Submitted:
17 July 2024
Posted:
17 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. H. pylori Isolate Collections
2.2. Antimicrobial Breakpoints
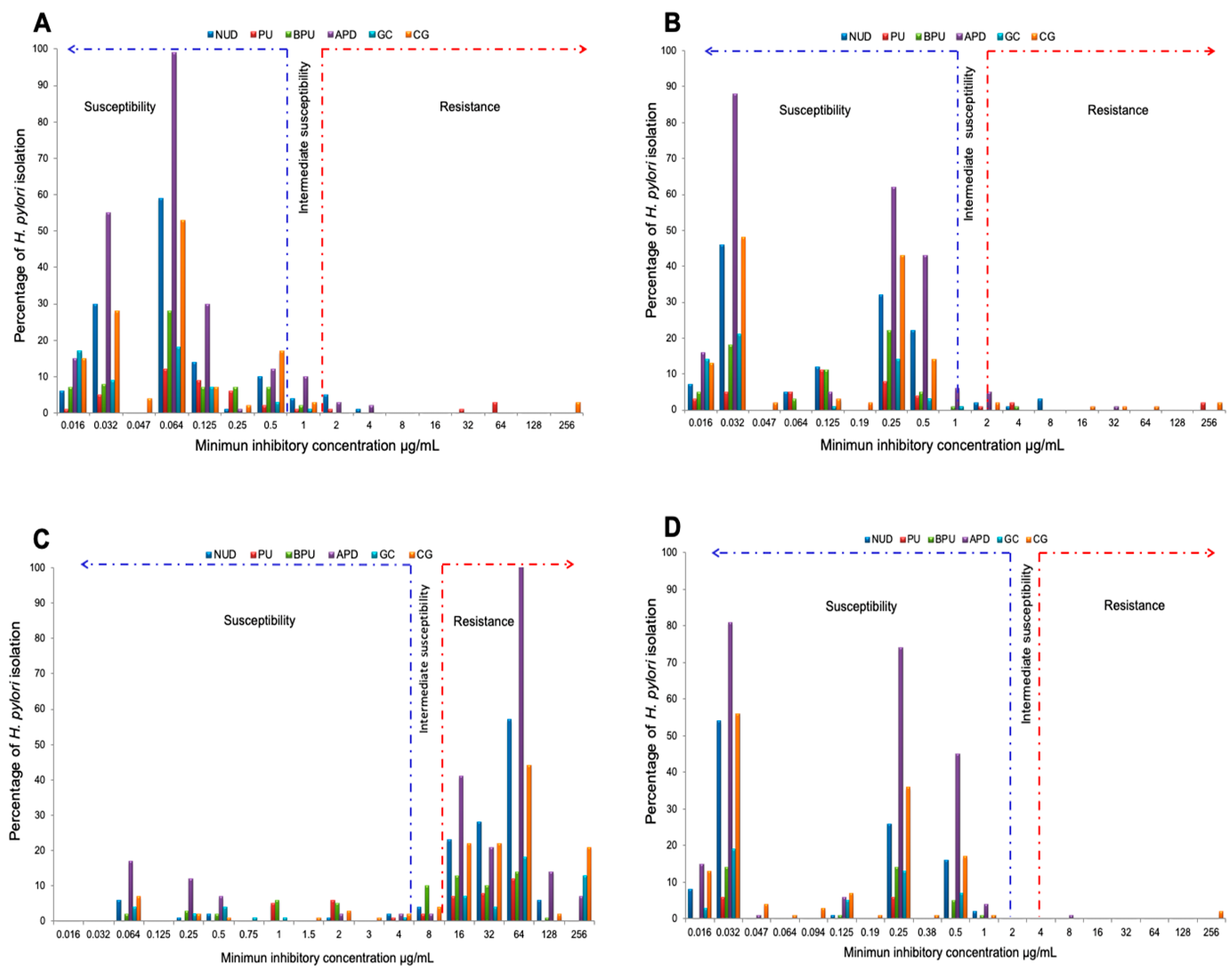
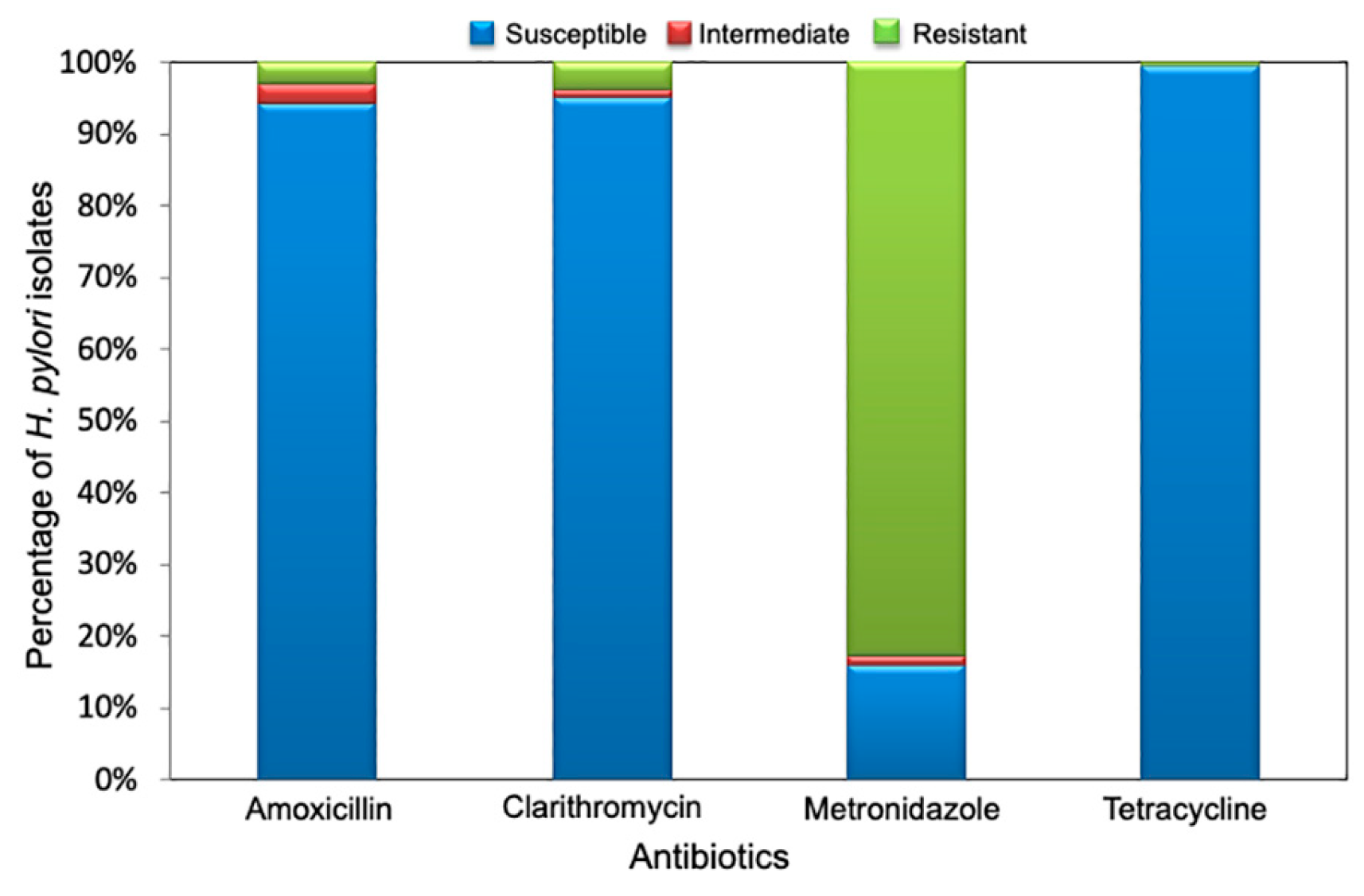
2.3. Determination of The Antimicrobial Susceptibility Profile
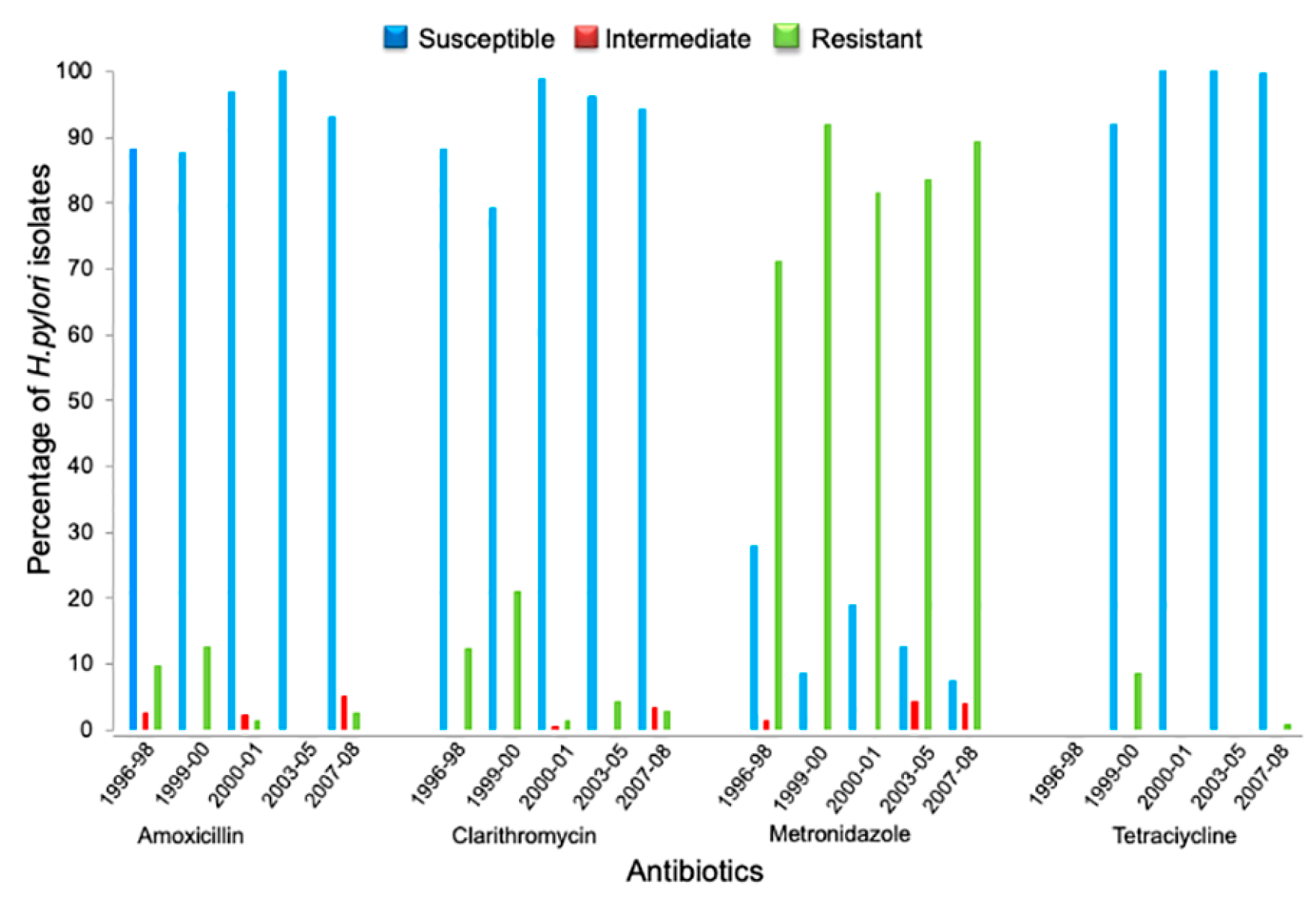
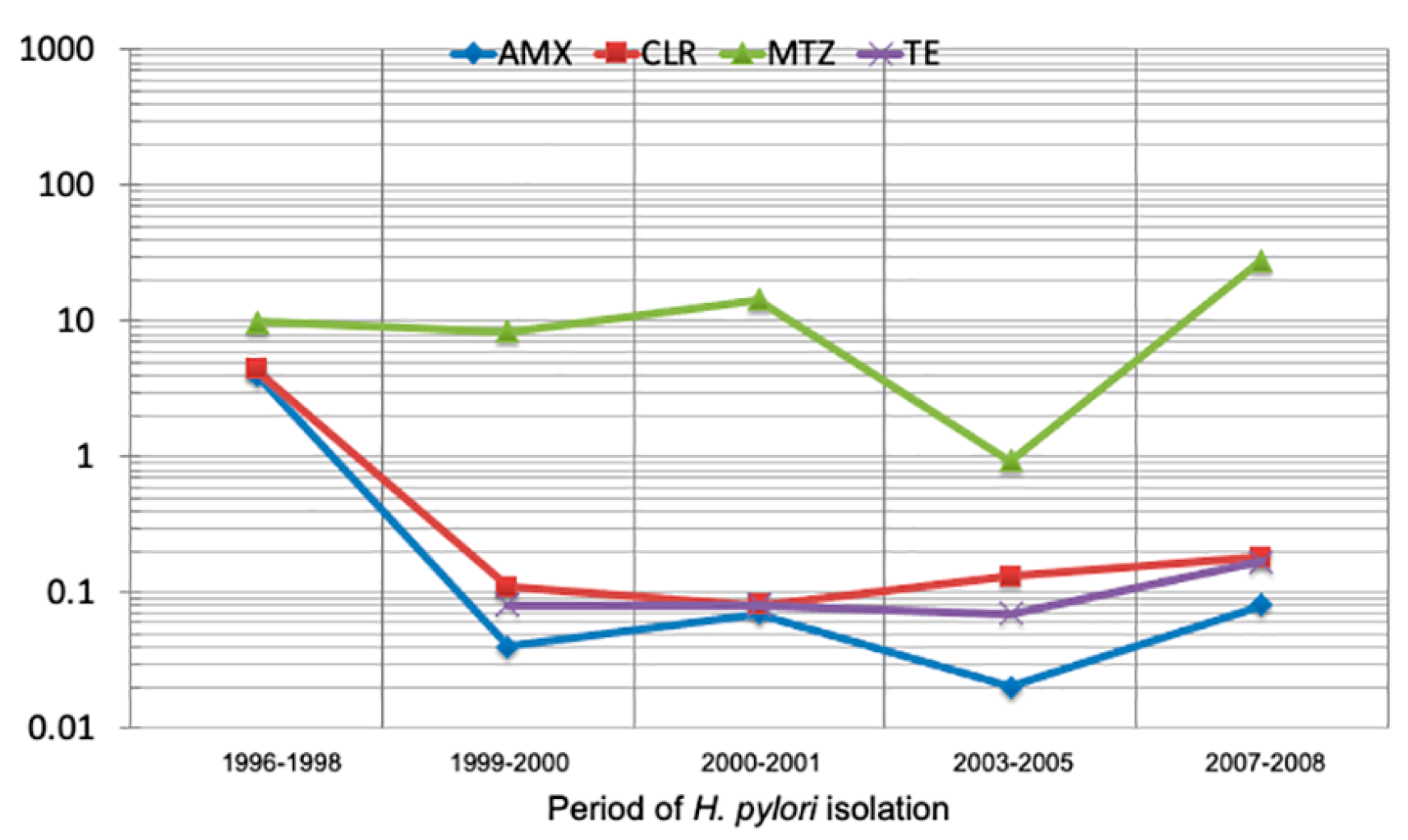
2.4. Secular Trend of Drug Resistance
2.5. Dual Resistance to Clarithromycin-Metronidazole
2.6. Analysis of Resistance By Gastric Pathology
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. H. pylori Strains
4.2. Susceptibility Test for H. pylori
4.3. Statistical Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malfertheiner, P.; Camargo, M.C.; El-Omar, E.; Liou, J.M.; Peek, R.; Schulz, C.; Smith, S.I.; Suerbaum, S. Helicobacter pylori infection. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2023, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malfertheiner, P.; Mégraud, F.; OʼMorain, C.; Bell, D.; Porro, B.G.; Deltenre, M.; Forman, D.; Gasbarrini, G.; Jaup, B.; Misiewicz, J.J.; Pajares, J.; Quina, M.; Rauws, E. Current European concepts in the management of Helicobacter pylori infection - the Maastricht Consensus Report. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 1997, 9, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malfertheiner, P.; Mégraud, F.; O’Morain, C.; Hungin, A.P.S.; Jones, R.; Axon, A.; Graham, D.Y.; Tytgat, G.; European Helicobacter pylori Study Group (EHPSG). Current concepts in the management of Helicobacter pylori infection -The Maastricht 2-2000 Consensus Report. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther 2002, 16, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malfertheiner, P.; Megraud, F.; O’Morain, C.; Bazzoli, F.; El-Omar, E.; Graham, D.; Hunt, R.; Rokkas, T.; Vakil, N.; Kuiper., E.J. Current concepts in the management of Helicobacter pylori infection: the Maastricht III Consensus Report. Gut 2007, 56, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malfertheiner, P.; Megraud, F.; O’Morain, C.A.; Atherton, J.; Axon, A.T.R.; Bazzoli, F.; Gensini, G.F.; Gisbert, J.P.; Graham, D.Y.; Rokkas, T.; El-Omar, E.M.; Kuipers, E.J.; European Helicobacter Study Group. Management of Helicobacter pylori infection—the Maastricht IV/ Florence Consensus Report. Gut 2012, 61, 646–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, L.G.; León-Barúa, R.; Quigley, E.M. Latin-American Consensus Conference on Helicobacter pylori infection. Latin-American National Gastroenterological Societies affiliated with the Inter-American Association of Gastroenterology (AIGE). Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2000, 95, 2688–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, L.G.; Coelho, M.C. Clinical Management of Helicobacter pylori: The Latin American Perspective. Dig. Dis. 2014, 32, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdo-Francis, J.M.; Uscanga, L.; Sobrino-Cossio, S.; Rivera-Ramos, J.F.; Huerta-Iga, F.; Tamayo de la Cuesta, J.L. [III Mexican Consensus on Helicobacter pylori]. Rev. Gastroenterol. Mex. 2007, 72, 323–338. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rollan, A.; Arab, J.P.; Camargo, M.C.; Candia, R.; Harris, P.; Ferreccio, C.; Rabkin, C.S.; Gana, J.C.; Cortés, p.; Herrero, R.; Durán, L.; García, A.; Toledo, C.; Espino, A.; Lusting, N.; Sarfatis, A.; Figueroa, C.; Torres, J.; Riquelme, A. Management of Helicobacter pylori infection in Latin America: A Delphi technique-based consensus. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 10969–10983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagari, R.M.; Romano, M.; Ojetti, V.; Stockbrugger, R.; Gullini, S.; Annibale, B.; Farinati, F.; Ierardi, E.; Maconi, G.; Rugge, M.; Calabrese, C.; Di Mario, F.; Luzza, F.; Pretolani, S.; Savio, A.; Gasbarrini, G.; Caselli, M. Guidelines for the management of Helicobacter pylori infection italy: The III Working Group Consensus Report 2015. Dig. Liver Dis. 2015, 47, 903–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, D.Y.; Fischbach, L. Helicobacter pylori treatment in the era of increasing antibiotic resistance. Gut 2010, 59, 1143–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mégraud, F.; Lehours, P. Helicobacter pylori detection and antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2007, 20, 280–322. [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Shen, Y.; Song, X.; Tang, X.; Hu, R.; Marshall, B.J.; Tang, H.; Benghezal, M. Need for standardization and harmonization of Helicobacter pylori antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Helicobacter 2022, 27, e12873. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CLSI M100; Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility testing. 32nd Ed. CLSI supplement M100. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, 2022.
