1. Introduction
The decline in arable land is putting pressure on agricultural producers. This is not only linked to changes in the ecosystem—soil degradation and climate change—but also to increasing urbanization. These changes are forcing farmers to look for alternatives—to produce more from less land per unit area. These global changes have led to a significant increase in soilless crop production in recent years [
1].
Soilless crop production can be 2–5 times more productive, with 10 times less water consumption compared to field production. This results in year-round production, better taste, and higher nutritional value [
2]. Switching from an outdoor soil-based crop production system to a soilless system can improve water use efficiency, especially in closed-loop systems with a recirculating solution of water and nutrients that is collected in a closed drainage water tank for reuse [
3,
4]. Another reason is related to ecology and environmental protection: the intensive destruction of peatland areas that are important for the ecosystem, and the use of artificial substrates, which cause waste accumulation problems and environmental pollution. Peat has been the dominant organic component of growing media in many parts of the world for the last 50 years due to its excellent physical properties, such as excellent air and water retention, low pH and salinity, and protection against pests and diseases [
5]. Due to its ease of use and beneficial properties, peat has over time become a key component of growing media and still dominates the greenhouse sector. Worldwide, around 40 million m
3 of peat is used annually in horticulture [
6], with Germany (8.5 million m
3) and the UK (2.5 million m
3) being the main consumers of peat in horticulture [
7]. Other resources, such as treated and untreated waste wood or its bark, can also be used as growing media or as components of growing media, and renewable raw materials have a high potential for their use in agriculture for growing plants in closed systems without soil. Preliminary studies by Dutch researchers have shown that the performance of five peat-pine bark mixtures in the region is comparable to that of perlite at the vegetative and early fruiting stages of cucumbers [
4,
8,
9]. Waste management strategies to reduce, reuse, and recycle waste should be further and more rigorously applied in soilless cropping systems [
2,
4,
9]. Wood-based substrates including pine bark and wood fiber have good air permeability and high saturated hydraulic conductivity [
10]. Wood-based substrates are more sustainable than peat and more readily available and cheaper than coir [
8]. Wood fiber or sawdust is a by-product of the wood industry, produced from clean, broken wood. Wood substrates are typically produced by chopping and grinding the tree, as well as from leaves, twigs, branches, and needles removed during forest thinning. Sawdust is a by-product of wood that remains after production operations and has been used as an ingredient in other growing media materials, especially where peat is scarce or expensive. Wood sawdust can be used as a component of growing media with peat [
4,
11]. Wood fiber is produced using mechanical defibrillation or, most commonly, water vapor—squeezing clean wood chips through a thermoplastic press. The wood fiber can be compressed for ease of transport [
12]. Wood fiber as a growing media date back to 2000 in Spain, France, and Germany [
13]. New wood waste recycling plants have been established in the USA, Ireland, Germany, the UK, and Latvia [
14]. Materials that are easy to produce, financially viable, environmentally friendly, and capable of providing quality growing media will become future substitutes for rockwool and peat.
Climate change, soil degradation, and other ecological problems will drive the development of soilless cropping systems and the choice of growing media in the near future. Growing crops in soilless culture systems involve high energy consumption for heating in the cold season and artificial lighting, expensive greenhouse construction [
15,
16], fertilizer use [
3], post-harvest transportation and packaging [
17]. On the other hand, SCS (soilless culture systems) help to alleviate many of the problems associated with conventional in situ cultivation, such as soil-borne diseases and pests, and precise control of water and fertilizer requirements [
18,
19]. The resulting high-quality production and higher yields in a shorter time justify the production costs in these systems [
20].
Innovative, sustainable, and renewable materials such as compost, bark, wood, coir, and other organic wastes with low production costs and short transport routes can become the growing media of the future and dominate the market for growing media raw materials. In the future, waste and organic materials will be highly competitive materials, similar to wood and bark today [
21]. As an alternative to synthetic and peat-based substrates, wood fiber from wood processing can be used, but further research is needed.
Nutrient availability is one of the main factors determining the suitability of organic substrates for plant growth [
22], which may depend on their elemental composition and other factors affecting nutrient forms and dynamics, including the presence of dissolved organic compounds, the biological stability of the growing media, and the adsorption capacity [
23]. The availability of nutrient elements, including magnesium, calcium, etc., directly influences the rate of synthesis of certain metabolites in plants [
24,
25]. The wood fiber in the growing media can influence the uptake of nutrients by the plant, as it has a nutrient storage function [
26]. Nutrient cycling in wood fiber growing media is a complex and dynamic process influenced by various environmental factors and plant species, making it difficult to predict nutrient availability and uptake [
27]. However, wood fiber is a suitable material for horticultural growing media due to its fibrous structure, hydrophilic nature, and low nutrient or growth-inhibiting content compared to other components such as bark [
28].
Given the above, this study was carried out to identify a suitable soilless media made of wood fiber and peat, select the optimum fertilization to compensate for nitrogen immobilization, and ensure the optimum nutrient uptake and physicochemical properties of the growing media.
3. Results
3.1. Cucumber Productivity and Physicochemical Properties of Growing Media
The moisture content of the cucumber growing media depended on the amount of wood fiber and additional N, but significant differences were found in the non-factor interaction (Growing media × Fertilization rate) (
Table 2). Increasing the amount of wood fiber in the media increased the moisture content from 9.8 to 35.0% compared to the moisture content of the peat substrate. Additional N fertilization significantly reduced the moisture content of the cucumber growing media by up to 37.6% compared to the growing media without additional fertilization. The density of the growing media was influenced only by its composition, decreasing with increasing wood fiber content. The electrical conductivity (EC) depended on the interaction of the factors, on the proportion of wood fiber in the growing media, and on the addition of N fertilizer. The highest EC was found in the growing media mixture WF/PS 25/75. The index decreased with increasing fiber content in the media. The EC in the wood fiber media was higher than in the peat substrate, but lower compared to the EC in the WF/PS 50/50 media. The additional fertilization with N
30 increased the EC by a factor of 1.1 to 3.3 compared to the EC in the media without additional fertilization. A higher proportion of the wood fiber in the growing media had an alkalizing effect by increasing the pH, while the additional fertilizer N
13–30 significantly decreased the pH of the media.
The dry mass and green mass of cucumber plants were significantly influenced by the interaction of factors. The higher proportion of wood fiber in the media (WF/PS 50/50 and WF) and the additional fertilization with higher rates of N23,30 significantly reduced the dry mass content of the aboveground mass of the plants. Aboveground green mass was significantly higher only when cucumbers were grown on peat substrate without additional N fertilization. Increasing the proportion of wood fiber and N fertilization in the growing media resulted in a significant decrease in the average aboveground green mass of the plant. The number and mass of cucumber fruits on the plant were influenced by the amount of wood fiber in the growing media and the additional N fertilization. The highest number of fruits was produced on the plant when they were grown in a 50/50 mixture of peat substrate and wood fiber WF/PS, with additional fertilization with the lowest rate of nitrogen N13. Cucumbers were also significantly higher in fruit mass when grown in a WF/PS 50/50 mixture without additional fertilizer and with the lowest rate of additional N13.
