Submitted:
16 July 2024
Posted:
17 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. RPL Challenges
2.1. Congestion Problem in IoT
- Packet Loss: When a network experiences congestion, the data packets arrive at a rate that exceeds the buffer’s capacity to store them for processing and forwarding. IoT devices, such as wireless sensor network nodes and LLN devices, have finite memory allocated for buffering packets. Once this memory (buffer) is filled due to congestion, any additional incoming packets cannot be accommodated, leading to what’s known as packet loss. This loss necessitates retransmissions if reliability is a requirement of the communication, which further contributes to the congestion, creating a feedback loop that exacerbates the network’s congested state.
- Increased Latency: Latency refers to the time a packet travels from its source to its destination. In congestion conditions, packets queue up at network nodes, waiting for their turn to be processed and forwarded. This queuing delay is a significant contributor to overall network latency. The more congested a network is, the longer the queues at network nodes are and, consequently, the higher the latency. For real-time applications and time-based monitoring, increased latency can severely degrade the quality of the service, leading to delays, destroying the cyber-physical system, or lags that impact user experience.
- Lower Throughput: Throughput in a network is the rate at which data is successfully delivered over a communication channel. Congestion leads to packet loss and increased latency, lowering the network’s effective throughput. As packets are dropped or delayed, the data transmission rate effectively decreases.
- Energy Waste: Congestion introduces significant energy waste in wireless sensor networks and IoT devices, which are often battery-powered and designed to operate efficiently to prolong battery life. When packets are lost due to congestion, they frequently need to be retransmitted to ensure the information reaches its intended destination. Each retransmission consumes energy for both the retransmitting device and potentially other devices in the network that participate in forwarding the packet. Moreover, devices in a congested network may need to stay in a higher power state longer to deal with the congestion, increasing energy consumption. This unnecessary energy expenditure reduces the overall lifetime of the devices and can be particularly problematic in IoT applications, where devices are expected to operate autonomously for extended periods [1].
2.2. Congestion Control in RPL
- Adaptive Retransmission Mechanisms: To further mitigate congestion, RPL can incorporate adaptive retransmission mechanisms that adjust the rate at which data is sent and the criteria under which retransmissions occur. The network can reduce unnecessary data traffic by monitoring the success rates of packet deliveries and dynamically adjusting retransmission strategies. For instance, increasing the retransmission timeout could prevent exacerbating the congestion in conditions where packet loss is due to congestion rather than poor link quality.
- Proactive Congestion Detection: RPL can be enhanced with proactive congestion detection algorithms that identify potential congestion before it becomes problematic. The network can predict and address congestion risks by analyzing trends in data flow rates, queue lengths, and node capacities. Proactive measures might include rerouting traffic, adjusting transmission rates, or temporarily suspending non-critical data transmissions to allow the network to recover.
- Multi-Path Routing: To enhance load balancing and traffic distribution, RPL supports multi-path routing [21]. This allows data to be sent over multiple paths, distributing the load evenly across the network and reducing the risk of any single path becoming a bottleneck. Multi-path routing contributes to congestion control and enhances network resilience by providing alternate routes for node or link failures.
- Energy-Aware Congestion Control: Given the energy constraints of devices in LLNs, RPL’s congestion control mechanisms are designed to be energy-aware. This includes optimizing the trade-off between energy consumption and network performance. For example, while reducing the data transmission rate can alleviate congestion, it can also mean that devices spend more time in active communication states, consuming more energy [22]. RPL aims to balance these factors to maintain network efficiency without unduly depleting node batteries.
- Integration with Application Layer Protocols: Congestion control in RPL is not limited to the network layer but involves coordination with application layer protocols such as CoAP. By integrating congestion control strategies across layers, RPL ensures that application layer behaviours—such as data generation rates and priority data transmissions—are aligned with the network’s congestion status. This cross-layer approach enables more sophisticated congestion management strategies that can adapt to the specific requirements and behaviours of IoT applications.
- Community Engagement and Feedback Loops: RPL incorporates mechanisms for community engagement and feedback loops, allowing the network to adapt to its nodes’ collective behaviour. By aggregating feedback on congestion levels, packet loss rates, and throughput across different parts of the network, RPL can adjust its overall congestion control strategies to reflect the current network conditions. This collective intelligence approach ensures that RPL remains responsive to the dynamic nature of LLNs.
2.3. Load Balancing in RPL
- Resource Constraints: IoT devices typically operate with limited computational power, memory, and energy supply. These constraints make it challenging to implement complex load-balancing algorithms that require significant processing power or memory resources. The challenge lies in designing lightweight load-balancing mechanisms that can operate efficiently within the limited capabilities of IoT devices [28].
- Dynamic Network Topologies: IoT networks are highly dynamic, with devices frequently joining or leaving the network [28,29]. This dynamic nature results in fluctuating network topologies, complicating a balanced load distribution. Load-balancing solutions must be adaptive and capable of responding promptly to changes in the network structure without imposing excessive overhead.
- Diverse Traffic Patterns: IoT applications can generate highly diverse traffic patterns, ranging from periodic telemetry data transmissions to event-driven alerts. This diversity challenges load-balancing efforts, as algorithms must accommodate varying data rates, packet sizes, and transmission frequencies to prevent congestion and ensure fair resource allocation [10].
- Congestion Detection and Response: Accurately detecting congestion in its early stages is critical for preemptive load balancing. However, due to IoT networks/RPL, traditional congestion detection mechanisms may not be directly applicable. Moreover, once congestion is detected, the protocol must swiftly reroute traffic without exacerbating the network’s energy consumption or disrupting ongoing communications.
- Energy-Efficiency Considerations: In battery-powered IoT devices, energy conservation is paramount [30]. Load balancing strategies must distribute network traffic evenly and minimize energy consumption. This requirement often leads to trade-offs between achieving optimal load distribution and prolonging the network’s operational lifetime.
- Compatibility and Standardization: Ensuring that load balancing enhancements are compatible with the existing RPL specifications and interoperable across different implementations is crucial [23]. Any modification to the RPL protocol to support load balancing must adhere to standardization efforts to facilitate widespread adoption and maintain network interoperability.
- Qos Requirements: IoT applications may have specific QoS requirements, such as low latency or high reliability [23]. Load balancing mechanisms must meet these application-specific demands while managing network resources efficiently. Balancing the QoS requirements with the goal of load balancing adds another layer of complexity to the design and implementation of RPL enhancements.
3. Learning Automata
- Environment: The dynamic setting in which the automaton operates. It is a source of stimuli where the automaton performs actions and receives feedback based on the outcomes of these actions.
- Actions: These are the decisions or moves the automaton can make. The probability of choosing each action is updated continuously based on the feedback received from the environment.
- Response: The feedback from the environment following an action, which can be positive (reward) or negative (penalty), influencing how the probabilities of actions are updated.
- Learning Algorithm: The method used to update the probabilities of actions in response to the feedback, to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of the decision-making process.
3.1. Pseudocode for Learning Automaton
| Algorithm 1 Learning Automaton Procedure |
|
3.2. Linear Reward-Penalty Scheme
-
Updating Probabilities When an Action is Rewarded:When action is rewarded, the probability of choosing this action in the next time step, , is increased. The formula used is (Equation 1):This equation means that the new probability is the old probability increased by a fraction of the remaining probability space . The parameter controls how much the probability increases — larger results in a larger increase.For all other actions , the probability of selecting each of these actions is reduced proportionally (Equation 2):Here, each other action’s probability is scaled down by the factor , ensuring that the total probability across all actions remains equal to 1.
-
Updating Probabilities When an Action is Penalized:Conversely, if action is penalized, its probability is reduced (Equation 3):In this equation, is the penalty parameter. The new probability is the previous probability reduced by a factor of , meaning a larger decreases the probability more significantly.For all other actions , their probabilities are updated as follows (Equation 4):This adjustment ensures that the total probability is still 1. The increase for each other action is partly a fixed amount , which redistributes the reduced probability of the penalized action equally among them, and partly the old probability scaled down by .
-
Parameters and their Roles:
- (reward parameter): Determines how strongly an action’s probability is increased upon receiving a reward.
- (penalty parameter): Determines how strongly an action’s probability decreases after being penalized.
- r (total number of actions): Affects the redistribution of probabilities when an action is penalized.
The LRP scheme is a straightforward yet effective adaptive strategy for balancing exploration (trying out different actions) and exploitation (favoring actions that have previously led to positive outcomes) in environments where actions have probabilistic outcomes. This method ensures that actions that lead to success are more likely to be chosen in the future, while those that lead to negative outcomes are less likely to be repeated.
4. Proposed LALARPL
-
Parent Set Formation: Initially, a collection of proximate parents is formulated for every child node. This phase solely utilizes DIO-indicator packets, distinguishing it from subsequent procedures. During this phase, parent sets are established for each node through a process where parent nodes broadcast DIO-indicator packets within their communicable range. These packets are characterized by three specific fields: the IP address of the broadcasting node, the minimal number of hops to the root from a parent node, and the parent node’s traffic index. Prior to the transmission of a DIO-indicator packet, the aforementioned fields are initialized by the parent node. Upon receipt of DIO-indicator packets, other nodes in the network undertake the update of their parent tables, adjusting the sending priorities based on the data received within their respective parent sets as delineated below:
- Should a node receive merely a singular DIO-indicator packet, the information contained within is recorded in its parent set table, and the originating node is incorporated into its parent set with a selection probability assigned as 1.
-
Conversely, in scenarios where multiple DIO-indicator packets are received, nodes are tasked with selecting between a minimum of two and a maximum of five parent nodes. The selection criteria encompass proximity (regarding the number of hops) and the residual energy of the potential parent nodes. These chosen nodes are added to the recipient node’s parent set or routing path. The formulation for the selection probability of each potential parent node is given as follows (Equation 6):Herein:
- i indexes the enumeration of parent senders,
- quantifies the traffic index associated with parent i,
- specifies the number of hops from node i to the network root,
- N represents the total count of potential parent nodes under consideration,
- is a weighting parameter within the interval [0,1], modulating the relative contributions of hop count and traffic index to the selection probability.
-
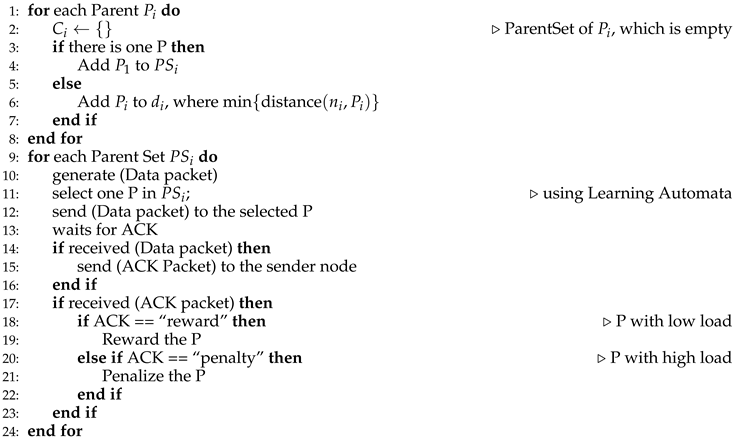
Distributed Load Balancing: Following the parent set formation stage, the procedure for data transmission commences. Child nodes initiate the transmission of data packets toward their selected parent nodes, as indicated within their parent set tables. Concomitantly, parent nodes respond by dispatching Acknowledgment (Ack) packets, which encapsulate the sender’s identification number and the traffic index. To curtail the message volume and consequently diminish the network load, a parameter designated as p is introduced. This parameter dictates that each node transmits a set of p data packets to a predetermined parent node, which issues a single Ack packet in response to the accumulation of p packets. Additionally, the architecture of the routing tables is elucidated, revealing four principal fields: the Parent IP address, the selection probability assigned to that parent, the Traffic Index, and the hop count to the network root. An integral feature of the algorithm is the incorporation of a learning automaton within each child node. This automaton executes operations correlating with the number of parent nodes listed in the node’s routing table or parent set, thereby enabling adaptive decision-making based on dynamic network conditions. The methodology governing the issuance of rewards or penalties after the receipt of an Ack packet is articulated as follows:
- –
- A reward is allocated when the parent’s traffic index (the Ack’s sender) is observed to be less than 50% of the average traffic index pertinent to other parents within the identical set.
- –
- Should the traffic index exceed 50% yet remain below 80% of the average traffic index of the other parents in the set, and the parent node exhibits the minimal number of hops to the root, a reward is similarly conferred.
- –
- Conversely, a penalty is imposed when the traffic index surpasses the average traffic index associated with other parents in the set.
| Algorithm 2 Load Balancing Algorithm based on Learning Automata |
 |
- with being a damping factor that adjusts the impact of hop count differences.
- where helps modulate the influence of the maximum hop count dynamically.
- where scales the squared difference between average and individual traffic indices, emphasizing deviations.
- and are computed as the maximum and average traffic indices among the set, potentially including more sophisticated aggregation rules based on network topology or traffic patterns.
