Submitted:
12 July 2024
Posted:
15 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Laboratory and Clinical Data
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
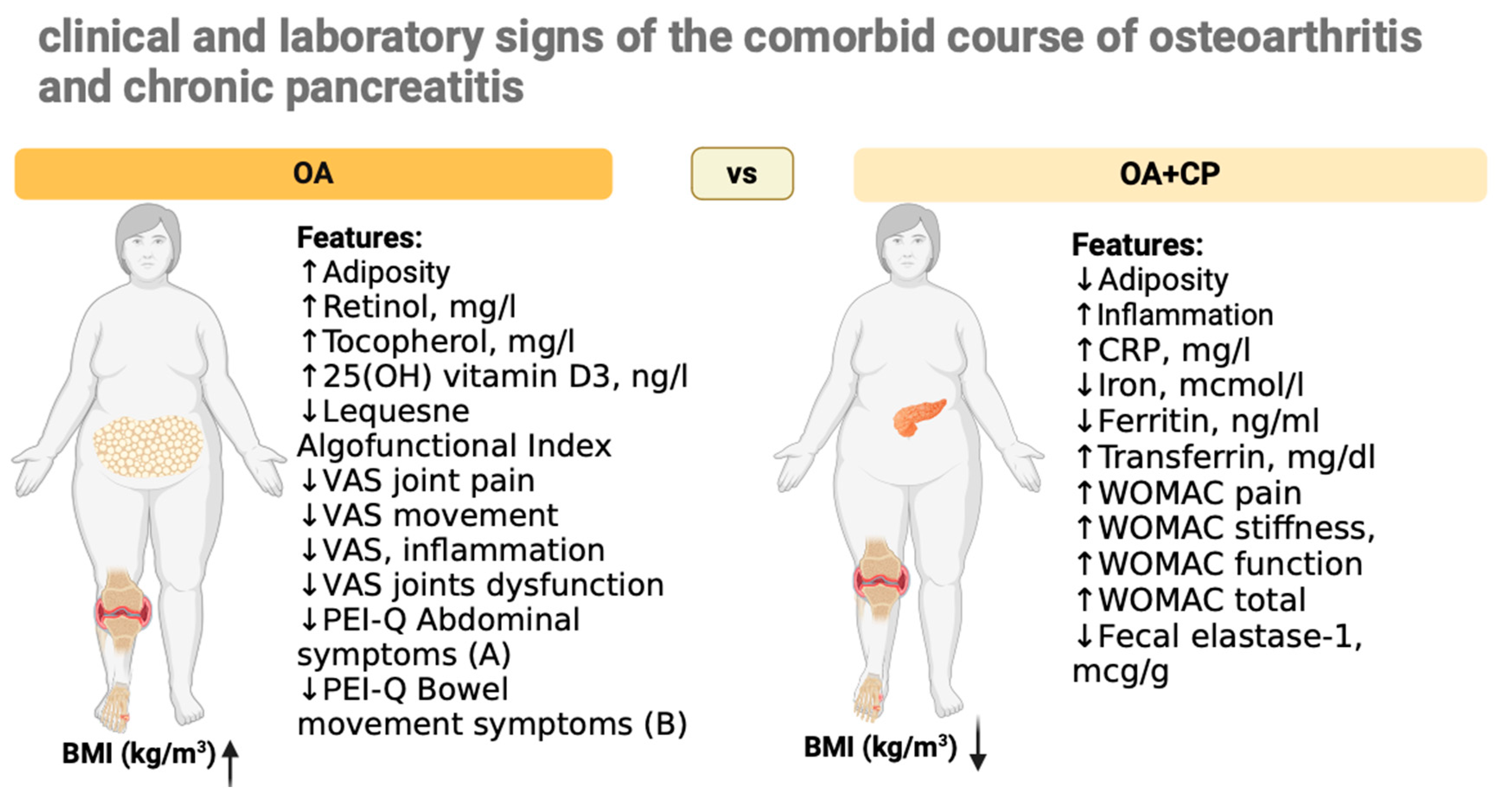
3.1. Comparing Group Expression
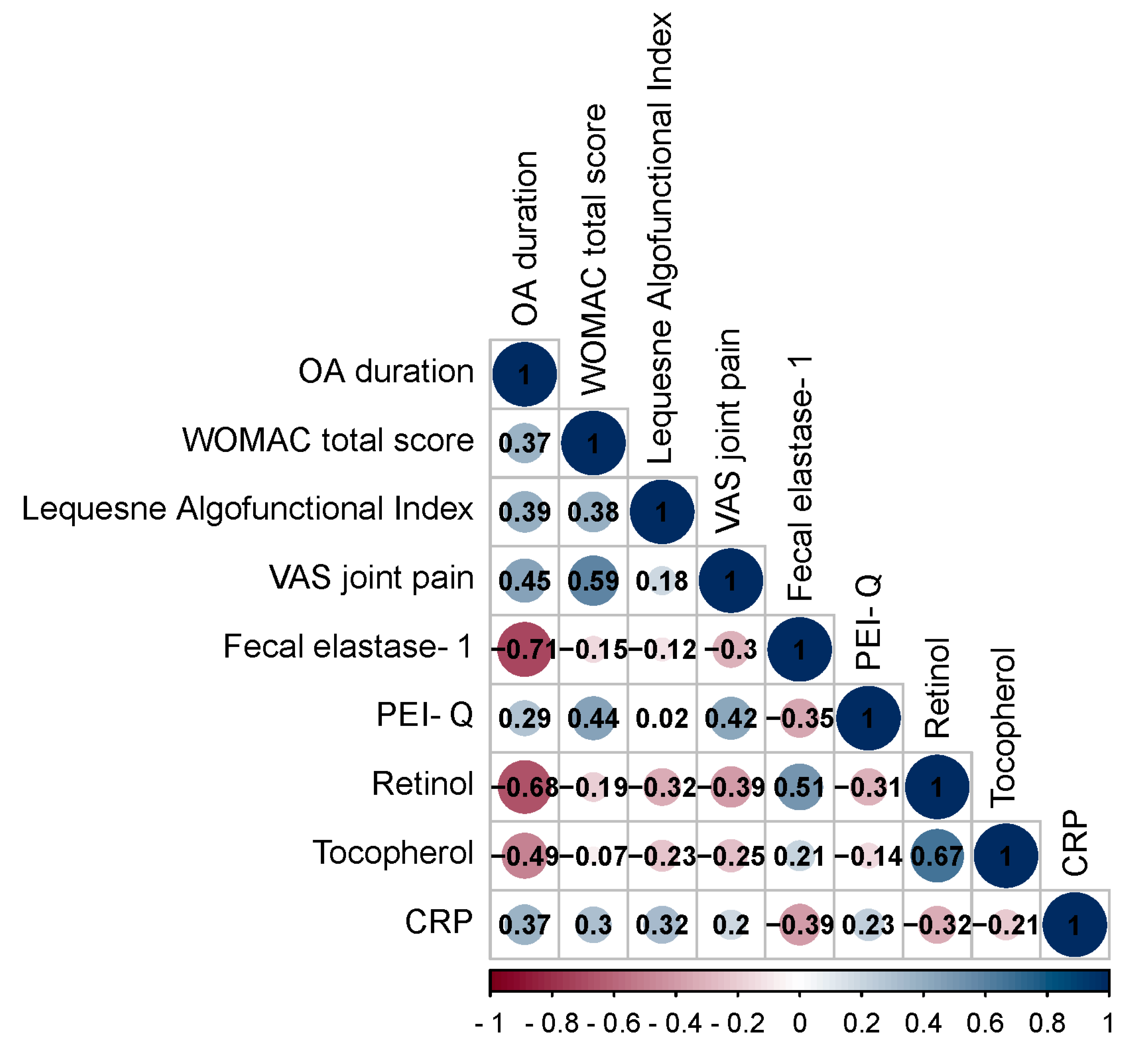
3.2. Correlation Analysis of Data in Patients with OA and OA+CP
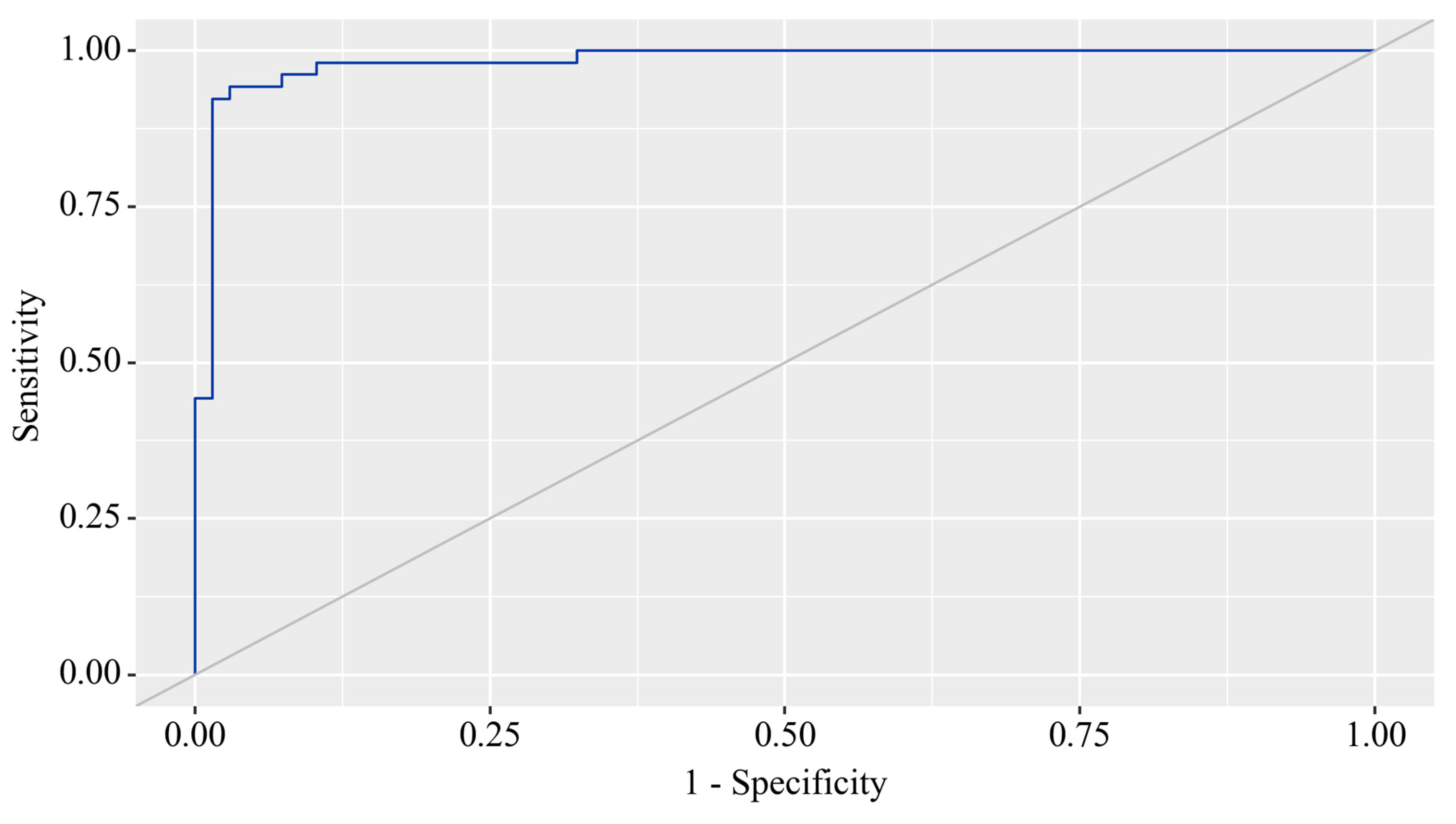
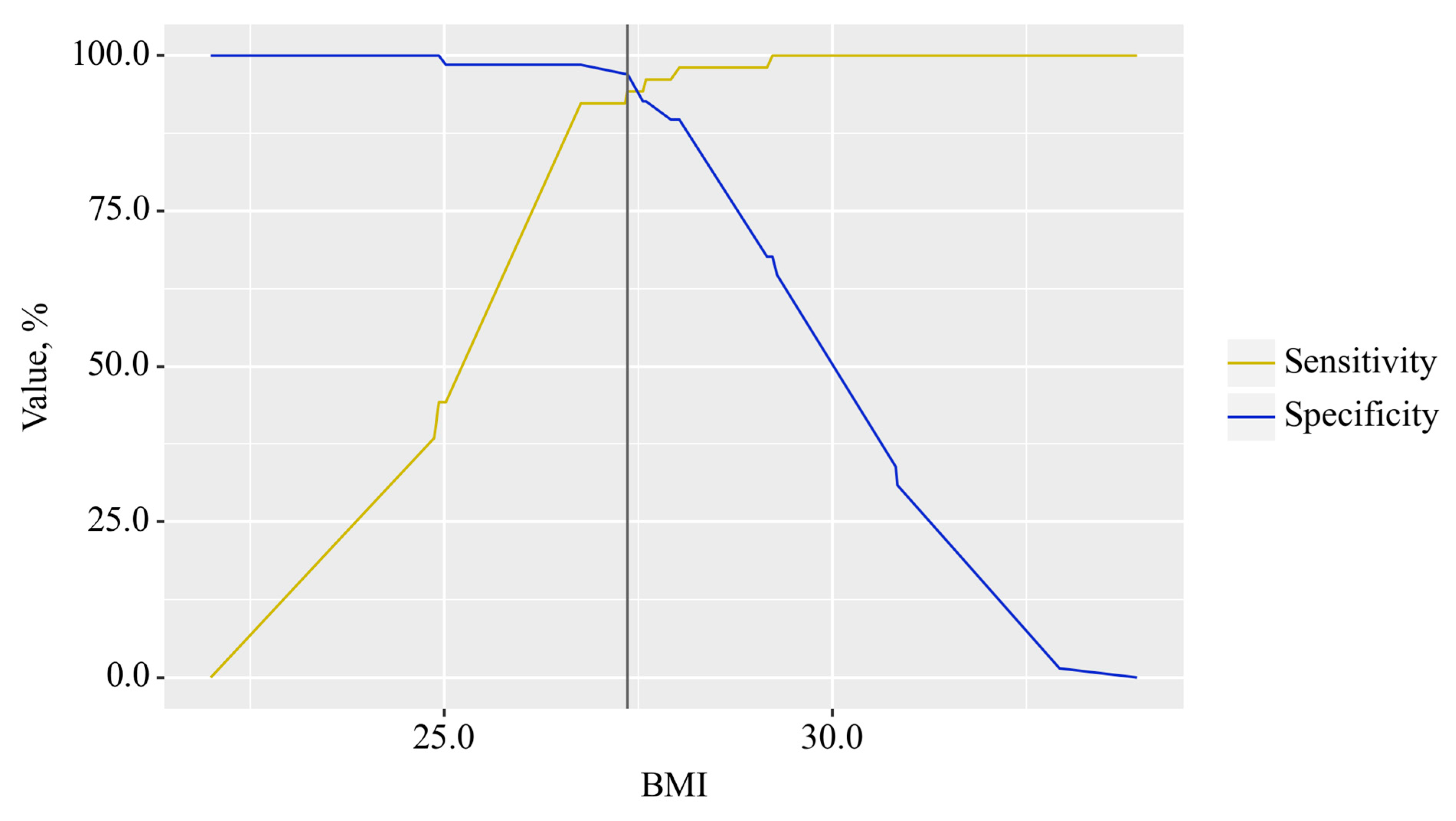
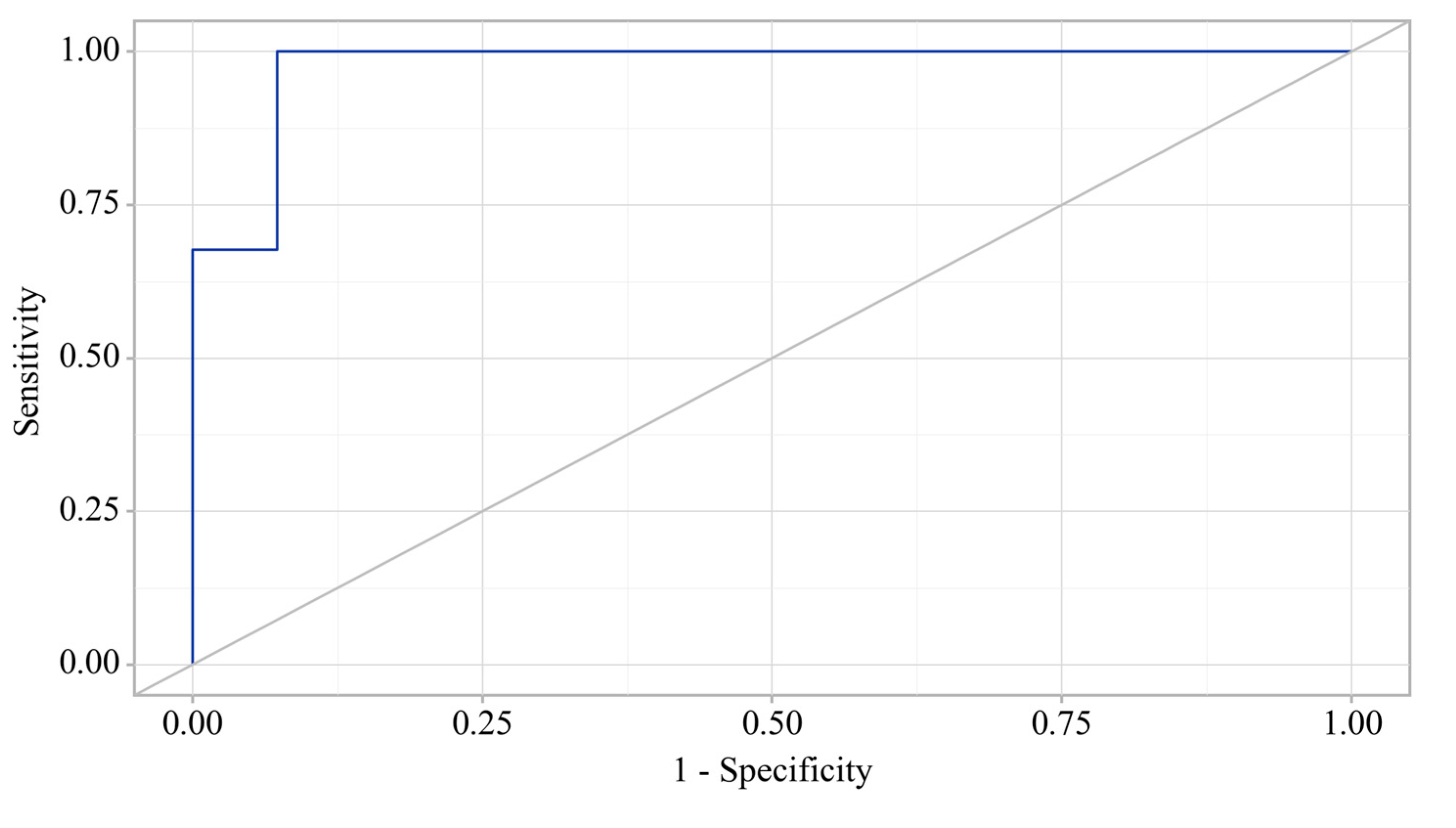
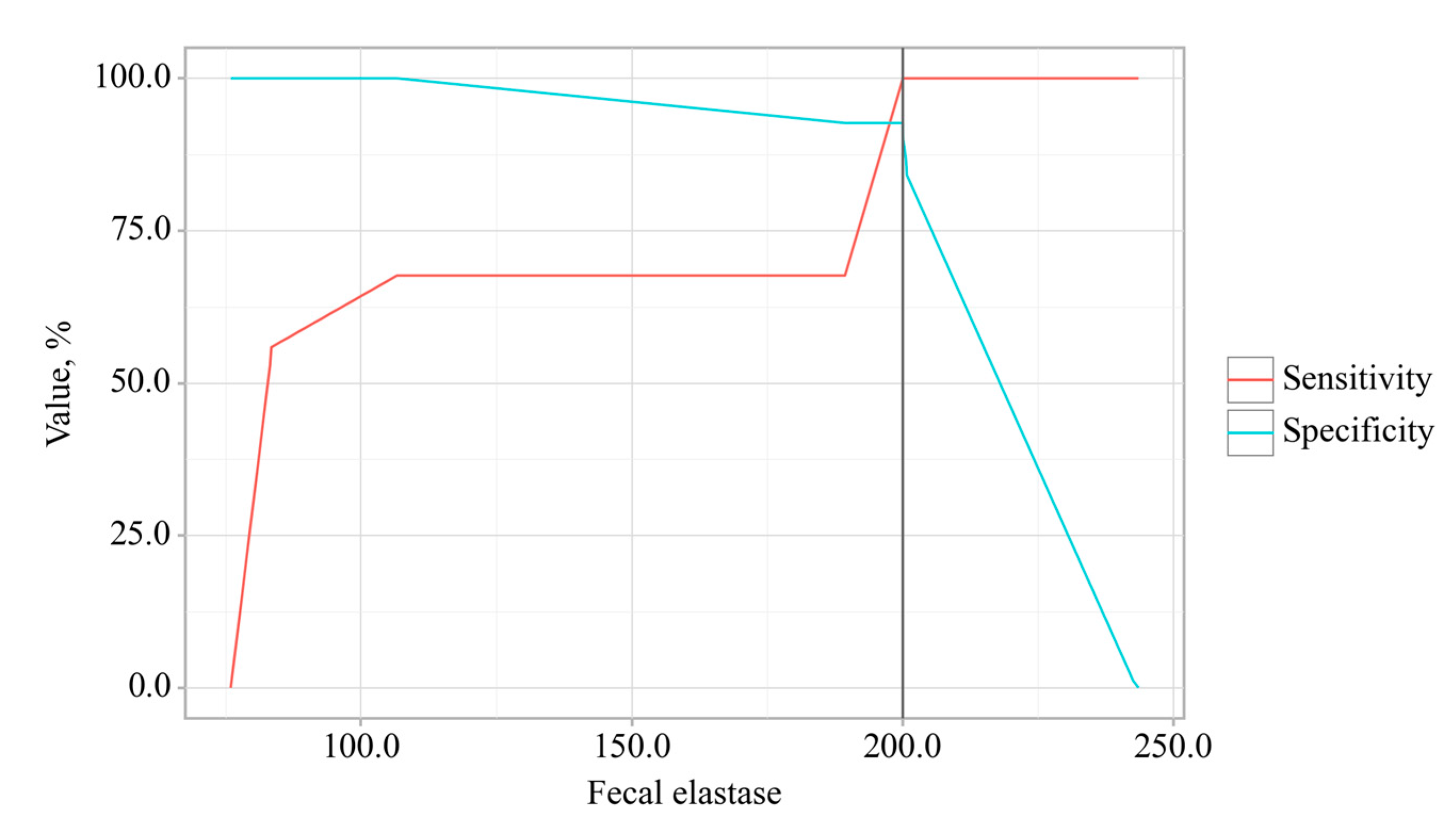
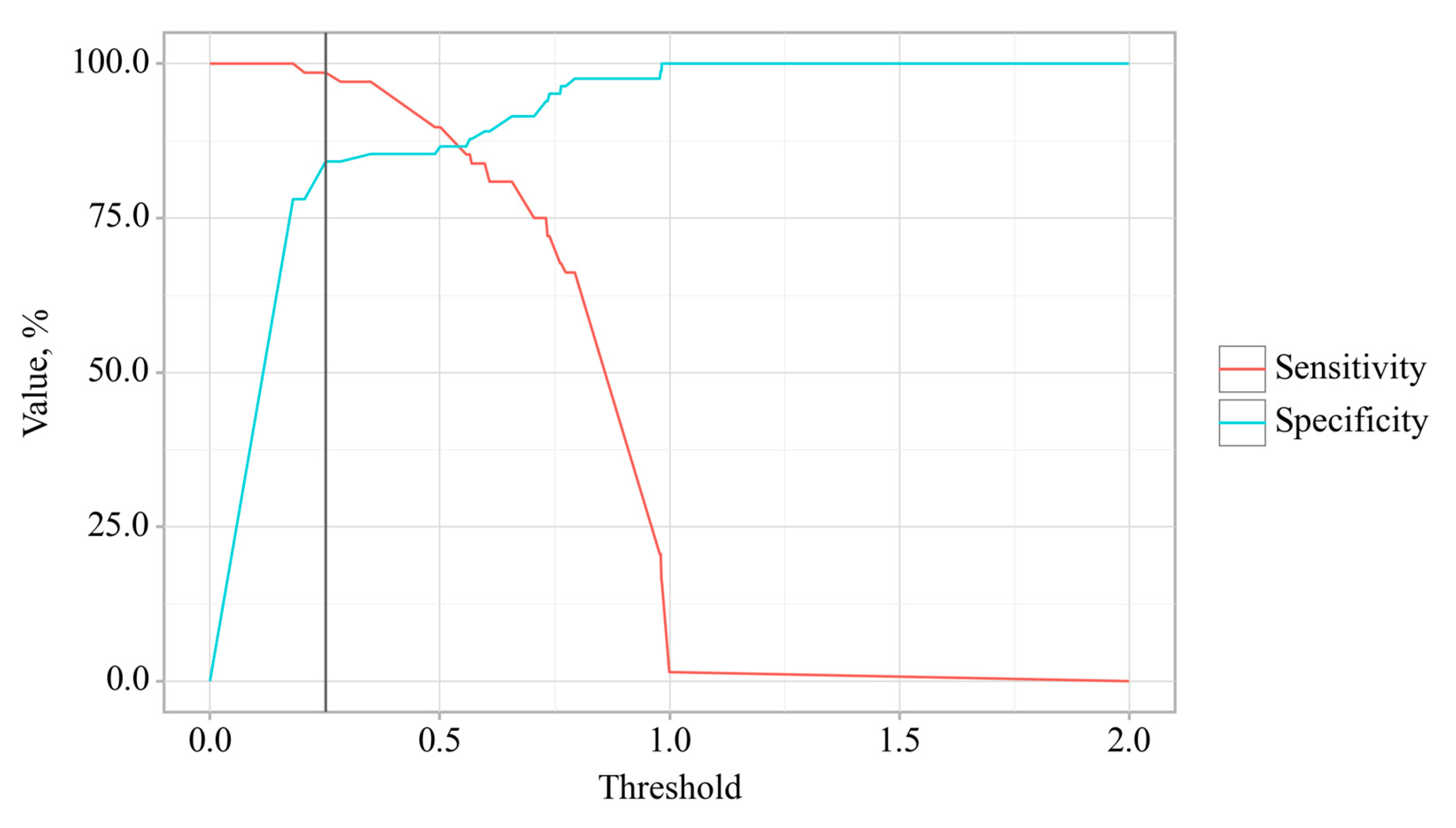
3.3. Predictors Analysis of OA and CP comorbidity and EPI
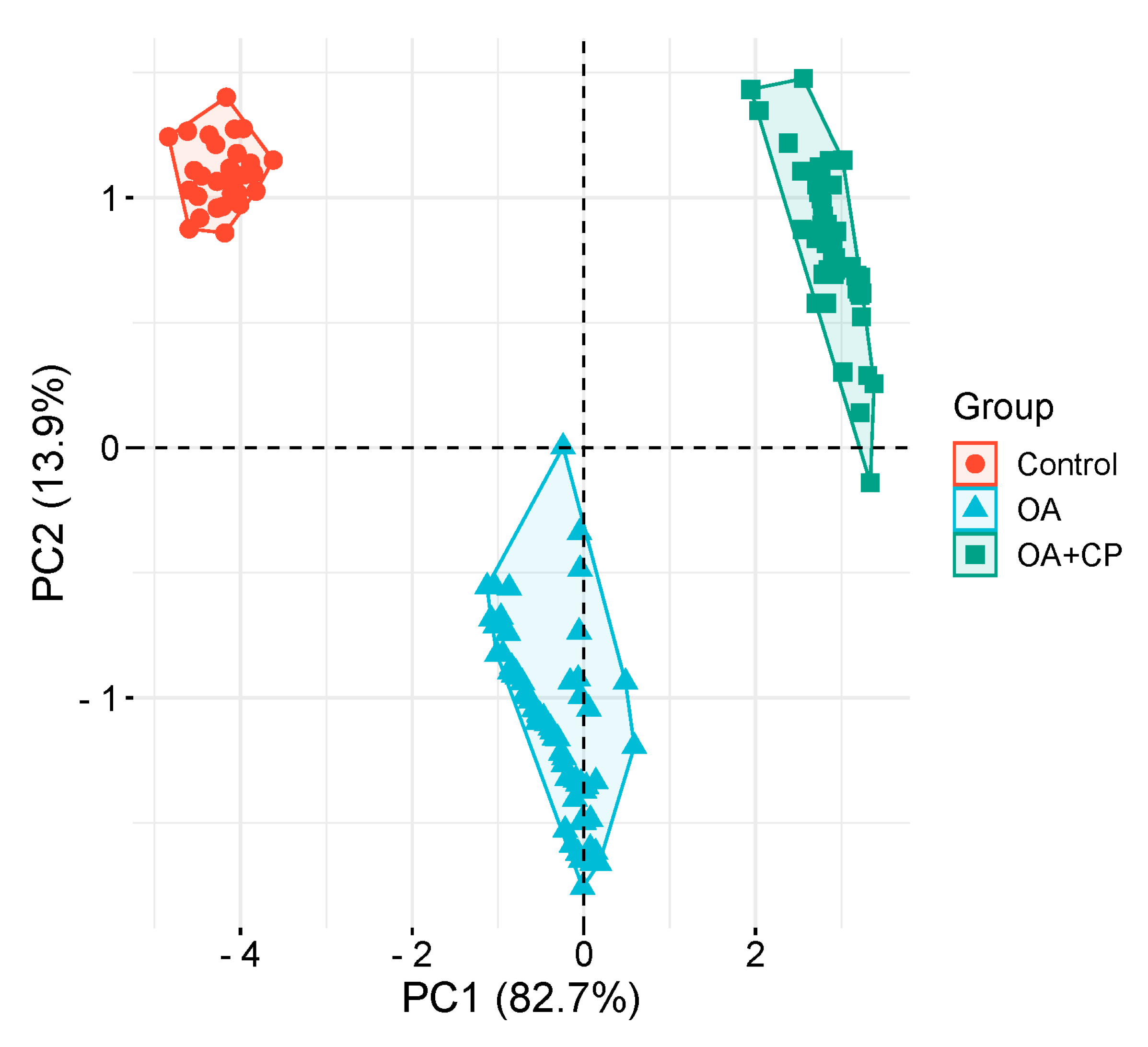
3.4. Principal Component Analysis
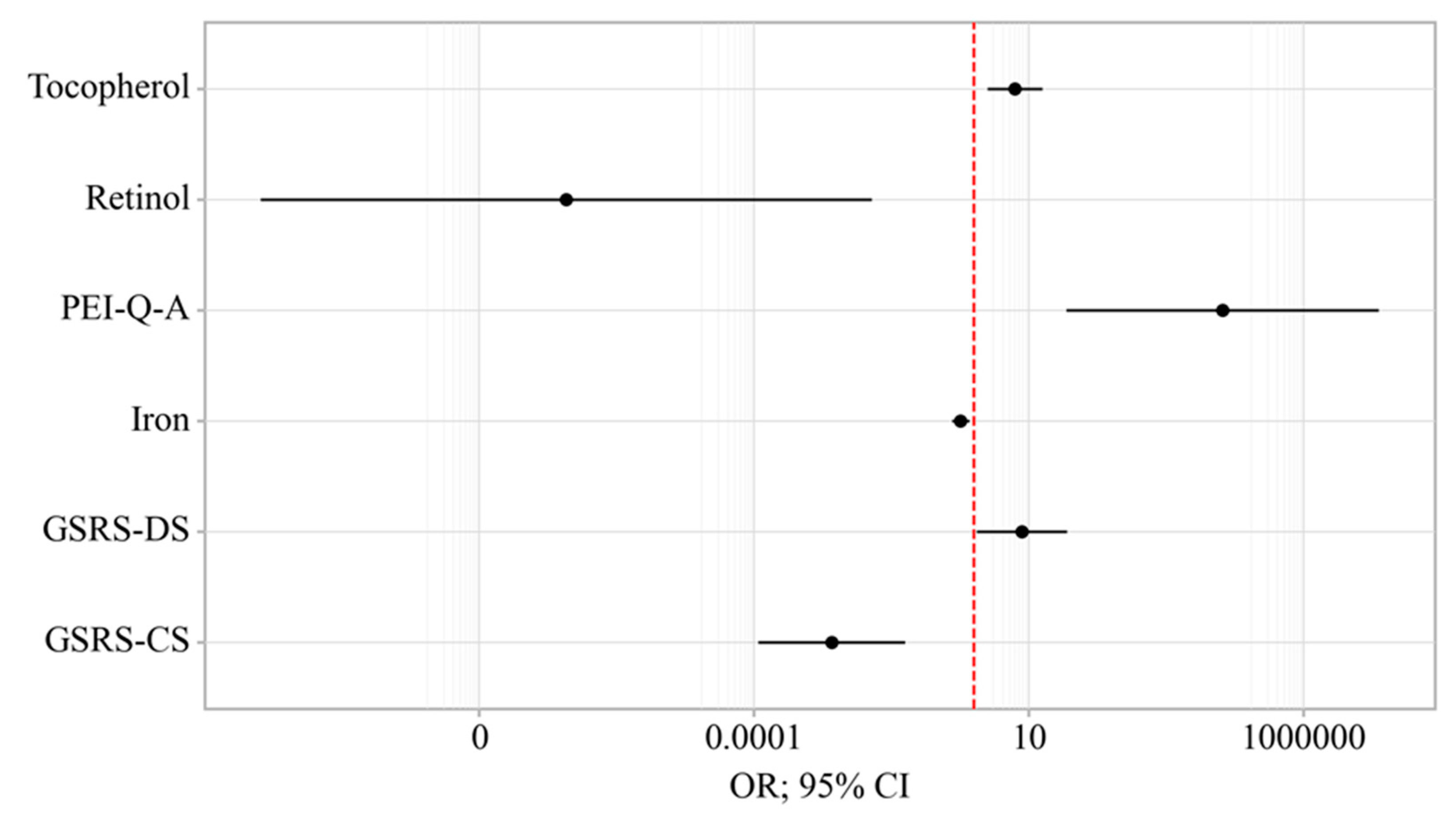
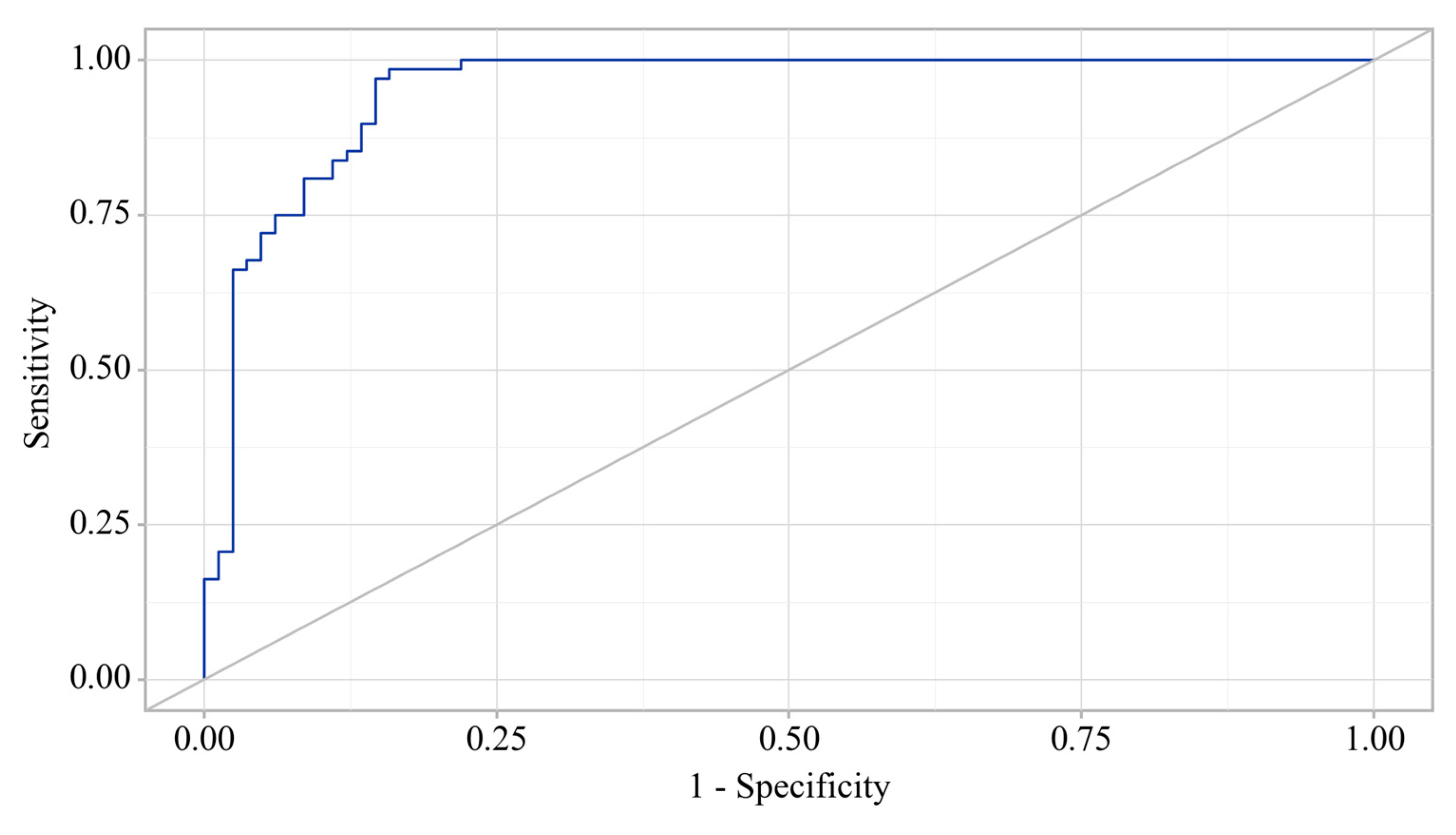
3.5. Binary Logistic Regression
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Swain, S.; Kamps, A.; Runhaar, J.; Dell'Isola, A.; Turkiewicz, A.; Robinson, D.; Strauss, V.; Mallen, C.; Kuo, C. F.; Coupland, C.; Doherty, M.; Sarmanova, A.; Prieto-Alhambra, D.; Englund, M.; Bierma-Zeinstra, S. M. A.; Zhang, W. , Comorbidities in osteoarthritis (ComOA): a combined cross-sectional, case-control and cohort study using large electronic health records in four European countries. BMJ open 2022, 12, e052816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, X.; Hua, Y. , Identification of four-gene signature to diagnose osteoarthritis through bioinformatics and machine learning methods. Cytokine 2023, 169, 156300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Xu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Cao, Y. , Associations between weather conditions and osteoarthritis pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Annals of medicine 2023, 55, 2196439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zemedikun, D. T.; Lee, H.; Nirantharakumar, K.; Raza, K.; Chandan, J. S.; Lord, J. M.; Jackson, T. A. Comorbidity phenotypes and risk of mortality in patients with osteoarthritis in the UK: a latent class analysis. Arthritis research & therapy, 2022; 24, 231. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, M. J.; Miller, R. E.; Malfait, A. M. , The Genesis of Pain in Osteoarthritis: Inflammation as a Mediator of Osteoarthritis Pain. Clinics in geriatric medicine 2022, 38, 221–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amodeo, G.; Magni, G.; Galimberti, G.; Riboldi, B.; Franchi, S.; Sacerdote, P.; Ceruti, S. , Neuroinflammation in osteoarthritis: From pain to mood disorders. Biochemical pharmacology 2024, 116182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swain, S.; Sarmanova, A.; Coupland, C.; Doherty, M.; Zhang, W. , Comorbidities in Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Arthritis care & research, 2020; 72, 991–1000. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Yang, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, C.; Lv, N. , Exploration beyond osteoarthritis: the association and mechanism of its related comorbidities. Frontiers in endocrinology 2024, 15, 1352671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hines, O. J.; Pandol, S. J. , Management of chronic pancreatitis. BMJ (Clinical research ed.), 2024; 384, e070920. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, E.; Chakrabarty, S.; Shariff, S.; Bardhan, M. , Genetics and Genomics of Chronic Pancreatitis with a Focus on Disease Biology and Molecular Pathogenesis. Global medical genetics 2023, 10, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamin, O.; Lappin, S. L. Chronic Pancreatitis. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing.
- Copyright © 2024, StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island (FL) ineligible companies. Disclosure: Sarah Lappin declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies., 2024.
- Capurso, G.; Tacelli, M.; Vanella, G.; Ponz de Leon Pisani, R.; Dell'Anna, G.; Abati, M.; Mele, R.; Lauri, G.; Panaitescu, A.; Nunziata, R.; Zaccari, P.; Archibugi, L.; Arcidiacono, P. G. , Managing complications of chronic pancreatitis: a guide for the gastroenterologist. Expert review of gastroenterology & hepatology, 2023; 17, 1267–1283. [Google Scholar]
- Beyer, G.; Habtezion, A.; Werner, J.; Lerch, M. M.; Mayerle, J. , Chronic pancreatitis. Lancet (London, England), 2020; 396, 499–512. [Google Scholar]
- Löhr, J. M.; Dominguez-Munoz, E.; Rosendahl, J.; Besselink, M.; Mayerle, J.; Lerch, M. M.; Haas, S.; Akisik, F.; Kartalis, N.; Iglesias-Garcia, J.; Keller, J.; Boermeester, M.; Werner, J.; Dumonceau, J. M.; Fockens, P.; Drewes, A.; Ceyhan, G.; Lindkvist, B.; Drenth, J.; Ewald, N.; Hardt, P.; de Madaria, E.; Witt, H.; Schneider, A.; Manfredi, R.; Brøndum, F. J.; Rudolf, S.; Bollen, T.; Bruno, M. , United European Gastroenterology evidence-based guidelines for the diagnosis and therapy of