1. Introduction
Understanding reservoir water properties is crucial for assessing oil or gas field development feasibility. Water production can cause scale, corrosion, and plugging issues, requiring specialized treatments. Facilities are needed to handle and treat the produced water, impacting project costs and profitability [
1]. Initially, reservoir waters tend to be mixed with hydrocarbons under specific pressure and temperature conditions. Hydrocarbons in the formation are saturated with water until production begins. Besides this, reservoir rock open surfaces are typically coated with water, facilitating natural fluid flow. When production starts, pressure and temperature drop, causing water to separate from hydrocarbons. This pressure difference drives hydrocarbons from the formation up to the surface. Early-stage water production often forms emulsions, separated without treatment, usually sourced from connate water zones [
2,
3].
Water in oilfield formation is known as an important fluid in oil fields. By carefully analyzing it, important geological and geochemical information can be obtained. Those waters have mineral different cations and anions, including cations such as sodium (Na
+), calcium (Ca
2+), barium (Ba
2+), strontium (Sr
2+), potassium (K
+) and iron (Fe
2+), as well as chloride (Cl
-), sulfate (SO
42-), sulfide (S
2-), and bicarbonate (HCO
3-) anions. In the process of oil recovery operations in the subsurface formation, especially when seawater is used for injection, the precipitation of new minerals within the surface and subsurface equipments is significant. In other words, with the mixing of injected water and formation water, the concentration of minerals in the solution increases, promoting changes in mineral solubility, also due to changes in temperature and pressure conditions in the well [
4,
5]. Changes in mineral solubility can lead to the precipitation of mineral deposits in oil wells and ultimately reduce the production efficiency.
In this study, mineral ions in the water of the Formation in Bibi Hakimeh oil field have been analyzed, following previous studies on the thermodynamic properties of mineral ions in solid-liquid equilibrium systems [
15,
16,
17,
18,
19]. The formation of calcium sulfate, gypsum, calcium carbonate and magnesium carbonate, in the present-day operating conditions, has been modeled with StimCade2 software.
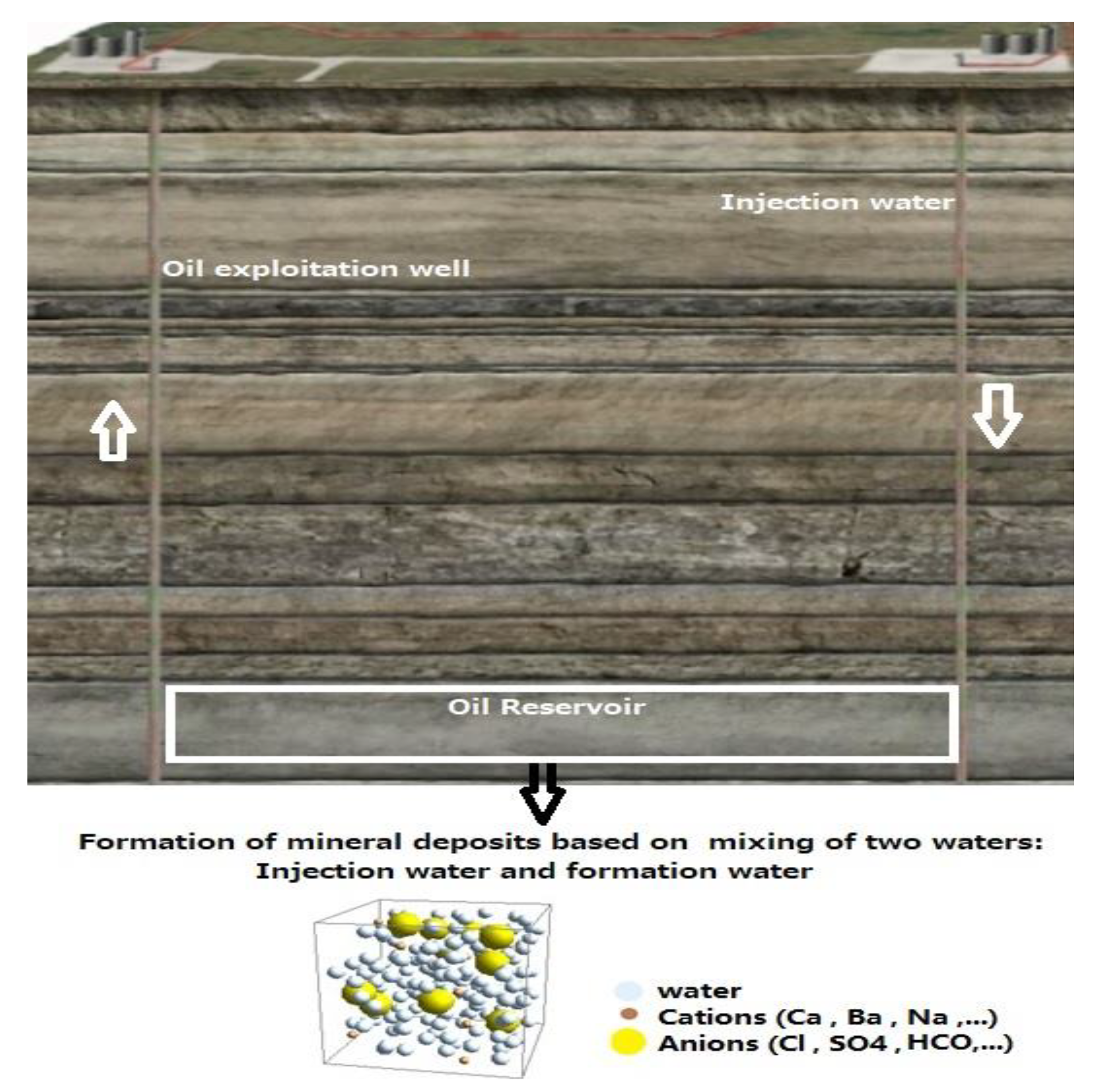
Figure 1 shows a schematic of the formation of mineral deposits in the oil industry.