5. Simulation Results
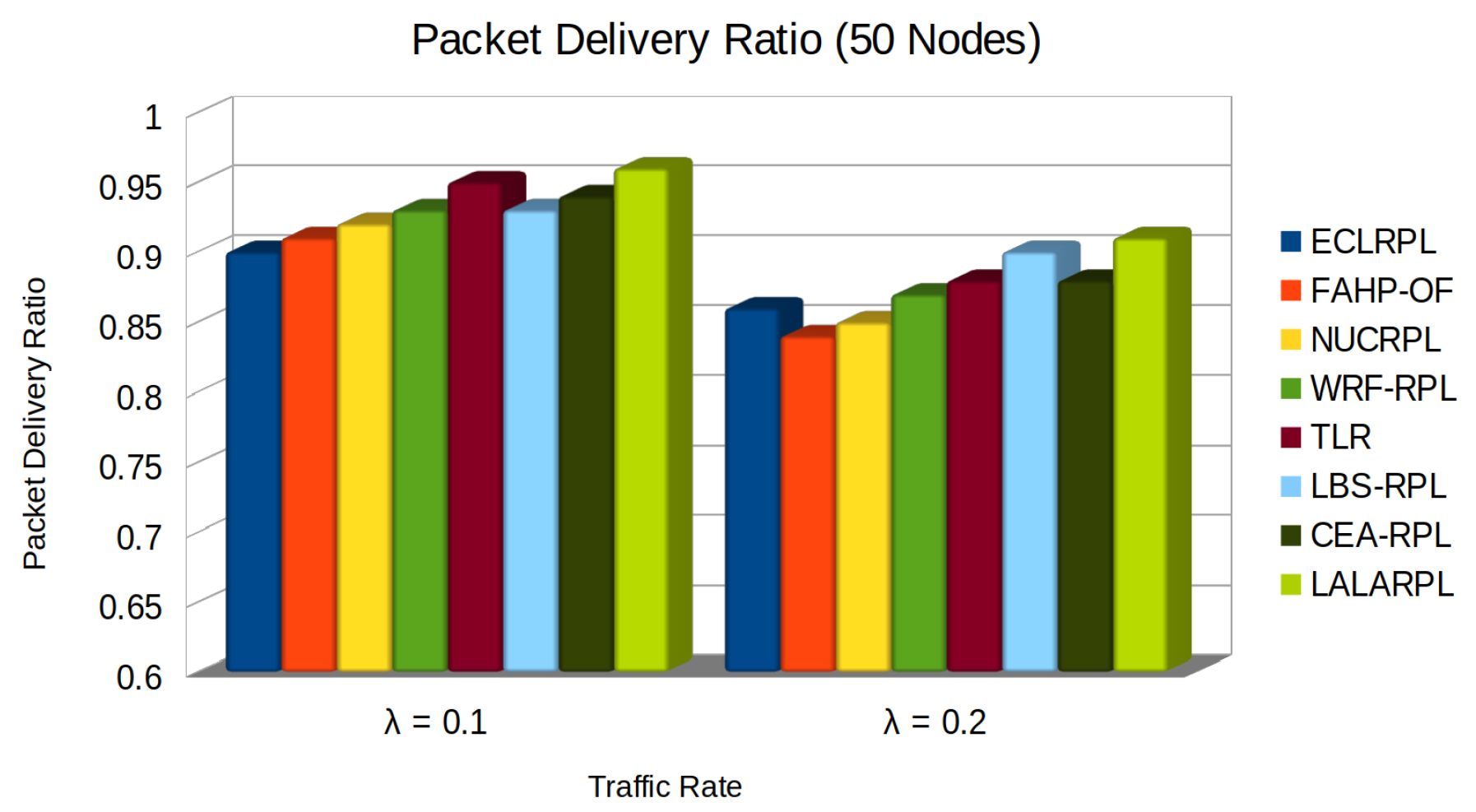
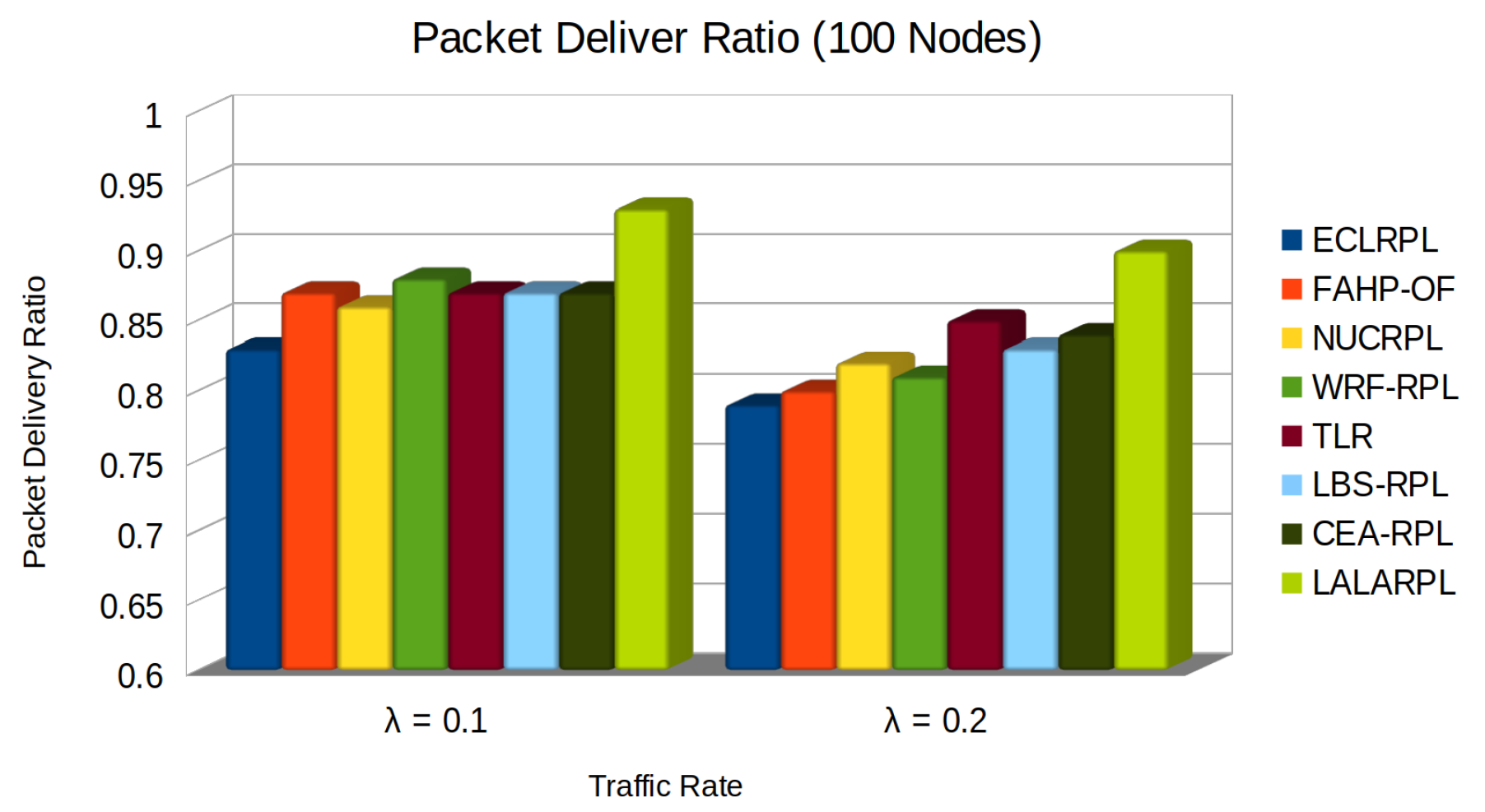
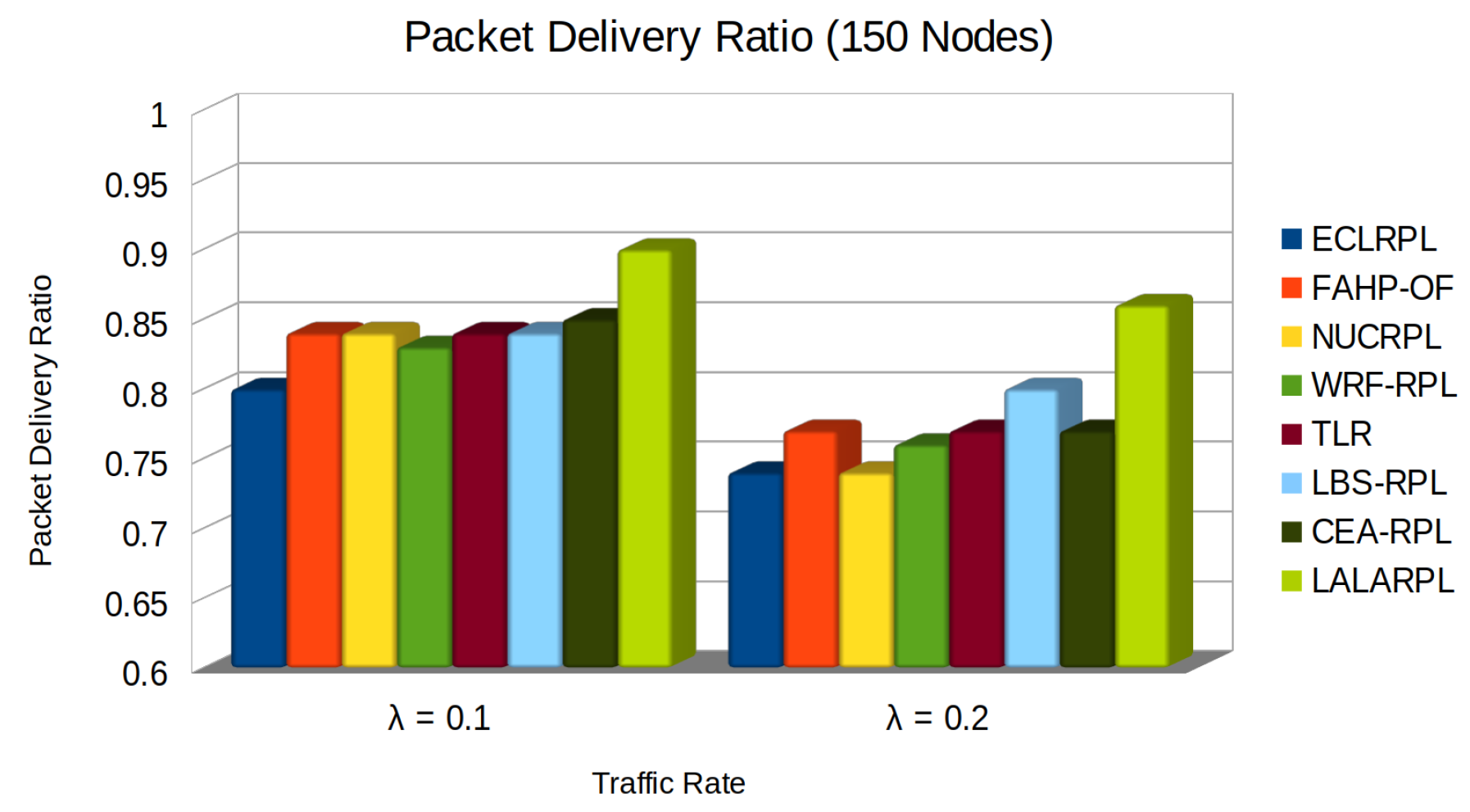
5.1. Packet Delivery Ratio Test
- denotes the total data packets successfully received,
- represents the total data packets sent.