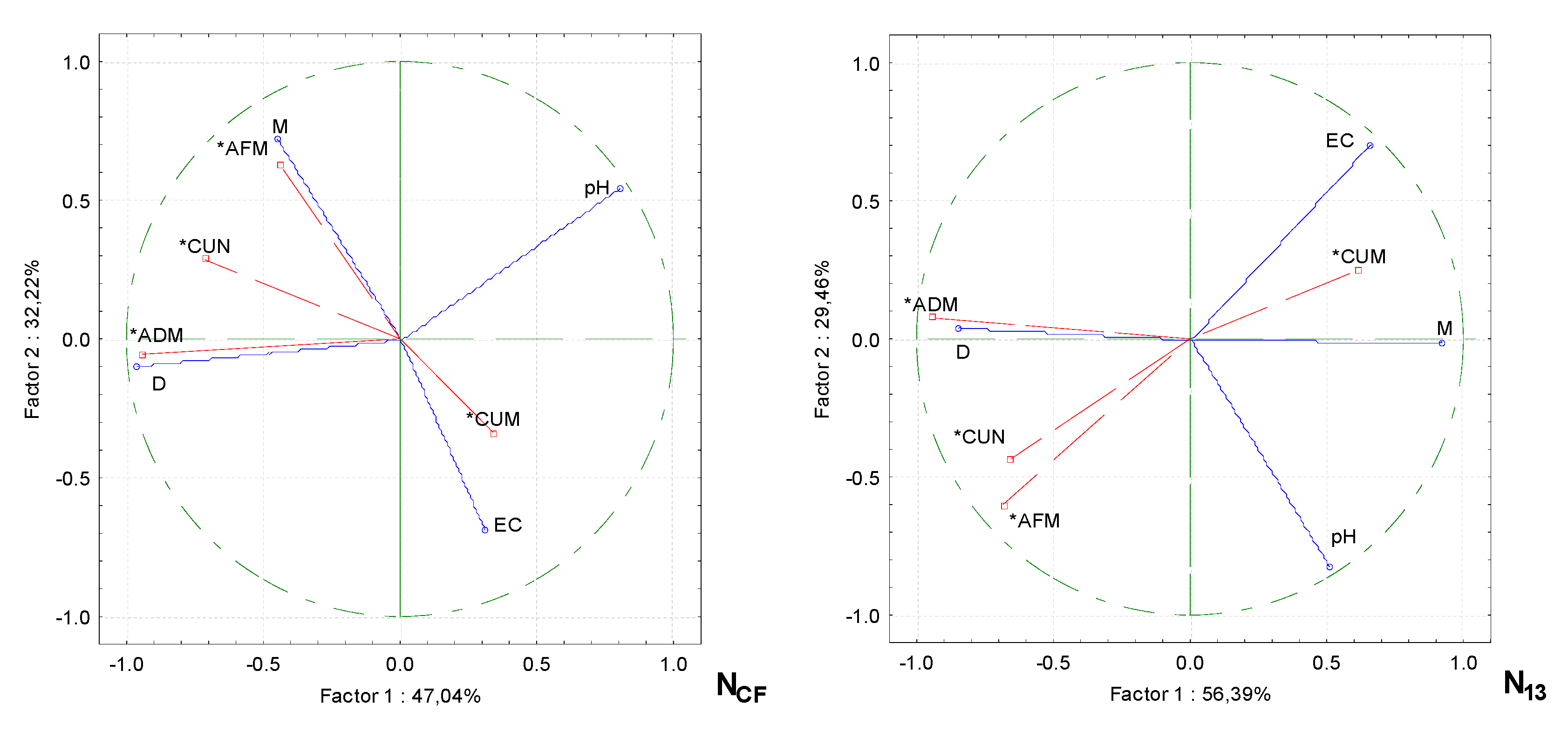
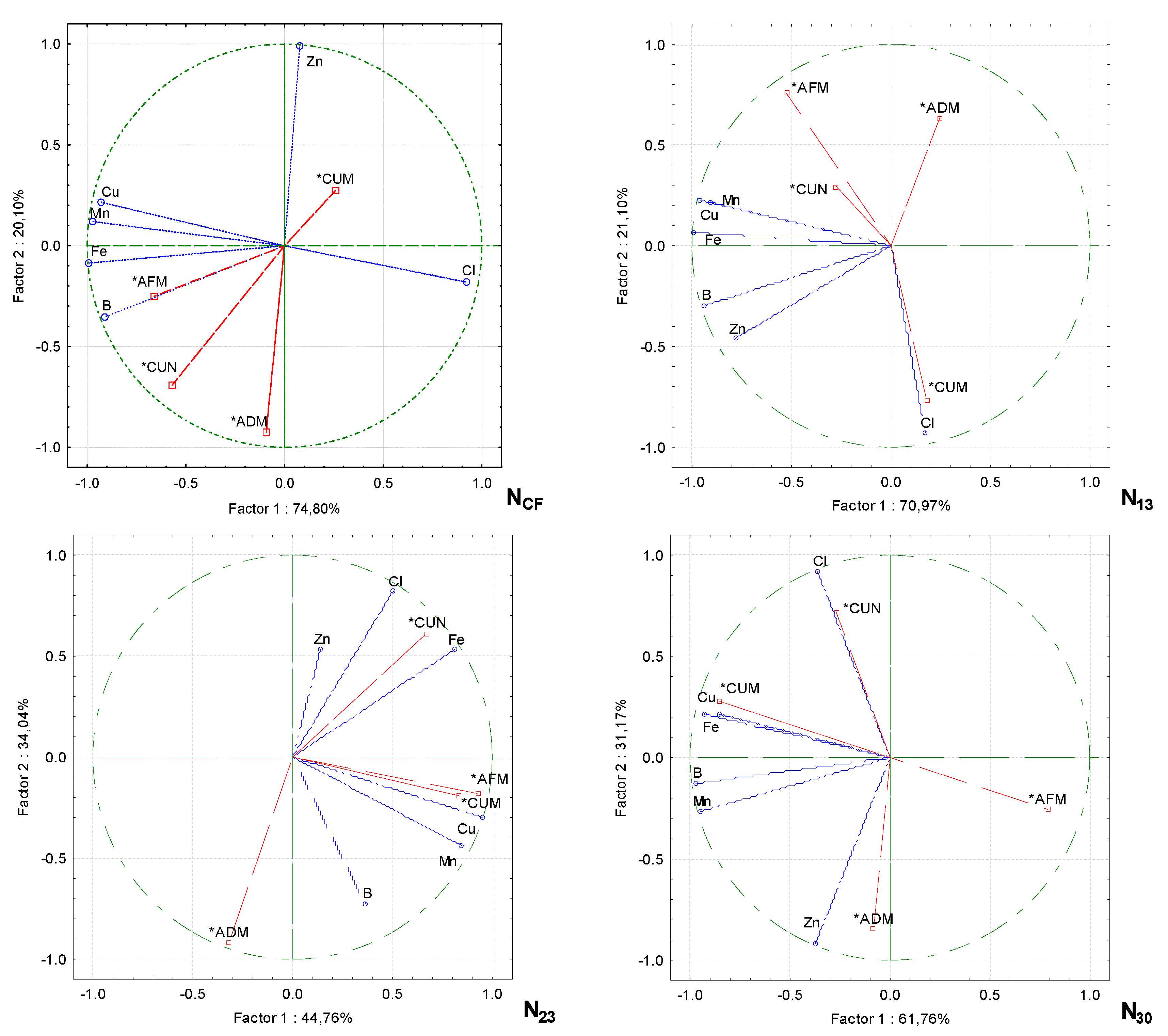
Principle component analysis (PCA) showed that the physicochemical properties of the growing media were altered by increasing the proportion of wood fiber and the rate of nitrogen fertilizer and that the productivity of cucumbers depended on them (
Figure 3). Only the pH of the growing media had no significant effect on cucumber performance, irrespective of the rate of nitrogen fertilization. The other physicochemical properties of the growing media were correlated in distinct groups. When cucumbers were grown without supplementary fertilization (CF), the green aboveground mass and the fruit content on the plant correlated strongly with the moisture content of the growing media, while the dry mass content of the aboveground mass was influenced by the density of the media. There was a strong correlation between the EC of the growing media and the mass of fruit on the plant, but a negative correlation was found between the moisture of the growing media.