chronic pancreatitis (HaPanEU). United European gastroenterology journal 2017, 5, 153–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleeff, J.; Whitcomb, D. C.; Shimosegawa, T.; Esposito, I.; Lerch, M. M.; Gress, T.; Mayerle, J.; Drewes, A. M.; Rebours, V.; Akisik, F.; Muñoz, J. E. D.; Neoptolemos, J. P. , Chronic pancreatitis. Nature reviews. Disease primers 2017, 3, 17060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nag, D. S.; Swain, B. P.; Anand, R.; Barman, T. K. ; Vatsala, Pain management in chronic pancreatitis. World journal of clinical cases 2024, 12, 2016–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, K.; Johnson, M. H.; Truter, S.; Pandanaboyana, S.; Windsor, J. A. , Pain assessment in chronic pancreatitis: A comparative review of methods. Pancreatology : official journal of the International Association of Pancreatology (IAP)... [et al.], 2016; 16, 931–939. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Q. Y.; Tan, K.; Zhang, X. L.; Han, X.; Pan, J. P.; Huang, Z. Y.; Tang, C. W.; Li, J. , Incidence, prevalence, and comorbidities of chronic pancreatitis: A 7-year population-based study. World journal of gastroenterology 2023, 29, 4671–4684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, A. E.; Faghih, M.; Drewes, A. M.; Singh, V. K.; Yadav, D.; Olesen, S. S. , Psychiatric Comorbidity in Patients With Chronic Pancreatitis Associates With Pain and Reduced Quality of Life. The American journal of gastroenterology 2020, 115, 2077–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redkva, O. V.; Babinets, L. S.; Halabitska, I. M. , EVALUATION OF PARAMETERS OF ACTUAL TYPICAL PATHOGENETIC SYNDROMES IN COMORBIDITY OF TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS AND CHRONIC PANCREATITIS. Wiadomosci lekarskie (Warsaw, Poland : 1960), 2021; 74, 2557–2559. [Google Scholar]
- Halabitska, I. M.; Babinets, L. S.; Vysotskyi, V. I. , POSSIBILITIES OF METABOLIC AND FUNCTIONAL DISORDERS CORRECTION IN OSTEOARTHRITIS WITH COMPLEX COMORBIDITY. Wiadomosci lekarskie (Warsaw, Poland : 1960), 2022; 75, 645–648. [Google Scholar]
- Tomaszewska, E.; Hułas-Stasiak, M.; Dobrowolski, P.; Świątkiewicz, M.; Muszyński, S.; Tomczyk-Warunek, A.; Blicharski, T.; Donaldson, J.; Arciszewski, M. B.; Świetlicki, M.; Puzio, I.; Bonior, J. , Does Chronic Pancreatitis in Growing Pigs Lead to Articular Cartilage Degradation and Alterations in Subchondral Bone? International journal of molecular sciences, 2024; 25. [Google Scholar]