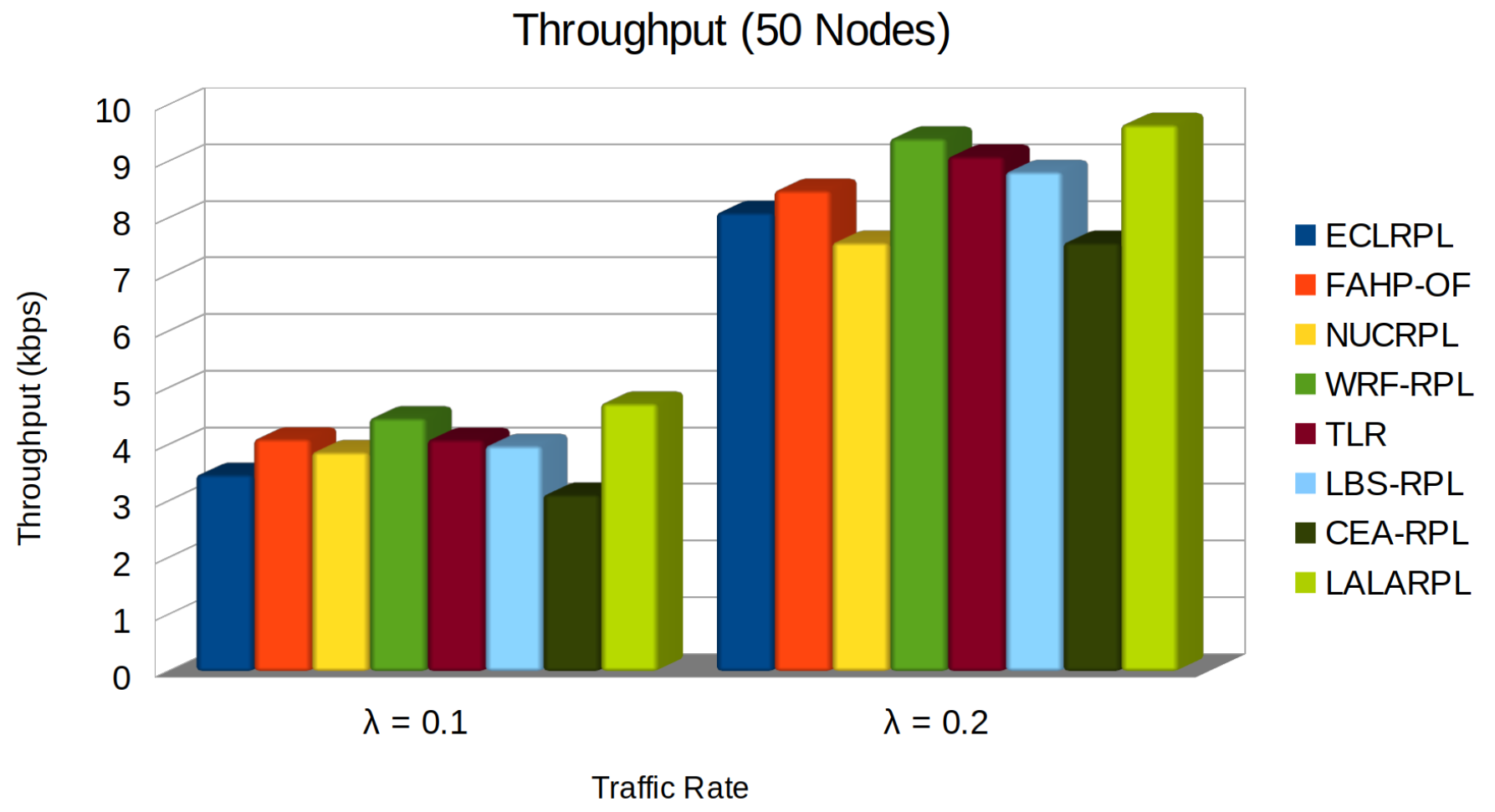
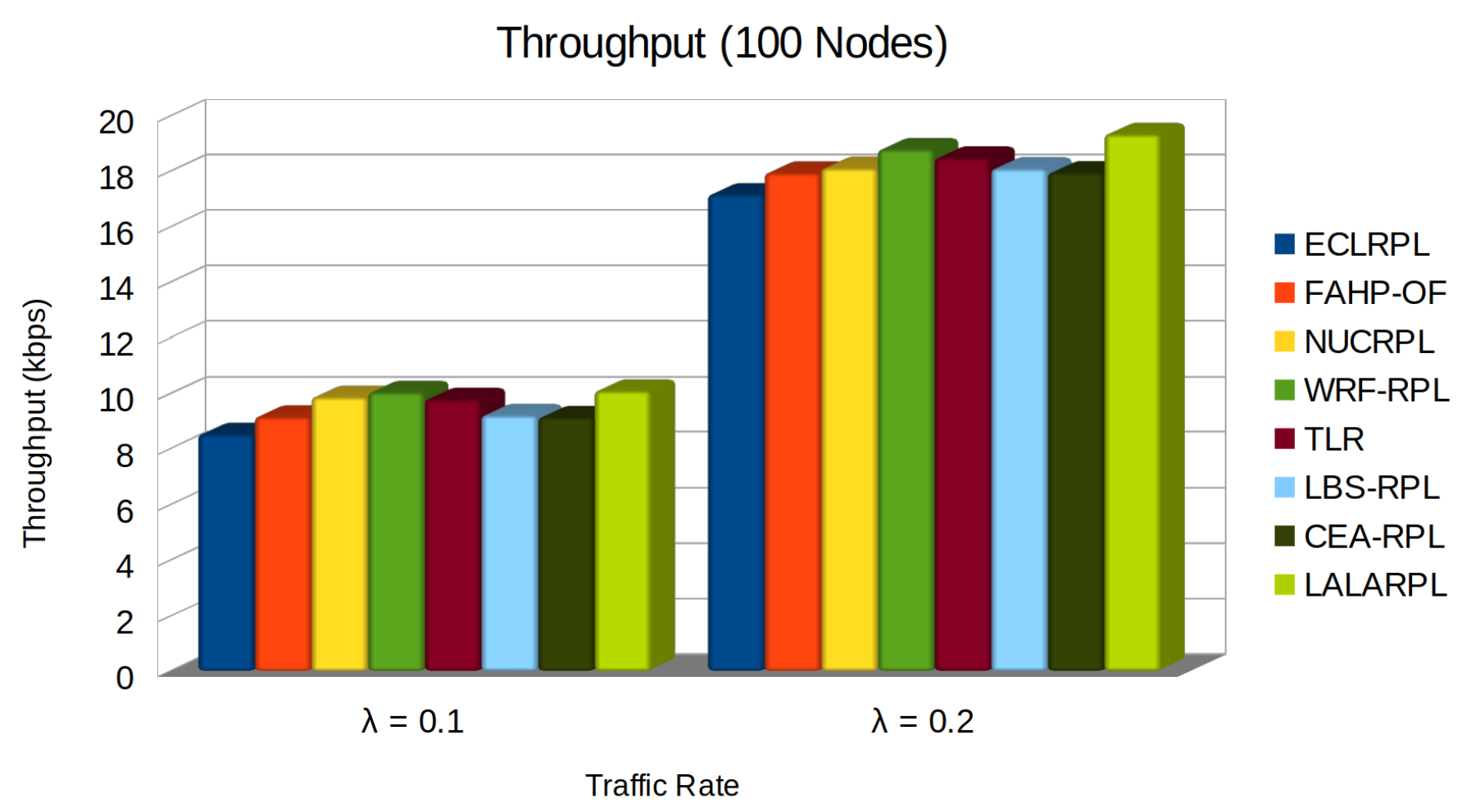
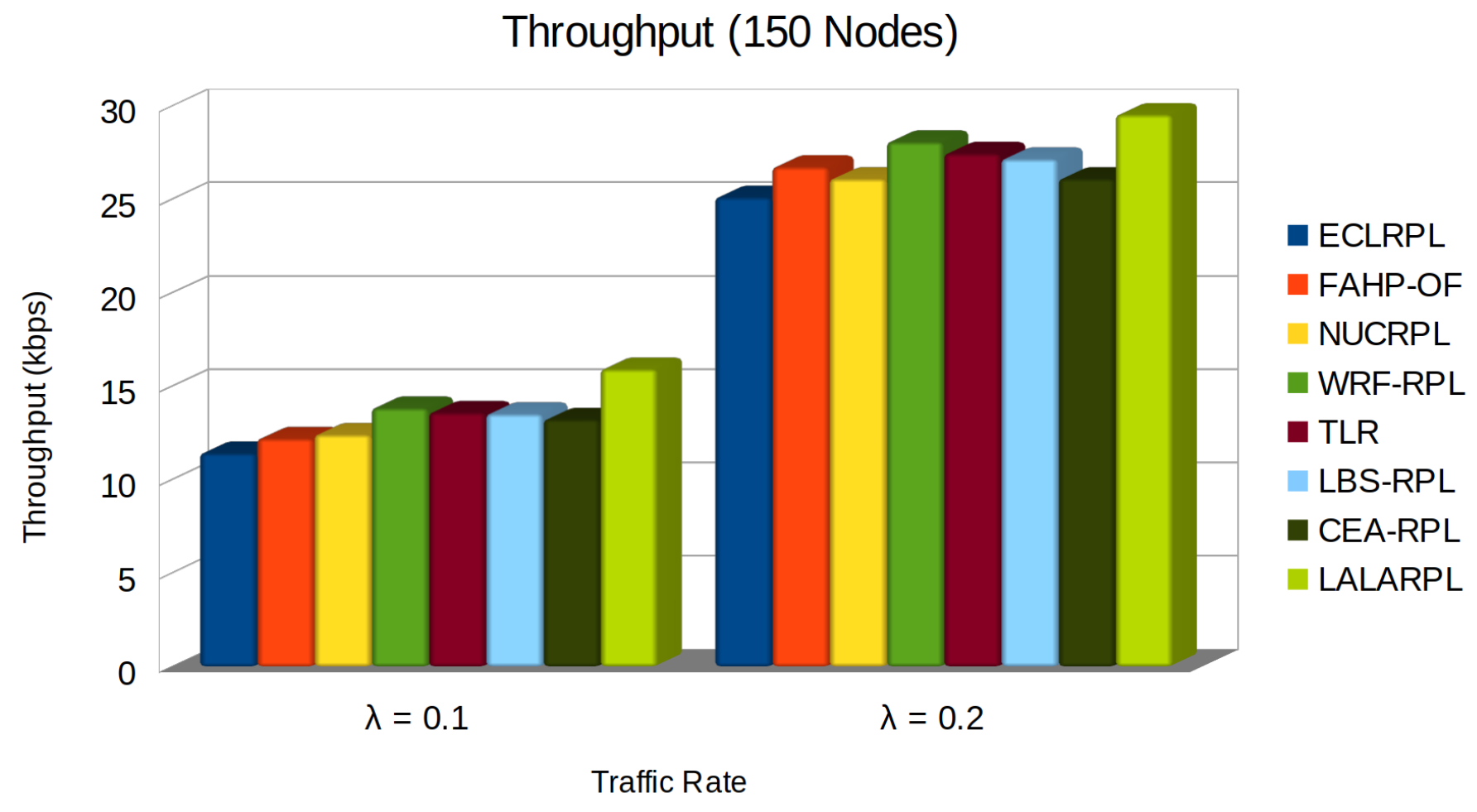
5.2. Throughput
- is the throughput of the i-th node.
- represents the total packets received by node i from its j-th neighbour.
- is the time interval the throughput is measured.
- is the link quality indicator between node i and its j-th neighbour, which affects the reliability and speed of the transmitted data.
- is the number of child nodes for node i, influencing the load handled by the node.
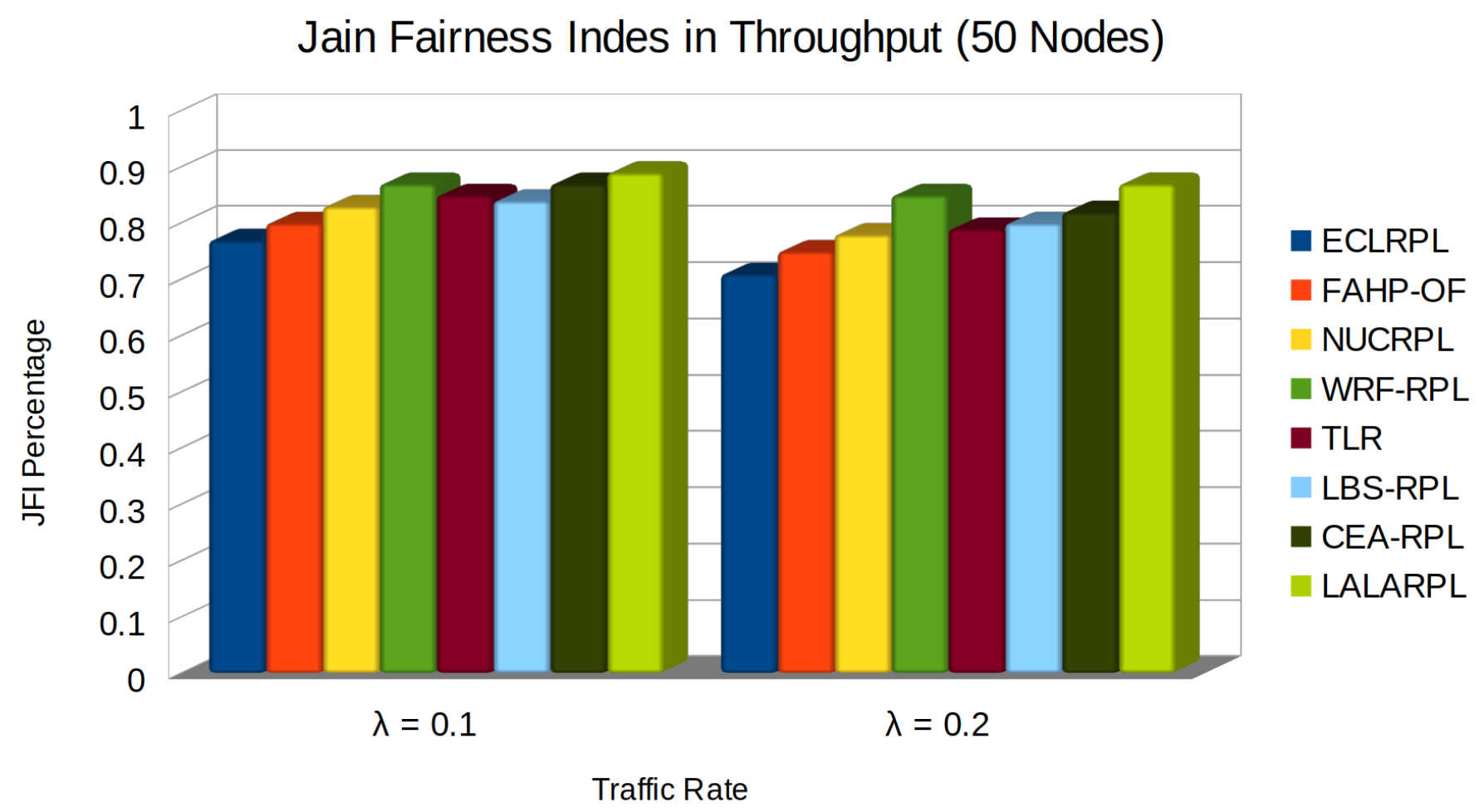
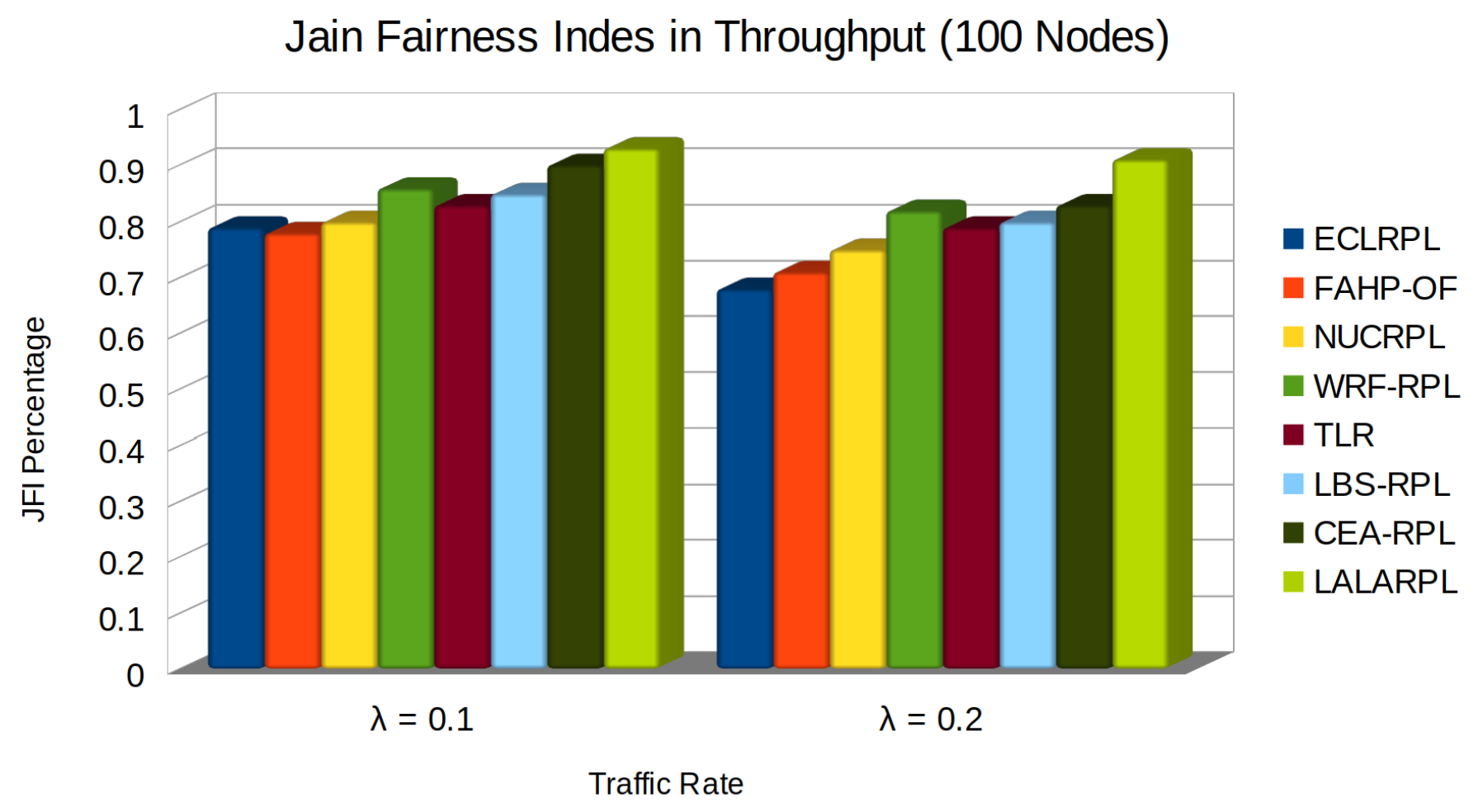
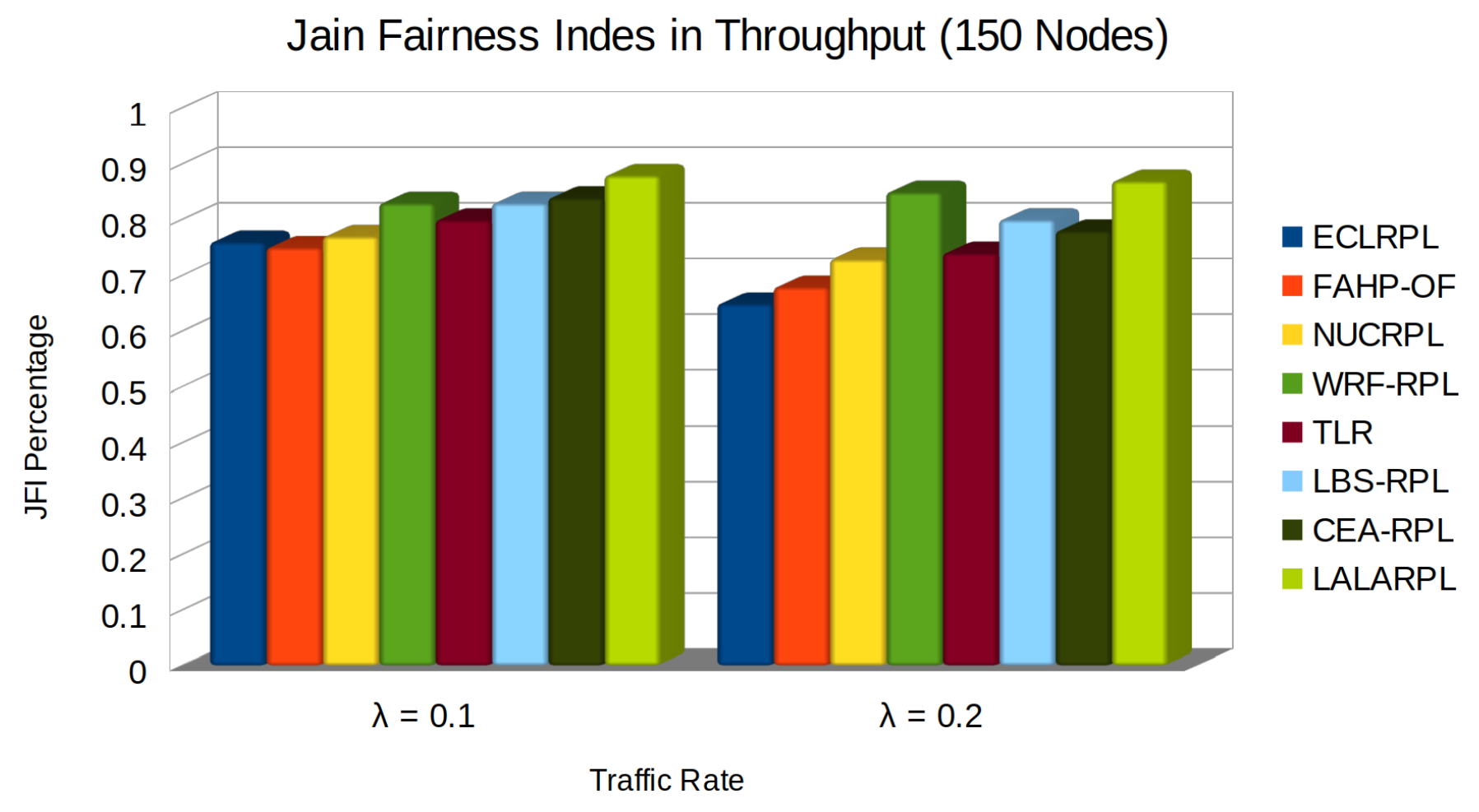
5.3. Jain Fairness Index in Throughput
