Submitted:
16 July 2024
Posted:
17 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
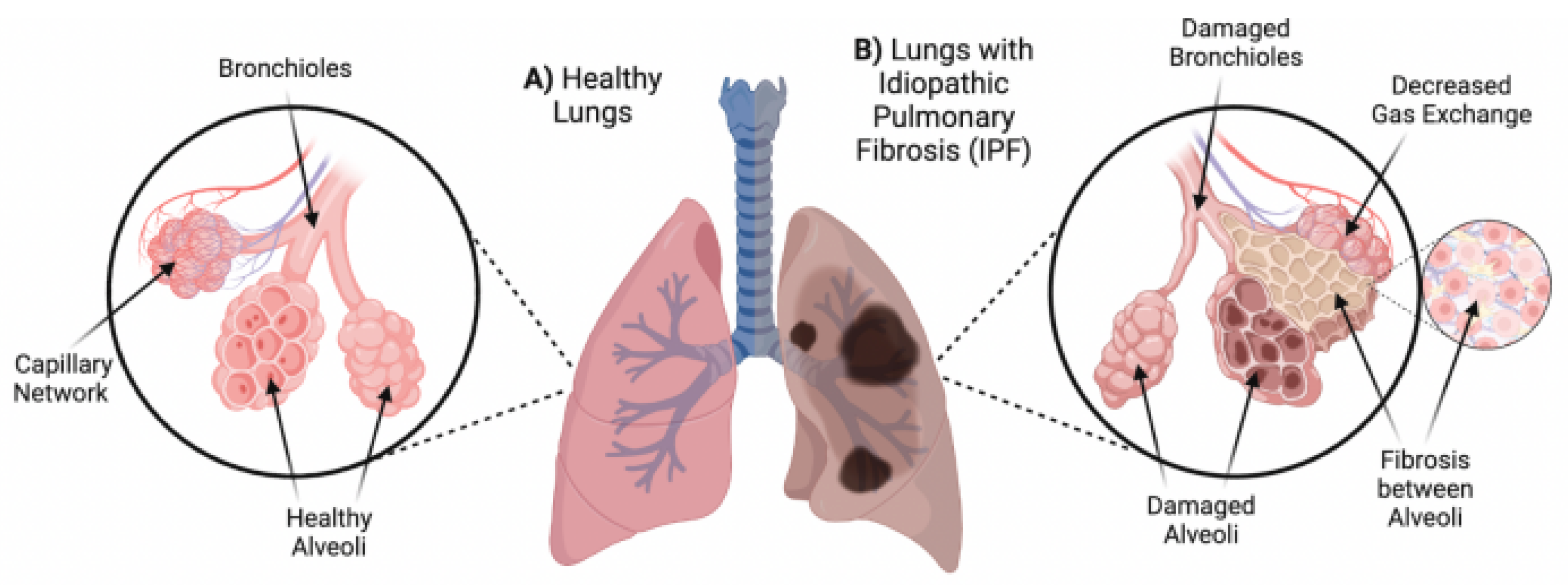
1. Introduction
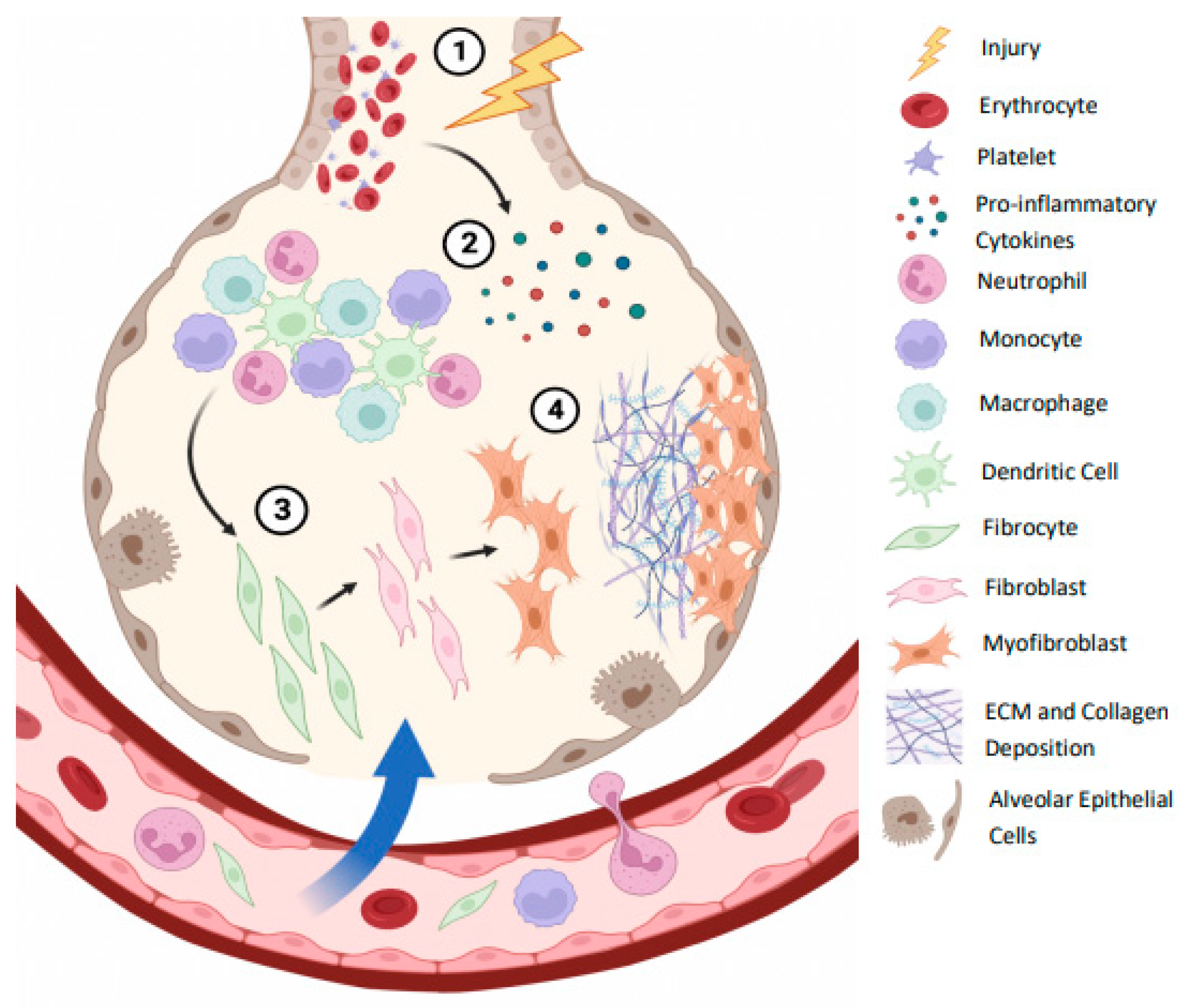
2. Pathogenesis
3. Cytokines and IPF
4. Regulatory Cells
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Antoniou KM, Margaritopoulos GA, Tomassetti S, Bonella F, Costabel U, Poletti V. Interstitial lung disease. Eur Respir Rev. 2014 Mar 1;23(131):40–54.
