Submitted:
18 July 2024
Posted:
19 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
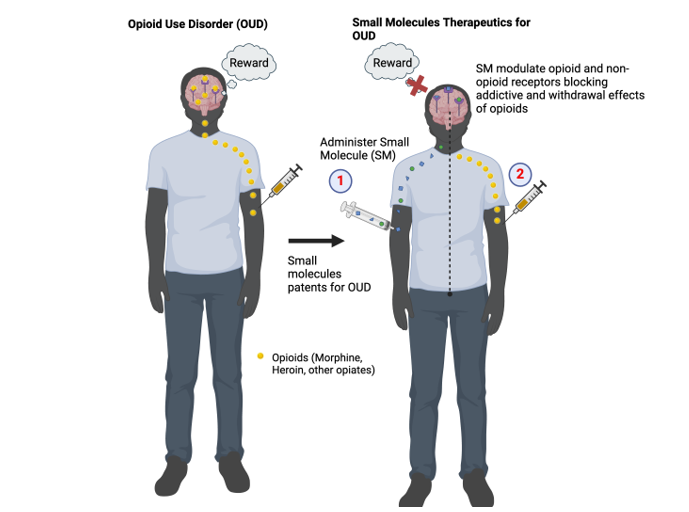
Keywords:
1. Introduction
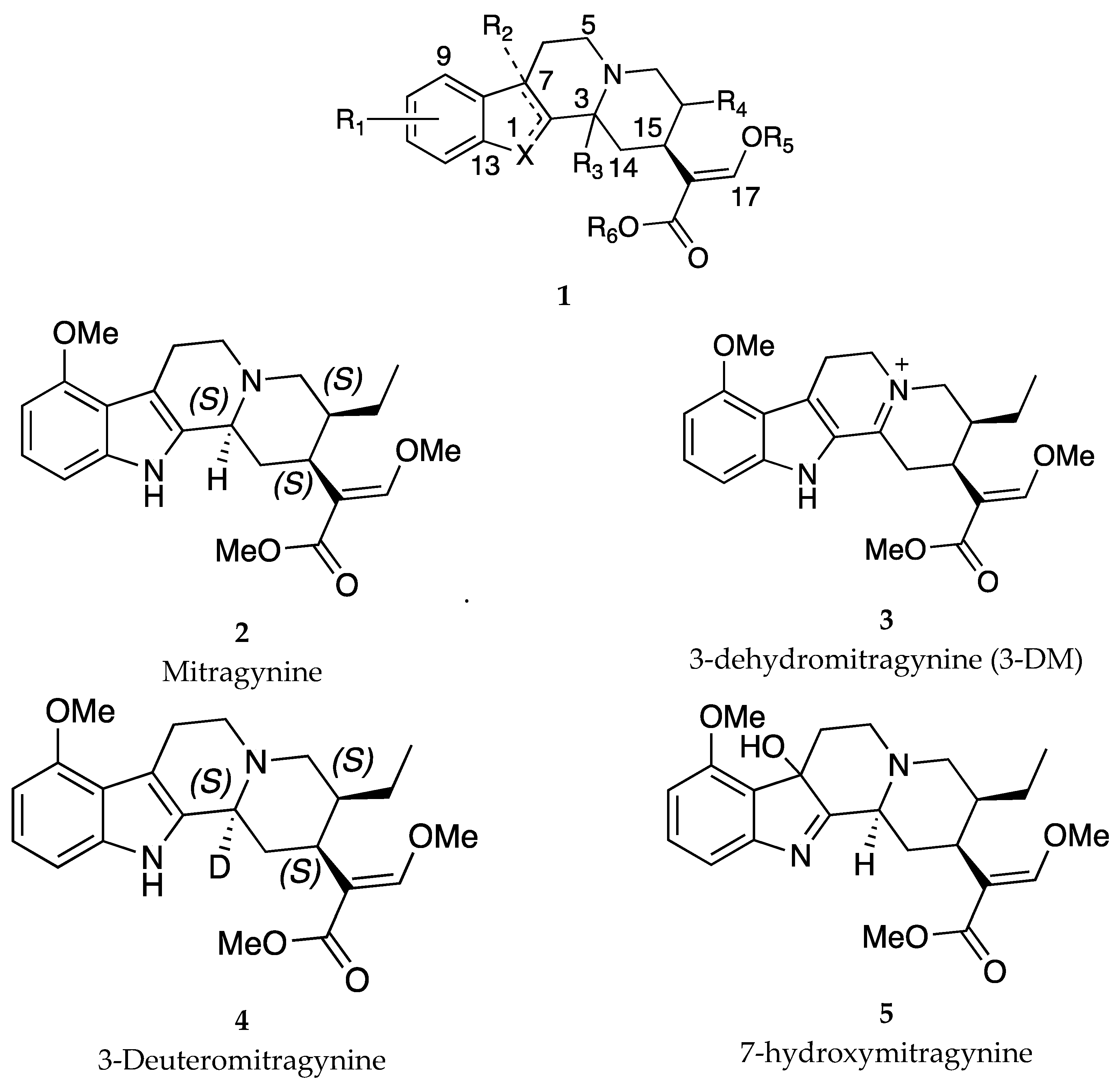
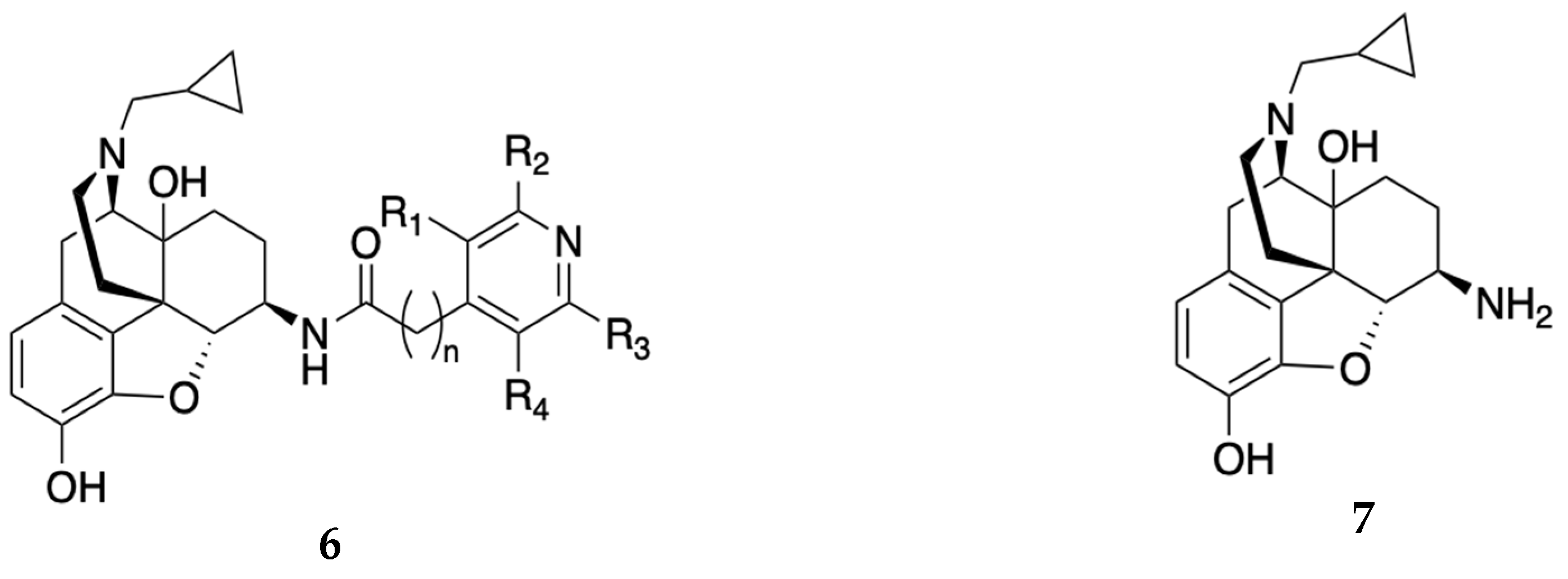
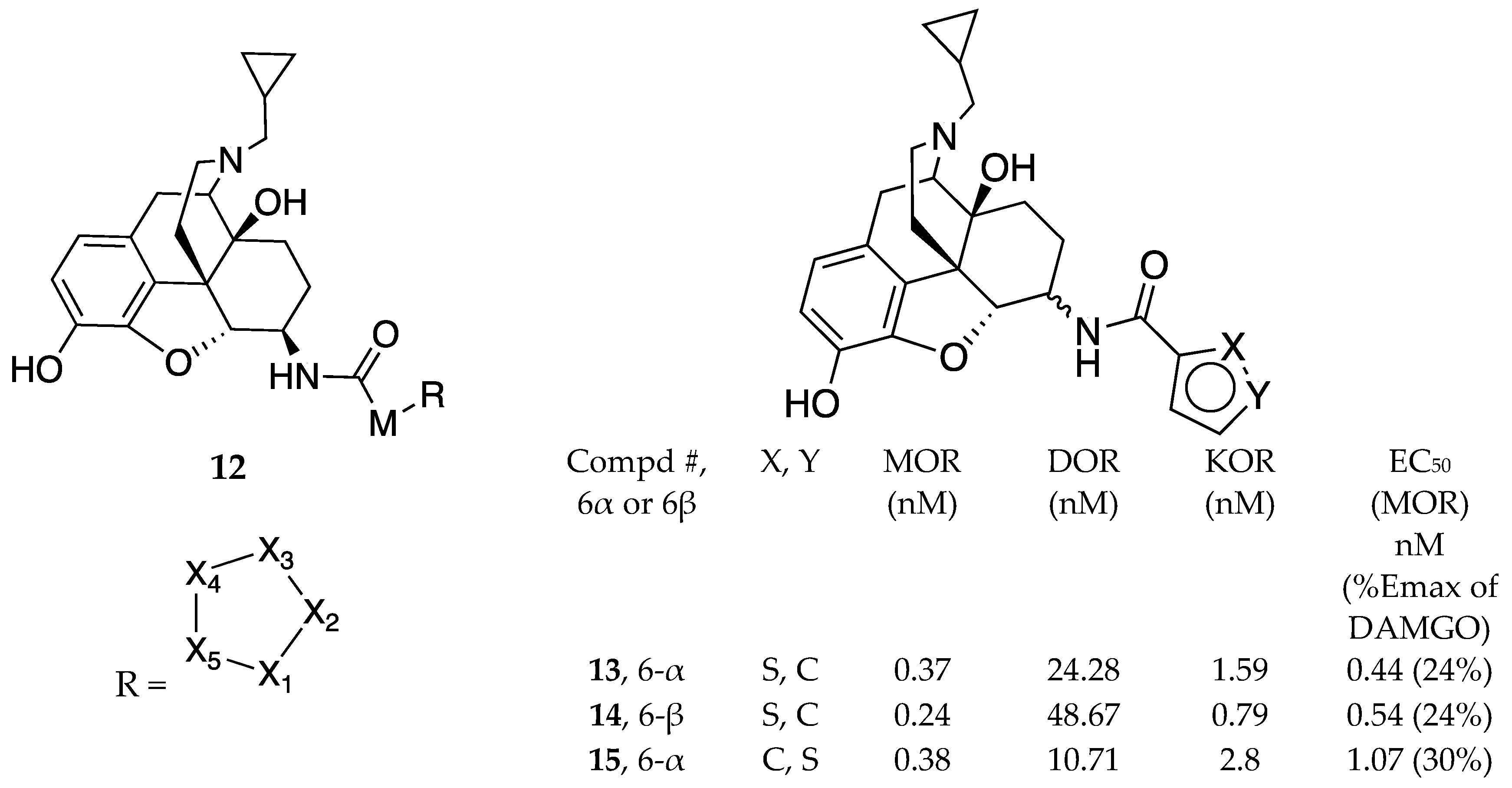
2.1. Small Molecules Targeting Opioid Receptors
2.1. Small Molecules Targeting Non-Opioid Receptors
3. Conclusion and Expert Perspective
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blondell, R.D.; Azadfard, M.; Wisniewski, A.M. Pharmacologic Therapy for Acute Pain. Am Fam Physician 2013, 87, 766–772.