- denotes the throughput for the i-th node, considering the data transmitted, the quality of the links (LQI), and the number of child nodes (C).
- The numerator is the square of the sum of the throughputs for all nodes.
- The denominator represents the product of the number of nodes and the sum of the squares of individual throughputs, reflecting the dispersion of throughput across the network and facilitating the assessment of the load balancing effectiveness in terms of fairness.
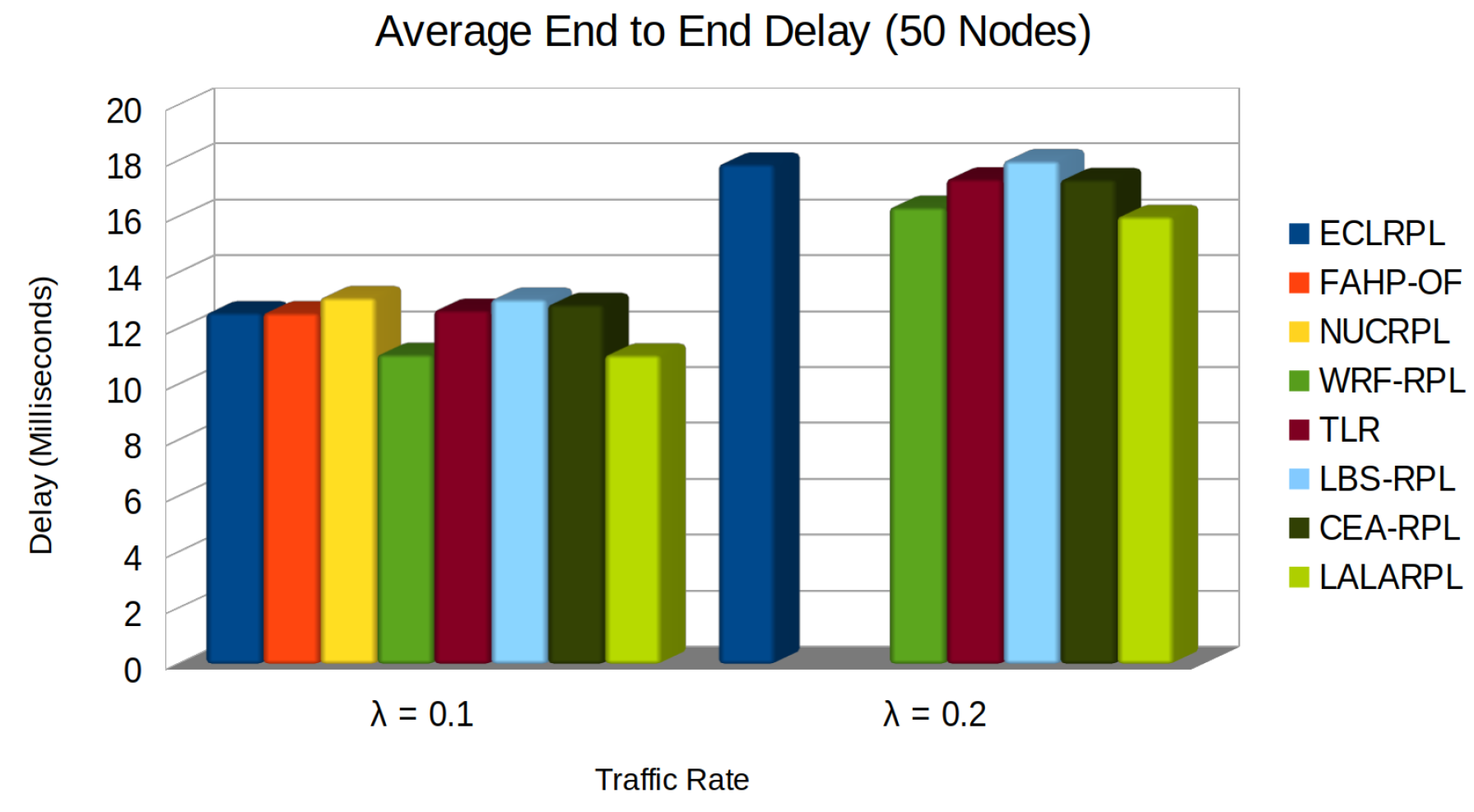
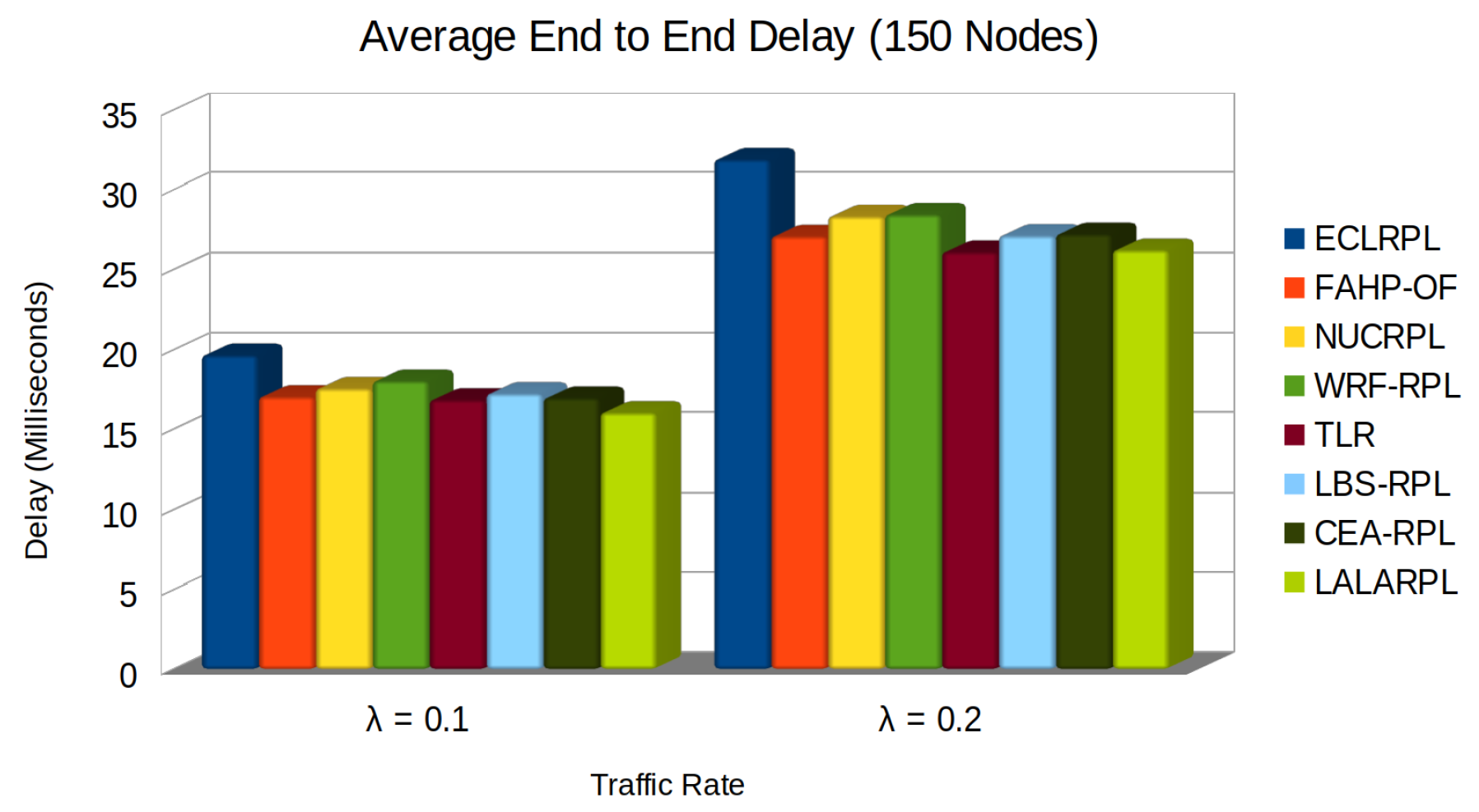
5.4. Average End to End Delay
- is the processing delay at node i,
- is the queuing delay at node i,
- is the transmission delay at node i,
- is the propagation delay from node i.