- Knights, A. J.; Redding, S. J.; Maerz, T. , Inflammation in osteoarthritis: the latest progress and ongoing challenges. Current opinion in rheumatology 2023, 35, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, T. M.; Scanzello, C. R. , Innate inflammation and synovial macrophages in osteoarthritis pathophysiology. Clinical and experimental rheumatology 2019, 120(5), 57–63. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Cai, D.; Bai, X. , Macrophages regulate the progression of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis and cartilage 2020, 28, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, T. L.; Gomoll, A. H.; Lattermann, C.; Hernandez, A. J.; Bueno, D. F.; Amano, M. T. , Macrophage: A Potential Target on Cartilage Regeneration. Frontiers in immunology 2020, 11, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dainese, P.; Mahieu, H.; De Mits, S.; Wittoek, R.; Stautemas, J.; Calders, P. , Associations between markers of inflammation and altered pain perception mechanisms in people with knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review. RMD open, 2023; 9. [Google Scholar]
- Tanţău, A.; Leucuţa, D. C.; Tanţău, M.; Boţan, E.; Zaharie, R.; Mândruţiu, A.; Tomuleasa, I. C. , Inflammation, Tumoral Markers and Interleukin-17, -10, and -6 Profiles in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma and Chronic Pancreatitis. Digestive diseases and sciences 2021, 66, 3427–3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Lou, N.; Jiao, J.; Guo, F.; Xiang, H.; Shang, D. , Macrophages in pancreatitis: Mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & pharmacotherapie, 2020; 131, 110693. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, H.; Yu, H.; Zhou, Q.; Wu, Y.; Ren, J.; Zhao, Z.; Tao, X.; Dong, D. , Macrophages: A rising star in immunotherapy for chronic pancreatitis. Pharmacological research 2022, 185, 106508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L. L.; Ren, Z. N.; Yang, J.; Li, B. B.; Huang, Y. W.; Song, D. X.; Li, X.; Xu, J. J.; Bhatia, M.; Zou, D. W.; Zhou, C. H.; Sun, J. , Gut microbiota controls the development of chronic pancreatitis: A critical role of short-chain fatty acids-producing Gram-positive bacteria. Acta pharmaceutica Sinica. B 2023, 13, 4202–4216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlo, P.; Kamyshna, I.; Kamyshnyi, A. , Effects