- Benyamin, R.; Trescot, A.M.; Datta, S.; Buenaventura, R.; Adlaka, R.; Sehgal, N.; Glaser, S.E.; Vallejo, R. Opioid Complications and Side Effects. Pain Physician 2008, 11, S105-20.
- Strang, J.; Volkow, N.D.; Degenhardt, L.; Hickman, M.; Johnson, K.; Koob, G.F.; Marshall, B.D.L.; Tyndall, M.; Walsh, S.L. Opioid Use Disorder. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2020, 6, 3. [CrossRef]
- GBD 2017 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators Global, Regional, and National Incidence, Prevalence, and Years Lived with Disability for 354 Diseases and Injuries for 195 Countries and Territories, 1990-2017: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2018, 392, 1789–1858. [CrossRef]
- Hser, Y.-I.; Huang, D.; Chou, C.-P.; Anglin, M.D. Trajectories of Heroin Addiction: Growth Mixture Modeling Results Based on a 33-Year Follow-up Study. Eval Rev 2007, 31, 548–563. [CrossRef]
- CDC-NCHS. U.S. Overdose Deaths Decrease in 2023, First Time Since 2018. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/pressroom/nchs_press_releases/2024/20240515.htm (accessed on 21 May 2024).
- Florence, C.; Luo, F.; Rice, K. The Economic Burden of Opioid Use Disorder and Fatal Opioid Overdose in the United States, 2017. Drug Alcohol Depend 2021, 218, 108350. [CrossRef]
- Stein, C. Opioid Receptors. Annu Rev Med 2016, 67, 433–451. [CrossRef]
- Dugosh, K.; Abraham, A.; Seymour, B.; McLoyd, K.; Chalk, M.; Festinger, D. A Systematic Review on the Use of Psychosocial Interventions in Conjunction With Medications for the Treatment of Opioid Addiction. J Addict Med 2016, 10, 93–103. [CrossRef]
- Doughty, B.; Morgenson, D.; Brooks, T. Lofexidine: A Newly FDA-Approved, Nonopioid Treatment for Opioid Withdrawal. Annals of Pharmacotherapy 2019, 53, 746–753. [CrossRef]
- Timko, C.; Schultz, N.R.; Cucciare, M.A.; Vittorio, L.; Garrison-Diehn, C. Retention in Medication-Assisted Treatment for Opiate Dependence: A Systematic Review. J Addict Dis 2016, 35, 22–35. [CrossRef]
- Ciccarone, D. The Triple Wave Epidemic: Supply and Demand Drivers of the US Opioid Overdose Crisis. Int J Drug Policy 2019, 71, 183–188. [CrossRef]
- Kruegel, A.; Sames D.; Javiitch, J.; Majumdar, S.; inventors; The Trustees of Columbia University in the City of New York, The Research Foundation for Mental Hygiene, Inc., Sloan-Kettering Institute for Cancer Research, assignee. Deuterated Mitragynine Analogs As Safer Opioid Modulators In The Mitragynine Class. WIPO patent 2020160280A1. August 06,2020.
- Kruegel, A.C.; Gassaway, M.M.; Kapoor, A.; Váradi, A.; Majumdar, S.; Filizola, M.; Javitch, J.A.; Sames, D. Synthetic and Receptor Signaling Explorations of the Mitragyna Alkaloids: Mitragynine as an Atypical Molecular Framework for Opioid Receptor Modulators. J Am Chem Soc 2016, 138, 6754–6764. [CrossRef]
- Haile, C.N.; Kosten, T.A.; Das, J.; inventors; University of Houston Systems, assignee. Combination of Mitragynine and Naltrexone for Substance Use Disorders. WIPO patent WO2024/076660A1. April11, 2024..
- Zhang, Y.; inventors; Virginia Commonwealth University, assignee. Non-Peptide Opioid Receptor Modulators For Treatment Of Opioid Abuse And Addiction, Alcoholism And Neurological Disorders Associated With Opioid Receptors. WIPO patent 2020041159A1. February 27, 2020.
- Yuan, Y.; Elbegdorj, O.; Chen, J.; Akubathini, S.K.; Zhang, F.; Stevens, D.L.; Beletskaya, I.O.; Scoggins, K.L.; Zhang, Z.; Gerk, P.M.; et al. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of 17-Cyclopropylmethyl-3,14β-Dihydroxy-4,5α-Epoxy-6β-[(4’-Pyridyl)Carboxamido]Morphinan Derivatives as Peripheral Selective μ Opioid Receptor Agents. J Med Chem 2012, 55, 10118–10129. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Obeng, S.; Wang, H.; Jali, A.M.; Peddibhotla, B.; Williams, D.A.; Zou, C.; Stevens, D.L.; Dewey, W.L.; Akbarali, H.I.; et al. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of the Third Generation 17-Cyclopropylmethyl-3,14β-Dihydroxy-4,5α-Epoxy-6β-[(4’-Pyridyl)Carboxamido]Morphinan (NAP) Derivatives as μ/κ Opioid Receptor Dual Selective Ligands. J Med Chem 2019, 62, 561–574. [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Aschenbach, L.C.; Chen, J.; Cassidy, M.P.; Stevens, D.L.; Gabra, B.H.; Selley, D.E.; Dewey, W.L.; Westkaemper, R.B.; Zhang, Y. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of 6alpha- and 6beta-N-Heterocyclic Substituted Naltrexamine Derivatives as Mu Opioid Receptor Selective Antagonists. J Med Chem 2009, 52, 1416–1427. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.A.N.; inventor; Virginia Commonwealth University, assignee. Naltrexamine Derivatives Bearing 5-Member Heterocyclic Ring Systems as Opioid Receptor Modulators. WIPO Patent WO 2023/163969 A3. October 5, 2023.
- German, N.; Hossain, M.A.; inventors; Texas Tech University System, assignee. Novel Opioid Antagonists and Methods Related Thereto. US patent 20200131183A1. April 30, 2020.
- German, N.; Neugebauer, V.; Hossain, M.A.; Abbruscatto, T. inventors; Texas Tech University System, assignee. Novel Selective Kappa Opioid Receptor Antagonists And Methods Related Thereto For Treatment Of Addiction And Neuropathic Pain. WIPO Patent 2020092996A1. May 7, 2020.
- Shahbazi Nia, S.; Hossain, M.A.; Ji, G.; Jonnalagadda, S.K.; Obeng, S.; Rahman, M.A.; Sifat, A.E.; Nozohouri, S.; Blackwell, C.; Patel, D.; et al. Studies on Diketopiperazine and Dipeptide Analogs as Opioid Receptor Ligands. Eur J Med Chem 2023, 254, 115309. [CrossRef]
- Peltier, J.; Surman, M.; Golden, K.; Pasetto, P.;Jin, X.; Camara, F.; Jiang, X.; inventors; Waterville Valley Technologies, Inc., assignee. Preparation Of Oxycodone Analogs and Compositions for Preventing Opioid Abuse. US patent 20160326182A1. November 10, 2016.
- Medina, J.C.; Nerurkar, A.; Sadlowski, C.; Seidl, F.; Cheng, H.; Duquette, J.; Lee, J.; Holan, M.; Ding, P.; Wang, X.; et al., inventors; Epiodyne Inc., assignee. Opioid Receptor Modulators. WIPO Patent WO 2022/216750 A1. October 13, 2022.
- Rice, K.C.; Jacobson, A.; Sulima, A.; Chambers, D.; Roth, H.; inventors; US Health, assignee. Selective Opioid Receptor Agonists and Antagonists. WIPO patent 2024/026350A1. February 1, 2024.
- Brents, L.; Tobacyk, J.; Crooks, P.; Janganati, V.; inventors. Bio Ventures LLC, assignee. Deuterated Buprenorphine as a Protective Agent for Fetal Subjects Against Full-Agonist Opioid Exposure. WIPO patent 2024/036337A2. February 15, 2024.
- Griffin, B.A.; Caperton, C.O.; Russell, L.N.; Cabanlong, C. V; Wilson, C.D.; Urquhart, K.R.; Martins, B.S.; Zita, M.D.; Patton, A.L.; Alund, A.W.; et al. In Utero Exposure to Norbuprenorphine, a Major Metabolite of Buprenorphine, Induces Fetal Opioid Dependence and Leads to Neonatal Opioid Withdrawal Syndrome. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2019, 370, 9–17. [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Kehner, G.B.; Cowan, A.; Liu-Chen, L.Y. Comparison of Pharmacological Activities of Buprenorphine and Norbuprenorphine: Norbuprenorphine Is a Potent Opioid Agonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2001, 297, 688–695.
- Rubi, L.; Eckert, D.; Boehm, S.; Hilber, K.; Koenig, X. Anti-Addiction Drug Ibogaine Prolongs the Action Potential in Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes. Cardiovasc Toxicol 2017, 17, 215–218. [CrossRef]
- Sames, D.; Hemby, S.; Havel, V.; inventors; The Trustees of Columbia University In The City Of New York, High Point University, assignee. Oxa-Ibogaine Analogues for Treatment of Substance Use Disorders. WIPO patent 2022178099A1. August 25, 2022.
- Sames, D.; Havel, V.; Hwu, C.; inventors; The Trustees Of Columbia University In The City Of New York, assignee. Ibogaine Analogs as Therapeutics for Neurological and Psychiatric Disorders. WIPO patent 2022020352A1. January 27, 2022.
- Kargbo, R.B. Ibogaine and Their Analogs as Therapeutics for Neurological and Psychiatric Disorders. ACS Med Chem Lett 2022, 13, 888–890. [CrossRef]
- Noller, G.E.; Frampton, C.M.; Yazar-Klosinski, B. Ibogaine Treatment Outcomes for Opioid Dependence from a Twelve-Month Follow-up Observational Study. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse 2018, 44, 37–46. [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.K.; Alper, K. Treatment of Opioid Use Disorder with Ibogaine: Detoxification and Drug Use Outcomes. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse 2018, 44, 24–36. [CrossRef]
- Belgers, M.; Leenaars, M.; Homberg, J.R.; Ritskes-Hoitinga, M.; Schellekens, A.F.A.; Hooijmans, C.R. Ibogaine and Addiction in the Animal Model, a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Transl Psychiatry 2016, 6, e826. [CrossRef]
- Glick, S.D.; Maisonneuve, I.M.; Szumlinski, K.K. Mechanisms of Action of Ibogaine: Relevance to Putative Therapeutic Effects and Development of a Safer Iboga Alkaloid Congener. Alkaloids Chem Biol 2001, 56, 39–53. [CrossRef]
- Dolmetsch, R.C.E.; Gasparini, F.; Gomez-Mancilla, B.; inventors; Novartis A.G., assignee Use of mGluR5 Antagonists. WIPO patent 2022013809 A2. January 20, 2022.
- van der Kam, E.L.; de Vry, J.; Tzschentke, T.M. Effect of 2-Methyl-6-(Phenylethynyl) Pyridine on Intravenous Self-Administration of Ketamine and Heroin in the Rat. Behavioural pharmacology 2007, 18, 717–724. [CrossRef]
- Kuesters, E.; Acemoglu, M.; Lustenberger, P.; Sedelmeier, G.; Schmidt, B.; Penn, G.; inventors; Novartis A.G., assignee. Processes for the preparation of 4-oxo-octahydro-indole-1-carbocylic acid methyl ester and derivatives thereof. WIPO patent 2022013809A2. February 18, 2010.
