1. Introduction
The term misophonia, derived from the greek μισοφωνία (hatred of sound), was coined in audiology studies to denote a strong aversion to specific sounds, triggering broad negative emotional reactions [
1,
2,
3]. Recently, the Delphi study conducted by an expert panel reached a consensus on the definition of misophonia, emphasizing its characterization by intense negative emotional reactions to specific sounds, which are disproportionate and cause significant distress or impairment [
4]. The most bothersome sounds typically originate from the mouth and nose, including chewing, crunching, lip-smacking, breathing, snoring, and nasal suction. Pen and mouse clicks and keyboard typing sounds are also considered misophonic triggers [
2,
3,
5]. These sounds evoke neurophysiological and behavioral reactions often misunderstood by peers, friends, and family [
6,
7]. Common responses to trigger sounds include irritation, anger, disgust, annoyance, sadness, physical reactions, and loss of control [
2,
6,
8]. However, these reactions depend more on psychological profiles, prior experiences, and contextual factors than on sound intensity or frequency [
2,
3,
5]. Initially, misophonia was confused with other abnormalities, such as phonophobia; however, in most cases, typical fear reactions, such as extreme anxiety, are not observed [
2,
6,
8,
9]. Although the literature reports various reactions, such as extreme anxiety, compulsive disorders, depression, and aggression, there is no consensus among researchers regarding their occurrence in patients solely diagnosed with misophonia [
6].
Concerning the manifestations of the disorder, the first symptoms emerge during childhood and worsen during adolescence [
2,
8,
10]. Emotional instability during this phase often leads to reduced tolerance to trigger sounds, causing difficulties such as social withdrawal, learning challenges, and family conflicts [
2,
11]. While adults show increased tolerance to trigger sounds, the disorder persists throughout life [
2,
12,
13,
14,
15]. Moreover, the misophonic spectrum ranges from the subclinical, mild, and moderate forms to the less common severe form [
6,
8,
13]. Individuals with mental disorders may exhibit misophonia symptoms, suggesting a correlation [
8,
15,
16,
17].A study on phenotyping misophonia revealed significant associations with various psychiatric disorders, including anxiety, depression, and obsessive-compulsive disorder, as well as medical conditions such as gastrointestinal issues and tinnitus [
18]. However, individuals with these disorders may exhibit misophonia symptoms without the reverse being true. This indicates that misophonic individuals can be clinically diagnosed independent of comorbidities [
8].
Epidemiological studies on misophonia are scarce and lack sufficient data to estimate its global occurrence. It has been suggested that misophonia prevalence in the general population may be approximately 3.0% [
19,
20]. Nevertheless, In a study conducted in Ankara, Turkey, Kilic et al. examined a random sample representative of the general population, consisting of 541 individuals aged 15 and older, and reported a prevalence of 12.8% [
12]. In a similar study, Vitoratou et al. examined a large, representative sample of the UK general population and estimated the prevalence to be 18% [
16]. In Germany, Jakubovski investigated a sample of 2,519 individuals from the general population and found a prevalence rate of 5%. [
15]. However, specific population studies have reported a high prevalence. For instance, a study on medical students in the United Kingdom found that 49.1% exhibited clinically significant misophonic symptoms [
13]. Another study of Turkish high school and university students reported that 13.8% had moderate to severe misophonia, and 41.8% had mild clinical presentations [
7]. Zhou et al. investigated 415 university students in Shanghai and observed that 20% of individuals complained of misophonic sounds [
17]. Similarly, Brennan et al. identified a prevalence of misophonia ranging from approximately 8% to 20% in a sample of 1,084 respondents from a total of 12,131 undergraduate and graduate students aged 18 to 25 [
21]. As of May 2024, no studies on misophonia prevalence in South American populations exist.
Therefore, this study aimed to evaluate misophonia prevalence in students from integrated technical and higher education levels at a Brazilian federal institute using the MisoQuest questionnaire[
22].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design
We conducted a cross-sectional study to investigate the prevalence of misophonia.
