Submitted:
17 July 2024
Posted:
18 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
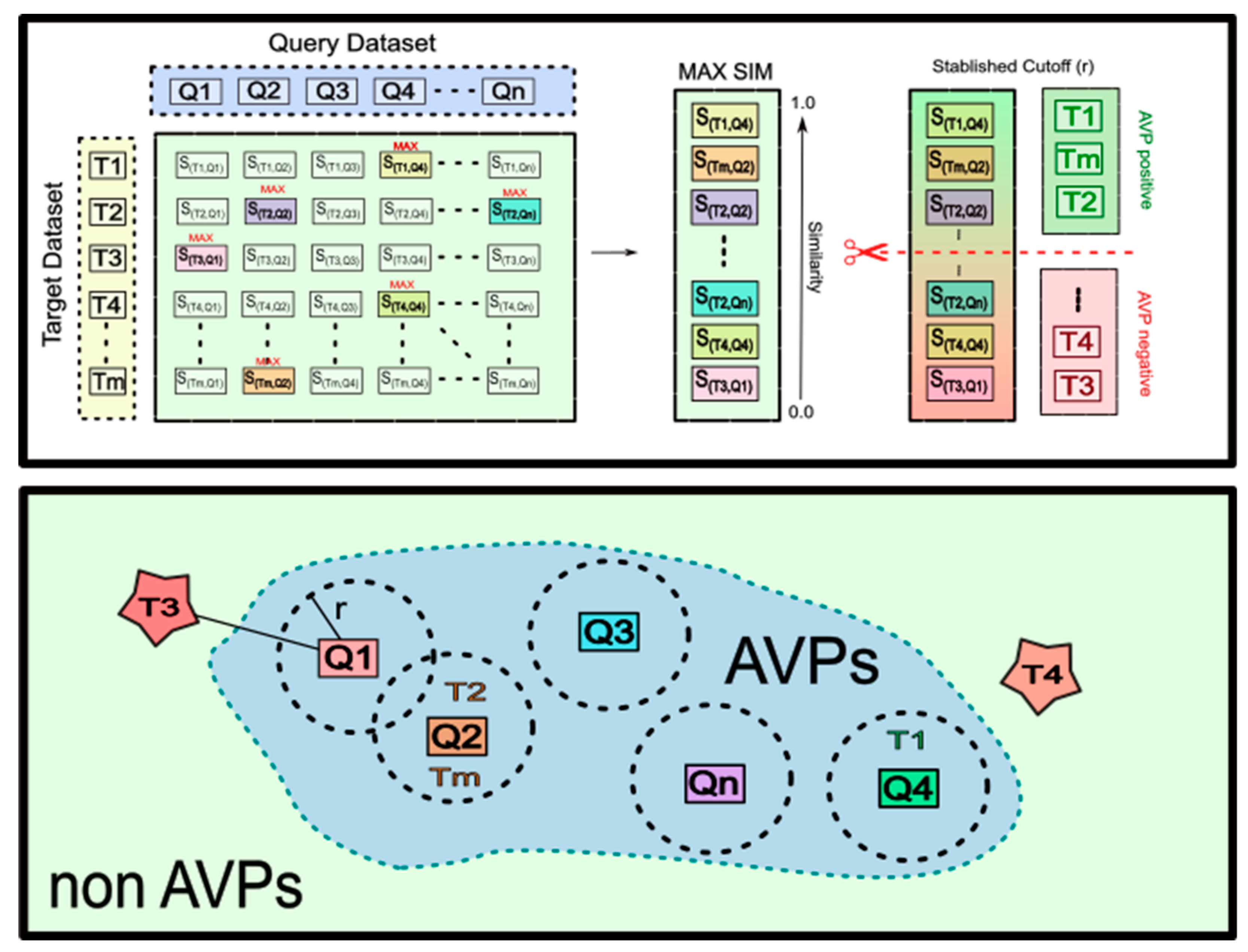
2.1. The Multi-Query Similarity Search Model (MQSSM). The Overall Approach
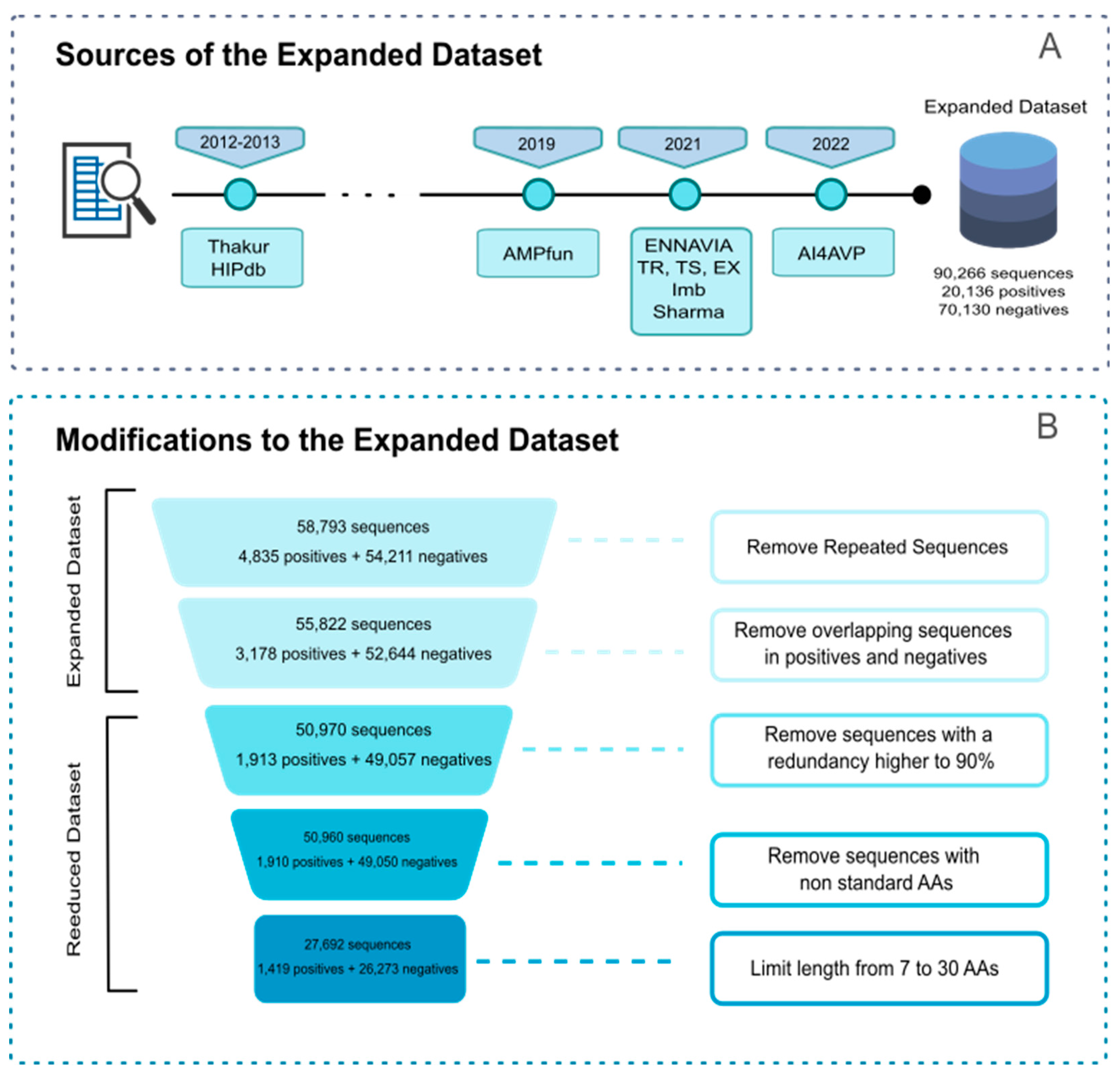
2.2. Construction of Query/Reference Datasets
2.2.1. Recalling the Scaffold Extraction Procedure
2.3. Target Datasets for Calibration and Validation of MQSSMs
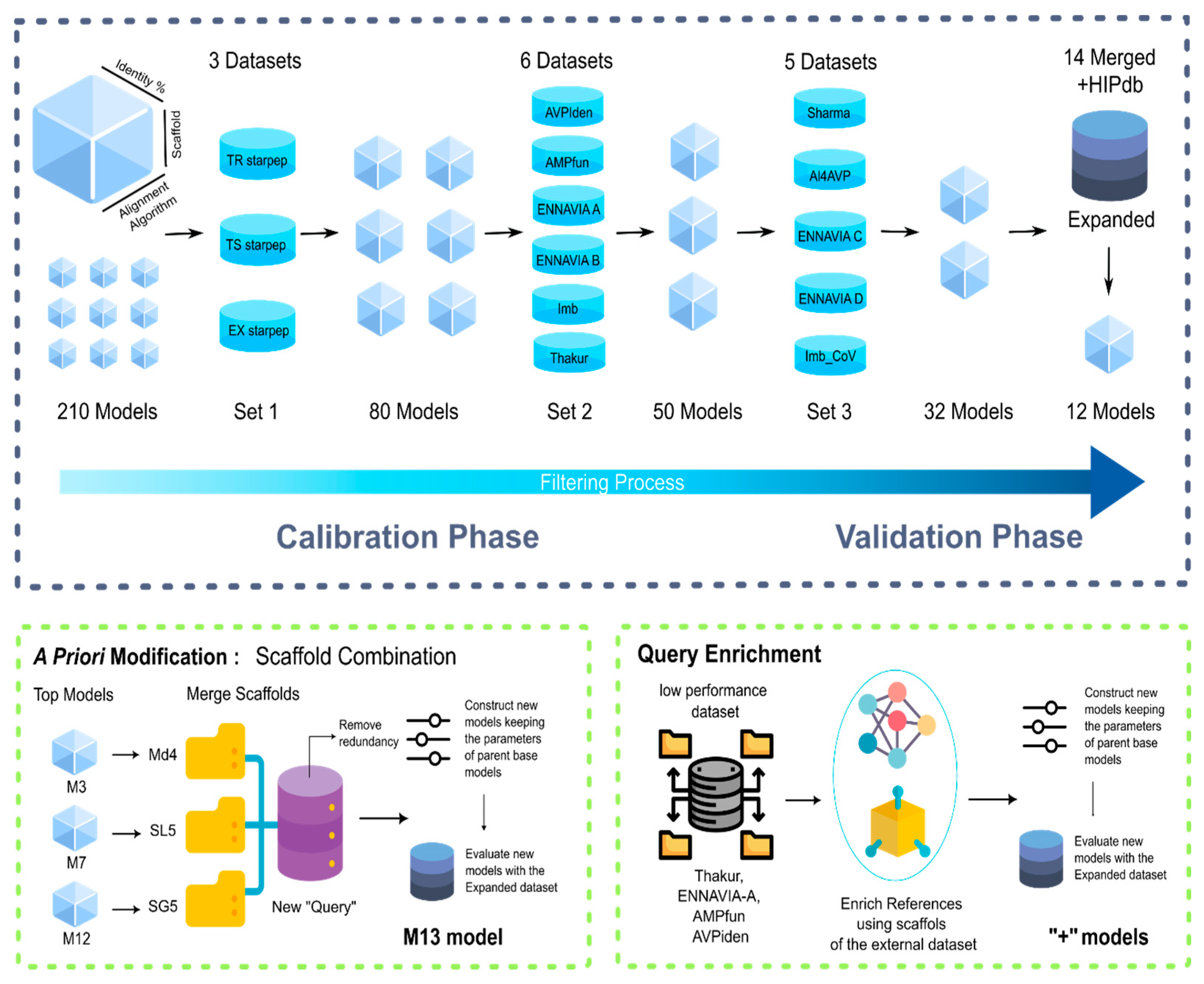
2.4. Construction, Selection and, Improvement of MQSSMs
2.5. Scaffold Fusion
2.6. Scaffold Enrichment
2.7. Performance Evaluation
2.8. Comparison with State-of-the-Art
3. Results and Discussion
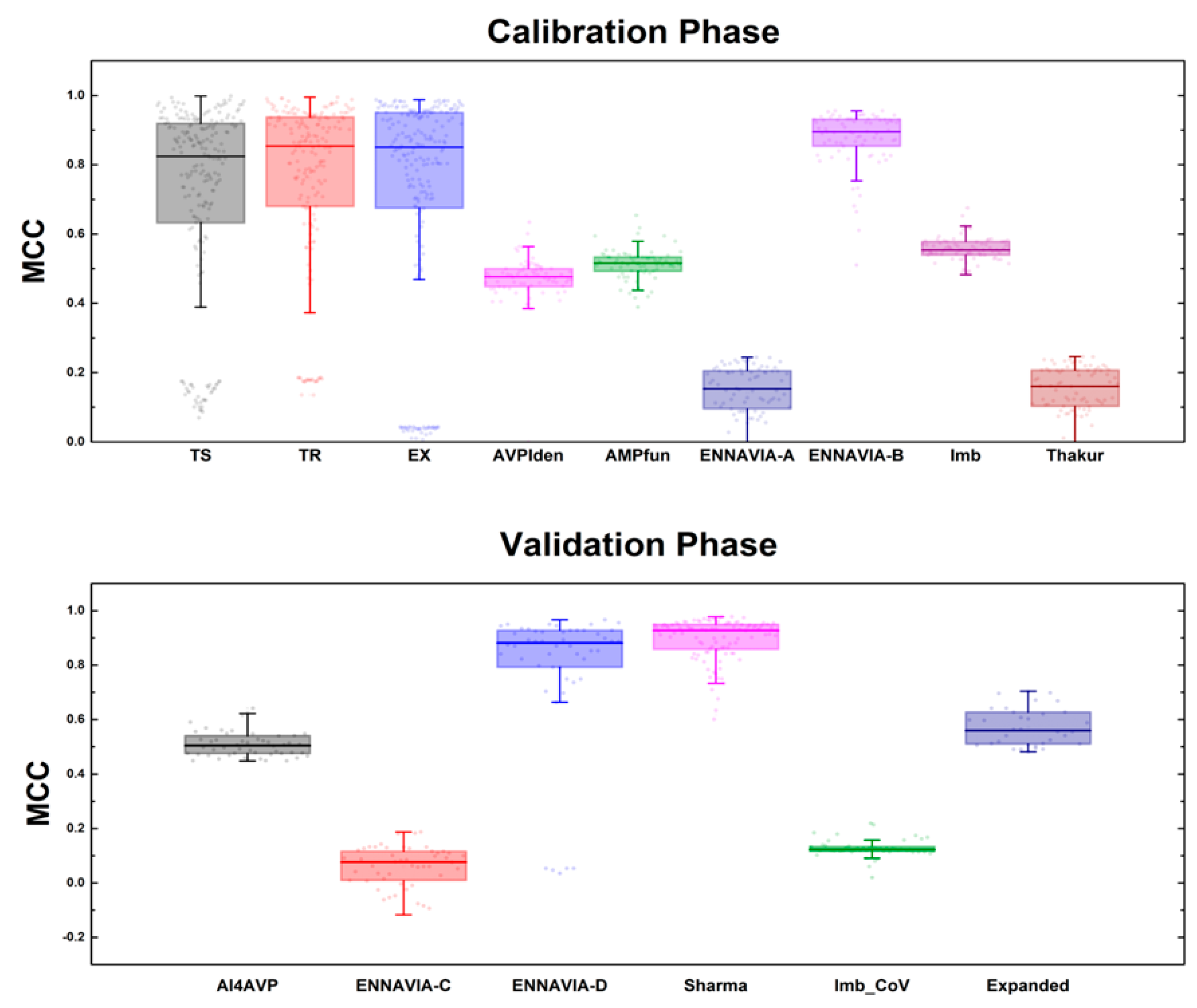
3.1. Performance of MQSSMs at the Calibration Phase
3.2. Performance of MQSSMs at the Validation Phase
3.3. Improving MQSSMs Performance by Fusing Scaffolds
3.4. Improving MQSSMs Performance by Enriching the Best Scaffolds
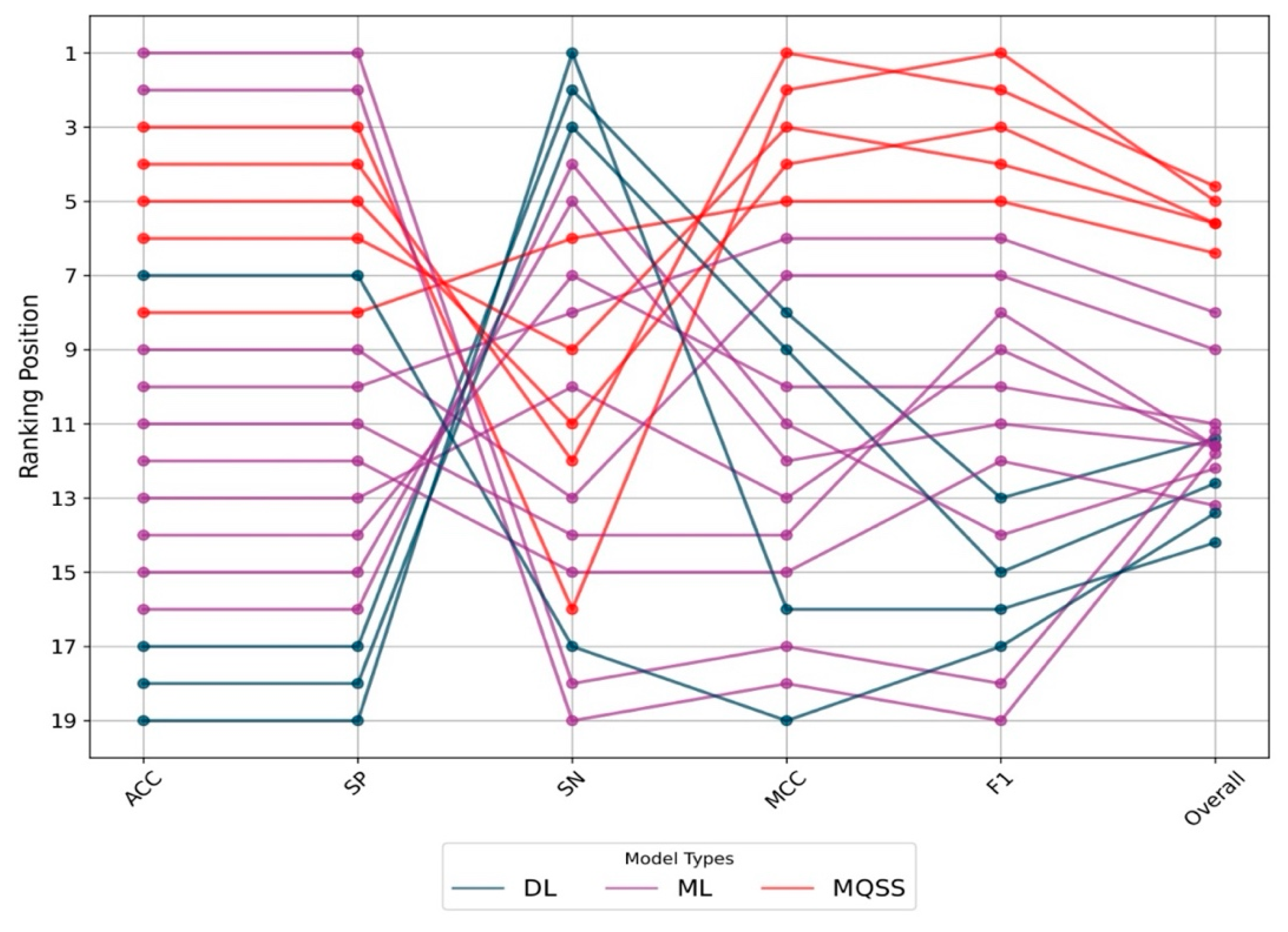
3.5. Benchmarking the Best MQSSMs against State-of-the-Art Predictors
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Enquist, L.W. Virology in the 21st Century. J Virol 2009, 83, 5296–5308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, N.; Zhang, W.; Cheng, X.; Yan, Z.; Shao, G.; Wang, X.; Wang, R.; Fu, C. Therapeutic Peptides: Current Applications and Future Directions. Sig Transduct Target Ther 2022, 7, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjuán, R.; Domingo-Calap, P. Mechanisms of Viral Mutation. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 4433–4448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoud, A. New Vaccines: Challenges of Discovery. Microb. Biotechnol. 2016, 9, 549–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- P Carter, E.; G Ang, C.; M Chaiken, I. Peptide Triazole Inhibitors of HIV-1: Hijackers of Env Metastability. CPPS 2023, 24, 59–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agamennone, M.; Fantacuzzi, M.; Vivenzio, G.; Scala, M.C.; Campiglia, P.; Superti, F.; Sala, M. Antiviral Peptides as Anti-Influenza