2. Previous Studies
The formation of mineral deposits in oil systems is a major operational concern and it has been considered by many researchers in recent decades.
Mitchell and Grist (1980) [
6] studied the formation of carbonate and sulfate mineral sediments at the North Sea Fortis Reservoir. According to their research, due to the operation of injecting seawater into the reservoir and mixing two impure waters containing dissolved salts, the formation of barium sulfate and strontium sulfate mineral deposits is significant.
Jordan et al. (2000) [
7] studied the formation of mineral sediments in the Ab Formation, in northern Alaska. Their experimental work showed that, during the process of oil recovery operations, the high amounts of strontium, barium and calcium cations promoted significant precipitation of sulfate deposits.
Moghadasi et al. (2003) [
8] evaluated the formation of mineral sediments and permeability changes in the porous environment of the oil zone reservoir. The combination of water containing calcium cation with water rich in sulfate and carbonate ions in the porous medium of the reservoir has been studied. A significant reduction in the permeability ratio in the porous environment of the reservoir has been modeled and observed, due to the composition of the gross mineral solution and temperature changes.
Nasruddin et al. (2004) [
9] studied the inter-action of water formation and injected water in oil recovery operations. Their research critical approached saturation index and calcium sulfate mineral precipitation with OKSCALE software, showing the effect of two incompatible waters mixing in the precipitation of mineral deposits.
Raju (2009) [
10] studied the formation of mineral deposits in Saudi Aramco wells, due to water injection operations. According to the results of his study, the formation of calcium carbonate deposits can be due to conditions such as pressure drop and pH.
Al-Roomi and Hossein (2016) [
11] studied the importance of reaction kinetics in the precipitation of mineral deposits and pointed to the role of the excessive mineral cations and anions.
Ghalib and Almallah (2017) [
12] studied the water of Mishrif Formation to investigate the precipitation of mineral deposits during water injection operations. In this study, they combined the water of Mishrif Formation with sea water, Euphrates river water and the main drainage water of the waterfall, predicting mineral precipitation at reservoir conditions. According to their results, calcium carbonate and barium sulfate mineral sediments are the most serious problem in terms of inorganic sediments in the reservoir of Mishrif Formation.
Wang et al. (2018) [
13] studied the formation of calcium carbonate deposits despite inhibitors during oil recovery operations (EOR). The oil recovery method used injectable chemicals with a combination of surfactant and polymer, as well as inhibitors of triphosphonate, pentaphosphonate and polyacrylate-based chemicals. According to the results, the performance of calcium carbonate precipitate inhibitors can be significantly affected by EOR chemicals.
Hashemi et al. (2019) [
4], applied a thermodynamic model to study the conditions of water injection operations and precipitation if barium sulfate and strontium sulfate deposits in Siri and Nusrat oil fields. The studies were based on the composition of the formation water and of the injected water (Persian Gulf water) and operating conditions. The results showed that the precipitation of barium sulfate and strontium sulfate in the Nusrat oil field is significant, whereas for the Siri oil field, with different formation waters and operating conditions, the formation of deposits is not significant.
Hashemi & Hashemi (2020) [
5] studied the of Nusrat oil field waters, with high concentration of mineral ions. According to the results of their study, the formation of mineral deposits of calcium carbonate, magnesium carbonate and barium sulfate in the Nusrat oil field can cause problems during operation.
Ghalib et al. (2023) [
14] studied the formation of oil field scales in Mashrif formation of Halfaya oil field by mixing it with different water sources including Tigris river water and Gulf sea water. Using geochemical modeling, Middle Kirkuk formation water was identified as the most suitable water for injection. The results obtained in their work, showed that understanding mineral precipitation through geochemical modeling can optimize injection water selection and increase oil production efficiency.