2.2. Participants
This study enrolled students from technical and undergraduate programs at the Federal Institute of Education, Science, and Technology in Goias, Brazil. The technical courses at the Federal Institute are offered in two modalities: integrated with high school education and in the form of Adult and Youth Education (AYE). The first modality comprises young individuals aged between 13 and 18 years, while the second includes adults aged over 18 years. The research team visited students in their respective classes, inviting them to participate in the study. During these visits, students were informed about the research objectives and the procedures for accessing and completing the online questionnaire. Additionally, it was emphasized that minors were required to obtain parental consent through the signing of the Informed Assent Form before accessing the questionnaire. Students with physical, intellectual limitations, or known mental disorders were excluded from the study. Undergraduate students (over 18 years old) from various courses at the Federal Institute were contacted, invited, and instructed about the research through course and class groups.All participants completed a Free and Informed Consent Form signed by their parents/legal guardians and individually signed the Informed Consent Form. Ethical approval for this study was granted by the Research Ethics Committee (reference number: 5.631.371).
2.3. Online Assessments
The initial page of the form featured an exhaustive task description and researchers’ contact details. The data gathered encompassed the following information: name, email, gender, and age. The MisoQuest was made available to participants during the period between September 15, 2022, and August 15, 2023.
The participants completed the MisoQuest [
22] questionnaire, a deliberate choice based on its distinction as a singular, fully validated misophonia questionnaire. The MisoQuest, a recently developed self-report questionnaire, has been demonstrated to possess robust psychometric properties, making it an ideal tool for assessing the prevalence of misophonia. The instrument exhibits high internal consistency, with Cronbach’s alpha values exceeding 0.90, indicating that its items are reliably measuring the construct of misophonia. Furthermore, the MisoQuest has shown strong test-retest reliability, ensuring stability and consistency of the results over time [
22]. The MisoQuest is composed of 14 items, and each of the 14 items is rated on a scale of 1 to 5, representing varying degrees of agreement. The total score is derived by summing the scores for each item, yielding a range of 14-70. A total score equal to or exceeding 61 signifies a detection of misophonia [
22]. The establishment of this cutoff by Siepsiak et al. [
22] involved deducting one standard deviation (SD = 4.3) from the mean total score of individuals with misophonia (mean = 65.72). The Brazilian Portuguese version was derived from the original English version provided by the creators of the MisoQuest [
22]. Two translations were conducted: one by the authors of the present study and another by a bilingual professional. Both translations were back-translated and compared with the original version.The MisoQuest was administered through online forms.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using the Python programming language [
23] in conjunction with Jupyter Notebooks [
24] for the development and execution of interactive scripts. The statistical libraries used included NumPy [
25], Pandas [
26], and SciPy [
27]. To comprehensively assess the occurrence of misophonia among students, we employed a range of statistical tests to analyze the data obtained from the MisoQuest.
2.4.1. Descriptive Statistics
Mean, standard deviation, frequencies, and percentages were used to summarize the responses to the 14 items on the MisoQuest. These statistics offered a foundational understanding of the general trends and patterns within the dataset.
2.4.2. Internal Consistency Reliability
The internal consistency of the MisoQuest was evaluated using Cronbach’s alpha. This test ensured that the items on the MisoQuest reliably measured the construct of misophonia, with Cronbach’s alpha values exceeding the acceptable threshold of 0.70, indicating high reliability.
2.4.3. Factor Analysis
To validate the construct validity of the MisoQuest, both exploratory and confirmatory factor analyses were performed. Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA) was conducted to identify the underlying factor structure, while Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA) was used to confirm the hypothesized structure. These analyses verified that the MisoQuest accurately measures the intended constructs related to misophonia.
3. Results
3.1. Misophonia Prevalence among Students by MisoQuest
A total of 549 students (Mean= 23.2 years old, SD= 9.3) were enrolled in our study, comprising 285 females, 260 males, and four individuals who did not disclose their gender. Following the framework described by Siepziak et al.[
22], we assessed misophonia using the MisoQuest tool, with scores ranging from 14 to 70 and a predefined cutoff value of 61 [
14,
22]. Considering this value, 4.5% of the participants were positive for misophonia.
3.2. Statistical Analysis and Reliability
The psychometric properties of the MisoQuest were evaluated through both exploratory factor analysis (EFA) and confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) to assess its factor structure, as well as through the calculation of Cronbach’s alpha to determine its internal consistency.