- Barratt, S.L.; Creamer, A.; Hayton, C.; Chaudhuri, N. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF): An Overview. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glassberg, M.K. Overview of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, evidence-based guidelines, and recent developments in the treatment landscape. Am J Manag Care. 2019, 25, S195–S203. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lancaster, L.; Bonella, F.; Inoue, Y.; Cottin, V.; Siddall, J.; Small, M.; Langley, J. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Physician and patient perspectives on the pathway to care from symptom recognition to diagnosis and disease burden. Respirology 2021, 27, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimoto, H.; Kobayashi, T.; Azuma, A. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Treatment and Prognosis. Clin. Med. Insights: Circ. Respir. Pulm. Med. 2015, 9s1, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strongman, H.; Kausar, I.; Maher, T.M. Incidence, Prevalence, and Survival of Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis in the UK. Adv. Ther. 2018, 35, 724–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nalysnyk, L.; Cid-Ruzafa, J.; Rotella, P.; Esser, D. Incidence and prevalence of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: review of the literature. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2012, 21, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghu G, Remy-Jardin M, Myers JL, Richeldi L, Ryerson CJ, Lederer DJ, et al. Diagnosis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Clinical Practice Guideline. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018 Sep 1;198(5):e44–68.
- Cameli, P.; Refini, R.M.; Bergantini, L.; D’alessandro, M.; Alonzi, V.; Magnoni, C.; Rottoli, P.; Sestini, P.; Bargagli, E. Long-Term Follow-Up of Patients With Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Treated With Pirfenidone or Nintedanib: A Real-Life Comparison Study. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, D.S.; Grossfeld, D.; Renna, H.A.; Agarwala, P.; Spiegler, P.; DeLeon, J.; Reiss, A.B. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Current and future treatment. Clin. Respir. J. 2022, 16, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sgalla, G.; Iovene, B.; Calvello, M.; Ori, M.; Varone, F.; Richeldi, L. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: pathogenesis and management. Respir. Res. 2018, 19, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Sun, J.; Zhang, S.; Nie, Y.; Zhou, S.; Zeng, Y. Progress in understanding and treating idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: recent insights and emerging therapies. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1205948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richeldi L, Collard HR, Jones MG. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lancet. 2017 May 13;389(10082):1941–52.
- López-Ramírez, C.; Valdivia, L.S.; Portal, J.A.R. Causes of Pulmonary Fibrosis in the Elderly. Med Sci. 2018, 6, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caminati, A.; Madotto, F.; Conti, S.; Cesana, G.; Mantovani, L.; Harari, S. The natural history of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in a large European population: the role of age, sex and comorbidities. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2021, 16, 1793–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florez-Sampedro, L.; Song, S.; Melgert, B.N. The diversity of myeloid immune cells shaping wound repair and fibrosis in the lung. Regeneration 2018, 5, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhyatmika, A.; Putri, K.S.S.; Beljaars, L.; Melgert, B.N. The Elusive Antifibrotic Macrophage. Front. Med. 2015, 2, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipolla, E.M.; Alcorn, J.F. Repair of the Lung by Regulatory T Cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2020, 63, 405–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wynn, T.A. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of fibrosis. J. Pathol. 2008, 214, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evrard, S.M.; D′Audigier, C.; Mauge, L.; Israël-Biet, D.; Guerin, C.L.; Bieche, I.; Kovacic, J.C.; Fischer, A.; Gaussem, P.; Smadja, D.M. The profibrotic cytokine transforming growth factor-β1 increases endothelial progenitor cell angiogenic properties. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2012, 10, 670–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arce-Sillas, A.; Álvarez-Luquín, D.D.; Tamaya-Domínguez, B.; Gomez-Fuentes, S.; Trejo-García, A.; Melo-Salas, M.; Cárdenas, G.; Rodríguez-Ramírez, J.; Adalid-Peralta, L. Regulatory T Cells: Molecular Actions on Effector Cells in Immune Regulation. J. Immunol. Res. 2016, 2016, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, A.; Oberle, N.; Krammer, P.H. Molecular Mechanisms of Treg-Mediated T Cell Suppression. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergeron A, Soler P, Kambouchner M, Loiseau P, Milleron B, Valeyre D, et al. Cytokine profiles in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis suggest an important role for TGF-beta and IL-10. Eur Respir J. 2003 Jul;22(1):69–76.