Agents. IJMS 2022, 23, 11433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divyashree, M.; Mani, M.K.; Reddy, D.; Kumavath, R.; Ghosh, P.; Azevedo, V.; Barh, D. Clinical Applications of Antimicrobial Peptides (AMPs): Where Do We Stand Now? PPL 2020, 27, 120–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Cooper, C.L.; Wang, G.; Morwitzer, M.J.; Kota, K.; Tran, J.P.; Bradfute, S.B.; Liu, Y.; Shao, J.; Zhang, A.K.; et al. Engineered Human Cathelicidin Antimicrobial Peptides Inhibit Ebola Virus Infection. iScience 2020, 23, 100999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackman, J.A.; Costa, V.V.; Park, S.; Real, A.L.C.V.; Park, J.H.; Cardozo, P.L.; Ferhan, A.R.; Olmo, I.G.; Moreira, T.P.; Bambirra, J.L.; et al. Therapeutic Treatment of Zika Virus Infection Using a Brain-Penetrating Antiviral Peptide. Nature Mater 2018, 17, 971–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilas Boas, L.C.P.; Campos, M.L.; Berlanda, R.L.A.; de Carvalho Neves, N.; Franco, O.L. Antiviral Peptides as Promising Therapeutic Drugs. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 3525–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, J.L.; Dunn, M.K. Therapeutic Peptides: Historical Perspectives, Current Development Trends, and Future Directions. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 2018, 26, 2700–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, M.; Singh, A.; Kumar, S. PTPAMP: Prediction Tool for Plant-Derived Antimicrobial Peptides. Amino Acids 2023, 55, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, S.; Karnik, S.; Nilawe, P.; Jayaraman, V.K.; Idicula-Thomas, S. ClassAMP: A Prediction Tool for Classification of Antimicrobial Peptides. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. and Bioinf. 2012, 9, 1535–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, N.; Qureshi, A.; Kumar, M. AVPpred: Collection and Prediction of Highly Effective Antiviral Peptides. Nucleic Acids Research 2012, 40, W199–W204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Wang, P.; Lin, W.