3. Materials and Methods
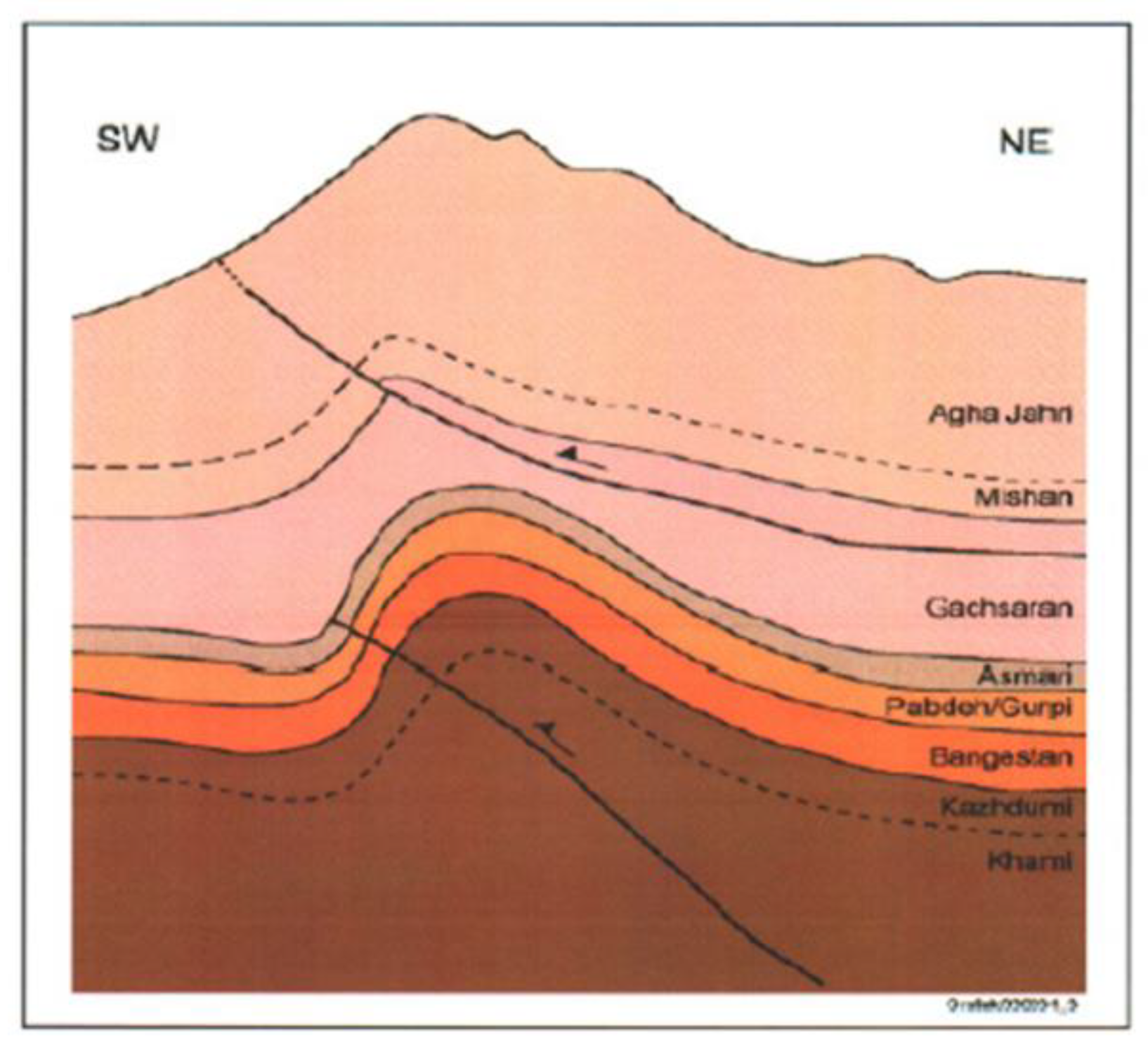
This study has been developed in waters and wells form the Bibi Hakimeh oil field, situated in the southwest of Iran, one of the largest oil fields in the region. It is located northeast of the Delam Port, adjacent to Pazanan, Sarboury, Garangan Chilingar, Sulabdar, and Ragh-e Sefid fields. It lies to the south of the Dezful depression, with its main reservoir formations comprising Asmari and Sarvak siliciclastic formations. Additionally, it holds potential for gas production from carbonate formations. The reservoir oil layer, with an initial thickness of 1000 meters above the oil-water contact at a depth of 1979 meters below sea level, features a gas cap at 250 meters below sea level. Production formations of Asmari and Bangestan, separated by Pabdeh & Gurpi layers with a thickness of 400 meters, yield minimal oil output [
20,
21,
22]. In
Figure 2, the stratigraphy and fault pattern of Bibi Hakimeh field are shown.
Five samples collected from formation waters of the Bibi Hakimeh field have been analyzed, representing 5 different wells of this field. In this study, the measurement method for calcium and magnesium ions based on ASTM-D511 [
23] standard, chlorine ion based on ASTM-D512 [
24] standard, iron ion based on HACH 8008 [
25], sodium ion using Flamephotometer, sulfate ion based on HACH 8051[
26] and bicarbonate based on handbook Betz [
27] is done.
StamCad 2 software was used to predict sulfate and carbonate mineral sediment. This software is used to simulate the working acid of wells and also to predict the deposition of mineral salts in oil fields. The allowable temperature range in this software is between -50 to 600 degrees Fahrenheit and the pressure is between 15.99 to 24999.988 psia. Carbonate, calcium sulfate (anhydrite), calcium water sulfate (gypsum), strontium sulfate, barium sulfate and iron sulfide. This software reports saturation percentage, sediment amount and pH.
Figure 3 shows the home page of this software.
4. Results and Discussion
This section may be divided by subheadings. It should provide a concise and precise description of the experimental results, their interpretation, as well as the experimental conclusions that can be drawn.