- N is the total number of packets successfully delivered during the observation period,
- represents the time the i-th packet takes to travel from its source to its destination.
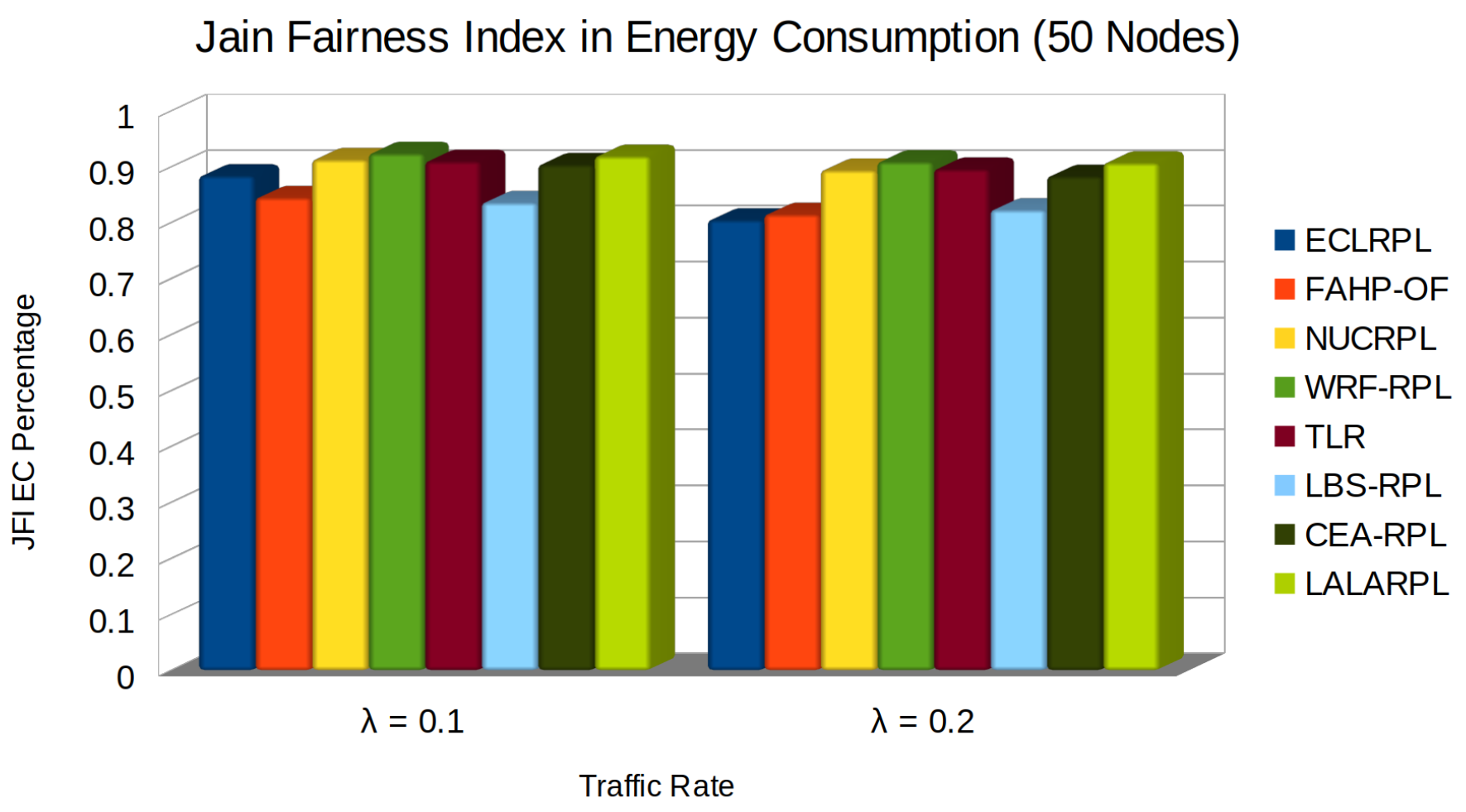
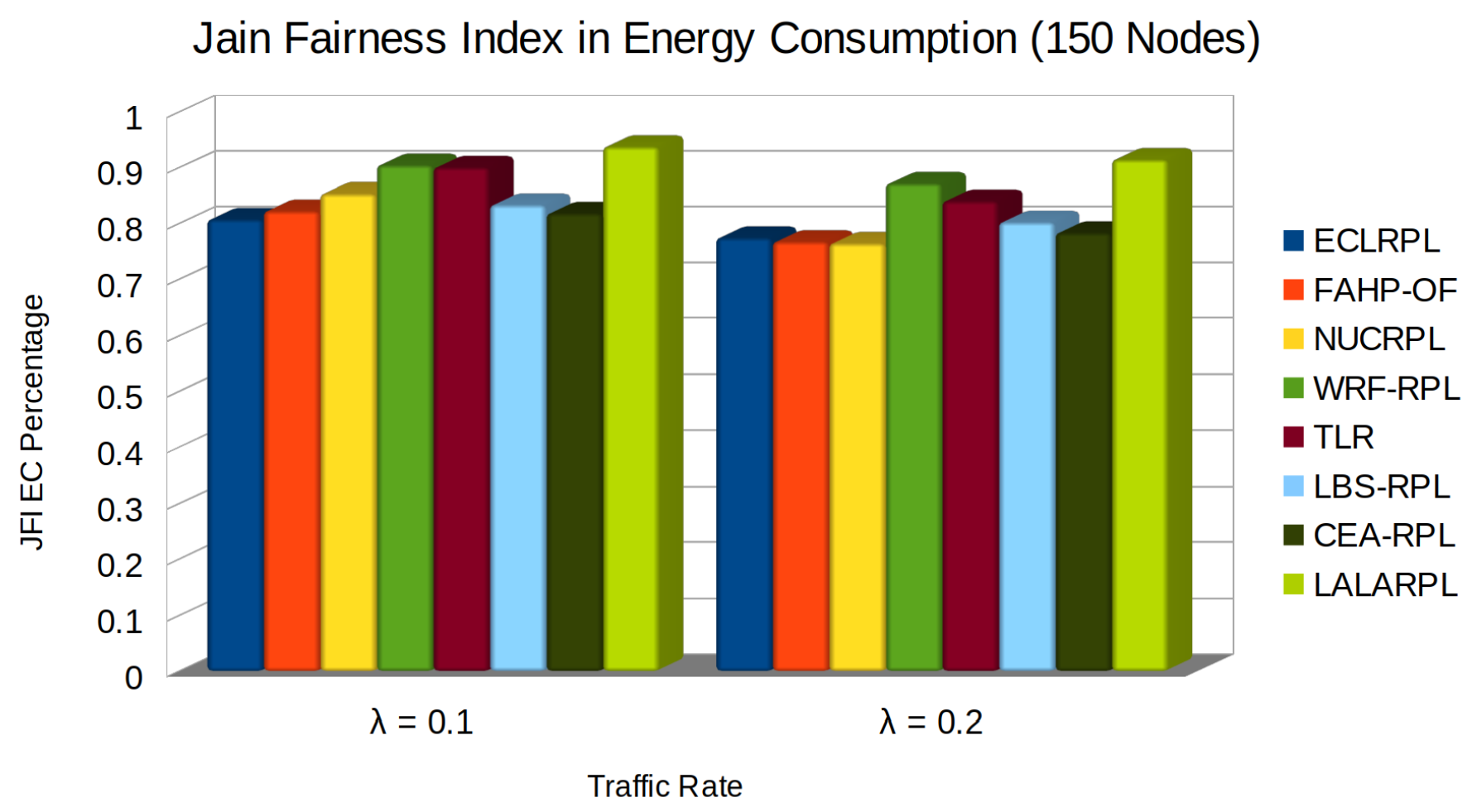
5.5. JFI in Energy Consumption
- , , , represent the power consumption while transmitting, receiving, idling, and sleeping, respectively,
- , , , are the durations spent in each corresponding state.
- Optimized Path Selection: LALARPL carefully chooses routes that minimize energy expenditure, thereby preserving node battery life and reducing the need for frequent transmissions.
- Load Distribution: By restricting the number of potential parents for a child node, LALARPL prevents the excessive energy drain of any single node, promoting a more uniform energy consumption across the network.
- Adaptive Learning: Incorporating learning automata in LALARPL enables the network to adapt to changing conditions and optimize the routing dynamically. This adaptation means the network can avoid energy-intensive routes that might lead to retransmissions or increased processing.