-Z.; Jia, J.-H.; Chou, K.-C. iAMP-2L: A Two-Level Multi-Label Classifier for Identifying Antimicrobial Peptides and Their Functional Types. Analytical Biochemistry 2013, 436, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurata, H.; Tsukiyama, S.; Manavalan, B. iACVP: Markedly Enhanced Identification of Anti-Coronavirus Peptides Using a Dataset-Specific Word2vec Model. Briefings in Bioinformatics 2022, 23, bbac265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaduangrat, N.; Nantasenamat, C.; Prachayasittikul, V.; Shoombuatong, W. Meta-iAVP: A Sequence-Based Meta-Predictor for Improving the Prediction of Antiviral Peptides Using Effective Feature Representation. IJMS 2019, 20, 5743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.-R.; Kuo, T.-R.; Wu, L.-C.; Lee, T.-Y.; Horng, J.-T. Characterization and Identification of Antimicrobial Peptides with Different Functional Activities. Briefings in Bioinformatics 2020, 21, 1098–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmons, P.B.; Hewage, C.M. ENNAVIA Is a Novel Method Which Employs Neural Networks for Antiviral and Anti-Coronavirus Activity Prediction for Therapeutic Peptides. Briefings in Bioinformatics 2021, 22, bbab258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, X. Pep-CNN: An Improved Convolutional Neural Network for Predicting Therapeutic Peptides. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems 2022, 221, 104490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-T.; Sun, Y.-Y.; Wang, C.-T.; Cheng, W.-C.; Lu, I.-H.; Lin, C.-Y.; Chen, S.-H. AI4AVP: An Antiviral Peptides Predictor in Deep Learning Approach with Generative Adversarial Network Data Augmentation. Bioinformatics Advances 2022, 2, vbac080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Zhou, C.; Su, R.; Zou, Q. PEPred-Suite: Improved and Robust Prediction of Therapeutic Peptides Using Adaptive Feature Representation Learning. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 4272–4280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Jacas, C.R.; Pinacho-Castellanos, S.A.; García-González, L.A.; Brizuela, C.A. Do Deep Learning Models Make a Difference in the Identification of Antimicrobial Peptides? Briefings in Bioinformatics 2022, 23, bbac094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Cai, J.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Y.; Wong, D.F.; Siu, S.W.I. Recent Progress in the Discovery and Design of Antimicrobial Peptides Using Traditional Machine Learning and Deep Learning. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basith, S.; Manavalan, B.; Hwan Shin, T.; Lee, G. Machine Intelligence in Peptide Therapeutics: A Next-generation Tool for Rapid Disease Screening. Med Res Rev 2020, 40, 1276–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Mendieta, K.; Agüero-Chapin, G.; Santiago Vispo, N.; Márquez, E.A.; Perez-Castillo, Y.; Barigye, S.J.; Marrero-Ponce, Y. Peptide Hemolytic Activity Analysis Using Visual Data Mining of Similarity-Based Complex Networks; MATHEMATICS & COMPUTER SCIENCE, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Romero, M.; Marrero-Ponce, Y.; Rodríguez, H.; Agüero-Chapin, G.; Antunes, A.; Aguilera-Mendoza, L.; Martinez-Rios, F. A Novel Network Science and Similarity-Searching-Based Approach for Discovering Potential Tumor-Homing Peptides from Antimicrobials. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala-Ruano, S.; Marrero-Ponce, Y.; Aguilera-Mendoza, L.; Pérez, N.; Agüero-Chapin, G.; Antunes, A.; Aguilar, A.C. Network Science and Group Fusion Similarity-Based Searching to Explore the Chemical Space of Antiparasitic Peptides. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 46012–46036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera-Mendoza, L.; Ayala-Ruano, S.; Martinez-Rios, F.; Chavez, E.; García-Jacas, C.R.; Brizuela, C.A.; Marrero-Ponce, Y. StarPep Toolbox : An Open-Source Software to Assist Chemical Space Analysis of Bioactive Peptides and Their Functions Using Complex Networks. Bioinformatics 2023, 39, btad506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Llano