3.1. Thermodynamic Analysis
Table 1 presents the analysis of mineral ions in 5 samples of Bibi Hakimeh oil field wells. Based on the results obtained in
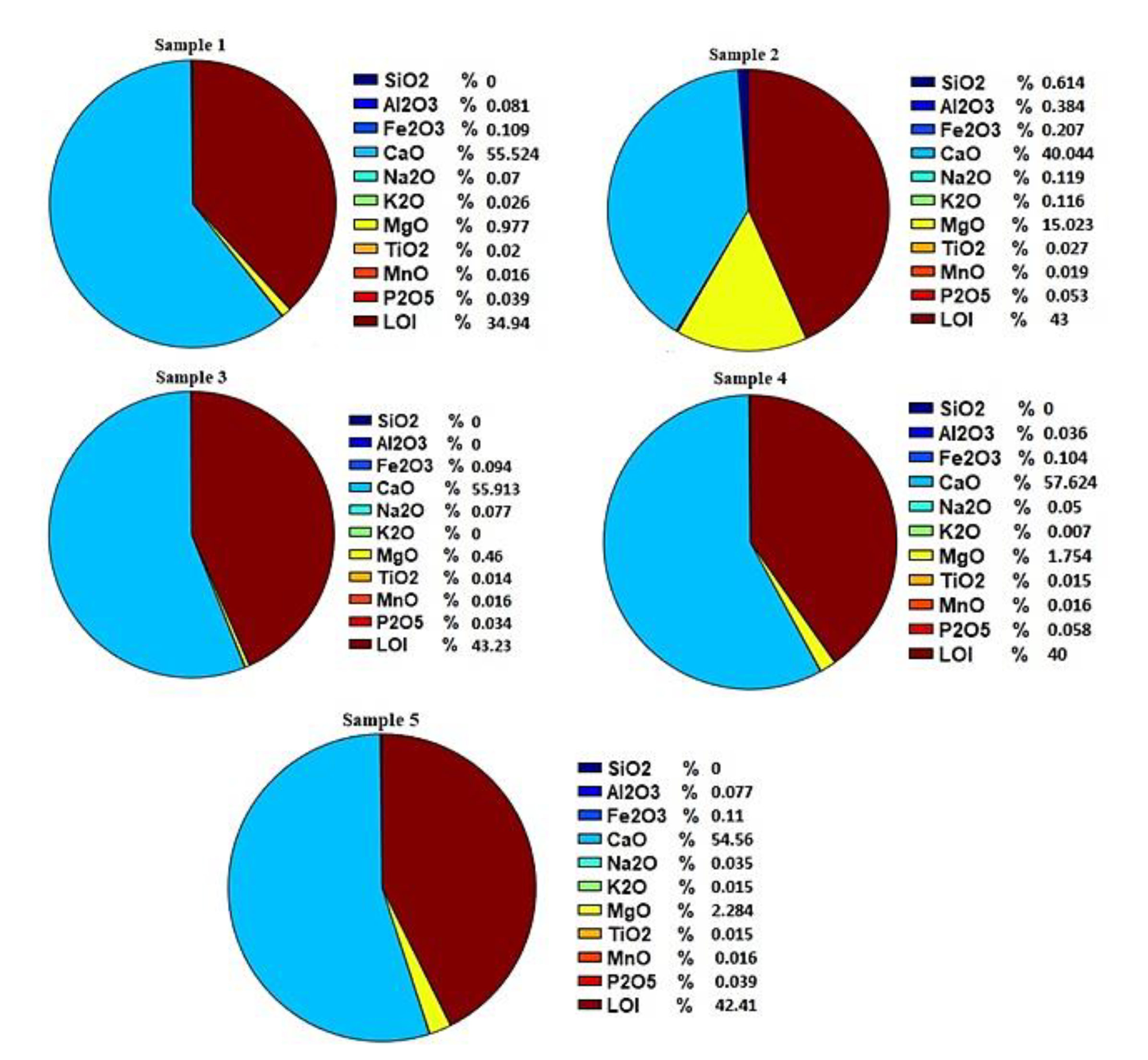
Table 1, the cations of calcium, magnesium, sodium as well as anion sulfate, chloride and bicarbonate in the water of the oil field formation are significant, whereas the amount of iron ion was not observed in the 5 samples studied.
Sulfate ions have a higher concentration than bicarbonate, which can be due to the dissolution of calcium sulphate. Also, according to the obtained results, there is a significant amount of chlorine ion in Bibi Hakimeh Formation, the source of which can be the dissolution of minerals containing chlorine ion in the water of the formation. According to the results of
Table 1, due to the change in concentration (mg/l) of sodium, calcium, magnesium, chloride, sulfate and bicarbonate ions (change in ionic strength), the solubility of mineral ions in aqueous solution water changes. In other words, due to the electrostatic forces between the ions and the short-range forces between the ions and water, electrolytic solutions can make the behavior of the aqueous solution non-ideal at low and high concentrations. By changing the solubility of mineral ions based on the appropriate temperature and pressure conditions of the reservoir, the formation of mineral sediment at the inlet of the well in the reservoir and along the well is exploited.
The level of saltiness in underground water depends on factors like water flow, depth, movement, how well substances dissolve, chemical exchanges, the creation of minerals, reducing sulfate, and how water passes through clayey shale layers [
28]. Sulfate reduction in oil field water is thought to happen alongside certain minerals (like gypsum, celestite, and barite) forming from cations like calcium, strontium, and barium. These reactions are connected to interactions with hydrocarbons and might decrease over time [
29]. Even though sodium dissolves easily, having a lot of it doesn't always lead to building up alkaline deposits. Two-charged ions can easily switch places with one-charged ions [
30].
pH values of formation water samples in Bibi Hakimeh oil and gas field range from 6.16 to 6.99 (
Table 1). Tthese results emphasize that the formation water in this area is mainly acidic water. Bicarbonates mainly come from carbonates dissolving when the pH is acidic, typically between 5 and 7 [
31].