With additional N13 fertilization, a strong correlation was obtained in the group between the EC of the growing media and the mass of the fruit on the plant, with a weaker correlation with the moisture content of the media. The other strongly correlated group was plant aboveground dry mass and density of the growing media. The cucumber fruit content and plant aboveground green mass were negatively correlated with the EC of the growing media.
When the nitrogen fertilizer rate was increased to N23, only the dry mass content of the aboveground plant correlated with the density of the growing media. The other cucumber performance parameters were not affected by physical characteristics. When cucumbers were fertilized at the maximum rate of N30, the largest group of correlated parameters was the aboveground dry mass of the plant with the electrical conductivity and density of the growing media. In another group, there was a strong correlation between cucumber fruit mass and the moisture content of the growing media.
3.2. Micronutrient Content, Nitrogen Content, and C:N at the End of the Growing Season in the Growing Media
Plants grown under climate-controlled conditions take in more nutrients from the growing media than those grown outdoors. The high nutrient demand is due to the shallow penetration of the root system (limited by the volume of the vegetative container), the weak suction power of the roots, and the large difference between the mass of the aboveground part of the plant and the root system. To provide the plants grown with wood fiber under controlled climatic conditions in different media with the required micronutrient content, the micronutrient content of the media at the beginning and the end of the study was determined. Wood fiber contains a significant amount of nutrients and the concentration of these nutrients in the wood varies between tree species and depends on the nutrient supply of the soil [
29]. The study found that the highest uptake of micronutrients during the growing season was observed in plants grown in the wood fiber (
Table 3). Plants grown in this media had a 37 percentage points higher copper uptake than plants grown in peat substrate with conventional fertilization. Plants grown on wood fiber showed the best uptake of zinc and manganese when fertilized with the highest N fertilization rate of N
30, which was 13 and 28 percentage points, respectively, compared to conventional fertilization on wood fiber. Only the iron uptake of the plants grown in the wood fiber decreased with increasing nitrogen levels. Plants fertilized with N
30 nitrogen absorbed 15 percentage points less iron than plants grown in the wood fiber with conventional fertilization, but 6 percentage points more than plants grown on peat substrate with conventional fertilization.
The higher nitrogen content N30 interfered with the uptake of copper and zinc by plants growing on peat substrate and on WF/PS 50/5 and WF/PS 25/75 wood fiber media. The maximum N30 fertilization on the peat substrate reduced zinc uptake by 39 percentage points, by 7 percentage points on the WF/PS 50/50 growing media and by 21 percentage points on the WF/PS 25/75 growing media, compared with the zinc uptake by the plants on the conventional fertilization. Thus, the plants grown in these growing media showed the best uptake of zinc under conventional fertilization. Plants grown in WF/PS 50/50 and WF/PS 25/75 had the best uptake of copper when fertilized with N23. Copper uptake increased by 2 and 16 percentage points, respectively, compared to conventional fertilization.
Manganese and iron uptake by the plants was better when fertilized with increased nitrogen. Plants grown on peat substrate showed the best uptake of these trace elements when fertilized with N
13 nitrogen, with increases of 19 and 15 percentage points, respectively, compared to conventional fertilization. Plants grown on WF/PS 50/50 media showed the best uptake of manganese and iron when fertilized with N
23 nitrogen. Plants grown on WF/PS 25/75 had the best uptake of manganese when fertilized with N
13 nitrogen and iron when fertilized with N
23 nitrogen. Cucumbers grown on WF media showed a better uptake of Fe and Mn than cucumbers grown on the other growing media studied. Cucumbers fertilized with conventional fertilizer (CF) in WF were 32 percentage points more efficient in Fe uptake than in PS. Fe use efficiency can contribute to improving plant physiology by playing a key role as a component of the catalytic centers of various bio-protein redox enzymes including cytochromes, peroxidases, and catalases. This trace element is vital for nitrogen assimilation and photosynthesis [
30].
The trends of boron and chlorine content in the growing media were similar. The lowest changes in these elements during the growing season were observed in the media where the plants were fertilized with conventional fertilization. When the plants were fertilized with N13 nitrogen, the boron content of the growing media increased from 19 percentage points in the WF/PS 25/75 growing media to 45 percentage points in the wood fiber, and the chlorine content increased from 23 percentage points in the WF/PS 50/50 growing media to 73 percentage points in the WF/PS 25/75 growing media, compared with the levels of these elements in the media where the plants were treated with conventional fertilization. As the nitrogen supply to the plants was further increased up to the maximum rate of N30, the levels of these chemical elements increased in all the growing media studied, and at the end of the cucumber growing season, the levels of boron increased from 30 percentage points in WF to 80 percentage points in WF/PS 50/50, and the level of chlorine increased from 106 percentage points in WF/PS 25/75 to 191 percentage points in PS, compared with the level of the growing media where the plants were treated with conventional fertilization.
At the end of the cucumber growing season, the micronutrient content of the growing media was determined to assess how the plant nutrient uptake depended on the fertilization with different nitrogen rates and the amount of wood fiber in the growing media. A comparison of the copper content of all media at all fertilizer rates showed that, at the end of the growing season, the WF media contained significantly less copper, by as much as 99%, and the WF/PS 25/75 media contained significantly more copper than the PS media under conventional fertilization (CF).
The study showed that the highest uptake of micronutrients during the growing season was observed for plants grown on WF. Plants grown on this media had a 37-percentage point higher copper uptake than plants grown on PS. Plants grown in the wood fiber had the best uptake of zinc and manganese when fertilized with the highest nitrogen rate N30, which was 13 and 28 percentage points, respectively, compared to the conventional fertilizer WF. Only the uptake of iron by WF plants decreased with increasing nitrogen levels. Plants fertilized with N30 absorbed 15 percentage points less of it than WF and conventional fertilization, but 6 percentage points more than PS and conventional fertilization (CF). Boron content was more influenced by the composition of the media than by nitrogen fertilization. Boron uptake by the plants was better from PS and WF without additional nitrogen fertilizer. The higher nitrogen rate made the uptake of boron from the growing media more difficult.
At the end of the cucumber growing season, the highest levels of total and mineral nitrogen were found in the WF/PS 25/75 growing media, but the carbon/nitrogen ratio was found in the WF media (
Table 4). PS had the lowest Fe content compared to WF growing media and mixed media, with an average of 1.9 times the content of this trace element. The total and mineral nitrogen content of the growing media increased with increasing nitrogen fertilization. The C:N ratio was more dependent on the proportion of wood fiber in the growing media and decreased with increasing nitrogen fertilizer rate up to N
30.
