Submitted:
17 July 2024
Posted:
17 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
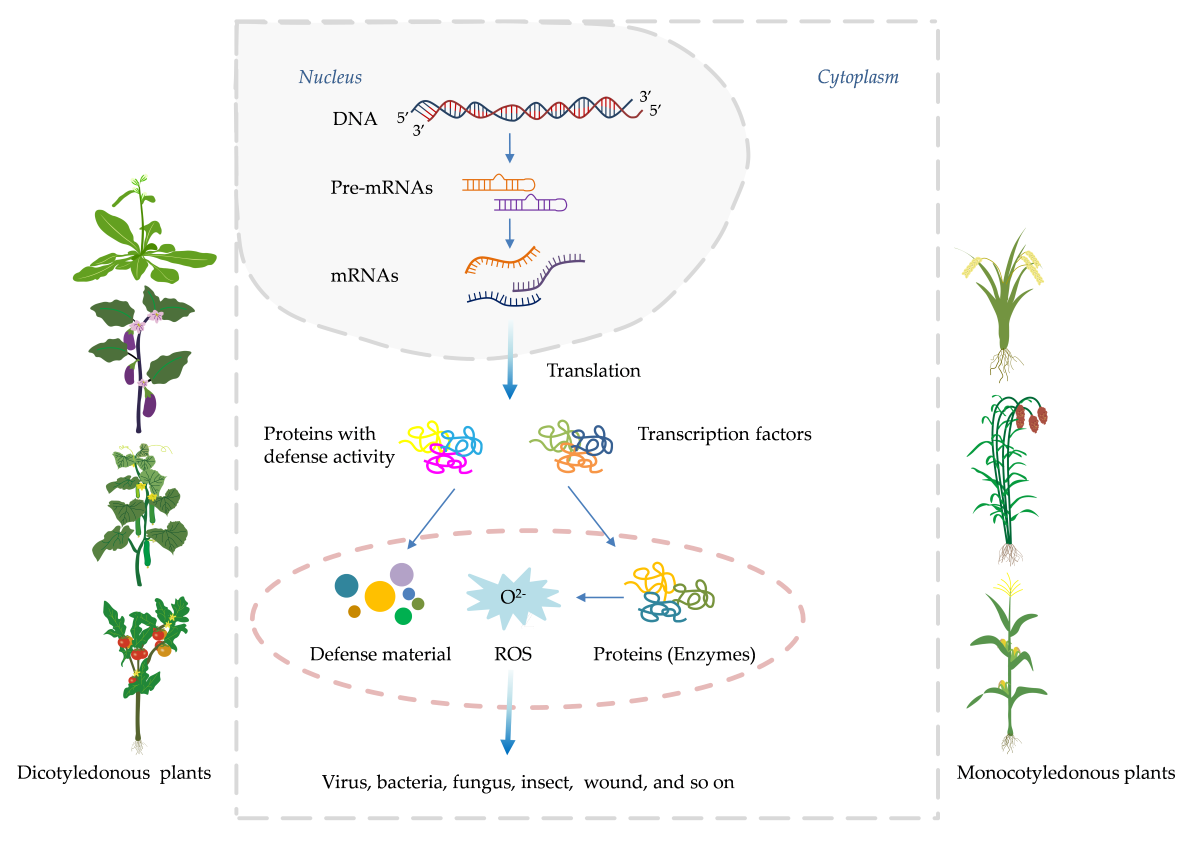
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Plants Receptors Trigger an Immune Response
2.1. The Past of Plant Activators
2.1. The Usage of Plant Activators
2.1.1. Screening Methods of Plant Activators
2.1.2. Interaction Study of Target-Plant Activator
2.2. Plant Activators against the SA Signal Pathway
2.2.1. HrBP1
2.2.2. Validamycin A and Validoxylamine A (VMA)
2.2.3. Probenazole (PBZ)
2.2.4. (D, L)-3-Aminobutyric Acid (BABA)
2.2.5. Imprimatins
2.2.6. Diuretics
3. Plant Activators Acted in the Downstream of SA in the SA Signal Pathway
3.1. Downstream Activators
3.1.1. Benzothiadiazole (BTH)
3.1.2. N-Cyanomethyl-2-Chloroisonicotinamide (NCI)
3.1.3. 2,6-Dichloroisonicotinic Acid (INA)
3.1.4. Tiadinil (TDL)
3.1.5. 3-Chloro-1H-Pyrazole-5-Carboxylic Acid (CMPA)
3.1.6. Benzoylsalicylic Acid (BzSA) and Acetylsalicylic Acid (ASA)
3.1.7 3,5-Dichlorosalicylic Acid (3, 5-DCSA), 4-Chlorosalicylic Acid (4-CSA), and 5-Chlorosalicylic Acid (5-CSA)
3.1.8. Dichloroanthranilic Acid (DCA)
3.1.9. Imprimatins C1 and Imprimatins C2
3.1.10. Oxycom™
4. Activators with Unclear Action Sites
4.1. 3,4-dichloro-2’-Cyano-1, 2-Thiazole-5-Carboxanilide (Isotianil)
4.2. Polypeptide-Product
4.3. β,γ-Methyleneadenosine 5’-Triphosphate (AMP-PCP)
4.4 2, 2-dichloro-3, 3-Dimethylcyclopropane Carboxylic Acid (DDCC)
4.5 Hyaluronic Acid (HA)
5. The Development of Plant Activator against the SA Signal Pathway in the World at Present
5.1. Plant Activators Developed in China in Recent Years
5.2. Limited Understanding of Molecular Targets
6. Future of Plant Activators
6.1. Action Mechanism of Plant Activators
6.2. Metabolism Mechanism of Plant Activators
6.3. Screening Models of Plant Activators
6.4. Discovery of Lead Compound Based on Novel Action Target
7. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
Submission Declaration
References
- Hayes, J.D.; Strange, R.C. Glutathione S-transferase polymorphisms and their biological consequences. Pharmaco. 2000, 61, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shine, M.; Xiao, X.; Kachroo, P.; Kachroo, A. Signaling mechanisms underlying systemic acquired resistance to microbial pathogens. Plant Sci. 2019, 279, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Thilagam, P.; Shikha, D.; Saikanth, D.; Rahmani, U.; Huded, S.; Panigrahi, C.K. Adapting plant protection strategies to meet the challenges posed by climate change on plant diseases: a review. Int. J. Environ. Clim. Chang. 2023, 13, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y. Salicylic acid: biosynthesis and signaling. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2021, 72, 761–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.; Fariduddin, Q.; Castroverde, C.D.M. Salicylic acid: A key regulator of redox signalling and plant immunity. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 168, 381–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Han, X.; Kahmann, R. Microbial effectors target multiple steps in the salicylic acid production and signaling pathway. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 140488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.M. Upscaling plant defense system through the application of plant growth-promoting fungi (PGPF). In: Microbial Technology for Agro-Ecosystems. Elsevier. 2024, 61–95. [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Dolatabadian, A.; Fernando, W.D. The wonderful world of intrinsic and intricate immunity responses in plants against pathogens. Cana. J. Plant Pathol. 2022, 44, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zeng, M.; Song, B.; Hou, C.; Hu, D.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Fan, H.; Bi, L.; Liu, J. Dufulin activates HrBP1 to produce antiviral responses in tobacco. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durrant, W.E.; Dong, X. Systemic acquired resistance. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2004, 42, 185–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Guo, W.; Zhao, L.; Yu, Y.; Chen, S.; Tao, L.; Cheng, L.; Kang, Q.; Song, X.; Wu, J. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the WRKY transcription factor family in flax (Linum usitatissimum L.). BMC Genomics 2021, 22, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentham, A.R.; De la Concepcion, J.C.; Mukhi, N.; Zdrzałek, R.; Draeger, M.; Gorenkin, D.; Hughes, R.K.; Banfield, M.J. A molecular roadmap to the plant immune system. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 14916–14935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, W.S.; Wang, T.; Meng, X.F.; Chen, T.T.; Huang, X.X.; Li, Y.J.; Hou, B.K. Methyl salicylate glucosylation regulates plant defense signaling and systemic acquired resistance. Plant Physiol. 2019, 180, 2167–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.M.; Kachroo, A.; Kachroo, P. Chemical inducers of systemic immunity in plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 1849–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, A.; Sharma, G. Management of host plant resistance through immunization: an overview. J. Hill Agric. 2016, 7, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malamy, J.; Carr, J.P.; Klessig, D.F.; Raskin, I. Salicylic acid: a likely endogenous signal in the resistance response of tobacco to viral infection. Science 1990, 250, 1002–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Métraux, J.; Signer, H.; Ryals, J.; Ward, E.; Wyss-Benz, M.; Gaudin, J.; Raschdorf, K.; Schmid, E.; Blum, W.; Inverardi, B. Increase in salicylic acid at the onset of systemic acquired resistance in cucumber. Science 1990, 250, 1004–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaffney, T.; Friedrich, L.; Vernooij, B.; Negrotto, D.; Nye, G.; Uknes, S.; Ward, E.; Kessmann, H.; Ryals, J. Requirement of salicylic acid for the induction of systemic acquired resistance. Science 1993, 261, 754–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, E.R.; Uknes, S.J.; Williams, S.C.; Dincher, S.S.; Wiederhold, D.L.; Alexander, D.C.; Ahl-Goy, P.; Metraux, J.P.; Ryals, J.A. Coordinate gene activity in response to agents that induce systemic acquired resistance. Plant Cell 1991, 3, 1085–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Bowling, S.A.; Gordon, A.S.; Dong, X. Characterization of an Arabidopsis thaliana mutant that is nonresponsive to inducers of systemic acquired resistance. Plant Cell. 1994, 6, 1583–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, J.; Kachroo, P.; Klessig, D.F. The Arabidopsis thaliana ssi1 mutation restores pathogenesis-related gene expression in npr1 plants and renders defensin gene expression salicylic acid dependent. Plant Cell. 1999, 11, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapin, D.; Bhandari, D.D.; Parker, J.E. Origins and immunity networking functions of EDS1 family proteins. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2020, 58, 253–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jirage, D.; Tootle, T.L.; Reuber, T.L.; Frost, L.N.; Feys, B.J.; Parker, J.E.; Ausubel, F.M.; Glazebrook, J. Arabidopsis thaliana PAD4 encodes a lipase-like gene that is important for salicylic acid signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 1999, 96, 13583–13588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eulgem, T.; Somssich, I.E. Networks of WRKY transcription factors in defense signaling. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2007, 10, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Y.; Eulgem, T. Transcript-level expression control of plant NLR genes. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2018, 19, 1267–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thibaud, M.C.; Gineste, S.; Nussaume, L.; Robaglia, C. Sucrose increases pathogenesis-related PR-2 gene expression in Arabidopsis thaliana through an SA-dependent but NPR1-independent signaling pathway. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2004, 42, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bockhaven, J.; De Vleesschauwer, D.; Höfte, M. Towards establishing broad-spectrum disease resistance in plants: silicon leads the way. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 1281–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, G.; Chen, J.; Chang, M.; Chen, H.; Hall, K.; Korin, J.; Liu, F.; Wang, D.; Fu, Z.Q. Pandemonium breaks out: disruption of salicylic acid-mediated defense by plant pathogens. Mol. Plant 2018, 11, 1427–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reglinski T, Dann E, Deverall B. Integration of induced resistance in crop production. Induced resistance for plant defence: A sustainable approach to crop protection. 2007, 201–228. [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.; Chen, J.Q.; Shi, Y.X.; Sun, M.J.; Li, P.F.; Zhao, Z.J.; Zhu, W.P.; Li, H.L.; Xu, Y.F.; Li, B.J. The discovery of new scaffold of plant activators: from salicylic acid to benzotriazole Chin. Chem. Lett. 2017, 28, 919–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; He, B.; Hu, M.; Bao, J.; Yan, W.; Han, X.; Ye, Y. Fluorescent probes for imaging and detection of plant hormones and their receptors. Adv. Agrochem. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zipfel, C. Plant pattern-recognition receptors. Trends. Immunol. 2014, 35, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, H.; Qi, J.; Wan, B.; Ye, W.; Lin, Y.; Shao, Y.; Dong, S. Leucine-rich repeat receptor-like gene screen reveals that Nicotiana RXEG1 regulates glycoside hydrolase 12 MAMP detection. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Z.; Xia, Y.; Wang, L.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, M.; Xiao, Y.; Han, Z. Plant receptor-like protein activation by a microbial glycoside hydrolase. Nature 2022, 610, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snoeck, S.; Garcia, A.G.; Steinbrenner, A.D. Plant receptor-like proteins (RLPs): structural features enabling versatile immune recognition. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2023, 125, 102004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, F.; Zeng, M.; Wang, L.; Liu, H.; Sun, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Xu, Y. Convergent evolution of immune receptors underpins distinct elicitin recognition in closely related Solanaceous plants. Plant Cell 2023, 35, 1186–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; Liu, Y.; Bai, B.; Han, Z.; Tang, J.; Zhang, H.; Yaghmaiean, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chai, J. Structural basis for BIR1-mediated negative regulation of plant immunity. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 1521–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Zeng, M.; Sun, Y.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Z.; Wang, L.; Cui, J.R.; Zhang, F.; Lv, D.; Chen, X. BAK1 protects the receptor-like kinase BIR2 from SNIPER2a/b-mediated degradation to promote pattern-triggered immunity in Nicotiana benthamiana. Plant Cell 2023, 35, 3566–3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Jackson, E.; Liu, X.; Huang, X.; van der Hoorn, R.A.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X. Proteolysis in plant immunity. Plant Cell 2024, koae142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlöffel, M.A.; Salzer, A.; Wan, W.L.; van Wijk, R.; Del Corvo, R.; Šemanjski, M.; Symeonidi, E.; Slaby, P.; Kilian, J.; Maček, B.; Munnik, T.; Gust, A.A. The BIR2/BIR3-associated phospholipase Dγ1 negatively regulates plant immunity. Plant Physiol. 2020, 183, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Wersch, R.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y. Mighty dwarfs: Arabidopsis thaliana autoimmune mutants and their usages in genetic dissection of plant immunity. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Ruan, X.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Feng, B. BAKing up to survive a battle: functional dynamics of BAK1 in plant programmed cell death. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 9, 393664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Feng, B.; He, P.; Shan, L. From chaos to harmony: responses and signaling upon microbial pattern recognition. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2017, 55, 109–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faize, L.; Faize, M. Functional analogues of salicylic acid and their use in crop protection. Agronomy 2018, 8, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, Z.; Dai, X.; Xu, J.; Liu, Z.; Guo, Y.; Gao, Z.; Meng, F. Medicinal chemistry strategies toward broad-spectrum antiviral agents to prevent next pandemics. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 271, 116442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X. Salicylic acid: biosynthesis, perception, and contributions to plant immunity. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2019, 50, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klessig, D.F.; Choi, H.W.; Dempsey, D.M.A. Systemic acquired resistance and salicylic acid: past, present, and future. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2018, 31, 871–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, B. Salicylic acid: An efficient elicitor of secondary metabolite production in plants. Biocatal. Agr. Biotech. 2020, 31, 101884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, R.K.; Saha, D.; Skalicky, M.; Mishra, U.N.; Chauhan, J.; Behera, L.P.; Lenka, D.; Chand, S.; Kumar, V.; Dey, P. Crucial cell signaling compounds crosstalk and integrative multi-omics techniques for salinity stress tolerance in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 670369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; He, C.Q.; Ding, N.Z. Abiotic stresses: general defenses of land plants and chances for engineering multistress tolerance. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhuo, R. Recent advances in phyto-combined remediation of heavy metal pollution in soil. Biotechnol. Adv. 2024, 108337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, D.; Zhang, P.; Wang, S. Advances in structure-based drug design: The potential for precision therapeutics in psychiatric disorders. Neuron. 2024, 112, 526–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, D.K.; Bhat, J.A.; Antoniou, C.; Kandhol, N.; Singh, V.P.; Fernie, A.R.; Fotopoulos, V. Redox regulation by priming agents towards a sustainable agriculture. Plant Cell Physiol. 2024, pcae031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, A.; Sarsaiya, S.; Singh, R.; Gong, Q.; Wu, Q.; Shi, J. Omics approaches in understanding the benefits of plant-microbe interactions. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1391059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, M.D.G.C.; Medeiros, A.O.; Converti, A.; Almeida, F.C.G.; Sarubbo, L.A. Biosurfactants: promising biomolecules for agricultural applications. Sustainability 2024, 16, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Bian, L.; Shi, Q.; Li, X.; Sun, Y.; Li, M.; Zhao, A.; Peng, X.; Yu, Y. The Vitis yeshanensis U-box E3 ubiquitin ligase VyPUB21 enhances resistance to powdery mildew by targeting degradation of NIM1-interacting (NIMIN) protein. Plant Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conrath, U. Systemic acquired resistance. Plant Signal. Behave. 2006, 1, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Wang, W. Recent advances in synthetic chemical inducers of plant immunity. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 425103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoshru, B.; Mitra, D.; Joshi, K.; Adhikari, P.; Rion, M.S.I.; Fadiji, A.E.; Alizadeh, M.; Priyadarshini, A.; Senapati, A.; Sarikhani, M.R. Decrypting the multi-functional biological activators and inducers of defense responses against biotic stresses in plants. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Wang, W.; Zeng, S.; Chen, Z.; Yang, A.; Shi, J.; Zhao, X.; Song, B. Label-free quantitative proteomics analysis of Cytosinpeptidemycin responses in southern rice black-streaked dwarf virus-infected rice. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2018, 147, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadass, M.; Thiagarajan, P. Current trends and emerging technologies for pest control management of rice (Oryza sativa) plants. Environ. Biotech. 2021, 4, 125–179. [Google Scholar]