García, D.; Rodríguez Cabrera, H.M.; Yachay, U. de I. de T.E. A Novel Network Science and Similarity-Searching-Based Approach for Discovering Potential Antiviral Peptides /; Urcuquí, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Aguilera-Mendoza, L.; Marrero-Ponce, Y.; Beltran, J.A.; Tellez Ibarra, R.; Guillen-Ramirez, H.A.; Brizuela, C.A. Graph-Based Data Integration from Bioactive Peptide Databases of Pharmaceutical Interest: Toward an Organized Collection Enabling Visual Network Analysis. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 4739–4747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera-Mendoza, L.; Marrero-Ponce, Y.; García-Jacas, C.R.; Chavez, E.; Beltran, J.A.; Guillen-Ramirez, H.A.; Brizuela, C.A. Automatic Construction of Molecular Similarity Networks for Visual Graph Mining in Chemical Space of Bioactive Peptides: An Unsupervised Learning Approach. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 18074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchiori, M.; Latora, V. Harmony in the Small-World. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications 2000, 285, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, Y.; Tang, J.; Hu, Y.; Wang, H.; Bai, L. Efficient Algorithm for the Identification of Node Significance in Complex Network. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 28947–28955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera-Mendoza, L.; Marrero-Ponce, Y.; Tellez-Ibarra, R.; Llorente-Quesada, M.T.; Salgado, J.; Barigye, S.J.; Liu, J. Overlap and Diversity in Antimicrobial Peptide Databases: Compiling a Non-Redundant Set of Sequences. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 2553–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinacho-Castellanos, S.A.; García-Jacas, C.R.; Gilson, M.K.; Brizuela, C.A. Alignment-Free Antimicrobial Peptide Predictors: Improving Performance by a Thorough Analysis of the Largest Available Data Set. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2021, 61, 3141–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Yao, L.; Jhong, J.-H.; Wang, Z.; Lee, T.-Y. AVPIden: A New Scheme for Identification and Functional Prediction of Antiviral Peptides Based on Machine Learning Approaches. Briefings in Bioinformatics 2021, 22, bbab263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Jhong, J.-H.; Lee, T.-Y. Identifying Anti-Coronavirus Peptides by Incorporating Different Negative Datasets and Imbalanced Learning Strategies. Briefings in Bioinformatics 2021, 22, 1085–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Shrivastava, S.; Singh, S.K.; Kumar, A.; Singh, A.K.; Saxena, S. Deep-AVPpred: Artificial Intelligence Driven Discovery of Peptide Drugs for Viral Infections. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2022, 26, 5067–5074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, A.; Thakur, N.; Kumar, M. HIPdb: A Database of Experimentally Validated HIV Inhibiting Peptides. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.Y.; Yang, J.-R. Analysis and Prediction of Highly Effective Antiviral Peptides Based on Random Forests. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcalá-Fdez, J.; Sánchez, L.; García, S.; Del Jesus, M.J.; Ventura, S.; Garrell, J.M.; Otero, J.; Romero, C.; Bacardit, J.; Rivas, V.M.; et al. KEEL: A Software Tool to Assess Evolutionary Algorithms for Data Mining Problems. Soft Comput 2009, 13, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otović, E.; Njirjak, M.; Kalafatovic, D.; Mauša, G. Sequential Properties Representation Scheme for Recurrent Neural Network-Based Prediction of Therapeutic Peptides. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2022, 62, 2961–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, A.S.; Reehl, S.M.; Kehn-Hall, K.; Bishop, B.; Webb-Robertson, B.-J.M. Better Understanding and Prediction of Antiviral Peptides through Primary and Secondary Structure Feature Importance. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 19260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beltrán Lissabet, J.F.; Belén, L.H.; Farias, J.G. AntiVPP 1.0: A Portable Tool for Prediction of Antiviral Peptides. Computers in Biology and Medicine 2019, 107, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diakou, I.; Papakonstantinou, E.; Papageorgiou, L.; Pierouli, K.; Dragoumani, K.; Spandidos, D.; Bacopoulou, F.; Chrousos, G.; Eliopoulos, E.; Vlachakis, D. Novel Computational Pipelines in Antiviral Structure-based Drug Design (Review). Biomed Rep 2022, 17, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Dataset | Size | Positives | Negatives | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TR_StarPep | 4,642 | 2,321 | 2,321 | [36] |
| TS_StarPep | 1,246 | 623 | 623 | |
| Ex_Starpep | 12,001 | 1,230 | 10,771 | |
| AVPIden | 53,113 | 2,662 | 51,116 | [37] |
| AMPfun | 5,826 | 2,001 | 3,825 | [18] |
| ENNAVIA-A | 974 | 557 | 420 | [19] |
| ENNAVIA-B | 1,154 | 557 | 597 | |
| ENNAVIA-C | 465 | 109 | 356 | |
| ENNAVIA-D | 469 | 110 | 359 | |
| Imb | 12,234 | 2,038139 (Anti-CoV) | 10,196 | [38] |
| Thakur | 1,056 | 604 | 452 | [14] |
| Sharma | 6,544 | 3,273 | 3,271 | [39] |
| AI4AVP | 20,222 | 2,934 | 17,288 | [21] |
| Hipdb | 981 | 981 | - | [40] |
| Expanded | 55,822 | 3,178 | 52,644 | - |
| Reduced | 27,692 | 1,419 | 26,273 | - |
| Predictor | Year | Algorithm | Implementation | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AI4AVP | 2022 | CNN | https://axp.iis.sinica.edu.tw/AI4AVP/ | [21] |
| iACVP | 2022 | RF | http://kurata35.bio.kyutech.ac.jp/iACVP/ | [16] |
| PTPAMP | 2022 | SVM | http://www.nipgr.ac.in/PTPAMP/ | [12] |
| seqpros | 2022 | MLP, LSTM | https://github.com/cotovic/seqpropstherapeutic | [43] |
| ProDcal | 2021 | RF, RNN | https://biocom-ampdiscover.cicese.mx/ | [36] |
| AMPfun | 2020 | RF | http://fdblab.csie.ncu.edu.tw/AMPfun/index.html | [18] |
| FIRM-AVP | 2020 | RF SVM, DL | https://github.com/pmartR/FIRM-AVP | [44] |
| Meta-iAVP | 2019 | hybrid | http://codes.bio/meta-iavp/ | [17] |
| AntiVPP | 2019 | RF | https://github.com/bio-coding/AntiVPP | [45] |