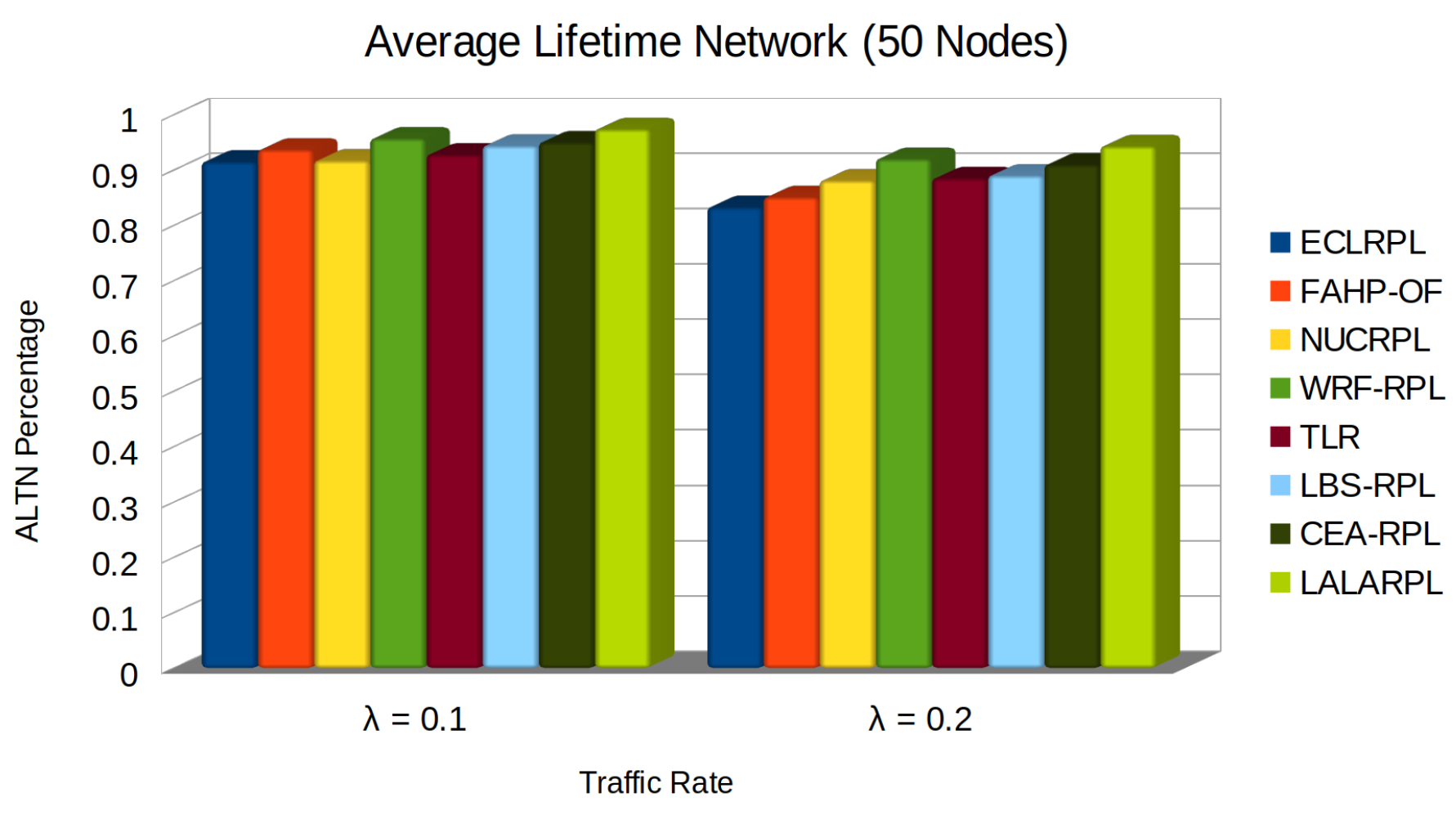
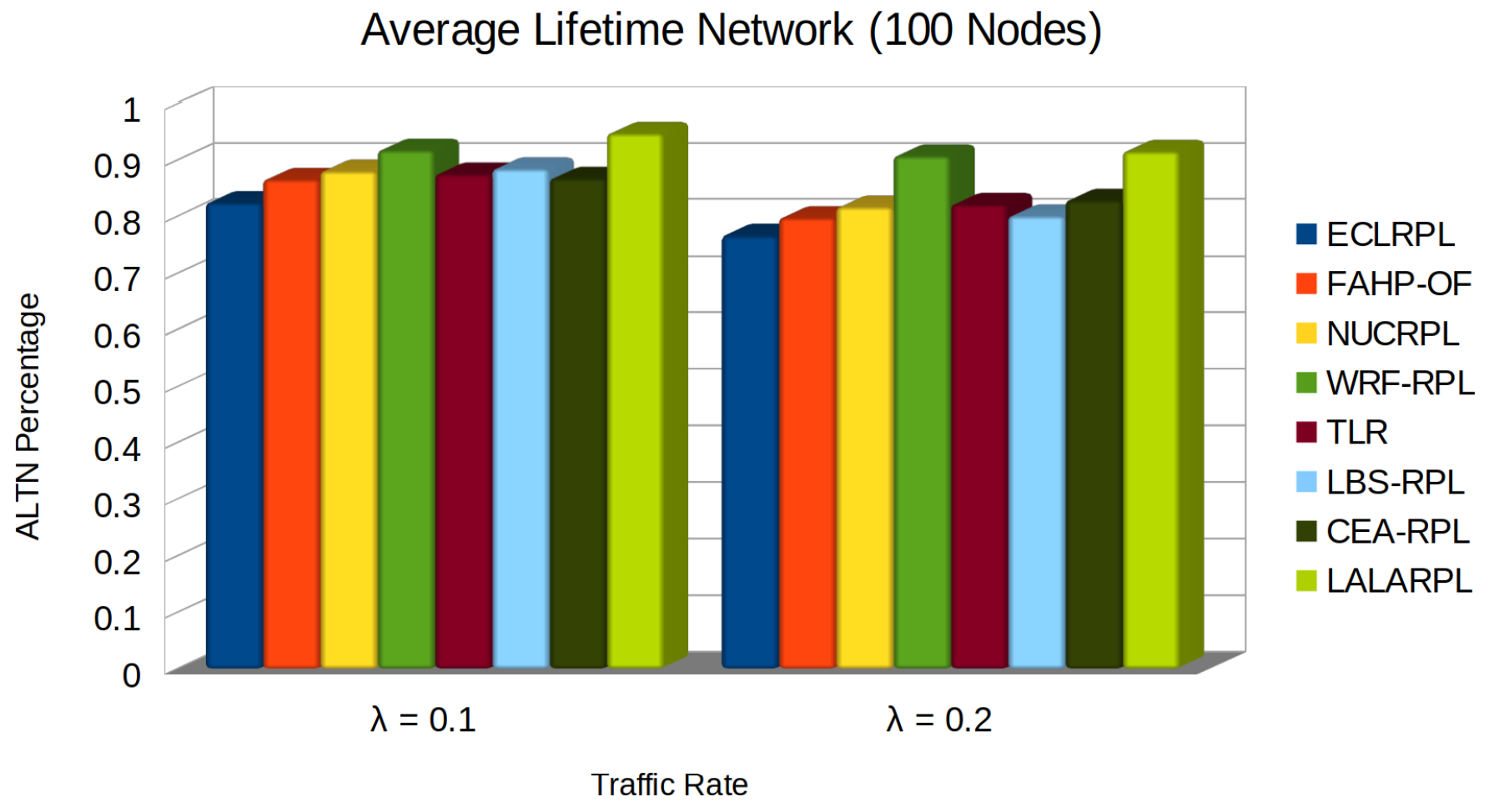
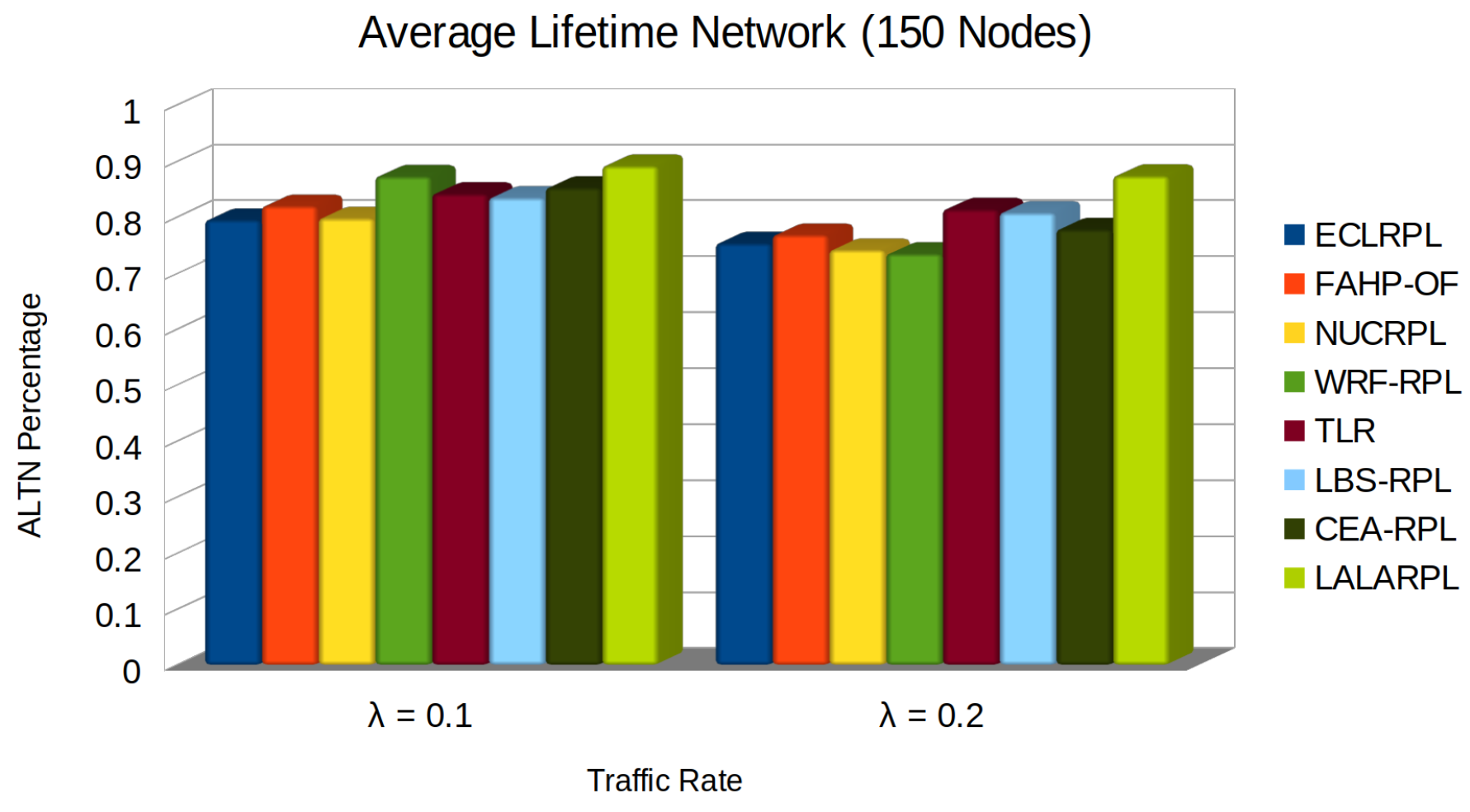
5.6. Average Lifetime Network
- denotes the time of death of the i-th node, crucial for understanding when each node exhausts its energy reserves.
- N represents the total number of nodes in the network, providing the denominator for averaging the lifetimes.
- M is the number of nodes still operational at the end of the simulation period, indicating the network’s resilience.
- ℘ signifies the predefined or estimated maximum lifetime for the surviving nodes, offering a way to estimate the potential maximum longevity of the network’s operational capability.
- Efficient Energy Management: By intelligently limiting the communication and processing tasks per node, LALARPL prevents premature energy depletion, which directly translates to a longer ALTN.
- Learning Automata: The protocol’s use of learning automata ensures that routing decisions are optimized in real-time. This adaptability prevents nodes from expending unnecessary energy, especially in high-traffic conditions, thereby delaying the time to the first node’s death.
- Load Balancing: LALARPL’s load balancing mechanisms evenly distribute the energy demands across the network, ensuring no single node bears excessive burden. This prevents the formation of energy hotspots and results in a longer average node lifetime.
6. Conclusion
References
- Lakshmi, M.S.; Ramana, K.S.; Ramu, G.; Shyam Sunder Reddy, K.; Sasikala, C.; Ramesh, G. Computational intelligence techniques for energy efficient routing protocols in wireless sensor networks: A critique. Transactions on Emerging Telecommunications Technologies 2023, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainaddin, D.A.; Hanapi, Z.M.; Othman, M.; Ahmad Zukarnain, Z.; Abdullah, M.D.H. Recent trends and future directions of congestion management strategies for routing in IoT-based wireless sensor network: a thematic review. Wireless Networks 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darabkh, K.A.; Al-Akhras, M.; Zomot, J.N.; Atiquzzaman, M. RPL routing protocol over IoT: A comprehensive survey, recent advances, insights, bibliometric analysis, recommendations, and future directions. Journal of Network and Computer Applications 2022, 207, 103476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzammal, S.M.; Murugesan, R.K.; Jhanjhi, N.Z. A Comprehensive Review on Secure Routing in Internet of Things: Mitigation Methods and Trust-Based Approaches. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2021, 8, 4186–4210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, J.; Vasseur, J. The Routing Protocol for Low-Power and Lossy Networks (RPL) Option for Carrying RPL Information in Data-Plane Datagrams. RFC 6553, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almutairi, H.; Zhang, N. A Survey on Routing Solutions for Low-Power and Lossy Networks: Toward a Reliable Path-Finding Approach. Network 2024, 4, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estepa, R.; Estepa, A.; Madinabeitia, G.; Garcia, E. RPL Cross-Layer Scheme for IEEE 802.15.4 IoT Devices With Adjustable Transmit Power. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 120689–120703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzammal, S.M.; Murugesan, R.K.; Jhanjhi, N.Z. A Comprehensive Review on Secure Routing in Internet of Things: Mitigation Methods and Trust-Based Approaches. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2021, 8, 4186–4210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zormati, M.A.; Lakhlef, H.; Ouni, S. Review and analysis of recent advances in intelligent network softwarization for the Internet of Things. Computer Networks 2024, 241, 110215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.K.; Singh, O.; Kumar, A.; Puthal, D. Hybrid Mode of Operations for RPL in IoT: A Systematic Survey. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management 2022, 19, 3574–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadigotla, S.; Murthy, J.K. A Comprehensive Study on RPL Challenges. 2020 Third International Conference on Advances in Electronics, Computers and Communications (ICAECC). IEEE, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Lamaazi, H.; Benamar, N. A comprehensive survey on enhancements and limitations of the RPL protocol: A focus on the objective function. Ad Hoc Networks 2020, 96, 102001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheshwari, A.; Yadav, R.K.; Nath, P. Enhanced RPL to Control Congestion in IoT: A Review 2023. p. 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Homaei, M.H.; Soleimani, F.; Shamshirband, S.; Mosavi, A.; Nabipour, N.; Varkonyi-Koczy, A.R. An Enhanced Distributed Congestion Control Method for Classical 6LowPAN Protocols Using Fuzzy Decision System. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 20628–20645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S., P.S.; B., S. RPL Protocol Load balancing Schemes in Low-Power and Lossy Networks. International Journal of Scientific Research in Computer Science and Engineering 2023, 11, 7–13. [CrossRef]
- P., A.; Vimala, H.; J., S. Comprehensive review on congestion detection, alleviation, and control for IoT networks. Journal of Network and Computer Applications 2024, 221, 103749. [CrossRef]
- Shabani Baghani, A.; Khabbazian, M. RPL Point-to-Point Communication Paths: Analysis and Enhancement. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2023, 10, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahyoub, M.; Hasan Mahmoud, A.S.; Abu-Amara, M.; Sheltami, T.R. An Efficient RPL-Based Mechanism for Node-to-Node Communications in IoT. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2021, 8, 7152–7169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, V.K.; Mazumdar, A.P.; Faruki, P.; Govil, M.C. Congestion control in Internet of Things: Classification, challenges, and future directions. Sustainable Computing: Informatics and Systems 2022, 35, 100678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safaei, B.; Monazzah, A.M.H.; Ejlali, A. ELITE: An Elaborated Cross-Layer RPL Objective Function to Achieve Energy Efficiency in Internet-of-Things Devices. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2021, 8, 1169–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghizadeh, S.; Elbiaze, H.; Bobarshad, H. EM-RPL: Enhanced RPL for Multigateway Internet-of-Things Environments. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2021, 8, 8474–8487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopal, K.; Basavaraju, T.G. Congestion and Energy Aware Multipath Load Balancing Routing for LLNs. International journal of Computer Networks & Communications 2023, 15, 71–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, S.; Kumar, A.; Bagchi, A.; Yadav, S.; Kumar, S. RPL Based Routing Protocols for Load Balancing in IoT Network. Journal of Physics: Conference Series 2021, 1950, 012073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darabkh, K.A.; Al-Akhras, M. RPL over Internet of Things: Challenges, Solutions, and Recommendations. 2021 IEEE International Conference on Mobile Networks and Wireless Communications (ICMNWC). IEEE, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Magubane, Z.; Tarwireyi, P.; Abu-Mafouz, A.; Adigun, M. Extended Context-Aware and Load Balancing Routing Protocol for Low power and Lossy Networks in IoT networks (ECLRPL). 2021 3rd International Multidisciplinary Information Technology and Engineering Conference (IMITEC). IEEE, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Pancaroglu, D.; Sen, S. Load balancing for RPL-based Internet of Things: A review. Ad Hoc Networks 2021, 116, 102491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopal, K.; Basavaraju, T. Load balancing routing in RPL for the internet of things networks: a survey. International Journal of Wireless and Mobile Computing 2023, 24, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaezian, A.; Darmani, Y. MSE-RPL: Mobility Support Enhancement in RPL for IoT Mobile Applications. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 80816–80832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiagarajan, C.; Samundiswary, P. Enhanced RPL-Based Routing with Mobility Support in IoT Networks. 2023 Second International Conference on Advances in Computational Intelligence and Communication (ICACIC). IEEE, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Grover, D. An Optimized RPL Protocol for Energy Efficient IoT Networks. 2023 International Conference on Data Science and Network Security (ICDSNS). IEEE, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Haque, K.F.; Abdelgawad, A.; Yanambaka, V.P.; Yelamarthi, K. An Energy-Efficient and Reliable RPL for IoT. 2020 IEEE 6th World Forum on Internet of Things (WF-IoT). IEEE, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Hariharan, N. DCRL-RPL: Dual context-based routing and load balancing in RPL for IoT networks. IET Communications 2020, 14, 1869–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyfollahi, A.; Ghaffari, A. A lightweight load balancing and route minimizing solution for routing protocol for low-power and lossy networks. Computer Networks 2020, 179, 107368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, H.; Moritz, G.L.; Souza, R.D.; Munaretto, A.; Fonseca, M. Increased Network Lifetime and Load Balancing Based on Network Interface Average Power Metric for RPL. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 48686–48696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Babulak, E.; Tang, Y. SL-RPL: Stability-aware load balancing for RPL. Transactions on Machine Learning and Data Mining 2020, 13, 27–39. [Google Scholar]
- Sebastian, A. Child Count Based Load Balancing in Routing Protocol for Low Power and Lossy Networks (Ch-LBRPL) 2019. p. 141–157. [CrossRef]