- Iwai, T.; Seo, S.; Mitsuhara, I.; Ohashi, Y. Probenazole-induced accumulation of salicylic acid confers resistance to Magnaporthe grisea in adult rice plants. Plant Cell Physiol. 2007, 48, 915–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokotani, N.; Hasegawa, Y.; Kouzai, Y.; Hirakawa, H.; Isobe, S. Transcriptome analysis of tomato plants following salicylic acid-induced immunity against Clavibacter michiganensis ssp. michiganensis. Plant Biotechnol. 2023, 40, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; He, H.; Wang, R.; Shen, Z.; Wu, Z.; Song, R.; Song, B. Synthesis, bioactivities, and antibacterial mechanism of 5-(Thioether)-N-phenyl/benzyl-1, 3, 4-oxadiazole-2-carboxamide/amine derivatives. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 1444–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, G.; Chen, Z.; Cai, X. J.; Song, B. A.; Bhadury, P. S.; Yang, S.; Jin, L. H.; Xue, W.; Hu, D. Y.; Zeng, S. Synthesis and antiviral activity of novel pyrazole derivatives containing oxime esters group. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 9699–9707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Guo, R.; Tang, Y.; Guo, S.; Xu, Y.; Sun, W.; Tu, H.; Wu, J. Plant antiviral compounds containing pyrazolo [3, 4-d] pyrimidine based on the systemin receptor model. Arab. J. Chem. 2024, 105849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shetehy, M.; Moradi, A.; Maceroni, M.; Reinhardt, D.; Petri-Fink, A.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B.; Mauch, F.; Schwab, F. Silica nanoparticles enhance disease resistance in Arabidopsis thaliana plants. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, P.; Huang, M.; Hu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, P.; Chen, S.; Zhang, D.; Cao, S.; Zhu, W.A. Ralstonia solanacearum effector targets TGA transcription factors to subvert salicylic acid signaling. Plant Cell 2022, 34, 1666–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhang, M.; Ma, Q.; Wang, X.; Ma, Z. The G-protein α subunit GhGPA positively regulates Gossypium hirsutum resistance to Verticillium dahliae via induction of SA and JA signaling pathways and ROS accumulation. Crop J. 2021, 9, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, S.H.; Anand, S.; Singh, B.; Bohra, A.; Joshi, R. WRKY transcription factors and plant defense responses: latest discoveries and future prospects. Plant Cell Rep. 2021, 40, 1071–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, M.; Cheng, C. High-throughput proteomics: a methodological mini-review. Lab. Invest. 2022, 102, 1170–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Wang, J.; Lv, H.; Peng, Q.; Schreiner, M.; Baldermann, S.; Lin, Z. Integrated proteomic and metabolomic analyses reveal the importance of aroma precursor accumulation and storage in methyl jasmonate-primed tea leaves. Hortic. Res. 2021, 8, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovelace, A.H.; Dorhmi, S.; Hulin, M.T.; Li, Y.; Mansfield, J.W.; Ma, W. Effector identification in plant pathogens. Phytopathology 2023, 113, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.N.; Li, Y.T.; Wu, Y.Z.; Li, T.; Geng, R.; Cao, J.; Zhang, W.; Tan, X.L. Plant disease resistance-related signaling pathways: recent progress and future prospects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 16200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, T.; Wang, W.; Yang, B.; Shen, L.; Sun, T.; Gao, S.J.; Zhang, S. Pathogenesis related-1 proteins in plant defense: regulation and functional diversity. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2024, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Clinton, M.; Qi, G.; Wang, D.; Liu, F.; Fu, Z.Q. Reprogramming and remodeling: transcriptional and epigenetic regulation of salicylic acid-mediated plant defense. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 5256–5268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altmann, M.; Altmann, S.; Rodriguez, P.A.; Weller, B.; Elorduy Vergara, L.; Palme, J.; Marín-De la Rosa, N.; Sauer, M.; Wenig, M.; Villaécija-Aguilar, J.A. Extensive signal integration by the phytohormone protein network. Nature 2020, 583, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.M.; Zhang, Y. Plant immunity: danger perception and signaling. Cell 2020, 181, 978–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.; Yan, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, J.; Liu, T.; Xie, X.; Li, X. Research on the interaction mechanism between α mino-phosphonate derivative QR and harpin-binding protein 1 in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) plants. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 621875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Showalter, A.M. Structure and function of plant cell wall proteins. Plant Cell 1993, 5, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghouili, E.; Sassi, K.; Hidri, Y.; M’Hamed, H.C.; Somenahally, A.; Xue, Q.; Jebara, M.; Nefissi Ouertani, R.; Riahi, J.; de Oliveira, A.C. Effects of date palm waste compost application on root proteome changes of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Plants 2023, 12, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.; Wu, Z.; Li, J.; Ding, Y.; Chen, S.; Li, X. Plant protection against viruses: an integrated review of plant immunity agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kvitko, B.H.; Collmer, A. Discovery of the Hrp type III secretion system in phytopathogenic bacteria: how investigation of hypersensitive cell death in plants led to a novel protein injector system and a world of inter-organismal molecular interactions within plant cells. Phytopathology 2023, 113, 626–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Ma, W.; Li, X. Characteristics, roles and applications of proteinaceous elicitors from pathogens in plant immunity. Life 2023, 13, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakata, N.; Fujikawa, T.; Uke, A.; Ishiga, T.; Ichinose, Y.; Ishiga, Y. HexR transcription factor contributes to Pseudomonas cannabina pv. alisalensis virulence by coordinating type three secretion system genes. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Cao, J.; Cai, X.; Wang, J.; Kong, F.; Wang, D.; Wang, J. Antagonistic activity of volatile organic compounds produced by acid-tolerant Pseudomonas protegens CLP-6 as biological fumigants to control tobacco bacterial wilt caused by Ralstonia solanacearum. Appl. Environ. Microb.. 2023, 89, e01892–01822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Kang, I.J.; Lee, S. Current status and future prospects in genomic research and breeding for resistance to Xanthomonas citri pv. Glycines in soybean. Agronomy 2023, 13, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, P.; Li, N.; Li, B.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Meng, X.; Li, B.; Cao, K.; Hu, T. An endophytic strain Bacillus velezensis JZ51 controlled pink mold rot of postharvest apple fruit via antagonistic action and disease resistance induction. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2024, 210, 112793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Hameed, A.; Muhae-Ud-Din, G.; Ikhlaq, M.; Ashfaq, M.; Atiq, M.; Ali, F.; Zia, Z.U.; Naqvi, S.A.H.; Wang, Y. Citrus canker: a persistent threat to the worldwide citrus industry an analysis. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karačić, V.; Miljaković, D.; Marinković, J.; Ignjatov, M.; Milošević, D.; Tamindžić, G.; Ivanović, M. Bacillus species: excellent biocontrol agents against tomato diseases. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.H.; Ajaharuddin, S.M.; Rahman, S.S.; Saha, S.; Goswami, S.; Islam, S.; Barik, S.; Hossain, A. Latef, A.A.H.A. Citrus lemon and stressful conditions. In Medicinal plant responses to stressful conditions, 1st Edition; CRCPress: Boca Raton, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Ma, H.; Ren, X.; Shi, H.; Liu, Z.; Liang, J. Exogenous glucose reduces the incidence of black rot disease in apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.) by regulating energy metabolism and ROS. Sci. Hortic-Amsterdam. [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Chen, Y.; Cai, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhao, X. Effects of harpin and carbendazim on antioxidant accumulation in young jujube leaves. Open Chem. 2023, 21, 20220284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delmas, C.E.; Bancal, M.O.; Leyronas, C.; Robin, M.H.; Vidal, T.; Launay, M. Monitoring the phenology of plant pathogenic fungi: why and how? Biol. Rev. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Yue, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lu, C.; Yin, Z.; Li, Y.; Ding, X. Plant biostimulant as an environmentally friendly alternative to modern agriculture. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 5107–5121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.; Gdanetz, K.; Outwater, C.A.; Slack, S.M.; Sundin, G.W. Evaluation of plant defense inducers and plant growth regulators for fire blight management using transcriptome studies and field assessments. Phytopathology 2023, 113, 2152–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khadiri, M.; Boubaker, H.; Lahmamsi, H.; Taoussi, M.; Ezzouggari, R.; Askarne, L.; Farhaoui, A.; Barka, E.A.; Lahlali, R. Challenges in apple preservation: Fungicide resistance and emerging biocontrols. Physiol. Mol. Plant P. 2023, 102205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, Q.; Liu, H.; Cheng, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J. Two salivary proteins Sm10 and SmC002 from grain aphid Sitobion miscanthi modulate wheat defense and enhance aphid performance. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1104275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ang, M.C.Y.; Saju, J.M.; Porter, T.K.; Mohaideen, S.; Sarangapani, S.; Khong, D.T.; Wang, S.; Cui, J.; Loh, S.I.; Singh, G.P. Decoding early stress signaling waves in living plants using nanosensor multiplexing. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kongala, S.I.; Mamidala, P. Harpin-loaded chitosan nanoparticles induced defense responses in tobacco. Carbohydr. Polym. Tech. 2023, 5, 100293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Feng, S.; Tang, S.; Dong, P.; Li, Z. Biological control of potato late blight with a combination of Streptomyces strains and biochar. Biol. Control. 2023, 183, 105248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, N.; Yamaguchi, T.; Kameda, Y.; Matsui, K. Effect of validamycins on glycohydrolases of Rhizoctonia solani. J. Antibiot. 1987, 40, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Ma, X.; Sun, T.; Zhu, Q.-H.; Feng, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, F.; Zhang, X.; Sun, J.; Li, Y. VdPT1 encoding a neutral trehalase of Verticillium dahliae is required for growth and virulence of the pathogen. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 25, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asim, M.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Guo, M.; Khan, R.; Wang, X.L.; Hussain, Q.; Shi, Y. Leaf senescence attributes: the novel and emerging role of sugars as signaling molecules and the overlap of sugars and hormones signaling nodes. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2023, 43, 1092–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Yue, Z.; Wang, J.; Dou, T.; Chen, T.; Li, J.; Dai, H.; Yu, J. Study of cabbage antioxidant system response on early infection stage of Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris. BMC Plant Bio. 2024, 24, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, F.; Ma, J.; Peng, M.; Xi, C.; Chang, S.; Yang, Y.; Tian, S.; Zhou, B.; Liu, T. Lactic acid induced defense responses in tobacco against Phytophthora nicotianae. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 9338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.M.; El-Sappah, A.H.; Ali, H.M.; Zandi, P.; Huang, Q.; Soaud, S.A.; Alazizi, E.M.; Wafa, H.A.; Hossain, M.A.; Liang, Y. Pathogenesis-related proteins (PRs) countering environmental stress in plants: a review. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2023, 160, 414–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.J.; Lim, G.H. Salicylic acid and mobile regulators of systemic immunity in plants: Transport and metabolism. Plants 2023, 12, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, M.; Sharkhuu, N.; Zhang, Y.; Kadota, T.; Ohata, T. Ground thermal and moisture conditions at the southern boundary of discontinuous permafrost, Mongolia. Permafrost Periglac. 2005, 16, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Hu, D.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Zu, G.; Song, B. First discovery of novel cytosine derivatives containing a sulfonamide moiety as potential antiviral agents. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 6026–6036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, X.; Hu, D.; Li, P.; Wu, J.; Chen, X.; Xue, W.; Song, B. Design, synthesis, antiviral activity and three-dimensional quantitative structure activity relationship study of novel 1, 4-pentadien-3-one derivatives containing the 1, 3, 4-oxadiazole moiety. Pest Manag. Sci. 2016, 72, 534–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Liu, Q.; Li, S.; Zeng, L.; Yao, J.; Li, H.; Shen, Z.; Lu, F.; Wu, Z.; Song, B. Design, synthesis, antibacterial activity, and mechanisms of novel benzofuran derivatives containing disulfide moieties. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 10195–10205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, L.; Wei, C.; Shen, Z.; He, H.; Yang, X.; Shi, S.; Hu, D.; Song, B. Splicing indoles and 4, 5-dihydro-1 H-pyrazoline structure gave birth to novel antiviral agents: Design, synthesis, and mechanism study. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 7239–7249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Song, R.; Wu, S.; Cai, D.; Wu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Hu, D.; Song, B. Discovery of pyrido [1, 2-a] pyrimidinone mesoionic compounds incorporating a dithioacetal moiety as novel potential insecticidal agents. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 15136–15144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, Q.T.; Ueda, K.; Kihara, J.; Ueno, M. Induction of resistance in rice against Magnaporthe oryzae by culture filtrates of Biscogniauxia sp. O821. J. Phytopathol. 2016, 164, 990–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, E.K.; Ghoniem, K.E.; Badr, E.S.; Emeran, A.A. The potential of dimetindene maleate inducing resistance to blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae through activating the salicylic acid signaling pathway in rice plants. Pest Manag. Sci. 2022, 78, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Asami, T. Chemical regulators of plant hormones and their applications in basic research and agriculture. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2018, 82, 1265–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korbecka-Glinka, G.; Piekarska, K.; Wiśniewska-Wrona, M. The use of carbohydrate biopolymers in plant protection against pathogenic fungi. Polymers 2022, 14, 2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakashita, H.; Yasuda, M.; Nitta, T.; Asami, T.; Fujioka, S.; Arai, Y.; Sekimata, K.; Takatsuto, S.; Yamaguchi, I.; Yoshida, S.; Yoshida, S. Brassinosteroid functions in a broad range of disease resistance in tobacco and rice. Plant J. 2003, 33, 887–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, B.; Guo, Q.; Shi, L.; He, M.; Qin, Z.; Li, L.; He, P.; Wang, Z.; Hu, D. A time-course proteomic analysis of rice triggered by plant activator BTH. J. Plant Growth. Regul. /: 392–409. https, 1007. [Google Scholar]
- Midoh, N.; Iwata, M. Cloning and characterization of a probenazole-inducible gene for an intracellular pathogenesis-related protein in rice. Plant Cell Physiol. 1996, 37, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshioka, K.; Nakashita, H.; Klessig, D.F.; Yamaguchi, I. Probenazole induces systemic acquired resistance in Arabidopsis thaliana with a novel type of action. Plant J. 2001, 25, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Long, S.; Liu, K.; Zhu, T.; Gong, J.; Gao, S.; Wang, R.; Zhang, L.; Liu, T.; Xu, Y. Paclobutrazol ameliorates low-light-induced damage by improving photosynthesis, antioxidant defense system, and regulating hormone levels in tall fescue. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osés-Ruiz, M.; Cruz-Mireles, N.; Martin-Urdiroz, M.; Soanes, D.M.; Eseola, A.B.; Tang, B.; Derbyshire, P.; Nielsen, M.; Cheema, J.; Were, V. Appressorium-mediated plant infection by Magnaporthe oryzae is regulated by a Pmk1-dependent hierarchical transcriptional network. Nat microbiol. 2021, 6, 1383–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyakov, Y.T.; Dzhavakhiya, V.; Korpela, T. Molecular basis of plant immunization. Compr. Mol. Phytopathol Elsevier 2007, 423–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bektas, Y.; Eulgem, T. Synthetic plant defense elicitors. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 5, 122149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuteja, N.; Gill, S.S.; Trivedi, P.K.; Asif, M.H.; Nath, P. Plant growth regulators and their role in stress tolerance. Plant Nutr. Abiotic Stress Toler. I Plant Stress 2010, 4, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.T.; Kim, S.G.; Kang, Y.H.; Wang, Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Yi, N.; Kim, J.K.; Rakwal, R.; Koh, H.J.; Kang, K.Y. Proteomics analysis of rice lesion mimic mutant (spl1) reveals tightly localized probenazole-induced protein (PBZ1) in cells undergoing programmed cell death. J. Proteome Res. 2008, 2008. 7, 1750–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergne, E.; Ballini, E.; Marques, S.; Sidi Mammar, B.; Droc, G.; Gaillard, S.; Bourot, S.; DeRose, R.; Tharreau, D.; Nottéghem, J.L. Early and specific gene expression triggered by rice resistance gene Pi33 in response to infection by ACE1 avirulent blast fungus. New Phytol. 2007, 174, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakab, G.; Cottier, V.; Toquin, V.; Rigoli, G.; Zimmerli, L.; Métraux, J.P.; Mauch-Mani, B. β-Aminobutyric acid-induced resistance in plants. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2001, 107, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, Y.; Vaknin, M.; Mauch-Mani, B. BABA-induced resistance: milestones along a 55-year journey. Phytoparasitica 2016, 44, 513–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enebe, M.C.; Babalola, O.O. The impact of microbes in the orchestration of plants’ resistance to biotic stress: a disease management approach. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutt, J.R.; Harpster, M.H.; Dixon, D.C.; Carr, J.P.; Dunsmuir, P.; Klessig, D.F. Disease response to tobacco mosaic virus in transgenic tobacco plants that constitutively express the pathogenesis-related PR1b gene. Virology 1989, 173, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, D.P.; Maurya, S.; Yerasu, S.R.; Chaurasia, A.; Prabha, R.; Shukla, R.; Satnami, L.; Rai, N.; Behera, T.K. Proteomics analysis of wild and cultivated tomato species challenged with Alternaria solani unveiled differential tolerance mechanisms. Research Square 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehra, A.; Mazumdar-Leighton, S. The sublime art of war: Herbivore-induced plant volatiles. Resonance 2024, 29, 29–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odenbreit, S.; Kavermann, H.; Püls, J.; Haas, R. CagA tyrosine phosphorylation and interleukin-8 induction by Helicobacter pylori are independent from alpAB, HopZ and bab group outer membrane proteins. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2002, 292, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouzai, Y.; Kimura, M.; Yamanaka, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Matsui, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Ichinose, Y.; Toyoda, K.; Onda, Y.; Mochida, K. Expression profiling of marker genes responsive to the defence-associated phytohormones salicylic acid, jasmonic acid and ethylene in Brachypodium distachyon. BMC Plant Biol. 2016, 16, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Lu, M.; Wu, Y.; Jing, T.; Zhao, M.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, Y.; Wang, J.; Gao, T. Salicylic acid carboxyl glucosyltransferase UGT87E7 regulates disease resistance in Camellia sinensis. Plant Physiol. 2022, 188, 1507–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dean, J.V.; Delaney, S.P. Metabolism of salicylic acid in wild-type, ugt74f1 and ugt74f2 glucosyltransferase mutants of Arabidopsis thaliana. Physiol. Plantarum 2008, 132, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Kwon, C.S.; Woo, J.Y.; Lee, G.J.; Kim, Y.J.; Paek, K.H. Suppression of UDP-glycosyltransferase-coding Arabidopsis thaliana UGT74E2 gene expression leads to increased resistance to Psuedomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000 infection. Plant Pathol. J. 2011, 27, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhao, F.; Jiang, L.; Chen, C.; Wu, L.; Liu, Z. Different pathogen defense strategies in Arabidopsis: more than pathogen recognition. Cells 2018, 7, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noutoshi, Y.; Okazaki, M.; Kida, T.; Nishina, Y.; Morishita, Y.; Ogawa, T.; Suzuki, H.; Shibata, D.; Jikumaru, Y.; Hanada, A. Novel plant immune-priming compounds identified via high-throughput chemical screening target salicylic acid glucosyltransferases in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 3795–3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, I.A.; Chen, H.; Chen, J.; Chang, M.; Li, M.; Liu, F.; Fu, Z.Q. Novel salicylic acid analogs induce a potent defense response in Arabidopsis thaliana. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fürstenberg-Hägg, J.; Zagrobelny, M.; Bak, S. Plant defense against insect herbivores. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 10242–10297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Künstler, A.; Gullner, G.; Ádám, A.L.; Kolozsváriné Nagy, J.; Király, L. The versatile roles of sulfur-containing biomolecules in plant defense-a road to disease resistance. Plants 2020, 9, 1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, M.Y.; Mehraj, S.; Rather, R.; Rani, S.; Hajam, O.; Ganie, N.; Mir, M.; Baqual, M.; Kamili, A.S. Systemic acquired resistance (SAR): A novel strategy for plant protection with reference to mulberry. Int. J. Chem. Stud. 2018, 6, 1184–1192. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández, J.A.; Diaz-Vivancos, P.; Barba-Espín, G.; Clemente-Moreno, M.J. On the role of salicylic acid in plant responses to environmental stresses. Salicylic acid:a multifaceted hormone 2017, 17–34. [CrossRef]
- Reitsma, J.M.; Liu, X.; Reichermeier, K.M.; Moradian, A.; Sweredoski, M.J.; Hess, S.; Deshaies, R.J. Composition and regulation of the cellular repertoire of SCF ubiquitin ligases. Cell 2017, 171, 1326–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osés-Ruiz, M.; Cruz-Mireles, N.; Martin-Urdiroz, M.; Soanes, D.M.; Eseola, A.B.; Tang, B.; Derbyshire, P.; Nielsen, M.; Cheema, J.; Were, V. Appressorium-mediated plant infection by Magnaporthe oryzae is regulated by a Pmk1-dependent hierarchical transcriptional network. Nat. Microbiol. 2021, 6, 1383–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salotti, I.; Liang, Y.J.; Ji, T.; Rossi, V. Development of a model for Colletotrichum diseases with calibration for phylogenetic clades on different host plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1069092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Rad, U.; Mueller, M.J.; Durner, J. Evaluation of natural and synthetic stimulants of plant immunity by microarray technology. New Phytol. 2005, 65, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, B.; Mandal, S.; Csinos, A.; Martinez, N.; Culbreath, A.; Pappu, H. Biological and molecular analyses of the acibenzolar-S-methyl-induced systemic acquired resistance in flue-cured tobacco against Tomato spotted wilt virus. Phytopathology 2008, 98, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gozzo, F.; Faoro, F. Systemic acquired resistance (50 years after discovery): moving from the lab to the field. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 12473–12491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, D.L. The efficacy of acibenzolar-S-methyl, an inducer of systemic acquired resistance, against bacterial and fungal diseases of tobacco. Crop Prot. 1999, 18, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frąckowiak, P.; Pospieszny, H.; Smiglak, M.; Obrępalska-Stęplowska, A. Assessment of the efficacy and mode of action of benzo (1, 2, 3)-thiadiazole-7-carbothioic acid s-methyl ester (bth) and its derivatives in plant protection against viral disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gozzo, F. Systemic acquired resistance in crop protection: from nature to a chemical approach. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 4487–4503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidhyasekaran, P. ; Bioengineering and molecular manipulation of salicylic acid signaling system to activate plant immune responses for crop disease management. Plant innate immunity signals and signaling systems: bioengineering and molecular manipulation for crop disease management.; Springer: Dordrecht, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, K.; Desveaux, D. Message in a bottle: chemical biology of induced disease resistance in plants. Plant Pathology J. 2008, 24, 245–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, S.; Xi, D.; Yuan, S.; Wang, J.; Xu, M.; Lin, H. Interaction between Cucumber mosaic virus and Turnip crinkle virus in Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Phytopathol. 2010, 158, 833–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Tang, C.; Wang, Q.; Su, Y.; Zhang, Q. Synergistic effects of oligochitosan and pyraclostrobin in controlling leaf spot disease in Pseudostellaria heterophylla. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, L.; Ying, S.; Yu, C. Cucumber PGIP2 is involved in resistance to gray mold disease. Gene 2024, 923, 148588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Chu, R.; Shah, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X. Antagonistic effect of Bacillus and Pseudomonas combinations against Fusarium oxysporum and their effect on disease resistance and growth promotion in watermelon. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2024, 135, lxae074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, B.; Qu, Z.; Mehmood, M.A.; Xie, J.; Cheng, J.; Fu, Y.; Jiang, D. Schizotrophic Sclerotinia sclerotiorum-mediated root and rhizosphere microbiome alterations activate growth and disease resistance in wheat. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e00981–00923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, Q.; Pan, Z.; Zhang, C.; Yu, H.; Zhang, M.; Gu, X.; Zhang, X.; Pan, H.; Zhang, H. Colonization by Klebsiella variicola FH-1 stimulates soybean growth and alleviates the stress of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. J. Integr. Agr. 2023, 22, 2729–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinari, S. Systemic acquired resistance activation in solanaceous crops as a management strategy against root-knot nematodes. Pest Manag. Sci. 2016, 72, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chicowski, A.S.; Qi, M.; Variz, H.; Bredow, M.; Montes-Serey, C.; Caiazza, F.; Dong, H.; Margets, A.C.; Mejias, J.; Walley, J. A soybean rust effector protease suppresses host immunity and cleaves a 3-deoxy-7-phosphoheptulonate synthase. Plant biol. bioRxiv. 2023, 556260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Monem, M.O.; Azeiz, A.Z.A.; Khalil, R.; Elsayed, N.A.; Hassan, M.G. Effect of rhizosphere bacteria to reduce Fusarium infection in tomato plant. J. Basic Environ. Sci. 2024, 11, 166–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbey, J.; Jose, S.; Percival, D.; Jaakola, L.; Asiedu, S.K. Modulation of defense genes and phenolic compounds in wild blueberry in response to Botrytis cinerea under field conditions. BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burketová, L.; Štillerová, K.; Feltlová, M. Immunohistological localization of chitinase and β-1, 3-glucanase in rhizomania-diseased and benzothiadiazole treated sugar beet roots. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2003, 63, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawton, K.A.; Friedrich, L.; Hunt, M.; Weymann, K.; Delaney, T.; Kessmann, H.; Staub, T.; Ryals, J. Benzothiadiazole induces disease resistance in Arabidopsis thaliana by activation of the systemic acquired resistance signal transduction pathway. Plant J. 1996, 10, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Li, M.; Ren, X.; Wang, C.; Sun, X.; Sun, M.; Yu, X.; Wang, X. Enhancement of broad-spectrum disease resistance in wheat through key genes involved in systemic acquired resistance. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1355178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohler, A.; Schwindling, S.; Conrath, U. Benzothiadiazole-induced priming for potentiated responses to pathogen infection, wounding, and infiltration of water into leaves requires the NPR1/NIM1 gene in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol. 2002, 128, 1046–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Fukuzawa, N.; Hyodo, A.; Kim, H.; Mashiyama, S.; Ogihara, T.; Yoshioka, H.; Matsuura, H.; Masuta, C.; Matsumura, T. Role of salicylic acid glucosyltransferase in balancing growth and defence for optimum plant fitness. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2020, 21, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimono, M.; Koga, H.; Akagi, A.; Hayashi, N.; Goto, S.; Sawada, M.; Kurihara, T.; Matsushita, A.; Sugano, S.; Jiang, C.J. Rice WRKY45 plays important roles in fungal and bacterial disease resistance. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2012, 13, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toquin, V.; Braun, C.A.; Sirven, C.; Assmann, L.; Sawada, H. Host defense inducers. Research & Development Crop Science, Small Molecules, Pest ControlChemistry, Crop Prot. Compounds., third Edition Insecticides.; Wiley-VCH: Germany, 2019, 2, 959–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, R.; Sabatini, B.L.; Svoboda, K. Plasticity of calcium channels in dendritic spines. Nat. Neurosci. 2003, 6, 948–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Daele, J.; Blancquaert, D.; Kiekens, F.; Van Der Straeten, D.; Lambert, W.E.; Stove, C.P. Degradation and interconversion of plant pteridines during sample preparation and ultra-high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2016, 194, 1189–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakashita, H.; Yoshioka, K.; Yasuda, M.; Nitta, T.; Arai, Y.; Yoshida, S.; Yamaguchi, I. Probenazole induces systemic acquired resistance in tobacco through salicylic acid accumulation. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2002, 61, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saint-Macary, M.E.; Barbisan, C.; Gagey, M.J.; Frelin, O.; Beffa, R.; Lebrun, M.H.; Droux, M. Methionine biosynthesis is essential for infection in the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0111108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashita, H.; Yasuda, M.; Nishioka, M.; Hasegawa, S.; Arai, Y.; Uramoto, M.; Yoshida, S.; Yamaguchi, I. Chloroisonicotinamide derivative induces a broad range of disease resistance in rice and tobacco. Plant Cell physiol. 2002, 43, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawrath, C.; Métraux, J.P. Salicylic acid induction–deficient mutants of Arabidopsis thaliana express PR-2 and PR-5 and accumulate high levels of camalexin after pathogen inoculation. Plant Cell. 1999, 11, 1393–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pokotylo, I.; Kravets, V.; Ruelland, E. Salicylic acid binding proteins (SABPs): the hidden forefront of salicylic acid signalling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandía, N.P.; Matsuhiro, B. Characterization of a fucoidan from Lessonia vadosa (Phaeophyta) and its anticoagulant and elicitor properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2008, 42, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Wei, H.; Yao, K.; Wu, H.; Huang, T.; Han, M.; Su, T.; Cao, F. Integrative omics studies revealed synergistic link between sucrose metabolic isogenes and carbohydrates in poplar roots infected by Fusarium wilt. Plant Mol. Biol. 2024, 114, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sharkawy, E.E.; ElSharawy, A.A. The Influence of resistance chemical inducers against anthracnose on cucumber and pepper plants. Catrina 2024, 29, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thepbandit, W.; Athinuwat, D. Rhizosphere microorganisms supply availability of soil nutrients and induce plant defense. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Y.; Huang, S.; Zhao, C.; Jiang, Z.; Gu, Y.; Xiao, J.; Wu, Y.; Ying, R. Decipher soil resistance and virulence gene risks in conventional and organic farming systems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 133788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dass, A.; Venkatesh, P.; Choudhary, A.K.; Upadhyay, P.K.; Chandrashekar, A.B.; Francaviglia, R.; Sannagoudar, M.S.; Rangappa, U.M.; Singh, V.K.; Harish, M.N. Soil moisture dynamics, rooting traits, crop and water productivity of wheat under different tillage, irrigation and nutrition conditions. Farming System 2024, 2, 100087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Figueroa, J.; Gómez-Rojas, A.; Escobar, C. Functional studies of plant transcription factors and their relevance in the plant root-knot nematode interaction. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1370532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riseh, R.S.; Vazvani, M.G.; Vatankhah, M.; Kennedy, J.F. Chitin-induced disease resistance in plants: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 131105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, R.M.; Fouad, M.S. Approaches to antioxidant defence system: An overview of coping mechanism against lithium/nickel exposure in plants. Lithium and Nickel Contamination in Plants Environ, 2024, 95–138. [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Zhao, X.; Bai, J.; Lv, W.; Chen, Q.; Hu, J.; Liu, G.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, H.; Zhao, M. Transcriptome analysis of genes involved in the pathogenesis mechanism of potato virus Y in potato cultivar YouJin. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1353814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berlanga, D.J.; Molina, A.; Torres, M.Á. Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase 1 controls broad spectrum disease resistance in Arabidopsis thaliana through diverse mechanisms of immune activation. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1374194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, S.H.; Khan, I.U.; Noh, B.; Noh, Y.S. Genomic overview of INA-induced NPR1 targeting and transcriptional cascades in Arabidopsis. Nucleic Aci. Res. 2024, gkae019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amokrane, L.; Pokotylo, I.; Acket, S.; Ducloy, A.; Troncoso-Ponce, A.; Cacas, J.L.; Ruelland, E. Phospholipid signaling in crop plants: a field to explore. Plants 2024, 13, 1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsubata, K.; Kuroda, K.; Yamamoto, Y.; Yasokawa, N. Development of a novel plant activator for rice diseases, tiadinil. J. Pestic. Sci. 2006, 31, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Li, C.Y.; Wang, X.M.; Yang, Y.H.; Zhu, H.L. 1, 3, 4-Thiadiazole: synthesis, reactions, and applications in medicinal, agricultural, and materials chemistry. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 5572–5610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, K.; Ogino, A.; Yamada, K.; Sonoda, R. Induction of disease resistance in tea (Camellia sinensis L.) by plant activators. JARQ-Jpn. Agr. Res. Q. 2010, 44, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, T.; Ishiwari, H. Tiadinil, a plant activator of systemic acquired resistance, boosts the production of herbivore-induced plant volatiles that attract the predatory mite Neoseiulus womersleyi in the tea plant Camellia sinensis. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2012, 58, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, X.; Li, K.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, N.; Gao, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Fan, Z. Plant defense responses to a novel plant elicitor candidate LY5-24-2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasuda, R.; Harvey, C.D.; Zhong, H.; Sobczyk, A.; Van Aelst, L.; Svoboda, K. Supersensitive ras activation in dendrites and spines revealed by two-photon fluorescence lifetime imaging. Nat. Neurosci. 2006, 9, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakashita, H. Studies on regulation of plant physiology by pesticides. J. Pestic. Sci. 2021, 46, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasuda, M.; Nishioka, M.; Nakashita, H.; Yamaguchi, I.; Yoshida, S. Pyrazolecarboxylic acid derivative induces systemic acquired resistance in tobacco. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2003, 67, 2614–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishioka, M.; Nakashita, H.; Yasuda, M.; Yoshida, S.; Yamaguchi, I. Induction of resistance against rice bacterial leaf blight by 3-Chloro-1-methyl-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxylic acid. J. Pestic. Sci. 2005, 30, 47–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandersson, E.; Mulugeta, T.; Lankinen, Å.; Liljeroth, E.; Andreasson, E. Plant resistance inducers against pathogens in Solanaceae species from molecular mechanisms to field application. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, S.; Roychowdhury, R.; Ray, S.; Hada, A.; Kumar, A.; Sarker, U.; Aftab, T.; Das, R. Salicylic acid (SA)-mediated plant immunity against biotic stresses: an insight on molecular components and signaling mechanism. Plant Stress 2024, 100427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, T.A.; Taha, N.A.; Taher, D.I.; Metwaly, M.M.; El-Beltagi, H.S.; Rezk, A.A.; El-Ganainy, S.M.; Shehata, W.F.; El-Ramady, H.R.; Bayoumi, Y.A. Paclobutrazol improves the quality of tomato seedlings to be resistant to Alternaria solani blight disease: biochemical and histological perspectives. Plants 2022, 11, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.; Xi, D.H.; Yuan, S.; Xu, F.; Zhang, D.W.; Lin, H.H. Salicylic acid and jasmonic acid are essential for systemic resistance against tobacco mosaic virus in Nicotiana benthamiana. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact 2014, 27, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mur, L.A.; Naylor, G.; Warner, S.A.; Sugars, J.M.; White, R.F.; Draper, J. Salicylic acid potentiates defence gene expression in tissue exhibiting acquired resistance to pathogen attack. Plant J. 1996, 9, 559–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, B.; Zhang, Z.; Qin, G.; Chen, T.; Tian, S. Molecular mechanisms underlying multi-level defense responses of horticultural crops to fungal pathogens. Hortic. Res. 2022, 9, uhac066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamatham, S.; Neela, K.B.; Pasupulati, A.K.; Pallu, R.; Singh, S.S.; Gudipalli, P. Benzoylsalicylic acid isolated from seed coats of Givotia rottleriformis induces systemic acquired resistance in tobacco and Arabidopsis thaliana. Phytochemistry 2016, 126, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamatham, S.; Pallu, R.; Pasupulati, A.K.; Singh, S.S.; Gudipalli, P. Benzoylsalicylic acid derivatives as defense activators in tobacco and Arabidopsis thaliana. Phytochemistry 2017, 143, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Z.; Guo, H.; Shen, S.; Yu, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhu, E.; Zhang, P.; Song, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, K. Generation of the salicylic acid deficient Arabidopsis thaliana via a synthetic salicylic acid hydroxylase expression cassette. Plant Methods 2022, 18, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Chen, Z. Salicylic acid induces rapid inhibition of mitochondrial electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation in tobacco cells. Plant Physiol. 1999, 120, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.F. Acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) induces resistance to tobacco mosaic virus in tobacco. Virology 1979, 99, 410–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saberi Riseh, R.; Gholizadeh Vazvani, M. Unveiling methods to stimulate plant resistance against pathogens. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) IMR Press: 2024, 29, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bektas, Y.; Rodriguez-Salus, M.; Schroeder, M.; Gomez, A.; Kaloshian, I.; Eulgem, T. The synthetic elicitor DPMP (2, 4-dichloro-6-{(E)-[(3-methoxyphenyl)imino]methyl}phenol) triggers strong immunity in Arabidopsis thaliana and tomato. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, S.-J.; Choi, H.J.; Noh, S.W.; Cecchini, N.M.; Greenberg, J.T.; Jung, H.W. Genetic requirements for infection-specific responses in conferring disease resistance in Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1068438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, I.A.; Chen, H.; Chen, J.; Chang, M.; Li, M.; Liu, F.; Fu, Z.Q. Novel salicylic acid analogs induce a potent defense response in Arabidopsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urban, L.; Lauri, F.; Ben Hdech, D.; Aarrouf, J. Prospects for increasing the efficacy of plant resistance inducers stimulating salicylic acid. Agronomy 2022, 12, 3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoth, C.; Salus, M.S.; Girke, T.; Eulgem, T. The synthetic elicitor 3, 5-dichloroanthranilic acid induces NPR1-dependent and NPR1-independent mechanisms of disease resistance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol. 2009, 150, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Zhou, S.; Yang, D.; Fan, Z. Revealing shared and distinct genes responding to JA and SA signaling in Arabidopsis thaliana by meta-analysis. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 512053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenberg, J.A. A conceptual framework for integrated pest management. Trends Plant Sci. 2017, 22, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, M.P.; Vendeville, B.C.; Schultz-Ela, D.D. Structural dynamics of salt systems. Annu. Rev. Earth Pl. Sc. 1994, 22, 93–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z. Small GTPases: versatile signaling switches in plants. Plant Cell 2002, 14, S375–S388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidhyasekaran, P. Manipulation of reactive oxygen species, redox and nitric oxide signaling systems to activate plant innate immunity for crop disease management. In: plant innate immunity signals and signaling Systems: Bioengineering and molecular manipulation for crop disease management. Springer, 2020, 51–135. [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Chen, X.; Yang, R.; Cheng, J.; Chen, Y.; Joosten, M.H.; Du, Y. The potato StMKK5-StSIPK module enhances resistance to Phytophthora pathogens through activating the salicylic acid and ethylene signalling pathways. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2023, 24, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Loon, L.C.; Rep, M.; Pieterse, C.M. Significance of inducible defense-related proteins in infected plants. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2006, 44, 135–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, J.P.; Lewsey, M.G.; Palukaitis, P. Signaling in induced resistance. Adv. Virus Res. 2010, 76, 57–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza Cândido, E.; Pinto, M.F.S.; Pelegrini, P.B.; Lima, T.B.; Silva, O.N.; Pogue, R.; Grossi-de-Sá, M.F.; Franco, O.L. Plant storage proteins with antimicrobial activity: novel insights into plant defense mechanisms. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 3290–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AbuQamar, S.; Moustafa, K.; Tran, L.S. Mechanisms and strategies of plant defense against Botrytis cinerea. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2017, 37, 262–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeier, J. New insights into the regulation of plant immunity by amino acid metabolic pathways. Plant Cell Environ. 2013, 36, 2085–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Borba, M.C.; Velho, A.C.; de Freitas, M.B.; Holvoet, M.; Maia-Grondard, A.; Baltenweck, R.; Magnin-Robert, M.; Randoux, B.; Hilbert, J.L.; Reignault, P. A laminarin-based formulation protects wheat against Zymoseptoria tritici via direct antifungal activity and elicitation of host defense-related genes. Plant Dis. 2022, 106, 1408–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coqueiro, D.S.O.; de Souza, A.A.; Takita, M.A.; Rodrigues, C.M.; Kishi, L.T.; Machado, M.A. Transcriptional profile of sweet orange in response to chitosan and salicylic acid. BMC Genomics 2015, 16, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, K.; Zhu, X.; Peng, X.; Qin, S. Chitosan antimicrobial and eliciting properties for pest control in agriculture: a review. Agrono. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 35, 569–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiei, Z.; Hosseini, S.; Dehestani, A.; Pirdashti, H.; Beiki, F. Exogenous hexanoic acid induced primary defense responses in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) plants infected with Alternaria Solani. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 295, 110841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djami-Tchatchou, A.T.; Ncube, E.N.; Steenkamp, P.A.; Dubery, I.A. Similar, but different: structurally related azelaic acid and hexanoic acid trigger differential metabolomic and transcriptomic responses in tobacco cells. BMC Plant Biol. 2017, 17, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adigun, O.A.; Nadeem, M.; Pham, T.H.; Jewell, L.E.; Cheema, M.; Thomas, R. Recent advances in bio-chemical, molecular and physiological aspects of membrane lipid derivatives in plant pathology. Plant Cell Environ. 2021, 44, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiadkong, K.; Fauzia, A.N.; Yamaguchi, N.; Ueda, A. Exogenous riboflavin (vitamin B2) application enhances salinity tolerance through the activation of its biosynthesis in rice seedlings under salinity stress. Plant Sci. 2024, 339, 111929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Xu, X.; Xie, J.; Yu, W.; Zhang, S.; Wu, H.; Peng, Y.; Ji, H. P-aminobenzoic acid and vitamin B9 enhance rice defence against sheath blight disease caused by Rhizoctonia solani. Plant Pathol. 2024, 73, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghallab, D.S.; Shawky, E.; Khalifa, A.A.; Ibrahim, R.S. Insights into the molecular mechanisms of spirulina platensis against rheumatoid arthritis through integrative serum pharmacochemistry and network pharmacology analysis. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 103902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, R.O.; Al-Ouqaili, M.T.; Ali, E.; Alhajlah, S.; Kareem, A.H.; Shakir, M.N.; Alasheqi, M.Q.; Mustafa, Y.F.; Alawadi, A.; Alsaalamy, A. lncRNA-microRNA axis in cancer drug resistance: particular focus on signaling pathways. Med. Oncol. 2024, 41, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 243. Reglinski, T.; Havis, N.; Rees, H.J.; de Jong, H. The practical role of induced resistance for crop protection. Phytopathology 2023, 113, 719–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khokhar, M.; Sharma, S.; Gupta, R. Influence of sowing dates on incidence and severity of post flowering stalk rot of maize caused by Fusarium verticillioides. J. Mycol. Plant Pathol. 2014, 44, 205. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, G.; Khosa, J.; Sharma, M.; Meena, O.; Dhatt, A. Phenotypic and molecular characterization of vernalization sensitivity and pre-mature bolting in onion (Allium cepa L.). Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. [CrossRef]
- Giusti, P.; Vendramin, A.; Zusso, M. The penicillin saga: a different tale. Top Italian Scientists Journal 2024, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virk, V.; Deepak, H.; Taneja, K.; Srivastava, R.; Giri, S. Amelioration in nanobiosensors for the control of plant diseases: current status and future challenges. Front. Nanotechnol. 2024; 6, 1310165. [CrossRef]
- Gouveia, C.; Santos, R.B.; Paiva-Silva, C.; Buchholz, G.; Malhó, R.; Figueiredo, A. The pathogenicity of Plasmopara viticola: a review of evolutionary dynamics, infection strategies and effector molecules. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jemil, N.; Besbes, I.; Gharbi, Y.; Triki, M.A.; Cheffi, M.; Manresa, A.; Nasri, M.; Hmidet, N. Bacillus methylotrophicus DCS1: production of different lipopeptide families, In vitro antifungal activity and suppression of Fusarium wilt in tomato plants. Curr. Microbiol. 2024, 81, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, F.M.; Mou, Z. Damage-associated molecular patterns and systemic signaling. Phytopathology 2024, 114, 308–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.M.; El-Sappah, A.H.; Ali, H.M.; Zandi, P.; Huang, Q.; Soaud, S.A.; Alazizi, E.M.Y.; Wafa, H.A.; Hossain, M.A.; Liang, Y. Pathogenesis-related proteins (PRs) countering environmental stress in plants: a review. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2023, 160, 414–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Tang, M.; Xu, X. Mechanism of uptake, accumulation, transport, metabolism and phytotoxic effects of pharmaceuticals and personal care products within plants: a review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 892, 164413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajid, Q.ul. ain.; Elçi, E. Knockdown of orthotospovirus-derived silencing suppressor gene by plant-mediated RNAi approach induces viral resistance in tomato. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2024, 131, 102264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartwright, D.; Langcake, P.; Pryce, R.J.; Leworthy, D.P.; Ride, J.P. Chemical activation of host defence mechanisms as a basis for crop protection. Nature 1977, 267, 511–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Wang, X.; Xu, Y.; Wang, S.; Jiang, X.; Liu, X.; Cui, W.; Wu, Y.; Yan, C.; Liu, H.; et al. The peroxidase gene OsPrx114 activated by OsWRKY50 enhances drought tolerance through ROS scavenging in rice. Plant Physiol. Bioch. 2023, 204, 108138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yang, J.; Liu, M.; Xu, X.; Yang, L.; Liu, X.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, Z. Early molecular events in the interaction between Magnaporthe oryzae and rice. Phytopathol. Res. 2024, 6, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Sharma, A.; Sharma, A.; Kumar, Y.; Sharma, P.; Bhardwaj, R.; Sharma, I. Polyphenol phytoalexins as the determinants of plant disease resistance. In Plant phenolics in biotic stress management; Springer, 2024; 243–274. [CrossRef]
- Rayee, R.; Anh, L.H.; Khanh, T.D.; Xuan, T.D. Potential momilactones in rice stress tolerance and health advantages. Agronomy 2024, 14, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, H.; Legeai, F.; Kageyama, D.; Sugio, A.; Simon, J.C. Genomic insights into spiroplasma endosymbionts that induce male-killing and protective phenotypes in the pea aphid. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2024, 371, fnae027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shikina, E.V.; Kovalevsky, R.A.; Shirkovskaya, A.I.; Toukach, P.V. Prospective bacterial and fungal sources of hyaluronic acid: a review. Comput. Struct. Biotec. 2022, 20, 6214–6236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Lorente, S.E.; Martí-Guillén, J.M.; Pedreño, M.Á.; Almagro, L.; Sabater-Jara, A.B. Higher plant-derived biostimulants: mechanisms of action and their role in mitigating plant abiotic stress. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.; Paul, D.; Kim, E.; Kloepper, J.W. Hyaluronic acid of Streptococcus sp. as a potent elicitor for induction of systemic resistance against plant diseases. World J. Microbio. Biot. 2008, 24, 1153–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, F.; Hossain, M.M.; Kubota, M.; Hyakumachi, M. Elicitation of systemic resistance against the bacterial speck pathogen in Arabidopsis thaliana by culture filtrates of plant growth-promoting fungi. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 2008, 30, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Qiu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Bhandari, D.D.; Zhao, C.; Bautor, J.; Parker, J.E. Antagonism of transcription factor MYC2 by EDS1/PAD4 complexes bolsters salicylic acid defense in Arabidopsis thaliana effector-triggered immunity. Mol. Plant 2018, 11, 1053–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarecka-Boncela, A.; Spychalski, M.; Ptaszek, M.; Włodarek, A.; Smiglak, M.; Kukawka, R. The effect of a new derivative of benzothiadiazole on the reduction of fusariosis and increase in growth and development of tulips. Agriculture 2023, 13, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Qian, X.; Qian, Z.; Tian, W.; Zhong, J. Novel, unnatural benzo-1, 2, 3-thiadiazole-7-carboxylate elicitors of taxoid biosynthesis. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 8793–8798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Song, F.; Zheng, Z. OsBISAMT1, a gene encoding S-adenosyl-L-methionine: salicylic acid carboxyl methyltransferase, is differentially expressed in rice defense responses. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2006, 33, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Q.S.; Zhao, Z.J.; Zhu, W.P.; Xu, Y.F.; Qian, X.H. Synthesis and biological activity of novel benzo-1, 2, 3-thiadiazole carboxylic ester derivatives. Chin. J. Pestic. Sci.. 2010, 12, 499–502. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, X.; Hu, D.; Wang, Y.; Yu, L.; Song, B. Novel trans-ferulic acid derivatives containing a chalcone moiety as potential activator for plant resistance induction. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 4367–4377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, C.M.; Hu, C.H.; Reddy, M.; Kloepper, J.W. Different signaling pathways of induced resistance by rhizobacteria in Arabidopsis thaliana against two pathovars of Pseudomonas syringae. New Phytol. 2003, 160, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, T.J.; Lu, Y.; Narusaka, M.; Shi, C.; Yang, Y.B.; Wu, J.X.; Zeng, H.Y.; Narusaka, Y.; Yao, N. A novel pyrimidin-like plant activator stimulates plant disease resistance and promotes growth. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Jia, Y.; Shen, Y.; He, H.; Fang, R.; Chen, X.; Hao, X. 3-Acetonyl-3-hydroxyoxindole: a new inducer of systemic acquired resistance in plants. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2008, 6, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bashir, A.; Nabi, M.; Tabassum, N.; Afzal, S.; Ayoub, M. An updated review on phytochemistry and molecular targets of Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal (Ashwagandha). Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1049334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhu, H.; Ai, G.; Yu, J.; Dou, D. Plant genes related to phytophthora pathogens resistance. Phytopathol. Res. 2024, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Guo, S.; Shi, J. Structural insights into ligand recognition and receptor activation of plant leucine-rich repeat (LRR) transmembrane receptors. New Crops 2024, 100022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Teng, X.; Li, Y. Unleashing plant synthetic capacity: navigating regulatory mechanisms for enhanced bioproduction and secondary metabolite discovery. Curr. Opin. Biotech. 2024, 88, 103148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Xu, Y.; Li, Q.; Cao, Y.; Yang, D.; Liu, S.; Wang, X.; Mi, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ding, C. A lncRNA fine-tunes salicylic acid biosynthesis to balance plant immunity and growth. Cell Host Microbe 2022, 30, 1124–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J. Zhou, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y. Roles of long non-coding RNAs in plant immunity. PLoS Pathog. 2023, 19, e1011340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Liu, S.; Qi, H.; Cai, H.; Xu, M. Research progress on plant long non-coding RNA. Plants 2020, 9, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Huang, H. K.; Xia, Z. Q.; Yang, Y. Q.; Jiang, X. Y.; Yang, Y. Y.; Wang, D. L.; Li, X. L.; Chen, Z. Sequence data, functional annotation, and relationship analysis between mRNAs and long non-coding RNAs from tea leaves during infection by the fungal pathogen Epicoccum sorghinum. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2022, 35, 875–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, Y. Y.; Jiang, X. Y.; Yang, Y. Q.; Jiang, S. L.; Guo, D.; Li, Z.; Wang. D. L. ; Chen, Z. The sequence and integrated analysis of competing endogenous RNAs originating from tea leaves infected by the pathogen of tea leaf spot, Didymella segeticola. Plant Dis. 2022, 106, 1286–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H. L.; Huang, H. K.; Xia, Z. Q.; Yang, Y. Y.; Jiang, X. Y.; Huang, C.; Yang, Y. Y.; Wang. D. L.; Chen, Z. Sequencing, functional annotation, and interaction prediction of mRNAs and candidate long non-coding RNAs originating from tea leaves during infection by the fungal pathogen causing tea leaf spot, Didymella bellidis. Didymella bellidis. Plant Dis. 2023, 107, 2830–2834.
