1. Introduction
Activated carbon is the most versatile and frequently used adsorbent, employed for purification and separation in numerous industrial processes, including medical applications, gas storage, pollutant and odor removal, as well as water and soil purification from petroleum products [
1,
2,
3,
4]. The advantages of activated carbon sorbents stem from their large specific surface area, extensive internal surface area, significant pore volume, good chemical stability, and various oxygen-containing functional groups on the surface. In recent years, there has been growing interest in research on producing activated carbon sorbents using renewable and cost-effective precursors. Agricultural waste can serve as such renewable and economical carbon precursors [
5,
6]. Utilizing domestic biomaterials as raw materials for activated carbon is particularly significant as it reduces production costs by minimizing logistics expenses [
7]. Consequently, numerous studies have investigated activated carbons derived from agricultural waste, such as acorn shells [
8,
9], pistachio shells [
10], grape seeds [
11], corn cobs [
12], banana stalks [
13], apricot kernels [
14], sawdust [
15,
16], rice husks [
17,
18], walnut shells [
19], sugar cane bagasse, and sunflower seed husks [
20].
Activated carbon can be derived from a wide range of raw materials, primarily through two methods: physical or chemical activation. In recent years, a combination of both processes, known as physico-chemical activation, has garnered significant attention in research.
The method of physical activation involves the carbonization of raw materials followed by activation at high temperatures in the presence of active agents such as water vapor, carbon dioxide, or a mixture of these gases [
21,
22]. In contrast, the chemical activation method begins with impregnating the starting materials with a dehydrating chemical (e.g., KOH, H
3PO
4, ZnCl
2 and H
2SO
4) before undergoing heat treatment. The dehydrating agents are then carbonized at temperatures ranging from 170°C to 600°C.
Compared to chemical activation, physical activation occurs at higher temperatures typically ranging from 700°C to 1100°C [
23]. The dehydrating effect of the active substances used in chemical activation inhibits tar formation [
24,
25], leading to higher yields of porous carbon and lower activation temperatures compared to physical activation methods [
26,
27].
Prahas et al. reported that chemical activation methods, using agents such as H
3PO
4 and ZnCl
2, are effective for activating previously carbonized lignocellulosic materials. On the other hand, agents like KOH are suitable for activating charcoal or charcoal-like precursors [
28,
29]. Rice husks (genus
Oryza), reed stalks (genus
Phragmites), pine sawdust (genus
Pinus), and wheat straw (genus
Triticum) are abundant plant species native to Central Asia and Kazakhstan. Due to their availability and low cost, these residues are well-suited as raw materials for producing activated carbon. However, to our knowledge, despite their potential applications, there have been no reported studies on obtaining activated carbons OSL, PhAC, PSL and TAL using a two-stage KOH chemical activation process under air.
Thermal processes require high energy due to the elevated temperatures involved, making them both energetically and commercially expensive. The current challenges associated with the high energy consumption of thermal processes for producing activated carbon have spurred research into alternative regeneration methods aimed at reducing environmental impact [
30]. Air activation stands out as economically attractive due to its high yield, relatively short activation time, and low energy consumption [
31].
The primary objective of this study was to produce activated carbon from biomass plant residues: OSL, PhAC, PSL and TAL using KOH as the activating agent in a two-stage process designed to minimize energy consumption at lower air temperatures. Pyrolysis was conducted at various activation temperatures ranging from 300°C to 850°C, with a heating rate of 5°C/min. The study investigated the influence of activation temperature and time, as well as the KOH-to-carbon ratio, on the activated carbon derived from biomass. The optimal activation conditions for each biomass type OSL, PhAC, PSL, TAL were determined by analyzing parameters such as iodine number and specific surface area of the prepared activated carbon.
Incorporating activated carbon into soil serves as a long-term carbon storage reservoir, delaying its release into the atmosphere as CO₂, which contributes positively to climate change mitigation efforts. An additional advantage is that the raw materials for activated carbon production originate from renewable sources and organic waste from the agro-industry, which often pose environmental pollution challenges [
32,
33,
34,
35].
In the Republic of Kazakhstan, soil contamination with oil poses a significant environmental challenge, where activated carbon has shown promising applications. Its main competitive advantages include high sorption capacity for petroleum products, effective degradation of oil and petroleum substances, cost-effectiveness of reclamation technology, and rapid reclamation process. Furthermore, the production of modified activated carbon is environmentally less harmful.
This study investigates the physico-chemical properties of activated carbon derived from various plant residue sources in Kazakhstan, including wheat straw, rice husks, reed stalks, and pine sawdust. Additionally, it explores the application of these activated carbon samples to enhance soil fertility and remediate oil-contaminated areas near the “Zhanatalap” deposit in the Atyrau region.
2. Results
2.1. Investigation of the Physico-Chemical Characteristics of Activated Carbon Samples
Plant residues were selected as natural plant sources: OSL, PhAC, PSL and TAL. After two-stage pyrolysis at 850°C and chemical activation with potassium hydroxide, activated carbon samples were obtained. Experiments with the obtained activated carbon samples on the EDAX energy dispersive X-ray spectrometer showed that carbonized samples from reed stalks, pine sawdust and wheat straw consist of 87-97% by weight of carbon and contain insignificant amounts of hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen. In addition to the above components, carbonized rice husks contain from 5 to 10% silicon by weight. The latter allows the activated carbon sorbent from rice husks to have hydrophilic properties.
The main physico-chemical characteristics of different activated carbon samples are presented in
Table 1. The bulk density for carbonized samples of OSL, PhAC, PSL and TAL was 0.423 kg/m
3, 0.396 kg/m
3, 0.482 kg/m
3 and 0.388 kg/m
3, respectively.
Crushed OSL consists of fine-grained particles with sizes 0.25-0.35 mm and highly dispersed particles with sizes less than 40 microns. The particle sizes PSL were commensurate, the average particle size was in the range of 1.5-2.5 mm. Carbonized TAL and PhAC were easily crushed and contained carbon dust. The average particle size was 0.1-0.2 mm.
Calculation data based on the analysis of nitrogen sorption isotherms on activated carbon samples using the B-J-H method, as well as the D-R equations, showed that activated carbon samples PSL and OSL have a developed specific surface area and are 1.5-3 times superior to other samples. The porous structure of activated carbons PSL and OSL is represented by a developed micro- and mesoporous structure with a predominance of micropores by 63-71%.