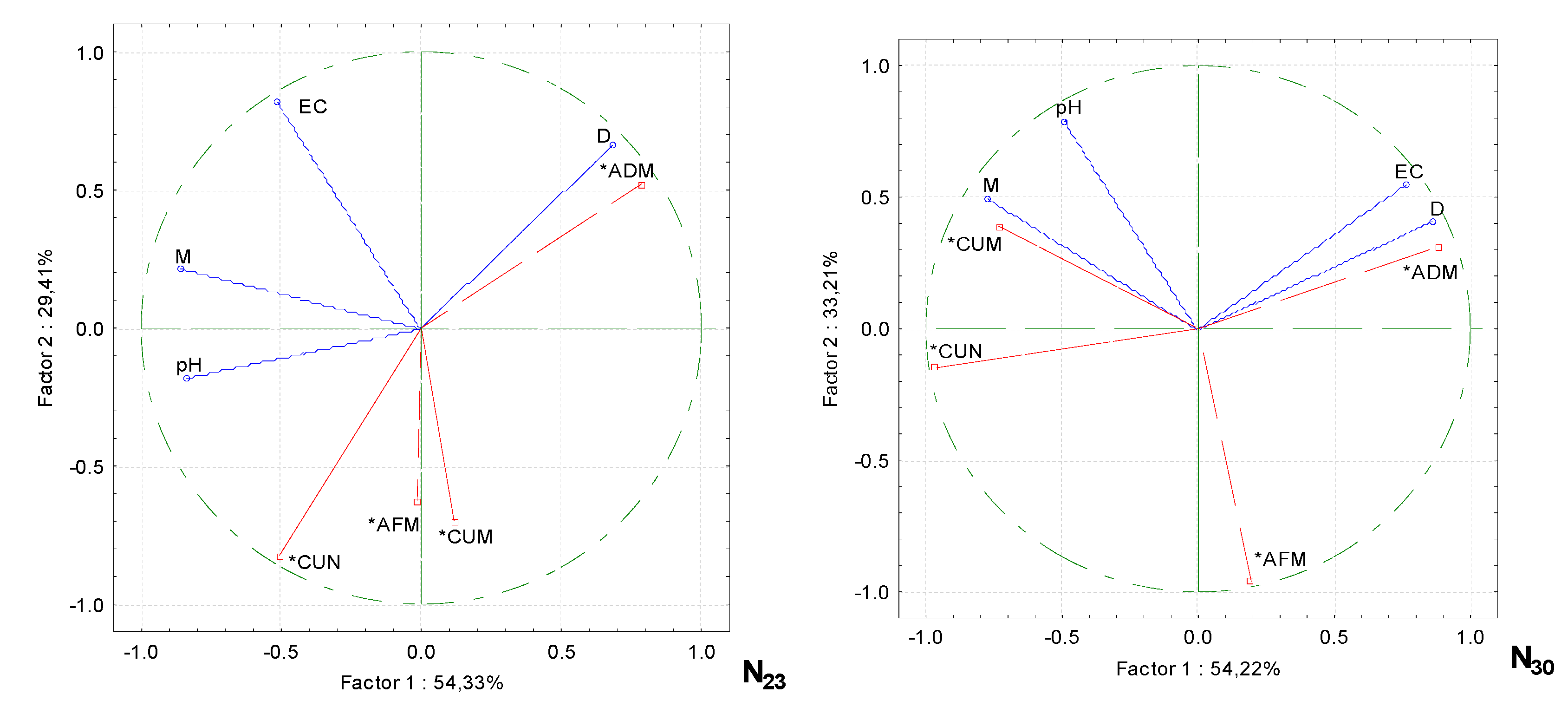
Principle component analysis showed that increasing the proportion of wood fiber and nitrogen fertilizer in the growing media resulted in a change in the trace element content of the media, which in turn influenced the cucumber performance. These parameters were correlated in separate groups (
Figure 4). The green mass of cucumber plants in the substrate without additional fertilization (NCF) was strongly dependent in the group on B, Fe, and to a lesser extent on Mn and Cu. Cucumber fruit set in pcs m
−2 was more dependent on B than on Fe content in the growing media and significantly less on Mn and Cu. Cucumber fruit mass per plant was strongly correlated with Zn, but there was a negative correlation between this trace element and plant dry mass.
In the growing media, increasing the nitrogen rate (N13), the number of cucumber fruit pieces m−2, and the green mass of the plants in kg m−2 correlated strongly with Mn and Cu and less strongly with the Fe content of the substrate. Cucumber fruit per plant (CUM) was strongly correlated with the Cl content of the growing media.
When the nitrogen fertilizer level was increased to N23, a correlation was observed in two groups. Cucumber fruit mass in units m−2 was strongly correlated with Zn, Cl, and Fe, while in the other group cucumber plant green mass and fruit mass were strongly correlated with Cu and Mn, with a weaker correlation with B. A negative correlation was found between plant dry mass and Zn.
When the fertilizer rate was increased to a maximum of N30, there was a very strong correlation between the fruit content and the Cl content, and the fruit mass was strongly dependent on the Cu and Fe content of the growing media. The dry mass content of the aboveground part of cucumber plants at N30 was already positively correlated with the Zn content of the growing media. A negative correlation was found between the green aboveground mass of the plants and the Cu and Fe content of the media.
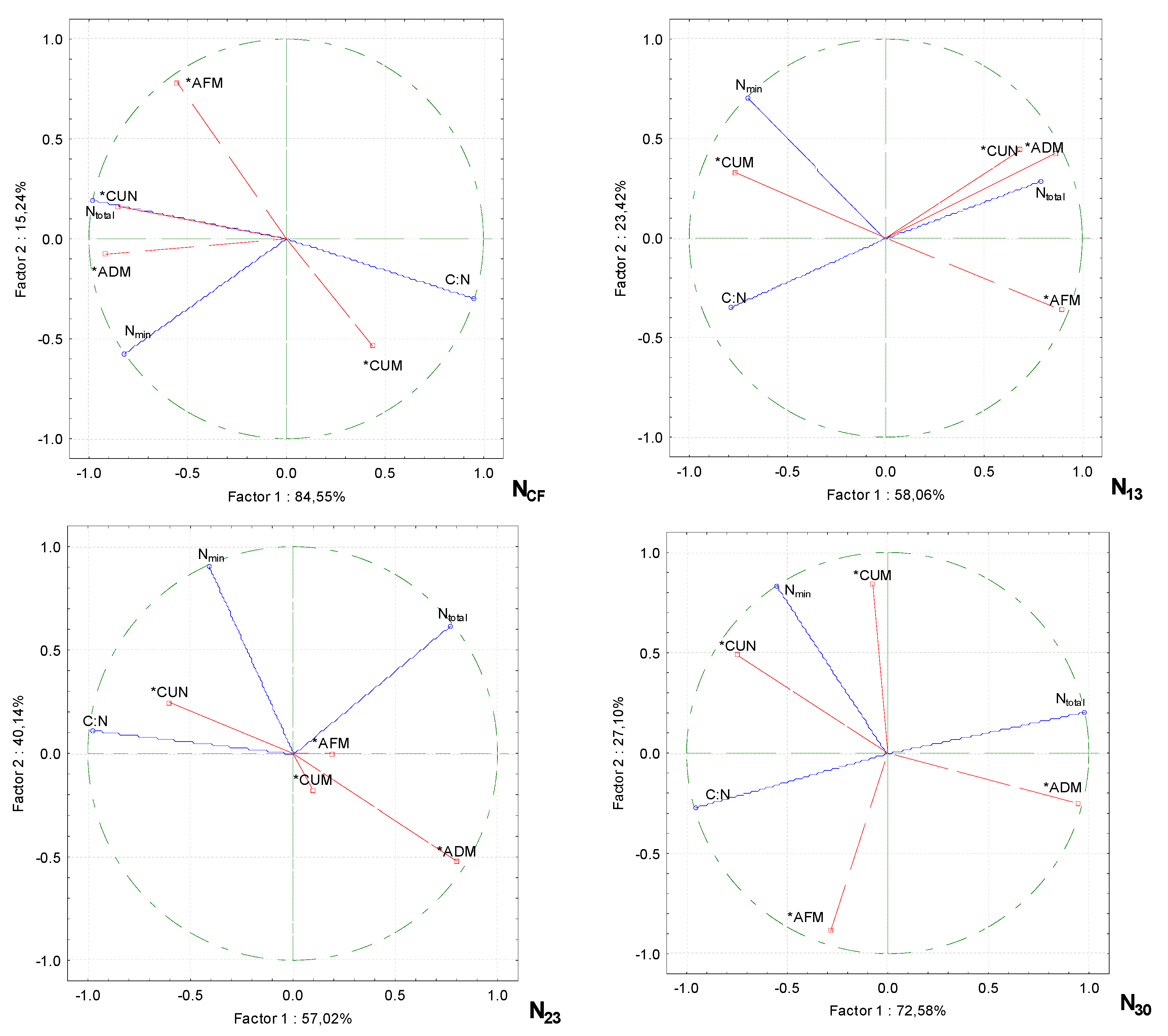
Principle component analysis showed that increasing the proportion of wood fiber and nitrogen fertilizer in the growing media resulted in changes in the total and mineral nitrogen content and the carbon/nitrogen ratio in the growing media and that these changes were related to the cucumber performance parameters (
Figure 5). Fruit mass was significantly influenced by the C:N ratio, while other performance parameters were not affected by higher nitrogen rates and C:N. In the substrate without supplementary nitrogen (N
CF), the number of cucumber fruit in pcs m
−2 was strongly influenced by N
total, while the dry mass content of the aboveground part of the plants correlated not only with N
total but also with N
min. When N fertilization was increased with N
13, cucumber fruit mass depended on N
min content, while fruit content and aboveground dry mass correlated strongly with N
total in the growing media. The fruit content of cucumbers on the N
min growing media was significantly influenced by the addition of a more intensive N fertilization with N
23. It was also strongly correlated with the C:N ratio. Cucumber green aboveground mass was strongly correlated with N
total content. A negative correlation was found between the mass of fruit on the plant and the N
min in the substrate.