- Rana, P.J.; Bhandari, K.S.; Zhang, K.; Cho, G. EBOF: A New Load Balancing Objective Function for Low-power and Lossy Networks. IEIE Transactions on Smart Processing & Computing 2020, 9, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoyanov, S.; Ghaleb, B.; Ghaleb, S.M. A Comparative Performance Evaluation of A load-balancing Algorithm using Contiki: “RPL vs QU-RPL”. International Journal of Advanced Trends in Computer Science and Engineering 2020, 9, 6834–6839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrouz Vaziri, B.; Toroghi Haghighat, A. Brad-OF: An Enhanced Energy-Aware Method for Parent Selection and Congestion Avoidance in RPL Protocol. Wireless Personal Communications 2020, 114, 783–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahyoub, M.; Hasan Mahmoud, A.S.; Abu-Amara, M.; Sheltami, T.R. An Efficient RPL-Based Mechanism for Node-to-Node Communications in IoT. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2021, 8, 7152–7169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, S.; Ramasubbareddy, S.; Luhach, A.K.; Nayyar, A.; Qureshi, B. CT-RPL: Cluster Tree Based Routing Protocol to Maximize the Lifetime of Internet of Things. Sensors 2020, 20, 5858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirwan, R.; al ani, m. Adaptive Load Balanced Routing in IOT Networks: A Distributed Learning Approach. Passer Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences 2021, 3, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, D. Load Balancing RPL Routing Protocol Based on Non-uniform Clustering. 2021 4th International Conference on Data Science and Information Technology. ACM, 2021, DSIT 2021. [CrossRef]
- Idrees, A.K.; Witwit, A.J. Energy-efficient load-balanced RPL routing protocol for internet of things networks. International Journal of Internet Technology and Secured Transactions 2021, 11, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo, P.D.; Jabba, D.; Sanmartin, P.; Valle, S.; Nino-Ruiz, E.D. WRF-RPL: Weighted Random Forward RPL for High Traffic and Energy Demanding Scenarios. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 60163–60174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatemifar, S.A.; Javidan, R. A new load balancing clustering method for the RPL protocol. Telecommunication Systems 2021, 77, 297–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royaee, Z.; Mirvaziri, H.; Khatibi Bardsiri, A. Designing a context-aware model for RPL load balancing of low power and lossy networks in the internet of things. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing 2020, 12, 2449–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassien, M.B.; Aljawarneh, S.A.; Eyadat, M.; Eaydat, E. Routing protocol for low power and lossy network–load balancing time-based. International Journal of Machine Learning and Cybernetics 2021, 12, 3101–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunachalam, V.; Nallamothu, N. Load Balancing in RPL to Avoid Hotspot Problem for Improving Data Aggregation in IoT. International Journal of Intelligent Engineering and Systems 2021, 14, 528–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarzoor, A.R. Optimizing RPL performance based on the selection of best route between child and root node using E-MHOF method. International Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering (IJECE) 2021, 11, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, M.; Alsukayti, I.; Alreshoodi, M. On the Need for Efficient Load Balancing in Large-scale RPL Networks with Multi-Sink Topologies. International Journal of Computer Science & Network Security 2021, 21, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadaya, N.N.; Alabady, S.A. New RPL Protocol for IoT Applications. Journal of Communications Software and Systems 2022, 18, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anita, C.; Sasikumar, R. Learning automata and lexical composition method for optimal and load balanced RPL routing in IoT. International Journal of Ad Hoc and Ubiquitous Computing 2022, 40, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awiphan, S.; Jathuphornpaserd, S. Load-Balanced Structure for RPL-Based Routing in Wireless Sensor Networks. 2022 4th International Conference on Computer Communication and the Internet (ICCCI). IEEE, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Koosha, M.; Farzaneh, B.; Alizadeh, E.; Farzaneh, S. FAHP-OF: A New Method for Load Balancing in RPL-based Internet of Things (IoT). 2022 12th International Conference on Computer and Knowledge Engineering (ICCKE). IEEE, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Kaviani, F.; Soltanaghaei, M. CQARPL: Congestion and QoS-aware RPL for IoT applications under heavy traffic. The Journal of Supercomputing 2022, 78, 16136–16166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagir Hussain, S.; Roopa, M. BE-RPL: Balanced-load and Energy-efficient RPL. Computer Systems Science and Engineering 2023, 45, 785–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantar, S.; Jafari, M.; Hashemipour, M. Energy and load balancing routing protocol for IoT. International Journal of Communication Systems 2022, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramani, P.S.; Bojan, S. Weighted Sum Metrics – Based Load Balancing RPL Objective Function for IoT. Annals of Emerging Technologies in Computing 2023, 7, 35–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, J.; Soni, S.; Chandra, P. IMPROVED LOAD BALANCING PROTOCOL FOR WSN. Journal of Data Acquisition and Processing 2023, 38, 6104. [Google Scholar]
- Venugopal, K.; Basavaraju, T.G. Congestion and Energy Aware Multipath Load Balancing Routing for LLNs. International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications 2023, 15, 71–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.K.; Farzaneh, B.; Boochanpour, E.; Alizadeh, E.; Farzaneh, S. TFUZZY-OF: a new method for routing protocol for low-power and lossy networks load balancing using multi-criteria decision-making. International Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering (IJECE) 2023, 13, 3474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Liu, J. Reinforcement learning-based load balancing for heavy traffic Internet of Things. Pervasive and Mobile Computing 2024, 99, 101891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabouche, A.; Djamaa, B.; Senouci, M.R.; Ouakaf, O.E.; Elaziz, A.G. TLR: Traffic-aware load-balanced routing for industrial IoT. Internet of Things 2024, 25, 101093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alilou, M.; Babazadeh Sangar, A.; Majidzadeh, K.; Masdari, M. QFS-RPL: mobility and energy aware multi path routing protocol for the internet of mobile things data transfer infrastructures. Telecommunication Systems 2023, 85, 289–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shashidhar, P.K.; Thanuja, T.C.; Kunabeva, R. Adaptive RPL Routing Optimization Model for Multimedia Data Transmission using IOT. Indian Journal Of Science And Technology 2024, 17, 436–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordestani, J.K.; Mirsaleh, M.R.; Rezvanian, A.; Meybodi, M.R. Advances in Learning Automata and Intelligent Optimization; Springer International Publishing, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Homaei, M.H.; Band, S.S.; Pescape, A.; Mosavi, A. DDSLA-RPL: Dynamic Decision System Based on Learning Automata in the RPL Protocol for Achieving QoS. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 63131–63148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Short Biography of Authors
 |
MOHAMMADHOSSEIN HOMAEI (M’19) was born in Hamedan, Iran. He obtained his B.Sc. in Information Technology (Networking) from the University of Applied Science and Technology, Hamedan, Iran, in 2014 and his M.Sc. from Islamic Azad University, Malayer, Iran, in 2017. He is pursuing his Ph.D. at Universidad de Extremadura, Spain, where his prolific research has amassed over 100 citations. Since December 2019, Mr. Homaei has been affiliated with Óbuda University, Hungary, as a Visiting Researcher delving into the Internet of Things and Big Data. His tenure at Óbuda University seamlessly extended into a research collaboration with J. Selye University, Slovakia, focusing on Cybersecurity from January 2020. His research voyage led him to the National Yunlin University of Science and Technology, Taiwan, where he was a Scientific Researcher exploring IoT and Open-AI from January to September 2021. His latest role was at the Universidade da Beira Interior, Portugal, in the Assisted Living Computing and Telecommunications Laboratory (ALLab), from June 2023 to January 2024, where he engaged in cutting-edge projects on digital twins and machine learning. He is the author of ten scholarly articles and holds three patents, highlighting his diverse research interests in Digital Twins, Cybersecurity, Wireless Communications, and IoT. An active IEEE member, Mr. Homaei has carved a niche for himself with notable contributions to Digitalization, the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), Information Security Management, and Environmental Monitoring. His substantial work continues to influence the technological and cybersecurity landscape profoundly. |



| Year/RFC | Aim | Strategy | Strengths |
| Year/RFC | Aim | Strategy | Strengths |
| 2020 - [31] | Enhance RPL for IoT focusing on energy efficiency and reliability | Evaluate performance of ETX and Energy-based OFs; propose a hybrid OF | Identifies trade-offs between energy efficiency and reliability; proposes a balanced approach through a hybrid OF |
| 2020 - [32] | Address routing overhead, packet losses, and load imbalance in RPL-based IoT networks | Introduce DCRL-RPL framework with grid construction, ranking-based grid selection, and dual context-based OF selection | Demonstrate improved network lifetime, packet delivery ratio, and reduced routing overhead |
| 2020 - [33] | Enhance RPL for IoT, focusing on load balancing | Introduce L2RMR with a novel OF and PF to prevent HDP, optimizing path length and load distribution | Significantly reduces packet loss, delay, and energy consumption, outperforming traditional RPL |
| 2020 - [34] | Improve load balancing and extend network lifetime in IoT | Introduce NIAP metric for balancing energy consumption, relying on average power estimation | Increases network lifetime by up to 24%, improves packet delivery ratio and reduces delay |
| 2020 - [35] | Address instability and inefficiency in RPL’s load balancing for IoT | Propose SL-RPL with stability-aware mechanism, utilizing PTR and ETX for parent selection | Enhances network stability and performance, reducing parent changes, packet loss, and energy usage |
| 2020 - [36] | Address load imbalance in RPL for IoT | Introduce Ch-LBRPL to improve load balance using a child count method, reducing parent switching and enhancing energy efficiency | More effective at achieving load balance, improving network stability and energy consumption |
| 2020 - [37] | Tackle load imbalance in RPL for IoT | Introduce EBOF combining ETX and CC for optimal path selection, extending network lifetime | Enhances network performance by balancing energy consumption and prolonging operational sustainability |
| 2020 - [38] | Evaluate QU-RPL’s load-balancing in RPL for IoT | Comparative analysis of RPL and QU-RPL focusing on power consumption, PDR, and latency | Finds QU-RPL does not significantly improve over traditional RPL, suggesting a need for further development |