2.2. Investigation of the Structural Characteristics of Activated Carbon Samples by SEM
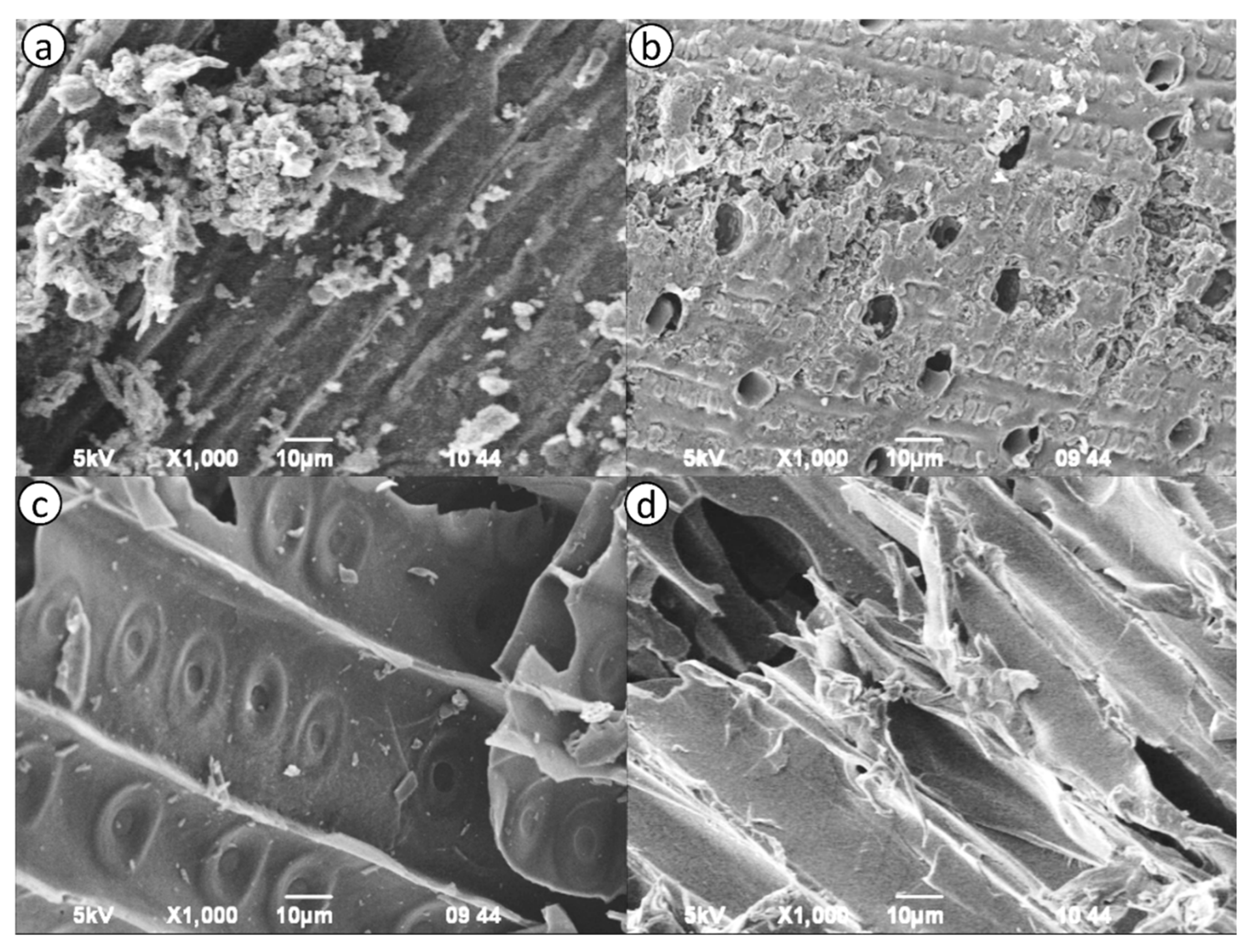
The study of the morphology of samples OSL (
Figure 1a) and PhAC by SEM (
Figure 1b) showed that the obtained samples of activated carbon differ in the presence of undisturbed particles and two-dimensional film-like structures prevail.
SEM images of the resulting activated sorbent sample are shown in
Figure 1a-d. SEM images showed an irregular and heterogeneous surface morphology with a well-developed porous structure. Microphotographs show that the outer surface of the activated sorbents has cracks, crevices and several grains of various sizes in large holes. Pores of various sizes and shapes could be observed.
According to the analysis of SEM images of activated carbons OSL and PhAC (
Figure 1a-b), as well as according to BET analysis, it is possible to judge the presence of not only macropores in the samples, but also the presence of meso- and micropores. SEM-images of activated carbon samples PSL (
Figure 1c) and TAL (
Figure 1d) did not reveal the presence of a developed porous structure, which correlates with small values of micro- and mesopore volumes.
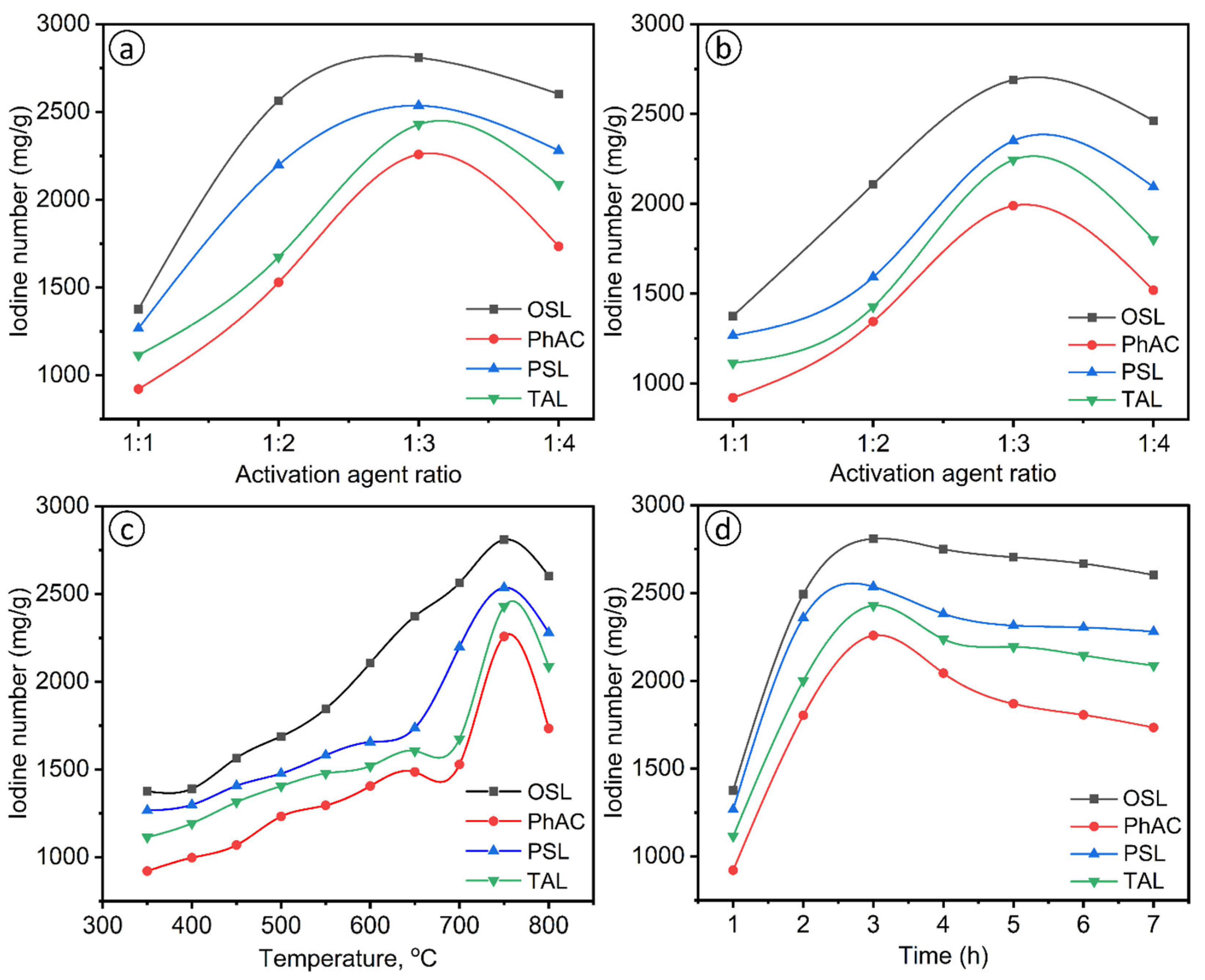
2.3. Effect of the Impregnation Coefficient
It is well known that the impregnation coefficient is one of the parameters that have a profound effect on the adsorption properties of activated carbon. With chemical activation of KOH, the activation time of 3 h and the preliminary activation temperature of 750°C were maintained continuously, while the ratio of sorbents to KOH varied from (1:1) to (1:4) to study the effects of iodine adsorption, respectively. The iodine numbers of sorbents prepared with varying degrees of impregnation using the KOH activating agent are shown in
Figure 2a-b, respectively. As can be seen in
Figure 2a, the iodine numbers of activated sorbents obtained by KOH activation increased with an increase in the ratio of sorbents to KOH in the ratio from (1:1) to (1:3) at 750°C and decreased with an increase in the ratio of plant residues to KOH from (1:3) to (1:4). The highest iodine number was achieved at 2,809 mg/g when biomass - plant residues: OSL, PhAC, PSL and TAL were activated at a ratio to KOH (1:3). However, when biomass - plant residues obtained during pretreatment at 250°C were exposed to an activation temperature of 750°C in a furnace, the iodine numbers of sorbents gradually increased with an increase in the ratio of biomass - plant residues: OSL, PhAC, PSL and TAL to KOH from (1:1) to (1:3) (
Figure 2b. According to these data, sorbents from biomass - plant residues: OSL, PhAC, PSL and TAL activated by the above method increased from 921 to 2690 mg/g of carbon with increasing the degree of impregnation from (1:1) to (1:3) and decreased with an increase in the ratio of sawdust to KOH from (1:3) - 2690 mg/g to (1:4) - 1519 mg/g. The results are shown in
Figure 2b. It is shown that the highest iodine number was obtained with an impregnation ratio (1:3).
2.4. Effect of Activation Temperature