- She, Y.X.; Yu, Q.Y.; Tang, X.X. Role of interleukins in the pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis. Cell Death Discov. 2021, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Liu, S.; Li, S.; Xia, Y. Targeting Growth Factor and Cytokine Pathways to Treat Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 918771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, T.H.G.; Paliogiannis, P.; Nasrallah, G.K.; Giordo, R.; Eid, A.H.; Fois, A.G.; Zinellu, A.; Mangoni, A.A.; Pintus, G. Emerging cellular and molecular determinants of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 78, 2031–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schupp, J.C.; Binder, H.; Jäger, B.; Cillis, G.; Zissel, G.; Müller-Quernheim, J.; Prasse, A. Macrophage Activation in Acute Exacerbation of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. PLOS ONE 2015, 10, e0116775–e0116775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.-L.; Yin, R.; Wang, S.-N.; Ying, R. A Review of CXCL1 in Cardiac Fibrosis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vu, T.N.; Chen, X.; Foda, H.D.; Smaldone, G.C.; Hasaneen, N.A. Interferon-γ enhances the antifibrotic effects of pirfenidone by attenuating IPF lung fibroblast activation and differentiation. Respir. Res. 2019, 20, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabay, C. Interleukin-6 and chronic inflammation. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2006, 8, S3–S3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fielding, C.A.; Jones, G.W.; McLoughlin, R.M.; McLeod, L.; Hammond, V.J.; Uceda, J.; Williams, A.S.; Lambie, M.; Foster, T.L.; Liao, C.-T.; et al. Interleukin-6 Signaling Drives Fibrosis in Unresolved Inflammation. Immunity 2014, 40, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh S, Anshita D, Ravichandiran V. MCP-1: Function, regulation, and involvement in disease. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 Dec;101(Pt B):107598.
- Scott, M.K.D.; Quinn, K.; Li, Q.; Carroll, R.; Warsinske, H.; Vallania, F.; Chen, S.; A Carns, M.; Aren, K.; Sun, J.; et al. Increased monocyte count as a cellular biomarker for poor outcomes in fibrotic diseases: a retrospective, multicentre cohort study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segel MJ, Izbicki G, Cohen PY, Or R, Christensen TG, Wallach-Dayan SB, et al. Role of interferon-gamma in the evolution of murine bleomycin lung fibrosis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2003 Dec;285(6):L1255-62.
- Schroder K, Hertzog PJ, Ravasi T, Hume DA. Interferon-gamma: an overview of signals, mechanisms and functions. J Leukoc Biol. 2004 Feb;75(2):163–89.
- Wilson MS, Madala SK, Ramalingam TR, Gochuico BR, Rosas IO, Cheever AW, et al. Bleomycin and IL-1beta-mediated pulmonary fibrosis is IL-17A dependent. J Exp Med. 2010 Mar 15;207(3):535–52.
- Ge, Y.; Huang, M.; Yao, Y.-M. Biology of Interleukin-17 and Its Pathophysiological Significance in Sepsis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.; Liu, K.; Huang, G.-Q.; Cui, Y.; Kaplan, H.J.; Shao, H.; Sun, D. Anti-Inflammatory Role of IL-17 in Experimental Autoimmune Uveitis. 2009; 182, 3183–3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Geffen C, Deißler A, Quante M, Renz H, Hartl D, Kolahian S. Regulatory Immune Cells in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Friends or Foes? Front Immunol. 2021;12:663203.