- Gasparini, F.; Auberson, Y.; Ofner, S., inventors; Novartis A.G., Novartis Pharma Gmbh., Gasparini Fabrizio, Auberson Yves, Ofner Silvio, assignee. Acetylene Derivatives Having mGluR 5 Antagonistic Activity. CA patent 2732095A1. June 12, 2003.
- Imbert, B.; Sung, V.; Dolmetsch, R.E.; Clyde, H.W.; inventors; Tempero Bio Inc., assignee. Methods of Treating Substance Use Disorder with 4-(3-Cyanophenyl)-6-Pyridinylpyrimidine mGlu5 Negative Allosteric Modulators 2023. WIPO patent 2023/249789A1. December 28, 2023.
- Newman, A.H.; Kumar, V.; Shaik, A.B.; inventors; The United States of America, As Represented By The Secretary, Department Of Health And Human Services, assignee. Dopamine D3 Receptor Selective Antagonists/Partial Agonists and Uses Thereof. March 19, 2020.
- Segal, D.M.; Moraes, C.T.; Mash, D.C. Up-Regulation of D3 Dopamine Receptor MRNA in the Nucleus Accumbens of Human Cocaine Fatalities. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 1997, 45, 335–339. [CrossRef]
- You, Z.-B.; Bi, G.-H.; Galaj, E.; Kumar, V.; Cao, J.; Gadiano, A.; Rais, R.; Slusher, B.S.; Gardner, E.L.; Xi, Z.-X.; et al. Dopamine D3R Antagonist VK4-116 Attenuates Oxycodone Self-Administration and Reinstatement without Compromising Its Antinociceptive Effects. Neuropsychopharmacology 2019, 44, 1415–1424. [CrossRef]
- Jordan, C.J.; Humburg, B.A.; Thorndike, E.B.; Shaik, A.B.; Xi, Z.-X.; Baumann, M.H.; Newman, A.H.; Schindler, C.W. Newly Developed Dopamine D 3 Receptor Antagonists, R -VK4-40 and R -VK4-116, Do Not Potentiate Cardiovascular Effects of Cocaine or Oxycodone in Rats. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 2019, 371, 602–614. [CrossRef]
- Jordan, C.J.; Humburg, B.; Rice, M.; Bi, G.-H.; You, Z.-B.; Shaik, A.B.; Cao, J.; Bonifazi, A.; Gadiano, A.; Rais, R.; et al. The Highly Selective Dopamine D R Antagonist, R-VK4-40 Attenuates Oxycodone Reward and Augments Analgesia in Rodents. Neuropharmacology 2019, 158, 107597. [CrossRef]
- Newman, A.H.; Bonifazi, A.; Battiti, F.O.; inventors; The United States of America, As Represented By The Secretary, Department Of Health And Human Services, assignee. Dual-Target Mu Opioid and Dopamine D3 Receptors Ligands; Preparation and Use Thereof. WIPO patent 2022187206A1. September 09, 2024.
- Laezza, F.; Zhou, J.; Chung, J.M.; Wang, P.; La, J.; Folorunso, O.; Singh, A.; inventors; The Board of Regents of The University Of Texas System, assignee. Novel Non-Opioid Anti-Pain Medication. WIPO patent 2020154679 A1. July 30, 2020.
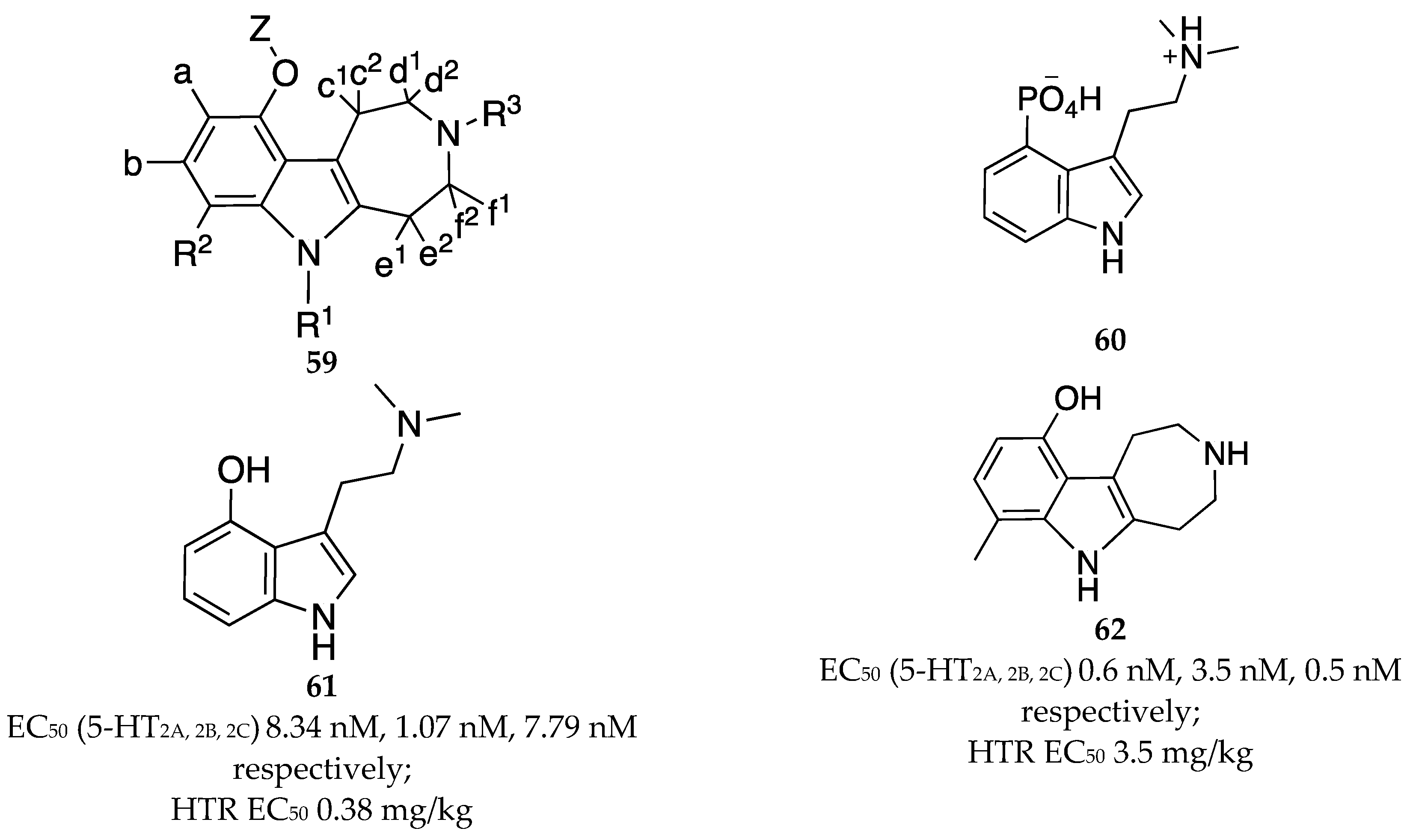
- Booth, R.; inventor; Northeastern University, assignee. Serotonin Receptor Modulators. WIPO patent 2022040395A2. February 24, 2022.
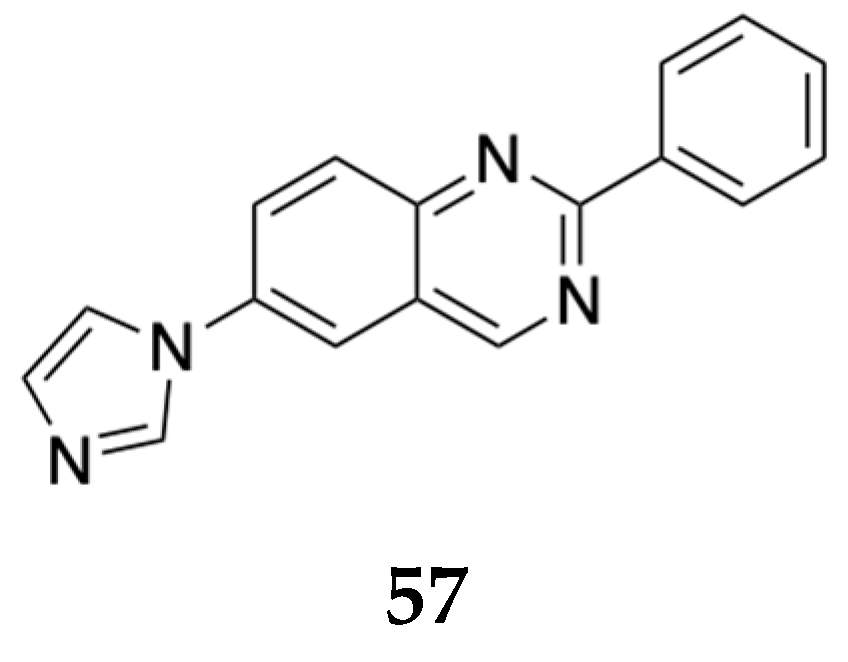
- Rovati, L.C.; inventor; Rottapharm Biotech S.R.L., assignee. Use of 2-phenyl-6-(1h-imidazol-1-yl) quinazoline for the prevention of abuse and of side effects of at least one opioid. WIPO patent WO2021104639 A1. June 3, 2021.
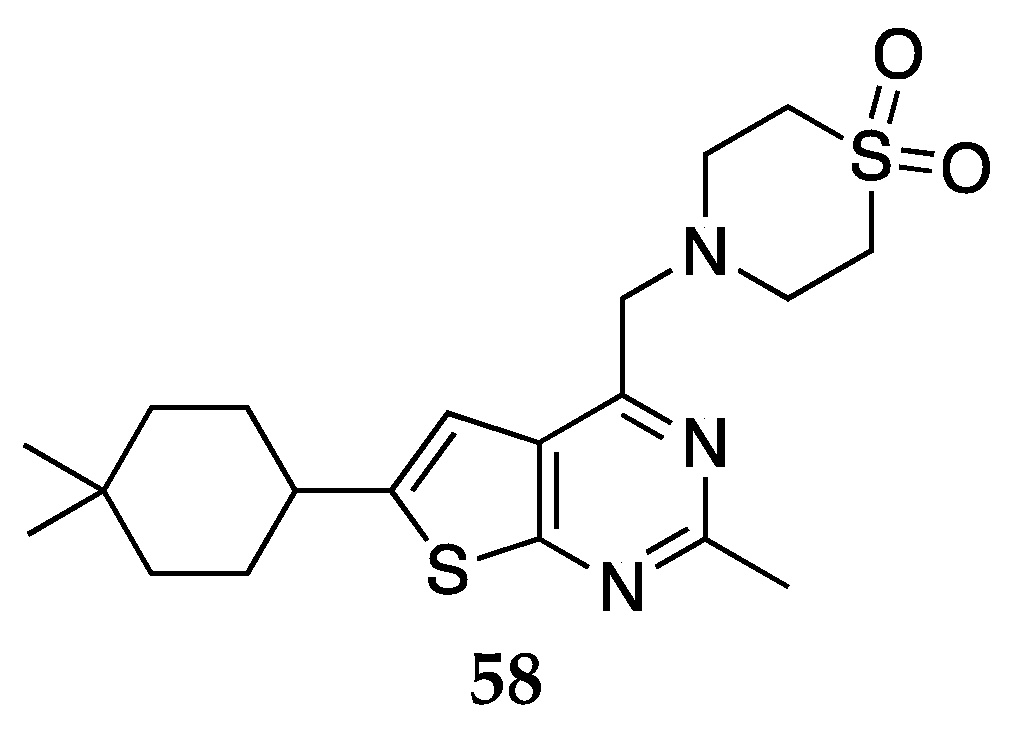
- Blahunka, P.; Gerard, M.; Mototsugu, I.; inventors; Astellas Pharma Global Dev Inc, assignee. Methods of Treating Substance Use Disorder. WIPO patent 2023028519 A2. March 2, 2023.