Activation time and duration (3 h), the ratio of biomass to plant residues: OSL, PhAC, PSL and TAL - KOH (1:3) and the temperature of the preliminary The treatments (250°C) were kept constant, while the pre-activation temperature and temperature regime varied from 350 to 800°C to study the effect of the iodine number. The iodine number of activated sorbents prepared at different temperatures using the KOH activating agent is shown in
Figure 2c. The iodine numbers of activated sorbents obtained by KOH activation increased with an increase in temperature in the range 350-750°C (1:3) to a value of 2258-2809 mg/g and decreased with an increase in temperature to 800°C. From the results shown in
Figure 4, it can be seen that the largest iodine number of activated sorbents was obtained OSL at 750°C and amounted to 2809 mg/g. Thus, the temperature of 750°C was chosen as the optimal activation temperature.
2.5. Effect of Activation Time
The preliminary activation temperature (250°C), activation temperature (750°C) and the ratio of biomass to plant residues were established: OSL, PhAC, PSL and TAL to KOH (1:3), and the activation time was varied from 1 to 7 hours to study the effect of activation time on the iodine number. The effect of activation time on the amount of iodine is shown in
Figure 2d. It was proved that the iodine number of biomass - plant residues decreased with increasing activation time. The iodine number gradually increased to 2809 mg/g with an increase in the activation time from 1 to 3 hours. Then, the amount of iodine decreased from 2809 to 1734 mg/g with an increase in the activation time from 3 to 7 hours, indicating that a longer duration of activation time led to an increase or even destruction of some pores.
2.6. BET Analysis and Pore Size Distribution
The adsorption-desorption isotherm of nitrogen at low temperature (-196°C) is usually used for the analysis of physical properties.
Table 2 shows the nitrogen adsorption-desorption isotherms at -196°C for an activated sorbent prepared taking into account the preliminary activation temperature (250°C), activation temperature (750°C) and the ratio of biomass- plant residues to KOH 1:3 surface area BET, for OSL, PhAC, PSL and TAL were 2790, 2305, 1330 and 1755 cm
3/g, respectively. The highest BET surface area was obtained, equal to 2790 m
2/g. The graphs show a typical type I isotherm indicating the presence of microporous adsorbents.
The volume of micropores was estimated using the D-R equation. When activated at a preliminary temperature (250°C), activation temperature (750°C), the maximum volume of micropores was 0.712 cm
3/g. The pore volume B-J-H and the pore radius for the best activated sorbent were 0.432 and 1.46 nm, indicating that most pores had a diameter of less than 4 nm (40°), respectively. This value indicates the presence of micropores. Semi-porosity provides excellent conditions for adsorption, since the adsorbing material can interact with many surfaces simultaneously. The porous activated sorbent is effectively used as adsorbents, catalysts and catalyst carriers, its chemical structure allows it to preferably adsorb organic materials and other non-polar compounds from gas or liquid streams. Due to these properties, they have been used for many decades for gas purification, separation of gas mixtures, purification of exhaust air, especially for solvent extraction, removal of heavy metals, solution discoloration and water purification [
43].