- Yang, X.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Y.; Schmid, M.; Wang, Y. miRNA mediated regulation and interaction between plants and pathogens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naz, M.; Benavides-Mendoza, A.; Tariq, M.; Zhou, J.; Wang, J.; Qi, S.; Dai, Z.; Du, D. CRISPR/Cas9 technology as an innovative approach to enhancing the phytoremediation: concepts and implications. J. Environ. Manage. 2022, 323, 116296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janik, E.; Niemcewicz, M.; Ceremuga, M.; Krzowski, L.; Saluk-Bijak, J.; Bijak, M. Various aspects of a gene editing system—crispr–cas9. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixit, S.; Sivalingam, P.N.; Baskaran, R.M.; Senthil-Kumar, M.; Ghosh, P.K. Plant responses to concurrent abiotic and biotic stress: unravelling physiological and morphological mechanisms. Plant Physiol. Rep. 2024, 29, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chen, J.; Sun, Z. Exploring the shared pathogenic strategies of independently evolved effectors across distinct plant viruses. Trends Microbiol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Chen, X.; Gong, P.; Long, H.; Wang, J.; Yang, W.; Yao, W. Siraitia grosvenorii as a homologue of food and medicine: a review of biological activity, mechanisms of action, synthetic biology, and applications in future food. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 6850–6870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Sundin, G.W.; Fuente, L.D.L.; Cubero, J.; Tatineni, S.; Brewer, M.T.; Zeng, Q.; Bock, C.H.; Cunniffe, N.J.; Wang, C. Key challenges in plant pathology in the next decade. Phytopathology 2024, 114, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhang, C. Carbon nanomaterials for plant priming through mechanostimulation: emphasizing the role of shape. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 10829–10839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasuda, M.; Kusajima, M.; Nakajima, M.; Akutsu, K.; Kudo, T.; Yoshida, S.; Nakashita, H. Thiadiazole carboxylic acid moiety of Tiadinil, SV-03, induces systemic acquired resistance in tobacco without salicylic acid accumulation. J. Pestic. Sci. 2006, 31, 329–334. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, T.; Quesada-Ocampo, L.M.; Wehner, T.C.; Bhatta, B.P.; Correa, E.; Malla, S. Recent advances and challenges in management of Colletotrichum orbiculare, the causal agent of watermelon anthracnose. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz, W.; Schurter, R.; Maetzke, T. The chemistry of benzothiadiazole plant activators. Pestic. Sci. 1997, 50, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, L.; Lawton, K.; Ruess, W.; Masner, P.; Specker, N.; Rella, M.G.; Meier, B.; Dincher, S.; Staub, T.; Uknes, S. A benzothiadiazole derivative induces systemic acquired resistance in tobacco. Plant J. 1996, 10, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Király, L.; Zechmann, B.; Albert, R.; Bacsó, R.; Schwarczinger, I.; Kolozsváriné Nagy, J.; Gullner, G.; Hafez, Y.M.; Künstler, A. Enhanced resistance to viruses in Nicotiana edwardsonii ‘Columbia’ is dependent on salicylic acid, correlates with high glutathione levels, and extends to plant-pathogenic bacteria and abiotic stress. Mol. Plant Microb. 2024, 37, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.; Yoon, H.M.; Jung, J.; Yu, S.; Choi, S.Y.; Bae, H.W.; Cho, Y.H.; Chung, E.H.; Lee, Y. Pleiotropic effects of N-acylhomoserine lactone synthase ExpI on virulence, competition, and transmission in Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum Pcc21. Pest Manag. Sci. 2024, 80, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Testi, S.; Kuhn, M.L.; Allasia, V.; Auroy, P.; Kong, F.; Peltier, G.; Pagnotta, S.; Cazareth, J.; Keller, H.; Panabières, F. The phytophthora parasitica effector AVH195 interacts with ATG8, attenuates host autophagy, and promotes biotrophic infection. BMC Biol. 2024, 22, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seth, T.; Asija, S.; Umar, S.; Gupta, R. The intricate role of lipids in orchestrating plant defense responses. Plant Sci. 2024, 338, 111904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 299. .Delaney, T.P.; Uknes, S.; Vernooij, B.; Friedrich, L.; Weymann, K.; Negrotto, D.; Gaffney, T.; Gut-Rella, M.; Kessmann, H.; Ward, E.; Ryals, J. A central role of salicylic acid in plant disease resistance. Science 1994, 266, 1247–1250 https://doi101126/science26651881247. [Google Scholar]