3.2.1. Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA)
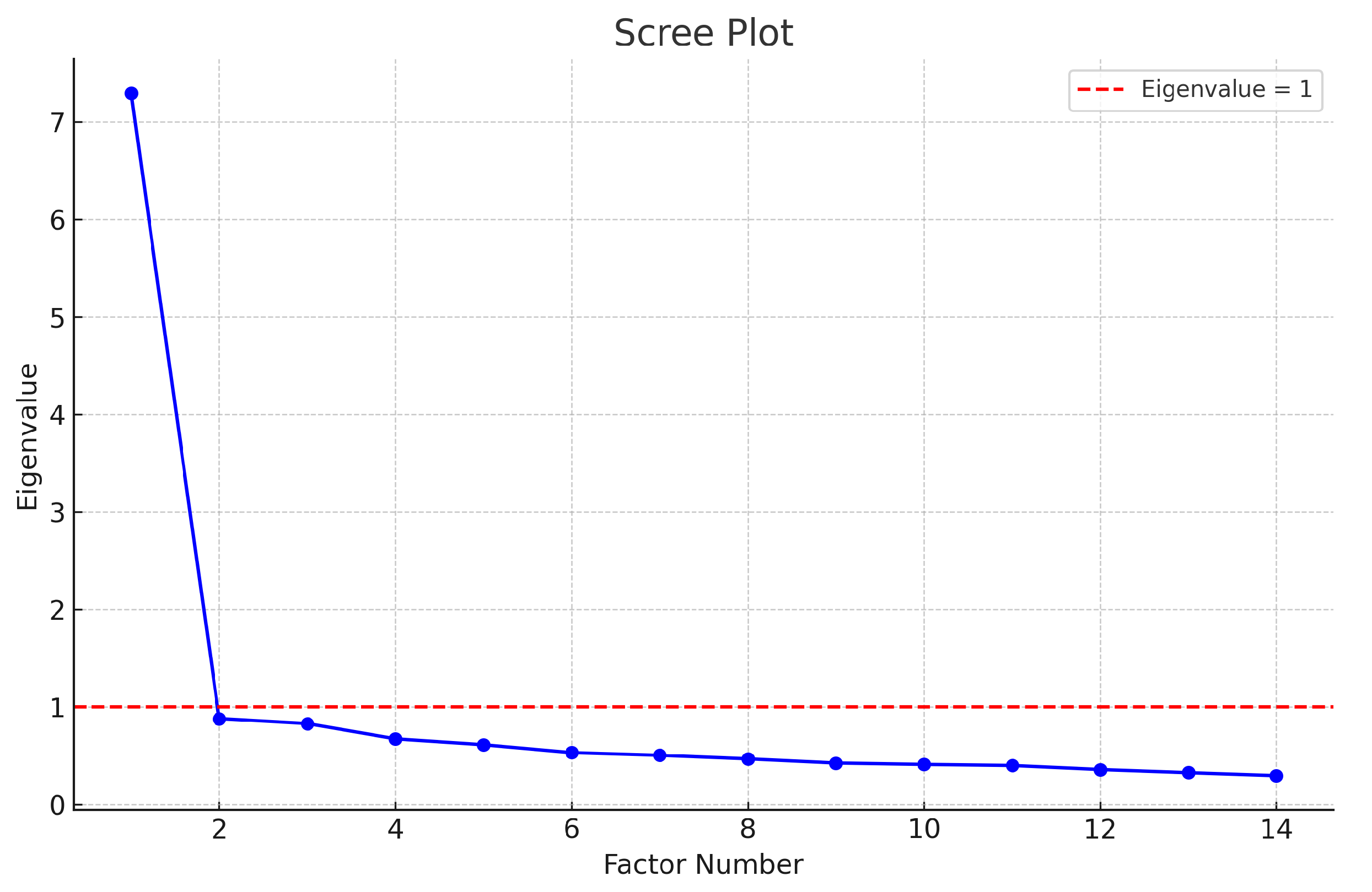
An EFA was conducted to identify the underlying factor structure of the MisoQuest. The eigenvalues obtained were as follows: [7.295, 0.880, 0.829, 0.672, 0.612, 0.531, 0.504, 0.467, 0.424, 0.410, 0.399, 0.357, 0.325, 0.295]. According to Kaiser’s criterion, only factors with eigenvalues greater than 1 should be retained. As shown in the scree plot
Figure 1, there is a clear inflection point after the first factor, indicating that the first factor explains the majority of the variance in the data. Therefore, a single-factor model was deemed appropriate for the MisoQuest.