Table 2 shows the pore size distribution curve of the best activated sorbent obtained at different pyrolysis temperatures by the D-A method, which is usually used to evaluate micropores of activated sorbent. With this approach, n reflects the width of the energy distribution, which is related to the pore size distribution. Values from 1 to 4 are observed for most carbon adsorbents, with a value of n>2 for activated carbons with very homogeneous fine micropores and values of n<2 for highly activated sorbents and heterogeneous carbons. The pore diameter of the activated sorbent of the best quality was 0.168 nm, and the degree index (n) in the range of 1.0 indicated mainly micropores. The volume of D-A micropores was 0.84 cm
3/g.
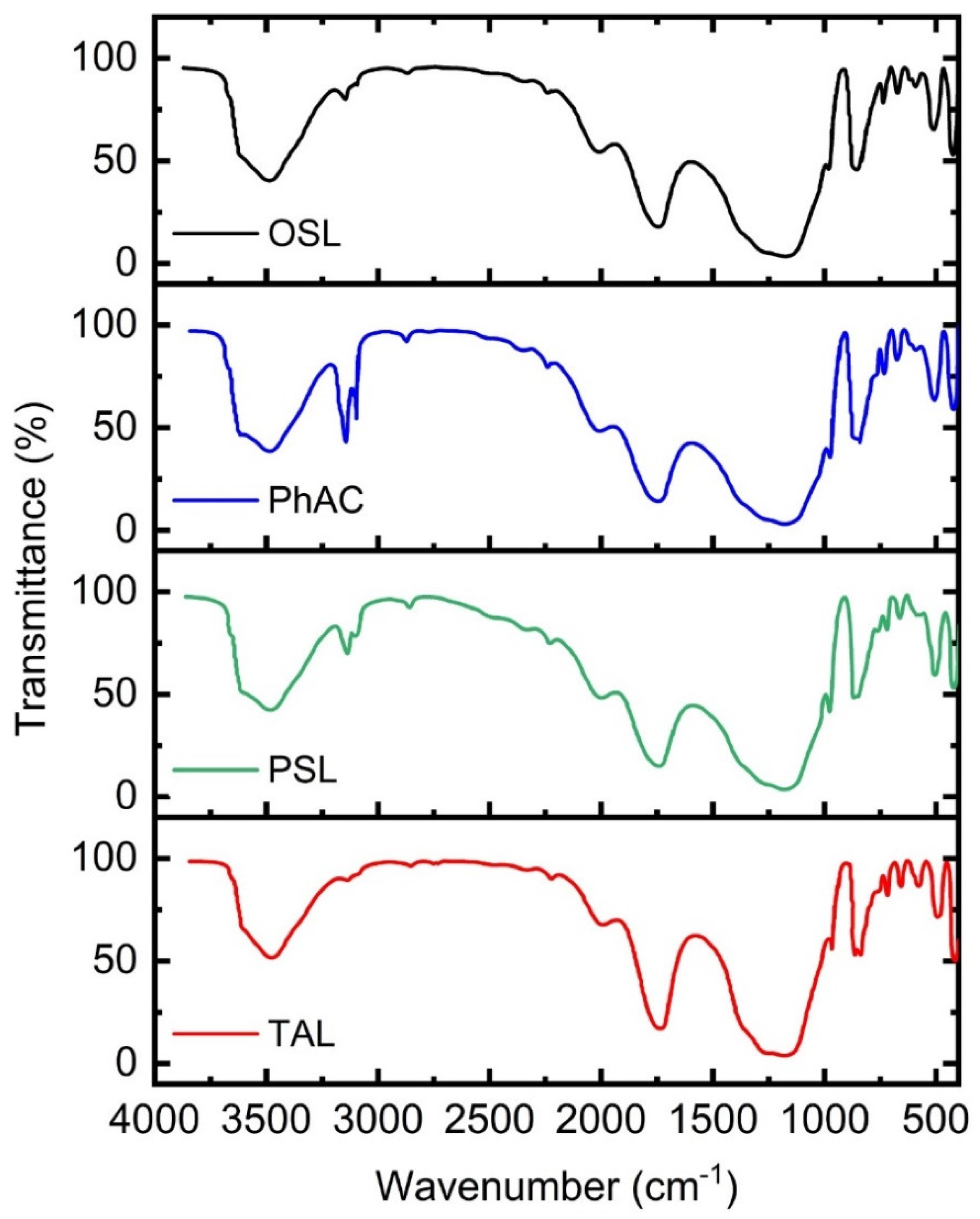
2.7. Functional Groups of Activated Carbons
The infrared spectrum of the obtained sample of the best activated sorbent is shown in
Figure 3. A wide absorption band at 3150-3800 cm
-1 with a maximum at about 3568 cm
-1 is characteristic of stretching vibrations of hydroxyl groups bound with hydrogen. Stripes at 3000-2800 cm
-1 indicate the presence of aliphatic stretching. A band of about 1600 cm
-1 is attributed to an aromatic ring or a stretching vibration C=C. This indicates the formation of carbonyl-containing groups and the aromatization of the precursor [
44]. The band at 2325 cm
-1 represents C≡C stretching fluctuations in alkyne groups. A wide band in the range from 1300 to 900 cm
-1 with maxima at 1056 and 1183-1312 cm
-1 is usually attributed to the stretching of C-O in acids, alcohols, phenols, simple and/or ester groups. The band located at the level of 797 cm
-1 is due to the out-of-plane C-H deformation regime for various substituted benzene rings.
Numerous applications of activated sorbent from activated carbon or biomass precursors have been reported in the literature.
Table 3 summarizes representative studies on the specific application of the activated sorbent, as well as the precursor material and the type of activation process used.
2.8. Investigation of the Sorption Capacity of Activated Carbons in Relation to Hydrocarbons
To determine the possibility of using activated carbon samples to clean the soil from oil pollution, studies of the processes of sorption of oil products on activated carbon samples in model experiments at room temperature were carried out.
The results of the sorption capacity of the studied activated carbon samples in relation to oil products are shown in
Table 4.
OSL showed the best sorption capacity in relation to oil products – gasoline, kerosene and diesel fuel and, accordingly, showed the following results: 9.3 g/g, 9.0 g/g and 10.1 g/g. This is explained by the presence of microporous and mesoporous structures in activated carbon images, which is confirmed by experimental data on the determination of sorption characteristics by calculating nitrogen adsorption/desorption isotherms.
Activated carbon PhAC showed average values of the sorption capacity of oil products – 7.0 g/g. Activated carbons PSL and TAL for a number of gasoline: kerosene: diesel fuel showed a low sorption capacity relative to oil products at the level of 4.5-5.1 g/g.
From the results of experiments to determine the sorption capacity of activated carbon samples, it can be seen that the absorption of gasoline and kerosene by all studied activated carbon samples is less than that of diesel fuel. This is due to differences in the viscosity characteristics of oil products, i.e., the more viscous the oil product, the higher the absorption capacity of activated carbon to it.