- Shiraishi, N.; Hoshii, H.; Hamaguchi, W.; Honjo, E.; Takuwa, T.; Kondo, Y.; Goto, T.; inventors; Astellas Pharma Inc., assignee. Sulfur-containing bicyclic compound. USPTO patent 9051339 B2. June 9, 2013.
- Kozikowski, A.; Tueckmantel, W.; inventors; Bright Minds Bioscienes, assignees. Azepinoindoles and Methods of Preparation Thereof 2023. WIPO patent 2023/212811 A1. November 9, 2023.
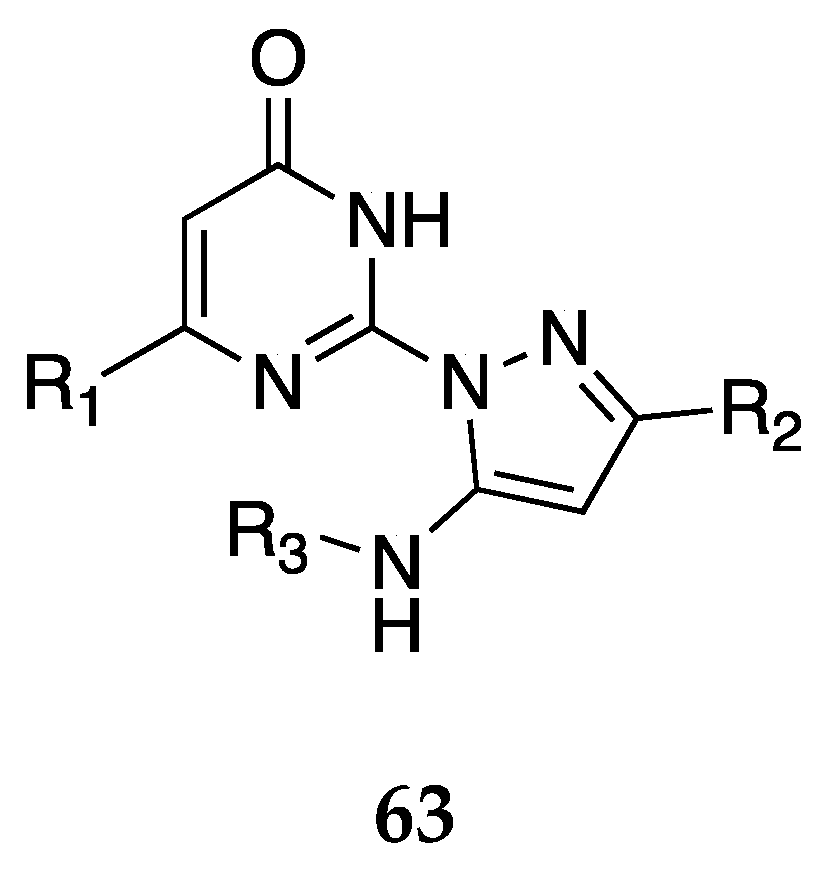
- Flaherty, D.P.; Watts, V.J.; Dwyer, T.S.; Annadka, S.; inventors; Purdue Research Foundation, assignee. Pyrazolyl Pyrimidinone Compounds and the Uses Thereof. US patent 20230250084 A1. August 10, 2023.
- Wang, W.; Prisinzano, T.; Uhl, G.; Henderson, I.; inventors; The Us Gov as Represented by the Department of Veterans Affairs , Wang Wei , Prisinzano Thomas; assignee. PTPRD Inhibitors and Uses Thereof. WIPO patent 2022232694A1. November 3, 2022.
- Zhan, C.; Zheng, F.; inventors; Univ Kentucky Res Found, assignee. Butyrylcholinesterase Inhibitors for Treatment of Opioid Use Disorder. US patent 20200368224A1. November 26, 2020.