- López-Vidal, Y.; Rangel-Frausto, M.S.; Calva, J.J. Antibiotic resistance of Helicobacter pylori in an infectious disease referral center. Rev. Investig. Clin. 1998, 50, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Torres, J.; Camorlinga-Ponce, M.; Pérez-Pérez, G.; Madrazo-De la Garza, A.; Dehesa, M.; González-Valencia, G.; Muñoz, O. Increasing Multidrug Resistance in Helicobacter pylori Strains Isolated from Children and Adults in Mexico. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 2677–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garza-González, E.; Pérez-Pérez, G.I.; Alanís-Aguilar, O.; Tijerina-Menchaca, R.; Maldonado-Garza, H.J.; Bosques-Padilla, F.J. Antibiotic Susceptibility Patterns of Helicobacter pylori Strains Isolated from Northeastern Mexico. J. Chemother. 2002, 14, 342–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chihu, L.; Ayala, G.; Mohar, A.; Hernández, A.; Herrera-goepfert, R.; Fierros, G.; González-Márquez, H.; Silva, J. Antimicrobial Resistance and Characterization of Helicobacter pylori Strains Isolated from Mexican Adults with Clinical Outcome. J. Chemother. 2005, 17, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyanova, L.; Hadzhiyski, P.; Gergova, R.; Markovska, R. Evolution of Helicobacter pylori Resistance to Antibiotics: A Topic of Increasing Concern. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camargo, C.M.; García, A.; Riquelme, A.; Otero, W.; Camargo, C.A.; Hernandez-García, T.; Candia, R.; Bruce, M.G.; Rabki, C.S. The Problem of Helicobacter pylori Resistance to Antibiotics: A Systematic Review in Latin America. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 109, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malfertheiner, P.; Megraud, F.; Rokkas, T.; Gisbert, J.P.; Liou, J.-M.; Schulz, C.; Gasbarrini, A.; Hunt, R.; Leja, M.; O’Morain, C.; Rugge, M.; Suerbaum, S.; Tilg, H.; Sugano, K.; El-Omar, E.M.; On behalf of the European Helicobacter and Microbiota Study Group. Management of Helicobacter pylori infection: the Maastricht VI/Florence Consensus Report. Gut 2022, 0, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malfertheiner, P.; Megraud, F.; O’Morain, C.A.; Gisbert, J.P.; Kuipers, E.J.; Axon, A.T.; Bazzoli, F.; Gasbarrini, A.; Atherton, J.; Graham, D.Y.; Hunt, R.; Moayyedi, P.; Rokkas, T.; Rugge, M.; Selgrad, M.; Suerbaum, S.; Sugano, K.; El-Omar, E.M.; European Helicobacter and Microbiota Study Group and Consensus panel. Management of Helicobacter pylori infection—the Maastricht V/Florence Consensus Report. Gut 2017, 66, 6–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chey, W.D.; Leontiadis, G.I.; Howden, C.W.; Moss, S.F. ACG Clinical Guideline: Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 112, 212–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.C.; Iyer, P.G.; Moss, S.F. AGA Clinical Practice Update on the Management of Refractory Helicobacter pylori Infection: Expert Review. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 1831–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosques-Padilla, F.J.; Remes-Troche, J.M.; González-Huezo, M.S.; Pérez-Pérez, G.; Torres-López, J.; Abdo-Francis, J.M.; Bielsa-Fernandez, M.V.; Camargo, M.C.; Esquivel-Ayanegui, F.; Garza-González, E.; Hernández-Guerrero, A.I.; Herrera-Goepfert, R.; Huerta-Iga, F.M.; Leal-Herrera, Y.; Lopéz-Colombo, A.; Ortiz-Olvera, N.X.; Riquelme-Pérez, A.; Sampieri, C.L.; Uscanga-Domínguez, L.F.; Velarde-Ruiz, V.J.A. IV consenso mexicano sobre Helicobacter pylori. Rev. Gastroenterol. Mex. 2018, 83, 325–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehesa, M.; Larisch, J.; Dibildox, M.; Di Silvio, M.; Lopez, L.H.; Ramirez-Barba, E.; Torres, J. Comparison of Three 7-Day Pantoprazole-Based Helicobacter pylori Eradication Regimens in a Mexican Population with High Metronidazole Resistance. Clin. Drug Investig. 2002, 22, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayala, G.; Galván-Portillo, M.; Chihu, L.; Fierros, G.; Sánchez, A.; Carrillo, B.; Román, A.; López-Carrillo, L.; Silva-Sánchez, J. , Study Group. Resistance to Antibiotics and Characterization of Helicobacter pylori Strains Isolated from Antrum and Body from Adults in Mexico. Microb. Drug Resist. 