Furthermore, the total sorption capacity of the activated carbon samples was investigated across different sorption times: 5, 10, 30, and 60 minutes.The analysis of the obtained data showed that during the sorption of oil and oil products, activated carbon, regardless of the sample, is saturated with hydrocarbons within 10 minutes and subsequently the interplane space between the pores in the structure of the carbon material is filled.
The efficiency of the sorption process was assessed by the degree of extraction of oil products from solutions. Activated carbon samples were left in contact with the solution for 2 hours, after which the solid phase was separated by decantation, oil products were extracted with hexane at a ratio of aqueous and organic phases 4:1 and their residual content was quantified.
The efficiency of the process was assessed by the degree of extraction of S(%) oil products from solutions according to the formula:
where: С
in и С
fin are the initial and final concentrations of oil products in solution, mg/l.
The most effective was a rice husk sample, which showed a degree of oil recovery from the solution of up to 90%. For pine sawdust, reed stalks and wheat straw, the maximum values of the degree of extraction were 70-80%. However, the soil is a more complex porous structure compared to the solution and the degree of extraction of hydrocarbons from the soil will be different.
Based on the conducted model studies, we conclude that the considered natural activated carbons can be used in sorption purification processes in case of oil spill into the soil.
2.9. Conducting Field Work On the Territory of Oil Producing Enterprises of Atyrau Region
At the beginning of the experiments, the oil-contaminated soil of the “Zhanatalap” deposit in the Isatai district of the Atyrau region was prepared (coordinates
47.053498158210495,
50.74402863920371). The nearest settlement is the village of Akkistau, located respectively 10 km to the northeast. The regional center of Atyrau is located 110 km to the southeast. The climate of the territories is sharply continental, the annual temperature fluctuation ranges from +40-50°C in summer and up to - 45°C in winter. The average annual precipitation ranges from 70 to 150 mm. The relief of the oil field area is the plain of the Caspian lowland. It is characterized by a soft soil with the inclusion of loam and with a natural gypsum content, the salt concentration is high (
Figure 4).
Figure 4.
“Zhanatalap” deposit in the Isatai district of Atyrau region (a snapshot of the territory from Google Map).
Figure 4.
“Zhanatalap” deposit in the Isatai district of Atyrau region (a snapshot of the territory from Google Map).
At the outset of the experiments, two plots were designated: the first served as a control for oil-contaminated soil, while the second plot involved testing activated carbon samples for remediation. Each plot measured 4 m2 (2.0m x 2.0m), with approximately 50 kg of soil per plot. Activated carbon derived from biomass plant residues (specifically rice husks, reed stalks, pine sawdust, and wheat straw) activated with potassium hydroxide through two-stage pyrolysis in air was introduced into the oil-contaminated soil.
Following the application of activated carbon, the soil was appropriately moistened and aerated. Soil samples were then periodically collected between 8 to 16 days after treatment to assess the oil content. The determination of oil content in soil samples was carried out using the weight method, involving extraction of hydrocarbons from soil samples using hot hexane in a Soxlet apparatus.
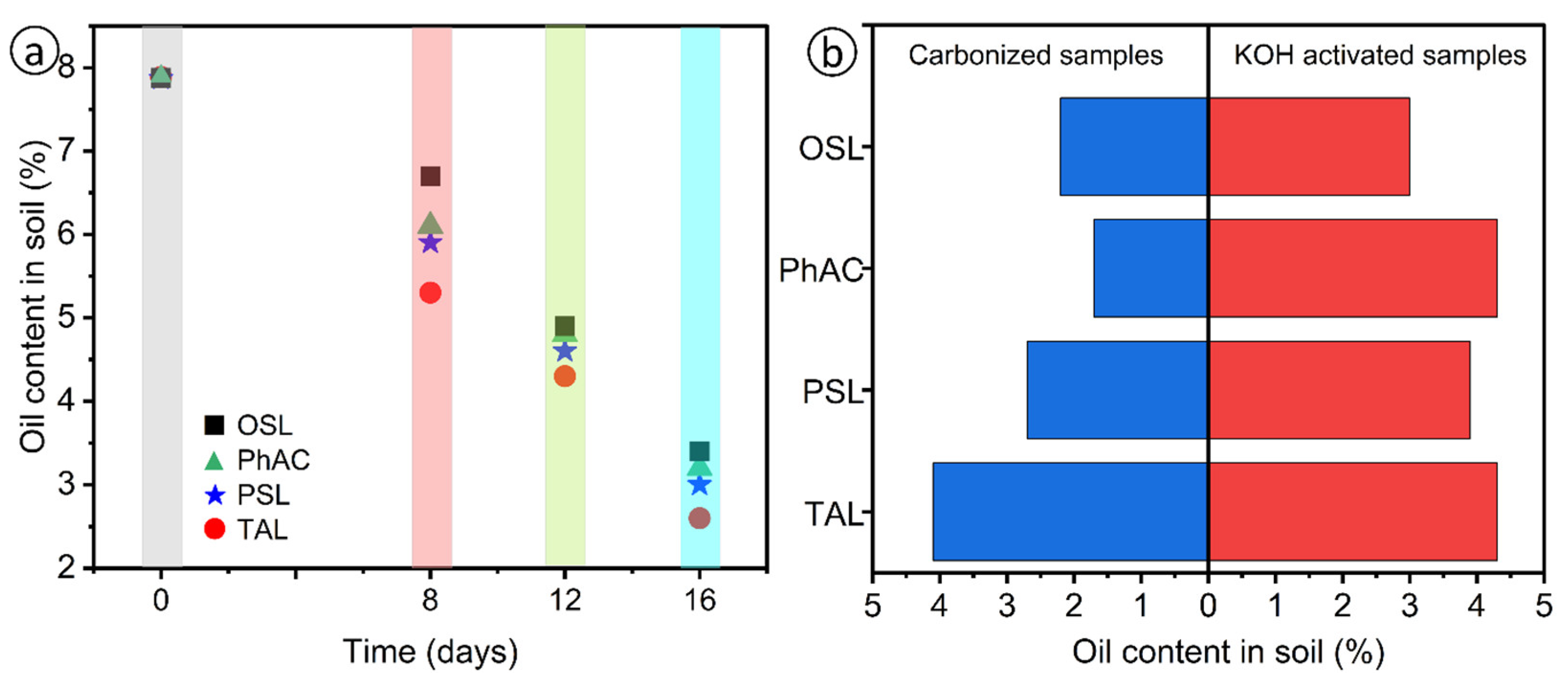
Figure 5a shows the values of the oil content in contaminated soils. The initial degree of soil contamination with petroleum hydrocarbons was 79.2 g/kg or 7.9 wt.%.
