https://dx.doi.org/10.1159/000539106. Accessed July 5, 2024. [CrossRef]
- Pandit, A.; Swami, G.; Kumar, K.D. Comparative Study of Percutaneous Dilatational Tracheostomy and Conventional Surgical Tracheostomy in Critically Ill Adult Patients. Indian Journal of Otolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery [online serial]. Springer; 2023;75:1568–1572. Accessed at: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12070-023-03666-9. Accessed July 5, 2024. [CrossRef]
- Cools-Lartigue, J.; Aboalsaud, A.; Gill, H.; Ferri, L. Evolution of percutaneous dilatational tracheostomy - A review of current techniques and their pitfalls. World J Surg [online serial]. Springer; 2013;37:1633–1646. Accessed at: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00268-013-2025-6. Accessed July 5, 2024. [CrossRef]
- Pfeffer, G.; Povitz, M. Respiratory management of patients with neuromuscular disease: current perspectives. Degener Neurol Neuromuscul Dis [online serial]. Degener Neurol Neuromuscul Dis; 2016;6:111–118. Accessed at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30050373/. Accessed April 8, 2023.
- Cedarbaum, J.M.; Stambler, N.; Malta, E., et al. The ALSFRS-R: A revised ALS functional rating scale that incorporates assessments of respiratory function. J Neurol Sci [online serial]. J Neurol Sci; 1999;169:13–21. Accessed at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10540002/. Accessed December 5, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Mehta, C.; Mehta, Y. Percutaneous Tracheostomy. Ann Card Anaesth [online serial]. Wolters Kluwer -- Medknow Publications; 2017;20:S19. Accessed at: /pmc/articles/PMC5299824/. Accessed December 7, 2023.
- Lim, S.; Park, H.; Lee, J.M.; Lee, K.; Heo, W.; Hwang, S.H. Comparison of Conventional Surgical Tracheostomy and Percutaneous Dilatational Tracheostomy in the Neurosurgical Intensive Care Unit. Korean J Neurotrauma [online serial]. Korean J Neurotrauma; 2022;18. Accessed at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36381441/. Accessed December 7, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Serry, M.A.; Alzamendi, G.A.; Zañartu, M.; Peterson, S.D. Modeling the influence of the extrinsic musculature on phonation. Biomech Model Mechanobiol [online serial]. Biomech Model Mechanobiol; 2023;22:1365–1378. Accessed at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37169957/. Accessed December 7, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Deckert, J.; Deckert, L. Vocal cord dysfunction. Am Fam Physician. American Academy of Family Physicians; 2010;81:156–159.
- Vahabzadeh-Hagh, A.M.; Pillutla, P.; Zhang, Z.; Chhetri, D.K. Dynamics of Intrinsic Laryngeal Muscle Contraction. Laryngoscope [online serial]. Laryngoscope; 2019;129:E21–E25. Accessed at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30325497/. Accessed December 7, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Sarasate, M.; González, N.; Córdoba-Izquierdo, A. , et al. Impact of Early Non-Invasive Ventilation in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial. J Neuromuscul Dis. IOS Press BV; 2023;10:627–637. [CrossRef]
- Jackson, C.E.; Heiman-Patterson, T.D.; Sherman, M., et al. Factors associated with Noninvasive ventilation compliance in patients with ALS/MND. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Frontotemporal Degener [online serial]. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Frontotemporal Degener; 2021;22:40–47. Accessed at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34348541/. Accessed December 7, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Stehling, F.; Bouikidis, A.; Schara, U.; Mellies, U. Mechanical insufflation/exsufflation improves vital capacity in neuromuscular disorders. Chron Respir Dis [online serial]. Chron Respir Dis; 2015;12:31–35. Accessed at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25472495/. Accessed April 8, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Shigematsu, T.; Fujishima, I. [Dysphagia and swallowing rehabilitation]. Brain Nerve [online serial]. Brain Nerve; 2015;67:169–182. Accessed at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25681362/. Accessed April 8, 2023.
- Hong, J.W.; Lee, W.J.; Hahn, S.B.; Kim, B.J.; Lew, D.H. The effect of human placenta extract in a wound healing model. Ann Plast Surg [online serial]. Ann Plast Surg; 2010;65:96–100. Accessed at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20548228/. Accessed April 8, 2023.
- Huang, Y.Z.; Rothwell, J.C.; Lu, C.S.; Wang, J.J.; Chen, R.S. Restoration of motor inhibition through an abnormal premotor-motor connection in dystonia. Mov Disord [online serial]. Mov Disord; 2010;25:696–703. Accessed at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20309999/. Accessed April 8, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Gungor, A. Balloon dilation of the pediatric airway: potential for disaster. Am J Otolaryngol [online serial]. Am J Otolaryngol; 2012;33:147–149. Accessed at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21784553/. Accessed April 8, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Khan, Y.S.; Bordoni, B. Anatomy, Head and Neck, Suprahyoid Muscle. StatPearls [online serial]. Epub 2019. Accessed at: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31536316. Accessed January 8, 2024.