Table 2 presents the mineral sediment prediction of calcium carbonate, magnesium carbonate, calcium sulfate and gypsum for 5 samples of wells in Bibi Hakimeh oil field. According to
Table 2, for samples 1 to 5, the formation of calcium carbonate precipitate is significant. Calcium sulfate mineral deposition is also expected for sample 5. However, based on the concentration of water-soluble ions and the temperature and pressure conditions of the well, the formation of gypsum and magnesium carbonate mineral deposits is not possible.
According to the results of
Table 2, with increasing temperature and pressure, the saturation of gypsum (CaSO4 .2H2O) decreases, whereas magnesium carbonate increases. This can be related to the solubility of magnesium carbonate and gypsum as well as the activity coefficient of calcium, magnesium, bicarbonate and sulfate ions.
In
Table 3, the amount of mineral sediment formation for the studied samples (based on well temperature and pressure conditions) in Bibi Hakimeh oil field is presented. According to the results of
Table 3, the formation of calcium carbonate and calcium sulfate (anhydrite) mineral deposits is significant. In other words, according to the results of Stimcad 2 software, calcium carbonate deposition in all the 5 studied samples is supersaturated and can cause problems in the facilities of this oil field, sample 3 having the highest and sample 1 the lowest amount of calcium carbonate deposition can be expected. Also, according to the evaluation of the formation of calcium sulfate (anhydrite), only in sample 5 the formation of this sediment is significant, while in the other four cases it is unsaturated. According to the results of
Table 3, the effect of operating conditions such as temperature and pressure on the process of increasing the formation of mineral sediments in oilfield facilities is significant.
3.2. Geochemical Analysis
Table 4 presents the hydrochemical properties of the mineral ions in the water of the Bibi Hakimeh oil field formation.
Sodium / Chloride ratio – this ratio is in the range 0.22 to 0.58, always less then 1, pointing to old residual seawater sealed in the reservoir, [
32,
33,
34]. The reason for the lower weight and molar ratio of sodium to chloride in oil brines is the ion exchange of sodium and its subsequent depletion over time. As sodium exits the environment gradually, the ratio of sodium decreases while chloride increases. This occurs due to the lack of reaction between chloride and other ions. Another characteristic of oil brines is their low sulfate content compared to halite brines [
35].
(Ca2++Mg2+)/ SO42- ratio - this ratio varies from 1.97 to 9,37, these high values pointing to oil brines, whereas in halite brines are typically around 1 [
35].
Ca2+ /Cl- ratio – this ratio is in the range of 0.018 to 0.06, with very low values suggesting a marine origin [
29].
Mg2+/Cl- ratio – this ration is in the range of 0.0073 to 0.0113, resulting from the presence of MgCl2 and signaling hydrocarbon accumulation or diagenetic processes [
29].
SO42- /Cl- ratio – this ratio is in the range of 0.0074 to 0.014, which is quite low, suggesting limited deep water circulation, leading to sulfate reduction [
29].
SO42- / HCO3- ratio – this ratio is in the range of 1.639 to 10.655, reflecting specific chemical reactions near hydrocarbon accumulations, serving as an indicator of water's proximity to hydrocarbons [
29].
Cl--Na+) / Mg2+ ratio – this ratio ia laso called the “Metamorphic coefficient” and considered to evaluate the degree of water-rock interaction and ion replacement [
36,
37]. According to
Table 4, this ratio in 5 water samples of the formation in Bibi Hakimeh is in the range of 46.57 to 73.18. Strong interactions between water and rock [
38] are one of the most important reasons for the high value of the metamorphic coefficient in the 5 samples studied in the Bibi Hakimeh oil field. Therefore, it is mainly displaced by Ca2+, two mineral ions Na+ and Mg2+, and as a result, they have high metamorphic coefficients.
(Mg2+ / Ca2+) ratio - the ratio of magnesium to calcium in the water of Bibi Hakimeh Formation is less than one. In other words, the concentration of calcium ions is higher than that of magnesium, which can be caused by dolomite formation (an important factor in controlling the concentration of Ca
2+ and Mg
2+) in the water of the formation conditions [
32,
39,
40,
41,
42,
43,
44]. Due to the fact that the Mg
2+ / Ca
2+ ratios are less than one, so in Bibi Hakimeh Formation, good hydrocarbon storage is evaluated [
38].
(HCO3
- - CO
32-) / Ca
2+) ratio - this ratio is in the range of 0.04 to 0.08, which is considered to be suitable for hydrocarbon storage and production [
46,
47,
48].
(HCO
3-) / Cl
- ratio – this ration is in the range of 0.00085 to 0.0046; considering that the ratio 0.006 ≥ (HCO
3-) / Cl
- and also the ratio of
)Cl
--Na
+) / Mg
2+ > 17.855 [
38], therefore, the formation of Bibi Hakimeh oil field has suitable conditions for gas storage and production.