- Peghaire, E.; Hamdache, S.; Galien, A.; Sleiman, M.; ter Halle, A.; El Alaoui, H.; Kocer, A.; Richard, C.; Goupil, P. Inducing plant defense reactions in tobacco plants with phenolic-rich extracts from red maple leaves: a characterization of main active ingredients. Forests 2020, 11, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, M.; Kusajima, M.; Nakajima, M.; Akutsu, K.; Kudo, T.; Yoshida, S.; Nakashita, H. Thiadiazole carboxylic acid moiety of tiadinil, SV-03, induces systemic acquired resistance in tobacco without salicylic acid accumulation. J. Pestic. Sci. 2006, 31, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niki, T.; Mitsuhara, I.; Seo, S.; Ohtsubo, N.; Ohashi, Y. Antagonistic effect of salicylic acid and jasmonic acid on the expression of pathogenesis-related (PR) protein genes in wounded mature tobacco leaves. Plant Cell Physiol. 1998, 39, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, G.; Jwa, N.S.; Han, K.-S.; Agrawal, V.; Rakwal, R. Isolation of a novel rice PR4 type gene whose mRNA expression is modulated by blast pathogen attack and signaling components. Plant Physiol. Bioch. 2003, 41, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uquillas, C.; Letelier, I.; Blanco, F.; Jordana, X.; Holuigue, L. NPR1-independent activation of immediate early salicylic acid-responsive genes in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol. Plant Microb. 2004, 17, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.T.; Bradford, K.J. Class I chitinase and β-1, 3-glucanase are differentially regulated by wounding, methyl jasmonate, ethylene, and gibberellin in tomato seeds and leaves. Plant Physio. 2003, 133, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitter, N.; Kazan, K.; Way, H.M.; Broekaert, W.F.; Manners, J.M. Systemic induction of an Arabidopsis thaliana plant defensin gene promoter by tobacco mosaic virus and jasmonic acid in transgenic tobacco. Plant Sci. 1998, 136, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, A.K.; Sahoo, L.P.; Sahoo, M.; Seth, T.; Patra, C. Induced resistance mechanism in plant and its importance in agriculture. Int. J. Plant Soil Sci. 2024, 36, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J.; Chang, K.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, H.; Qiu, N.; Bao, Y. Overexpression of GhGSTF9 enhances salt stress tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana. Genes 2024, 15, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaffney, T.; Friedrich, L.; Vernooij, B.; Negrotto, D.; Nye, G.; Uknes, S.; Ward, E.; Kessmann, H.; Ryals, J. Requirement of salicylic Acid for the induction of systemic acquired resistance. Science 1993, 261, 754–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, S.A.; Olson, D.G.; Argyros, D.A.; Miller, B.B.; Barrett, T.F.; Murphy, D.M.; McCool, J.D.; Warner, A.K.; Rajgarhia, V.B.; Lynd, L.R. Development of pyrF-based genetic system for targeted gene deletion in Clostridium thermocellum and creation of a pta mutant. Appl. Environ. Microbio. 2010, 76, 6591–6599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.; Kwok, S.F.; Bleecker, A.B.; Meyerowitz, E.M. Arabidopsis thaliana ethylene-response gene ETR1: similarity of product to two-component regulators. Science 1993, 262, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angulo, M.; García, M.J.; Alcántara, E.; Pérez-Vicente, R.; Romera, F.J. Comparative study of several Fe deficiency responses in the Arabidopsis thaliana ethylene insensitive mutants ein2-1and ein2-5. Plants 2021, 10, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meesters, C.; Mönig, T.; Oeljeklaus, J.; Krahn, D.; Westfall, C.S.; Hause, B.; Jez, J.M.; Kaiser, M.; Kombrink, E. A chemical inhibitor of jasmonate signaling targets JAR1 in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat. Chem. Bio. 2014, 10, 830–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, Y.M.; Kenton, P.; Mur, L.; Darby, R.; Draper, J. Hydrogen peroxide does not function downstream of salicylic acid in the induction of PR protein expression. Plant J. 1995, 8, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, M.; von Dahl, C.C.; Liu, P.P.; Friso, G.; van Wijk, K.J.; Klessig, D.F. The combined use of photoaffinity labeling and surface plasmon resonance based technology identifies multiple salicylic acid binding proteins. Plant J. 2012, 72, 1027–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, H.; Klessig, D.F. Identification of a soluble, high-affinity salicylic acid-binding protein in tobacco. Plant Physiol. 1997, 113, 1319–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Me’traux, J.P.; Lamodie’re, E.; Catinot, J.; Lamotte, O.; Garcion, C. Salicylic acid and induced plant defenses. Rec. Adv. Pol-ypheno Res. 2009, 1, 202–210. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; Wang, X.Z.; Tang, Y.Y.; Yu, H.T.; Ding, Y.F.; De Yang, C.; Cui, F.G.; Zhang, J.C.; Wang, C.T. Molecular cloning and characterization of NPR1 gene from Arachis hypogaea. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 5247–5256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D. Salicylic acid signaling in disease resistance. Plant Sci. 2014, 228, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durner, J.; Klessig, D.F. Inhibition of ascorbate peroxidase by salicylic acid and 2, 6-dichloroisonicotinic acid, two inducers of plant defense responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 1995, 92, 11312–11316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Tian, M.