- Mnatsakanian, A.; Minutello, K.; Black, A.C.; Bordoni, B. Anatomy, Head and Neck, Retropharyngeal Space. StatPearls [online serial]. StatPearls Publishing; Epub 2023 Jul 30. Accessed at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537044/. Accessed January 8, 2024.
- Nikbakhsh, N.; Amri, F.; Monadi, M.; Amri, P.; Bijani, A. Semi-surgical percutaneous dilatational tracheostomy vs. conventional percutaneous dilatational tracheostomy: A prospective randomized trial. Caspian J Intern Med [online serial]. Caspian J Intern Med; 2021;12:249–255. Accessed at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34221273/. Accessed December 7, 2023.
- Brass, P.; Hellmich, M.; Ladra, A.; Ladra, J.; Wrzosek, A. Percutaneous techniques versus surgical techniques for tracheostomy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev [online serial]. Cochrane Database Syst Rev; 2016;7. Accessed at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27437615/. Accessed April 8, 2023.
- Debucean, D.; Mihaiu, J.; Maghiar, A.M.; Marcu, F.; Marcu, O.A. A Multidisciplinary Approach to Swallowing Rehabilitation in Patients with Forward Head Posture. Medicina (Kaunas) [online serial]. Medicina (Kaunas); 2023;59. Accessed at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37763700/. Accessed January 8, 2024.
- Epstein, S.K. Late complications of tracheostomy. Respir Care [online serial]. Respir Care; 2005;50:542–549. Accessed at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15807919/. Accessed April 8, 2023.
- Wallace, S.; McGowan, S.; Sutt, A.L. Benefits and options for voice restoration in mechanically ventilated intensive care unit patients with a tracheostomy. J Intensive Care Soc [online serial]. J Intensive Care Soc; 2023;24:104–111. Accessed at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36874291/. Accessed January 8, 2024. [CrossRef]
- Desport, J.C.; Preux, P.M.; Truong, T.C.; Vallat, J.M.; Sautereau, D.; Couratier, P. Nutritional status is a prognostic factor for survival in ALS patients. Neurology [online serial]. Neurology; 1999;53:1059–1063. Accessed at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10496266/. Accessed April 8, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Morejón C de, D.S.; Barbeito, T.O.T. Effect of mechanical ventilation on intraabdominal pressure in critically ill patients without other risk factors for abdominal hypertension: An observational multicenter epidemiological study. Ann Intensive Care [online serial]. Springer Verlag; 2012;2012:1–12. Accessed at: https://annalsofintensivecare.springeropen.com/articles/10.1186/2110-5820-2-S1-S22. Accessed May 27, 2024.
- Peseschkian, T.; Cordts, I.; Günther, R., et al. A Nation-Wide, Multi-Center Study on the Quality of Life of ALS Patients in Germany. Brain Sciences 2021, Vol 11, Page 372 [online serial]. Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute; 2021;11:372. Accessed at: https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3425/11/3/372/htm. Accessed May 27, 2024. [CrossRef]
- High-calorie feeding may slow progression of ALS — Harvard Gazette [online]. Accessed at: https://news.harvard.edu/gazette/story/2014/02/high-calorie-feeding-may-slow-progression-of-als/. Accessed May 27, 2024.
- Körner, S.; Hendricks, M.; Kollewe, K., et al. Weight loss, dysphagia and supplement intake in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS): impact on quality of life and therapeutic options. BMC Neurol [online serial]. BMC Neurol; 2013;13. Accessed at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23848967/. Accessed May 27, 2024. [CrossRef]
- Lucia, D.; McCombe, P.A.; Henderson, R.D.; Ngo, S.T. Disorders of sleep and wakefulness in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS): a systematic review. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Frontotemporal Degener [online serial]. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Frontotemporal Degener; 2021;22:161–169. Accessed at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33191797/. Accessed May 27, 2024. [CrossRef]
- Chiò, A.; Mora, G.; Lauria, G. Pain in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Lancet Neurol [online serial]. Lancet Neurol; 2017;16:144–157. Accessed at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27964824/. Accessed May 27, 2024. [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, C.; Schradt, F.; Lindner-Pfleghar, B.; Schuster, J.; Ludolph, A.C.; Dorst, J. Pharyngeal electrical stimulation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a pilot study. Ther Adv Neurol Disord [online serial]. Ther Adv Neurol Disord; 2022;15. Accessed at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35154390/. Accessed December 7, 2023. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).