4. Discussion
Wood fiber, wood shavings, and sawdust are wastes from the wood industry. All products have good water and air retention. Wood fiber can be used in crop production as a stand-alone substrate or in combination with other components such as peat [
15,
31]. Typically, wood fiber-enriched substrates are used for growing ornamental plants, shrubs, or seedlings in pots [
32,
33], but are also used in vegetable production [
34]. The sorption capacity depends on many factors: the amount of wood fiber in the substrate, the physical and chemical properties of the fiber, and its type and origin [
35,
36]. In this study, the moisture absorption of the wood fiber/peat blend WF/PS 50/50 was significantly higher compared to PS and WF/PS 25/75 (
Table 2). Fertilization with higher nitrogen rates of N
23 and N
30 reduced the moisture absorption of the growing media, but there was no interaction between media composition and fertilization. Principle component analysis showed that by increasing the proportion of fiber in the growing media, the green mass of cucumber plants correlated very strongly with the moisture content of the growing media without additional fertilization with NCF (
Figure 3). The mass of cucumber fruit on the plant correlated strongly with the additional fertilization at the highest rate of N
30. B. [
37] points out that the addition of 40% and 50% wood fiber to peat reduces the water content by 16%
vv−1 and increases the air content of the substrate by the same amount, which indicates that it is more difficult to overwater, but also requires more accurate monitoring of the water content and the state of the nutrients. Wood fiber media needs to be watered more frequently than peat.
Pelargonium grown in wood fiber was also found to flower earlier than the ones grown in other media or mixtures with wood fiber [
11,
14]. In our experiment, cucumbers were irrigated equally in all media. However, the moisture content was significantly highest in WF but was reduced by additional fertilization with N
23 and N
30. Wood fiber has a high level of total porosity and, in most cases, a very high level of air-filled pores and a relatively low level of readily available water. It also has a higher air diffusion rate compared to peat [
11,
38]. Therefore, wood fiber is used to optimize the physical properties of other components in growing media, e.g., by reducing bulk density, increasing air capacity, and improving re-wetting capacity [
16,
39]. The density of the growing media was highly dependent on its composition. The density of the WF media and the WF/PS 50/50 mixture was significantly lower compared to PS. The lower proportion of wood fiber in the WF/PS 25/75 mixture was equivalent to the density of PS. Fertilization with N did not affect the density of the growing media. The dry mass of cucumber plants correlated very strongly with the density of the growing media as the proportion of wood fiber in the growing media increased (
Figure 3).
In their studies on growing media with wood fiber [
40], found that strawberries grown in a mixture of 75% wood fiber and 25% peat gave the best yields. This suggests that a mixture of growing media with wood fiber can improve plant performance. The composition of the growing media did not affect the chemical composition of the berries, but the berries of the plants grown in this mixture had a lower firmness than those grown in coir fiber. The most productive plants were in mixtures containing up to 75% wood fiber, even without starter fertilizer [
40]. Cucumbers were the most productive in a medium made of wood fiber 50% and peat 50% (Mūsų straipsnis, 2022). Other researchers’ studies on ornamental plants have shown that in growing media with 10% and 20% wood fiber, the leaf greenness index, flower mass, and visual score did not differ from those grown on 100% peat substrate. 40% wood fiber harmed all the growth parameters and the macro- and micronutrient content of the leaves. Plants grown on a peat substrate enriched with 20% wood fiber and fertilized with nitrogen had the highest leaf greenness index, the highest number of flowers, and the highest N, P, Ca, Na, Fe, Mn, and Cu content. The study showed that high-quality ornamental plants can be successfully grown in a growing media with 20% wood fiber and additional nitrogen fertilization [
9]. In our experiment, the most productive cucumbers were grown in a WF/PS 50/50 mixture with additional N
13 fertilizer. Higher nitrogen rates resulted in lower fruit number and mass per plant (
Table 2).
Electrical conductivity (EC) is an indicator of the concentrations of soluble salts (Na
+, Mg
2+, Ca
2+, Cl
−, SO
42−, HCO
3−, K
+, NO
3−, etc.) [
41]. High EC has negative effects on germination, photosynthesis, plant vigor, yield, and nutritional and economic value [
42]. Salinity is detrimental to plant growth and development due to water stress, cytotoxicity due to excessive levels of ions such as sodium (Na
+) and chloride (Cl
−), and nutritional imbalances. In our study, it was found that at the highest N
30 fertilizer rate, the dry mass content of the aerial part of the plant was dependent on the electrical conductivity (
Figure 3). On the other hand, a very low EC value of the media indicates a nutrient deficiency. During the anion exchange process, excess sodium ions can replace calcium and magnesium, leading to changes in the structure and fertility of the media. This results in the depletion of available nutrients. That different plants differ in their salt sensitivity-tolerance range [
43]. Cucumber is a salt-sensitive species, and the EC of the growing media must be <2.7 dS/m, otherwise significant yield losses are inevitable. Our results also showed that the EC was influenced by the mass of fruit grown without additional nitrogen fertilization and at the lowest N
13 rate (
Figure 3). Zucchini (moderately salt-sensitive) grow well in a media with an EC of 2.6–2.8 dS/m, while tomatoes can tolerate salt concentrations of up to 2.9 dS/m with no yield loss [
43]. An EC < 2.5 dS/m is considered optimal for creating an ideal substrate [
44], while reported that an EC < 3.5 dS/m is the most suitable for growing media and reported that substrates with high EC have higher nutrient sorption and buffering capacity [
39]. In our study, cucumber fruit mass with increasing WF in the growing media was strongly dependent on EC, but only without additional fertilizer (NCF) and with the lowest N
13 rate (
Figure 3). When the nitrogen rate was increased to N
30, a greater influence of EC was observed on aboveground dry mass than on fruit mass. Investigated the replacement of growing media with wood fiber for
Zinnia hibrida and
Tagetes erecta [
45]. They suggest that in media with wood fiber, fertilization with 100–200 mg L
−1 N can maintain adequate pH and EC levels of the substrate solution and plant growth without the need for additional N fertilization at later growth stages.
In our experiment, increasing the proportion of wood fiber in the growing media increased the pH from 5.2 to 6.6, while additional N fertilization reduced the pH value by 7.8%. Points out that wood waste materials also have a naturally higher pH compared to peat, which requires less limestone for initial pH adjustment and leaves unknown the effect on the substrate’s ability to protect itself against pH changes [
46]. Also show that the pH of the substrate solution decreases with increasing N concentration [
45]. Principle component analysis showed that pH had no significant effect on cucumber biometric parameters by increasing the proportion of wood fiber in the growth media (
Figure 3). A moderate strength relationship was found between fruit mass on the plant and pH when the plants were fertilized at the maximum rate of N
30.