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Xia, X.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, J.; Shi, K. Salicylic acid binding of mitochon-drial alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase E2 affects mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation and electron transport chain components and plays a role in basal defense against tobacco mosaic virus in tomato. New Phytol. 2015, 205, 1296–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manohar, M.; Tian, M.; Moreau, M.; Park, S.W.; Choi, H.W.; Fei, Z.; Friso, G.; Asif, M.; Manosalva, P.; von Dahl, C.C. Iden-tification of multiple salicylic acid-binding proteins using two high throughput screens. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 5, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
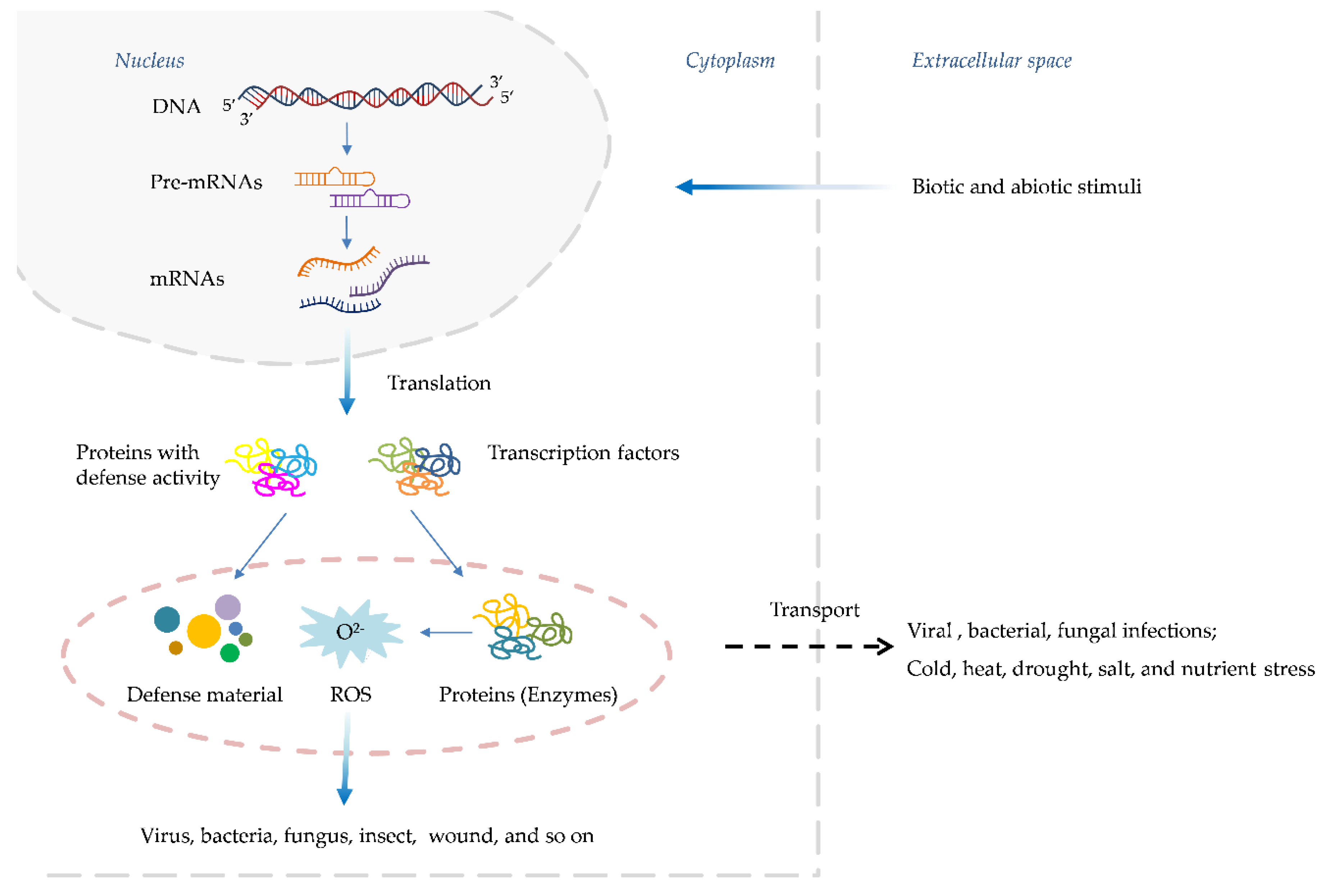
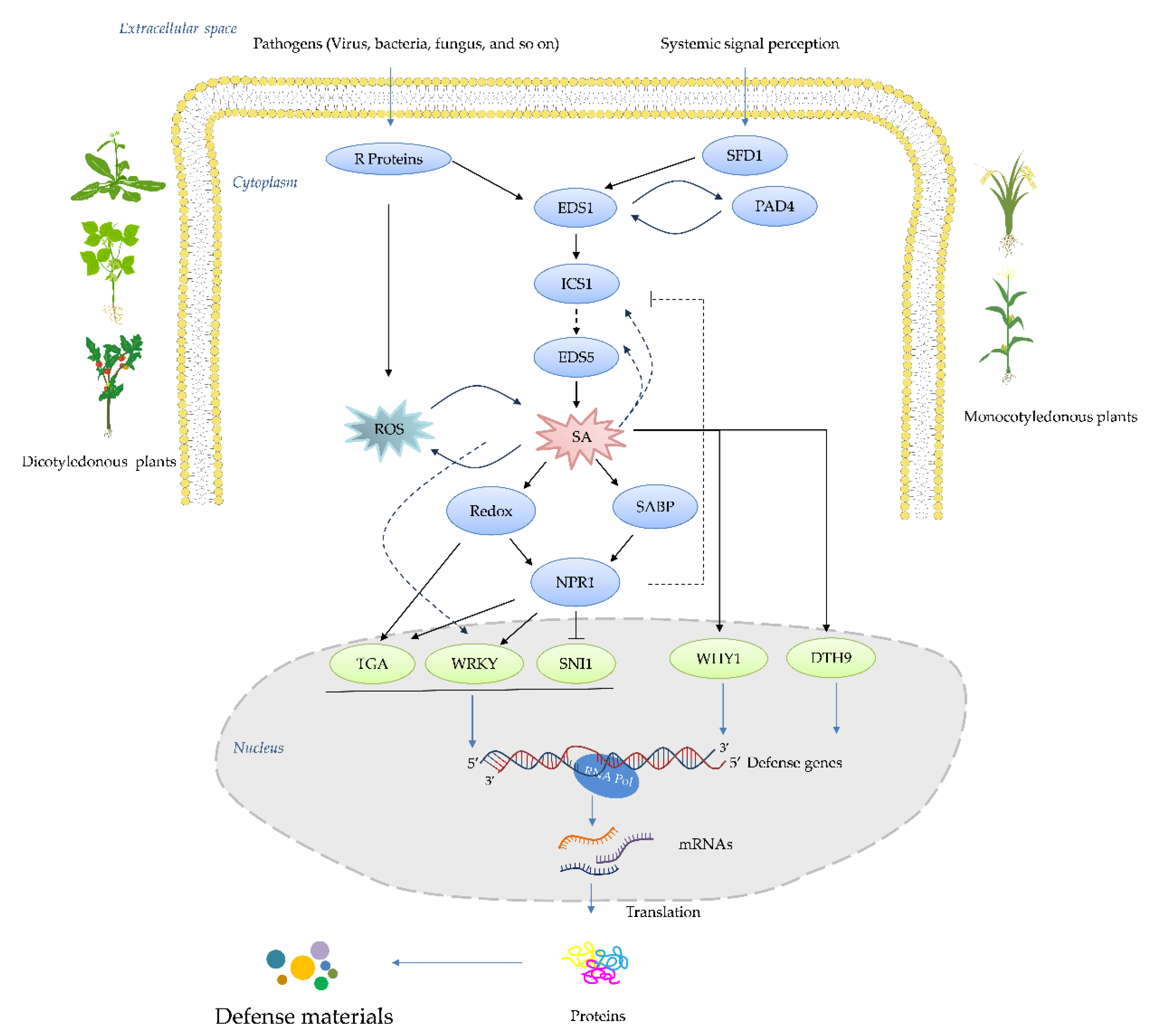
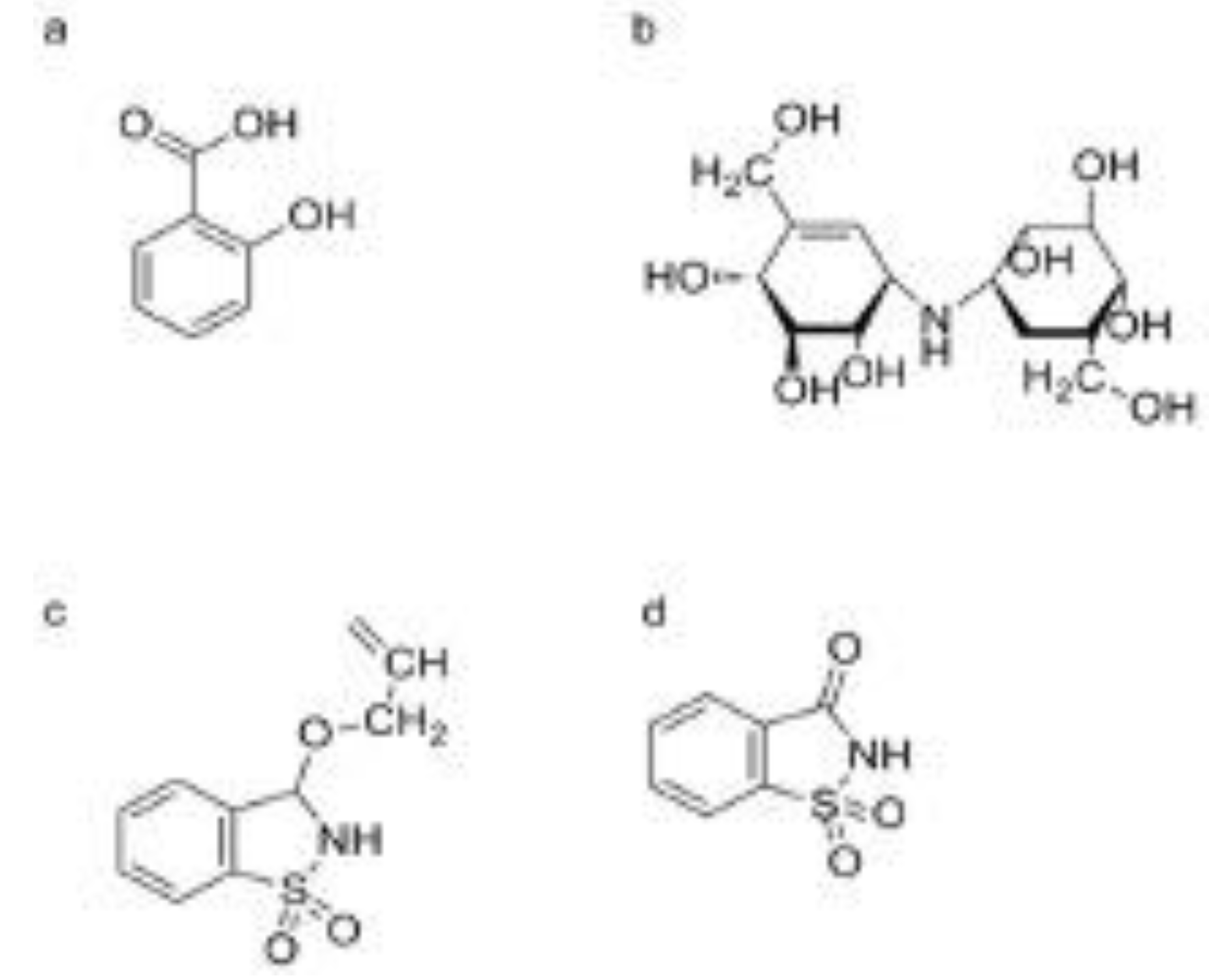
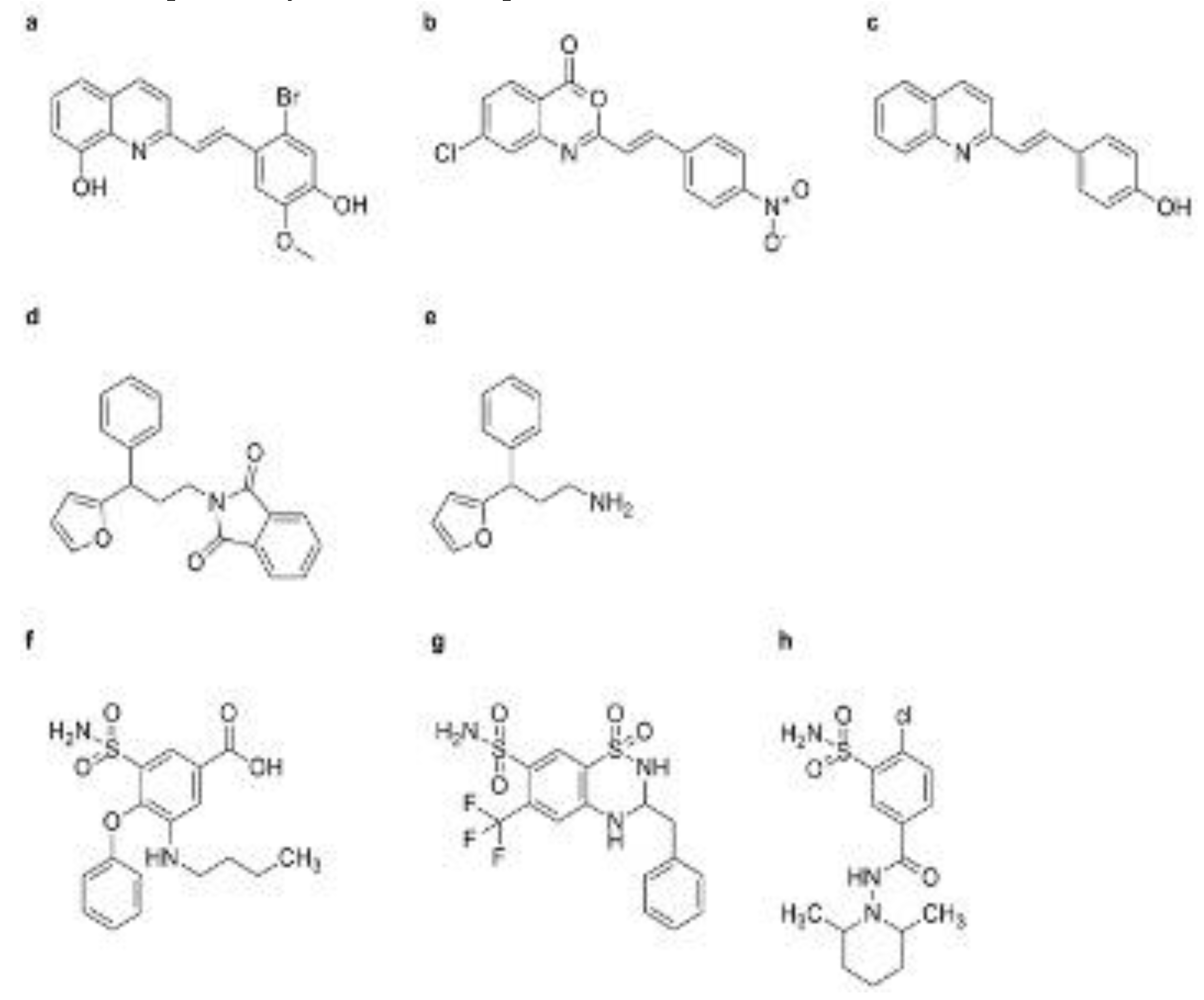
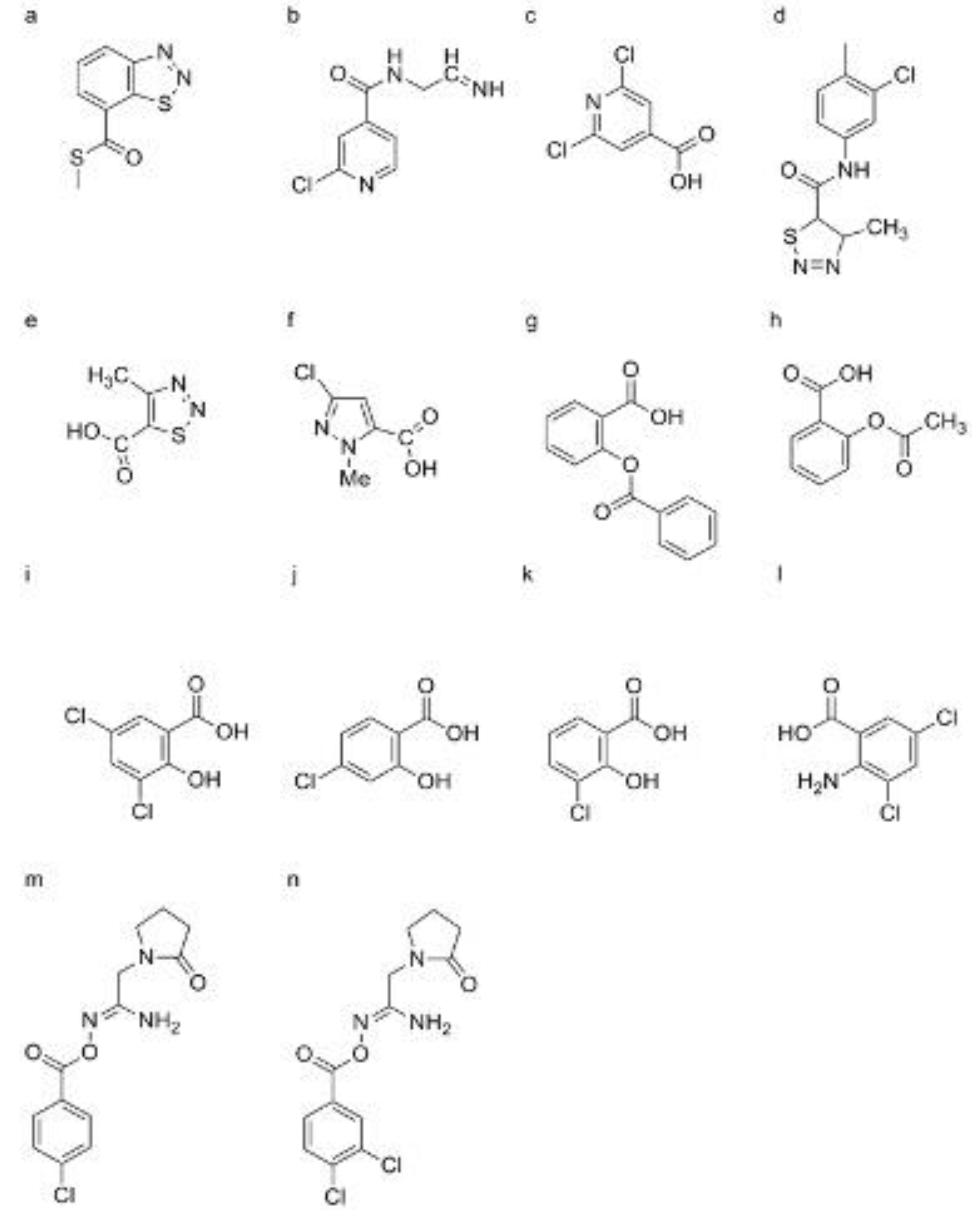
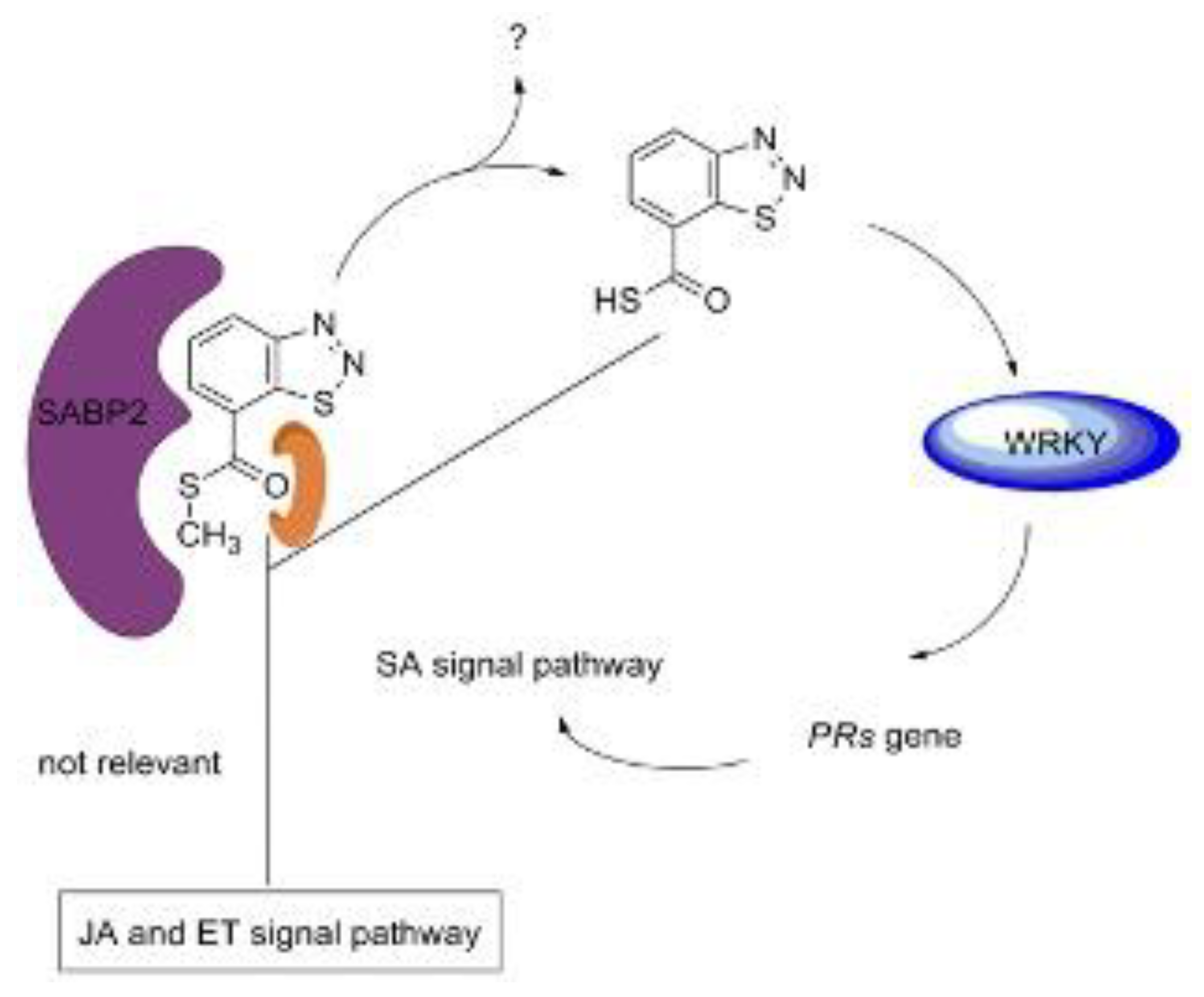
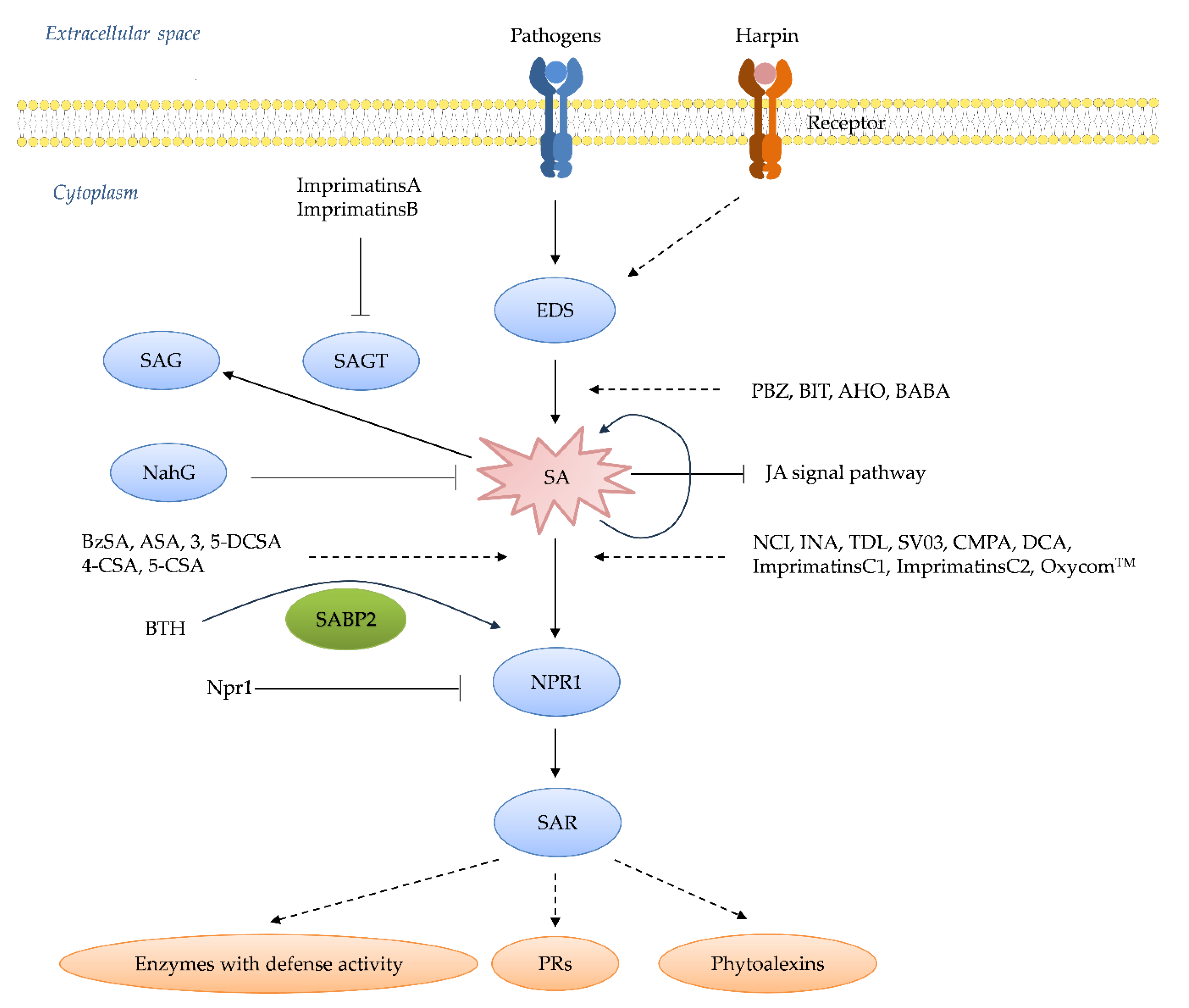
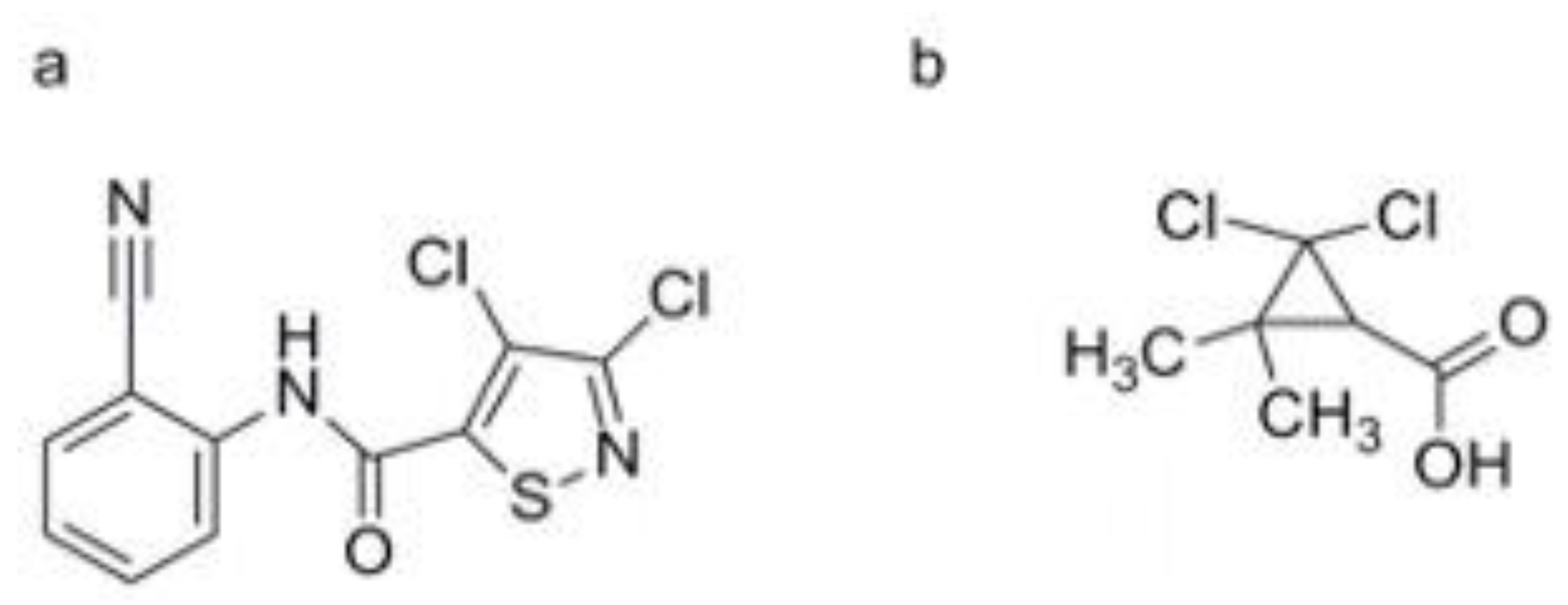
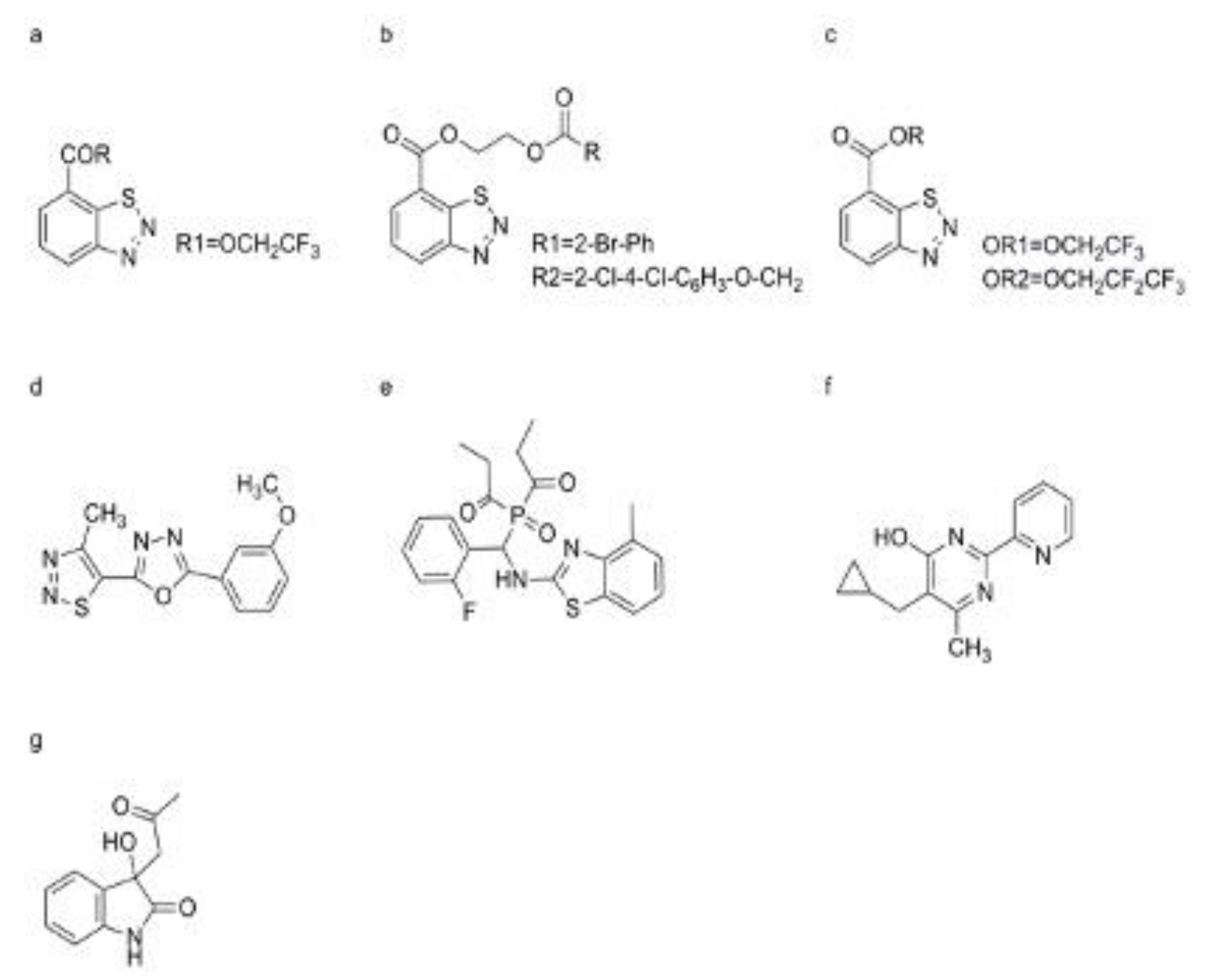
| Plants | Plant species | Pathogen names | Evaluation index | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cucumber | No mention | Colletotrichum lagenarium (Paserini) Ell. & Halst | Infected leaf area | [292,293] |
| Tobacco | N. tabacum cv. Xanthi nc | TMV | Lesion size | [294] |
| N. tabacum cv. Xanthi nc | Oidium lycopersici | Lesion size | [119] | |
| N. tabacum cv. Xanthi nc | Pst | CFU or disease severity | [290] | |
| N. tabacum cv. Xanthi nc | Cercospora nicotianae | Infected leaf area | [290,295] | |
| N. tabacum cv. Xanthi nc | Peronospora tabacina | Infected leaf area | [290] | |
| N. tabacum cv. Xanthi nc | Erwinia carotovora | Length of infected stem | [290,296] | |
| N. tabacum cv. Xanthi nc | Phytophthora parasitica | Disease severity | [297] | |
| A. thaliana | Peronospora parasitica pv. Emwa | Disease severity | [171,299] | |
| Rice | Oryza sativa cv. Aichiasahi | M. grisea | Lesion number | [178,298] |
| O. sativa cv. Aichiasahi | X. oryzae pv. oryzae | Lesion length | [202] |
| Plant | Signal pathways | Effector markers | Methods | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tobacco | SA | SA (free SA) | Organic solvent extract coupled with HPLC | [178,301] | |
| SA (total SA) | Methanol extract coupled with the high-performance liquid chromatographic | ||||
| SA (SAG) | Methanol extract coupled with the high-performance liquid chromatographic | [18] | |||
| Tobacco | SA | PR-1 | Northern blotting | [302] | |
| PR-1 | Western blotting | [172] | |||
| SA | PR-2 | Northern blotting | [302] | ||
| SA | PR-3 | Northern blotting | [303] | ||
| SA | PR-4 | Northern blotting | [304] | ||
| SA | PR-5 | Northern blotting | [155] | ||
| Arabidopsis | SA | PR-1 | Northern blotting, | [170] | |
| SA | PR-2 | Northern blotting, | [170,305] | ||
| SA | PR-5 | Northern blotting, | [170][122] | ||
| Tomato | SA | β-1, 3-glucanase | Western blotting | [306] | |
| Tobacco | JA | PDF1.2 | Northern blotting, | [307] | |
| Transgenics or mutants | Plants | Action sites | Signal pathways | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NahG transgenics | Tobacco | SA level | SA | [9,170,294,308,310] |
| SABP2-silenced transgenic | Tobacco | SA level | SA | [111] |
| nim mutant | A. thaliana | Downstream of SA | SA | [299] |
| npr1 mutant | A. thaliana | Downstream of SA | SA | [20] |
| etr1 mutant | A. thaliana | ET | [312] | |
| ein2 mutant | A. thaliana | ET | [313] | |
| jar1 mutant | A. thaliana | JA | [314] |
| Proteins interacted with SA | Sources | Ligands | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Catalase | N. tabacum | 14C-SA | [315] |
| Methyl esterase | N. tabacum | 3H-SA | [316,317] |
| Carbonic anhydrase | N. tabacum | 3H-SA | [318] |
| A protein with ankyrin repeat and BTB/POZ domain | A. thaliana | Genetics/T-DNA mutant | [319] |
| CUL3 adapter protein | A. thaliana | Genetics/NPR1 paralog | [320] |
| CUL3 adapter protein | A. thaliana | Genetics/NPR1 paralog | [320] |
| Ascorbate peroxidase | N. tabacum | 3H-SA | [321] |
| E2 subunit of α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase 2 | A. thaliana | 4-azido SA, SPR | [322] |
| Glutathione S-transferase 2 | A. thaliana | 4-azido SA, SPR | [1] |
| Glutathione S-transferase 8 | A. thaliana | 4-azido SA, SPR | [321] |
| Glutathione S-transferase 10 | A. thaliana | 4-azido SA, SPR | [322] |
| Glutathione S-transferase 11 | A. thaliana | 4-azido SA, SPR | [93] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