As can be seen from the
Figure 5a, after applying activated carbon samples to oil-contaminated soil, the oil content gradually decreases. On the soil samples with the addition of activated carbon on the 8th day, the oil content was 5.7-6.7%, on the 16th day - 2.6-3.3%. According to the oil content in soil samples, the degree of soil purification was calculated, the value of which after 16 days was 58.2-67.1% in soils with sorbent (
Table 5).
The conducted tests have demonstrated that the activated carbon samples exhibit a high efficacy in soil purification. Specifically, after 16 days, the degree of purification of oil-contaminated soil reached 67.71%.
Overall, the field tests conducted on real oil-contaminated soils underscore the effectiveness of utilizing pyrolyzed plant-derived activated carbon based on biomass plant residues.
Figure 5b shows the values of the oil content in contaminated soils during field work on the territory of oil-producing enterprises of the Atyrau region for cleaning with a biosorbent at certain intervals (16 days). As can be seen from the table, after applying the sorbent without modification and with modification to the oil-contaminated soil, the oil content gradually decreases. On soil samples with the introduction of sorbents without modification on the 16th day, the oil absorption content was 1.7-4.1 g/g. According to the oil content in soil samples, the degree of soil purification was calculated, the value of which after 16 days was 3.0-4.3 g/g in soils with modified sorbents.
Having pronounced sorption properties, the modified sorbent in the soil immobilizes hydrocarbons on its surface, preventing their spread to adjacent media, but at the same time slowing down their physico-chemical destruction. In this regard, the use of a hydrophobic sorbent for soil purification is possible provided it is extracted from the soil after adsorption of petroleum products and further processing at a specialized landfill.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Preparation of Materials
This study investigated the characteristics of activated carbon derived from biomass plant residues: OSL, PhAC, PSL, TAL. The starting materials were manually selected, purified with water, dried at 100-105°C for 48 hours in an oven, and then milled and sieved to obtain particles sized between 1 to 2 mm. The resulting material was stored in airtight containers for subsequent experiments.
3.2. Activated Carbon Production from Agricultural Wastes
The production of activated carbons from plant biomass was conducted in two stages:
(I) Impregnation and Preheating: Approximately 5 grams of conditioned plant waste were impregnated with 15 ml of KOH solutions at different sorbent/alkali ratios: (1:1), (1:2), (1:3), and a mixture (1:4) by weight. The impregnation process involved preheating from 30°C to 80°C and maintaining this temperature for 3 hours to ensure penetration of KOH into the biomass. The impregnated sorbents were then placed in a vertical electric furnace with air supply.
(II) Pyrolysis: In the second stage, pyrolysis of the samples was carried out at temperatures ranging from 300°C to 850°C with a heating rate of 5°C/min. After reaching the maximum temperature, the samples were held for 3 hours and then cooled to room temperature. The resulting product underwent thorough washing with 0.1 M hydrochloric acid followed by distilled water to remove alkali residues, with continuous monitoring of the pH value of the wash solution (optimal pH 6-7). After washing, the activated carbon samples were dried at 100-105°C.
3.3. Study of Physico-Chemical, Technological Properties of Activated Sorbents
After obtaining the activated carbon samples, their bulk density and porosity were determined. To analyze the chemical composition of the samples, the QUANTA 3D 200i device (FEI, USA) was used in combination with an energy dispersive X–ray spectrometer EDAX and a semiconductor detector with an energy resolution of 128 eV (polymer material, sensitive area – d = 0.3 mm) [
36].
The bulk density of activated carbon samples (kg/m
3) was determined by weighing a measuring cylinder filled with a substance according to [
37].
The bulk density is calculated using the formula:
where:
ρb – the bulk density of the activated carbon sample, kg/m
3;
m – the mass of activated carbon, kg;
V – the volume of activated carbon in the cylinder after pre-sealing, m
3.
Depending on the bulk density, activated carbon can be classified as follows: ρb > 2000 kg/m3 – very heavy; 2000 > ρb > 1100 kg/m3 – heavy; 1100 > ρb > 600 kg/ m3 – medium; ρb < 600 kg/m3 – light.
3.4. Sample Characteristics
The iodine number is a widely used method for assessing the adsorption capacity of activated carbons due to its simplicity and ability to rapidly evaluate sorbent quality. It quantifies the porosity of activated sorbents by measuring the amount of iodine adsorbed per gram of carbon (expressed as mg/g). The method involves impregnating activated carbon samples with an iodine solution under ambient conditions, followed by filtration. The iodine content in the filtrate is then determined through titration, typically using a standardized iodine solution of 0.100 ± 0.001 mol/l concentration [
38].
This adsorption capacity, often expressed in mg/g (typical range 500-1200 mg/g), indicates the level of activation, reflecting the micropore content in the activated carbon (0-20 Å or up to 2 nm) and corresponding to a surface area ranging from 900 m²/g to 1100 m²/g [
39]. Activated carbons produced OSL, PhAC, PSL and TAL through chemical activation with KOH demonstrate potential for industrial-scale development based on this criterion.
As a complementary surface assessment method, nitrogen adsorption-desorption isotherms were performed at -196°C using a “Sorbtometer-M” surface area analyzer after pre-gasification of samples at 250°C for 24 hours. BET method was applied to analyze the adsorption branch of the isotherms to determine surface areas [
40]. Microporosity was evaluated using the t-method, which combines micropore surface area and external surface area, and the volume of micropores was calculated using the (D-R) equation in logarithmic form. The surface tension of nitrogen was calculated at 8.72 MJ/m², with a molar volume of 34.7 cm³/mol [
19]. Mesopore volume was determined using the (B-J-H) method by analyzing the desorption branch of the isotherm [
41]. The size distribution of micropores was assessed using the (D-A) method based on the adsorption isotherm at low relative pressure [
42].
The morphology of the activated carbon samples (OSL, PhAC, PSL, TAL) was examined using a SEM (model JSM-6490 LA). SEM images were obtained in secondary electron mode at 20 kV acceleration voltage and 20 pA radiation current, with samples prepared in powdered form. Samples were mounted on a copper holder using conductive glue or adhesive tape. Infrared spectra of the activated carbon samples were recorded using a Spectrum 65, Perkin&Elmer 1100 FTIR spectrometer over the range of 4000-400 cm⁻¹, employing KBr pellets with a resolution of 1 cm⁻¹. The pellet for infrared studies was prepared by mixing a given sample with KBr crystals and pressed into a pellet.
3.5. Research of the Sorption Capacity of Activated Carbon in Relation to Hydrocarbons
Sorption activity in relation to oil products was studied under static conditions from model solutions. The model solutions were prepared as follows: aqueous solutions of oil products were obtained by mixing oil products with distilled water, followed by settling and separation of two phases in a Soxlet apparatus; water-oil emulsions were prepared by mixing water and oil products using a mechanical stirrer at high speeds. After sorption on activated carbon samples, the initial and current concentrations of oil products were determined fluorimetrically using the standard technique for “Fluorat-02”. Immediately before the studies, the active coals of the 2.5 + 0.5 mm fraction were dried at a temperature of 105-110°C for 2 hours.