2011, 17, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mucito-Varela, E.; Castillo-Rojas, G.; Calva, J.J.; López-Vidal, Y. Integrative and Conjugative Elements of Helicobacter pylori Are Hypothetical Virulence Factors Associated with Gastric Cancer. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 525335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camorlinga-Ponce, M.; Gómez-Delgado, A.; Aguilar-Zamora, E.; Torres, R.C.; Giono-Cerezo, S.; Escobar-Ogaz, A.; Torres, J. Phenotypic and Genotypic Antibiotic Resistance Patterns in Helicobacter pylori Strains From Ethnically Diverse Population in México. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 10, 539115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contreras-Omaña, R.; Escorcia-Saucedo, A.E.; Velarde-Ruiz, V.J.A. Prevalence and impact of antimicrobial resistance in gastrointestinal infections: A review. Rev. Gastroenterol. Mex. 2021, 86, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladrón-de-Guevara, L.; Bornstein-Quevedo, L.; González-Huezo, S.; Castañeda-Romero, B.; Costa, F.G.; di Silvio-López, M. Helicobacter pylori erradication in México with a levofloxacin-base scheme versus standard triple therapy: Results from an open-label, randomized, noninferiority phase iiib trial. Rev. Gastroenterol. Mex. 2019, 84, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesbros-Pantoflickova, D.; Corthésy-Theulaz, I.; Blum, A.L. Helicobacter pylori and Probiotics. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 812S–818S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdovinos, M.A.; Montijo, E.; Abreu, A.T.; Heller, S.; González-Garay, A.; Bacarreza, D.; Bielsa-Fernández, M.; Bojórquez-Ramos, M.C.; Bosques-Padilla, F.; Burguete-García, A.I.; Carmona-Sánchez, R.; Consuelo-Sánchez, A.; Coss-Adame, E.; Chávez-Barrera, J.A.; de Ariño, M.; Flores-Calderón, J.; Gómez-Escudero, O.; González-Huezo, M.S.; Icaza-Chávez, M.E.; Larrosa-Haro, A.; Morales-Arámbula, M.; Murata, C.; Ramírez-Mayans, J.A.; Remes-Troche, J.M.; Rizo-Robles, T.; Peláez-Luna, M.; Toro-Monjaraz, E.M.; Torre, A.; Urquidi-Rivera, M.E.; Vázquez, R.; Yamamoto-Furusho, J.K.; Guarner, F. The Mexican consensus on probiotics in gastroenterology. Rev. Gastroenterol. Mex. 2017, 82, 156–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslami, M.; Yousefi, B.; Kokhaei, P. , Moghadas, A.J.; Moghadam, B.S.; Arabkari, V.; Niazi, Z. Are probiotics useful for therapy of Helicobacter pylori diseases? Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 64, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Collection | n | Gender | Age | Period | |
| M | F | Mean (min -max value ) | |||
| I | 83 | 50 | 33 | 57.4 (30 – 72) | 1996 to 1998 |
| II | 24 | 3 | 21 | 42.7 (19 – 71) | 1999 to 2000 |
| III | 338 | 135 | 203 | 48.1 (15 – 87) | July 2000 to December 2001 |
| IV | 24 | 7 | 17 | 55.5 (29 – 79) | 2003 to 2005 |
| V | 182 | 54 | 128 | 46.9 (15 – 87) | May 2007 to January 2008 |
| TOTAL | 651 | 249 | 402 | ||
| Collection | Period | Isolates n |
Isolates resistant to | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMX n (%) |
CLR n (%) |
MTZ n (%) |
TE n (%) |
CLR-MTZ n (%) |
|||
| I | 1996 to 1998 | 83 | 10 (12.05) | 10 (12.05) | 60 (72.29) | NT | 1 (1.2) |
| II | 1999 to 2000 | 24 | 3 (12.5) | 5 (20.83) | 22 (91.67) | 2 (8.33) | 3 (12.5) |
| III | July 2000 to December 2001 | 338 | 11 (3.25) | 5 (1.48) | 275 (81.36) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (0.59) |
| IV | 2003 to 2005 | 24 | 0 (0.0) | 1 (4.17) | 21 (87.5) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (8.33) |
| V | May 2007 to January 2008 | 182 | 12 (7.15) | 11 (6.05) | 169 (92.86) | 1 (0.53) | 5 (2.75) |
| Total | 651 | 36 (5.53) | 32 (4.9) | 547 (84.02) | 3 (0.46) | 13 (1.99) | |
|
Pathology (n) |
Antibiotic resistance* | |||
|
1 n (%) |
2 n (%) |
3 n (%) |
4 n (%) |
|
| APD (227) | 168 (74) | 24 (10.57) | - | - |
| CG (132) | 107 (81.06) | 8 (6.06) | - | 2 (1.52) |
| NUD (130) | 108 (83.08) | 9 (6.92) | 4 (3.08) | - |
| BPU (66) | 46 (69.7) | 3 (4.55) | - | - |
| GC (55) | 41 (74.55) | 2 (3.64) | - | - |
| PU (41) | 25 (60.98) | 3( 7.32) | 4 (9.76) | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