Moderate salinity and/or nutritional stress and biofortification of vegetables with micronutrients beneficial to human health (iodine, iron, molybdenum, selenium, silicon, and zinc) are well-known methods that have been successfully used to enhance the content of health-promoting phytochemicals in vegetables [
47]. It has been shown experimentally that EC and pH vary with the growing media, depend on the wood components, and can modify the chemical properties of the substrate differently. Other work has shown that increasing the ratios of some wood components increases the pH of the substrate and decreases the EC during the growing season [
12]. The researchers provided this conclusion after 3 seasons of tomato cultivation in three different substrates—wood fiber, coir, and perlite. The growing media did not show significant differences in tomato yields, but yields were slightly earlier in wood fiber [
13,
48].
Plants grown under controlled climatic conditions take up more nutrients from the growing media than those grown outdoors. The high nutrient requirement is due to the shallow penetration of the root system (limited by the volume of the vegetative receptacle), the weak suction power of the roots, and the large difference between the mass of the aboveground part of the plant and the root system. The nitrogen concentration in the wood fiber is generally low, so additional nitrogen is added either at the production stage or by the consumer. Therefore, nutrient levels, especially nitrogen, can vary considerably depending on the production process. The addition of nitrogen during production can increase the level of water-soluble N. Levels of K, Na, Mg and Ca can also vary considerably. Some wood fibers have been found to have slightly elevated P levels. The level of extractable (plant-available) nutrients is higher, indicating that decomposition processes and nutrient exchange are taking place in the wood fiber [
49]. Wood fiber products used in combination with peat, the main component of the growing media, have been found to have a high water-holding capacity, which may have an impact on the retention of nutrients in the growing media [
50]. Another aspect to consider is the efficiency with which these mineral nutrients can be used to achieve good production without using too much fertilizer, which can cause environmental pollution. In our experiment, at the end of the cucumber growing season, the levels of Cu, Mn, Zn, Fe, and B were found to be significantly higher in the WF/PS 50/50 mixture than in the PS, the WF and the WF/PS 25/75 mixture (
Table 4). Only Cl was detected at higher levels in the WF growing media than in the other media. Researchers suggest that the accumulation of chloride should be attributed to unfavorable nutrients in the root environment [
51]. Additional fertilization with N
30 increased the levels of Cu, Zn, Fe, B, and Cl in the WF growth media. This may be related to the increase in EC, as the increase in N rate blocked the uptake of nutrients from the media, resulting in the highest micronutrient levels in the root zone. Sometimes Mn and Zn levels can vary over a wide range, but generally, the concentrations and availability of the other trace elements are very low. In general, the levels of trace elements in WF media are higher than those of water-soluble trace elements [
11]. Scientists have investigated the chemical composition of nutrient solutions in the root environment of tomatoes grown in wood fiber and rockwool under different levels of nitrate nitrogen in nutrient solutions at 200, 220, and 240 mg N-NO
3·dm
−3. Despite the wide range of carbon-to-nitrogen ratios (C:N) in wood fiber, no significant variation in nitrate content in the root environment was observed. This was the result of an appropriate frequency of nutrient solution application per day [
51]. Our results show that N
min and N
total increased significantly in the growing media (cucumber root zone), while C:N decreased significantly when the N fertilization rate was increased to N
23 (
Table 4). Although the N
min content in the WF media was highest at the end of the cucumber growing season, the C:N content was not as high as in the WF media. The addition of wood fiber to the growing media may improve macronutrient uptake in the short term but may reduce micronutrient uptake in the medium term, highlighting the complex effects of wood fiber on nutrient availability and plant growth [
52]. The decreasing effect of N-NH
4 and N-NO
3 content in wood fiber on cucumber growth can be attributed to biosorption due to the high C:N = 125 ratio in this media [
53].
In our experiment, similar results were obtained: the highest C:N ratio was found in the wood fiber growing media compared to the peat substrate and the media mixtures, but additional N fertilization reduced this ratio. The N
total content was lowest in the WF media at the end of the growing season. WF media had the highest N
min. but no significant difference compared to the WF/PS 50/50 growing media. It can be concluded that the cucumbers were grown on WF and WF/PS 50/50 nitrogen. uptake was more difficult than for cucumbers grown on PS and WF/PS 25/75 growing media. When fertilization was increased to N
23 and N
30, mineral N remained in the growing media (
Table 4). Wright et al. (2008) found that plants grown on soils containing woody material require about 100 mg L
−1 N more fertilizer to achieve a similar result to plants grown on peat substrates. Different types of wood components also differ in their physical properties and their ability to immobilize N. Differences in air and water porosity, total water-holding capacity and bulk density can also affect microbial activity and plant growth. The main cause of N immobilization is biosorption by microorganisms that use the N available in plants [
54]. This can lead to nutritional deficiencies in ornamental plants and a reduction in their aesthetic value [
50]. The negative effects of the sorption of N and other components on plant growth and flowering can be eliminated by appropriate fertilization. To overcome N-immobilization in growing media with wood fiber, it is necessary to provide additional nutrient solutions from the beginning of plant growth [
11,
39,
55].
Wood fiber-based growing media can be produced with the desired physical and chemical properties for optimal growth of a wide range of plants and vegetables. Studies on the yield of plants grown on wood fiber media show that additional fertilizers are needed, but growth may depend on the nature of the wood fiber and its content in the growing media. Wood fiber can be a reliable, consistent, renewable, and cost-effective alternative to traditional peat substrates in greenhouses. The use of wood fiber in growing media is in line with sustainable development policies and can help reduce the carbon footprint of the product.
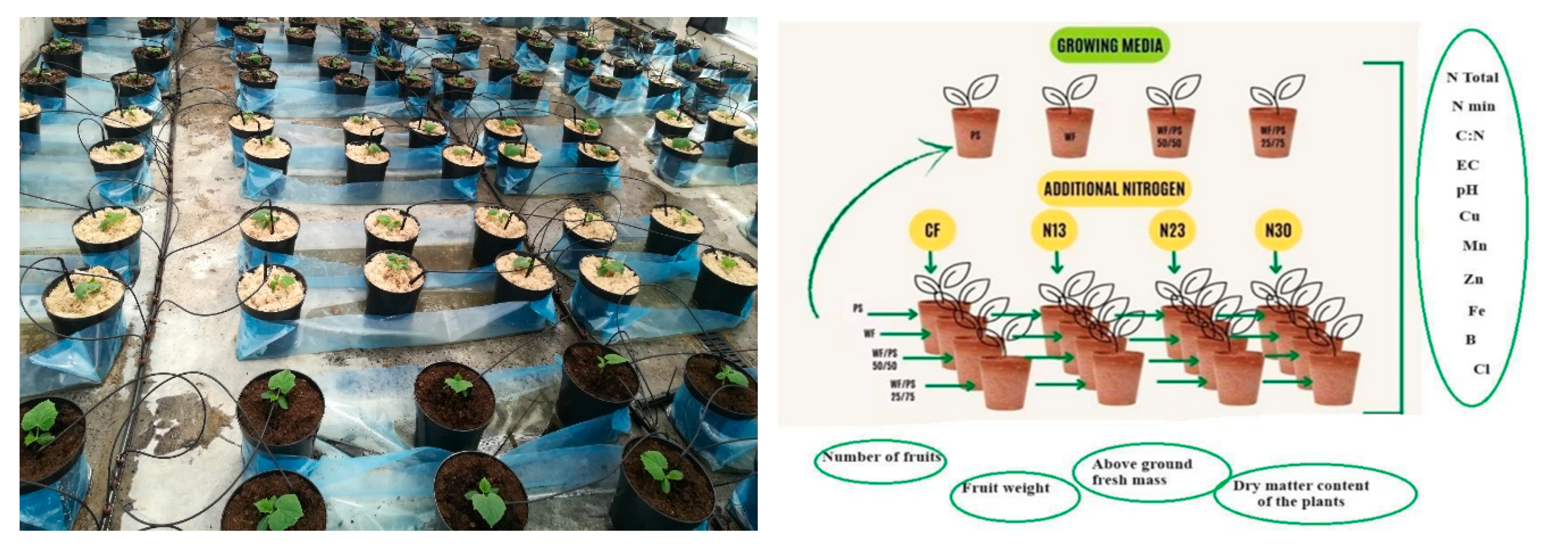
Figure 1.