of metformin on the gut microbiota: A systematic review. Molecular metabolism 2023, 77, 101805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petakh, P.; Kobyliak, N.; Kamyshnyi, A. , Gut microbiota in patients with COVID-19 and type 2 diabetes: A culture-based method. Frontiers in cellular and infection microbiology 2023, 13, 1142578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thursby, E.; Juge, N. , Introduction to the human gut microbiota. The Biochemical journal 2017, 474, 1823–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petakh, P.; Oksenych, V.; Kamyshnyi, A. , The F/B ratio as a biomarker for inflammation in COVID-19 and T2D: Impact of metformin. Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & pharmacotherapie, 2023; 163, 114892. [Google Scholar]
- Malesza, I. J.; Malesza, M.; Walkowiak, J.; Mussin, N.; Walkowiak, D.; Aringazina, R.; Bartkowiak-Wieczorek, J.; Mądry, E. , High-Fat, Western-Style Diet, Systemic Inflammation, and Gut Microbiota: A Narrative Review. Cells, 2021; 10. [Google Scholar]
- Gleason, B.; Chisari, E.; Parvizi, J. , Osteoarthritis Can Also Start in the Gut: The Gut-Joint Axis. Indian journal of orthopaedics 2022, 56, 1150–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bannuru, R. R.; Osani, M. C.; Vaysbrot, E. E.; Arden, N. K.; Bennell, K.; Bierma-Zeinstra, S. M. A.; Kraus, V. B.; Lohmander, L. S.; Abbott, J. H.; Bhandari, M.; Blanco, F. J.; Espinosa, R.; Haugen, I. K.; Lin, J.; Mandl, L. A.; Moilanen, E.; Nakamura, N.; Snyder-Mackler, L.; Trojian, T.; Underwood, M.; McAlindon, T. E. , OARSI guidelines for the non-surgical management of knee, hip, and polyarticular osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis and cartilage 2019, 27, 1578–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabha, M.; Hochberg, M. C. , Non-surgical management of hip and knee osteoarthritis; comparison of ACR/AF and OARSI 2019 and VA/DoD 2020 guidelines. Osteoarthritis and cartilage open 2022, 4, 100232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijos-Mallada, G.; Sostres, C.; Gomollón, F. , NSAIDs, gastrointestinal toxicity and inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterologia y hepatologia 2022, 45, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kefalakes, H.; Stylianides, T. J.; Amanakis, G.; Kolios, G. , Exacerbation of inflammatory bowel diseases