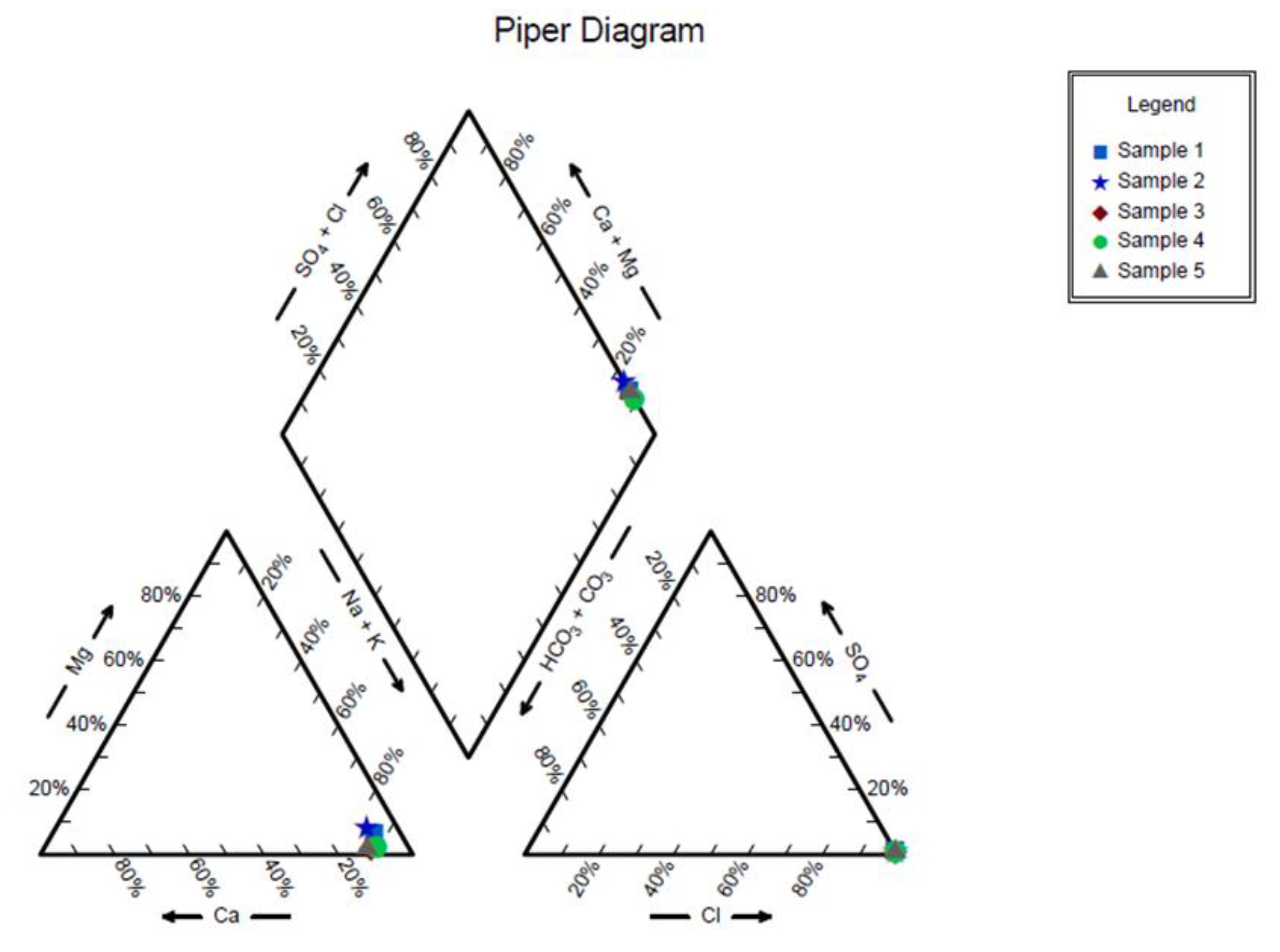
In
Figure 4, Piper diagrams can be seen for 5 water samples of the Bibi Hakimeh oil and gas field formation. In this figure, the distribution of mineral ions in the formation water can be seen, based on which the amount of chloride and sodium is significant. Also, the amount of calcium and magnesium in the 5 studied water samples is noticeable.
5. Conclusions
The significance of cationic and anionic mineral particles in aqueous solutions cannot be overstated, especially in chemical systems like oil fields where they can lead to mineral precipitation. Insufficient analysis and sampling can result in various issues, including decreased production efficiency and operational challenges in oil wells. This study focused on the hydrochemical analysis and water geochemistry of five wells at the Bibi Hakimeh oil and gas field, with the following key findings:
- -
a comparison between the water formation and Bibi Hakimeh formation rock indicates that, except for calcium (Ca2+) and magnesium (Mg2+) ions, the source of ions in the water reservoir is not the rock reservoir itself but rather marine original water.
- -
under the temperature and pressure conditions of the Bibi Hakimeh oil field, the precipitaion of calcium carbonate and calcium sulfate is expected.
- -
the concentration of mineral ions such as calcium, sodium, magnesium, sulfate, chloride, and bicarbonate in the water of the Bibi Hakimeh oil field formation can significantly impact the oil exploitation process.