3.2.2. Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA)
To confirm the single-factor structure identified in the EFA, a CFA was conducted. The standardized factor loadings, standard errors, z-values, and p-values for each item on the single factor (F1) are presented in
Table 1. The CFA results showed that the majority of the items had factor loadings ranging from 0.36 to 0.58, with Q1 fixed at 1.00 for scale identification. While some factor loadings were not statistically significant at the 0.05 level, the overall model provides a general indication of the strength of the relationships between items and the underlying factor.
3.2.3. Residual Variances
The residual variances for each item are all statistically significant (p < 0.05), indicating that there is a substantial amount of variance in the items that is not explained by the single factor, conform showed in
Table 2. This suggests the need for further refinement of the model or consideration of additional factors.
3.2.4. Reliability Analysis
Cronbach’s alpha was calculated to assess the internal consistency of the MisoQuest. The resulting alpha coefficient was 0.93, indicating excellent reliability. This high value suggests that the items on the MisoQuest are highly interrelated and measure the same underlying construct.
4. Discussion
The present study investigated the prevalence and psychometric properties of the MisoQuest in a sample of high school and undergraduate students, revealing insightful findings on the assessment of misophonia. Among the 549 participants (Mean age = 23.2 years, SD = 9.3), comprising 285 females, 260 males, and four individuals who did not disclose their gender, 4.5% were identified as positive for misophonia based on the MisoQuest score with a cutoff value of 61, as recommended by Siepsiak et al. (2020) [
22].
In the context of psychometric evaluation, the exploratory factor analysis (EFA) identified a dominant single-factor structure for the MisoQuest, with the first factor explaining the majority of the variance. The eigenvalues obtained ([7.295, 0.880, 0.829, 0.672, 0.612, 0.531, 0.504, 0.467, 0.424, 0.410, 0.399, 0.357, 0.325, 0.295]) supported this unidimensional structure based on Kaiser’s criterion. The scree plot further corroborated this finding, showing a clear inflection point after the first factor.
Confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) was employed to validate the single-factor model. The CFA results indicated that most items had factor loadings ranging from 0.36 to 0.58, with Q1 fixed at 1.00 for scale identification. Despite some factor loadings not being statistically significant, the overall model demonstrated a substantial relationship between the items and the underlying factor. Notably, the residual variances for each item were statistically significant (p < 0.05), suggesting a considerable amount of variance unexplained by the single factor, indicating the potential need for further model refinement or the consideration of additional factors.
The internal consistency of the MisoQuest was assessed using Cronbach’s alpha, yielding a coefficient of 0.93. This high value indicates excellent reliability, suggesting that the items are highly interrelated and effectively measure the same underlying construct of misophonia.
Comparing these findings with previous research, the prevalence rate of 4.5% is consistent with rates reported by other studies using similar tools and cutoff values [
14,
15,
28]. This consistency underscores the utility of the MisoQuest as a reliable instrument for identifying misophonia in diverse populations.
Moreover, the high internal consistency observed aligns with previous findings [
21,
29], further validating the MisoQuest as a robust measure. However, the significant residual variances highlight the complexity of the misophonia construct, suggesting that a unidimensional model may not capture all its nuances. This aligns with suggestions from Naylor et al. (2021) [
13] and Ay et al. (2024) [
30], advocating for a more nuanced approach in assessing misophonia’s multifaceted nature.
Furthermore, Siepsiak et al. (2020) [
22]demonstrated that early identification and intervention are crucial in managing misophonia symptoms. Providing appropriate support and accommodations in educational settings can significantly enhance the quality of life for affected students. Sarigedik and Gulle (2021) [
7] also noted the importance of tailored therapeutic approaches to address the unique triggers and reactions associated with misophonia.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, our study contributes to the growing body of literature on misophonia by validating the MisoQuest’s psychometric properties in a high school and undergraduate students sample. The findings support the use of MisoQuest as a reliable tool for identifying misophonia, while also highlighting areas for further refinement in its measurement model. Given the prevalence and impact of misophonia among young adults, particularly in academic settings, it is imperative to continue research in this area to develop effective assessment and intervention strategies. Future research should explore the underlying dimensions of misophonia to enhance our understanding and assessment of this condition, ultimately improving support for those affected.