associated with the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: myth or reality? European journal of clinical pharmacology 2009, 65, 963–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kvasnovsky, C. L.; Aujla, U.; Bjarnason, I. , Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and exacerbations of inflammatory bowel disease. Scandinavian journal of gastroenterology 2015, 50, 255–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A. C. F.; Monteiro, L. P. G.; Gomes, A. C. C.; Martel, F.; Santos, T. M.; Ferreira, B. , NSAID-Based Coordination Compounds for Biomedical Applications: Recent Advances and Developments. International journal of molecular sciences, 2022; 23. [Google Scholar]
- Bindu, S.; Mazumder, S.; Bandyopadhyay, U. , Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and organ damage: A current perspective. Biochemical pharmacology 2020, 180, 114147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjarnason, I.; Scarpignato, C.; Holmgren, E.; Olszewski, M.; Rainsford, K. D.; Lanas, A. , Mechanisms of Damage to the Gastrointestinal Tract From Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 500–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGettigan, M. J.; Menias, C. O.; Gao, Z. J.; Mellnick, V. M.; Hara, A. K. , Imaging of Drug-induced Complications in the Gastrointestinal System. Radiographics : a review publication of the Radiological Society of North America, Inc, 2016; 36, 71–87. [Google Scholar]
- Soreide, K. , Damage to the Gastrointestinal Tract From Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs: What About Perforations and the Healing Intestine? Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 1271–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serón-Arbeloa, C.; Labarta-Monzón, L.; Puzo-Foncillas, J.; Mallor-Bonet, T.; Lafita-López, A.; Bueno-Vidales, N.; Montoro-Huguet, M. , Malnutrition Screening and Assessment. Nutrients, 2022; 14. [Google Scholar]
- Dent, E.; Wright, O. R. L.; Woo, J.; Hoogendijk, E. O. , Malnutrition in older adults. Lancet (London, England), 2023; 401, 951–966. [Google Scholar]
- Capurso, G.; Traini, M.; Piciucchi, M.; Signoretti, M.; Arcidiacono, P. G. , Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency: prevalence, diagnosis, and management. Clinical and experimental gastroenterology 2019, 12, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| OA (n=68) | OA+CP (n=52) | p-value a | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kellgren-Lawrence grade | 1.5 (1–2) | 2 (1–2) | p = 0.1437 |