- Inturrisi, C.E.; Schultz, M.; Shin, S.; Umans, J.G.; Angel, L.; Simon, E.J. Evidence from Opiate Binding Studies That Heroin Acts through Its Metabolites. Life Sci 1983, 33 Suppl 1, 773–776. [CrossRef]
- Lockridge, O.; Mottershaw-Jackson, N.; Eckerson, H.W.; La Du, B.N. Hydrolysis of Diacetylmorphine (Heroin) by Human Serum Cholinesterase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1980, 215, 1–8.
- Polymeropoulos MH, Birznieks GP, et al., inventors; Vanda Pharmaceuticals Inc., University Of Kentucky Research Foundation, assignee. Method Of Treatment With Tradipitant. WIPO patent 2019236852A1. December 12, 2019.
- Felts, A.; Han, C.; Capstick, R.; Orsi, D.; Whomble, D.; Lindsley C.; Conn, P.; inventors; Univ Vanderbilt, assignee. Arylsulfonyl Derivatives and Their Use as Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor M5 Inhibitors. WIPO patent 2021/257977A1. December 23, 2021.
- Lindsley, W.; Jones, K.C.; Conn, P.J.; Han, C.; Felts, A.S.; Orsi, D.L.; Engers, J.L.; Li, J.; Capstick, R.A.; Whomble, D.L.; Temple, K.J.; inventors; Univ Vanderbilt, assignee. Competitive and Noncompetitive Inhibitors of the Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor M5. WIPO patent 2021237038 A1. November 25, 2021.
- Basile, A.S.; Fedorova, I.; Zapata, A.; Liu, X.; Shippenberg, T.; Duttaroy, A.; Yamada, M.; Wess, J. Deletion of the M5 Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor Attenuates Morphine Reinforcement and Withdrawal but Not Morphine Analgesia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2002, 99, 11452–11457. [CrossRef]
- Bender, A.M.; Garrison, A.T.; Lindsley, C.W. The Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor M5: Therapeutic Implications and Allosteric Modulation. ACS Chem Neurosci 2019, 10, 1025–1034. [CrossRef]
- Garrison, A.T.; Orsi, D.L.; Capstick, R.A.; Whomble, D.; Li, J.; Carter, T.R.; Felts, A.S.; Vinson, P.N.; Rodriguez, A.L.; Han, A.; et al. Development of VU6019650: A Potent, Highly