- -
the geochemical properties of water from the Bibi Hakimeh Oil and Gas Field Formation suggest suitable conditions for gas storage and production.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.H.H. and A.K.T.; Methodology; S.H.H. and A.K.T.; Software, S.H.H.; Validation and Data Curation, S.H.H., A.K.T., A.B., S.A.H., M.G. and N.P., Writing—original draft preparation, S.H.H. and A.K.; Writing—review and editing, N.P. and A.K.T., Supervision, S.H.H. and A.K.T.; authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
We encourage all authors of articles published in MDPI journals to share their research data. In this section, please provide details regarding where data supporting reported results can be found, including links to publicly archived datasets analyzed or generated during the study. Where no new data were created, or where data is unavailable due to privacy or ethical restrictions, a statement is still required. Suggested Data Availability Statements are available in section “MDPI Research Data Policies” at
https://www.mdpi.com/ethics.
Conflicts of Interest
“The authors declare no conflicts of interest.”
References
- Hashemi, S.H. , Niknam; A., Karimian Torghabeh; A., Pimentel, N. Thermodynamic and geochemical studies of formation water in Rag-e Sefid oil and gas field, Iran. AIMS Geosciences 2023, 9(3): 578-594.
- Hirasaki, G.J. Wettability: Fundamentals and Surface Forces. SPE Form Eval. 1991, 6(2).217-226.
- Endean, H.; Shelton, R. Water Initiated Problems in Production Operations. Champion Technologies, Inc., Houston. 1991.
- Hashemi, S. H; Din Mohammad, M; Mousavi Dehghani, S. A. Thermodynamic Prediction of Ba and Sr Sulfates Scale Formation in Waterflooding Projects in Oil Reservoirs. Journal of Mineral Resources Engineering 2019, 4(2), 23–37. [Google Scholar]
- Hashemi, S.H; Hashemi, S.A. Prediction of Scale formation according to water injection operations in Nosrat Oil Field. Modeling Earth Systems and Environment 2020, 6, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, W.; Grist, M. ; Boyle,J. Chemical Treatments Associated With North Sea Projects. Journal of Petroleum Technology 1980, SPE 7880, 904–912. [Google Scholar]
- Jordan,M.; Graff,J.,Cooper, N. Development and Deployment of a Scale Squeeze Enhancer and Oil-Soluble Scale Inhibitor To Avoid Deferred Oil Production Losses. International Symposium on Formation Damage Control, SPE 58725, Lafayette, Louisiana,, 2000.
- Moghadasi, J. ; Jamialahmadi M.; Muller-Steinhagen, H.; Sharif A. Scale Formation in Oil Reservoir and Production Equipment.The SPE European Formation Damage Conference SPE 82233: 1 –12. 2003.
- Nasr-El-Din, H.; Al-Saiari, H. ; Al-Hajji,H. A Single-Stage Acid Treatment to Remove and Mitigate Calcium Carbonate Scale. SPE International. Aberdeen, United Kingdom: SPE 87454, 2004.
- Raju,K. Successful Scale Mitigation Strategies. the SPE International Symposium on Oilfield, SPE 121679, The Woodlands, Texas, 2009.
- Al-Roomi, Y.M.; Hussain, K.F. Potential kinetic model for scaling and scale inhibition mechanism. Desalination 2016, 393, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghalib, H.B.; Almallah, I.A. R.Scaling simulation resulting from mixing predicted model between Mishrif formation water and different waters injection in Basrah oil field, southern Iraq. Modeling Earth Systems and Environment 2017, 3:1557–1569.
- Wang, Q.; Liang, F. ; Al-Nasser W; Al-Dawood F, Al-Shafai T; Al-Badairy H; Shen Sh; Al-Ajwad H. Laboratory study on efficiency of three calcium carbonate scale inhibitors in the presence of EOR chemicals. Petroleum 2018, 4(4), 375–384. [Google Scholar]
- Ghalib, H.B.; Al-Hawash, A.B.; Muttashar, W.R.; et al. Determining the effect of mineral scaling formation under different injection water sources on the performance of Mishrif carbonate reservoir in Halfaya oilfield, Southern Iraq. J. Petrol Explor. Prod Technol 2023, 13, 1265–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, S.H.; Mousavi Dehghani, S.A.; Khodadadi, H.; Dinmohammad, M.; Hosseini, S.M.; Hashemi, S.H. Optimization of Extended UNIQUAC Parameter for Activity Coefficients of Ions of an Electrolyte System Using Genetic Algorithms. Korean Chemical Engineering Research 2017, 55(5), 652–659. [Google Scholar]
- Hashemi, S.H.; Mousavi Dehghani, S.A.; Samimi, S.E.; Dinmohammad, M.; Hashemi, S.A. Performance comparison of GRG algorithm with evolutionary algorithms in an aqueous electrolyte system. Modeling Earth Systems and Environment 2020, 6, 2103–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, S.H. Thermodynamic Study of water activity of Single Strong Electrolytes. Journal of Applied and Computational Mechanics 2017, 3(2), 150–157. [Google Scholar]
- Hashemi S., H. , Bagheri M. , Hashemi, S. A. Thermodynamic study of the effect of concentration and ionic strength on osmotic coefficient of aqueous sulfate and chloride solutions at 298.15 K. Modeling Earth Systems and Environment 2020, 6, 2189–2196. [Google Scholar]
- Hashemi, S.H.; Dinmohammad, M.; Bagheri, M. Optimization of Extended UNIQUAC model parameter for mean activity coefficient of aqueous chloride solutions using Genetic+PSO. Journal of Chemical and Petroleum Engineering 2020, 54(1), 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Abtahi, S.T. Bibi Hakima oil field development plan. Exploration and Production 2009, 55, 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Ebadi, N.; Yaram Taghlousohrabi, M.; Rahimi, T.; Varnasari, N. Performance and development of fractures in the Asmari reservoir, one of the southwestern fields of Bibi Hakimeh field. International Conference on Research in Science and Technology. 2015.