The experiment after transplanting cucumbers into growing containers and experimental design.
Figure 1.
The experiment after transplanting cucumbers into growing containers and experimental design.
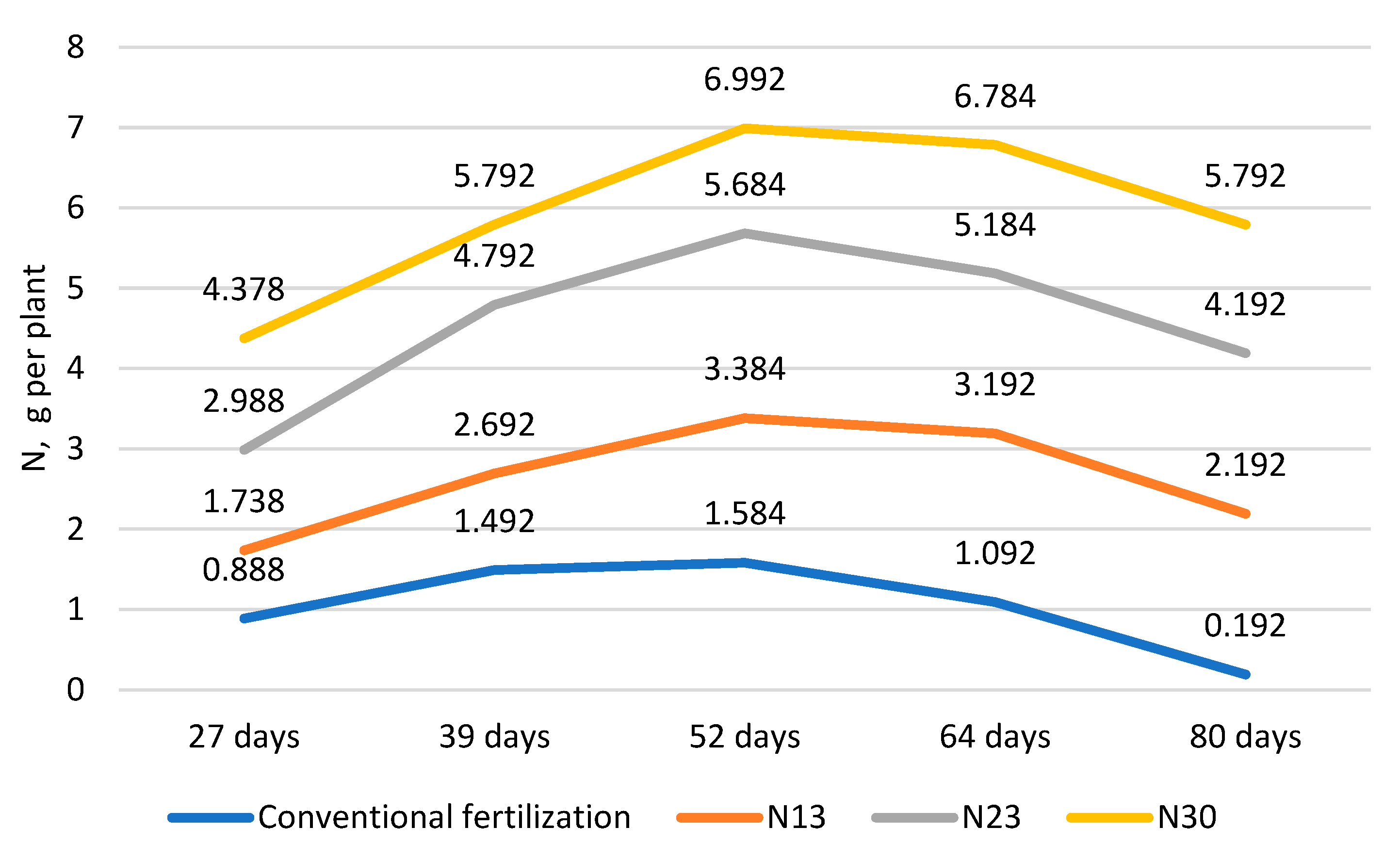
Figure 2.
Nitrogen fertilization during the cucumber growing season (days after transplanting). N13, N23, and N30—additional nitrogen fertilization.
Figure 2.
Nitrogen fertilization during the cucumber growing season (days after transplanting). N13, N23, and N30—additional nitrogen fertilization.
Figure 3.
PCA analysis shows the relationship between the physicochemical properties of growing media with wood fiber and productivity parameters for cucumbers under different nitrogen fertilization rates. Note: density of the growing media (D), the electrical conductivity of the growing media (EC), moisture of the growing media (M), aboveground dry mass content of plant (ADM), aboveground fresh mass content of plant (AFM), number of cucumbers per plant (CUN), cucumber mass per plant (CUM), conventional fertilization (CF), fertilization rates (N13, N23 and N30), actives variables (*).
Figure 3.
PCA analysis shows the relationship between the physicochemical properties of growing media with wood fiber and productivity parameters for cucumbers under different nitrogen fertilization rates. Note: density of the growing media (D), the electrical conductivity of the growing media (EC), moisture of the growing media (M), aboveground dry mass content of plant (ADM), aboveground fresh mass content of plant (AFM), number of cucumbers per plant (CUN), cucumber mass per plant (CUM), conventional fertilization (CF), fertilization rates (N13, N23 and N30), actives variables (*).
Figure 4.
PCA analysis shows the relationship between the micronutrients on the growing media with wood fiber and productivity parameters for cucumbers under different nitrogen fertilization rates. Note: density of the growing media (D), the electrical conductivity of the growing media (EC), moisture of the growing media (M), aboveground dry mass content of plant (ADM), aboveground fresh mass content of plant (AFM), number of cucumber fruits per plant (CUN), cucumber fruit per plant (CUM), conventional fertilization (CF), fertilization rates (N13, N23 and N30), actives variables (*).
Figure 4.
PCA analysis shows the relationship between the micronutrients on the growing media with wood fiber and productivity parameters for cucumbers under different nitrogen fertilization rates. Note: density of the growing media (D), the electrical conductivity of the growing media (EC), moisture of the growing media (M), aboveground dry mass content of plant (ADM), aboveground fresh mass content of plant (AFM), number of cucumber fruits per plant (CUN), cucumber fruit per plant (CUM), conventional fertilization (CF), fertilization rates (N13, N23 and N30), actives variables (*).
Figure 5.
PCA analysis shows the relationship between the Ntotal, Nmin, and C:N in the growing media with wood fiber on productivity parameters for cucumbers under different nitrogen fertilization rates. The density of the growing media (D), the electrical conductivity of the growing media (EC), moisture of the growing media (M), aboveground dry mass content of plant (ADM), aboveground fresh mass content of plant (AFM), number of cucumber fruits per plant (CUN), cucumber fruit per plant (CUM), conventional fertilization (CF), fertilization rates (N13, N23 and N30), actives variables (*).
Figure 5.