| WOMAC pain | 10 (10–11) | 16 (16–16) | p < 0.001 |
| WOMAC stiffness, | 3 (3–3) | 4(4–5) | p = 0.02 |
| WOMAC function | 28 (28–29) | 38 (37–39) | p < 0.001 |
| WOMAC total | 42 (41–43) | 58 (57.75–60) | p < 0.001 |
| Lequesne Algofunctional Index | 5 (5–6) | 8 (8–8) | p < 0.001 |
| VAS joint pain | 31 (30–32.25) | 44 (43–45) | p < 0.001 |
| VAS movement | 37 (36–38.25) | 52 (51–52) | p < 0.001 |
| VAS inflammation | 16 (15–17) | 28 (27–29) | p < 0.001 |
| VAS joint dysfunction | 15 (14–16) | 30 (29–31) | p < 0.001 |
| Control (n=30) | OA (n=68) | OA+CP (n=52) | p-value b | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fecal elastase-1, mcg/g | 233.88 (228.46–237.38) | 201.24 (198.93–204.28) | 81.43 (76–87.9) | p < 0.001 | ||||||||
| Total bilirubin, µmol/L | 5.05 (4.44–5.71) | 5.11 (4.77–5.61) | 5.14 (4.63–5.64) | p = 0.923 | ||||||||
| Direct bilirubin, µmol/L | 1.96 (1.55–2.2) | 1.86 (1.47–2.2) | 2.09 (1.65–2.34) | p = 0.1767 | ||||||||
| Indirect bilirubin, µmol/L | 3.39 (3.13–3.61) | 3.41 (3.11–3.76) | 3.44 (2.99–3.78) | p = 0.6505 | ||||||||
| ALT, µkat/L | 0.28 (0.19–0.38) | 0.3 (0.23–0.38) | 0,36 (0,23–0,51) | p = 0.0787 | ||||||||
| AST, µkat/L | 0.24 (0.21–0.29) | 0.24 (0.19–0.32) | 0.29 (0.22–0.32) | p = 0.1886 | ||||||||
| GGT, U/L | 18.09 (17.01–19.02) | 18.11 (17.33–18.73) | 16.77 (14.52–20.57) | p = 0.7773 | ||||||||
| Alkaline phosphatase, U/L | 77.32 (73.04–80.53) | 78.99 (75.48–86.43) | 80.93 (75.75–85.64) | p = 0.0633 | ||||||||
| PEI-Q | ||||||||||||
| OA (n=68) | OA+CP (n=52) | p-value a | ||||||||||
| Abdominal symptoms (А) | 0.31 (0.25–0.37) | 1.86 (1.78–1.91) | p < 0.001 | |||||||||
| Bowel movement symptoms (В) | 0.27 (0.23–0.31) | 1.8 (1.72–1.85) | p < 0.001 | |||||||||
| Total symptom score | 0.29 (0.25–00.33) | 1.83 (1.75–1.89) | p < 0.001 | |||||||||
| Impact (С) | 0 (0–0) | 1.89 (1.79–1.96) | ||||||||||
| Total summary score | 0 (0–0) | 1.85 (1.78–1.9) | ||||||||||
| GSRS | ||||||||||||
| Control (n=30) | OA (n=68) | OA+CP (n=52) | ||||||||||
| GSRS-AP | 1.22 (1.01–1.44) | 4.9 (4.74–5.13) | p < 0.001 | |||||||||
| GSRS-IS | 0.91 (0.76–1.11) | 4.75 (4.61–4.91) | p < 0.001 | |||||||||
| GSRS-DS | 1.23 (1.01–1.37) | 4.61 (4.41–4.74) | p < 0.001 | |||||||||
| GSRS-CS | 0.47 (0.4–0.52) | 4.14 (3.99–4.22) | p < 0.001 | |||||||||