- Gabrilovich, D.I.; Nagaraj, S. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells as regulators of the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, I.E.; Greiffo, F.R.; Frankenberger, M.; Bandres, J.; Heinzelmann, K.; Neurohr, C.; Hatz, R.; Hartl, D.; Behr, J.; Eickelberg, O. Peripheral blood myeloid-derived suppressor cells reflect disease status in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 48, 1171–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wynn, T.A.; Vannella, K.M. Macrophages in Tissue Repair, Regeneration, and Fibrosis. Immunity 2016, 44, 450–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, G.; Liu, A.; Herzog, E.L. Evolving Perspectives on Innate Immune Mechanisms of IPF. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrison, G.; Huang, S.K.; Okunishi, K.; Scott, J.P.; Penke, L.R.K.; Scruggs, A.M.; Peters-Golden, M. Reversal of Myofibroblast Differentiation by Prostaglandin E2. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2013, 48, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uematsu, S.; Matsumoto, M.; Takeda, K.; Akira, S. Lipopolysaccharide-Dependent Prostaglandin E2 Production Is Regulated by the Glutathione-Dependent Prostaglandin E2 Synthase Gene Induced by the Toll-Like Receptor 4/MyD88/NF-IL6 Pathway. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 5811–5816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asai, Y.; Chiba, H.; Nishikiori, H.; Kamekura, R.; Yabe, H.; Kondo, S.; Miyajima, S.; Shigehara, K.; Ichimiya, S.; Takahashi, H. Aberrant populations of circulating T follicular helper cells and regulatory B cells underlying idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir. Res. 2019, 20, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shevyrev D, Tereshchenko V. Treg Heterogeneity, Function, and Homeostasis. Front Immunol. 2019;10:3100.
- Dhamne C, Chung Y, Alousi AM, Cooper LJN, Tran DQ. Peripheral and thymic foxp3(+) regulatory T cells in search of origin, distinction, and function. Front Immunol. 2013;4:253.
- Lee, J.; Kim, D.; Min, B. Tissue Resident Foxp3+ Regulatory T Cells: Sentinels and Saboteurs in Health and Disease. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 865593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artsen, A.M.; Rytel, M.; Liang, R.; King, G.E.; Meyn, L.; Abramowitch, S.D.; Moalli, P.A. Mesh induced fibrosis: The protective role of T regulatory cells. Acta Biomater. 2019, 96, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Ye, Q.; Qiu, M.; Hao, Y.; Han, J.; Zeng, H. Increased activated regulatory T cells proportion correlate with the severity of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir. Res. 2017, 18, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Xia, H.; Yao, S. Regulatory T cells are a double-edged sword in pulmonary fibrosis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 84, 106443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author[s] and contributor[s] and not of MDPI and/or the editor[s]. MDPI and/or the editor[s] disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
| Cytokine | Main Functions | Relevance to Study | Supporting Literature |
|---|---|---|---|
| IL-6 | Pro-inflammatory cytokine Involved in the transition from acute to chronic inflammatory responses |
Possesses pro-fibrotic properties Previously significantly increased in IPF patients Suggested to drive fibrosis in unresolved inflammation |
[24,30,31] |
| CXCL1 | Pro-inflammatory chemokine Involved in chemoattraction of neutrophils to the site of inflammation |
Previously significantly increased in IPF patients with acute exacerbation | [27,28] |
| MCP-1 | Pro-inflammatory chemokine Role in recruitment and activation of monocytes |
Previously significantly increased in IPF patients Monocytes suggested as a possible marker of IPF severity |
[26,32,33] |
| TGF-b | Both pro- and anti-inflammatory properties Essential in wound healing and tissue repair |
Pro-fibrotic cytokine and key mediator in fibrotic progression Significantly increased in IPF Produced and secreted by Tregs |
[20,21,22] |
| IFN- | Pro-inflammatory cytokine Involved in the activation and regulation of numerous immune cells |
Typically anti-fibrotic Potential to be combined with anti-fibrotic drug pirfenidone Suggested pro-fibrotic nature in certain contexts |
[29,34,35] |
| IL-10 | Anti-inflammatory cytokine Maintains homeostasis by suppressing immune activity |
Both pro- and anti-fibrotic effects Previously significantly increased in IPF patients Produced and secreted by Tregs |
[21,23,26] |
|
IL-17 (IL-17A) |
Both pro- and anti-inflammatory properties Has implications in autoimmunity and chronic inflammation |
Has demonstrated pro-fibrotic properties Previously significantly increased in IPF patients |
[24,36,37,38] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