PCA analysis shows the relationship between the Ntotal, Nmin, and C:N in the growing media with wood fiber on productivity parameters for cucumbers under different nitrogen fertilization rates. The density of the growing media (D), the electrical conductivity of the growing media (EC), moisture of the growing media (M), aboveground dry mass content of plant (ADM), aboveground fresh mass content of plant (AFM), number of cucumber fruits per plant (CUN), cucumber fruit per plant (CUM), conventional fertilization (CF), fertilization rates (N13, N23 and N30), actives variables (*).
Table 1.
Characteristics of wood fiber and Sphagnum peat used in the experiment as growing media and their pats.
Table 1.
Characteristics of wood fiber and Sphagnum peat used in the experiment as growing media and their pats.
| Parameter |
Wood Fiber |
Sphagnum Peat |
| pH |
4.6 |
5.3 |
| EC mS m−1
|
58 |
76 |
| C:N |
435 |
80 |
| N total % DW * |
0.22 |
1.08 |
| P mg kg−1 DW |
57 |
181 |
| K mg kg−1 DW |
472 |
674 |
| Mg mg kg−1 DW |
29.3 |
23.2 |
| Fe mg kg−1 DW |
113.0 |
86.2 |
| Cu mg kg−1 DW |
2.9 |
3.0 |
| Zn mg kg−1 DW |
10.4 |
12.4 |
| B mg kg−1 DW |
15.3 |
14.0 |
| Cl mg kg−1 DW |
117.0 |
29.9 |
Table 2.
Indicators of cucumber productivity and physicochemical properties of growing media as a function of nitrogen fertilization rate and wood fiber content in the growing media.
Table 2.
Indicators of cucumber productivity and physicochemical properties of growing media as a function of nitrogen fertilization rate and wood fiber content in the growing media.
| Factors |
Physicochemical Properties of Growing Media |
Indicators of Cucumber Productivity |
| Growing Media (A) |
N Fertilization Rate (B) |
Moisture, % |
Density, g cm−2
|
EC, mS m−1
|
pH |
Dry Mass Content of the Plants, % |
Aboveground Fresh Mass, g per Plant |
Number of Fruits, per Plant |
Fruit Mass, kg per Plant |
| Growing media |
| PS |
|
41.48 c |
0.39 a |
399 c |
5.18 c |
18.95 a |
195.6 a |
35.15 b |
5.61 b |
| WF/PS 25/75 |
|
45.55 c |
0.39 a |
513 a |
5.85 b |
17.43 b |
164.1 d |
34.85 b |
5.48 b |
| WF/PS 50/50 |
|
50.98 b |
0.30 b |
370 d |
6.55 a |
16.48 c |
187.6 b |
41.18 a |
6.22 a |
| WF |
|
55.99 a |
0.23 b |
420 b |
5.98 b |
14.30 d |
172.0 c |
36.80 b |
5.68 b |
| Fertilization |
| |
CF |
55.40 a |
0.33 a |
172 d |
6.18 a |
17.13 ab |
212.9 a |
36.61 b |
6.06 a |
| |
N13
|
54.90 a |
0.33 a |
434 c |
5.88 b |
17.25 a |
204.0 a |
40.00 a |
6.03 a |
| |
N23
|
49.14 b |
0.33 a |
522 b |
5.80 b |
16.13 c |
157.5 b |
34.55 b |
5.40 b |
| |
N30
|
34.56 c |
0.33 a |
575 a |
5.70 b |
16.65 b |
144.9 c |
36.82 b |
5.51 b |
| Influence and interactions |
| A |
|
** |
* |
** |
** |
** |
** |
** |
** |
| B |
|
** |
ns |
** |
** |
** |
** |
** |
** |
| A × B |
|
ns |
ns |
** |
ns |
** |
** |
** |
** |
Table 3.
Variation (%) of micronutrient content in the growing media during the growing season, taking into consideration the amount obtained with fertilizer.
Table 3.
Variation (%) of micronutrient content in the growing media during the growing season, taking into consideration the amount obtained with fertilizer.
| Growing Media |
Fertilization Rate |
Cu |
Zn |
Mn |
Fe |
B |
Cl |
| PS |
CF |
−2 |
−67 |
−18 |
−65 |
1 |
853 |
| N13
|
−4 |
−66 |
−37 |
−80 |
21 |
586 |
| N23
|
16 |
−42 |
−36 |
−78 |
76 |
870 |
| N30
|
−11 |
−28 |
−26 |
−64 |
44 |
1044 |
| WF/PS 25/75 |
CF |
13 |
−45 |
−1 |
−59 |
31 |
14 |
| N13
|
7 |
−33 |
−9 |
−74 |
50 |
97 |
| N23
|
−3 |
−36 |
−2 |
−77 |
56 |
91 |
| N30
|
35 |
−24 |
−7 |
−59 |
102 |
120 |
| WF/PS 50/50 |
CF |
−31 |
−47 |
−14 |
−47 |
1 |
−9 |
| N13
|
−25 |
−52 |
−22 |
−49 |
26 |
14 |
| N23
|
−33 |
−48 |
−22 |
−63 |
36 |
119 |
| N30
|
−20 |
−40 |
−21 |
−63 |
81 |
144 |
| WF |
CF |
−39 |
−62 |
−60 |
−86 |
−18 |
118 |
| N13
|
−39 |
−70 |
−77 |
−82 |
27 |
150 |
| N23
|
−39 |
−53 |
−71 |
−62 |
25 |
232 |
| N30
|
−39 |
−75 |
−78 |
−71 |
12 |
269 |
Table 4.
Influence of N fertilization rate and wood fiber content of the growing media on micronutrient content, nitrogen content, and C:N at the end of the growing season.
Table 4.
Influence of N fertilization rate and wood fiber content of the growing media on micronutrient content, nitrogen content, and C:N at the end of the growing season.
| Factor |
Micronutrient Content of the Growing Media mg kg−1
|
Ntotal % |
Nminmg kg−1
|
C:N |
| Growing Media (A) |
N Fertilization Rate (B) |
Cu |
Mn |
Zn |
Fe |
B |
Cl |
| Growing media |
| PS |
|
2.73 b |
17.11 c |
6.59 ab |
27.25 c |
18.98 b |
281 b |
1.28 b |
136.4 bc |
52.50 b |
| WF/PS 25/75 |
|
2.92 b |
22.28 b |
5.32 b |
45.50 b |
20.93 ab |
312 ab |
1.35 a |
116.6 c |
48.25 c |
| WF/PS 50/50 |
|
10.61 a |
36.39 a |
7.44 a |
76.00 a |
23.95 a |
292 b |
1.26 b |
154.1 ab |
47.92 c |
| WF |
|
2.52 b |
11.70 d |
6.78 ab |
34.58 c |
17.08 b |
342 a |
0.88 c |
186.6 a |
94.75 a |
| Fertilization |
| |
CF |
4.37 b |
24.80 a |
6.51 b |
50.25 a |
15.43 b |
225 d |
0.90 c |
74.9 c |
79.17 a |
| |
N13
|
4.65 ab |
20.38 b |
5.70 c |
41.75 b |
19.58 a |
262 c |
1.05 b |
155.4 b |
62.75 b |
| |
N23
|
4.25 b |
21.63 b |
7.14 a |
42.33 b |
22.05 a |
344 b |
1.37 a |
224.5 a |
51.75 c |
| |
N30
|
5.52 a |
20.68 b |
6.78 ab |
49.00 a |
23.88 a |
395 a |
1.45 a |
239.0 a |
49.75 d |
| Influence and interactions |
| A |
|
** |
** |
* |
** |
* |
* |
** |
** |
** |
| B |
|
* |
* |
* |
* |
* |
** |
* |
** |
** |
| A × B |
|
* |
* |
* |
* |
ns |
* |
* |
** |
** |