- Beydoun, Z.R.; Hughes Clark, M.W.; Stonely, R. Petroleum in Zagros Basin: A late Tertiary foreland basin overprinted on to the outer edge of vast hydrocarbon rich Paleozoic Mesozoic passive margin shelf. American Association Petroleum Geology journal 1992, 23(5), 309–339. [Google Scholar]
- https://www.astm.org/Standards/D511.htm.
- https://www.astm.org/Standards/D512.htm.
- https://images.hach.com/asset-get.download.jsa?id=31948984029. 3194.
- https://images.hach.com/asset-get.download.jsa?code=56093 . 5609.
- Betz, L. Betz Handbook of Industrial Water Conditioning. Sixth Edition. Publ. Betz, Trevose, Pennsylvania, 1962.
- Collins, A.G. Geochemistry of Oilfield Waters. Developments in Petroleum Science, Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company, Oxford-New York, 1975.
- Awadh, S.M. Chemical, physical characterization and salinity distribution of the oilfield water in the Upper Sandstone Member of the Zubair reservoir at Rumaila North Oilfield, Southern Iraq. Iranian Journal of Oil & Gas Science and Technology 2018, 7(1), 20-39.
- Hem, J.D. Study and Interpretation of the Chemical Characteristics of Natural Water. USGS Water Supply Papers-2254, Vol. 253, 1985.
- Taylor, E.W. The Examination of Water and Water Supplies, Church Hill Ltd., Press, 1958.
- De Choudens-Sanchez, V.; Gonzalez, L.A. Calcite and aragonite precipitation under controlled instantaneous supersaturation: elucidating the role of CaCO3 saturation state and Mg/Ca ratio on calcium carbonate polymorphism. Journal of Sedimentary Research 2009, 79(6), 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborn, S.G.; Vengosh, A.; Warner, N.R.; Jackson, R.B. Methane contamination of drinking water accompanying gas-well drilling and hydraulic fracturing. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2011, 108(20), 8172–8176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, C.; Flores, R.; Stricker, G.; Ellis, M. Chemical and stable isotopic evidence for water/rock interaction and biogenic origin of coalbed methane, Fort Union Formation, Powder River Basin, Wyoming and Montana USA. International Journal of Coal Geology 2008, 76(1-2), 76-85.
- Mirzaee, S.Y.; Zarasvandi, A.; Orang, M. Geochemical effect of Asmari Oil Reservoirs on Masjed-e-Solaiman Karstic Water Resources. Advanced Applied Geology 2016, 5(4), 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Ranasinghe, P.; Dissanayake, C.; Rupasinghe, M. Application of geochemical ratios for delineating gem-bearing areas in high grade metamorphic terrains. Applied Geochemistry 2005, 20(8), 1489–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.-F. Metamorphic chemical geodynamics in continental subduction zones. Chemical Geology 2012, 328, 5–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Wang, Z.; Rezaee, R.; Zhang, Y.; Nwidee, L.N.; Liu, X.; Verrall, M.; Iglauer, S. Formation water geochemistry for carbonate reservoirs in Ordos basin, China: Implicationsfor hydrocarbon preservation by machine learning, Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering 2020, 185, 106673.
- Folk, R.L.; Land, L.S. Mg/Ca ratio and salinity: two controls over crystallization of dolomite. AAPG Bulletin 1975, 59(1), 60–68. [Google Scholar]
- Koleini, M.M.; Mehraban, M.F.; Ayatollahi, S. Effects of low salinity water on calcite/brine interface: A molecular dynamics simulation study. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects 2018, 537, 61-68.
- Lear, C.H.; Rosenthal, Y.; Slowey, N. Benthic foraminiferal Mg/Ca-paleothermometry: A revised core-top calibration. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 2002, 66(19), 3375–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, M.R.; et al. Inhibition of calcite growth: combined effects of Mg2+ and SO42–. Crystal Growth & Design 2016, 16(11), 6199-6207.
- Shariatpanahi, S.F.; Strand, S.; Austad, T. Initial wetting properties of carbonate oil reservoirs: effect of the temperature and presence of sulfate in formation water. Energy & Fuels 2011, 25(7), 3021-3028.
- Wilkinson, B.H.; Algeo, T.J. Sedimentary carbonate record of calcium-magnesium cycling. American Journal of Science, 289(10): 1158-1194.1989.
- Van Voast, W.A. Geochemical signature of formation waters associated with coalbed methane. AAPG bulletin, 87(4): 667-676. 2003.
- Chen, T.; Neville, A.; Yuan, M. Calcium carbonate scale formation—assessing the initial stages of precipitation and deposition. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 46(3): 185-194. 2005.
- Kurita, Y.; et al. Identification of intestinal bicarbonate transporters involved in formation of carbonate precipitates to stimulate water absorption in marine teleost fish. American Journal of Physiology-Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology, 294(4): R1402-R1412.2008.
- Palandri, J.L.; Reed, M.H. Reconstruction of in situ composition of sedimentary formation waters. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 65(11), 1741-1767.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).