| GSRS-RS | 1.01 (0.85–1.14) | 4.25 (4.12–4.33) | p < 0.001 | |||||||||
| Control (n=30) | OA (n=68) | OA+CP (n=52) | p-value b | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Retinol, mg/l | 0.71 (0.63–079) | 0.43 (0.37–0.49) | 0.19 (0.15–0.23) | p < 0.001 |
| Tocopherol, mg/l | 11.92 (11.34–12.33) | 6.96 (6.69–7.19) | 3.69 (3.37–3.94) | p < 0.001 |
| 25(OH) vitamin D3, ng/l | 42.59 (42.07–43.44) | 32.07 (30.95–33.55) | 21.81 (20.77–23.81) | p < 0.001 |
| Thiamine, µg/L | 60.45 (52.82–65.82) | 60.73 (55.57–64.9) | 59.24 (57.16–60.96) | p = 0.6889 |
| Pyridoxine, µg/L | 25.33 (24.42–26.6) | 23.31 (19.57–27.58) | 21.89 (15.79–30.18) | p = 0.1408 |
| BMI, kg/m² | 20.55 (20.17–20.9) | 29.78 (28.84–30.97) | 25.1 (24.21–25.63) | p < 0.001 |
| RBC, 10¹²/L | 3.66 (3.45–3.99) | 3.84 (3.56–4.06) | 3.64 (3.39–3.89) | p = 0.0688 |
| WBC, 10[9]/L | 4.68 (4.33–4.95) | 4.91 (4.53–5.48) | 4.87 (4.55–5.48) | p = 0.065 |
| Hemoglobin, g/L | 130 (119–137.25) | 125.5 (112.75–135) | 123 (114.25–135) | p = 0.3282 |
| Iron, mcmol/l | 27.31 (25.43–28.61) | 15.73 (13.69–17.58) | 6.61 (5.37–7.73) | p < 0.001 |
| Ferritin, ng/ml | 88.98 (86.78–92.25) | 64.18 (60.61–66.66) | 36.29 (34.43–38.15) | p < 0.001 |
| Transferrin, mg/dl | 318.17 (313.28–321.83) | 461.7 (456.23–466.88) | 527.57 (521.64–534.79) | p < 0.001 |
| CRP, mg/l | 1.00 (0.81–1.22) | 2.68 (2.54–2.77) | 4.52 (4.33–4.64) | p < 0.001 |
| Component | ||
|---|---|---|
| Factor 1 | Factor 2 | |
| WOMAC total score | -0,890 | 0,429 |
| Fecal elastase-1 | 0,976 | 0,172 |
| CRP | -0,979 | 0,104 |
| BMI | -0,110 | 0,992 |
| Ferritin | 0,978 | -0,135 |
| Retinol | 0,920 | -0,227 |
| Tocopherol | 0,947 | -0,289 |
| 25(OH) vitamin D3 | 0,957 | -0,187 |
| Predictors | Unadjusted | Adjusted | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| COR; 95% CI | p | AOR; 95% CI | p | |
| GSRS-DS | 2.773; 2.061 – 3.732 | < 0.001* | 7.592; 1.146 – 50.350 | 0.036* |
| GSRS-CS | 2.511; 1.916 – 3.294 | < 0.001* | 0.003; 0.000 – 0.057 | < 0.001* |
| PEI-Q-A | 10.285; 5.186 – 20.389 | < 0.001* | 34207.493; 48.570 – 24082596.484 | 0.002* |
| Retinol | 0.000; 0.000 – 0.000 | < 0.001* | 0.000; 0.000 – 0.014 | 0.009* |
| Tocopherol | 0.399; 0.296 – 0.538 | < 0.001* | 5.651; 1.793 – 17.814 | 0.003* |
| Iron | 0.705; 0.634 – 0.784 | < 0.001* | 0.577; 0.399 – 0.835 | 0.004* |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