Selective, and Systemically Active Orthosteric Antagonist of the M5 Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor for the Treatment of Opioid Use Disorder. J Med Chem 2022, 65, 6273–6286. [CrossRef]
- Teal, L.B.; Bubser, M.; Duncan, E.; Gould, R.W.; Lindsley, C.W.; Jones, C.K. Selective M5 Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor Negative Allosteric Modulator VU6008667 Blocks Acquisition of Opioid Self-Administration. Neuropharmacology 2023, 227, 109424. [CrossRef]
- Lopez, D.A.; Gross, G.M.; inventors; Pannex Therapeutics Inc, assignee. Pannexin-1 Modulators and Methods of Treating Disorders in which Pannexin-1 is Implicated. WIPO patent 2024049929 A2. March 7, 2024.
- Buresh, M.; Stern, R.; Rastegar, D. Treatment of Opioid Use Disorder in Primary Care. BMJ 2021, n784. [CrossRef]
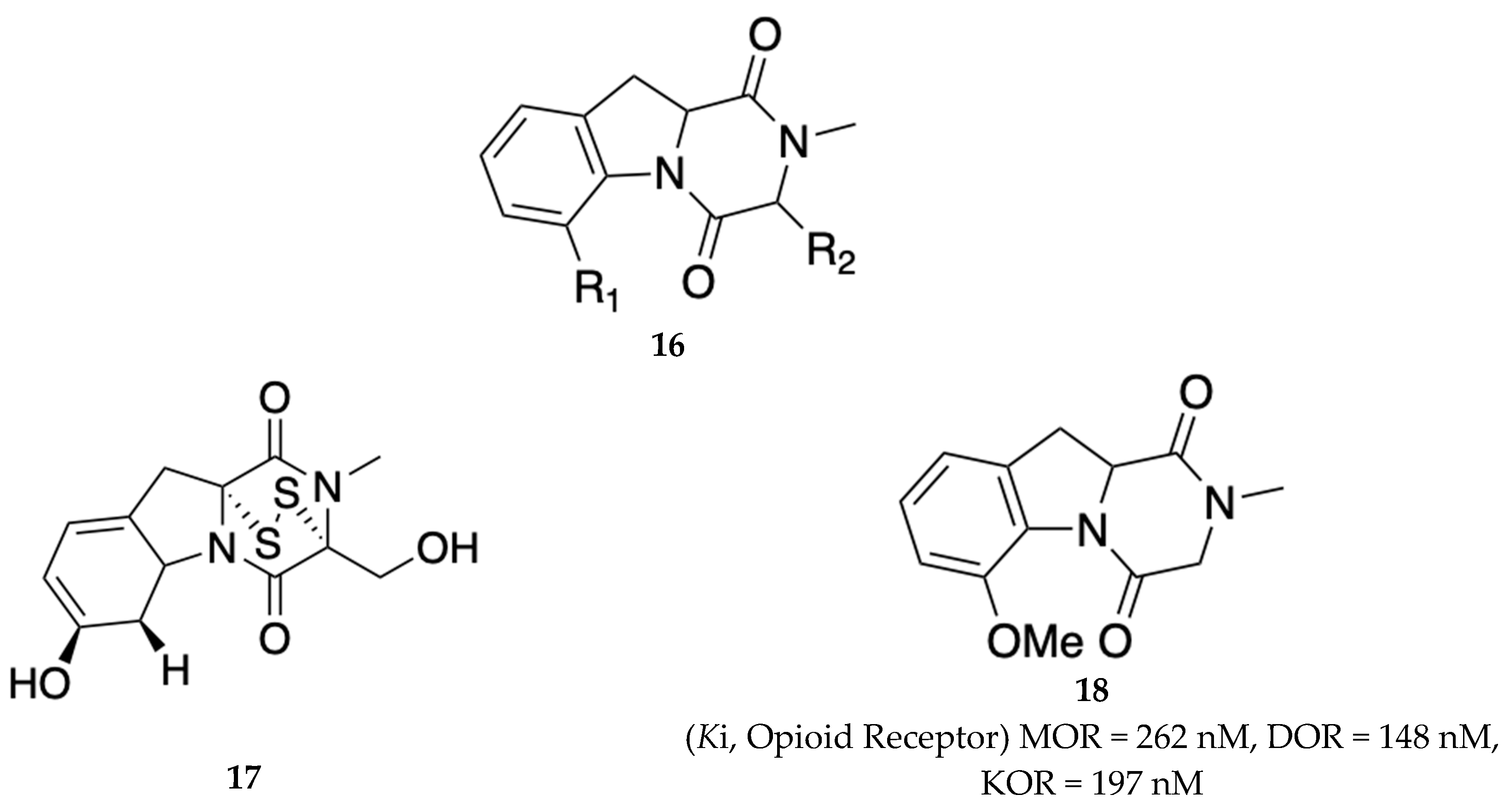

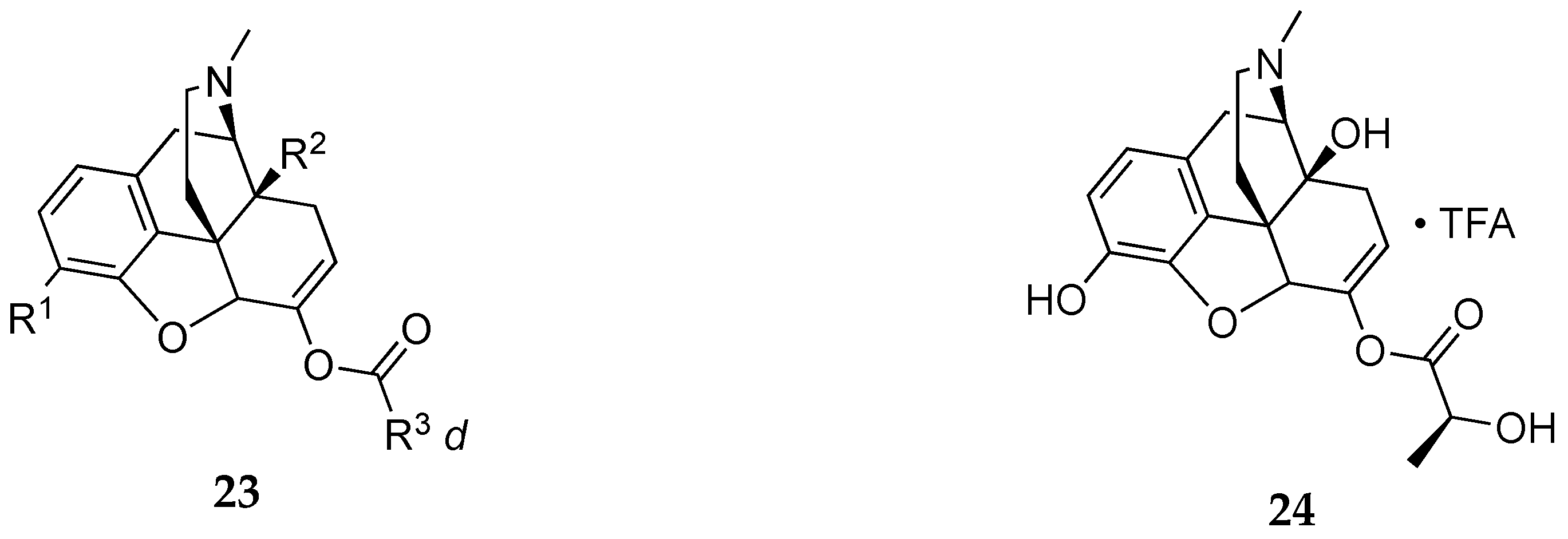
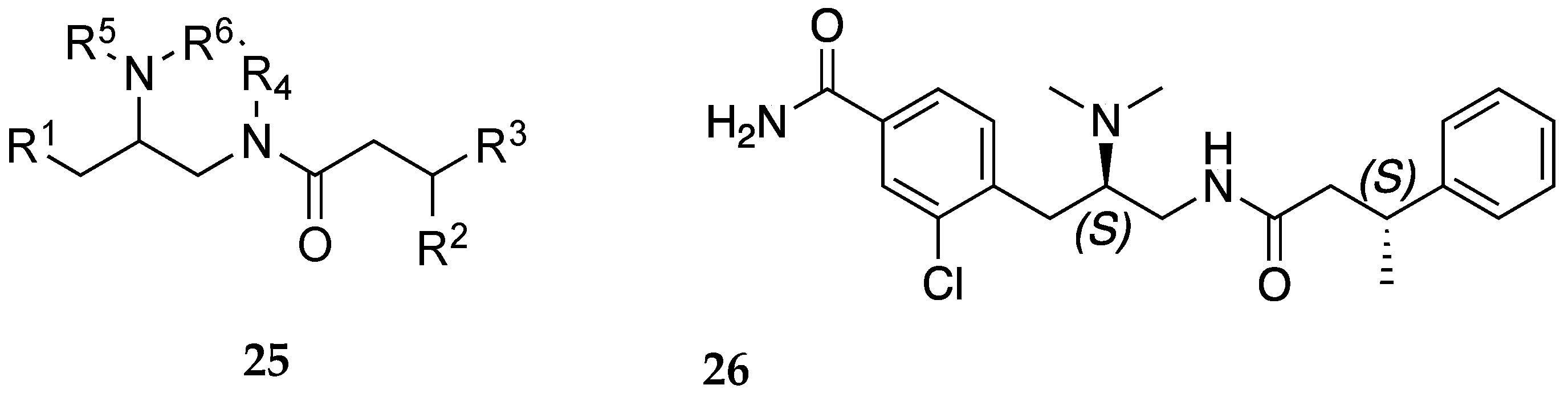
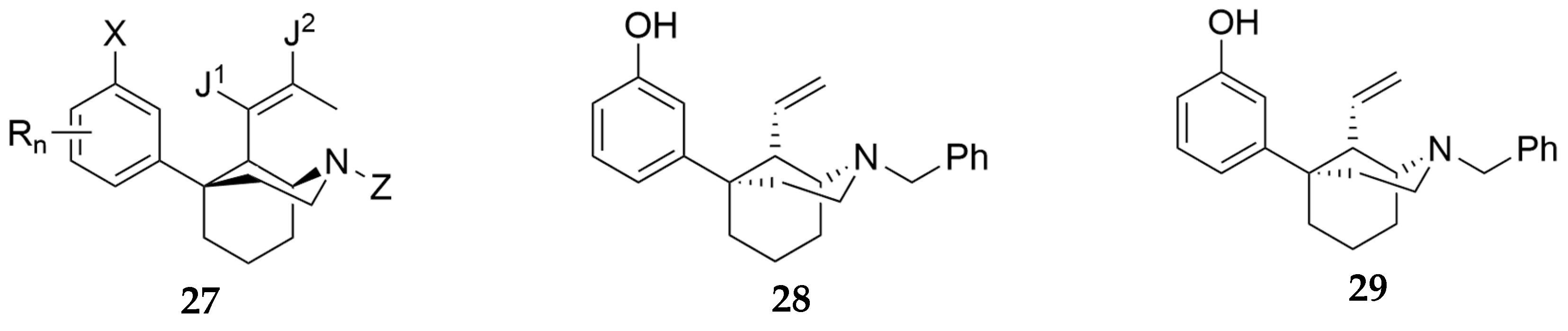
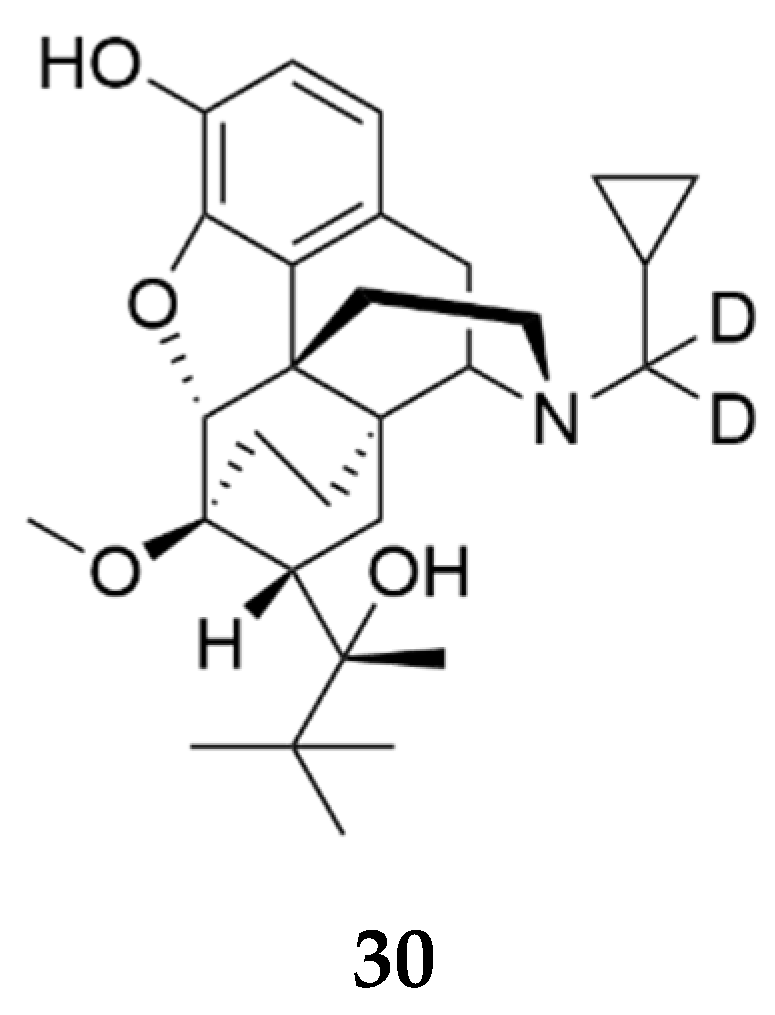