5. Conclusions
In this study, to obtain activated sorbents from biomass - plant residues: OSL, PhAC, PSL and TAL, the KOH chemical activation method was used at two different temperature stages in the range of 250°C and 350-800°C. The effect of the concentration of the impregnating agent, the temperature and duration of activation, and the impregnation time on the area of activated sorbents was investigated. With an increase in the activation temperature, the iodine number of the activated sorbent obtained increased. These materials were characterized by N2 adsorption/desorption to determine the BET and SEM areas. It was found that the maximum surface area of BET is 2790 m2/g for an activated sorbent prepared taking into account the preliminary activation temperature (250°C), activation temperature (750°C) and the ratio of biomass - plant residues to KOH 1:3. The difference in values between the micropore surface areas showed that the activated sorbents were predominantly microporous adsorbents. The pore diameter of the obtained best activated sorbent was 0.168 nm, and the exponent (n) in the range of 1.0 indicated mainly micropores. The detected volume of D-R micropores was 0.712 cm3/g. The structural morphology of the activated sorbent was evaluated by the SEM method. It was clearly visible that the activated sorbents were full of cavities. The chemical characteristics of the surface of the activated sorbent were determined by IR spectroscopy. Additionally, nitrogen adsorption and desorption studies confirmed the presence of a well-developed structure featuring both meso- and micropores. Field tests conducted in the “Zhanatalap” field in the Isatai district of the Atyrau region demonstrated the promising application of plant-derived activated carbon in sorption purification processes for the remediation of oil pollution.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Ye.D., A.S. and M.A.; Methodology, Ye.D. and A.S.; Formal analysis, Ye.D., A.S. and M.A.; Investigation, Ye.D., A.S., M.A., O.D., K.S., K.T., A.K. and A.O.; Resources, Ye.D. and A.S.; Writing- original draft, Ye.D.; Supervision, Ye.D. and A.S.; Project administration, Ye.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Republic of Kazakhstan grant (AP14870186) “Development of methods for recovery of oil-contaminated soil using biodegradable sorbents of plant origin”.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Garcia-Rincon, J.; Gatsios, E.; Lenhard, R.J.; Atekwana, E.A.; Naidu, R. Advances in the Characterisation and Remediation of Sites Contaminated with Petroleum Hydrocarbons. Environ. Contam. Rem. Manage. 2024. [CrossRef]
- da Silva Correa, H.; Blum, C.T.; Galvao, F.; Maranho, L.T. Effects of oil contamination on plant growth and development: a re-view. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 43501-43515. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liang, X.; Li, X. Interfacial Interaction of Clay and Saturates in Petroleum-Contaminated Soil: Effect of Clay Surface Heterogeneity. Molecules 2022, 27, 7950. [CrossRef]
- Taurbekov, A.; Abdisattar, A.; Atamanov, M.; Kaidar, B.; Yeleuov, M.; Joia, R.; Amrousse, R.; Atamanova, T. Investigations of Activated Carbon from Different Natural Sources for Preparation of Binder-Free Few-Walled CNTs/Activated Carbon Electrodes. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7(11), 452. [CrossRef]
- Mohan, P.R. Effective acrylamide adsorption in aqueous environments using maize straw nanobiochar (MNBC), Nanotechnol. Environ. Eng. 2024. [CrossRef]
- Ngo, Th.C.Q.; Tran, Th.K.N.; Chau, H.D.; Hoang, B.N. The material potential and application of activated carbon from nut shells: Mini review. Materials Today: Proceedings 2024. [CrossRef]
- Seitzhanova, M.; Azat, S.; Yeleuov, M.; Taurbekov, A.; Mansurov, Z.; Doszhanov, E.; Berndtsson, R. Production of Graphene Membranes from Rice Husk Biomass Waste for Improved Desalination. Nanomaterials 2024, 14(2), 224. [CrossRef]
- Saka, C. BET, TG-DTG, FT-IR, SEM, Iodine Number Analysis and Preparation of Activated Carbon from Acorn Shell by Chemical Activation with ZnCl2. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2012, 95, 21-24. [CrossRef]
- Sahin, O., Saka, C. Preparation and characterization of activated carbon from acorn shell by physical activation with H2O-CO2 in two-step pretreatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 136, 163-168. [CrossRef]
- Robles, E.; Izaguirre, N.; Martin, A.; Moschou, D.; Labidi, J. Assessment of Bleached and Unbleached Nanofibers from Pistachio Shells for Nanopaper Making. Molecules 2021, 26(5), 1371. [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Wu, Y.; Hou, Zh.; Jiang, E. Influence of biomass components, temperature and pressure on the pyrolysis behavior and biochar properties of pine nut shells. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 313, 123682. [CrossRef]
- Vuong, T.X.; Stephen, J.; Nguyen, T.T.T.; Cao, V.; Pham, D.T.N. Insight into the Speciation of Heavy Metals in the Contaminated Soil Incubated with Corn Cob-Derived Biochar and Apatite. Molecules 2023, 28, 2225. [CrossRef]
- Salman, J.M.; Njoku, V.O.; Hameed, B.H. Adsorption of pesticides from aqueous solution onto banana stalk activated carbon. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 174, 2, 41-48. [CrossRef]
- Janković, B.; Manić, N.; Dodevski, V.; Radović, I.; Pijović, M.; Katnić, Đ.; Tasić, G. Physico-chemical characterization of carbonized apricot kernel shell as precursor for activated carbon preparation in clean technology utilization. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 236, 1, 117614. [CrossRef]
- Usino, D.O.; Ylitervo, P.; Richards, T. Primary Products from Fast Co-Pyrolysis of Palm Kernel Shell and Sawdust. Molecules 2023, 28, 6809. [CrossRef]
- Ganaraja, A.Y.; Machado, A.A.; Mulky, L. A Comparative Study of Treatment Methods of Raw Sugarcane Bagasse for Adsorption of Oil and Diesel. Water, Air, Soil Pollut. 2023, 234:213. [CrossRef]
- Kenes, K.; Yerdos, O. Zulkhair, M.; Yerlan, D. Study on the effectiveness of thermally treated rice husks for petroleum adsorption. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2012, 358(22), 2964-2969. [CrossRef]
- Lesbayev, B.; Rakhymzhan, N.; Ustayeva, G.; Maral, Y.; Atamanov, M.; Auyelkhankyzy, M.; Zhamash, A. Preparation of Nanoporous Carbon from Rice Husk with Improved Textural Characteristics for Hydrogen Sorption. J. Compos. Sci. 2024, 8(2), 74. [CrossRef]