| ClassAMP | 2012 | RF SVM | http://www.bicnirrh.res.in/classamp/ | [13] |
| AVPpred | 2012 | SVM | http://erdd.osdd.net/servers/avppred/ | [14] |
| Model | ACC | SP | SN | MCC | FPR | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E1 | 0.966 | 0.995 | 0.481 | 0.624 | 0.005 | 0.614 |
| E2 | 0.961 | 0.995 | 0.398 | 0.562 | 0.005 | 0.54 |
| M12 | 0.958 | 0.962 | 0.891 | 0.704 | 0.038 | 0.708 |
| M12+ | 0.736 | 0.724 | 0.937 | 0.33 | 0.276 | 0.288 |
| M13 | 0.964 | 0.98 | 0.694 | 0.667 | 0.02 | 0.686 |
| M13+ | 0.969 | 0.979 | 0.802 | 0.731 | 0.021 | 0.746 |
| M3 | 0.935 | 0.944 | 0.782 | 0.568 | 0.056 | 0.577 |
| M3+ | 0.935 | 0.939 | 0.876 | 0.609 | 0.061 | 0.606 |
| M7 | 0.958 | 0.964 | 0.873 | 0.699 | 0.036 | 0.705 |
| M7+ | 0.736 | 0.724 | 0.933 | 0.329 | 0.276 | 0.287 |
| Model | ACC | SP | SN | MCC | FPR | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M3+ | 0.929 | 0.93 | 0.603 | 0.137 | 0.07 | 0.069 |
| M7 | 0.97 | 0.972 | 0.448 | 0.163 | 0.028 | 0.115 |
| M12 | 0.968 | 0.971 | 0.466 | 0.165 | 0.029 | 0.114 |
| M13+ | 0.983 | 0.986 | 0.422 | 0.214 | 0.014 | 0.18 |
| E1 | 0.993 | 0.996 | 0.19 | 0.184 | 0.004 | 0.187 |
| AI4AVP | 0.387 | 0.385 | 0.905 | 0.039 | 0.615 | 0.013 |
| AI4AVP(DA) | 0.379 | 0.376 | 0.871 | 0.034 | 0.624 | 0.012 |
| FIRM-AVP | 0.647 | 0.647 | 0.595 | 0.034 | 0.353 | 0.015 |
| Meta-iAVP | 0.594 | 0.593 | 0.647 | 0.032 | 0.407 | 0.014 |
| seqpros | 0.119 | 0.116 | 0.94 | 0.011 | 0.884 | 0.009 |
| AMPfun | 0.463 | 0.462 | 0.784 | 0.033 | 0.538 | 0.013 |
| iACVP | 0.893 | 0.895 | 0.517 | 0.088 | 0.105 | 0.041 |
| PTPAMP | 0.825 | 0.827 | 0.336 | 0.028 | 0.173 | 0.017 |
| ClassAMP | 0.795 | 0.798 | 0.31 | 0.018 | 0.202 | 0.013 |
| AntiVPP | 0.732 | 0.734 | 0.457 | 0.028 | 0.266 | 0.015 |
| ProtDcalRF | 0.995 | 1 | 0 | -0.001 | 0 | 0 |
| ProtDcalHier | 0.995 | 0.999 | 0 | -0.002 | 0.001 | 0 |
| ProtDcalRNN | 0.95 | 0.954 | 0.034 | -0.004 | 0.046 | 0.006 |
| AVPpred | 0.902 | 0.904 | 0.371 | 0.062 | 0.096 | 0.032 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