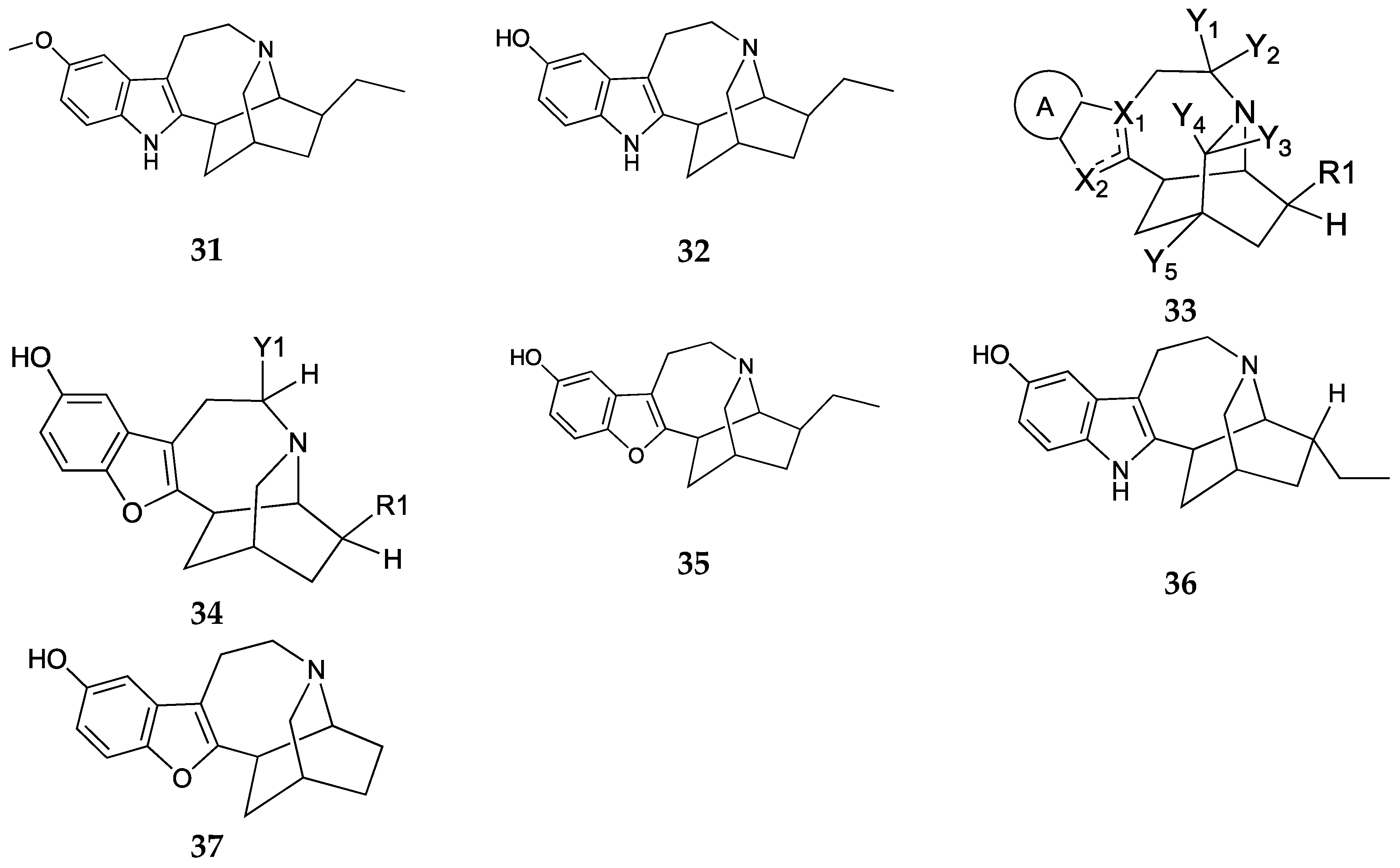
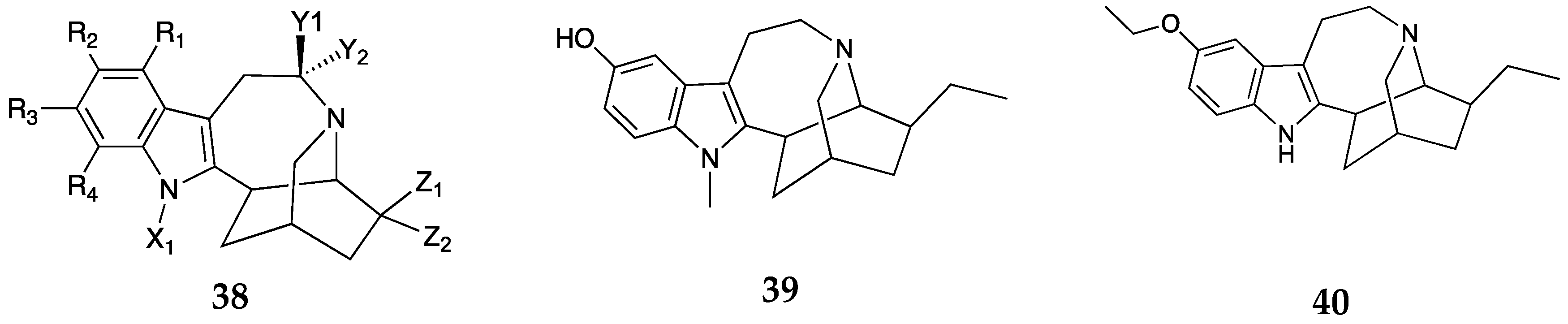
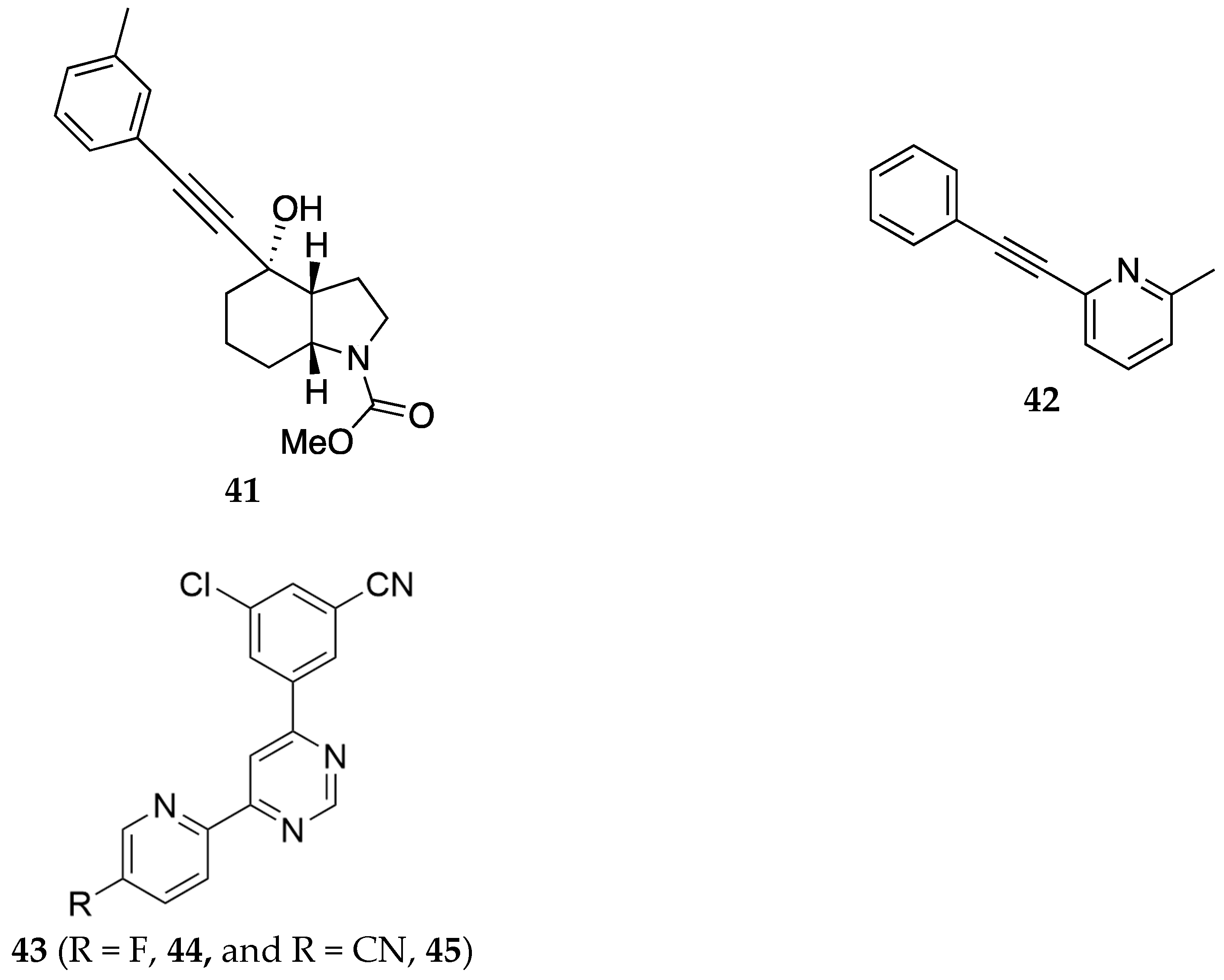
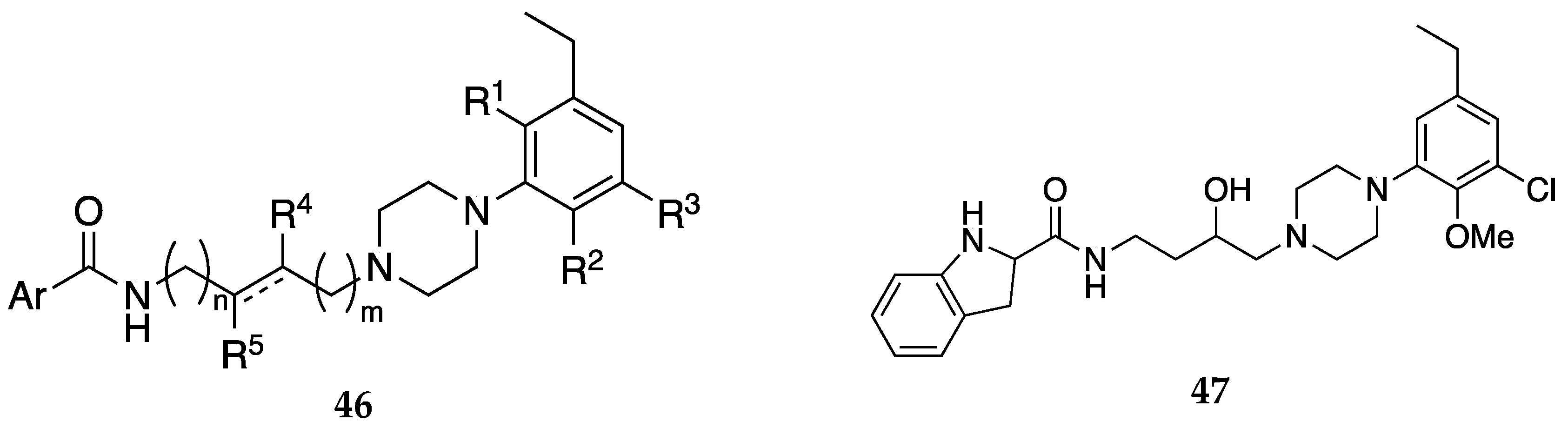
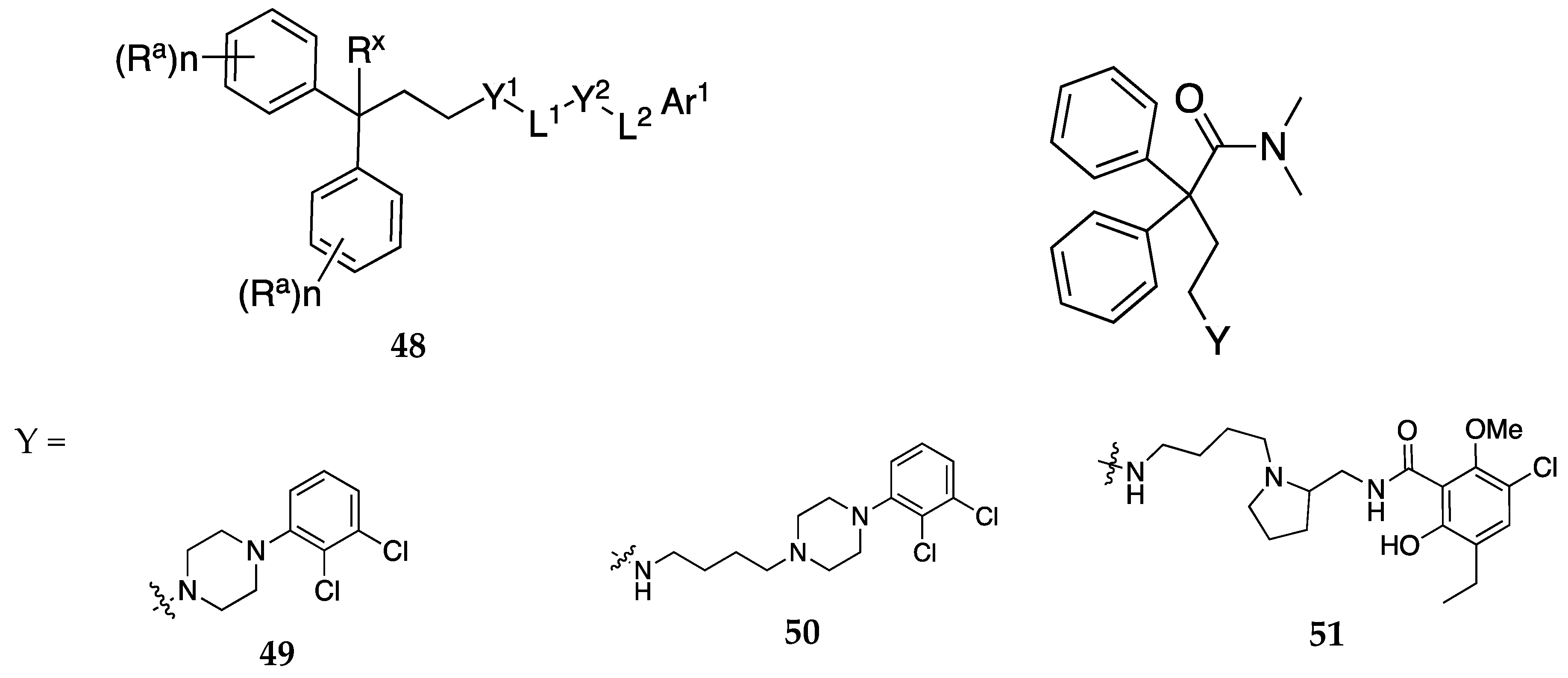
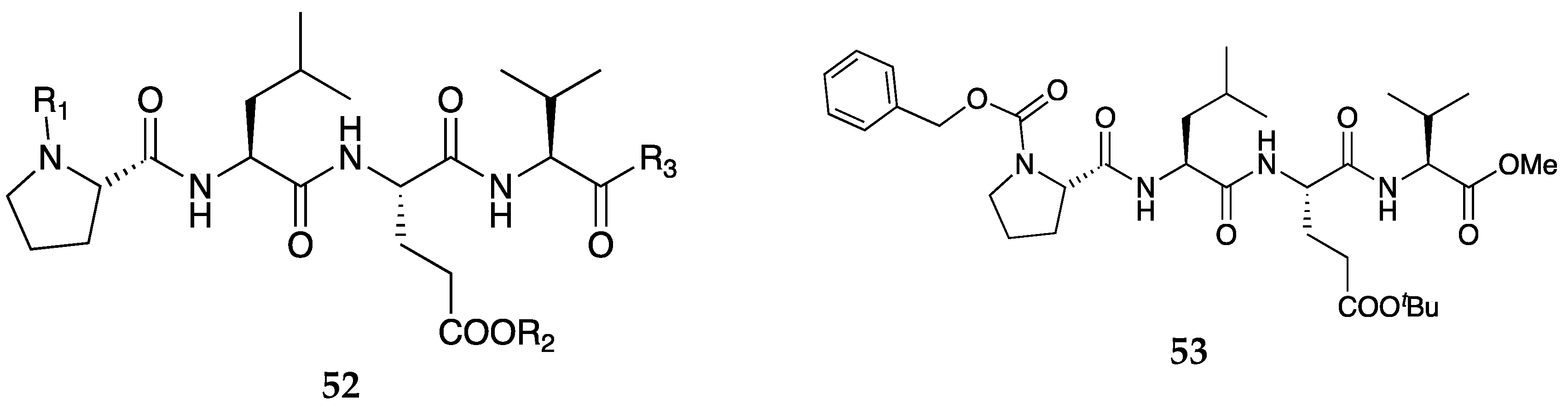
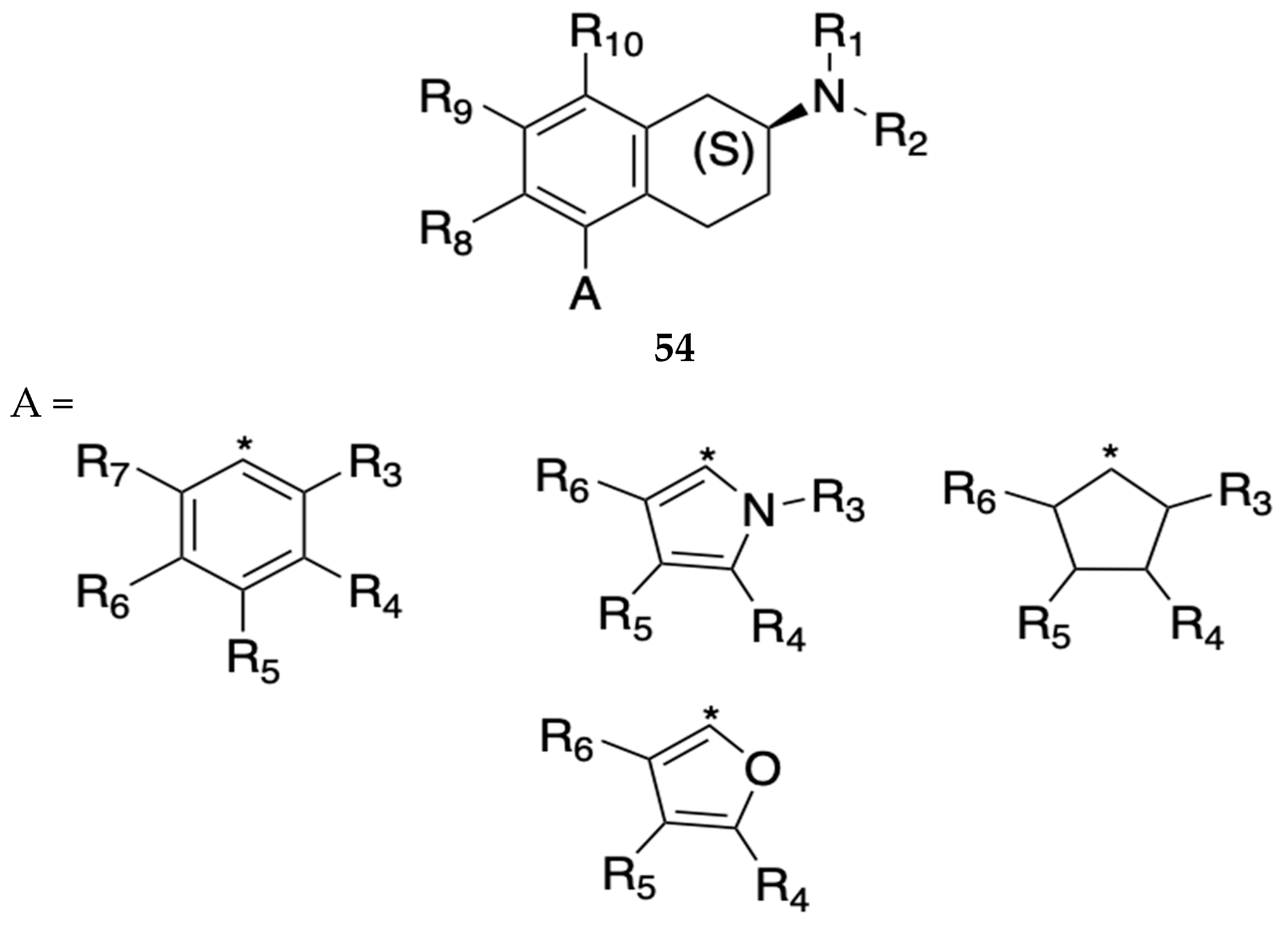

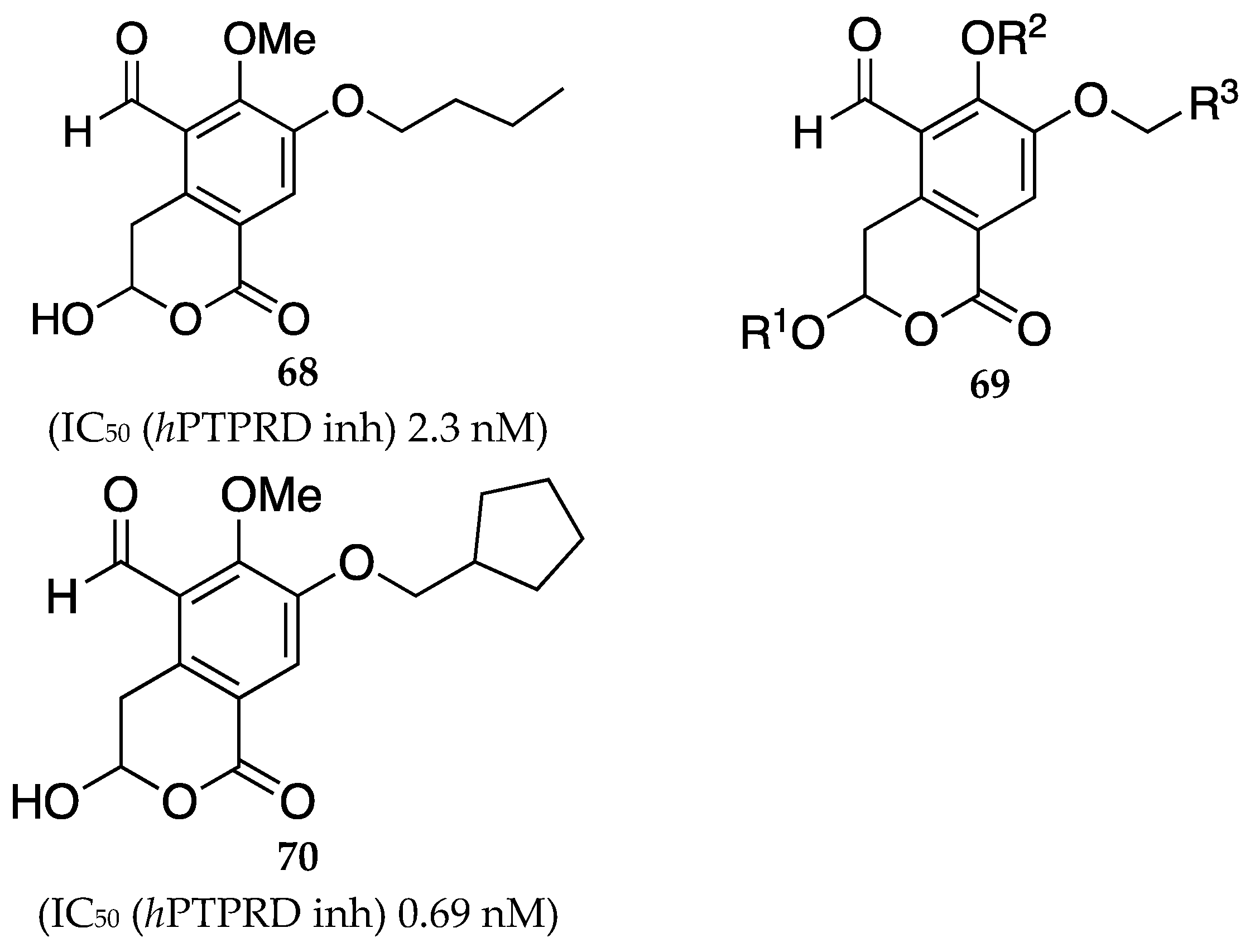
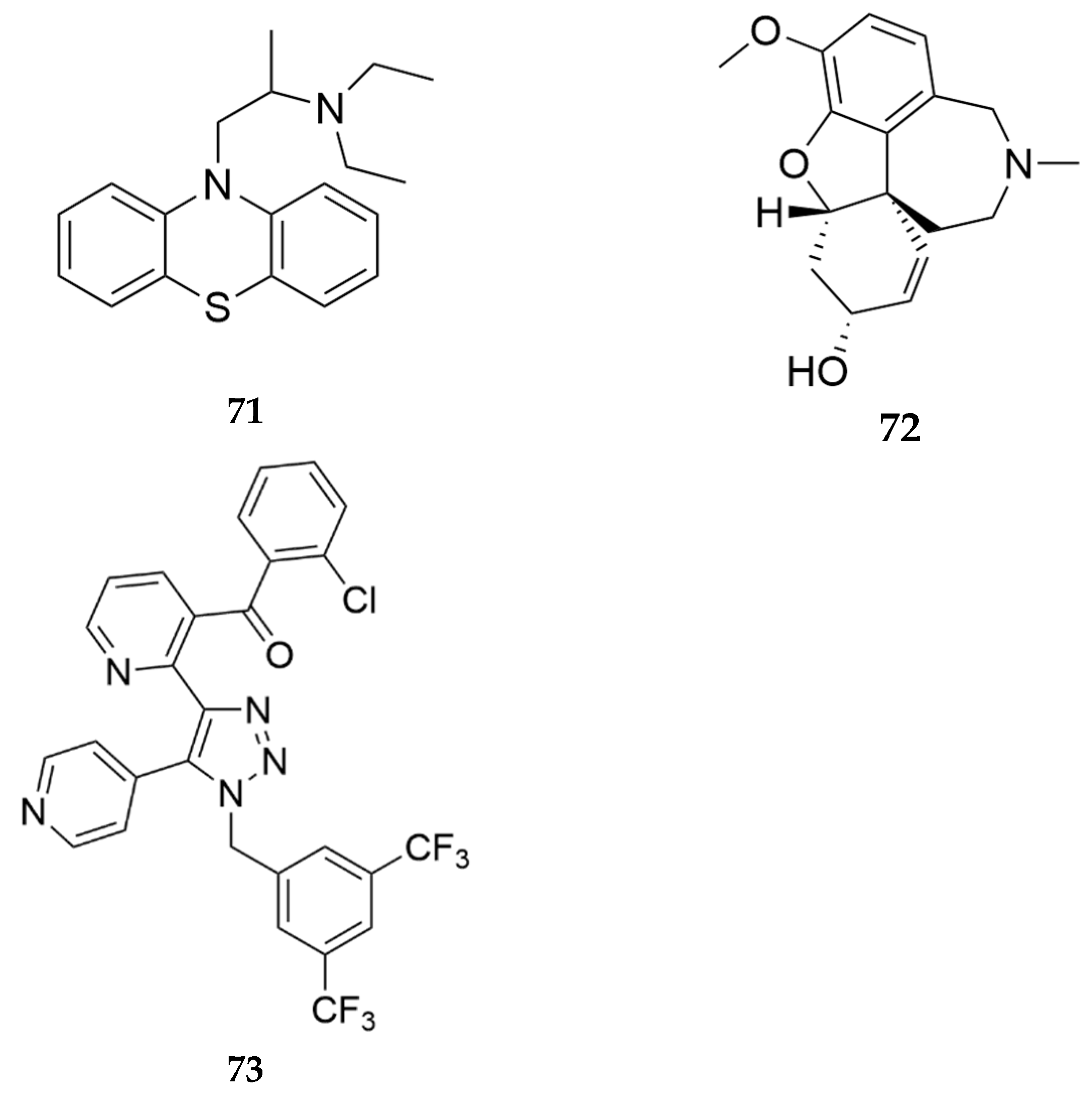
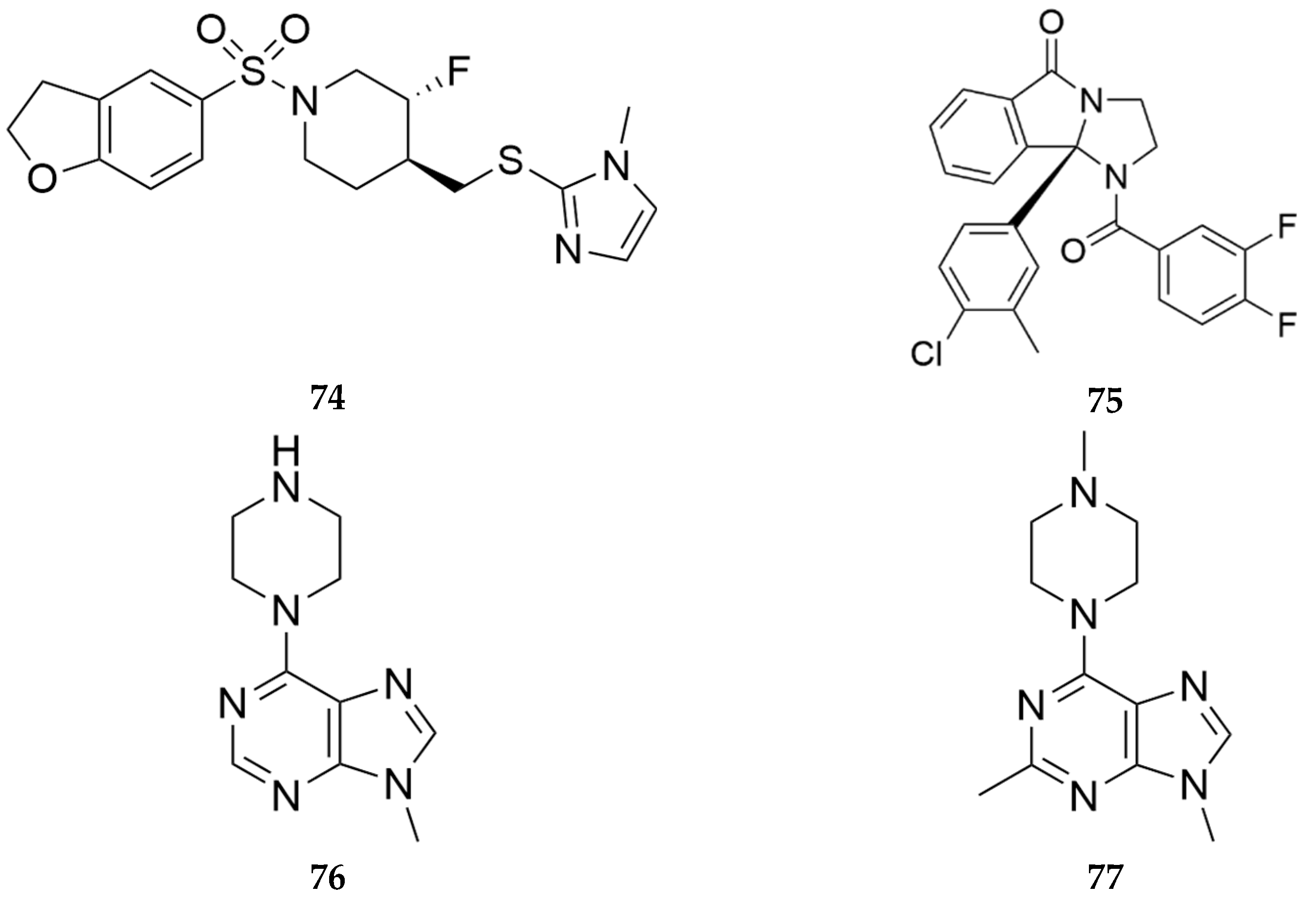
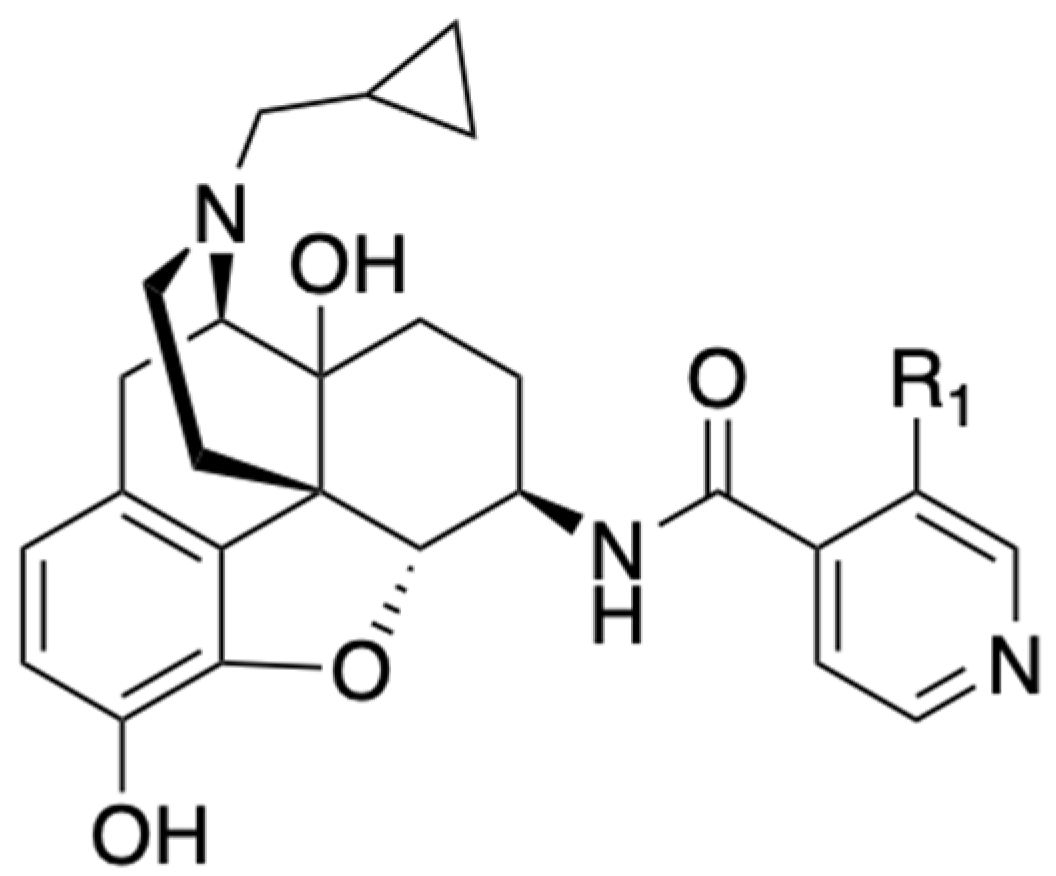
| Compound | Ki (nM) MOR | EC50 (nM) [MOR 35S-GPT(γS) ] (% of DAMGO) |
| NAP (8); R1 = H, | 0.37 | 1.14 (22.72%) |
| NFP (9); R1 = F, | 0.36 | 1.20 (34.97%) |
| NYP (10); R1 = CN, | 0.87 | 1.28 (26.05%) |
| NMP (11); R1 = CH3 | 0.58 | 1.52 (30.63%) |
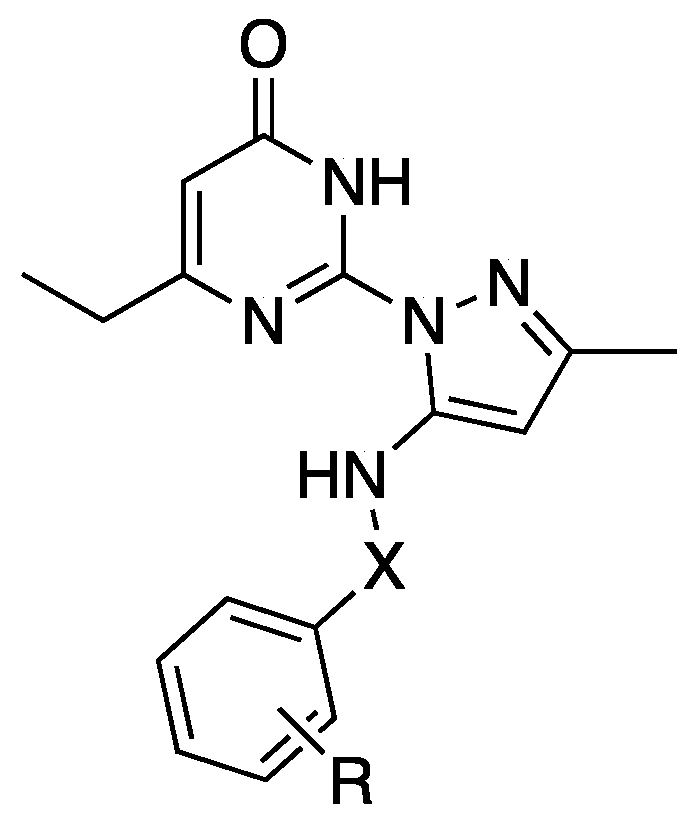
| # | X | R | IC50, AC1 | IC50, AC8 | Max AC8 Inh (%) |
| 64 | C(O) | 4-Cl | 0.3 | 9.5 | 32 |
| 65 | C(O) | 2-F | 0.4 | 5.5 | 60 |
| 66 | -CH2C(O)- | 3-CH3 | 10 | 50 | 59 |
| 67 | -CH2 | 3-CH3 | 0.2 | 3.3 | 31 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