| 2020 - [39] | Enhance energy-aware parent selection and congestion avoidance in RPL for IoT | Propose Brad-OF using ETX, delay, and residual energy for parent selection and a metric for congestion avoidance | Increases network lifetime by up to 65% and reduces packet loss by up to 81% |
| 2020 - [40] | Address N2N communication inefficiencies in LLNs for IoT | Propose HRPL, integrating link-state routing with RPL for efficient N2N routes and employing adaptive reporting and SSSP mechanisms | Significantly improves packet delivery ratio, reduces delay and energy consumption, maintaining RPL compatibility |
| 2020 - [41] | Extend network lifespan and reduce data traffic in IoT | Introduce CT-RPL with cluster formation, CH selection, and route establishment based on RER, QU, and ETX | Enhances network lifetime by 30-40% and packet delivery ratio by 5-10% |
| 2021 - [42] | Facilitate load-efficient IoT connectivity with anticipated device number surge | Leverage self-coordinating networks and distributed learning for dynamic communication parameter adaptation | Demonstrate improvements in reliability and traffic efficiency with lightweight learning |
| 2021 - [25] | Improve RPL in IoT by incorporating buffer occupancy for load balancing | Introduce ECLRPL, using a buffer occupancy metric in routing decisions to enhance throughput and network lifetime | Significantly outperforms standard RPL and CLRPL in packet delivery, power efficiency, and network delay |
| 2021 - [43] | Address load imbalance in LLNs with RPL by proposing a clustering-based protocol | Use non-uniform clustering and cluster head rotation based on node energy and priority for balanced load | Enhances network stability and efficiency by achieving balanced traffic distribution |
| 2021 - [44] | Develop an energy-efficient, load-balanced routing protocol for IoT networks | Incorporate a novel parent selection algorithm in EL-RPL, considering energy and packet counts | Outperforms existing protocols in energy conservation, control packet reduction, and extending network lifetime |
| 2021 - [45] | Enhance load balancing in high-traffic sensor networks | Introduce WRF-RPL with a routing metric considering remaining energy and parent count | Outperforms standard RPL in network lifetime, packet delivery, and energy consumption |
| 2021 - [46] | Improve routing in IoT networks | Propose C-Balance with a dual-ranking system for cluster formation and routing, using ETX, hop count, and energy metrics | Improves network longevity and energy efficiency, though increases end-to-end delay |
| 2021 - [47] | Address load imbalance in RPL for IoT | Develop AMRRPL with ant colony optimization for rank computation and stochastic automata for parent selection | Demonstrate improvements in packet delivery, network lifetime, energy efficiency, and convergence |
| 2021 - [48] | Address load balancing challenges in RPL for IoT | Introduce LBTB, combining neighbour count and node power with a modified trickle timer for message distribution | Reducing convergence time by up to 68%, power consumption by 16%, and delay by 56% |
| 2021 - [49] | Mitigate hotspot problem and improve data aggregation in IoT with RPL | Propose LoB-RPL with a composite metric for parent selection and adaptive trickle parameters | Significantly improves packet delivery, network lifetime, energy efficiency, and control overhead reduction |
| 2021 - [50] | Optimize RPL performance in IoT for reducing node congestion and latency | Introduce E-MHOF with a three-layer approach for parent and path selection, and child node minimization | Demonstrates significant improvements in network lifetime and latency reduction |
| 2021 - [51] | Improve routing and address node unreachability in LLNs for IoT | Propose MSLBOF with Memory Utilization metrics for sink selection and load balancing | Significantly reduces packet loss and improves network stability compared to standard MRHOF |
| 2022 - [52] | Address energy consumption and inefficiency in RPL for IoT | Propose a novel RPL OF incorporating Load, Residual Energy, and ETX to enhance network lifetime and efficiency | Shows a PDR increase of 58.425%, a decrease in packet loss ratio, and a reduction in power consumption |
| 2022 - [53] | Optimize RPL for energy efficiency and load balancing in IoT | Introduce a methodology using learning automata and lexical composition for critical routing metrics selection | Significantly improves packet delivery ratio, energy consumption, and network stability |
| 2022 - [54] | Improve load balancing in RPL-based by reducing node overload. | Identify neighbours at the same rank and exchange metrics like available connections and ETX to better select network parents. | Improved packet delivery and reduced packet loss compared to traditional methods, optimizing network traffic distribution. |
| 2022 - [55] | Enhance routing in RPL-based IoT networks | Develop FAHP-OF using Fuzzy Logic and AHP for dynamic parent selection optimization | Improves E2ED and PDR, enhancing network reliability and efficiency |
| 2022 - [56] | Propose CQARPL for IoT applications under heavy traffic conditions | Incorporates congestion control and enhanced QoS into RPL; uses multiple metrics for routing decisions | Enhances network lifetime, reduces queue loss ratio, improves packet reception, and lowers delay |
| 2023 - [57] | Introduce BE-RPL to address mobility issues in IoT LLN | Enhances RPL with mobility awareness and energy efficiency; focuses on load balancing and reactive parent selection | Demonstrates improvements in energy utilization, network control overhead, and packet delivery ratio |
| 2023 - [58] | Tackle energy management and traffic balance in IoT networks | Introduces ELBRP with ECAOF for parent node selection based on energy and congestion | Shows significant advancements in energy efficiency and packet delivery, with a slight increase in control overheads |
| 2023 - [59] | Achieve load balance and efficient routing in IoT networks | Propose WSM-OF using a combination of ETX, LQL, RE, and Child Count | Improves control overhead, jitter, packet delivery ratio, energy consumption, and network lifetime by up to 7.8% |
| 2023 - [60] | Enhance RPL for WSNs with integrated mobility management | Focus on micro-mobility to optimize energy consumption and load balancing | Reduces energy consumption, enhances packet delivery ratios, and ensures stable network operation |
| 2023 - [61] | Address load balancing and congestion in LLNs for IoT | Introduce CEA-RPL with CEA-OF leveraging Queue Occupancy, Expected Lifetime, and Child Count | Enhances power consumption, packet receiving rate, end-to-end delay, and network lifetime |
| 2023 - [62] | Address load balancing in RPL for IoT networks | Propose TFUZZY-OF integrating fuzzy logic with TOPSIS | Enhances PDR and reduces E2ED compared to traditional methods |
| 2024 - [63] | Optimize RPL routing in IoT environments using DRL | Develop RARL with a DRL model for intelligent routing decisions | Outperforms existing methods in network lifetime, queue loss ratio, packet reception ratio, and delay |
| 2024 - [64] | Address load-balancing issues in IIoT networks over 6TiSCH | Develop TLR with a traffic-aware proactive path selection strategy | Demonstrates superiority in throughput, reliability, latency, and energy efficiency over conventional RPL |
| 2024 - [65] | Integrate Q-learning and FSR in RPL for IoT to enhance mobility and energy efficiency | Propose QFS-RPL for efficient load balancing and improved PDR | Shows superior performance, especially in mobile node environments, enhancing network throughput and lifetime |
| 2024 - [66] | Enhance multimedia data transmission efficiency in IoT networks | Introduce ARPLO with a grid-based structure and ADNN for data classification | Improve energy efficiency, throughput, PDR, and network lifespan while reducing control overhead and delay |
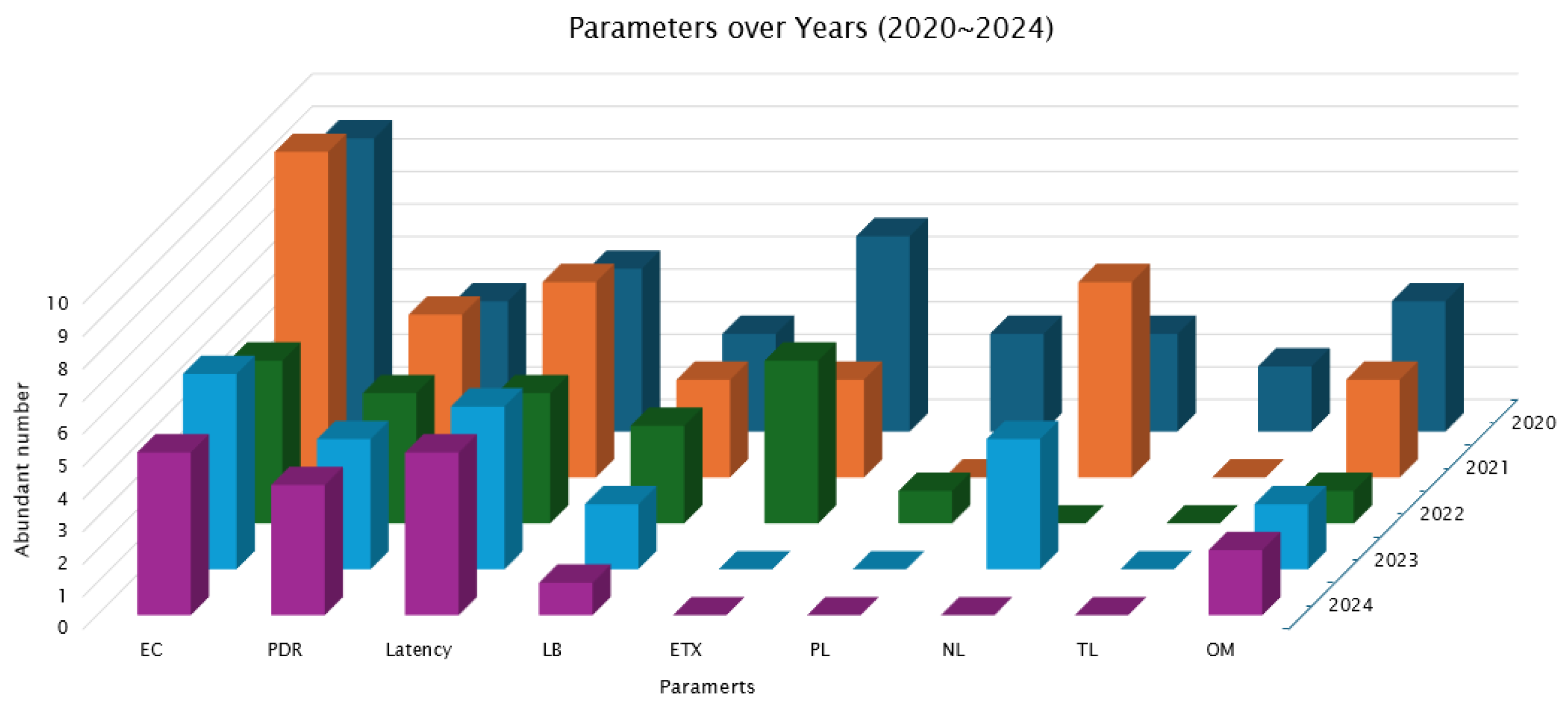
| Year | Ref | Key Parameters |
| 2020 | [31] | ETX, Energy |
| [32] | EC, LB, Overhead, PDR | |
| [33] | LB, Path Length, PL, Latency | |
| [34] | EC, PDR, Latency | |
| [35] | Stability (PTR, ETX), PL, EC | |
| [36] | Child Count, EC, Overhead | |
| [37] | EC, ETX, Child Count, NL | |
| [38] | EC, PDR, Latency | |
| [39] | ETX, Latency, EC, TL, PL | |
| [40] | Link-state, PDR, MAC state, Latency, EC | |
| [41] | EC, Queue, ETX, NL, TL | |
| 2021 | [42] | Reliability, Communication Efficiency |
| [25] | Buffer Occupancy, PDR, EC, Latency | |
| [43] | Clustering, Stability, TL | |
| [44] | EC, NL | |
| [45] | EC, LB, Parent Node Count | |
| [46] | ETX, Hop Count, EC, Number of Node Children, Network Longevity | |
| [47] | Congestion Mitigation, NL, EC, PDR | |
| [48] | Neighbour Count, EC, Trickle Timer, Convergence Time, Latency | |
| [49] | Composite Metric, Trickle Timer, PDR, NL | |
| [50] | Congestion Mitigation, ETX, RSSI, EC, Latency | |
| [51] | Memory Utilization, LB (Multi-Sink), PL | |
| 2022 | [52] | LB, EC, ETX, NL, PDR |
| [53] | EC, LB, Hop Count, ETX, TL, PDR | |
| [54] | ETX, PDR, Overhead | |
| [55] | Hop-count, ETX, RSSI, PDR, Latency | |
| [56] | Congestion, QoS, ETX, Hop Count, NL, QLR, PRR, Latency | |
| 2023 | [57] | Mobility Management, EC, LB, PDR |
| [58] | EC, Congestion, NL, Latency, Overhead | |
| [59] | ETX, Link Quality, EC, Child Count, Jitter, Parent Switching, Latency, NL | |
| [60] | Mobility Management, EC, PDR, Network Stability | |
| [61] | Congestion, EC, Queue, NL, Latency, PDR | |
| [62] | Hop Count, ETX, RSSI, PDR, Latency | |
| 2024 | [63] | EC, NL, Queue |
| [64] | TL, Queue, Throughput, Latency, EC | |
| [65] | Overhead, PDR, Latency, Throughput | |
| [66] | EC, Throughput, PDR, Overhead, Latency |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Simulator | NS-2 |
| Traffic Type | Constant Bit Rate (CBR) over UDP |
| Simulation Area | |
| Simulation Time | 1000 s |
| Number of Nodes | 50, 100, 150 |
| Sink Placement | Centralized |
| Node Placement | Random |
| Topology | RPL tree-based |
| MAC Layer Protocol | IEEE 802.15.4 |
| Data Rate | 250 kbps |
| Bandwidth | Up to 250 kbps (consistent with IEEE 802.15.4) |
| Radio Range | 100 m |
| Packet Size | 50 bytes (maximum for IEEE 802.15.4) |
| Energy Model | Enabled |
| Initial Energy per Node | 2 Joules |
| Mobility Model | Static nodes |
| Routing Protocol | LALARPL, and others for comparison |
| DIO Message Size | 80 bytes |
| DAO Message Size | 100 bytes |
| DIS Message Size | 77 bytes |
| DAO-Ack Message Size | 80 bytes |
| Traffic Rate () | 0.1, 0.2 packets/s |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