- Mansurov, Z.A.; Velasco, L.F.; Lodewyckx, P.; Doszhanov, E.O.; Azat, S. Modified Carbon Sorbents Based on Walnut Shell for Sorption of Toxic Gases. J. Eng. Phys. Thermophys. 2022, 95, 6, 1383-1392. [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Webley, P.A. Preparation of activated carbons from corncob with large specific surface area by a variety of chemical activators and their application in gas storage. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 162, 883-892. [CrossRef]
- Saka, C.; Sahin, Ö.; Küçük, M.M. Applications on Agricultural and Forest Waste Adsorbents for the Removal of Lead(II) from Contaminated Waters. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 9, 379-394. [CrossRef]
- Ilyin, Y.V.; Kudaibergenov, K.K.; Sharipkhanov, S.D.; Mansurov, Z.A.; Zhaulybayev, A.А.; Atamanov, M.K. Surface Modifications of CuO Doped Carbonaceous Nanosorbents and their CO2 Sorption Properties. Eurasian Chem.-Technol. J. 2023, 25(1), 33-38. [CrossRef]
- El-Hendawy, A.A.; Alexander, A.J.; Andrews, R.J.; Forrest, G. Effects of activation schemes on porous, surface and thermal properties of activated carbons prepared from cotton stalks. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2008, 82, 272-278. [CrossRef]
- Mopoung, S.; Dejang, N. Activated carbon preparation from eucalyptus wood chips using continuous carbonization-steam activation process in a batch intermittent rotary kiln. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11(1). [CrossRef]
- Yakaboylu, G.A.; Jiang, Ch.; Yumak, T.; Zondlo, J.W.; Wang, J.; Sabolsky, E.M. Engineered hierarchical porous carbons for supercapacitor applications through chemical pretreatment and activation of biomass precursors. Renewable Energy 2021, 163, 276-287. [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Chi, L.; Wenelska, K.; Wen, X.; Chen, X.; Mijowska, E. Eucalyptus derived heteroatom-doped hierarchical porous carbons as electrode materials in supercapacitors. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14631. [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, J.; Kazehaya, A.; Muroyama, K.; Watkinson, A.P. Preparation of activated carbon from lignin by chemical activation. Carbon 2000, 38(13), 1873-1878. [CrossRef]
- Prahas, D.; Kartika, Y.; Indraswati, N.; Ismadji, S. Activated carbon from jackfruit peel waste by H3PO4 chemical activation: Pore structure and surface chemistry characterization. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 140, 32-42. [CrossRef]
- Vargas, A.M.M.; Cazetta, A.L.; Garcia, C.A.; Moraes, J.C.G.; Nogami, E.M.; Lenzi, E.; Costa, W.F.; Almeida, V.C. Preparation and Characterization of Activated Carbon from a New Raw Lignocellulosic Material: Flamboyant (Delonix regia) Pods. J. Environ. Manage. 2011, 92, 178-184. [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Liu, Ch.; Cheng, S.; Li, T. Microwave thermal regeneration characteristics of spent activated carbon based on a coupled electromagnetic, heat and mass transfer multiphase porous media model. Energy 2024, 292, 130437. [CrossRef]
- Roy, Z.; Barman, S.; Halder, G. Carbon dioxide sorptive cooling in substitute model refrigeration system for replacing halogenated refrigerants. Environ. Technol. Innovation 2021, 23, 101636. [CrossRef]
- Unger, R.; Killorn, R. Effect of the Application of Biochar on Selected Soil Chemical Properties, Corn Grain, and Biomass Yields in Iowa. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2011, 42, 2441-2451. [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Liu, D.; Xu, Y.; Chen, J.; Yang, Y.; Xia, D.; Ding, Y.; Xu, W. Effects of two types of activated carbon on the properties of vegetation concrete and Cynodon dactylongrowth. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10(1), 14483. [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.I.; Ugulu, I.; Zafar, A.; Mehmood, N.; Bashir, H.; Ahmad, K.; Sana, M. Biomonitoring of heavy metals accumulation in wild plants growing at Soon valley, Khushab, Pakistan. Pakistan J. Bot. 2021, 53(1), 247-252. [CrossRef]
- Taurbekov, A.; Abdisattar, A.; Atamanov, M.; Yeleuov, M.; Daulbayev, C.; Askaruly, K.; Kaidar, B.; Mansurov, Z.; Castro-Gutierrez, J.; Celzard, A.; Fierro V.; Atamanova, T. Biomass Derived High Porous Carbon via CO2 Activation for Supercapacitor Electrodes. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7(10), 444. [CrossRef]
- Mansurov, Z.A.; Zhylybaeva, N.K.; Ualieva, P.S.; Mansurova, R.M. Obtaining procedure and properties of the sorbents from plant raw material. Chem. Sustain. Dev. 2002, 10, 321-328.
- GOST 1236-2013; Fertilizers. Method for determining bulk density without compaction: Мoscow, Russia, 2013.
- GOST 33618-2015; Activated carbon. Standard method for determination of iodine value: Мoscow, Russia, 2016.
- Gargiulo, V.; Alfè, M.; Raganati, F.; Zhumagaliyeva, A.; Doszhanov, Ye.; Ammendola, P.; Chirone, R. CO2 Adsorption under Dynamic Conditions: An Overview on Rice Husk-Derived Sorbents and Other Materials. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2019, 191, 9, 1484-1498. [CrossRef]
- Brunauer, S.; Emmett, P.H.; Teller, E. Adsorption of Gases in Multimolecular Layers. J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 1938, 60, 309-319. [CrossRef]
- Barrett, E.P.; Joyner, L.G.; Halenda, P.P. The Determination of Pore Volume and Area Distributions in Porous Substances. I. Computations from Nitrogen Isotherms. J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 1951, 73, 373-380. [CrossRef]
- Regadera-Macias, A.M.; Morales-Torres, S., Pastrana-Martinez, L.M.; Maldonado-Hódar, F.J. Optimizing filters of activated carbons obtained from biomass residues for ethylene removal in agro-food industry devices. Environ. Res. 2024, 248, 118247. [CrossRef]
- Smisek, M.; Cerney, S. Active Carbon: Manufacture, Properties and Aplications, Elsevier Publishing Comp. Amsterdam–London–New York 1970.
- Chen, Ch.; Yuan, Zh.; Sun, Sh.; Xie, J.; Zhang, K.; Zhai, Y.; Zuo, R.; Bi, E.; Tao, Y.; Song, Q. Remediation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon-Contaminated Soil by Using Activated Persulfate with Carbonylated Activated Carbon Supported Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron. Catalysts 2024, 14(5), 311. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).