Author Contributions
"Conceptualization, Lourival Silva and Matias Noll; methodology, Lourival Silva; software, Lourival Silva; validation, Lourival Silva, Matias Noll; formal analysis, Matias Noll; investigation, Lourival Silva, Gabriel Cunha and Alana Barbosa; resources, Matias Noll; data curation, Matias Noll; writing—original draft preparation, Lourival Silva; writing—review and editing, Lourival Silva; visualization, Matias Noll; supervision, Lourival Silva; project administration, Lourival Silva; funding acquisition, Matias Noll. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript."
Funding
"This research received no external funding".
Institutional Review Board Statement
“The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Research Ethics Committee of Federal Institute of Education, Science, and Technology (protocol code: 5.631.371, 09/08/2022).”
Informed Consent Statement
"Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study."
Acknowledgments
We thank the Federal Institute of Education, Science and Technology, National Council of Research (CNPq) for financial support.
Conflicts of Interest
"Authors must identify and declare any personal circumstances or interest that may be perceived as inappropriately influencing the representation or interpretation of reported research results. Any role of the funders in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript".
References
- Jastreboff, Margareth M.; Jastreboff, P.J. Components of decreased sound tolerance: hyperacusis, misophonia, phonophobia. ITHS Newsletter 2001, pp. 1–5.
- Edelstein, M.; Brang, D.; Rouw, R.; Ramachandran, V.S. Misophonia: physiological investigations and case descriptions. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience 2013, 7, 47988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelstein, M.;Monk,B.;Ramachandran,V.;Rouw,R. Context influences how individuals with misophonia respond to sounds. bioRxiv 2020, p. 2020.09.12.292391. ISBN: 10.1101/2020.09.1. [CrossRef]
- Swedo, S.E.; Baguley, D.M.; Denys, D.; Dixon, L.J.; Erfanian, M.; Fioretti, A.; Jastreboff, P.J.; Kumar, S.; Rosenthal, M.Z.; Rouw, R.; others. Consensus definition of misophonia: a delphi study. Frontiers in neuroscience 2022, 16, 841816.
- McKay, D.; Kim, S.K.; Mancusi, L.; Storch, E.A.; Spankovich, C. Profile Analysis of Psychological Symptoms Associated With Misophonia: A Community Sample. Behavior Therapy 2018, 49, 286–294, Publisher:Elsevier
Ltd.. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jager, I.; de Koning, P.; Bost, T.; Denys, D.; Vulink, N. Misophonia: Phenomenology, comorbidity and demographics in a large sample. PLoS ONE 2020, 15. Publisher: Public Library of Science. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarigedik, E.; Gulle, B. A Study on Validation of Amsterdam Misophonia Scale in Turkish and Misophonia’s Prevalence in Turkish High School/College Student Population. Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences 2021, 11, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, A.; Vulink, N.; Denys, D. Misophonia: Diagnostic Criteria for a New Psychiatric Disorder. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dozier, T.H.; Morrison, K.L. Phenomenology of Misophonia: Initial physical and emotional responses. American Journal of Psychology 2017, 130, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eijsker, N.; Schröder, A.; Smit, D.J.; van Wingen, G.; Denys, D. Structural and functional brain abnormalities in misophonia. European Neuropsychopharmacology 2021, 52, 62–71, Publisher:Elsevier B.V.. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tunç, S.; Başbuğ, H.S. An extreme physical reaction in misophonia: stop smacking your mouth! Psychiatry and Clinical Psychopharmacology 2017, 27, 416–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kılıç, C.; Öz, G.; Avanoğlu, K.B.; Aksoy, S. The prevalence and characteristics of misophonia in Ankara, Turkey: population-based study. BJPsych Open 2021, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor, J.; Caimino, C.; Scutt, P.; Hoare, D.J.; Baguley, D.M. The Prevalence and Severity of Misophonia in a UK Undergraduate Medical Student Population and Validation of the Amsterdam Misophonia Scale. Psychiatric Quarterly 2021, 92, 609–619, Publisher:Springer. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siepsiak, M.; Sobczak, A.M.; Bohaterewicz, B.; Cichocki, T.; Dragan, W.T. Prevalence of misophonia and correlates of its symptoms among inpatients with depression. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2020, 17, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakubovski, E.; Müller, A.; Kley, H.; de Zwaan, M.; Müller-Vahl, K. Prevalence and clinical correlates of misophonia symptoms in the general population of Germany. Frontiers in Psychiatry 2022, 13, 1012424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitoratou, S.; Hayes, C.; Uglik-Marucha, N.; Pearson, O.; Graham, T.; Gregory, J. Misophonia in the UK: Prevalence and norms from the S-Five in a UK representative sample. PloS One 2023, 18, e0282777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Wu, M.S.; Storch, E.A. Misophonia symptoms among Chinese university students: Incidence, associated impairment, and clinical correlates. Journal of Obsessive-Compulsive and Related Disorders 2017, 14, 7–12, Publisher:Elsevier Ltd.. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenthal, M.Z.; McMahon, K.; Greenleaf, A.S.; Cassiello-Robbins, C.; Guetta, R.; Trumbull, J.; Anand, D.; Frazer-Abel, E.S.; Kelley, L. Phenotyping misophonia: Psychiatric disorders and medical health correlates. Frontiers in Psychology 2022, 13, 941898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jastreboff, P.J.; Jastreboff, M.M. Treatments for decreased sound tolerance (hyperacusis and misophonia). Seminars in Hearing 2014, 35, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer-Torres, A.; Giménez-Llort, L. Misophonia: A Systematic Review of Current and Future Trends in This Emerging Clinical Field. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2022, 19, 6790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, C.R.; Lindberg, R.R.; Kim, G.; Castro, A.A.; Khan, R.A.; Berenbaum, H.; Husain, F.T. Misophonia and Hearing Comorbidities in a Collegiate Population. Ear and Hearing 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siepsiak, M.; Sliwerski, A.; Dragan, W.T. Development and psychometric properties of misoquest—A new self-report questionnaire for misophonia. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2020, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Python: Python Software Foundation. Python Language Reference, version 3.8.
- Kluyver, T.; Ragan-Kelley, B.; Pérez, F.; Granger, B.; Bussonnier, M.; Frederic, J.; Kelley, K.; Hamrick, J.B.; Grout, J.; Corlay, S.; Ivanov, P.; Avila, D.; Abdalla, S.; Willing, C.; Team, J.D. Jupyter Notebooks - a publishing format for reproducible computational workflows. International Conference on Electronic Publishing 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, C.R.; Millman, K.J.; van der Walt, S.J.; Gommers, R.; Virtanen, P.; Cournapeau, D.; Wieser, E.; Taylor, J.; Berg, S.; Smith, N.J.; et al. Array programming with NumPy. Nature 2020, 585, 357–362, Number:7825
Publisher: Nature Publishing Group. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKinney, W. Data Structures for Statistical Computing in Python. Proceedings of the 9th Python in Science Conference;, 2010; Vol. 445, pp. 56–61. [CrossRef]
- Virtanen, P.; Gommers, R.; Oliphant, T.E.; Haberland, M.; Reddy, T.; Cournapeau, D.; Burovski, E.; Peterson, P.; Weckesser, W.; Bright, J.; et al. SciPy 1.0: fundamental algorithms for scientific computing in Python. Nature Methods 2020, 17, 261–272, Number:3 Publisher:Nature Publishing Group. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aryal, S.; Prabhu, P. Misophonia: prevalence, impact and co-morbidity among Mysore University students in India-a survey. Neuroscience Research Notes 2022, 5, 161–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiffer, E.; Allroggen, M.; Sachser, C. [Misophonia in Childhood and Adolescence: A Narrative Review]. Zeitschrift Fur Kinder- Und Jugendpsychiatrie Und Psychotherapie 2023, 51, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ay, E.; Huviyetli, M.; Çakmak, E. The mediating role of anxiety in the relationship between misophonia and quality of life: findings from the validated Turkish version of MisoQuest. Frontiers in Psychology 2024, 15, 1361645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).